Human A&P 2: Organization
1/16
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Integumentary System
Components:
Skin & associated structures
Hair
Nails
Sweat Glands
Oil Glands
Functions:
Regulate body temp
Protection
Eliminates some wastes
Helps make vitamin D
Detect sensations
Stores fat & provides insulation
Skeletal System
Components:
Bones
Joints
Cartilages
Functions:
Support & protect body
Area for muscle attachment
Stores cells that produce blood cells
Stores minerals & lipids
Muscular System
Components:
Skeletal muscle tissue
Functions:
Body movements
Maintains posture
Produces heat
Nervous System
Components:
Brain
Spinal Cord
Nerves
Eyes
Ears
Functions:
Regulate body activities
Detects change in environment
Responds to change with muscular contractions & glandular secretions
Endocrine System
Components:
Glands & tissues that produce hormones
Functions:
Regulates body activities through hormones transported by the blood to various target organs
Cardiovascular System
Components:
Blood
Heart
Blood Vessels
Functions:
Heart pumps blood through vessels
Blood carries nutrients to cells, wastes away from cells
Helps regulate acidity, water, and temperature
Blood components help defend against disease
Mend damaged vessels
Lymphatic System & Immunity
Components:
Lymphatic Fluid
Lymphatic Vessels
Spleen
Thymus
Lymph Nodes
Tonsils
B & T Cells
Functions:
Returns proteins & fluid to blood
Carries lipids from GI tract to blood
Contains B & T cells
Respiratory System
Components:
Lungs
Pharynx
Larynx
Trachea
Bronchial Tubes
Functions:
Transfers O2 to blood, CO2 out of blood
Helps regulate acidity of fluids
Produces sounds through vocal chords
Digestive System
Components:
Mouth
Pharynx
Esophagus
Stomach
Small, large intestines
Rectum
Anus
Salivary Glands
Liver
Gallbladder
Pancreas
Functions:
Physical & chemical breakdown of food
Absorbs nutrients
Eliminates solid wastes
Urinary System
Components:
Kidneys
Ureters
Urinary Bladder
Urethra
Functions:
Produces, stores eliminates urine
Eliminates wastes & regulates volume & chemical composition of blood
Helps regulate acid-base balance of fluids
Mineral balance
Regulates red blood cell production
Reproductive System
Components:
Testes/Ovaries
Uterine Tubes
Uterus
Vagina
Epididymis
Ductus Deferens
Penis
Mammary Glands
Functions:
Gonads produce gamete that unite to form new organism
release hormones that regulate reproduction
Store & transport gametes
Mammary glands produce milk
Homeostasis
Tendency toward a relatively stable equilibrium between interdependent elements, especially as maintained by physiological processes
3 Homeostatic Control Mechanisms
Receptor: Provides info about stimuli
Control Center: Tells what a particular value should be
Effector: Elicits response that change conditions in the internal environment
Negative Feedback Systems
Reverse changes in a controlled condition
Regulation of BP, body temp, glucose regulation
5 Steps of Homeostatic Control
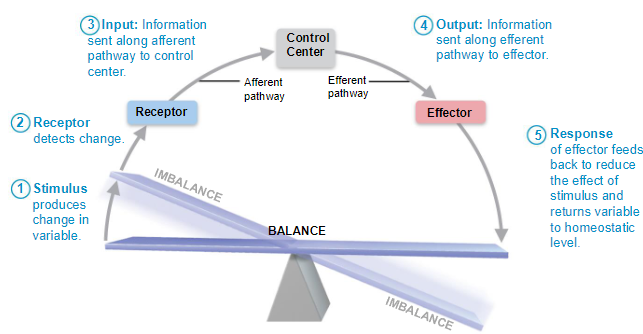
Homeostasis Example
Stimulus: Body temp exceeds 37C
Receptor: Skin senses the warmth
Input: Skin sends message to Hypothalamus
Control Center: Hypothalamus
Output: Hypothalamus signals the release of sweat
Response: Body sweats & releases heat
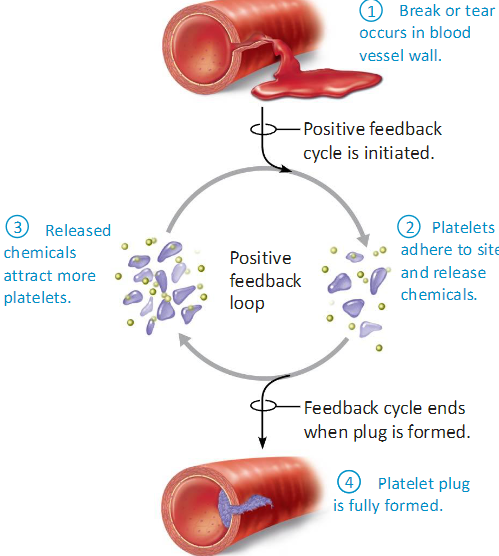
Homeostasis Positive Feedback Example