AP Pre-Calculus Need-To-Know
1/112
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
a²-b²
(a+b)(a-b)
a²+b²
No factor, is prime
a²+2ab+b²
(a+b)²
a²-2ab+b²
(a-b)^2
a³+b³
(a+b)(a²-2ab+b²)
a³-b³
(a-b)(a^2 + ab + b^2)
Function is increasing if
if a < b, then f(a) < f(b)
Function is decreasing if
if a < b, then f(a) > f(b)
Concave Up
Rate of Change is Increasing
Concave Down
Rate of Change is decreasing
Average rate of Change on [a, b]
Slope Formula
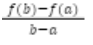
Degree in Standard Form
Highest Exponent
Degree in Factored Form
Sum of exponents
Local Min
Polynomial changes from decreasing to increasing
At a left endpoint where the polynomial is increasing
At a right endpoint where the polynomial is decreasing
Local Max
Polynomials changes from increasing to decreasing
At a left endpoint where polynomial is decreasing
At a right endpoint where polynomial is increasing
Absolute Max
largest y-value
Absolute Min
Smallest y-value
Point of Inflection
when concavity changes signs
End Behavior: Even Degree have
the same end behavior
End Behavior: Odd Degree have
opposite end behavior
Odd-Degree Roots
“cut” through the x-axis
Even-Degree Roots
“bounces” on the x-axis
Even function
f(-x) = f(x)
Odd Function
f(-x) = -f(x)
Positive Right End Behavoir
lim x → infinity f(x) = Infinity
Negative Right End Behavior
lim x → infinity f(x) = -Infinity
Positive Left End Behavior
lim x → - infinity f(x) = infinity
Negative Left End Behavior
lim x → - infinity f(x) = - infinity
Horizontal Asymptote at y = b if
lim x → infinity f(x) = b
lim x → - infinity f(x) = b
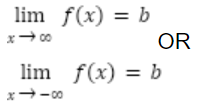
Vertical Asymptote at x = a if
lim x → a+- f(x) = +- infinity
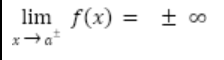
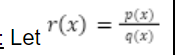
Let r(x) = p(x) / q(x)
When is there a zero
p(x) = 0
q(x) ≠ 0
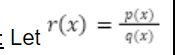
Let r(x) = p(x) / q(x)
When is there a Hole
p(x) = 0
q(x) = 0
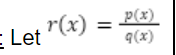
Let r(x) = p(x) / q(x)
When is there a Slant Asymptote
p(x) is 1 degree higher than q(x)
Pascal’s Triangle
Row # ____
Put Numbers for that row (note, first row is degree 0)
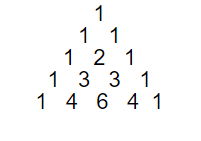
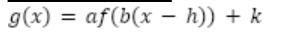
What is a
vertical dilation by a factor of |a|
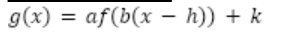
What is b
horizontal dilation by a factor of |1/b|
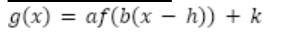
What is h
horizontal translation by h units (left or right)
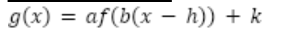
What is k
vertical translation by k units (up or down)
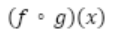
(f * g)(x) =
f(g(x))
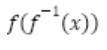
Inverse: f(f-1(x)) =
x
Arithmetic Sequence equation
an = a0 + dn
or
an = ak + d(n-k)
Geometric Sequence equation
gn = g0(r)n
or
gn = gk(r)(n - k)
lim x → infinity b^x =
infinity
lim x → - infinity b^x =
0
lim x → infinity (1/b)^x =
0
lim x → - infinity (1/b)^x =
infinity
b^m * b^n
b^m+n
(b^n)^m
b^m*n
b^-n (Simplified)
1/b^n
b^(1/k) = (simplify)
^k Sqrt B
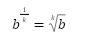
lim x → 0^+ logb (x) =
-infinity
lim x → infinity logb (x) =
infinity
Exponential Growth: y = (in terms of b)
b^x
Decay: y = (in terms of b)
(1/b)^x
Change of base: logb (x) =
loga (x) / loga (b)
logb (xy) = (Expanded Form)
logb (x) + logb(y)
logb (x/y) = (expanded version)
logb (x) - logb(y)
logb (x)^n = (expanded form)
n * logb (x)
b^x = (in terms of c^log something)
c^(logc(b) * x)
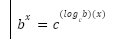
Linear Model for the semi-log plot: (using base of n, and variables b & a)
y = logn(b) * x + logn(a)
sin(θ) =
y/r
cos(θ) =
x/r
a sin(b(θ + c)) + d
midline: y = d
amplitude: |a|
period: 2pi/b
Frequency: b/2pi
a cos(b(θ +c)) + d
midline: y = d
amplitude: |a|
period: 2pi/b
Frequency: b/2pi
sin(θ) = cos(
θ - pi/2
cos(θ) = sin(
theta + pi/2
a tan(b(θ + c)) + d
Period: pi/b
Frequency: b/pi
y = sin^-1(x) Domain and Range
[-1, 1] and [-pi/2, pi/2]
y = cos^-1(x) Domain and Range
[-1, 1] and [0, pi]
y = tan^-1(x) Domain and Range
(-infinity, infinity) and (-pi/2, pi/2)
csc(x)
1/sin(x)
sec(x)
1/cos(x)
cot(x)
1/tan(x)
cos(x) / sin(x)
sin² + cos² =
1
1 + tan² =
sec^2
1 + cot² =
csc^2
sin(A + B)
sin(A)cos(B) + cos(A)sin(B)
sin(A - B)
sin(A)cos(B) - cos(A)sin(B)
cos(A + B)
cos(A)cos(B) - sin(A)sin(B)
cos(A - B)
cos(A)cos(B) + sin(A)sin(B)
sin(2x) =
2sin(x)cos(x)
cos(2x) =
2cos^2(x) - 1
1 - 2sin^2(x)
cos^2(x) - sin^2(x)
Polar x =
rcos(θ)
Polar y =
rsin(theta)
(Polar) x² + y² =
r²
The distance between r and the origin is increasing if
r is positive and increasing OR
r is negative and decreasing
The distance between r and the origin is decreasing if
r is positive and decreasing OR
r is negative and increasing
(Parametric) f(t) =
(x(t), y(t))
min and max of x(t)
horizontal extrema
min and max of y(t)
vertical extrema
t-value when y(t) = 0
x-intercept
t-value when x(t) = 0
y-interceptx
x(t) is decreasing
particle is moving left
x(t) is increasing
particle is moving right
y(t) is decreasing
particle is moving down
y(t) is increasing
particle is moving up
Parametric slope formula for x
(x(t2) - (x(t1)) / (t2 - t1)
(delta x / delta t)
Parametric slope formula for y
(y(t2) - y(t1)) / (t2 - t1)
(delta y / delta t)
Parametric average rate of change =
(delta y / delta t) / (delta x / delta t)
(delta y / delta x)
Ellipse Standard Form
(x-h)² /a²+ (y-k)² /b²= 1