Structure and Functions of the male reproductive system (Key Points)
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
a) 40 days
b) At birth
When should the testicles be fully descended in the a) dog b) cat ?
-Testicles
-Epididymis
-Scrotum
-Spermatic cord
-Urethra
-Penis
-Prepuce
-Prostate gland
-Bulbourethral glands
What does the male reproductive system comprise of?
a) To produce the male gamete (sperm) and seminal fluid
b) To facilitate coitus
What are the functions of the male reproductive system?
No - they vary considerably.
Are the reproductive tracts of male cats and dogs similar?
A skin covered sac that houses the testis.
What is the scrotum?
a) Between the hindlegs
b) Between the anus and the prepuce
Where is the scrotum situated in a) dog b) cat ?
The optimal temperature for spermatogenesis is slightly below normal body temperature.
Why is the scrotum situated outside the abdominal cavity?
Testicular septum.
What separates the two testes inside the scrotum?
-Inside the scrotum
-Left is positioned more caudal than the right
Describe the normal topography of the testis in the dog
Directly from the abdominal aorta.
Where does the testicular artery branch from?
Structure:
-Testicular vein forms a convoluted mesh around the testicular artery
Function:
-As blood moves towards the testicle it is cooled by blood leaving the testicle
Describe the structure and function of the pampiniform plexus
1) Production of male gamete
2) Production of oestrogen and nutritive fluid for sperm by Sertoli cells
3) Production of testosterone by Leydig cells
What are the 3 functions of the testicles?
Alongside the posterior side of each testicle in the scrotum.
Where is epididymis located?
Via the efferent ducts where it is stored.
How is sperm carried to the epididymis?
In the seminiferous tubules firstly by mitosis then by meiosis to produce immature sperm.
How does a spermatogonium (stem/germ cell) divide?
In the seminiferous tubules.
Where do immature sperm cells mature?
Epididymis to urethra.
Where does the spermatic cord run from?
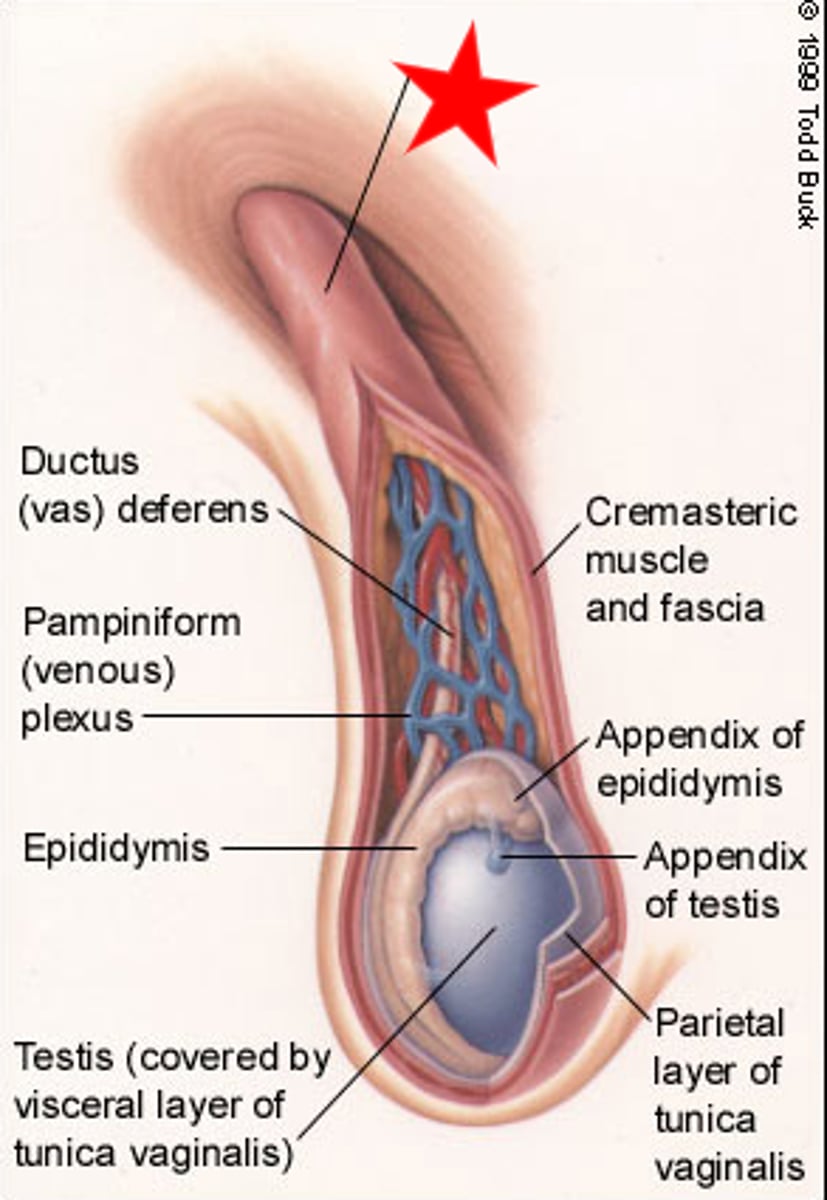
-Deferent duct (vas deferens)
-Testicular artery and vein
-Nerve supply
-Lymphatic supply
-Cremaster muscle
What does the spermatic cord consist of?
Alters the proximity of the testicles in relation to the body for temperature control of the testis.
What is the function of the cremaster muscle?
Within the tunica vaginalis.
Where are all components of the spermatic cord contained?
Through the inguinal canal.
How does the spermatic cord enter the abdominal cavity?
Urethra (shared with urinary tract).
Where does the deferent duct open into?
Dog:
-Long
-Curved
Cat:
-Short
-Straight
Describe the differences of the urethra between dogs and cats
Dogs:
-Ventral abdominal surface
-Point cranially
Cats:
-Below the testicles
-Point caudally
Where are the prepuce and penis situated in dogs and cats?
Structure:
-Outer surface covered in skin
-Inner surface lined with mucous membranes
Function:
-Houses distal part of penis
-Protects the penis
-Only drawn back when the penis is erect
Describe the structure and function of the prepuce
Structure:
-Mainly erectile tissue which fills with blood during arousal
Function:
-Allows mating to occur
Describe the structure and function of the penis
Dog:
-Smooth mucous epithelium
Cat:
-Barbed epithelium
Describe the differences of the surface of the penis between dogs and cats
Ossified erectile tissue forming a U-shaped bone in dogs and some cats.
What is the os penis?
Through the centre of the penis and groove of os penis, to terminate at the tip of the penis.
Where does the urethra run in the penis?
Pulls the penis back into the prepuce after mating.
What is the function of the retractor penis muscle?
-Arteries supplying the penis dilate increasing blood flow
-Drainage slowed by inhibition of venous supply via contraction of surrounding muscles
-Blood enters erectile tissue causing distension
Explain the mechanism of a penile erection
-Surrounding muscles relax, allowing venous drainage to occur and the arteries reduce in size
-Thus the penis returns to a flaccid state
What happens to the penis post-ejaculation?
Seminal fluid (makes up volume of ejaculate, contains nutrients for sperm).
What do the prostate and bulbourethral glands produce?
Junction of deferent duct and urethra (completely surrounds urethra)
Where is the prostate gland located?
a) Not present.
b) Distally around the urethra.
Where are the paired bulbourethral gland located in a) dog b) cat ?
Urethra.
Where are the secretions of the prostate and bulbourethral glands delivered?
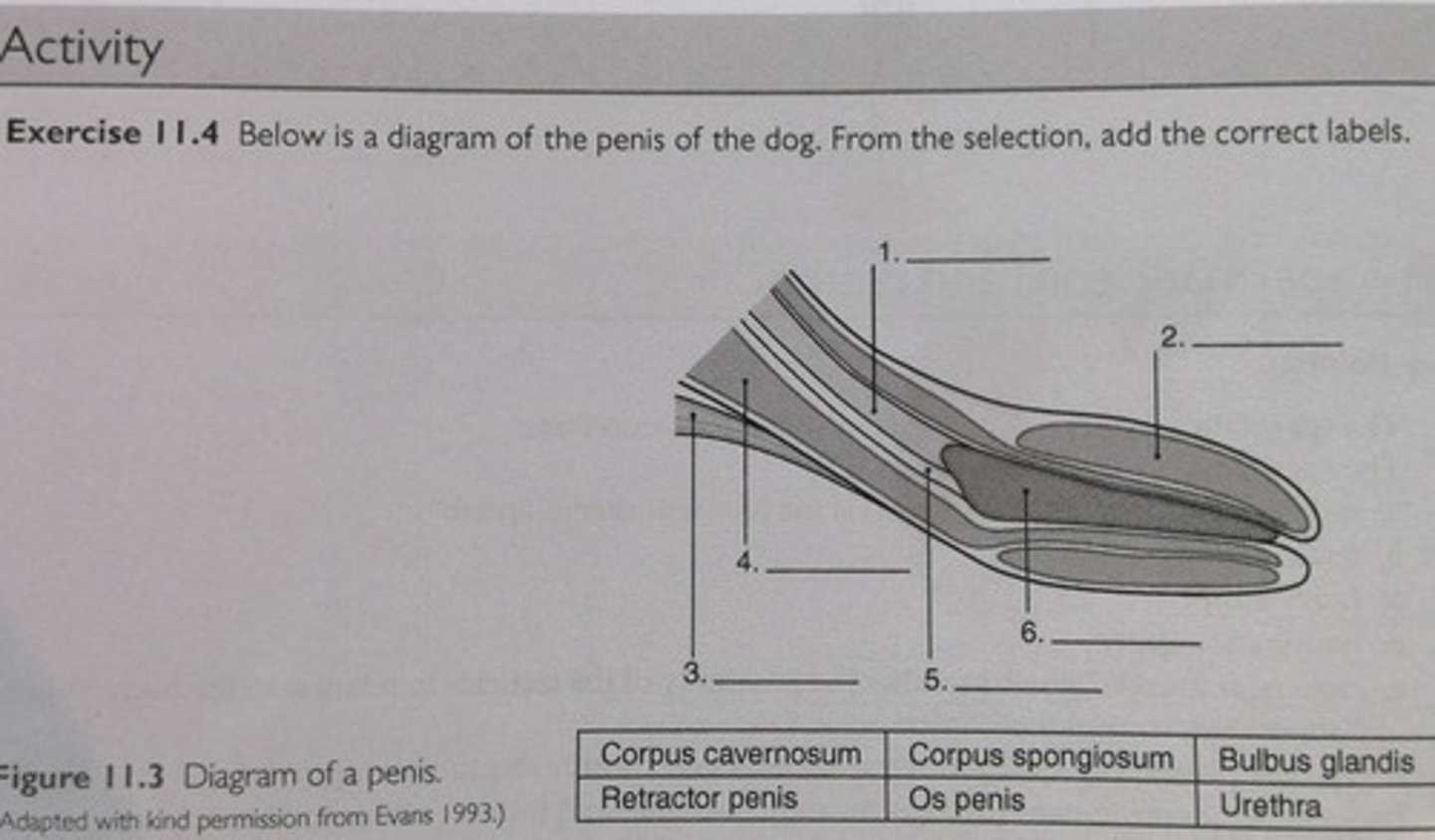
1. Corpus cavernosum
2. Bulbus glandis
3. Retractor penis
4. Corpus spongiosum
5. Urethra
6. Os penis
Label this image
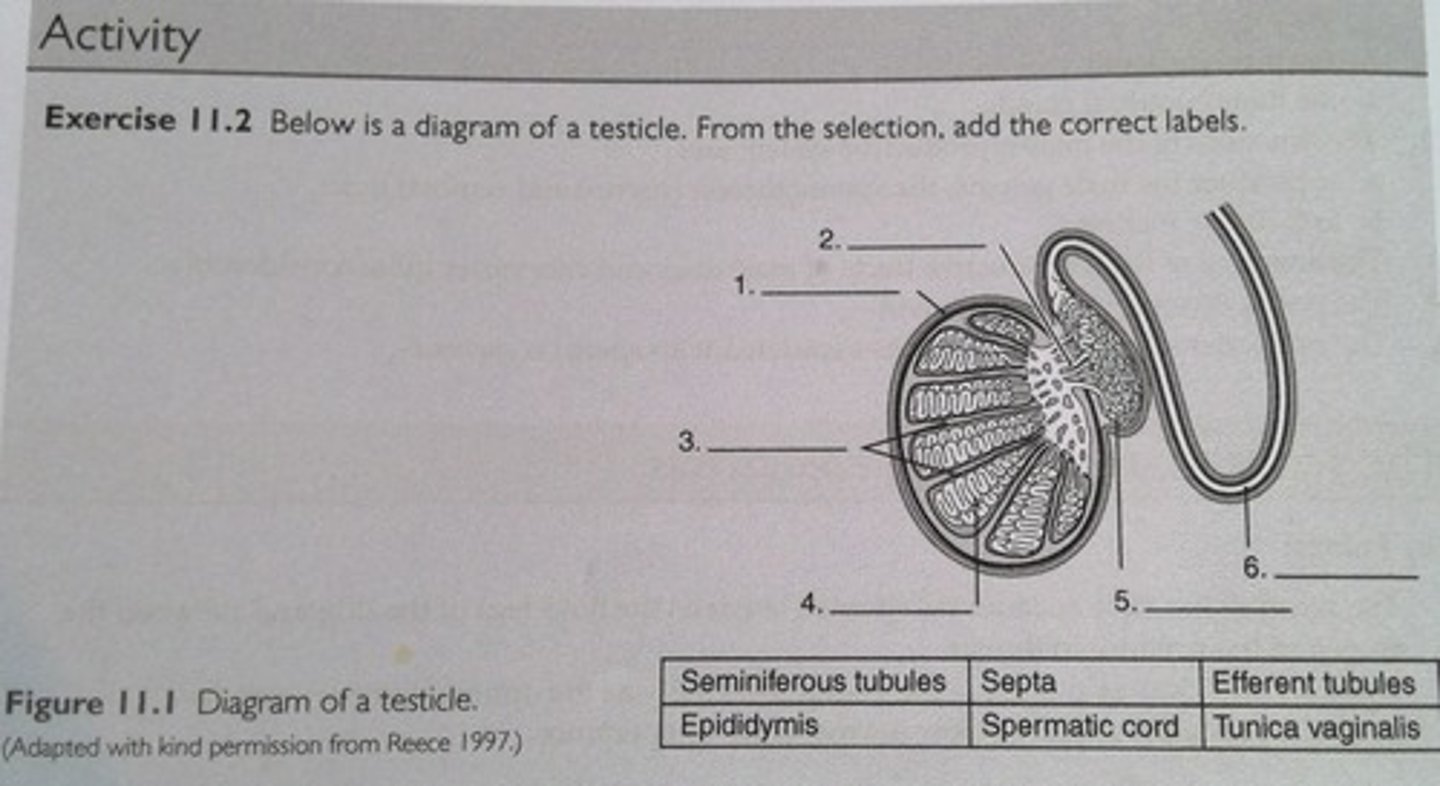
1. Tunica vaginalis
2. Efferent tubules
3. Septa
4. Seminiferous tubules
5. Epididymis
6. Spermatic cord
Label this image