Small Animal Vaccinations and Pet Travel
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What are the core vaccines for dogs in the UK?
Distemper, Hepatitis, Parvo, Leptospirosis.
What are core vaccines?
Those which ALL dogs & cats, regardless of circumstances or geographical location, should receive
What are non-core vaccines?
Vaccines that are required by only those animals whose geographical location, local environment or lifestyle places them at risk of contracting the disease.
What are the non-core vaccines for cats in the UK?
Rabies.
Describe the brief aetiology of canine distemper virus
Viral disease causing respiratory and neuro signs
Can lead to hypokeratosis (hard pad)
Describe the brief aetiology of canine hepatitis
Caused by Adenovirus, CAV-1.
Viral disease, causes hepatic disease due to viral replication in the liver.
Describe the brief aetiology of canine parvovirus
Extremely infectious viral disease affecting rapidly dividing cells in GI tract & bone marrow
Haemorrhagic D+ syndrome & leucopenia
Describe the brief aetiology of leptospirosis
Bacteria causing acute kidney injury and hepatic disease.
ZOONOTIC
What are the main vaccines in Britain for canines?
DHP
Lepto4
What components does the kennel cough vaccine contain?
Bordatella bronchiseptica, Canine parainfluenza virus
When would we normally administer DHP?
Two doses 2-4 weeks apart - 6 and 10 weeks of age
In dogs over 10 weeks single dose is likely to be sufficient to immunise
When would you normally administer L4 in a puppy?
Two vaccinations with the first 6-9 weeks of age and the second between 10-13 weeks of age
What are the different options for boosters in canines?
DHP every 3 years after one booster, L4 every year
Bring one vaccination forward 26 weeks to catch any non-responders
Some practices do third vaccine at 16 weeks of age or older to ensure dose given when MDA waned (would not do 26 week vaccine)
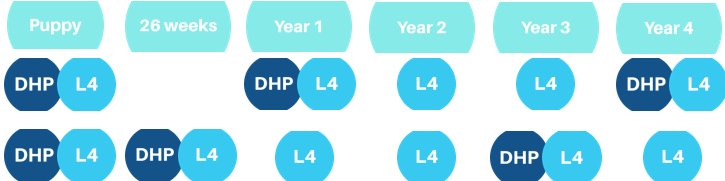
Why aren't 2nd vaccines given before 10 weeks old?
As at around 10wk/o the maternally derived antibodies (MDAs) begin to decline in the young animal. This means that they would be vulnerable around 10wk/o so it is best giving the 2nd vaccine shortly after this age.
What are the non-core vaccines for dogs in the UK?
Parainfluenza, rabies, herpes, Bordetella bronchiseptica (kennel cough).
What does parainfluenza cause?
Viral disease causing respiratory signs - part of kennel cough complex
Describe the brief aetiology of Bordatella bronchiseptica
Causes infectious respiratory infection. Delivered as a live vaccine (do not give to dogs with immunocompromised owners).
When is the herpes vaccine given?
For breeding/pregnant animals and rarely used/given in general practice
When is the rabies vaccine given?
Part of pet travel requirements —> varies on individual country requirements
What are the core vaccines for cats in the UK?
Feline calicivirus, Feline herpesvirus, Feline panleucopenia, Feline leukaemia virus (for outdoor cats).
Describe the brief aetiology of feline calicivirus
Viral disease causing signs such as oral ulceration, gingival-stomatitis. Commonly isolated with "cat flu".
Describe the brief aetiology of feline herpes virus
Viral disease causing corneal ulceration, keratitis, chemosis. Can be persistently infected with flares —> associated with stress & isolated witth “cat flu”
Describe the brief aetiology of feline panleucopenia
Extremely infectious viral disease that has a high mortality rate in affected kittens.
Affects rapidly dividing cells in GI tract & bone marrow
Haemorrhagic D+ w/ leucopenia
Describe the brief aetiology of feline leukaemia virus
Retroviral disease causing immunosuppression, anaemia, neoplasia.
What are the feline vaccinations in practice?
Nobivac Tricat (Calici, Herpes, Panleucopaenia)
FeLV
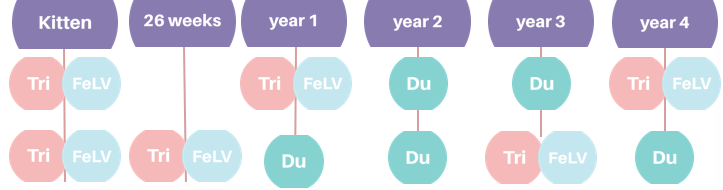
When would you carry out the Tricat and FeLV vaccination in kittens?
Two single dose inoculations 3-4 weeks apart - first at 8 weeks and second at 12 weeks
What cats are classed as high risk, medium risk and low risk?
Which vaccines are given to each risk group?
High - Outdoor cats —> Tricat & FeLV primary course
Medium - cats that live with outdoor cats or indoor cats who go to catteries —> Tricat & FeLV primary course
Low - Indoor cats —> Tricat inly
At what weeks does the VGG recommend vaccinating kittens?
(vaccinations guidelines group)
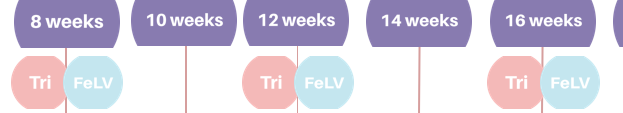
How would giving boosters differ between high and low risk felines?
Tricat/FeLV every 3 years, Ducat annually (calici/herpes)
What are the requirements for a dog, cat or ferret to travel in the EU?
Microchip
Rabies vaccine (must be over 12wk/o)
21 days later travel is possible with a animal health certificate issued by a vet (within 10 days of travel)
Tapeworm within 5 days of travel for certain countries
valid for 4 months of onward travel within EU or return to UK within this time
What are the requirements for a dog, cat or ferret to travel in to Northern Ireland?
Microchip
PTD issued —> valid for the lifetime of the pet
Inform DEFRA of travel plans 10 working days ahead of travel
How many pets and owners are on the animal health certificate (AHC)?
5 pets to 1 owner max.