cytoskeleton
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
classes of cytoskeleton
actin filaments
intermediate filaments
microtubules
actin is found in
all eukaryotic cells
actin filaments are
a polymer made up of actin monomers
exists as a globular protein
why are rings of actin important in axons
maintain the structure and diameter of axon
therefore important for action potentials
actin is organised in
bundles or meshed networks/branched arrays
actin is important for
force exertion
cell movement
cell division
actin based structures in motile cells
stress fibres
lamellipodium
filopodia
actin in yeast cells/yeast budding
high density of actin at edges of yeast budding
the actin filaments force the yeast cells to divide/ cytoplasm to divide
mutations in actin cause multiple disorders including
muscular dystrophy
haemolytic anaemias
polymerisation of actin filaments
G-actin reversibly polymerise to form F-actin, a double-helical actin filament with a diameter of 5–8 nm.
Actin filaments are polar, with a plus (barbed) end and a minus (pointed) end.
Subunits add to both ends, but faster at the barbed end.
ATP-bound actin adds to the filament; ATP is then hydrolysed to ADP, making the filament less stable at the pointed end.
As actin adds at the plus end and dissociates at the minus end, monomers appear to move along the filament — this is actin treadmilling.
what is microtubule
filament of tubulin monomers
a sarcomere is
the basic unit of contractile muscle fibres
composed of actin and myosin
myosin II is a
motor protein that interacts with F-actin
4 classes of intermediate filaments
keratins → in epithelia
vimentin & vimentin-related → in connective tissue, muscle cells, glial cells
neurofilaments → in nerve cells
nuclear lamins → in all animal cells
when pressure is applied on cells
the tension can spread across the intermediate filaments
keratin monomers are
fibrous proteins
microtubules originate in
MTOCs such as the centrosome
MTOC
microtubule organising centre
point where polymerisation starts
why are microtubules in cilia in lung cells important
for sweeping away mucus, keeping pathogens away
kinesin
type of motor protein that act on microtubules
from minus to plus end
dynein
type of motor protein that acts on microtubules
move from plus to minus end
movement of motor proteins along microtubules
use ATP to generate kinetic energy and carry proteins, RNA, vesicles, organelles etc. along
lamins are
intermediate filaments that support the nuclear envelope
centrosome is
cell’s organising centre for microtubule growth
Myosin filaments
are bundles of motor proteins that interact with actin fibres in muscle
which factors destabilise microtubules
vinblastine
nocodazole
colchicine
by inhibiting microtubule formation
arrangement of cytoskeleton
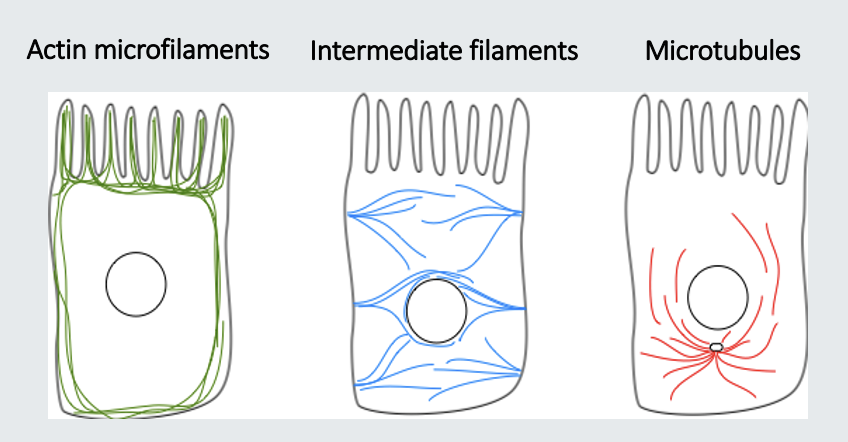
a form of dynein enables
cilia to beat