Load Metrics
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
PAX
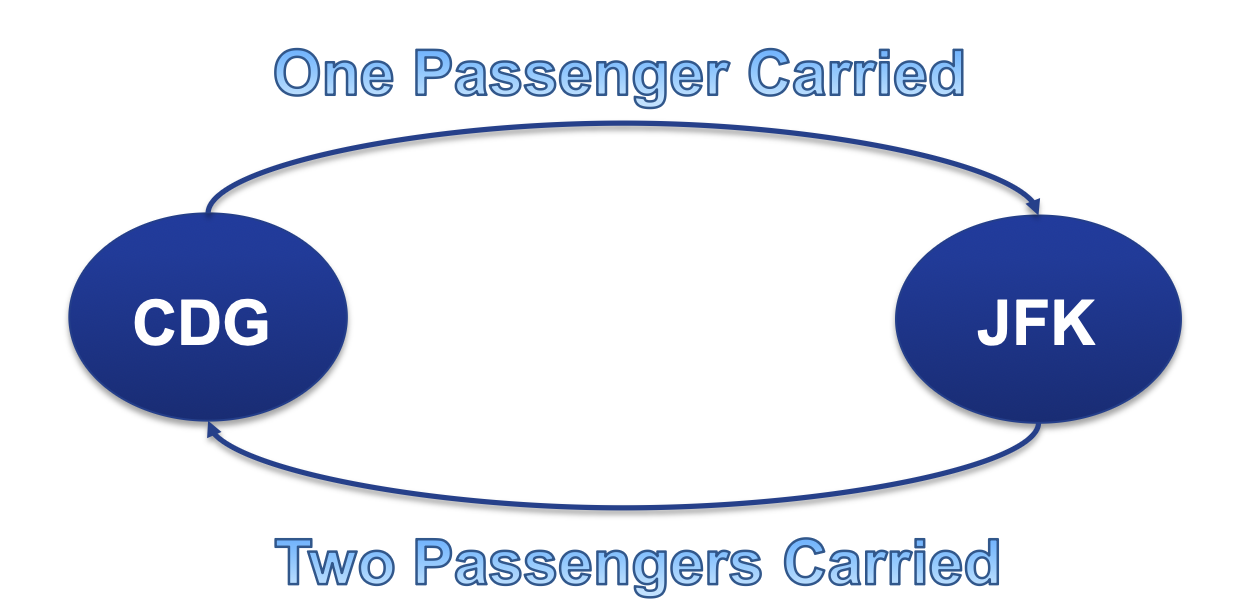
the number of passengers carried over a single leg.
A passenger travels to Prague for a vacation trip, then they fly to Hong Kong to visit their family, and finally returns home. In this situation, how many passengers are carried?
3 PAX
The total number of passengers carried is 3, consisting of one passenger's trips to Prague, Hong Kong, and back home.
MOV
the metric for aircraft movement
What other related metrics use MOV?
the number of flights, number of departures, or number of sectors.
What difference does the number of flights, number of departures, or number of sectors have with aircraft movement?
aircraft movement refers specifically to the number of takeoffs and landings of aircraft, while number of flights, number of departures, or number of sectors represent ONLY the take-offs.
RPK
Revenue Passenger Kilometre
Describe RPK.
a measure of distance, representing the number of kilometres traveled by revenue-paying passengers.
Define RPK. How is it calculated? What is it dependent on?
The number of revenue-paying passengers and the average distance traveled by those passengers.

PASL
Passenger Average Sector Length
Describe PASL.
the average distance flown by passengers in kilometres.
Why is PASL important to airlines?
It helps airlines understand travel patterns, optimize routes, and maximize revenue by assessing the efficiency of passenger journeys.
Cargo is often referred to as…
FRT
Define FRT.
the number of tonnes of fright that is carried over a single leg.
FASL
Fright Average Sector Length
Describe FASL.
the average distance that cargo is carried.
The preferred metric for the amount of freight that an airline carries is?
RFTK
Describe RFTK.
The weight of revenue cargo that is carried and flown over a distance by an airline.
Define RFTK. How is it calculated? What is it dependent on?
Taking the product of the weight of cargo (FRT) and the average distance which it is flown (FASL).

The main difference between FRT and RFTK.
FRT is independent of the distance flown: FRT refers to JUST the weight of the cargo. RFTK refers to the distance AND the weight that the cargo is flown and carried.
Revenue Passenger Tonne Kilometres
RPTK
Describe RPTK.
A passenger load metric that combines the distance that passengers have flown and average weight (in tonnes) that is bought on by these revenue passengers.
Define how RPTK is calculated.
Taking the Revenue Passenger Kilometres and multiplying with the Average Passenger Weight.

Average passenger weight
APW
What 3 weight components contribute to the total APW?
passengers’s body weight
cabin baggage
checked-in baggage
How many kg is in 1 tonne?
1000
What unit is APW is calculated in?
kg
Describe APW.
The average passenger weight that is bought onto the aircraft.
Define how APW is calculated:
Taking the calculated revenue passenger tonne kilometres and dividing it by the total revenue passenger kilometre. Lastly, take the quotient and multiply by 1000 to convert into correct units used for APW.

Revenue Tonne Kilometres
Revenue Tonne Kilometres

What type of statistics is RTK utilised for?
For an airline’s distance and weight statistics.
RTK is the sum of…
RPTK and RFTK

Describe RTK.
The total freight and passenger load of an airline.