Chapter 2, Lesson 3: Energy and Chemical Reactions
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards from Chapter 2, Lesson 3 of McGraw Hill Anatomy and Physiology, Ninth Edition, by Kenneth S. Saladin.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Energy
The capacity to do work; all body activities are work
Potential energy
Energy stored in an object but not currently doing work (e.g. water behind a dam)
Chemical energy
Potential energy in molecular bonds
Free energy
Potential energy available in a system to do useful work
Kinetic energy
The energy of motion which is doing work (e.g. water flowing through a dam)
Heat
The kinetic energy of molecular motion
Electromagnetic energy
The kinetic energy of moving packets of radiation called photons
Chemical reaction
Process in which a covalent or ionic bond is formed or broken
Chemical equation
Symbolizes the course of a chemical reaction; reactions on the left → products on the right
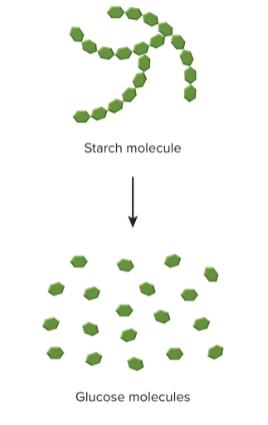
Decomposition reactions
Large molecule breaks down into two or more smaller ones; AB → A + B
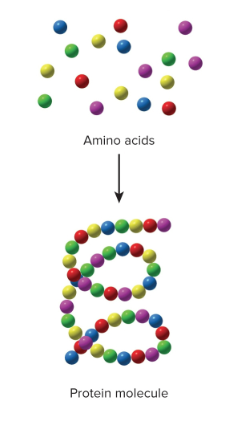
Synthesis reactions
Two or more smaller molecules combine to form a larger one; A + B → AB
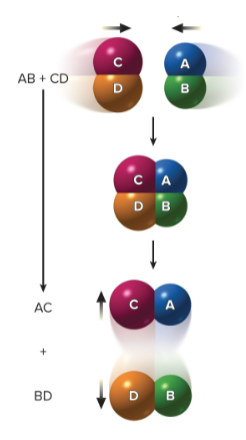
Exchange reactions
Two molecules exchange atoms or a group of atoms; AB + CD → ABCD → AC + BD
Reversible reactions
Reactions that can reverse under different circumstances; symbolized with a double-headed arrow
Law of mass action
Direction of reaction determined by relative abundance (quantity) of either side of equation
Increasing reaction rate causes
Rising temperature, concentrated reactants, catalysts like enzymes to lower the reaction energy
Metabolism
All chemical reactions of the body
Catabolism
Energy releasing (exergonic) decomposition reactions that break covalent bonds and produce smaller molecules
Anabolic reactions
Energy storing (endergonic) synthesis reactions that require energy input (e.g. production of fat)
Oxidation
A chemical reaction in which a molecule gives up electrons and releases energy
Reduction
Any chemical reaction in which a molecule gains electrons or energy
Oxidizing agent or reduced molecule
The molecule that accepts the electrons; oxygen is often the acceptor
Reducing agent or oxidized molecule
The molecule that donates electrons
Oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions
Oxidation of one molecule (giving away electrons) is always accompanied by reduction of another (gaining electrons); electrons are transferred as hydrogen atoms