AP Chemistry Unit 2
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
The process of bonding redistributes (blank)
valence electrons so each atom in a bond can have eight assigned to it.
The octet rule
bonds can have 8 assigned to it
Atoms redistribute valence electrons by (blank)
transferring them fully to other atoms, or by sharing with other atoms
The energy required to pull them apart and break the resulting bond is called (blank)
Bond energy
Metals lose electrons to become (blank)
cations
Nonmetal gain electrons to become (blank)
anions
The electrostatic attractions ions experience is an (blank)
ionic bond
Ionics which are also called salts, are made of these ions arranged in a (blank)
Lattice structure
Melting or boiling salts requires (blank)
breaking the ions out of the lattice so they are free to move around as a liquid or gas
Salts tend to have tremendously (blank)
high melting and boiling points
the bond energy required to break ions out is called (blank)
Lattice energy
The strength of the ionic bond is directly proportional to the (blank)
Magnitude of charge on the ions and inversely proportional to the distance between them
Ex: NaF has a +1 charge and MgO2 has +2, therefore MgO2 would have the higher melting and boiling point
Can’t use charge to rank ALL of the ions
Metal bonds are generally stationary but their valence electrons don’t belong to a specific atom, this is called
Sea of electrons
“Fluid” electrons explain why (blank)
metals are such good conductors of electricity and heat and why metals are malleable. Also why they do not mix well with other phases
Ex: not soluble in water
Metals can bond with each other to form (blank)
alloys
Interstitial Alloy and Substitutional alloy
interstitial Alloy are metal atoms with two vastly different radii combine
Substitutional alloy forms between atoms of similar radii
In a covalent bond, two atoms share (blank)
electrons
The law of definite proportions states (blank)
that molecules of a certain compound are made of a characteristic number of different types of atoms
The first covalent bond formed between two atoms is called (blank)
a sigma bond
Additional bonds (double/triple) between the two atoms are formed are called (blank)
pi bonds
This (blank) corresponds to the distance where the atoms are most stable with the lowest potential energy
internuclear distance
The depth of the well below zero potential energy is the (blank)
Bond Strength
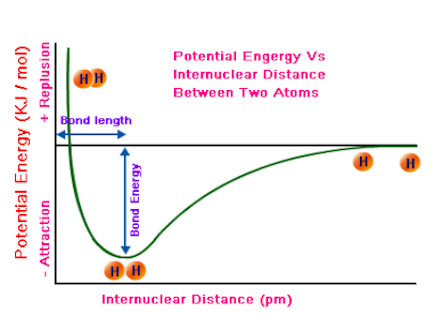
What do the 3 areas in this graph mean?
The point at 0 means they’re not interacting
further left and below zero, this favorable interactions gets them to a more stable state with lower potential energy than not interacting at
The highest point means that the nuclei repel each other as they get too close together
In a (blank) atoms are held together in a lattice of covalent bonds.
Network Solid
Network Solids are (blank)
very hard, have very high melting and boiling points, and are insoluble in water.
Network Solids contain (blank)
Carbon or Silicon because they have four valence electrons, which means they can form many covalent bonds
Electricity is conducted through the (blank)
Ions and Electrons
Solid Ionic substances are not conductors of electricity because (blank)
The ions trapped in the lattice structure on to their electrons and are immobile
If a salt is dissolved in water or melted, the (blank)
Lattice breaks down and the mobile ions formed can conduct electricity.
Solid and liquid metals conduct electricity because (blank)
of their highly mobile sea of valence electrons
Why don’t Covalent substances conduct electricity?
Their valence electrons are immobilized between the atoms and there are no ions to speak of.
Is pure water a good conductor?
No because most water that humans use is not very pure.
How well an aqueous solution conducts electricity depends on the (blank)
total concentration of dissolved ions.
How to draw a lewis dot structure
Count the total number of valence electrons, (for anions or cations make sure to either add or subtract)
Draw atomic symbols and draw lines connecting them
Calculate the number of electrons assigned to each atom
add and assign lone pairs until the peripheral atoms have 8 bonded and lone to fulfill the octet rule
Add remaining to the central atom
If the central tom has fewer than 8 than remove a pair from an outer atom to add another bond
How to find the average bond order?
The sum divided by the number of resonance structures.
Ex: 1+2+/3 (the top is the bonds, single bond, double bond
Some resonance forms are better than others, you can select which ones based on (blank)
Formal Charge
Formal charge is calculated by
subtracting the electrons assigned to an atom in molecule step from the number of valence electrons in the unbound atom.
Rules of Formal Charge
Negative chargers are more stable when they are on the electronegative atom
and the opposite for positive chargers
Incomplete Octets and Expanded Octets
Incomplete Octets means that some atoms are stable with less than eight atoms (Hydrogen, Helium, Beryllium and boron)
Expanded Octets Certain atoms are large enough to accommodate more than eight electrons but never more than 12 (Phosphorus, sulfur, chlorine, larger noble gases can also do this.
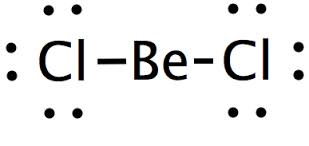
Name the shape, angle and amount of lone pairs and domains
Linear
180
0
2
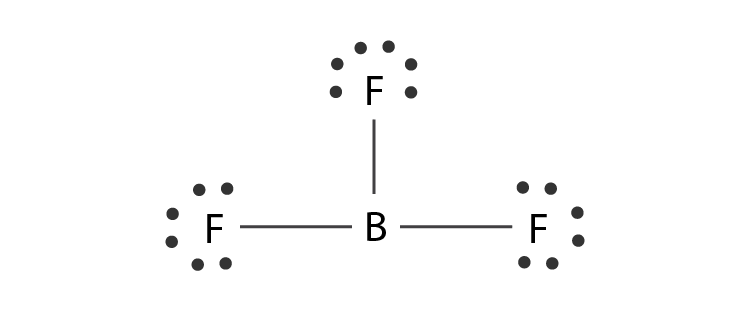
Name the shape, angle, amount of lone pairs and domains
Trigonal Planar
120
0
3
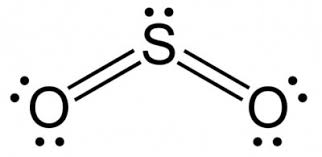
Name the shape, angle, amount of lone pairs and domains
Bent
120
1
3
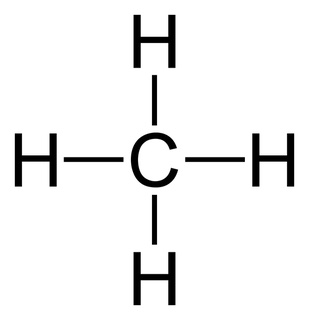
Name the shape, angle, amount of lone pairs and domains
Tetrahedral
109.5
0
4
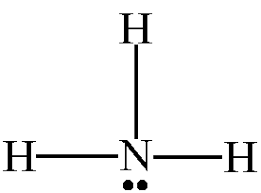
Name the shape, angle, amount of lone pairs and domains
Trigonal Pyramidal
109.5
1
4
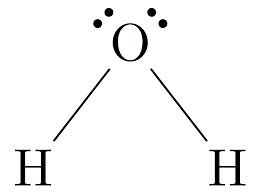
Name the shape, angle, amount of lone pairs and domains
Bent
109.5
2
4
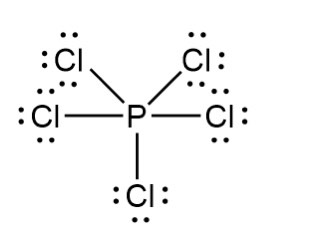
Name the shape, angle, amount of lone pairs and domains
Trigonal bipyramidal
120 and 90
0
5
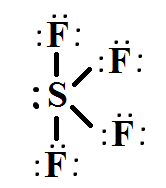
Name the shape, angle, amount of lone pairs and domains
seesaw
120 and 90
1
5
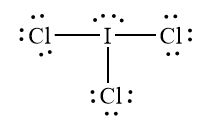
Name the shape, angle, amount of lone pairs and domains
T-shaped
120 and 90
2
5
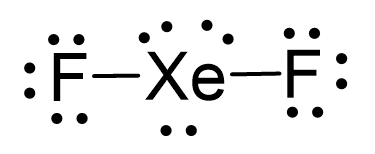
Name the shape, angle, amount of lone pairs and domains
Linear
120 and 90
3
5
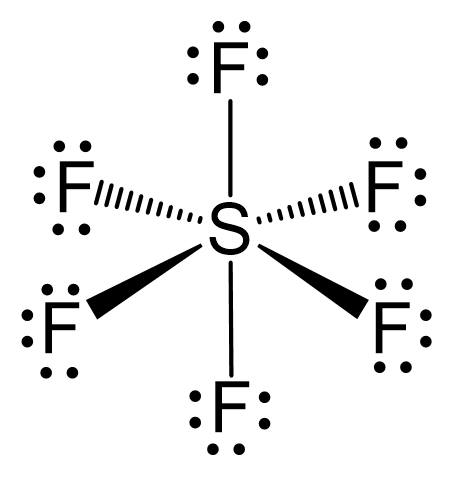
Name the shape, angle, amount of lone pairs and domains
Octahedral
90
0
6
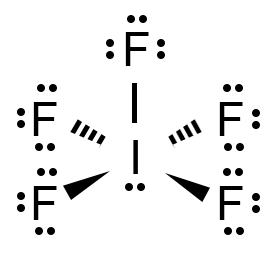
Name the shape, angle, amount of lone pairs and domains
Square Pyramidal
90
1
6
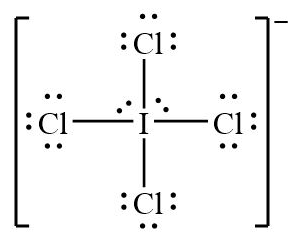
Name the shape, angle, amount of lone pairs and domains
Square Planar
90
2
6