NSG 501 Exam 4 With complete verified solutions 2025-2026
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
continuum of care
curative care, palliative care, hospice, death and bereavement care
preventative care
aims to improve and maintain health by ensuring people do not fall ill in the first place
(smoking cessation, healthy eating, weight loss, reducing alcohol use, etc)
curative care
treatment directed toward curing a patient's disease
palliative care
aims to improve the quality of life for clients and families coping with a life threatening and life limiting illness
hospice care
-must have a prognosis of 6 months or less
-cannot be receiving active medical treatment
-symptom management (especially pain), decision making about EOL issues, and support for client and family
advanced directives
a written statement of a person's wishes regarding medical treatment, often including a living will, made to ensure those wishes are carried out should the person be unable to communicate them to a doctor.
role of nurse in end of life issues
-pain management
-communication with patient is equal to or supersedes clinical skill in EOL care
-awareness of cultural differences
-spiritual needs
-presence
actual loss
can no longer see, touch, hear, or have near person or something
perceived loss
uniquely defined by the person experiencing the loss and is less obvious to other people
maturational loss
a lifetime of normal development processes. ex kid goes to school and mom feels loss, kid may also feel loss. They spend less time together.
situational loss
unpredictable external events that brings loss
signs of approaching death
-loss of appetite
-sleeping or coma
-decreased UO
-disorientation, restlessness, agitation
-changing vital signs
-severe dyspnea
-cool skin and change in color
-hearing last sense to go
care of the body after death
-confirm death
-is autopsy requested or required?
-verify organ/tissue donation status
-patient identifiers
-provide care that is sensitive/culturally appropriate
-elevate HOB
-remove equipment as appropriate
-cleanse and cover body
-prepare environment (deodorizer, lower lights)
-allow families to view body
-provide privacy for grieving
-determine disposition of belongings
-after viewing - shroud and place
-complete documentation
-maintain privacy and dignity on transport
loss vs grief
Loss: the experience of separation from something of personal importance
Grief: deep emotional and mental anguish that is a response to the subjective experience of loss of something significant
Loss is the act of losing something, whereas grief is the emotional response to the loss****
types of loss: possessions or objects
what is the value of the object?
what is the sentiment attached to it? what was its usefulness?
types of loss: familiar environment
is the loss due to situational or maturational events? does the loss occur because of illness or injury? does loneliness, social isolation threaten self-esteem, belonging, or hopefulness?
types of loss: significant other or relationship
close friends, family members, divorce, pets. does loss threaten safety, love concept?
types of loss: aspect of self
illness, injury, valued aspect (fertility), identity
types of loss: life
grieving occurs in the dying and those left behind
factors that influence responses to loss and grief
-age and stage of development
-relationship to the lost object/person
-significance and meaning of the loss
-culture and ethnicity
-spiritual and religious beliefs
-gender
-socioeconomic status
-support system
-coping strategies
-cause of loss or death
-multiplicity of losses
Kubler-Ross' 5 stages of grief
1. Denial
2. Anger
3. Bargaining
4. Depression
5. Acceptance
theories of loss: attachment theory
-numbing: protects the person from the full impact of the loss
-yearning and searching: emotional outbursts, acute distress
-disorganization and despair: endless examination of why
-reorganization: accepts the change
theories of loss: grief tasks model
-accepts the reality of the loss
-experiences the pain of grief
-adjusts to a world without the loved one/thing
-emotionally relocates the decreased and moves on with life
theories of loss: Rando's R process model
-recognizing the loss
-reacting to the pain of separation
-reminiscing
-relinquishing old attachments
-readjusting to life after loss
-reminiscence
theories of loss: dual process model
-loss-oriented
-restoration-oriented
theories of loss: trajectories of bereavement
-common grief
-chronic grief
-chronic depression
-depression followed by improvement
-resilience
cultural differences of EOL care
-how are decisions made?
-who should information be directed to?
-what are views about suffering?
-what are views about death, EOL care, "pulling the plug"?
organ donation
Donating or giving one's organs and/or tissues after death; one may designate specific organs or may donate any needed organs
cardiac death
death in which the heart has stopped functioning
brain death
a diagnosis of death based on the cessation of all signs of brain activity, as measured by electrical brain waves
nurse's role in organ donation
-contact Organ Procurement Organization (OPO) before discussion with family
-OPO initiates conversation with patient
-no cost to a family for the gift of organ and tissue donation
-all major religions in the US support donation as an unselfish act of charity to save or improve someone's life
-if you are sick or injured and admitted to a hospital, the #1 priority is to save your life
-when matching donor organs to recipients, the computerized matching system considers issues such as severity of illness, blood type, time spent waiting, other important medical information, and geographic location. Recipient's financial or celebrity status or race does not figure in
loss and grief: assessment
-be present
-use active listening, silence, therapeutic touch
-use open, honest communication
-ask open-ended questions
loss and grief: nursing diagnosis
-death anxiety
-risk for aspiration
-risk for imbalanced body temperature
-bowel incontinence
-decreased cardiac output
loss and grief: planning
-goals and outcomes based on nursing diagnosis
-setting priorities (encourage patient to share their priorities for care, give priority to a patient's most urgent physical or psychological needs), maintain an ongoing assessment to revise the plan of care according to patient needs and preferences)
-teamwork and collaboration
loss and grief: implementation
-health promotion (focus on coping and optimizing health)
-palliative care
-hospice care
-use therapeutic communication
-provide psychological care
-manage symptoms
-promote dignity and self-esteem
-maintain a comfortable and peaceful environment
-promote spiritual comfort and hope
-protect against abandonment and isolation
-support the grieving family
-assist with EOL decision making
-facilitate mourning
-care after death
loss and grief: evaluation
-patient outcomes (ask evaluations, short- and long-term achievements)
what are the stages of the sleep cycle?
NREM-1, NREM-2, NREM-3, REM
NREM-1
light sleep
NREM-2
onset of sleep, body is becoming disengaged from surroundings, body temp starts dropping
NREM-3
deepest and most restorative
-decrease BP, RR
-decrease muscle tone, increase blood supply
-tissue growth and repair
-hormones
REM
-rapid eye movement
-active brain, muscle atonia
-brain restoration
factors that affect sleep
age, environment, light, blue light device use, temperature, noise, alcohol, caffeine, pain, mood (anxiety/worry), patterns of elimination, exercise, shift work, lifestyle, medications
insomnia
recurring problems in falling or staying asleep
narcolepsy
uncontrollable sleep attacks
sleep apnea
a sleep disorder characterized by temporary cessations of breathing during sleep and repeated momentary awakenings
circadian rhythm disorders
disturbances of the sleep-wake cycle such as jet lag and shift work
restless leg syndrome
uncomfortable sensations in legs causing movement and loss of sleep
parasomnias/night terrors
Seven arousals in which the person, often a child, is physically active. Often hallucinatory, and expresses a strong emotions such as terror.
- unlike nightmares, occurs during stage III NREM sleep.
hospital-acquired sleep alterations
-alarms, buzzers, call lights
-pain
-unfamiliar environment
-lines/drains
-bright lights
-unnecessary interventions
-unmonitored noise levels (hallway conversations, squeaky wheels)
-depression
-anxiety
-poor sleep hygiene
sleep promotion: role of the nurse
-assessment (questions, sleep diary, STQ)
-potential diagnosis (readiness for enhanced sleep, sleep deprivation, disturbed sleep pattern)
-outcomes (manageable steps, pt will report being able to fall asleep within 30 minutes of going to bed)
-interventions (depends on underlying cause - pain control, noise reduction, lighting, bundle/clustering care, bathing, music therapy, ear plugs)
-evaluation
sleep hygiene
The practice of following good sleep habits to sleep soundly and be alert during the day
consequences of sleep deprivation
accidental death, impaired brain activity, yawning, cognitive dysfunction, memory problems, moodiness, hallucinations, depression, micro sleep, accident prone, weakened immune response, cold/flue, weight gain, type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, heart disease
sex assigned at birth
sex organs someone was born with
gender
the socially constructed roles and characteristics by which a culture defines male and female
gender identity
our sense of being male or female
cisgender
term used when gender identity and/or expression aligns with the sex assigned at birth
transgender
an umbrella term describing people whose gender identity or expression differs from that associated with their birth sex
TGNC
transgender or gender nonconforming
transgender woman (MTF)
a woman who was assigned male at birth
transgender man (FTM)
a man who was assigned female at birth
non-binary
gender identities that are not exclusively masculine or feminine
gender role behavior
the behavior a person conveys about being male or female, which may or may not be the same as biologic gender or gender identity
gender noncomformity
individuals expressing behavior and attitudes consistently characteristic of the opposite sex
sexuality
desire, sexual preference, and sexual identity and behavior
sexual health
a state of physical, emotional, mental, and social well-being in relation to sexuality
sexual identity/orientation
our sense of self as it relates to the type of sexual attraction we have for others
sexual behavior
the kind(s) of sex someone is having, who and what
sexuality through the lifespan: infancy
0-1
assigned gender role of male or female
sexuality through the lifespan: toddler/early childhood
1-3
-gender identity develops - "I am a boy" or "I am a girl"
-body exploration and genital fondling
sexuality through the lifespan: preschool/late childhood
3-6
-aware of their body and other's body - "I'll show you mine"
-media influences understanding about male/female and gender role learning of how to behave like a boy or girl
sexuality through the lifespan: school age/early adolescent
6-12
-enter into puberty (growth of genitals, breast development)
-closeness of same gendered friends
sexuality through the lifespan: adolescent
12-18
-development of secondary sex characteristics with changes in physical and emotions
-menstruation and sperm production
-greater awareness of sexual identity and gender identity
-strong need for independence
-possibility of sexual activity and pregnancy
sexual health: assessment
assess all adolescent patients aged 11 and older about
1. puberty and sex
2. gender identity
3. sexual attraction/orientation
4. sexual activity
sexuality through the lifespan: adult
18-40
-decision-making about partnerships, marriage, family, careers
-sexual activity, pregnancy
sexuality through the lifespan: middle adult
40-60
-sexual activity
-bodily changes (erections, vaginal dryness, libido)
-menopause
sexuality through the lifespan: older adult
60+
sexual activity
role of the nurse: sexuality awareness
self-examination of bias
role of the nurse: sexuality skill and knowledge
-assessing the sexual health of your patient; know the right questions to ask and potential health risks that exist
-applying the nursing process (ADPIE)
inter professional collaborative practice
When multiple health workers from different professional backgrounds work together with patients, families, [careers], and communities to deliver the highest quality of care
benefits of inter professional teams
Organization
-reduced hospitalization time and costs
team
Team
-efficient use of healthcare resources
Patients
-improved outcomes and quality of care; reduced errors
Individuals
-enhanced job satisfaction
-enhanced wellbeing
Team STEPPS
Team Strategies and Tools to Enhance Performance and Patient Safety
-team structure
-communication
-leadership
-situation monitoring
-mutual support
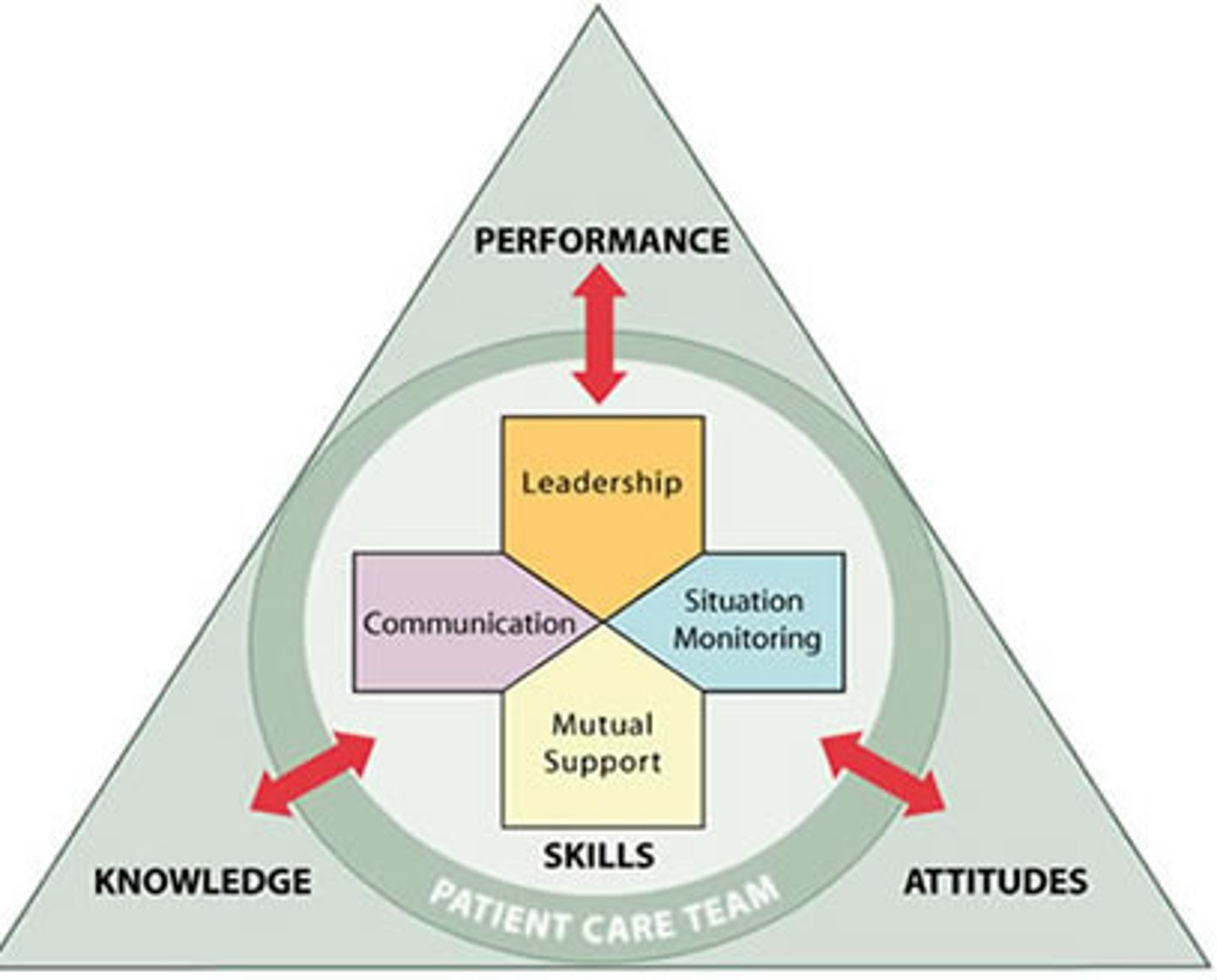
Communication: SBAR
S: situation, what is going on with the patient
B: background, what is the clinical background or context
A: assessment, what do I think the problem is
R: recommendation, what would I recommend
Communication: Call-out
-strategy used to communicate important or critical information
-informs all team members simultaneously during emergent situations
"air status" ... "airway clear"
Communication: Check back
using closed-loop communication to ensure that information conveyed by the sender is understood by the receiver as intended
"give 25mg Benadryl IV push"... "25mg Benadryl IVP"
Communication: CUS
I am concerned
I am uncomfortable
This is a safety issue
Communication: Hand off
I pass the baton
Team STEPPS: leadership
-maximizes activities of the team
-articulates goals
Team STEPPS: situation monitoring
ongoing awareness
Team STEPPS: mutual support
providing feedback
statutory law
legislative acts declaring, commanding, or prohibiting something
Nurse Practice Act
defines the legal boundaries of nursing practice in each state
administrative law
The body of law created by administrative agencies in order to carry out their duties and responsibilities.
State Board of Nursing
requires hospitals to report nurses who are incompetent
common law
(civil law) a law established by following earlier judicial decisions
Darling v Charleston Community Memorial Hospital
corporate liability
broken leg resulted in amputation;
rules hospital didn't have enough staff to review doctors' and nurses' work
Standards of Care for nurses
-legal guidelines for nursing practice and provide the minimum acceptable nursing care
-what a reasonably prudent nurse would do in the same or similar circumstances
who sets the Standards of Care for nurses?
-ANA (American Nurses Association)
-Nurse Practice Act(s)
-Specialty nursing organizations (ONC, CMSRN, AORN, ACNM)
-Policies and procedures of the institution (RUMC, P&Ps)
Tort law
Law that deals with harm to a person or a person's property.
Intentional torts
assault and battery
assault vs battery
Assault = placing a person in fear or immediate bodily harm
Battery = unlawfully touching a person