Social Cognition: Mirror Neurons and Embodied Processing
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What are shared representations in social cognition?
Alignments of bodies and minds that include empathy, gestures, gaze, body language, mental states, feelings, desires, intentions, perspectives, beliefs, and knowledge.
What is embodied processing?
The concept that our body contributes to social cognition through automatic and deliberate processes, such as copying body movements to learn new actions.
How does the brain support embodied processing?
Brain processes and knowledge are grounded in the outside world via sensory apparatus, with large parts of the brain controlling body actions that support cognition.
What does embodiment refer to in the context of cognition?
The role of the body in the brain, where mental structures originally evolved for perception or action are co-opted to assist in thinking and knowing.
What is the role of the mirror neuron system (MNS) in understanding others?
The MNS activates when performing or observing actions, helping with empathy and understanding others' intentions.
What is simulation theory in social cognition?
The idea that people understand others by using their own experiences to mentally simulate others' experiences, emotions, and thoughts.
What is theory-theory in social cognition?
The suggestion that people understand others by forming and updating mental theories about their thoughts, emotions, and behaviors.
What is the significance of social mimicry in social cognition?
Social mimicry, facilitated by the MNS, leads to implicit alignment with others and can enhance pro-social behavior.
What did Rizzolatti and colleagues discover about mirror neurons?
Mirror neurons in monkeys respond to both performing and observing actions, indicating a role in action understanding.
What findings support the involvement of mirror neurons in action understanding?
Studies show that mirror neurons respond to the meaning of an action, not just its visual features, and can signal action even in the absence of visual stimuli.
What are the brain areas associated with the mirror neuron system in monkeys?
The premotor cortex area F5 and the rostral part of the inferior parietal cortex, linked with the superior temporal sulcus.
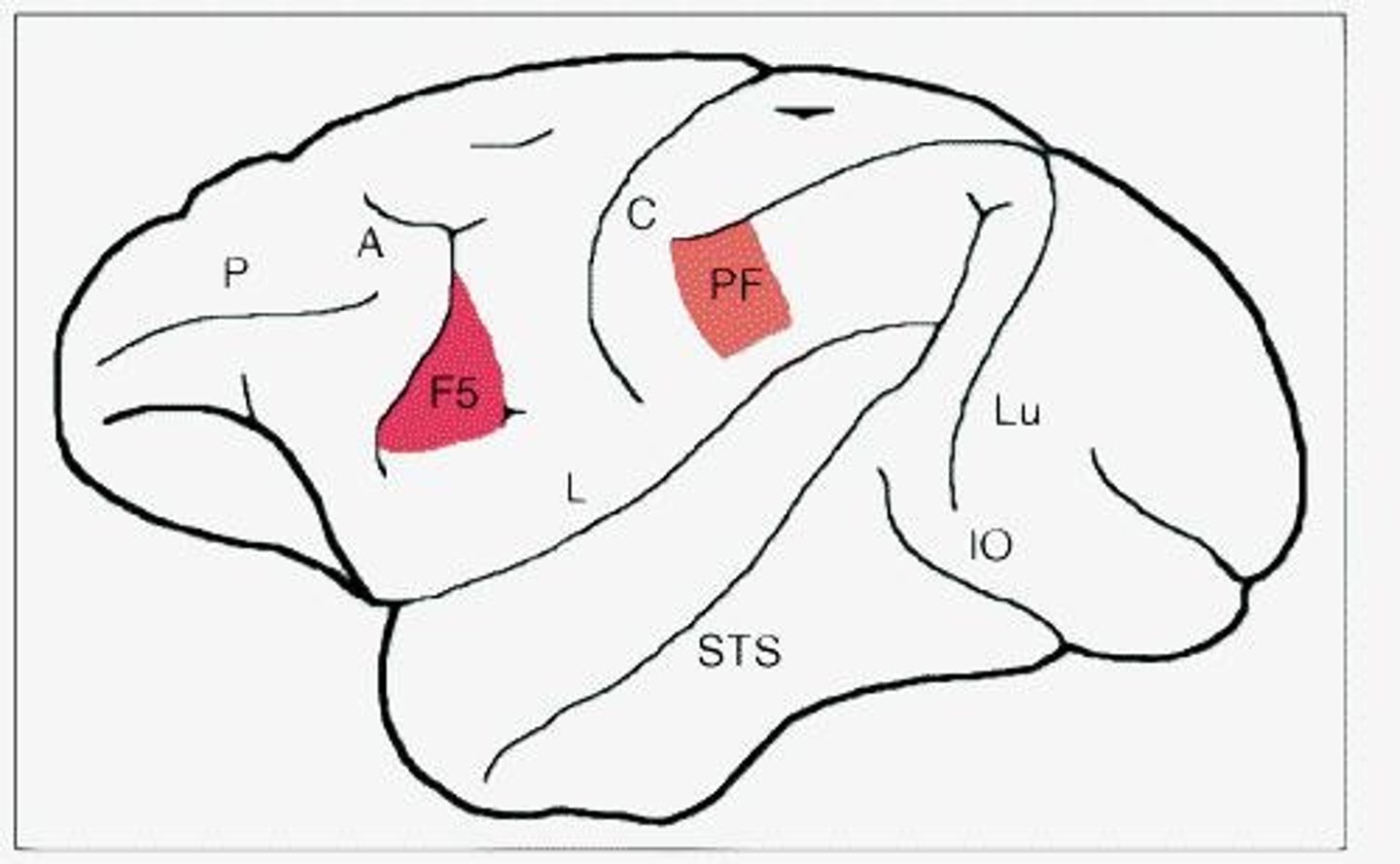
How do mirror neurons in humans differ from those in monkeys?
Human mirror neurons respond to intransitive actions and trace movements forming an action, indicating more precise imitation.
What is the role of the basal ganglia and cerebellum in embodiment?
These 'old' brain areas are involved in action/motor and somatosensory processing, contributing to cognitive processing.
What is the relationship between action words and body areas in the brain?
Action words activate specific body control areas in the sensorimotor cortex, reflecting a body-based topography.
What is the implication of multimodal representations in semantic memory?
Multimodal representations may incorporate action and proprioception, influencing how we understand and process actions.
What is the concept of implicit alignment with others?
Implicit alignment refers to automatic embodied sharing through the mirror neuron system, facilitating social connections.
What is the significance of the chameleon effect in social cognition?
The chameleon effect demonstrates that mimicked individuals tend to like their mimickers more and engage in pro-social behavior.
What is the role of the inferior parietal lobule (IPL) in the mirror neuron system?
The IPL is linked with the MNS and is involved in understanding intentions through context-dependent action encoding.
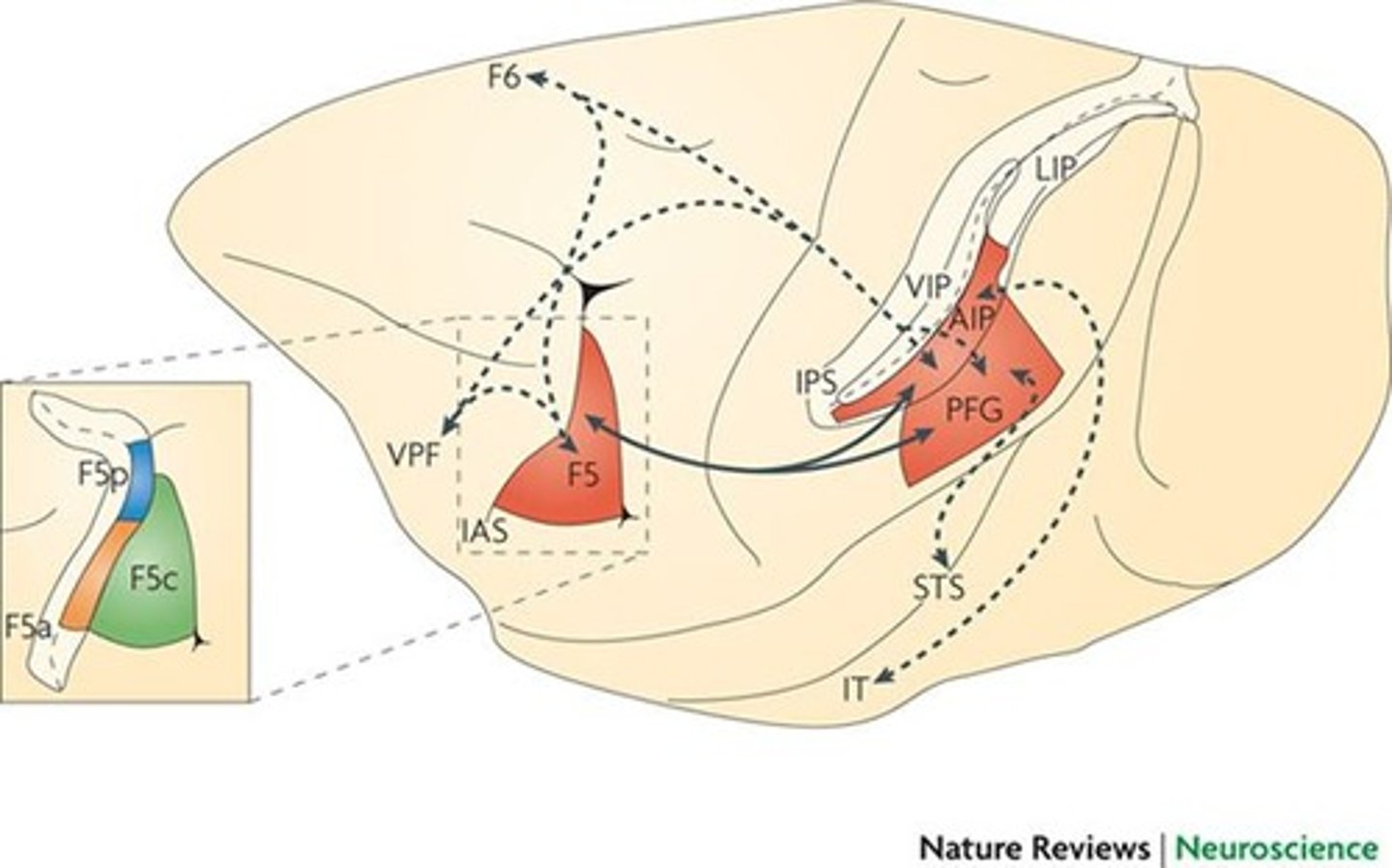
What does the term 'goal-dependent discharge' refer to in mirror neuron research?
It refers to the idea that mirror neurons encode actions in ways that depend on the context and intended outcome of the action.
How do mirror neurons contribute to social cognition?
They provide a neural basis for understanding others' actions and intentions, facilitating empathy and social interactions.
What are the two forms of embodied processing?
Implicit (automatic, possibly innate) and explicit (deliberate, conscious, and learned throughout development).
What is the relevance of the temporal coding of mirror neurons?
Temporal coding indicates that human mirror neurons trace the movements forming an action, enhancing our understanding of actions.
What findings did Fogassi et al. (2005) contribute to mirror neuron research?
They suggested that neurons in the parietal cortex encode actions in context-dependent ways, providing insight into understanding intentions.
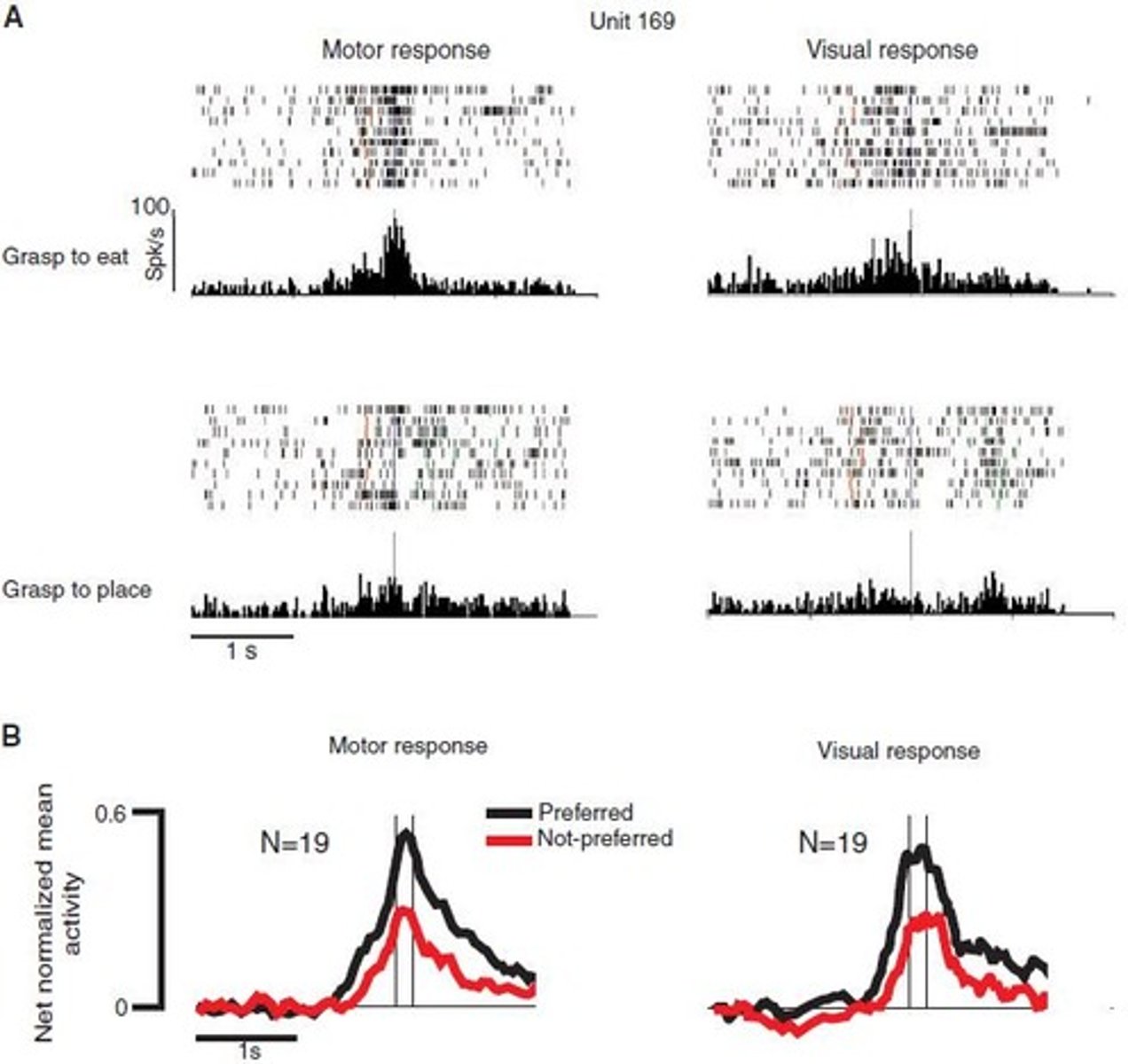
How does embodied processing relate to learning new actions?
Copying and imagining body movements can facilitate learning in activities like dancing, sports, and martial arts.
What is the significance of the research by Hauk et al. (2004) on action words?
It demonstrated that action words activate specific areas in the brain related to the corresponding physical actions.
What is the main focus of the next discussion in the course?
The flexibility of the mirroring system in humans and its practical applications.