Lecture 6: Human-environment relationships
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Climate is a function of the interaction of what 5 spheres?
Atmosphere → gases
Hydrosphere → oceans, large bodies of water
Lithosphere → plate tectonics
Cryosphere → glaciers, ice sheets, snow cover
Biosphere → vegetation, animals, humans
If the climate has always been changing, what’s the concern about climate change today?
RATE of the temperature change
When was the last glacial period? Was Canada covered?
18,000 years ago
all of canada except northern yukon was covered
Why has there been a rapid rise in global temps since the 1900s?
Human industry —> increase in GHG’s
What are the 4 causes of climate change?
Variations in solar radiation → natural
Changes in compositions (gases) → human impact
Changes in earth’s surface → natural
Variations in earth’s orbit → natural
What is a sunspot?
a cool region of high magnetism on the sun
cool areas on the sun that are surrounded by faculae (bright areas that emit high amounts of energy)
they occur in cycles and reach a max every 11 years
When does the sun emit more energy?
During periods of high sunspot activity
more sunspots = more solar energy
What was Maunder Minimum (1645-1715)?
A period with no sunspots
corresponds to a time known as the Little Ice Age
How do changes in composition of the atmosphere affect climate change?
The addition of greenhouse gases (carbon dioxide, water vapour, methane) increases global temperature
CO2 has a long residence time in the atmosphere (100 years)
Therefore, even though we are reducing carbon dioxide today, the effects will not be felt for decades
What are the 2 ways we can determine past climates?
The width of an ice layer
Dendrochronology (tree rings)
How do ice layers help us determine past climates?
provides insight on the temperature and snowfall of that year.
Each year, a new layer of ice forms.
Bubbles of air are trapped in the ice (can show us gases composition)
Ice cores provide climate data for up to 600,000 years in the past
How do tree rings (dendrochronology) help us determine past climates?
Wide ring = warmer/wetter
Narrow ring = cooler/drought
Tree rings provide climate data for up to 1000 years in the past
How do changes in Earth’s surface affect the climate?
The collision of converging plates results in uplift and the creation of mountains
This affects wind, temperature, and precipitation patterns on the surrounding landscape
What is the Milankovitch Theory?
Proposes that 3 separate phenomena relating to earth’s orbit contribute to climate change
What are the 3 Milankovitch cycles?
Eccentricity
Precession
Obliquity
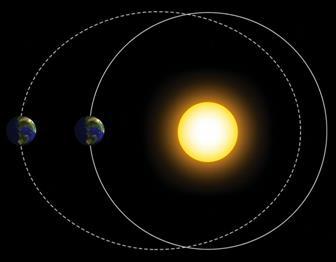
What is eccentricity?
Changes in the shape of earth’s orbit (from circular to elliptical)
100,000-year cycle
This cycle accounts for ice ages
most impactful cycle
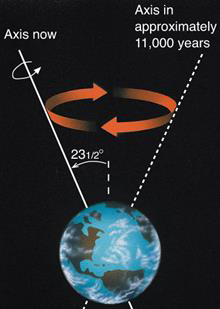
What is precession?
The wobble of earth’s axis
23,000-year cycle
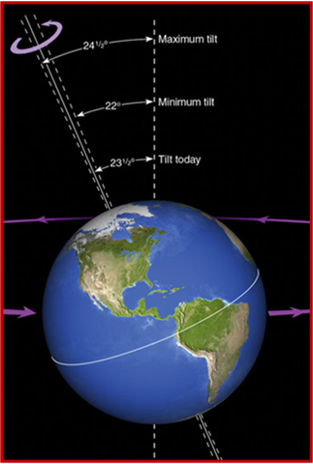
What is obliquity?
Changes in tilt of earth’s axis
41,000 year cycle
Changes in seasons
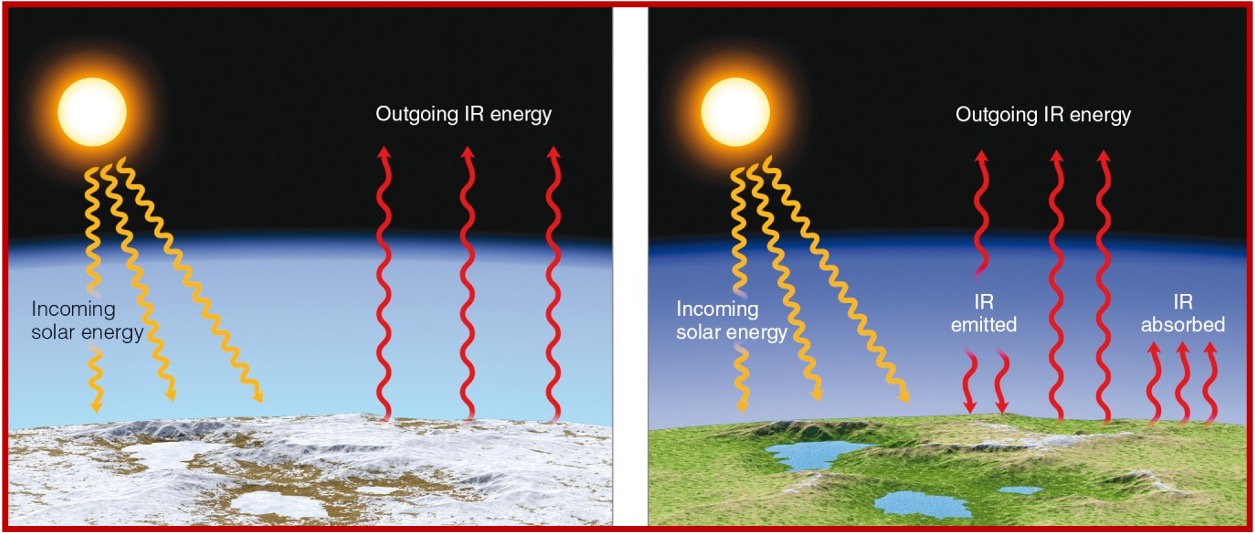
Why does the greenhouse effect exist?
greenhouse gases allow solar radiation to pass through, but they absorb infrared radiation from earth
Gases don’t allow heat to leave
How are humans enhancing the greenhouse effect?
By adding greenhouse gases, especially CO2
Because more infrared radiation from the earth is absorbed by the atmosphere
Carbon dioxide emissions are rapidly increasing in China and India as the economies in these countries continue to industrialize
What is ozone?
It is a gas composed of oxygen with a pungent smell
Forms naturally in the stratosphere
ozone in stratosphere = good
It forms in the troposphere by chemical reactions with other gases
ozone in troposphere = bad
protects us from suns harmful UV rays
No ozone = damage to skin
What is the major cause of the destruction of the ozone layer?
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
CFCs were found in inefficient appliances, spray cans, and industrial processes
Non essential uses of CFC were banned in North America in the 1970s
Called the Montreal Protocol (1987) **ban CFCs
Example of a worldwide agreement that has been successful (everyone signed!!)
How do CFC’s destroy the ozone layer?
Ultraviolet radiation breaks up CFC molecules causing the release of chlorine.
Chlorine rapidly destroys ozone
A CFC molecule can remain in the atmosphere for many decades
have a high residence time
What is acid precipitation?
Precipitation that combines with pollutants that turn it acidic
Main sources: sulfur oxides, nitrogen oxides
What are the effects of acid precipitation?
slows tree growth
reduces fish population in lakes
erodes materials
What is the pH scale range?
0-14
<7 = acidic
>7 basic
What is the natural pH of precipitation
5.5 → slightly acidic
Where is acid precipitation most common?
Most common in Eastern North America.
When is the pH of lakes unliveable for aquatic life?
Aquatic life cannot survive when pH < 4.8 → too acidic
What was the Canada-U.S. Air Quality Agreement (1991)?
Treaty designed to reduce transboundary air pollution that harms human health and natural resources
Specifically targeting acid rain and smog by setting limits on:
sulfur dioxide
nitrogen oxides
volatile organic compounds (VOCs)
What is a positive feedback loop?
A process in a system that encourages the continuation of the original process
What is an example of a positive feedback loop specific to climate change?
Less snow/ice decreases the reflectivity of solar radiation (because snow is highly reflective)
Therefore, after snow/ice melts, more solar radiation is absorbed rather than reflected
This process leads to continually warmer conditions
It is the reason why the polar regions are warming the fastest (going from high albedo to low albedo)
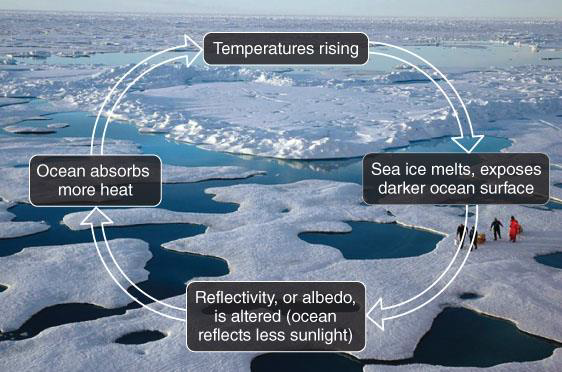
By 2050, where is the only remaining sea ice expected to be?
Ellesmere Island & Northern Greenland
How do we estimate how much the Earth will warm in the future?
Climate models
work by solving a series of mathematical equations
What do the variables in the equations represent?
greenhouse gases, solar radiation, other climatological components
How much do climate models forecast that the earth will warm by in the next 100 years?
at least 1.5o C
What does the IPCC stand for?
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
What was the Kyoto Protocol (1997)?
A global agreement aiming to slow climate change
Objective was to reduce GHG emissions to 5 % below 1990 levels by 2010
US and Australia did not sign
Canada pulled out once they realized they wouldn't reach the goal
unsuccessful
What are the 4 main impacts of climate change?
polar areas will warm most
boreal forests will expand northward → agriculture will shift northward
precipitation patterns will change
may be increased intensity of tropical storms & hurricanes
The issue of sea level rise:
As sea level rises, erosion is affecting areas farther inland; some areas are eroding at 10 m annually
Sea level is projected to rise as global climate changes and ice sheets continue to melt
North America cities at greatest risk: Vancouver, Miami, New Orleans and New York
Example of mitigating effects of sea level rise:
The Maldives
~80% of country <1m above sea level
Seawalls have been built around many of its islands to protect from waves up to 2 m in height
What are the 4 main ways climate change affects humans?
Food production
Tourism
Human health
Biodiversity
What effects does climate change have on biodiversity?
Warming temperatures will affect plant and animal habitats
Coral bleaching (sensitive to warming ocean temps)
Loss of flora and fauna
Extinction risk for polar bears
What is the most serious impact of climate change on humans?
The spread of malaria
secondly is malnutrition
Two philosophies of human-environment relations:
Living in harmony with nature → sustainable development
Exploiting nature for economic gain → ignoring the costs of resource extraction
What are the realities of natural resources?
many natural resources are finite
using resources create waste products
Why is wind energy a good source of energy?
Wind energy is a renewable and pollution-free
Winds farms are viable in areas with constant moderate winds
What are the 2 main issues preventing the growth of wind farms?
habitat disruption
appearance/aesthetics
Where are the best spots for wind turbines?
Along flat open land and coasts