Cumulative Vocab
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
all of the vocabulary from every study guide we have in the course (IN PROGRESS)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Iwan (taq)
A vaulted space or hall in Islamic architecture, typically open at one end and often used as an entrance or a place for gathering.
Early Caliphates
The three major caliphates (or government systems) after Muhammad's death, known for their rapid expansion of the Islamic state and establishment of governance. This occurred during the Umayyad dynasty, Abbasid dynasty, and Fatamids.
Mosaic
A decorative art form using small pieces of colored glass, stone, or other materials to create images or patterns, commonly found in Islamic architecture.
Visual Culture
The practices, symbols, and artifacts that define a community's visual expression, including art, architecture, and design. Within Islamic art, some examples would be calligraphy, geometric patterns, vegetative and floral motifs, and Aniconism.
Sassanian Empire
A Persian Empire: Zoroastrian/ practiced Zoroastrianism, located in Greater Iran and Mesopotamia. This empire competed with the Byzantine Empire and is known for its influence on the rise of Islam.
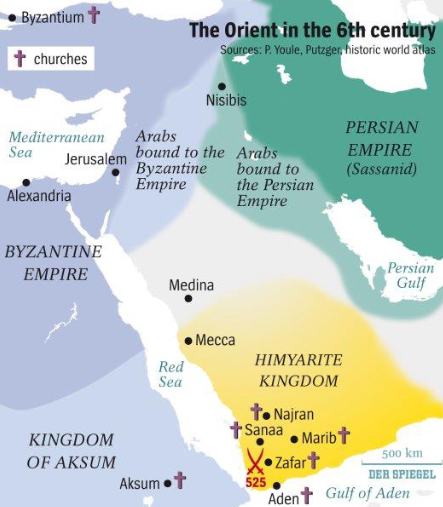
Byzantine Empire
Christian and Jewish religions. Capital city was Constantinople, and was located in Greater Syria, Anatolia, Egypt, and Western Mediterranean. This empire competed with the Sassanian Empire and is known for its influence on the rise of Islam.
Umayyad Caliphate
The Umayyad Caliphate was established after the Arab conquest in the 7th century. It was led by the Umayyad clan, with the caliph as the successor to the Prophet Muhammad. The capital cities were Jerusalem and later Damascus. Notable founders include Abd al-Malik and Al-Walid.
Vernacular materials and techniques
architecture made from locally sourced materials and traditionally used in specific regions. An Example for Islamic art would be ceramic tiling in mosques, or local stones and materials used to build mosques
Mesopotamia
The ancient region between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, known for its early development of writing, art, and architecture, including ziggurats and cylinder seals.
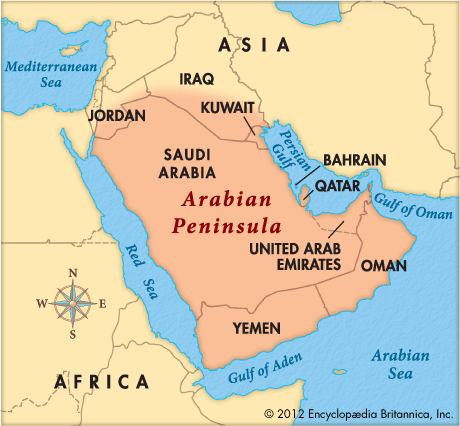
Arabian Peninsula
A large peninsula located in Southwest Asia, bordered by the Red Sea to the west, the Arabian Sea to the south, and the Persian Gulf to the north.
Sunnism
The largest branch of Islam, known for its emphasis on following the teachings of the Prophet Muhammad and the early caliphs
Shi’i
The second-largest branch of Islam, which emphasizes the leadership of Muhammad's family, particularly Ali
Ka’ba
The second-largest branch of Islam, which emphasizes the leadership of Muhammad's family, particularly Ali
Dinar (Umayyads and Unique Coins)
The Umayyads developed the dinar coin, influenced by Byzantine and Sassanian styles. They innovated by removing human images and replacing them with Arabic script and Islamic motifs, emphasizing monotheism and the caliphate's legitimacy.
Epigraphy
written word recorded on hard or durable material.
Calligraphy
Islamic calligraphy is a highly regarded art form in Islamic culture that involves the artistic writing of words and phrases in Arabic script
Mihrab
(concave niche) in the center of the qibla wall; developed
in al-Walid’s mosques

Minbar
(Prophet‘s seat; seat of imam/leader on Fridays)

Maqsura
enclosed space in front of the mihrab, often domed
Minaret
Tower-like structure, associated with mosques, presumed for adhan (call to prayer). Acts as a visual marker for mosques

Mayda’a
place for ablutions = fountain in courtyard or faucets at edges of mosque

Hypostyle
The hypostyle mosque plan is a type of mosque architecture that features a large prayer hall supported by many columns, creating a spacious interior space for worship
Cruciform/ 4-iwan
The four-iwan plan (cruciform) has four iwans arranged around a central square or rectangular courtyard, with the iwans aligned with the central axes of the courtyard.
Centralized plan
This style originated in the Ottoman Empire and is characterized by a central dome surrounded by smaller semi-domes. The Hagia Sophia in Istanbul influenced this style.

Arcade
Arcades are structures that are supported by columns or piers and defined by their arches. They can be free-standing or blind, meaning they are attached to the side of another structure.
Sahn/courtyard
courtyard in Islamic architecture, especially the formal courtyard of a mosque (where Mayda’a is typically located)
Khutba or Sermon
A khutba is a sermon or speech given by a Muslim religious leader or imam during important religious occasions or Friday prayers. It is a key form of religious communication in Islam, and is used to convey teachings, guidance, and important messages to the community.
Madina
Madina was the capital of a rapidly increasing Muslim caliphate under Muhammad's leadership
Diwan
The term "diwan" refers to official reception/throne rooms. It is only for the ruler(s) and highly esteemed members.
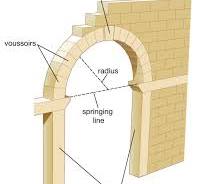
Roman Arch (Round Arch)
a semi-circular arch that is a characteristic feature of Roman architecture
Iconoclast
A belief that figural images should not exist in religion - and the act of destroying or defacing any figural images in this context.
Aniconic
A hesitancy or act of avoiding images with living beings in religious contexts
Tiraz
An armband with an inscription that shows status and loyalty to the king
Centralized System of rule
A system of governance where political power and decision-making are concentrated in a central authority, ensuring uniform laws, policies, and administration across the state or empire. Examples include the Umayyad Caliphate, with Damascus as its center.
Mawali
Non-Arab Muslims who converted to Islam and played significant roles in Islamic societies, especially under the Abbasids, despite initial social barriers.
Baghdad/ Madinat al-Salam
The Abbasid capital, founded in 762 by Caliph al-Mansur, designed as a circular city symbolizing a cosmic and centralized order with the palace and mosque at its center.
Fiat City
A city established by decree, such as Baghdad, designed with specific political, religious, and administrative purposes in mind.
Secluded Ruler
A concept in which the ruler is physically separated from the public, emphasizing divine authority and centralized power, as seen in Abbasid palaces.
Bureaucratic management of the Empire
A system where administrators and officials, rather than tribal or familial networks, governed the Abbasid Empire, ensuring efficient rule over vast territories.
Sassinian Round Cities
Pre-Islamic Persian cities with a circular design, such as Firouz Abad, influencing later Islamic urban planning with their centralized layouts.
Samarra
An Abbasid city founded in 836 by Caliph al-Mu'tasim, known for its vast palaces, unique stucco decorations, and the Great Mosque with its helicoidal minaret.
Linear Expansion
linear expansion refers to the architectural and artistic growth along a geographical line or axis, often seen in the spread of Islamic styles and influences across regions. This can manifest in the elongated layouts of structures or the adoption of similar artistic motifs that travel along trade routes or conquest pathways, adapting local styles into Islamic art
Helicoidal Towers
Helicoidal towers are architectural structures characterized by their spiral or twisted design, often found in mosque minarets and fortifications in Islamic architecture. They are notable for their unique shape and often serve both aesthetic and functional purposes