forensic anthropology exam I
1/209
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
210 Terms
What is the formal definition of forensic anthropology?
Forensic anthropology applies the methods and theories of anthropology to matters of legal concern.
What is the informal definition of forensic anthropology?
Finding and examining human skeletal remains for medical or legal purposes.
What are some fun facts about forensic anthropology?
Picture IDs are not a scientific form of identifying the dead.
The largest forensic anthropology lab is in Hawaii.
Forensic anthropologists often testify in court on issues like skeletal age, postmortem interval, and trauma.
What are the primary goals of forensic anthropology?
Identification of remains.
Complete recovery of remains.
Reconstruction of events around the time of death.
Providing dignity in death.
Why are forensic anthropologists often concerned with marginalized and vulnerable individuals?
Cases often involve marginalized and vulnerable people, and forensic anthropologists prioritize the dignity and care of the decedents.
During which seasons are forensic anthropology cases most common?
Spring and fall, especially during hunting season
What types of bones are commonly missing from forensic recoveries, and why?
Hands and other small bones are often missing due to animal scavenging.
Why are feet usually well-preserved in forensic anthropology cases?
Feet are usually well-preserved because they are protected by shoes.
How can deer tibia and human tibia bones be differentiated?
The tibia head in humans is wider at the knee joint because humans carry more weight in the lower half of their body.
What bone is the best for determining sex, and why?
The os coxa (hip bone) is the best for determining sex due to childbirth-related anatomy.
How is age estimated using the pubic symphysis?
Bone bumps start to break down around middle age.
What other bone is commonly used for estimating age?
Ribs
What is anthropology, and what does its name derive from
Anthropology is the study of humans, and the word derives from "anthropos" meaning "man" and "logos" meaning "logic
What is forensic anthropology a subfield of?
Forensic anthropology is a subfield of biological anthropology.
What is the role of forensic anthropology in a medicolegal context?
It examines human skeletal remains to address legal concerns, particularly in identifying remains and analyzing the cause and manner of death.
What does "medicolegal" mean in forensic anthropology
Medicolegal refers to the branch of medicine dealing with legal aspects of death, such as identification, cause of death, and manner of death.
What are the five manners of death recognized in forensic anthropology?
Accident, suicide, homicide, unknown, natural.
What are the four eras in the history of forensic anthropology?
Formative (1800s-1940s)
Consolidation (1940s-1970s)
Professionalization (1970s-1990s)
Modern (1990s-today)
What significant collections helped in early forensic anthropology research?
The Hamann-Todd collection in Cleveland, OH, and the Terry collection in Washington, D.C.
What was the Parkman murder case (1849), and why is it significant?
It was one of the first cases where scientific evidence, including forensic anthropology, was used in trial.
What is the Luetgert murder case known for in forensic anthropology?
George Dorsey testified and identified bone fragments as human, marking it as an early case using forensic anthropology
What was the first forensic anthropology textbook, and when was it published?
Guide to the Identification of Human Skeletal Material was published in 1939.
What role did WWII play in advancing forensic anthropology?
The Central Identification Laboratory was founded to identify the remains of service members, advancing techniques for dealing with decomposed remains.
When was forensic anthropology formalized as a professional field, and what organization was key in this?
In 1972, the American Academy of Forensic Sciences was key in formalizing the field.
What development in training helped professionalize forensic anthropology?
The establishment of graduate programs and formal training produced the first generation of forensic anthropologists.
How did the Daubert v. Merrell Dow (1993) case affect forensic anthropology?
It helped establish what qualifies as scientific evidence and who can testify on it in court.
What is the scope of modern forensic anthropology beyond the biological profile?
It includes sex, age, ancestry, stature estimation, and determining medicolegal significance.
What methods are used in modern forensic anthropology for identification?
Comparative medical radiology and population affinity estimation are used to facilitate identification.
What is the difference between cause and manner of death
Cause of death (COD) is what specifically killed the person (e.g., acute myocardial infarction, gunshot wound).
Manner of death (MOD) is the way in which the person was killed (e.g., natural, accidental, homicide, suicide, undetermined).
What are examples of immediate and underlying causes of death?
Immediate: Acute myocardial infarction, perforating brain trauma, pneumonia.
Underlying: Heart disease, gunshot to the head, influenza
What are the main purposes of a death investigation?
Convict the guilty and protect the innocent.
Aid civil litigation.
Provide data for public health surveillance and prevention programs.
Maintain accurate vital statistics.
Advance health and safety research.
According to the Texas Code of Criminal Procedure Section 49.25, when do deaths get investigated?According to the Texas Code of Criminal Procedure Section 49.25, when do deaths get investigated?
Accidents, homicides, suicides.
Unidentified remains or body parts.
Deaths of children under 6.
Deaths in prisons or jails.
Deaths unattended by physicians
What steps are involved in a death investigation?
Investigation of the death scene.
Collection of evidence.
External examination of the body.
Autopsy (if required).
What is an autopsy, and when is it performed?
An autopsy is an internal and external postmortem examination of the body to determine the cause and manner of death. It is performed:
To determine COD and MOD.
When foul play is suspected.
To recover evidence.
When required by law or requested by the district/county attorney, family, or doctor.
How often are autopsies performed in investigated deaths
Only about 20% of investigated deaths require an autopsy
When is an autopsy NOT performed?
When there is adequate medical information to explain the cause, manner, and circumstances of death.
When there is no suspicion of foul play or injury.
At the discretion of the medicolegal authority.
Who performs an autopsy, and what are their qualifications?
Forensic pathologists, who are doctors specializing in determining COD and MOD, perform autopsies. They:
Have a medical degree and training.
Collect medical and trace evidence.
Determine the presence or absence of disease.
Interpret injuries and document evidence of sexual assault.
Test body tissues and fluids (forensic toxicology).
Certify COD and MOD.
Is the medicolegal death investigation system unified across the U.S.?
No, it is not a unified system. It is handled at the county level, with 2,185 jurisdictions across 3,137 counties.
Who investigates deaths in the medicolegal system?
Medical examiners (MEs).
Coroners.
Justices of the peace.
What is the role of a medical examiner (ME)?
Appointed official at the county or state level.
Investigates deaths, issues death certificates, and determines COD and MOD.
Must be a licensed physician, but only performs autopsies if they are also a forensic pathologist.
What is the role of a coroner?
Elected official who investigates deaths, issues death certificates, and determines COD and MOD.
Performs autopsies only if they are a forensic pathologist.
May be a layperson with no specific medical education or training.
What is the role of a justice of the peace in death investigations?
Elected official responsible for investigating deaths in their precincts, especially in smaller counties.
Fills the role of the coroner but also handles duties such as overseeing traffic violations, small claims, and civil marriages.
A layperson with no specific medical training required.
How is the medicolegal death investigation system structured in Texas?
Texas uses an ME-JP hybrid system.
In counties with over 1 million people, a medical examiner system is required.
Smaller counties can choose between an ME or coroner system.
Forensic pathology services are often shared between multiple counties, with bodies moved to other counties for autopsies.
Why is the medicolegal death investigation system in the U.S. described as a patchwork network?
There are no national standards for training and qualifications.
Different levels of investment in personnel and facilities exist between states and counties.
What is osteology?
The study of bones.
How many bones are in the adult and child human skeleton
Adults have 206 bones.
Children have 270-300 bones.
How many teeth do adults and subadults have?
Adults have 32 teeth.
Subadults have 20 teeth.
What are the six functions of the skeleton?
Protection of organs.
Structure and support.
Movement.
Production of blood.
Storage of minerals.
Release of calcium and phosphate.
What role does the skeleton play in endocrine regulation
It regulates the release of repair and growth hormones.
What are the three levels of bone structure?
Molecular, microstructural, and tissue.
What are the organic and inorganic materials found in bone at the molecular level?
Organic: Collagen protein (flexibility).
Inorganic: Hydroxyapatite (calcium and phosphate) for rigidity.
What are the three types of bone cells, and what are their functions?
Osteoclasts: Resorb bone.
Osteoblasts: Form new bone.
Osteocytes: Regulate mineral deposition and chemistry.
What are the two main types of bone tissue?
Cortical (dense, external).
Trabecular (spongy, internal).
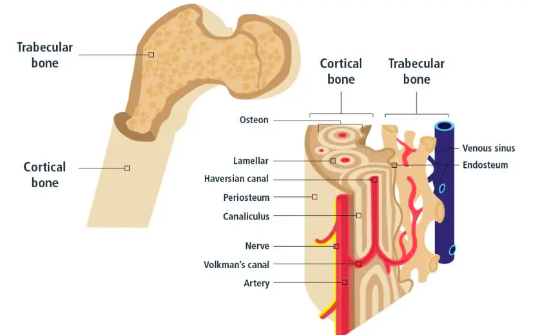
What is the function of trabecular bone?
It stores fat, produces blood, and provides shock absorption in joints.
What are the two components of the skull?
Cranium: Braincase.
Mandible: Lower jaw.
How many bones make up the skull?
28 bones.
How many vertebrae are in the human thorax, and how are they divided?
24 vertebrae:
7 cervical (neck).
12 thoracic (articulate with ribs).
5 lumbar (lower back).
What bones make up the shoulder girdle?
Clavicle and scapula.
What are the bones of the upper limbs?
Humerus, ulna, radius, carpals (8), metacarpals (5), and phalanges (14).
What bones make up the pelvic girdle?
Ossa coxae (right and left), ilium, ischium, pubis, sacrum, and coccyx (tailbone).
What is odontology?
The study of teeth.
What can the morphology of teeth be used to estimate?
Sex and age estimation.
When is a case relevant to the medicolegal system?
When human remains require further investigation to establish identity or determine the cause of death.
What are the three questions in the identification hierarchy?
Is it bone?
Is it human?
Is it recent?
What are the macroscopic features of bone?
Trabeculae (spongy interior), foramina (holes for blood vessels), and recognizable features like joint surfaces and muscle attachment sites.
What is the chemical composition of bone?
Calcium and phosphate (hydroxyapatite)
What machine can be used to determine the elemental composition of bone?
A portable X-ray fluorescence (pXRF) machine.
How do you determine if a bone is human?
Tooth shape: Humans have posterior teeth for grinding and chewing, and anterior teeth for ripping and tearing.
Mandible shape: Humans have short and wide jaws.
Long bones and pelvic/shoulder girdle: Humans are bipedal with specific structural adaptations.
What are the key differences in the long bones of humans and non-humans?
Human upper limb bones are thin and straight.
Non-human upper limb bones are thick and curved.
Human femur is long with a large head, whereas non-human femur is short with a small head.
What methods can help determine if a bone is recent?
Carbon-14 dating.
Presence of soft tissue or odor.
Greasy vs. dry bone (indicates fat content over time).
Signs of weathering or environmental exposure.
What are some indicators that can help date bone remains?
Medical procedures like surgeries.
Dental work.
Aesthetic or scientific modifications.
What are examples of scene context and associated evidence that can help determine medicolegal significance?
Interment conditions, cultural burial arrangements, grave goods, personal effects, and artifacts like weapons or ligatures
What are the main components of a biological profile?
Age.
Population affinity.
Stature.
Sex.
Biological characteristics (genetic makeup, hormones, external and internal sex organs, secondary sex characteristics).
What biological characteristics are considered in a biological profile?
Genetic makeup, hormones, hormone receptors, external sex organs, internal sex organs, and secondary sex characteristics.
What is sexual dimorphism?
Males and females of the same species exhibit different physical characteristics beyond the differences in their internal and external organs
Why might intersex conditions be relevant in a biological profile?
Because sex and/or gender may be listed on a missing person report, and for most people, sex assigned at birth, gender identity, and gender expression align.
How accurate is skull analysis for determining sex?
70-80% accurate.
What are some features of the skull used to estimate sex, and how are they scored?
Nuchal crest: Scored based on roughness (1-3-5 scale).
Mastoid process: Scored based on volume (1-3-5 scale).
Supraorbital margin: Scored based on projection (1-3-5 scale).
Supraorbital ridge/glabella: Scored based on projection (1-3-5 scale).
Mental eminence: Scored based on width/projection (1-3-5 scale).
How is the pelvis used to determine sex, and what is the scoring system?
Pelvis features are scored based on their ability to widen the pelvis
Sub-pubic concavity: 1 (concave) to 5 (convex).
Ichio-pubic ramus.
Ventral arch.
Greater sciatic arch.
Subpubic angle.
How accurate is the use of long bones in determining sex?
88-90% accurate.
What specific measurements of long bones help in determining sex?
Lengths, widths, and diameters of the femoral head.
What is important to remember when determining sex in sub-adults?
Sexually dimorphic traits do not show up well in sub-adults
What considerations should be made when determining sex in transgender individuals?
Transgender individuals may undergo physical transitions, including surgery or hormone therapy, which can affect skeletal traits.
Why is skeletal age estimation important beyond the biological profile?
It helps narrow down possible individuals and can identify people trying to appear older or younger
What are the two types of age related to skeletal estimation?
Chronological age vs. biological age
What factors influence chronological age?
Time
What factors influence biological age?
Chronological age, genetics, nutrition, environment, illness, activity level, and drug/alcohol abuse.
What is the trajectory effect in age estimation?
Minimal variation in age up to 6-8 months, but much more variation afterward.
How are subadult and adult ages defined?
Subadult = not skeletally mature, Adult = skeletally mature.
What are the age ranges for subadults?
Fetus: In utero
Neonate: At or around birth
Infant: 0-6
Child: 7-12
Adolescent: 13-20
What continues developing even if bone growth is slowed by illness or malnutrition?
Dental development.
What are the three stages of tooth formation?
Crown formation, root formation, and apex (root tip) formation.
At what ages do deciduous and permanent teeth erupt?
3 years: All deciduous teeth
6 years: 1st permanent molar
12 years: 2nd permanent molar
Late teens to early 20s: 3rd molar (maybe)
What osteological methods are used to estimate subadult age?
Bone measurements and epiphyseal union (fuses between ages 10-25).
How does adult age estimation differ from subadult age estimation?
It focuses on degeneration from activity using phase systems like pubic symphysis, sternal rib ends, and auricular surfaces.
How does the pubic symphysis surface change with age?
Younger: Linear bumps with no contour
Older: Smoother with a contour
Old: Small holes, light, and fragile
Where is the second most popular region for adult age estimation?
The sternal rib ends, at the joint between the 4th rib and costal cartilage.
What area is the third most popular region for adult age estimation?
The auricular surface between the ilium and sacrum.
What is histomorphometry, and how is it used in age estimation?
Counting osteons (haversian systems) per unit area of bone to estimate age
What are general clues to age estimation in the skeleton?
Cranial suture closure, arthritis, porosity, eburnation (shiny bone), and dental wear.