L7 RGC to SC and LGN
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Retinal Ganglion Cells
the third layer of retinal neurons whose axons leave the eyeball and form the optic nerve. they can tell whether or not they detect a light-dark boundary, their job is to emphasize boundaries and de-emphasize uniformities
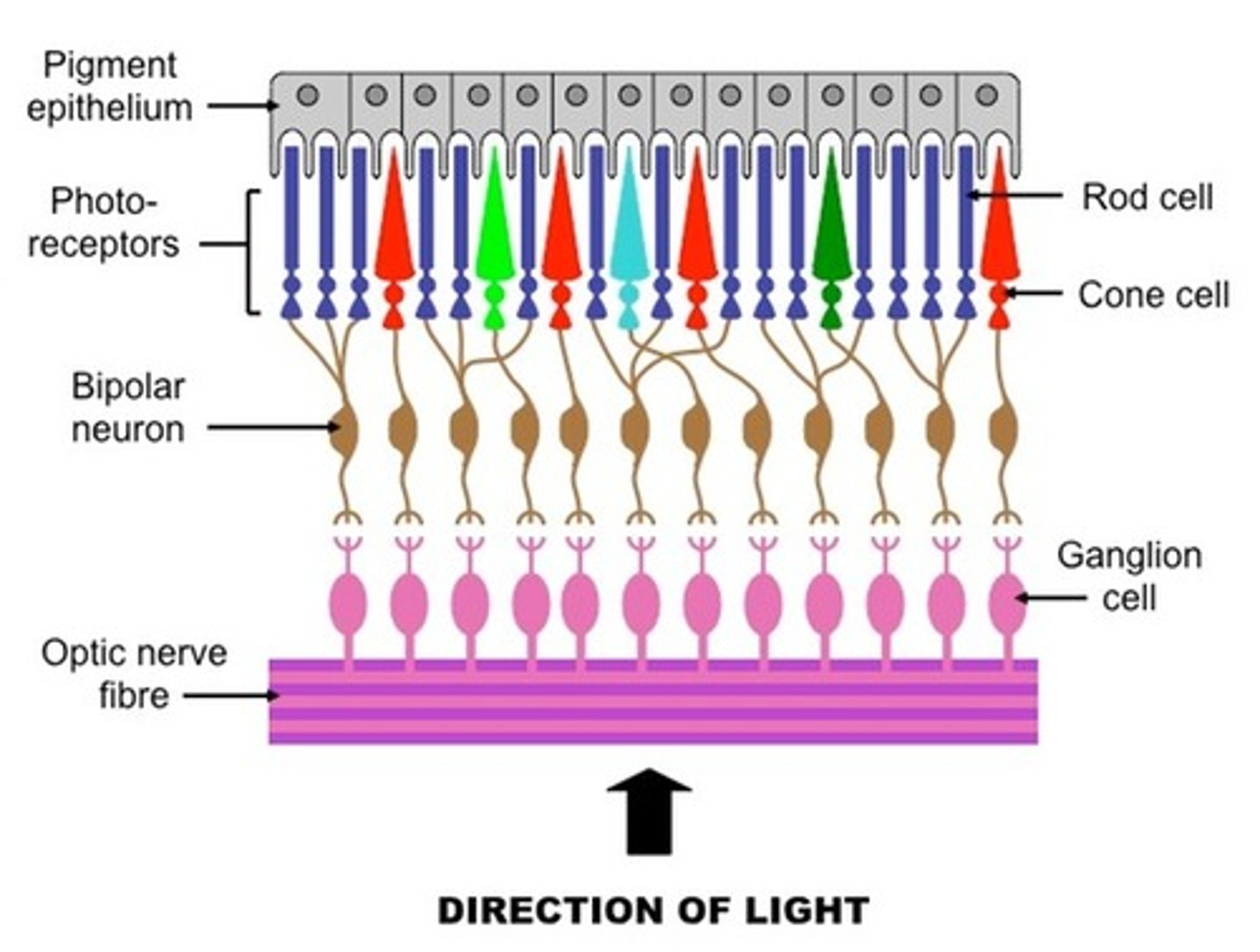
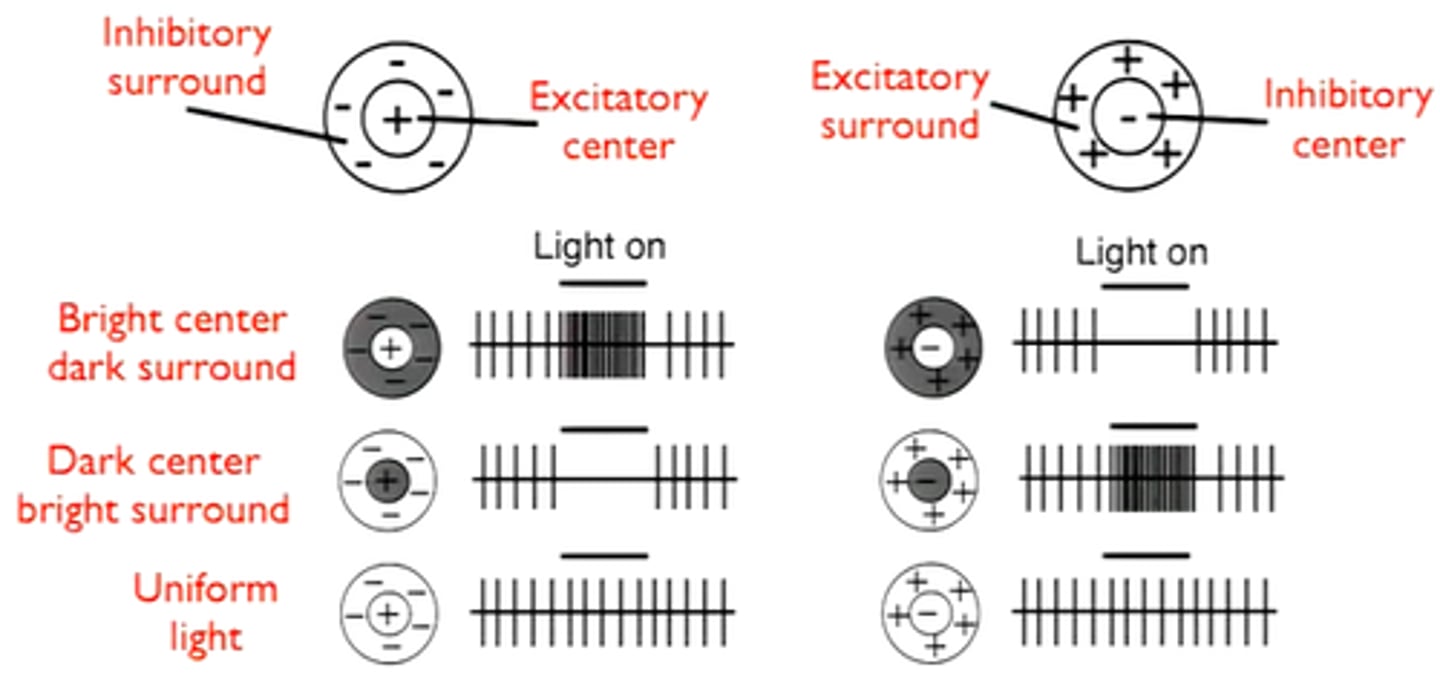
Receptive Field
the region of the sensory surface that, when stimulated, causes a change in the firing rate of that neuron; size is determined by how many photoreceptors coverage upon a retinal ganglion cell
Small bistratified ganglion cells
type of ganglion cells that synapse with S-cone bipolar cells; moderate photoreceptor convergence
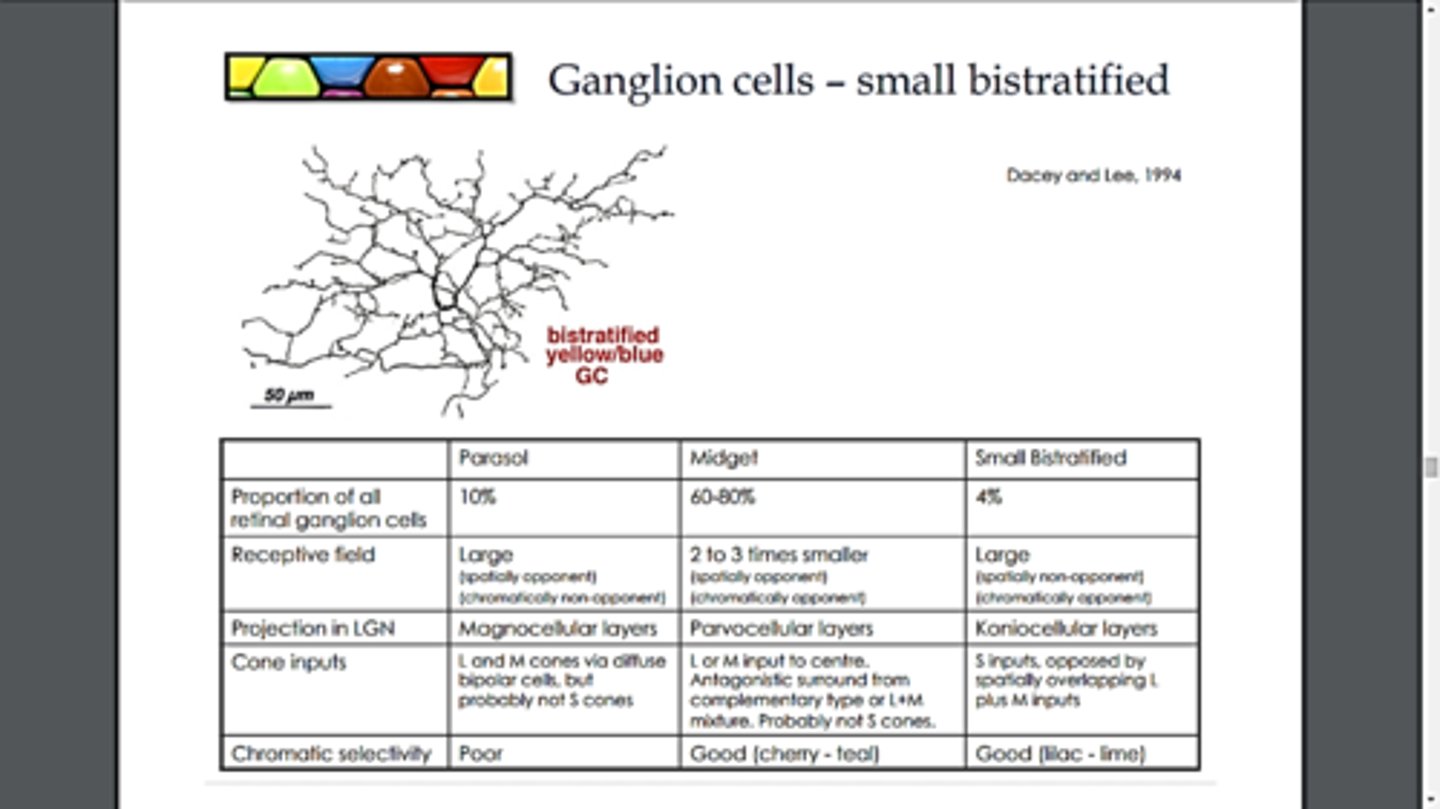
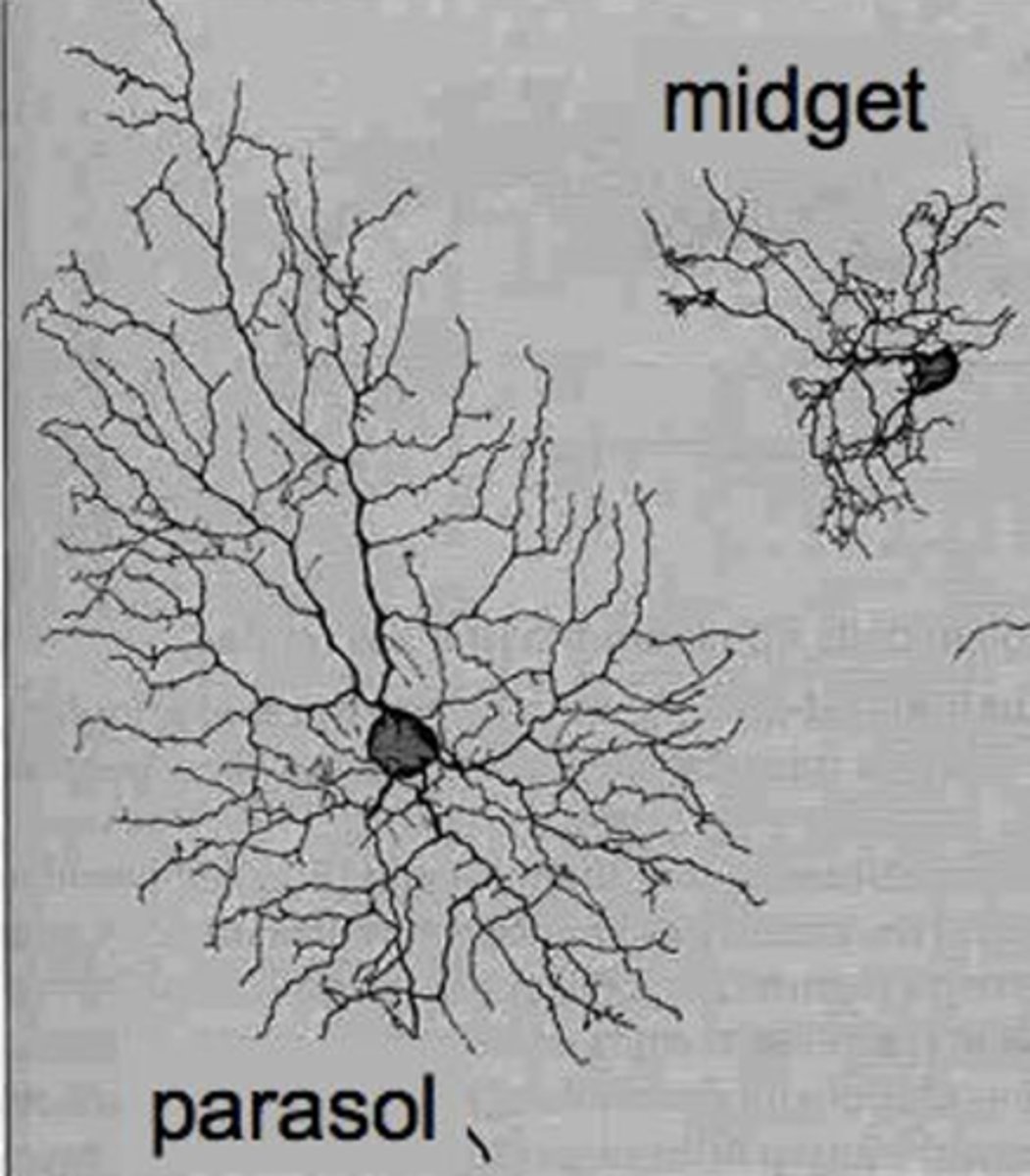
parasol retinal ganglion cells
RGCs that send signals to the magnocellular layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus, they synapse with rods; more photoreceptor convergence
small retinal ganglion cells
get signals primarily from M/L cones, less photoreceptor convergence
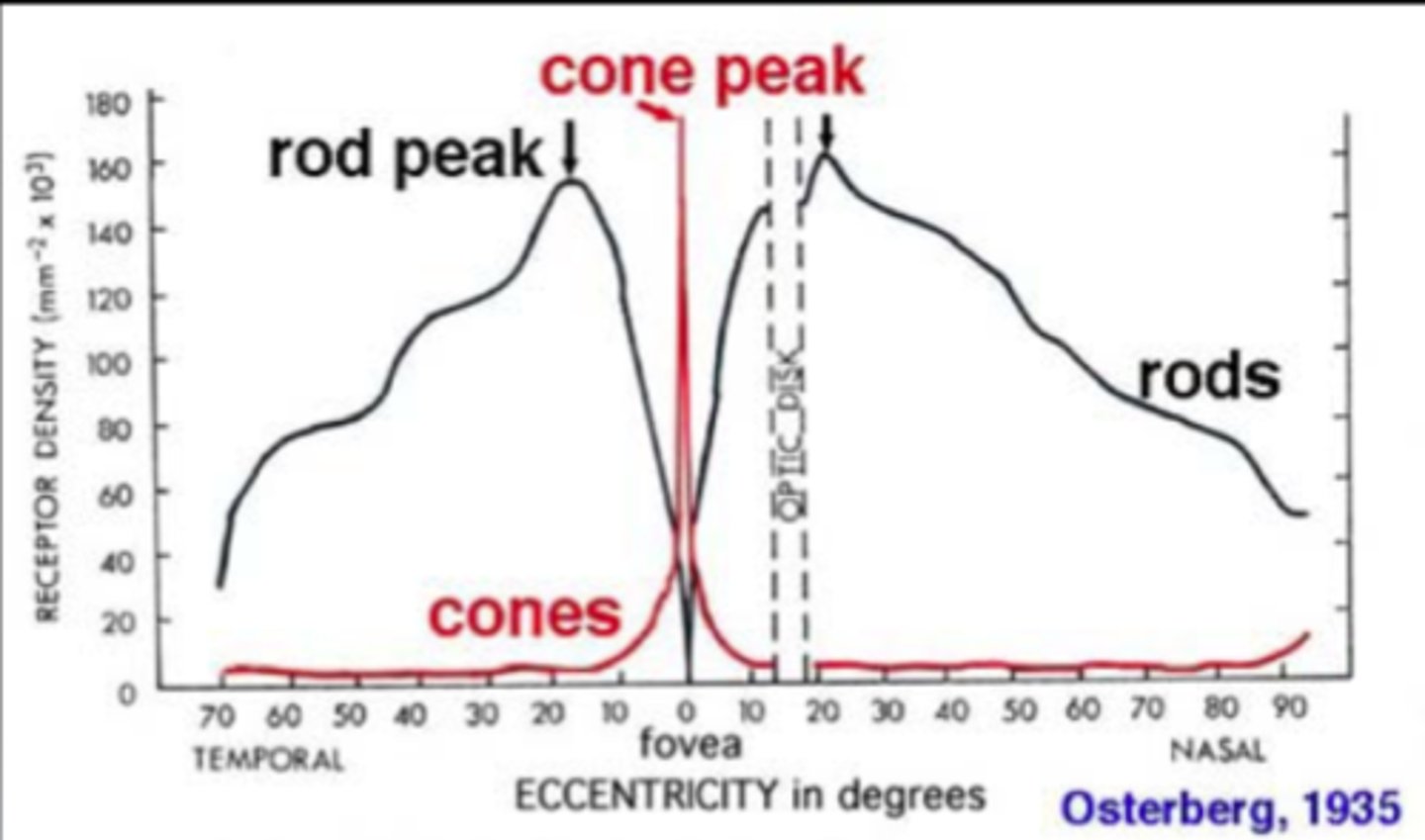
acuity
sharpness of vision
fovea
higher acuity, contains smaller receptive, thus allowing us to see more details
periphery
higher sensitivity and less acuity, contains larger receptive fields, making them more likely to detect faint stimuli
retinotopic mapping
An arrangement of neurons in the visual system whereby signals from retinal ganglion cells with receptive fields that are next to each other on the retina travel to neurons that are next to each other in each visual area of the brain; when light is focused on the retina we end up with an image and the spatial properties are preserved and spatially encoded
as we move into the brain we must
-stay organized (retinotopic mapping)
-integrate information from two eyes
-do even more organizing
ipsilateral fibers
In the case of vision, those optic nerve fibers that project from one eye to the same side of the brain.
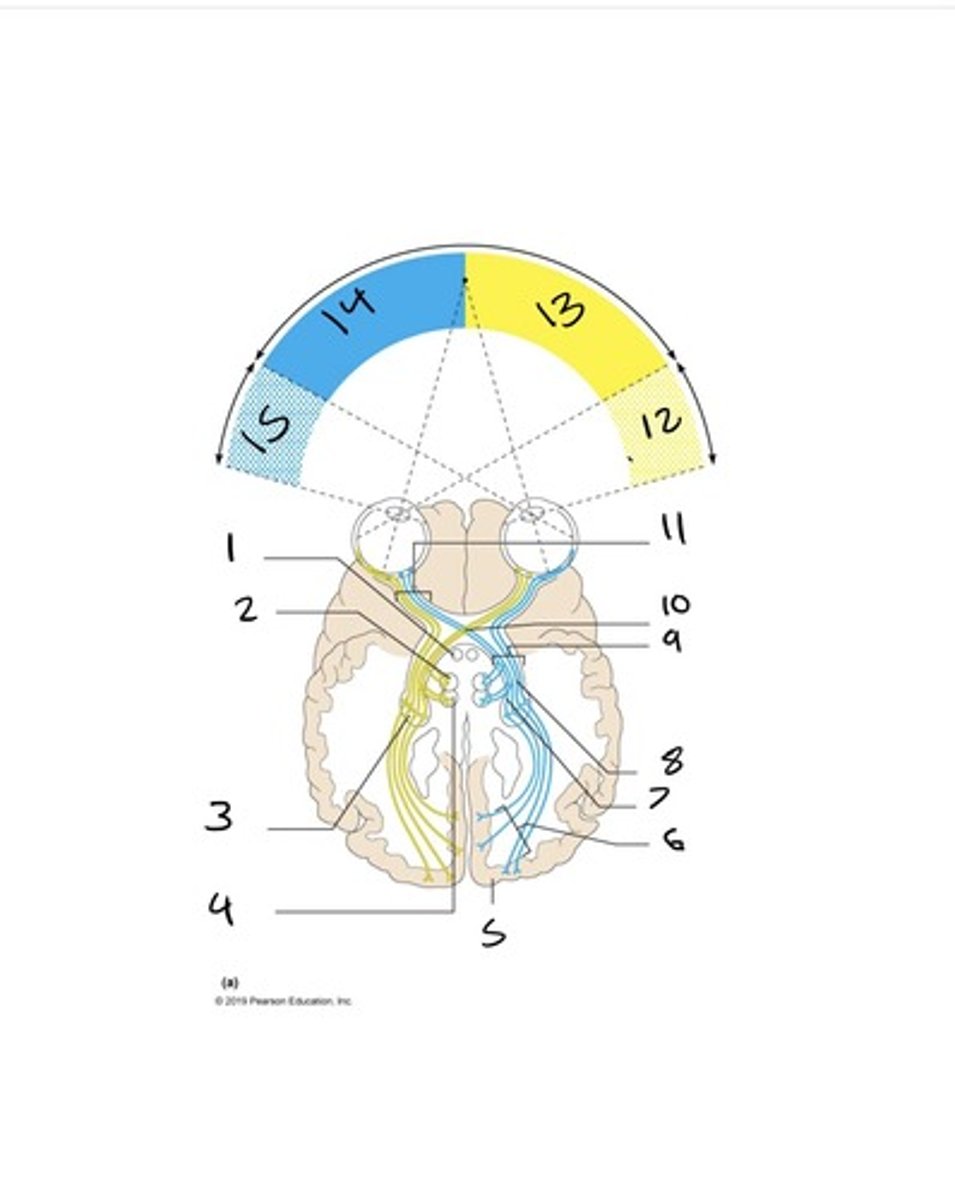
contralateral fibers
In the case of vision, those optic nerve fibers that project from one eye to the opposite side of the brain
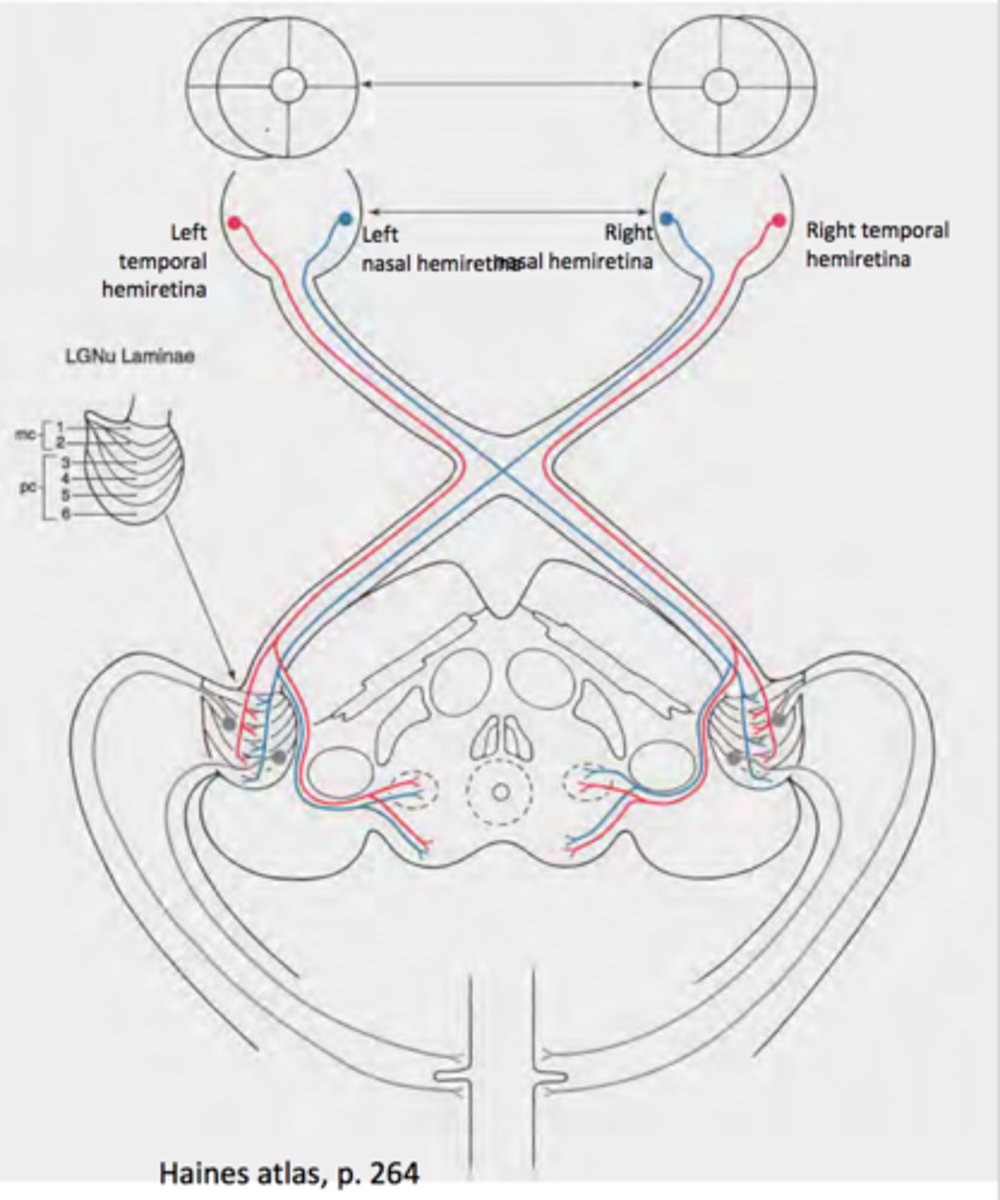
optic tracts
contain fibers from the lateral side of the eye on the same side and the medial side of the opposite eye
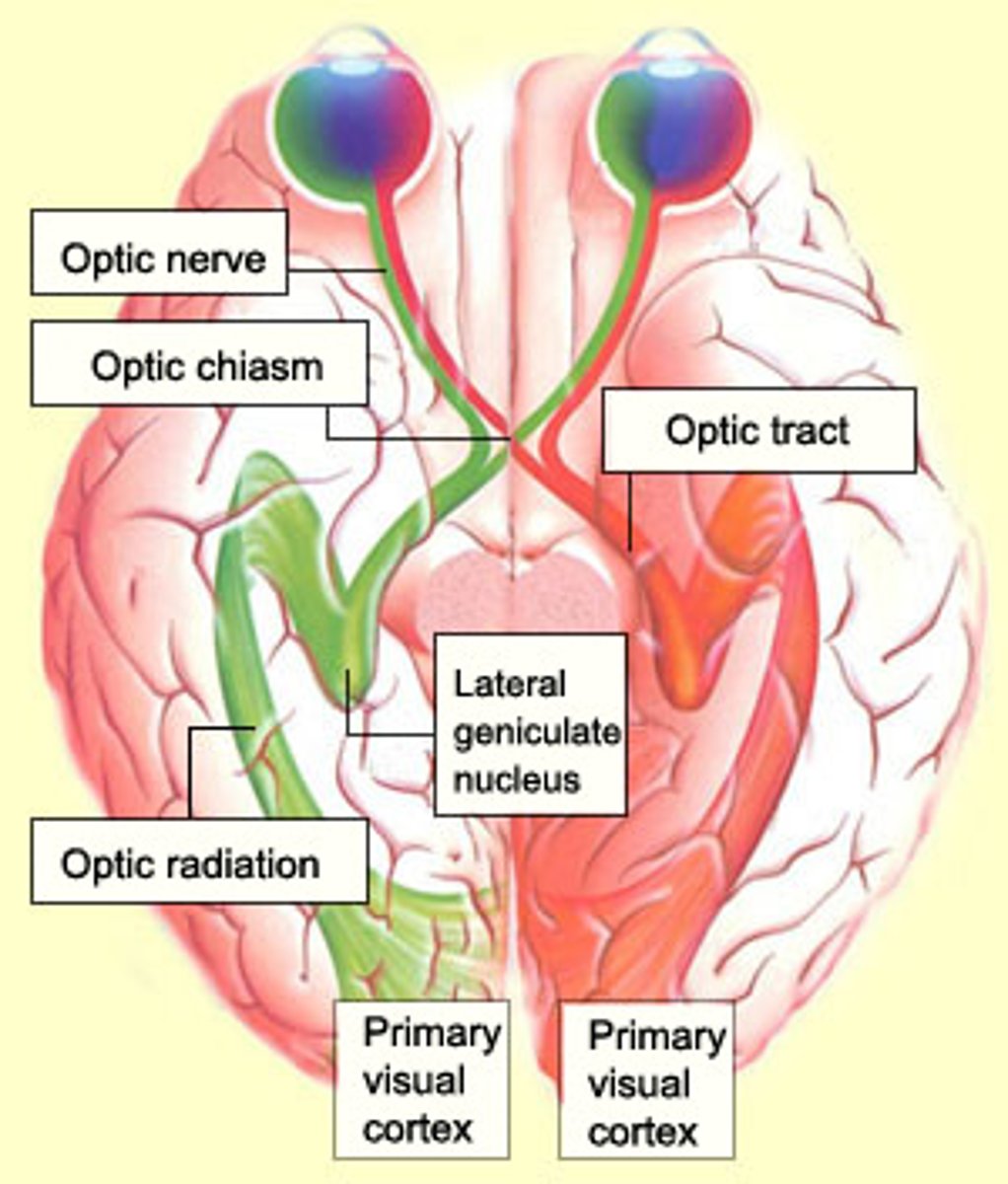
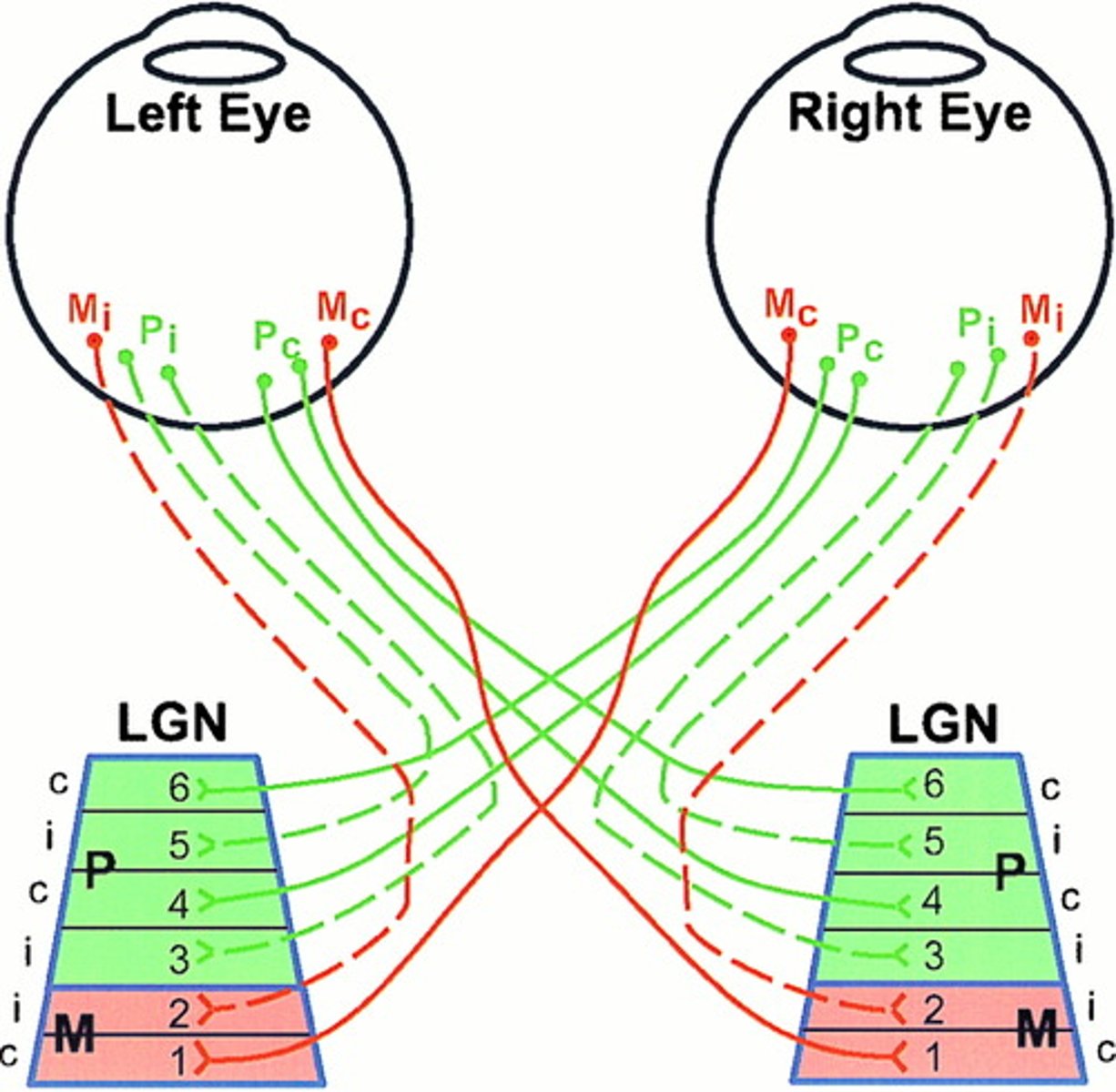
lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN)
the part of the thalamus that receives information from the optic tract and sends it to visual areas in the occipital cortex; around 90% of retinal ganglion cells project onto the LGN
superior colliculus
where>what; integrates from multiple senses to figure out where things are in space; coordinating and planning eye movement
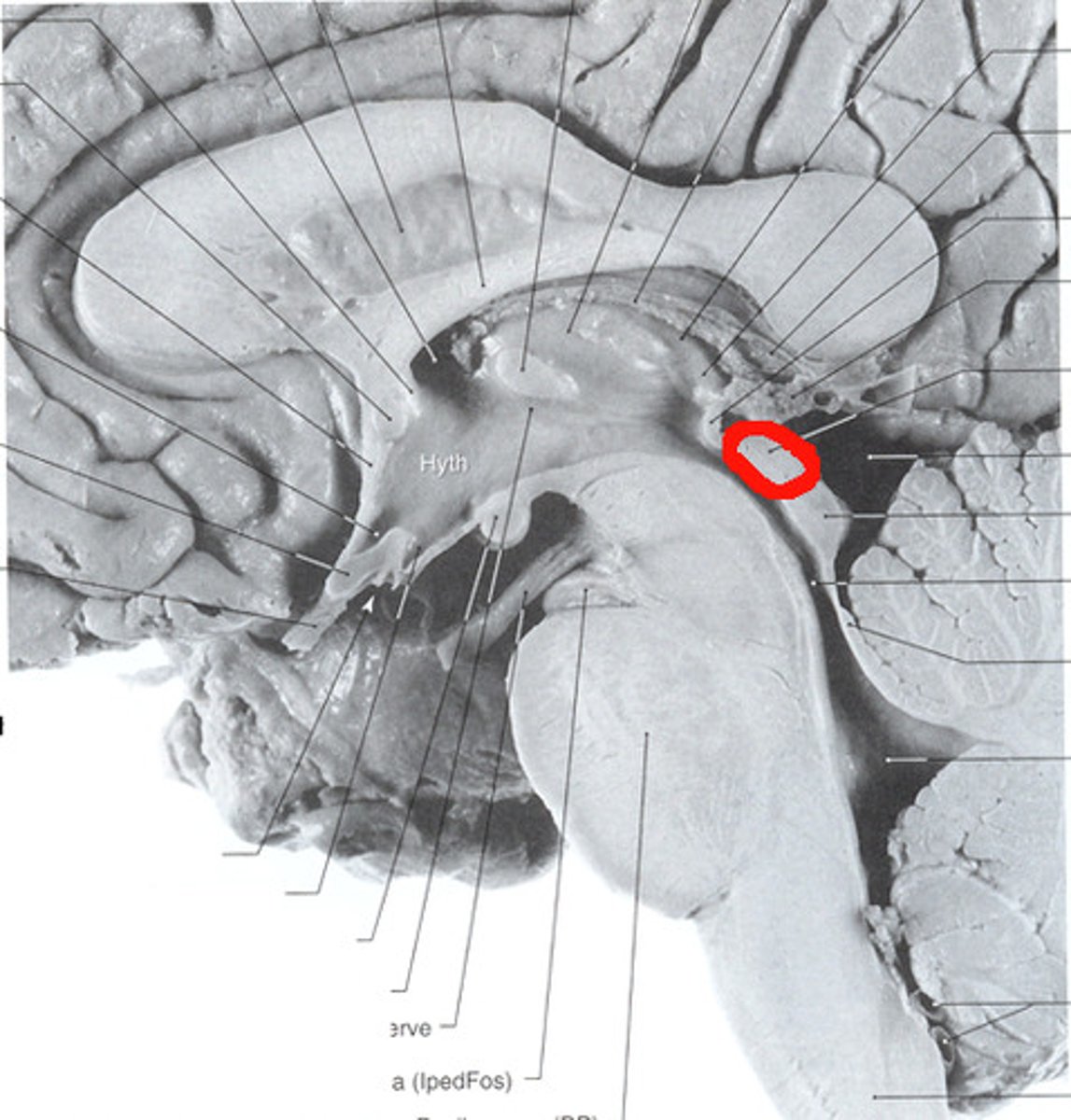
optic chiasm
the point in the brain where the visual field information from each eye "crosses over" to the appropriate side of the brain for processing
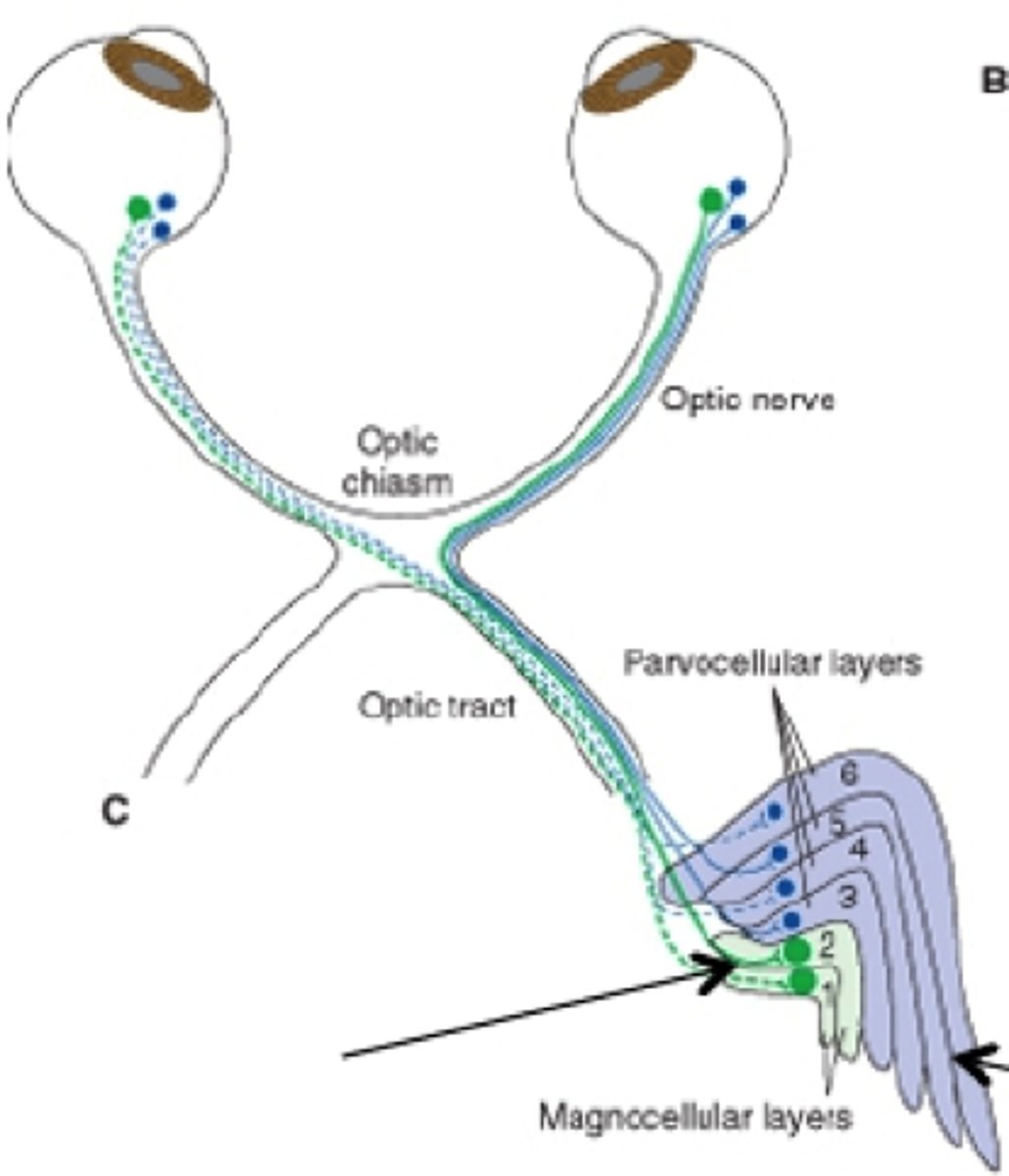
RGC axons terminate in different layers of...
lateral geniculate nucleus--->
koniocellular layers
parvocellular layers
magnocellular layers
koniocellular layers
(grains of sand)
S cones make up their receptive field because they make up the receptive field of small bistratified RGCs
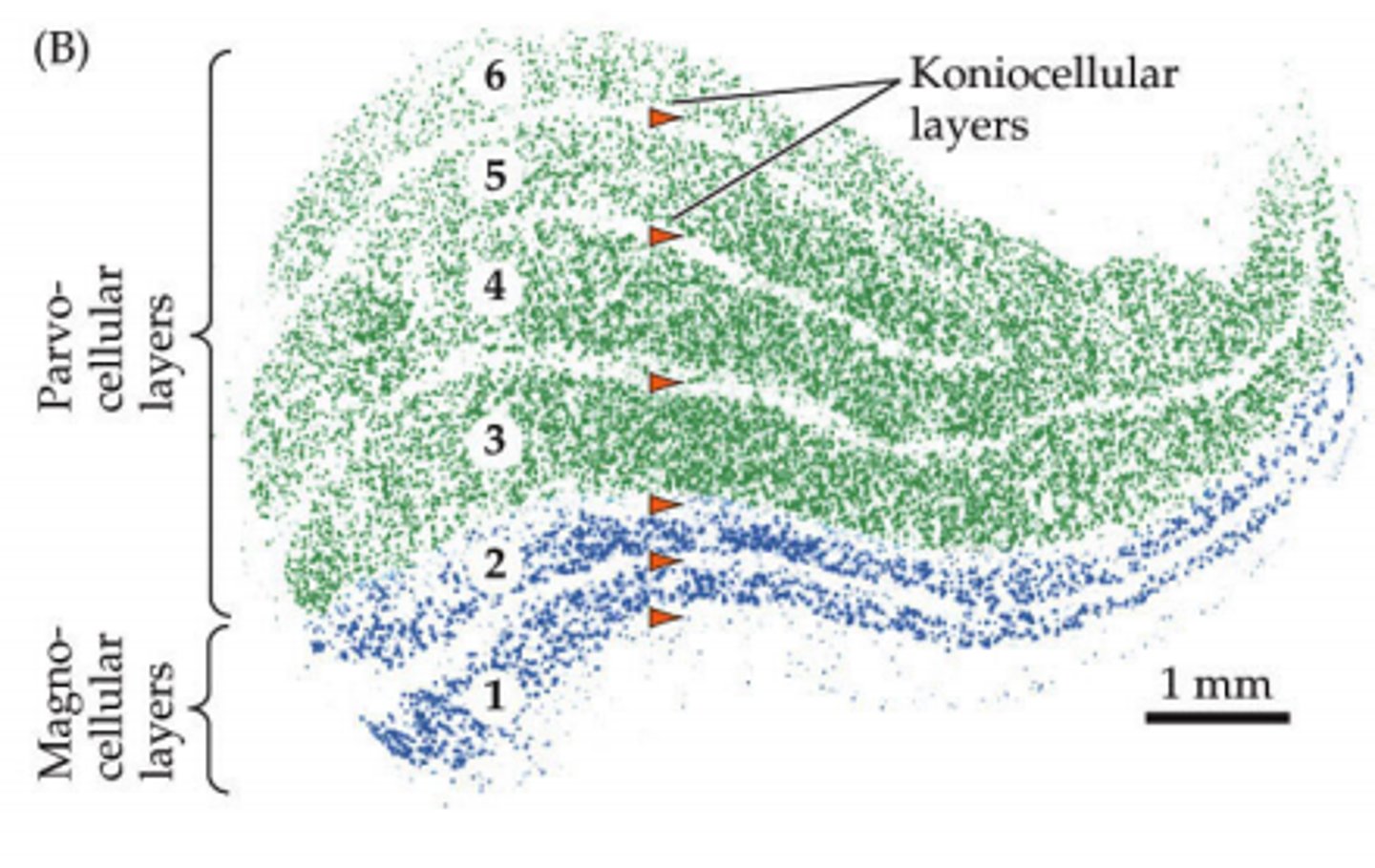
parvocellular layers
(smaller)
M and L cones make up the receptive field because they make up the receptive field of small RGCs
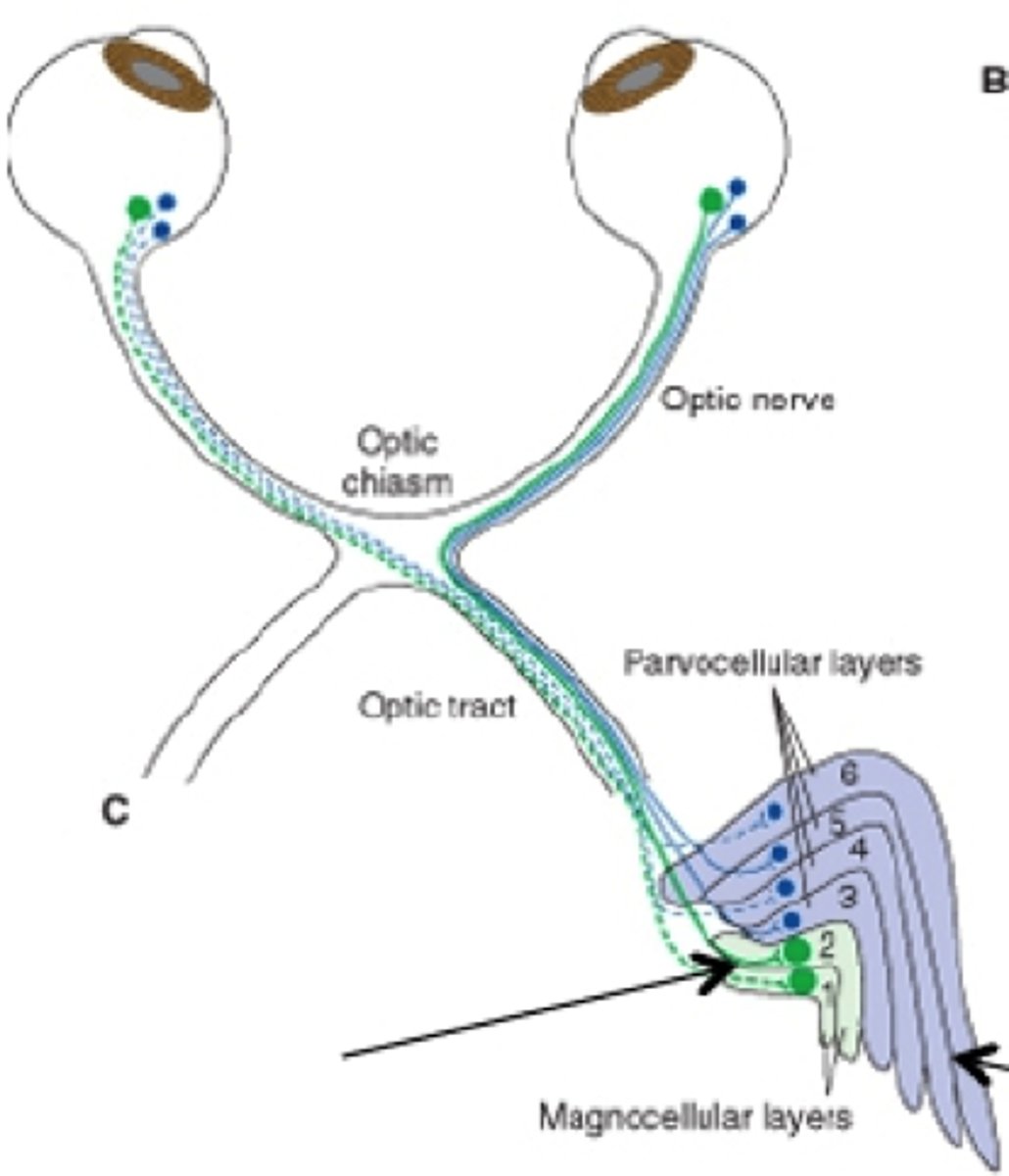
magnocellular layers
(bigger)
rods make up the receptive field because they make up the receptive field of parasol RGCs
retinotopic organization
the receptive fields of a set of neurons are organized in such a way as to reflect the spatial organization present in the retina;
if things are next to each other on the retina, they are next to each other on LGN;
each layer has it's retinotopic map, but layers are stacked so they line up
retinotopic map
Topological map that preserves spatial relationships found on Retina
M cells (magnocellular)
responsible for detecting fast changes, motions, flicker, bigger receptive fields
p and k cells (parvocellular and koniocellular)
color opponent cells; smaller receptive fields
(those receptive fields with R-G+ and B-Y+ looking notation)
functional role of LGN
it integrates information from the 2 eyes; clears up the signal from the retinal ganglion cells, accentuates boundaries and deemphasizes uniformities and keeps everything retinotopically organized so that it can get sent to the brain for further processing