bio unit 6
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Ribose differs from deoxyribose in that
ribose has an extra hydroxyl group.
Which of the following is a component of a nucleotide?
A five-carbon sugar
The central dogma of molecular biology states that information flows from
DNA to RNA to protein.
Translation is the process by which
proteins are synthesized from RNA.
Eukaryotic chromosomes are typically
multiple linear structures
The level of DNA packaging brought about by the formation of nucleosomes looks like
beads on a string.
A new nucleotide can be added to only which end of a growing DNA strand?
3’
Which enzyme is primarily responsible for proofreading a growing DNA strand?
DNA polymerase
The enzyme that catalyzes the addition of new nucleotides to a growing DNA strand is
DNA polymerase
Which statement about the strands of a newly replicated DNA molecule is correct?
One strand is new and the other is from the original molecule.
What is the result of DNA ligase’s action?
DNA fragments are joined together
Short DNA fragments are found on which strand of DNA?
The lagging strand
DNA always grows in which direction?
5’ to 3’
Transcription ends at a
terminator
Which is specific to the synthesis of only one type of protein?
A messenger RNA
Alternative splicing means that
different spliced forms contain different combinations of exons
The codon used to initiate protein synthesis is
AUG
How many nucleotides make up a codon?
3
An RNA transcript is synthesized in which direction?
5’ to 3’
A transcribed region of DNA has a 5′-to-3′ sequence GCGAC. The 5′-to-3′ sequence of an RNA transcribed from this DNA is
5′-GUCGC-3′
How many different types of aminoacyl tRNA synthetases are there?
20
Which type of protein interacts directly with a stop codon?
Release factor
Transcription starts at a
promoter
Which enzyme is responsible for proofreading during DNA replication?
DNA polymerase
Sometimes an activator protein interacts with a small molecule in the cell and undergoes a change in shape that alters its binding to DNA. This change in shape is an example of a(n)
allosteric effect.
One regulatory step in the process of gene expression and synthesis of proteins is the actual modification of proteins themselves, which is called
post translational modification.
In prokaryotes, inducers are small molecules that
bind to repressors and promote transcription.
Which statement about mutations is true?
A mutation may leave the amino acid sequence of a protein unchanged.
Histone modification
can change over time in response to environmental cues, allowing genes to be turned on or off as needed.
Using the natural processes of cell growth and development to replace diseased or damaged tissue is called
regenerative medicine
Movable DNA sequences are called
transposable elements
A point mutation that causes no change in the amino acid sequence of a protein is called a
silent mutation.
A point mutation that causes an amino acid replacement is called a
missense mutation.
Differentiation refers to the process by which
cells become progressively more specialized during development.
For the lactose operon, lactose acts as a(n):
inducer
The fertilized egg is totipotent, which means...
it can give rise to a complete organism.
The process by which a single primary RNA transcript is used to make multiple proteins is called
alternative splicing.
Imagine a gene in which the sequence that is transcribed into a GAG codon, which codes for glutamic acid, is mutated to GUG, which codes for valine. What type of mutation is this?
Missense
The Pax6 gene acts as a master regulator of eye development. If a Pax6 gene from a mouse were engineered to be expressed in the antenna of Drosophila, what would you expect to observe?
A compound eye develops on the antenna.
A cell in the lining the human gut is very different in structure and function from a white blood cell. How would you describe the genetic basis for this difference?
These different cell types express different sets of genes, although their genomes are identical.
A nonsense mutation
changes a codon for an amino acid into a codon for chain termination.
The technique that involves isolating genes from one species and introducing them into another is called
recombinant DNA technology.
The name of the technique used to amplify specific sequences of DNA is
PCR
In gel electrophoresis, DNA fragments migrate toward
the positive pole.
You run a PCR reaction for six cycles starting with a single DNA molecule. Theoretically, how many copies of your sequence would you now have?
64
What is the benefit of using Taq polymerase in PCR?
Because it is taken from bacteria that live in high temperatures, it stays active during the denaturation steps of the reaction
Which of the following is an example of a transgenic organism?
A fish that “glows in the dark” by expressing fluorescent jellyfish proteins
Which of the following is an application in a clinical health setting where DNA sequencing could be applied?
Determining whether a gene that may be related to a disease is being expressed in an individual
Restriction enzymes cut double-stranded DNA at specific short nucleotide sequences. A particular piece of DNA is 6216 bp long. The restriction enzyme XbaI cuts this piece of DNA at nucleotide positions 2316, 3142, and 4513. A scientist incubated the DNA with XbaI until it was completely digested, then ran the digested DNA on a gel. Which of the gels in the figure correctly represents the expected banding pattern? A labeled size ladder is shown on each gel to indicate fragment sizes.
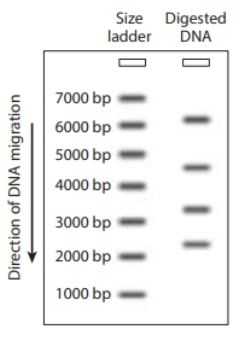

Forensic analysis often relies on very small amounts of DNA recovered from crime scenes. The recovered DNA can be compared to the DNA of people suspected to be involved in the crime. Forensic investigators examined the DNA recovered from a hair that was found at a crime scene and obtained the banding pattern shown on the gel below. They additionally examined the banding pat-terns of DNA from four potential suspects, which are also shown on the gel

Which step must be completed before running the gel?
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to copy the DNA found at the crime scene