Topic 1 Engineering Materials & Properties
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
What are the four main types of engineering materials?
Metals, polymers, ceramics, and composites.
What properties do metals possess due to their crystalline structure?
high strength
stiffness
hardness
toughness
ductility
good electrical conductivity
lustrous appearance
Good thermal conductivity
Define crystalline structures
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (i.e., atoms, molecules or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered and repeated pattern of arrangement throughout the entire volume of the solid
Define amorphous solids
Amorphous solids or non-crystals are not crystalline solids. Their constituents (i.e.,
atoms or molecules) are randomly arranged in the micro-structure of the solid
What is an alloy?
An alloy is a metal that is formed through melting and mixing 2 or more metallic elements or other elements to enhance its properties (i.e., hardness, strength, corrosion resistance, etc)
Define polymers
Polymers are molecular solids (solids composed of molecules) consisting of giant long chain molecules. The molecules are held together by Van der Waals forces of attraction.
Examples of polymers
Polyethylene (PE)
Polypropylene (PP)
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Polystyrene (PS)
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Polyisoprene (Natural Rubber)
List some properties of Polymers
Low density
Poor conductor of heat and electricity
Low in strength
Flexible
Low melting point
Why do polymers have low density?
They have a loosely packed molecular structure. The long chains of the molecules make it difficult for the chains to form regular arrangements (crystals),
thereby resulting in loose packing. As such, plastics have lower density than metals
Why do polymers have a poor conductor of electricity and heat?
The long chain polymer molecules consist of
a carbon backbone linked by covalent bonds. Polymers have no free electrons
available for conduction mechanisms present in metals
Why do polymers have low strength and flexible?
The long chain molecules are held together by weak Van der Waals forces of attraction. This allows the chains to slide pass one another when it is subjected to forces, resulting in weakness and flexibility of the polymer body.
Why do polymers have low melting point
The Van der Waals forces of attraction holding the polymer chains together in the solid can be overcome easily with heating. Once overcome, the plastic molecules slide pass one another easily and form a melt. When the polymer melt is cooled the Van der Waals forces are formed back quickly between the molecules and causes the material to resolidify.
What are ceramics primarily made from?
Ceramics are made from a combination of one or more metals with a non-metallic element.
Examples of ceramics
Metal oxides (ionic) – Al 2 O3 , Ti O2 , ZrO2
Metal carbides (ionic) – TiC, Fe2C, Cr3C2
Metal nitrides (ionic) – AlN
Non metallic ceramics – diamond (C), SiO2 , SiC, Si3N
List some properties of ceramics
High hardness (good wear resistance)
High stiffness
Brittle
High melting point
Poor conductor of heat and electricity
Why do ceramics have a high hardness and stiffness?
The very strong ionic and covalent bonds hold the atoms firmly in place
Why are ceramics poor conductors of heat and electricity
There are no free moving electrons that are able to conduct electricity or heat throughout the material
Why are ceramics brittle?
There is nowhere for that energy to go—no way for the glass to deform and to absorb the energy from the impact - so it shatters instead.
Why do ceramics have a high melting point?
The strong ionic or covalent bonds between the molecules need a large amount of energy to overcome, therefore a large amount of thermal energy is required, thus a high melting point
Define composites
Composites are made from two or more materials with significantly different physical or chemical properties; one material serves as a matrix, while the other serves as a reinforcing material
Examples of composites
Concrete
Glass-reinforced plastics (Fibreglass)
Carbon-reinforced plastic (carbon fiber composite)
Define an atom
Basic building block of all materials and smallest unit of ordinary matter that form a chemical element.
Define molecule
Molecules are formed from 2 or more atoms bonded together via a chemical bond.
Molecules can consist of as little as 2 atoms
Define element
They are basic materials consisting of only 1 type of atom. Elements can exist as
atoms (Au) or molecules (H2)
Define compounds
materials formed through the combination of 2 or more elements through a chemical reaction. The atoms in a compound are held together by chemical bonds and cannot be separated through physical processes. Compounds have properties that are different from their component elements (e.g., Al and Al2O3), and always contain the same ratio of its component atoms
Define mixtures
Composed of 2 or more different elements and/or compounds that are physically mixed together. Mixtures can be separated into their components by physical means (evaporation, heating, etc.)
Define atomic number
The atomic number of an element refers the number of protons present in the nucleus of
the atom of the element
Define mass number
The mass number of an element refers to the sum of the number of protons and neutrons
present in the nucleus of the atom of the element
What is ionic bonding?
Ionic bond: formed between the ion of a metal (cation) with the ion of a non-metal
(anion). The ionic bond is the electrostatic forces of attraction between the cation and
the anion. Examples include Al2O3, Fe2O3, NaCl, etc.
What is a covalent bond
formed between the atoms of non-metals of the same type (Sulphur, S8) or different types (CO2, H2O, etc). The bond is formed between atoms through, the sharing of valence electrons.
What is a metallic bond
They formed in metallic elements involving the electrostatic forces of attraction between the positive metal ions and the sea of free electrons. Examples include any metals
What is the role of the electron cloud in metallic bonding?
The electron cloud forms from detached valence electrons that float freely among metal ions, holding metal atoms together.
List physical properties
Melting
Boiling
Density
Specific Gravity
List thermal properties
Thermal expansion coefficient
specific heat capacity
Thermal conductivity
List chemical properties
Redox potential
Chemical resistance
Corrosion resistance
List aesthetic properties
Appearance
Surface texture
Ability to accept special finishing
List economic properties
Cost of raw materials and manufacturing
Time for fabrication
availability of materials
List technological properties
Machinability
castability
forgeability
weldability
formability
brazeability
List and define mechanical properties
Stiffness — resistance of a material to deformation
Strength — amount of loading forces a material can withstand before failure
Toughness — Resistance of a material to impact (amount of energy a material can absorb before fracture)
Ductility — amount of plastic deformation a material can sustain via stretching before failure
Malleability — amount of plastic deformation a material can sustain via compression before failure
Hardness — a material’s ability to withstand plastic deformation, scratches, wear and tear by another material
What are the three hardness tests?
Brinell
Vickers
Rockwell
List the advantages and limitations of Brinell hardness test
Advantages
• Applicable to both ferrous and non-ferrous materials
• Large contact area to provide accurate reading
• Results are accepted by industry
• Imperfections of the materials do not affect the readings
Limitations :
• Not suitable for harder materials > 500HB, may damage indenter
• Large indentation is left after the test
• Thickness of the test material => dia. of indenter
• Surface of test materials must be flat and smooth when small dia. indenter is used
List the advantages and limitations of Vickers hardness test
Advantages :
• square indentation is geometrically similar
• hardness value obtained is independent of the magnitude of applied force
• small indentation mark allows the test to be done on finish or thin components
• can test on a wide range of materials under varying loads
• can test on curved surfaces by applying correction factor
Limitations :
• smooth surface is needed in order to focus the edges of the indentation
• sensitive to imperfections in materials when small load is used
List the advantages and limitations of the Rockwell hardness test
Advantages :
• quick, simple with direct reading of hardness value • reading can be analog or digital types
• initial minor load avoids errors due to uneven surface • different scales allow measurement of variety of material hardness
Limitations :
• difficult to convert into Brinell or Vickers scale
• require to use appropriate scale to express the correct hardness value
• heavy indentation may damage the surface of specimen
What shapes are the indentors in the hardness tests?
Brinell: tungsten carbide ball
Vickers: Diamond pyramid
Rockwell: diamond or tungsten carbide cone
Define tensile stress
Tensile stress is defined as the magnitude F of the tensile force applied along an elastic rod
divided by the cross-sectional area A of the rod in a direction that is perpendicular to the
applied force. Tensile stress can be expressed mathematically by the formula;
σ = F / A
Define tensile strain
Tensile strain is defined as the ratio of the amount of deformation or elongation of a solid
body due to the application of a tensile force or stress to the original length of the body.
Tensile strain can be expressed mathematically by the formula:
ε = ΔL / L
What is impact strength?
Impact strength is the ability of a material to withstand shock loading and indicates the toughness of the material.
What is the difference between ductility and malleability?
Ductility is the ability to be stretched without breaking, while malleability is the ability to deform under compression without fracture.
What does a stress-strain curve indicate?
A stress-strain curve indicates how a material deforms under stress, showing both elastic and plastic deformation regions.
How is the Brinell hardness number calculated?
BHN is calculated based on the diameter of the indentation created by a tungsten carbide ball under load.
What is the difference between the Izod and Charpy impact tests?
Izod test uses a cantilever setup and hits the top of the specimen; Charpy test supports the specimen at both ends and hits the center.
What affects the density of a material?
Density is influenced by how closely the atoms are packed together.
What does the modulus of elasticity indicate?
The modulus of elasticity indicates a material's ability to deform elastically when a force is applied.
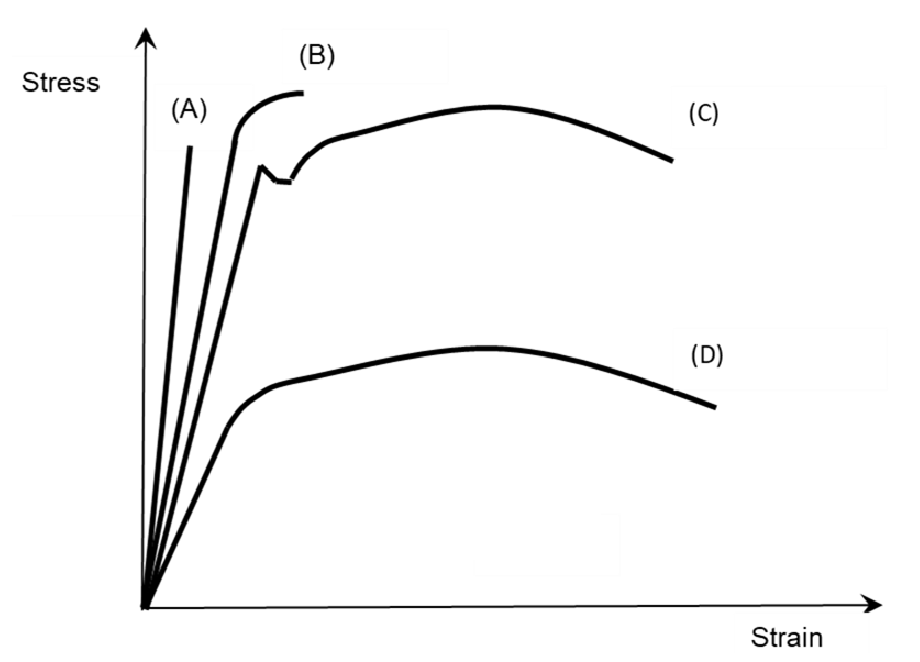
What material represents each point?
A: Glass
B: Cast Iron
C: Mild steel
D: Aluminum/Copper
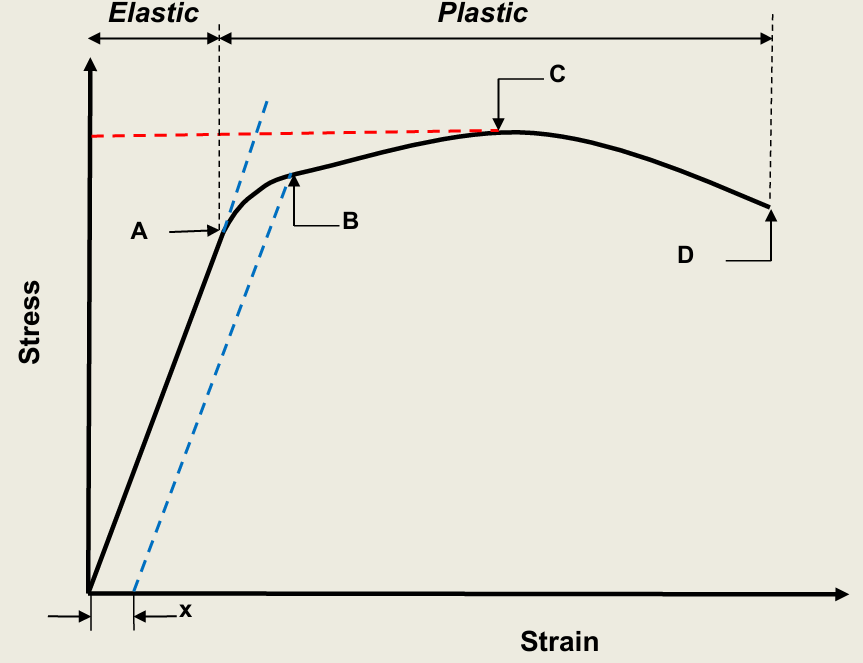
What do each points represent?
A: Elastic limit (beyond point A is plastic deformation/yielding)
B: Proof stress at x% strain
C: Maximum tensile stress
D: Facture stress
What is required to be measured to get the hardness scale from brinell?
mean diameter of indentation
What is required to be measured to get the hardness scale from Vickers?
mean diagonal of the indentation
What is required to be measured to get the hardness scale from Rockwell?
Depth of indentation