AQA A level Chemistry 3.2.5 Transitional Metals
1/140
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
141 Terms
Where are transitional metals found on the periodic table? (1)
D block (in the middle)
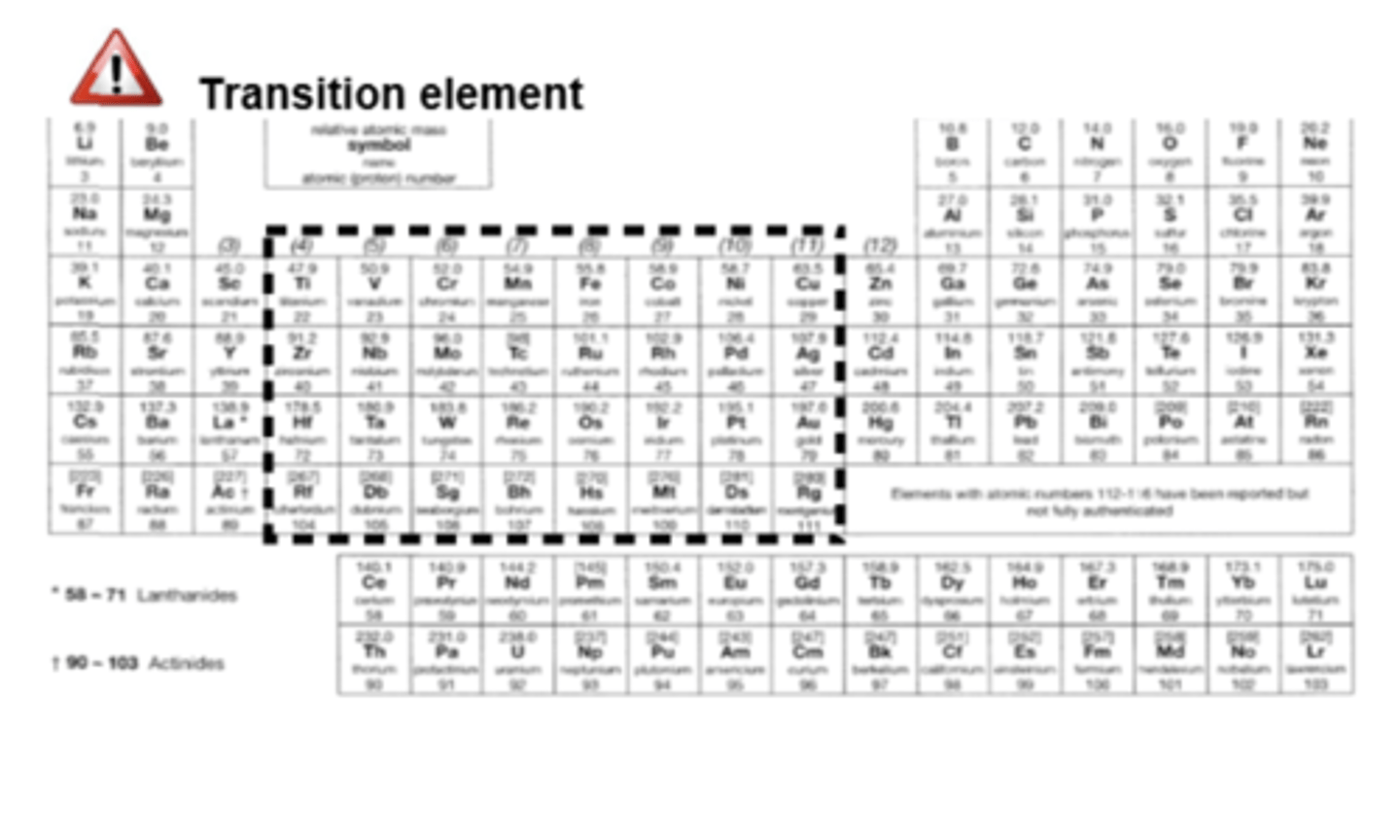
What is the definition of a transition element? (1)
Forms at least one stable ion with a partially filled d-subshell
What are the four characteristics of transitional metals? (4)
1. They form complexes
2. They form coloured ions
3. They have variable oxidation states
4. They possess the ability to act as a catalyst
What is a ligand? (1)
A molecule or ion that forms a coordinate bond with a transition metal.
What is a complex? (1)
A central metal or ion surrounded by ligands joined by coordinate bonds.
What is the coordination number? (1)
The number of coordinate bonds to the central metal atom or ion.
What is the coordination number for a linear complex? (1)
2
What is an example of a linear complex? (1)
Ag⁺ complexes.
What is the coordination number for a square planar complex? (1)
4
What are examples of square planar complexes? (1)
Pt²⁺ and Ni²⁺ complexes.
What is the coordination number for a tetrahedral complex? (1)
4
When do tetrahedral complexes form? (1)
When ligands are too big to fit six (e.g., Cl⁻).
What is the coordination number for an octahedral complex? (1)
6
When do octahedral complexes form? (1)
Most complexes with small ligands (e.g., H₂O and NH₃).
What is a monodentate ligand? (1)
A ligand that forms one co-ordinate bond to the transition metal ion.
Give examples of monodentate ligands. (5)
H₂O, NH₃, Cl⁻, CN⁻, OH⁻
Why are H₂O and NH₃ similar as monodentate ligands? (1)
They are very similar in size and are both neutral, so the overall charge on the complex is the same as the charge on the metal ion.
What is the effect of monodentate ligands such as Cl⁻, CN⁻, and OH⁻ on the charge of the complex ion? (1)
They have negative charges, so the overall complex ion charge will be a combination of these and the charge on the metal ion.
Give and draw an example of a linear complex (3)
[Ag(NH₃)₂]⁺
(Tollen's reagent)
![<p>[Ag(NH₃)₂]⁺</p><p>(Tollen's reagent)</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/1c4da4ec-0de3-4f72-9f2e-4aa88f48ce89.png)
Give and draw an example of a square planar complex (3)
[Pt(NH₃)₂(Cl)₂]
![<p>[Pt(NH₃)₂(Cl)₂]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/86d29449-bbb7-41d9-a169-165f41916424.jpg)
Give and draw an example of a tetrahedral complex (3)
[CuCl₄]²⁻
![<p>[CuCl₄]²⁻</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f2d61b4c-d946-48db-8543-2b851bd52aa4.png)
Give and draw an example of a octahedral complex (3)
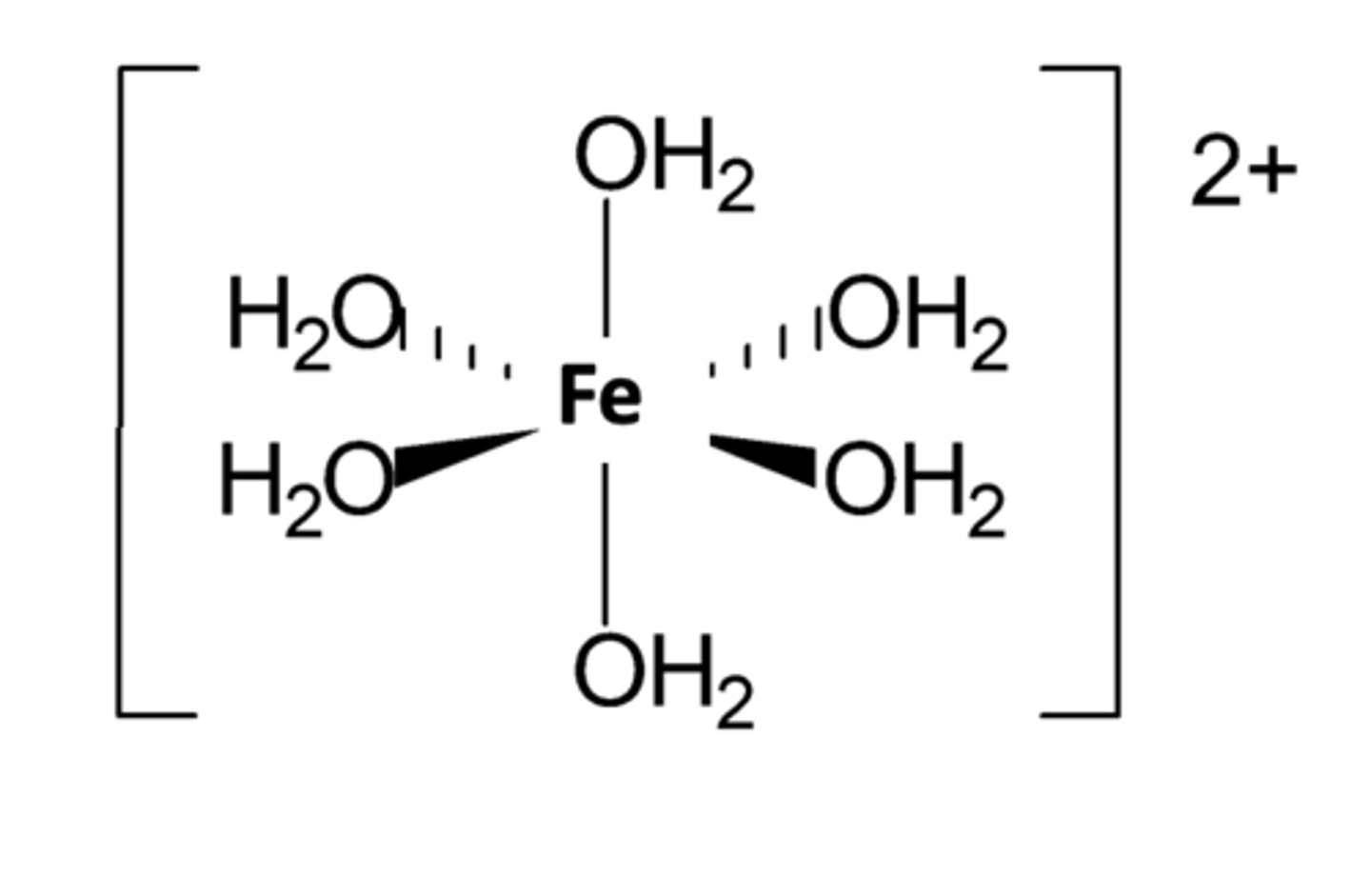
Why does the complex ion of chloride ligands have a different shape compared to those of H₂O ligands? (1)
Chloride ions are too big to fit more than four around one ion
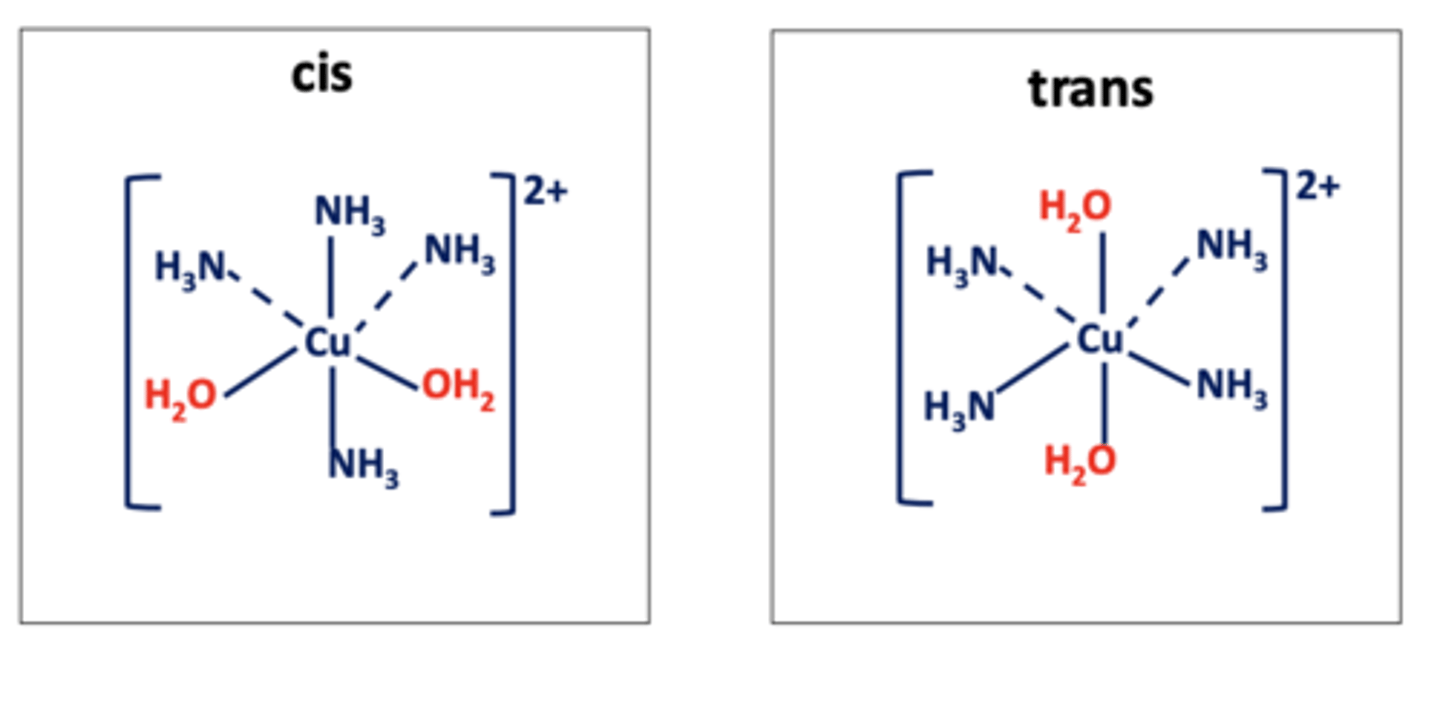
What do the terms "cis" and "trans" mean in transition metal complexes? (2)
- Cis: Ligands are on the same side of the complex.
- Trans: Ligands are on opposite sides of the complex
What are the advantages of cis-platin as an anti-cancer drug? (1)
It kills cancer cells
What are the disadvantages of cis-platin as an anti-cancer drug? (2)
- Causes hair loss
- Causes fertility issues
Draw the two possible isomers formed by e.g. [Cu(H₂O)₂(NH₃)₄]²⁺
What is a bidentate ligand? (1)
A ligand that forms two co-ordinate bonds to a transition metal ion through two different atoms on the same ligand.
What are the two requirements for a ligand to act as a bidentate ligand? (2)
- It must have two available lone pairs.
- Each lone pair must form a co-ordinate bond from separate atoms.
What are the two examples of bidentate ligands must you know? (2)
- NH₂CH₂CH₂NH₂
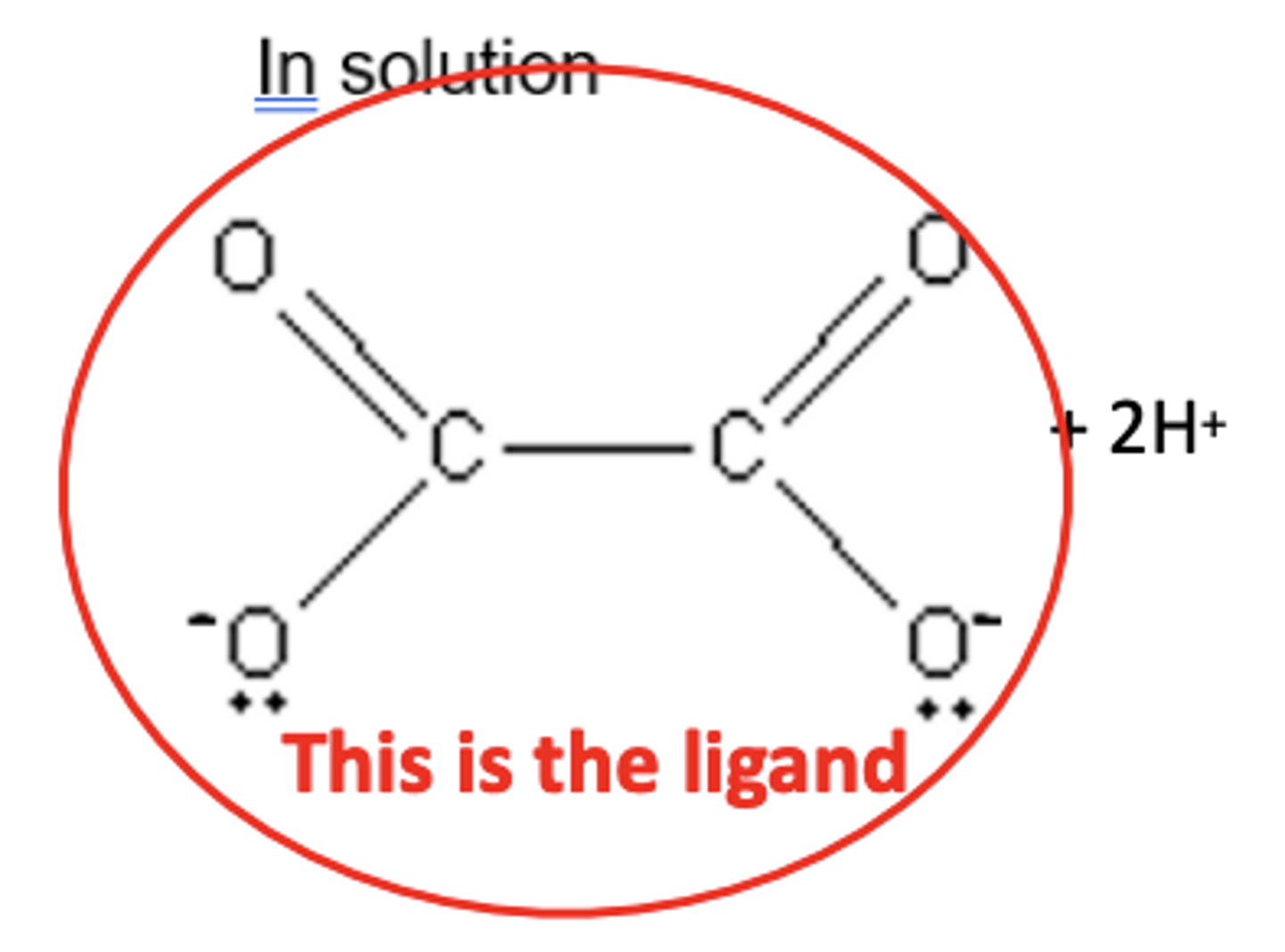
- [C2O4]2-
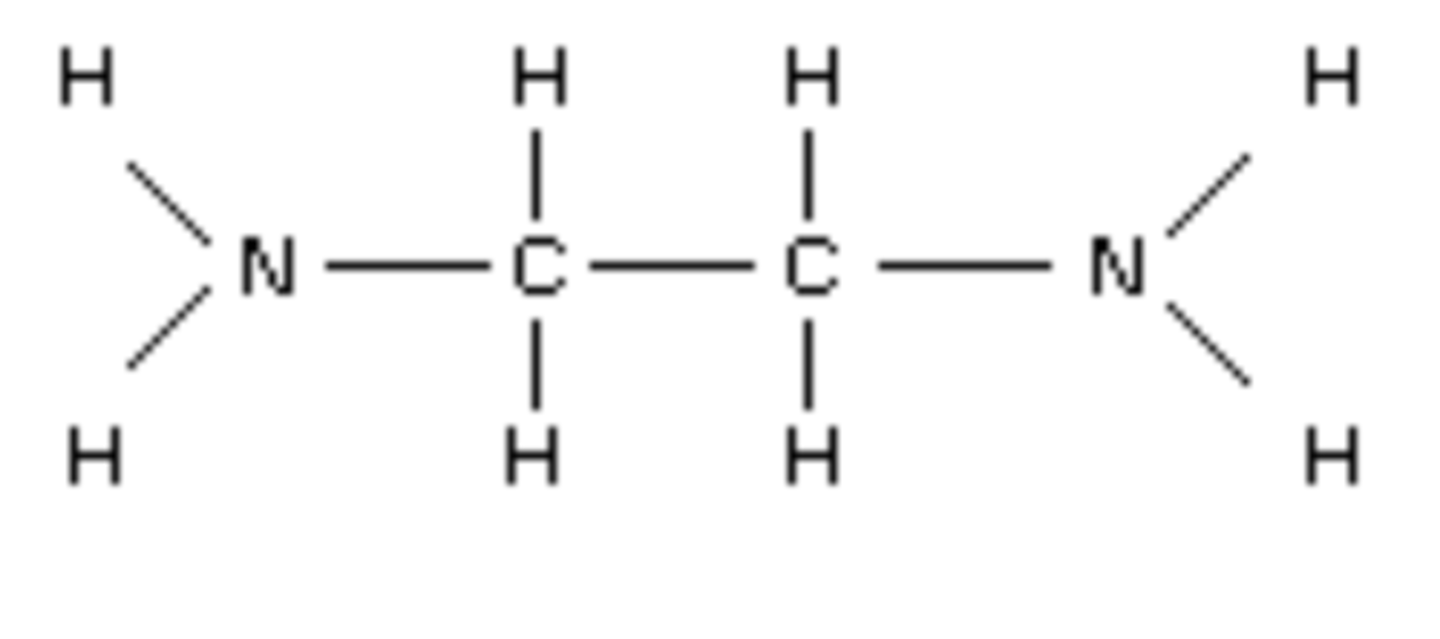
Draw the structure of 1,2-diaminoethane (2)
How many ligands are required to form a complex ion with a bidentate ligand? (1)
Three ligands
What is the co-ordination number for a complex ion formed with three bidentate ligands? (1)
Six
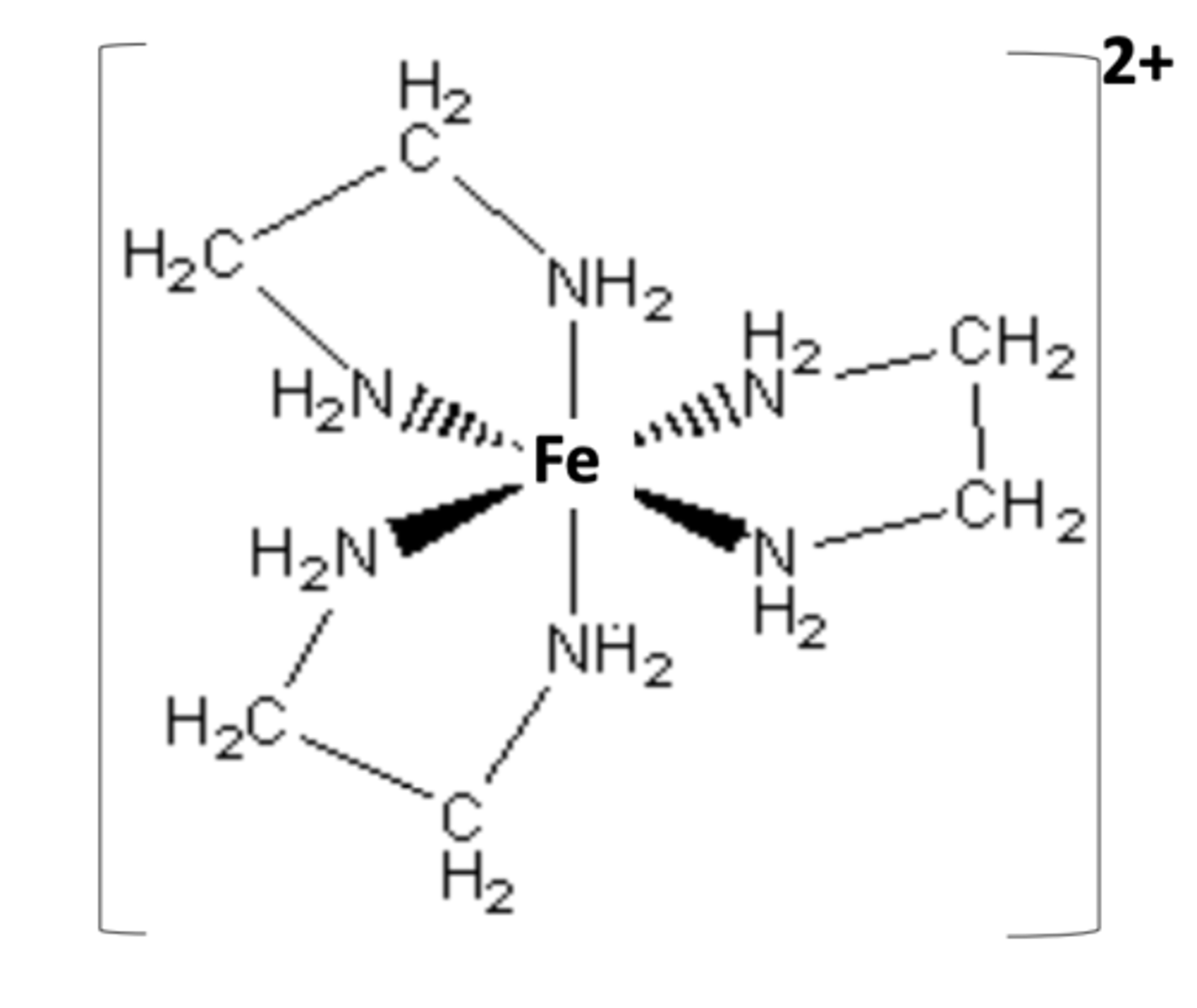
What is the general formula for a complex ion of 1,2-diaminoethane with M²⁺? (1)
[M(NH₂CH₂CH₂NH₂)₃]²⁺
What is the general formula for a complex ion of 1,2-diaminoethane with M³⁺? (1)
[M(NH₂CH₂CH₂NH₂)₃]³⁺
Draw the structure of [Fe(NH₂CH₂CH₂NH₂)₃]²⁺
Draw the structure of ethanedioate ions ([C2O4]2-) (2)
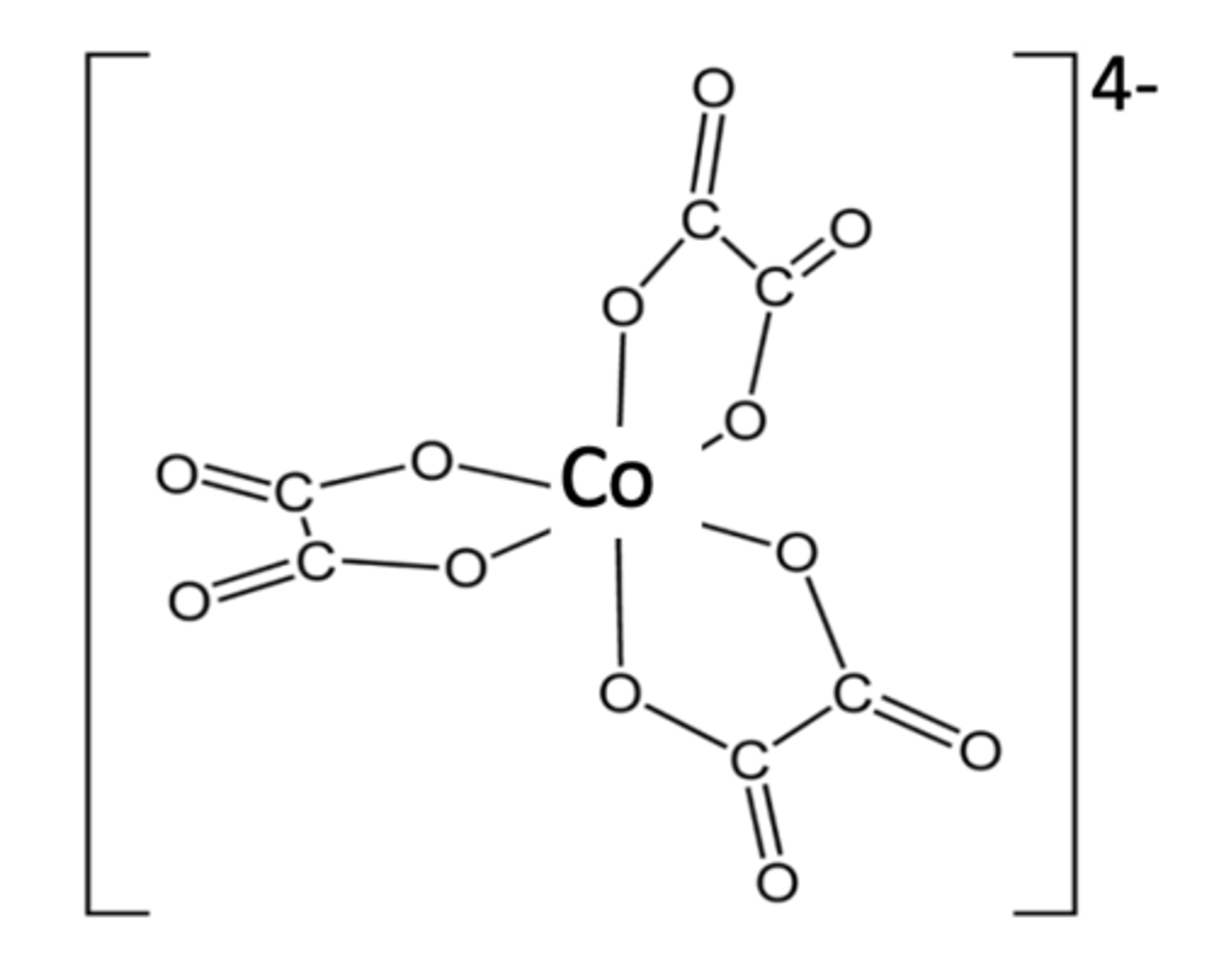
Draw the structure of [Co(C2O4)3]4- (2)
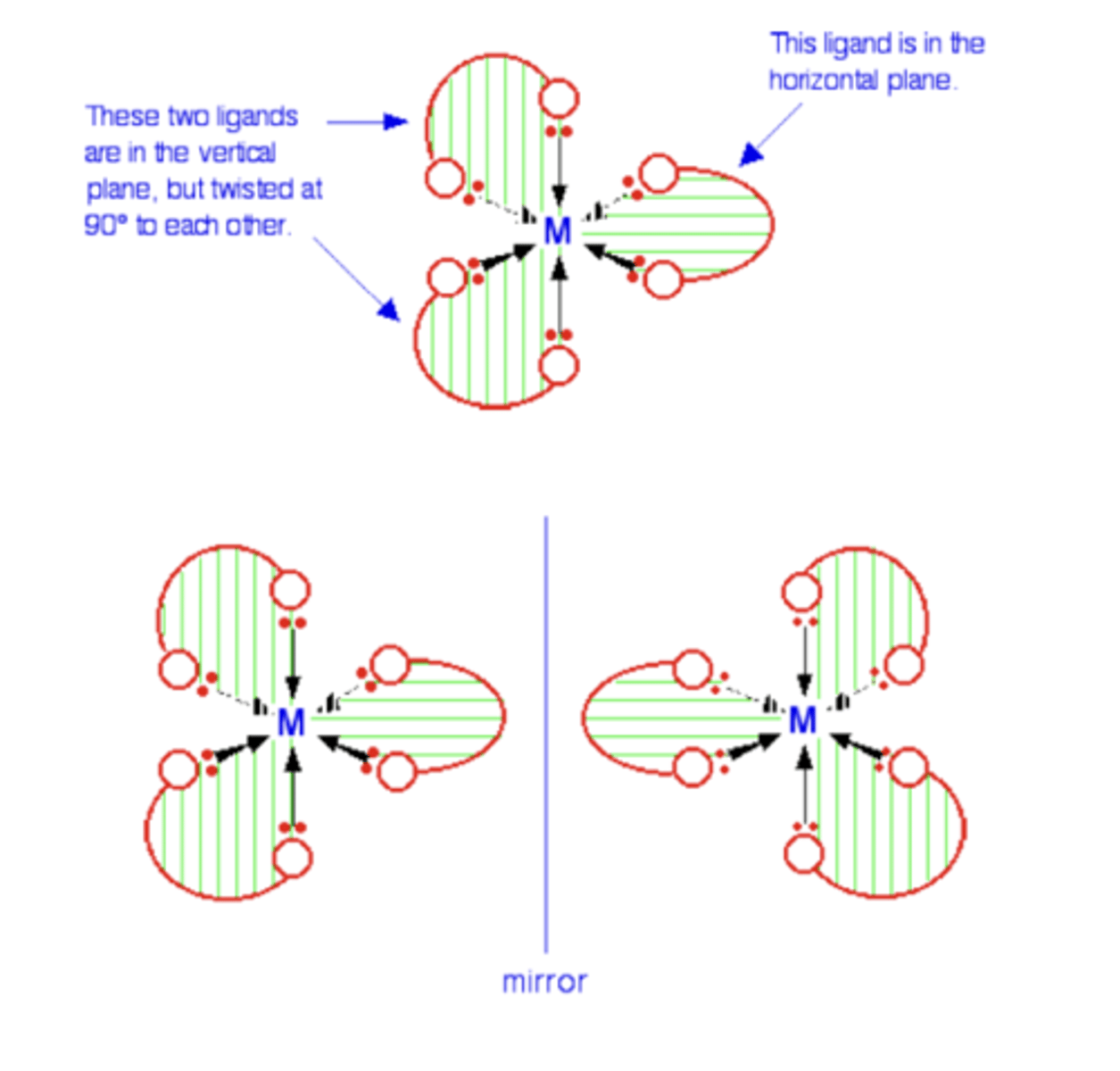
What is a key property of octahedral complexes formed with bidentate ligands? (1)
- They exhibit optical isomerism
- Forming two mirror-image isomers with all the characteristics of optical isomers.
What is a multidentate ligand? (2)
A ligand that can form two or more coordinate bonds to a transition metal ion from different atoms on the same ligand.
What is the maximum number of bonds a multidentate ligand can form? (1)
6 bonds
What are the two examples of multidentate ligands? (2)
- EDTA4-
- Porphyrin ring in haemglobin
What is the general formula for a complex ion with EDTA? (1)
[M(EDTA)]²⁻
How many ligands are in a complex ion with EDTA? (1)
1 ligand
What is the coordination number for a complex ion with EDTA? (1)
6
Why is EDTA most effective in alkaline conditions? (2)
The OH⁻ reacts with H⁺, shifting the equilibrium to the right, ensuring EDTA can form 6 coordinate bonds.
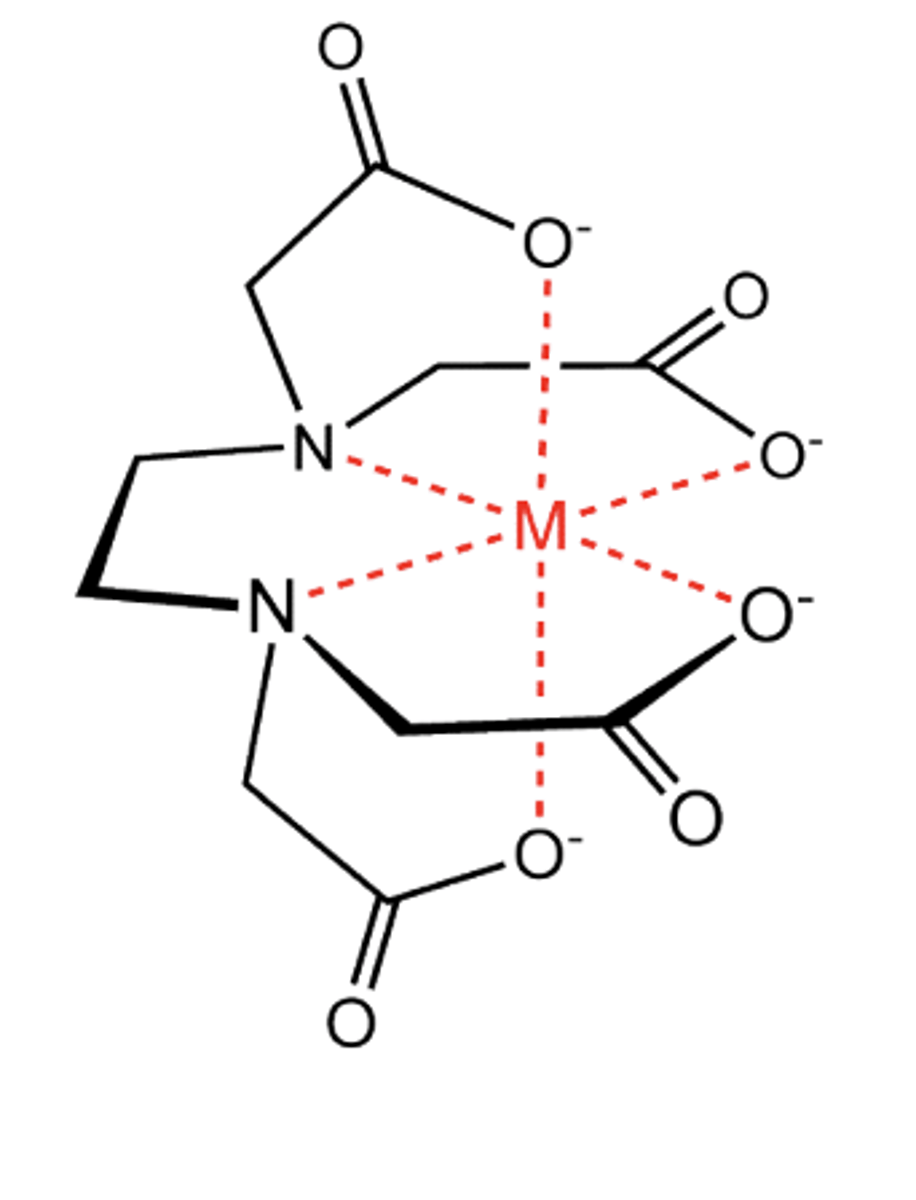
Draw the structure of an EDTA4- ligand (1)
You probably will be NEVER be asked to memorise the and draw the structure but familiarity is key
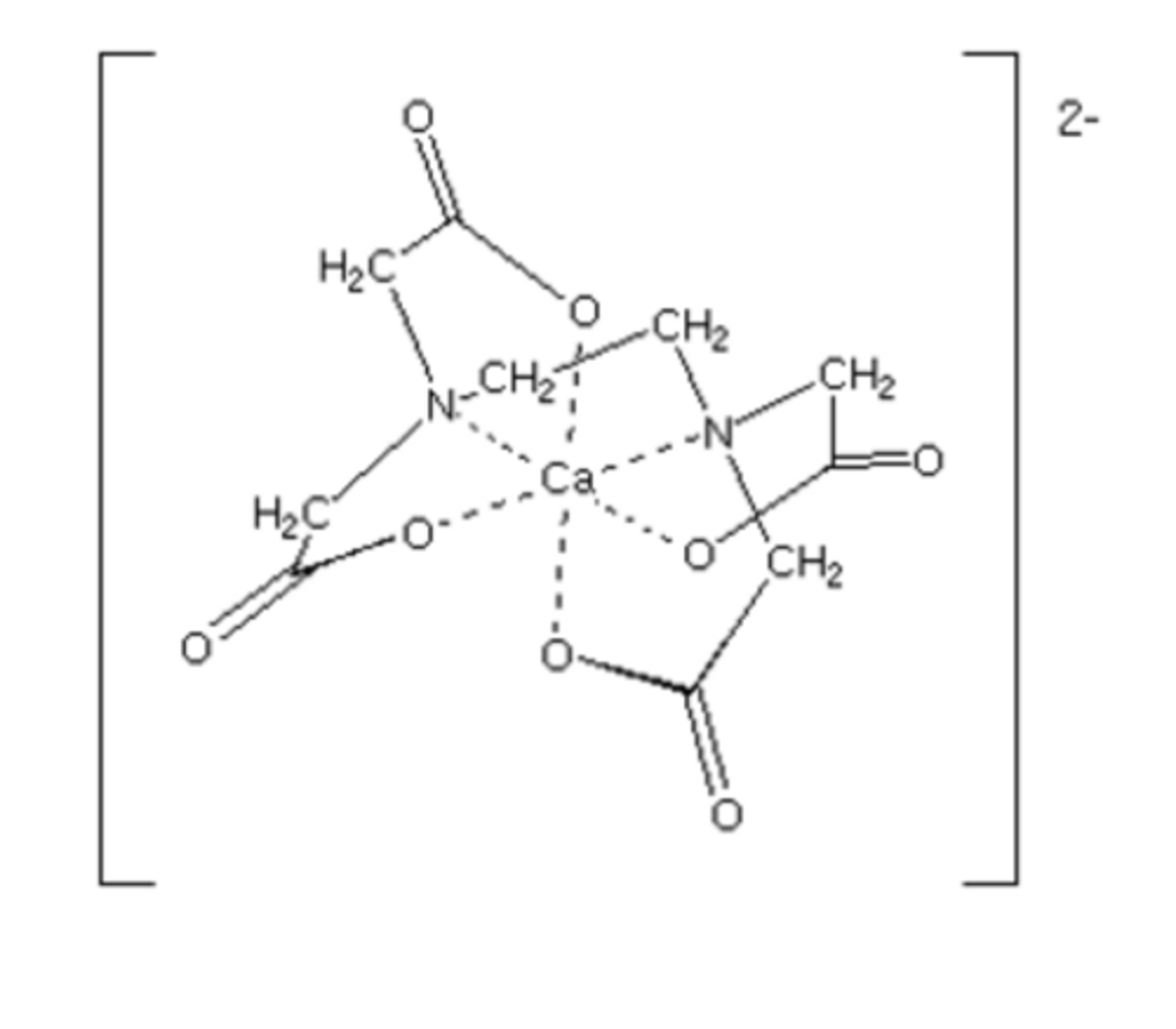
Draw a structure of a metal ion + EDTA4- complex (1)
What is the medicinal use of EDTA? (2)
- Used to treat patients suffering from lead poisoning through chelation therapy
- Where it binds to toxic ions and removes them from the bloodstream
What is the metal-to-EDTA ratio in metal-EDTA complexes? (1)
1:1
What is the function of haemoglobin? (1)
Haemoglobin transports oxygen around the body
What is the central metal ion and ligand in haemoglobin? (2)
Fe²⁺ is the central metal ion, and the porphyrin ring is the multi-dentate ligand
What acts as a monodentate ligand in oxygenated haemoglobin? (1)
Oxygen (O₂)
What happens when carbon monoxide is inhaled? (2)
Carbon monoxide forms a coordinate bond with Fe²⁺, replacing oxygen and preventing oxygen transport in the body
What is the equation for replacing all H2O ligands in [Co(H2O)6]2+ with NH3 ligands? (2)
[Co(H2O)6]2+ + 6NH3 → [Co(NH3)6]2+ + 6H2O
What is the equation for replacing some H2O ligands in [Cu(H2O)6]2+ with NH3 ligands? (2)
[Cu(H2O)6]2+ + 4NH3 → [Cu(H2O)2(NH3)4]2+ + 4H2O
What is the equation for replacing H2O ligands in [Cu(H2O)6]2+ with Cl⁻ ligands? (2)
[Cu(H2O)6]2+ + 4Cl⁻ → [CuCl4]2⁻ + 6H2O
What is the equation for replacing H2O ligands in [Fe(H2O)6]3+ with Cl⁻ ligands in concentrated HCl? (2)
[Fe(H2O)6]3+ + 4Cl⁻ → [FeCl4]⁻ + 6H2O
What is the equation for replacing H2O ligands in [Co(H2O)6]2+ with bidentate ligands? (2)
[Co(H2O)6]2+ + 3H2NCH2CH2NH2 → [Co(H2NCH2CH2NH2)3]2+ + 6H2O
What is the chelate effect? (2)
The process where monodentate ligands are substituted for bi/multidentate ligands to form a more stable complex
Why is the product of a chelation reaction more stable? (1)
There has been a positive ∆S (increase in entropy)
Write the equation for the ligand substitution reaction of [Cu(NH₃)₆]²⁺ with 3 ethane-1,2-diamine ligands. (1)
[Cu(NH₃)₆]²⁺ + 3NH₂CH₂CH₂NH₂ → [Cu(NH₂CH₂CH₂NH₂)₃]²⁺ + 6NH₃
Why does ∆S increase in the chelation reaction? (2)
4 moles are converted to 7 moles, leading to an increase in disorder
What is the value of ∆H in the chelation reaction, and why? (2)
∆H = 0 because the same number and same type of bonds are broken and formed (6 Cu-N bonds).
Explain why the free energy change (∆G) is negative for the chelation reaction. (3)
- ∆S is positive and ∆H = 0
- ∆G = ∆H - T∆S
- Since T∆S > ∆H, ∆G is negative, making the reaction feasible
What happens in the test for aldehydes using Tollens' reagent? (3)
1. Silver mirror forms in the presence of aldehydes
2. Ag⁺ in [Ag(NH₃)₂]⁺ is reduced to Ag (silver mirror).
3. Aldehyde is oxidised to carboxylic acid
What happens in the test for aldehydes using fehling's solution? (3)
1. Brick-red precipitate (Cu₂O) forms in the presence of aldehydes
2. Cu²⁺ is reduced to Cu⁺ in Cu₂O.
3. Aldehyde is oxidised to carboxylic acid.
What happens in the test for alcohols using acidified K₂Cr₂O₇? (3)
1. Colour changes from orange (Cr₂O₇²⁻) to green (Cr³⁺).
2. Cr(VI) is reduced to Cr(III).
3. Alcohols or aldehydes are oxidised.
Write the half equation for the reduction of Cr₂O₇²⁻ to Cr³⁺ in acidified K₂Cr₂O₇. (1)
14H⁺ + 6e⁻ + Cr₂O₇²⁻ → 2Cr³⁺ + 7H₂O
Write the half equation for the oxidation of ethanol to ethanal. (1)
CH₃CH₂OH → CH₃CHO + 2H⁺ + 2e⁻
Combine the two half equations for the redox reaction between ethanol and Cr₂O₇²⁻. (1)
8H⁺ + 3CH₃CH₂OH + Cr₂O₇²⁻ → 2Cr³⁺ + 3CH₃CHO + 7H₂O
What is the oxidation state and color of VO2+ in acidic solution? (1)
- +5
- Yellow
What is the oxidation state and color of VO2+ in the +4 oxidation state in acidic solution? (1)
- +4
- Blue
What is the oxidation state and color of V3+ in acidic solution? (1)
- +3 Image
- Green
What is the oxidation state and color of V2+ in acidic solution? (1)
- +2
- Purple
What is observed when ammonium metavanadate (NH4VO3) is dissolved in sodium hydroxide solution and acid is added? (2)
- Yellow VO2+ ions are formed
- Acidic conditions ensure VO2+ is the main ion present
What is the sequence of colours observed when zinc reduces vanadium from +5 to +2 oxidation states? (1)
Yellow → Blue → Green → Violet
What happens to vanadium(II) when exposed to oxygen in air? (3)
- Vanadium(II) oxidises to vanadium(III), turning green
- Further exposure oxidises it back to vanadium(IV)
- Turning blue
Why is cotton wool used to stopper the flask during the reduction of vanadium with zinc? (1)
To allow H2 gas to escape while minimising oxygen re-oxidation from the air
Write the half equation for the oxidation of zinc metal to Zn²⁺ ions. (1)
Zn → Zn²⁺ + 2e⁻
Write the half equation for the reduction of vanadium (V) to vanadium (II). (1)
VO₂⁺ + 4H⁺ + 3e⁻ → V²⁺ + 2H₂O
Construct an overall balanced equation for the redox reaction involving zinc and vanadium (V). (1)
2VO₂⁺ + 8H⁺ + 3Zn → 2V²⁺ + 4H₂O + 3Zn²⁺
What is the reducing agent when determining the percentage of iron in iron tablets using a redox titration? (1)
Fe²⁺
What is the oxidising agent in redox titrations involving acidified potassium manganate(VII), KMnO₄? (1)
MnO₄⁻
Construct the half-equation for the reduction of MnO₄⁻ (purple) to Mn²⁺ (colourless) in acidified conditions. (1)
MnO₄⁻ + 8H⁺ + 5e⁻ → Mn²⁺ + 4H₂O
Construct the half-equation for the oxidation of Fe²⁺ to Fe³⁺. (1)
Fe²⁺ → Fe³⁺ + e⁻
Combine the half-equations for the redox reaction of MnO₄⁻ with Fe²⁺. What is the molar ratio of MnO₄⁻ to Fe²⁺? (2)
- Reaction: MnO₄⁻ + 8H⁺ + 5Fe²⁺ → Mn²⁺ + 4H₂O + 5Fe³⁺
- Molar ratio: 1 : 5
What is the reducing agent when determining the molar mass of hydrated ethanedioic acid in a redox titration? (1)
C₂O₄²⁻
Construct the half-equation for the oxidation of C₂O₄²⁻ to CO₂. (1)
C₂O₄²⁻ → 2CO₂ + 2e⁻
Combine the half-equations for the redox reaction of MnO₄⁻ with C₂O₄²⁻. What is the molar ratio of MnO₄⁻ to C₂O₄²⁻? (2)
- Reaction: 2MnO₄⁻ + 16H⁺ + 5C₂O₄²⁻ → 2Mn²⁺ + 8H₂O + 10CO₂
- Molar ratio: 2 : 5
What is the reducing agent when determining the concentration of H₂O₂ in hair bleach? (1)
H₂O₂
Construct the half-equation for the oxidation of H₂O₂ to O₂. (1)
H₂O₂ → O₂ + 2H⁺ + 2e⁻
Combine the half-equations for the redox reaction of MnO₄⁻ with H₂O₂. What is the molar ratio of MnO₄⁻ to H₂O₂? (2)
- Reaction: 2MnO₄⁻ + 6H⁺ + 5H₂O₂ → 5O₂ + 2Mn²⁺ + 8H₂O
- Molar ratio: 2 : 5
Why do transition metals exhibit colour in their compounds? (3)
- Due to their partly filled d sub-levels.
- Electrons in the d sub-level can shift up and down between unoccupied orbitals
- Absorbing light energy in the process.
What is electron promotion in the context of transition metals? (1)
Electrons in the d sub-level absorb light energy to move to higher energy d orbitals
How is the colour of a transition metal compound observed? (1)
The colour transmitted is the light that is not absorbed during electron promotion
Why does the energy gap (ΔE) between d orbitals matter in colour chemistry? (2)
- The d orbitals are at specific energy values.
- The energy gap (ΔE) determines the amount of energy or light required for an electron to be promoted to a higher energy orbital.
What is the equation relating the energy gap (ΔE) between d orbitals to the frequency and wavelength of light? (1)
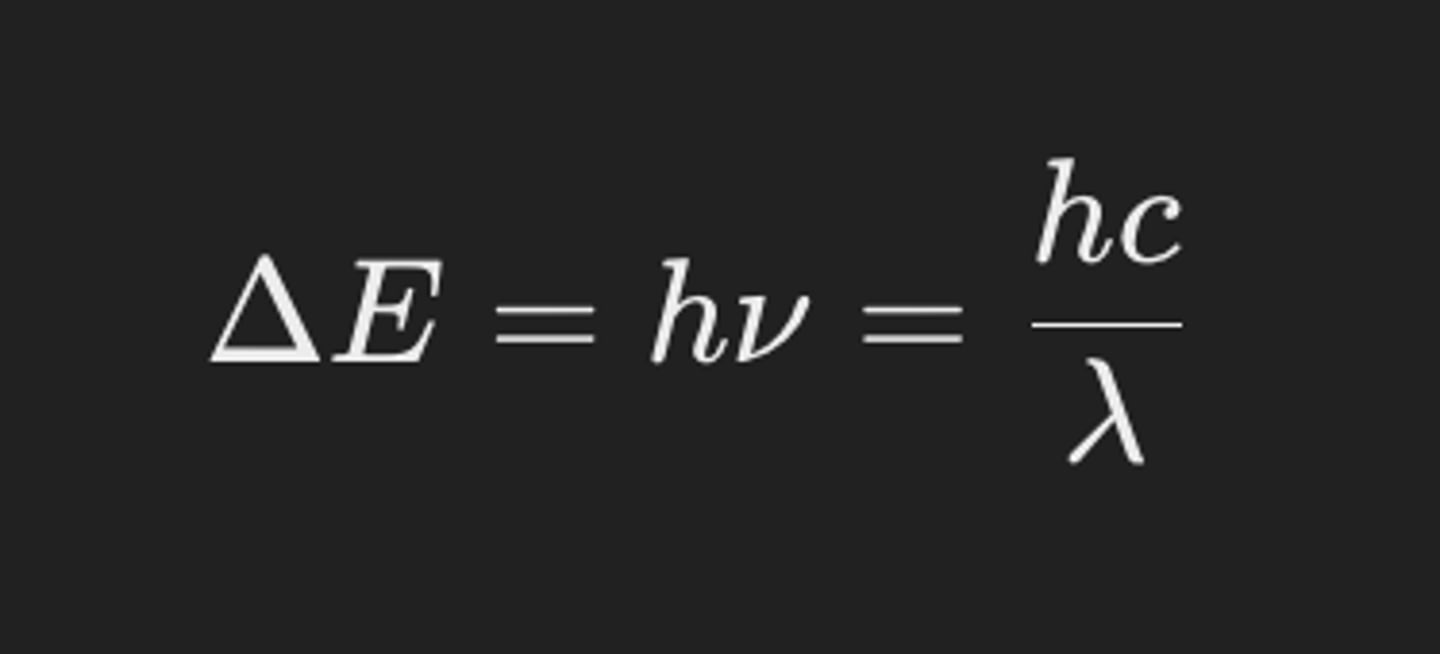
What is the unit of energy gap (ΔE) between d orbitals? (1)
Joules (J)
What is the unit of Planck's constant (h)? (1)
Joule seconds (Js)