Cog Neuro Lec 3 - Design Experiments: Part 1
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Different Brain imaging and equipment used to study structure and function of the brain
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
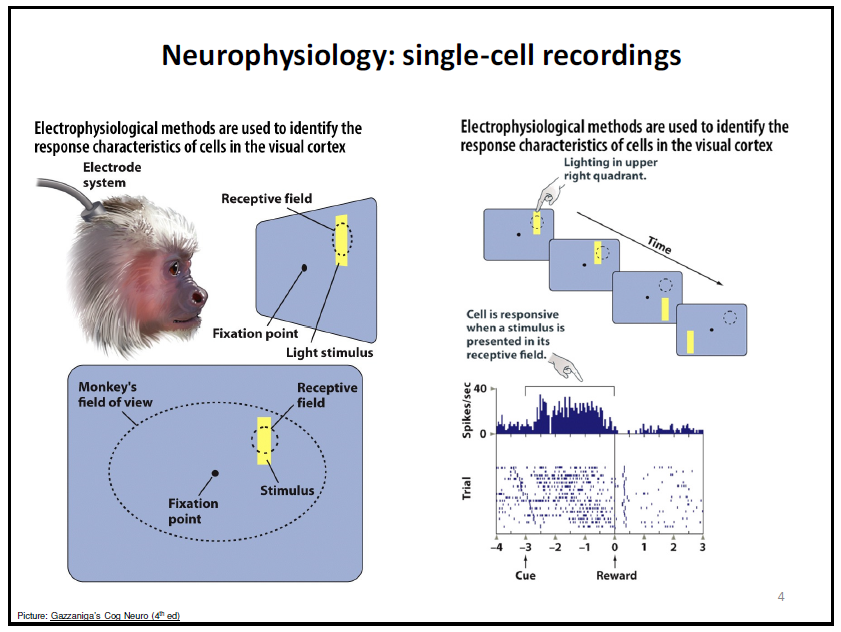
what is single-cell recordings for neurophysiology?
electrophysiological methods are used to identify the response characteristic of the cells in the visual cortex.
basically sticking in an electrode system to see what individual neurons are responding to
visual cortex example
what is lesion studies?
seeing the effects on an animals after damage to part of the brain
parietal lobe → reaching behaviour
good to know reaching and action behaviour but not for language
what is a limitation of single-cell recordings
very specific but we don’t see what else the brain is doing at the same time, higher level cognition
what is a limitation of legion studies?
we cannot see the effects of language in the brain through animals
cognitive neuroimaging
used for identifying pathophysiology and localizing anatomical and/or function disruptions (medical)
examining health/impaired brain topography (structure) and examining healthy/altered brain functioning (research)
what is computerized axial tomography (CT)?
pass radiation through the body and measuring how the body absorbs the radiation
3D image of the body
limitation of CT?
a lot of radiation
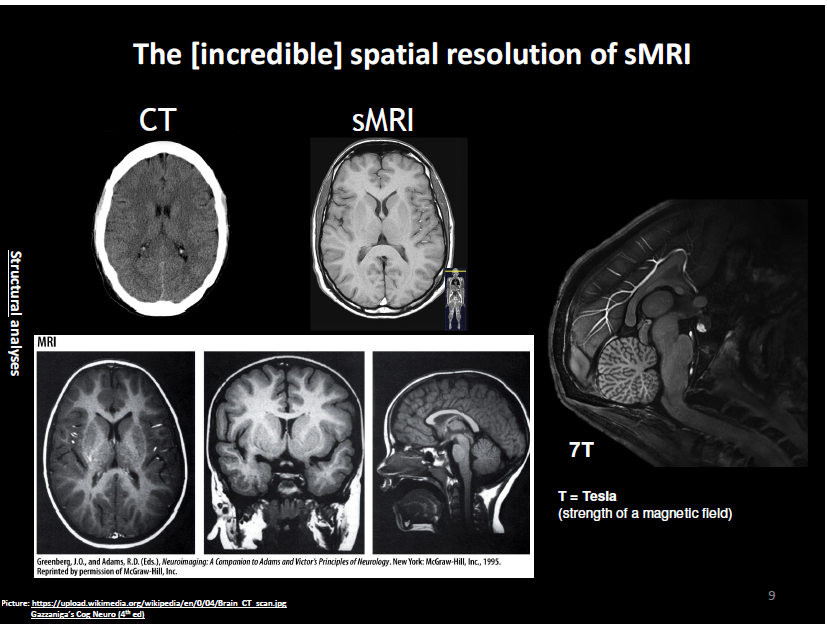
what is a structural magnetic resonance imaging (sMRI)
shows the structure of the body
why is this useful?
when atoms are in solid like bone, they don’t go very far (low measure of resonance) but in fluid, they will go farther
incredibly detailed and shows every single level of the brain in every single cut
What is the process of sMRIs?
Process:
uses a really strong magnetic field to change the position of protons and put all the H atoms into alignment
once the atoms are aligned, we knock them out of alignment by releasing a pulse
the knocking out of alignment causes the atoms to release a signal/energy from excited energy state (called resonance
come back into alignment and measure how far they get knocked out of alignment or how long it takes them to line back up
which one is clearer and more defined?
why would you not get an MRI
ppl with braces bc it distorts the image
back in the day knee screws or tattoos had iron that would be pulled by the magnet (no longer)
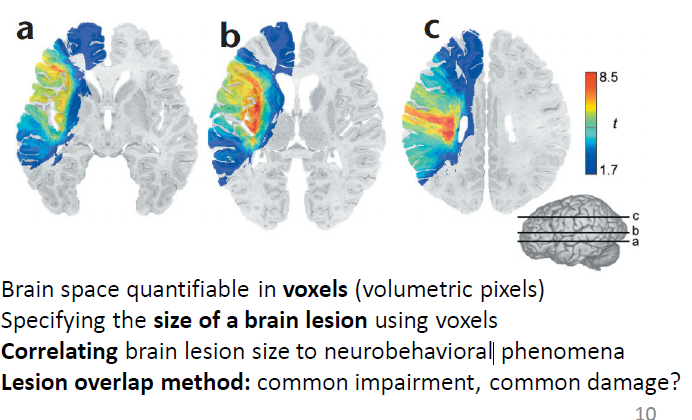
what is in volxel?
how brain space is quantified (volumetric pixels)
measuring depth
what happens when someone has a brain injury and the brain matter dies?
it gets filled with CSF
the bigger your hippocampus, the ____ your likelihood to get ptsd
lower (through correlation)
lesion overlap method
common impairment, common damage?
create a heat map and overlap all the brain images to see if there is an overlap in where the legion is and the damage is
can show where multiple places may be impacted and find the common one to see the core cause
the brain is measured in ____
voxels
what is diffusion tensor imaging (DTI)
looking at the diffusion of water in the brain because water moves in the same way as axons
therefore seeing the path that water readily moves in on direction vs another in the brain shows the path of axons
what can you use DTI for?
seeing the effect of axons due to damage
seeing how axons develop from childhood
why do they shake you up in the MRI scanner for DTI imaging?
to maximize diffusion
what is electroencephalography EEG
measuring electrical signals on the head
each electrode creates a recording channel
more electrodes, more recording channels
what is the difference between temporal resolution and spatial resolution?
temporal: telling you exactly when things are happening (time)
spatial: knowing were the signals are coming from in space (space)
are EEGs better for temporal resolution or spatial resolution
temporal
what is the purpose of EEGs
to tell you exactly what is happening in your head at the exact time
what are event-related potentials (ERP) from EEG data
averaged set of EEG signals to infer mental processes associated with that activity
Crucial importance of many trials, trial averaging
eliminates noise in the brain/third variables
what is the N400 wave for? (EEG)
understands semantic mistakes in speech
what are one of the limitations of EEG
skull, spatial resolution
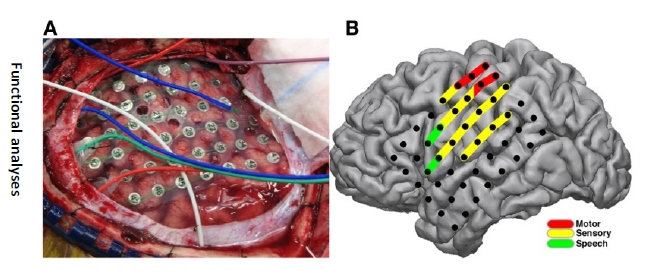
what is Electrocorticography (ECoG)?
EEG directly on the brain
what is Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI)?
watching the blood flow in the brain to see brain activity (Neurovascular coupling)
hemoglobin magnetic properties differ whether oxygenated or deoxygenated
what is the BOLD signal in fMRI?
Blood Oxygenation Level Dependent
high BOLD signal: active
low BOLD signal: inactive
visualizing activators and deactivators
activators: areas of the brain using the blood
deactivators: areas of the brain not using the blood
does fMRI have better spatial or temporal resolution
spatial
why is not having good temporal resolution such a problem for fMRI?
you only get to see what area of the brain is using the blood after 6 seconds and only get to see what happens after 1 second of scanning
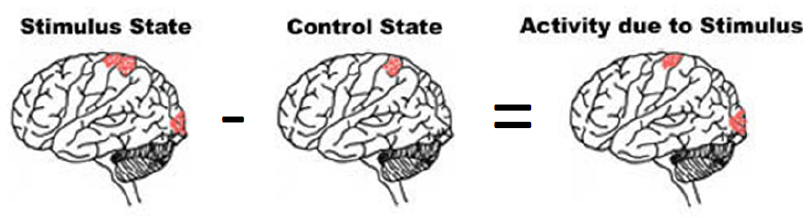
Subtraction Method
stimulus state - control state = activity due to stimulus
ex. to isolate colour, show image of house with colour, scan, and then again without colour and scan again. See which areas are involved in just colour
what’s a limit of studying lesions in the brain
often times the lesions are large therefore not specific to where it can be cause of certain loss of ability
What is Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
stimulating brain dysfunction
Does TMS have good spatial or temporal resolution
both
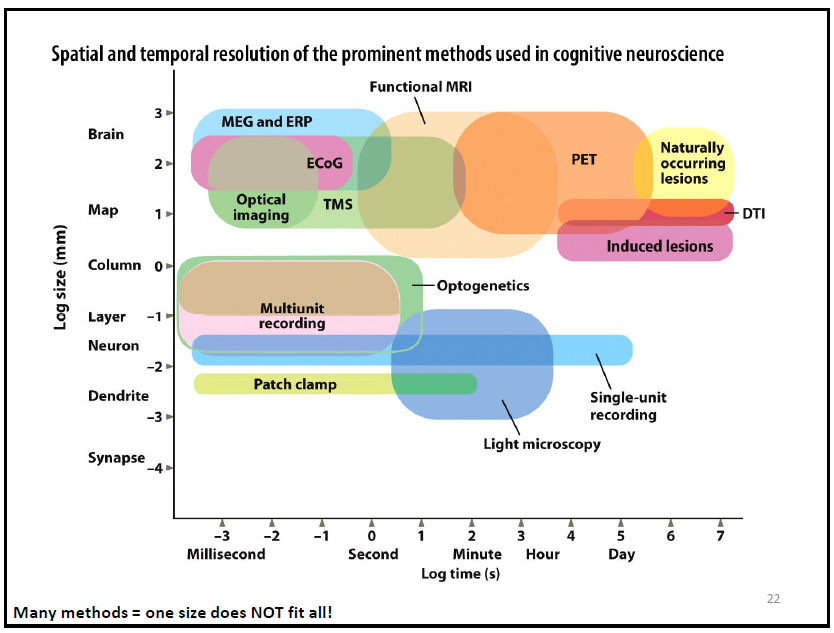
study this slide
what are the fundamentals of experimental design?
why is this process of interest
provide a clear conceptual definition (ie. what is working memory)
operational definition (ie. how working memory will be measured in my study)