Med Surg II Exam 3 - CV Assessments, Aneurysms, HF, MI
1/169
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
170 Terms
COLDSPA
How do you assess chest pain?
character, onset, location, duration, severity, pattern, associated factors
What does COLDSPA stand for?
decreased BP, cool clammy skin, decreased LOC, dizziness, fatigue, anxiety, SOB, diaphoresis, decreased UO, chest pain, cyanosis
What are signs of decreased CO?
electrolytes, creatinine and BUN, CBC, lipid profile, cardiac biomarkers, CRP
What labs might be drawn when a patient comes in with chest pain?
<200
What is a normal total cholesterol level?
>40 (good cholesterol)
What is a normal HDL level?
<100 ("lousy" = bad)
What is a normal LDL level?
<150
What is a normal triglyceride level?
troponin, BNP
What are examples of cardiac biomarkers?
rise in 4-6 hours after infarction and peak at 24 hours (need to keep patients for at least 23 hours to monitor levels)
What is important to know about troponin levels?
BNP
released into the bloodstream when the heart is working harder than normal to pump blood
released with ventricular stretching
>100
What BNP level indicates heart failure?
indicates inflammation or infection in cardiac tissue such as inflammation of coronary artery plaques
higher values mean patients are at greater risk for an acute coronary event
What does an elevated c-reactive protein (CRP) indicate?
transthoracic, transesophageal, stress echo
What are the different types of echocardiograms?
transthoracic echocardiogram (best to lay patient in left lateral position)
An echocardiogram acquired through the chest
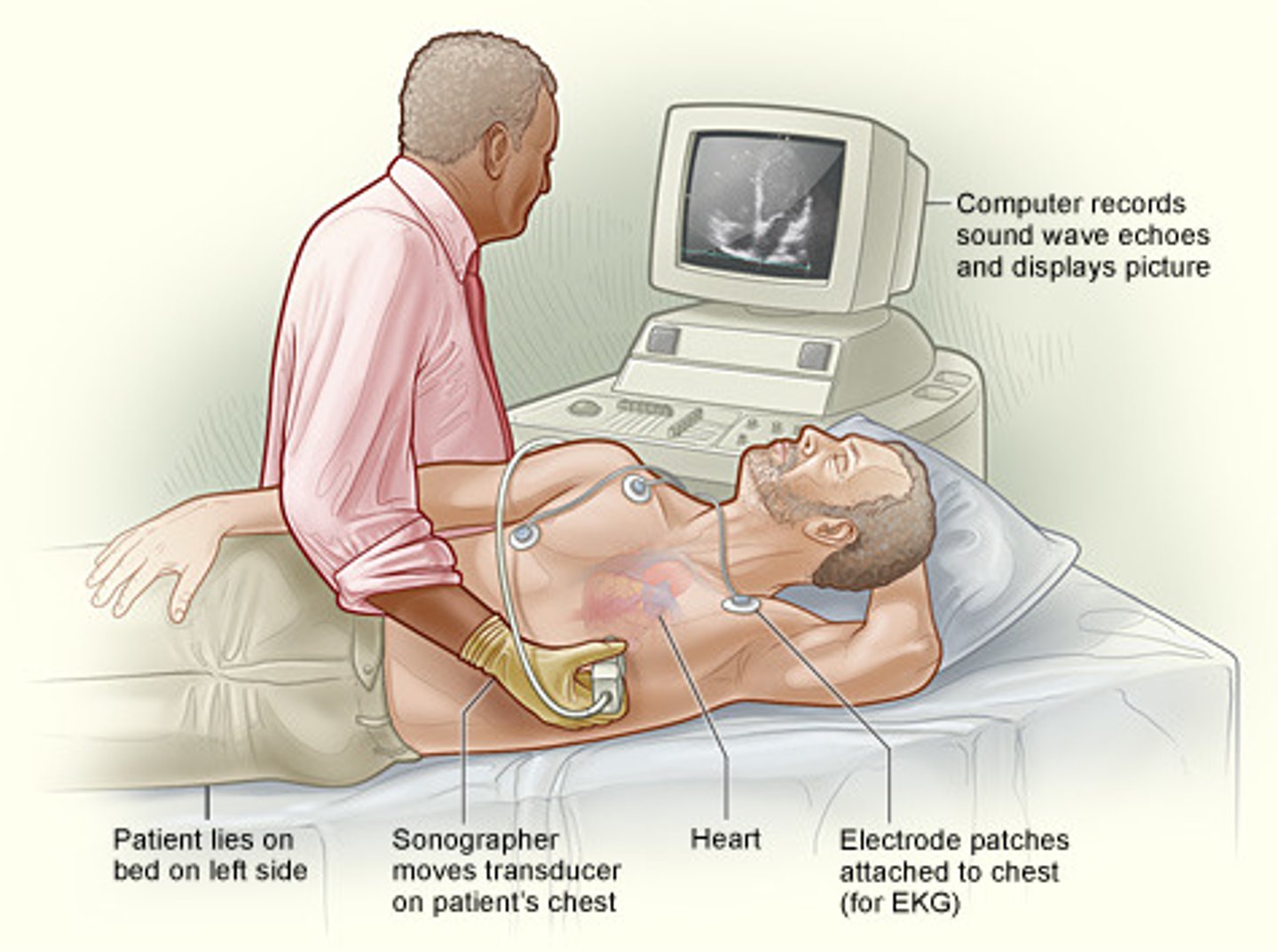
transesophageal echocardiogram
ultrasound test that examines cardiac function and structure by using an ultrasound probe placed in the esophagus, which provides views of the heart structures
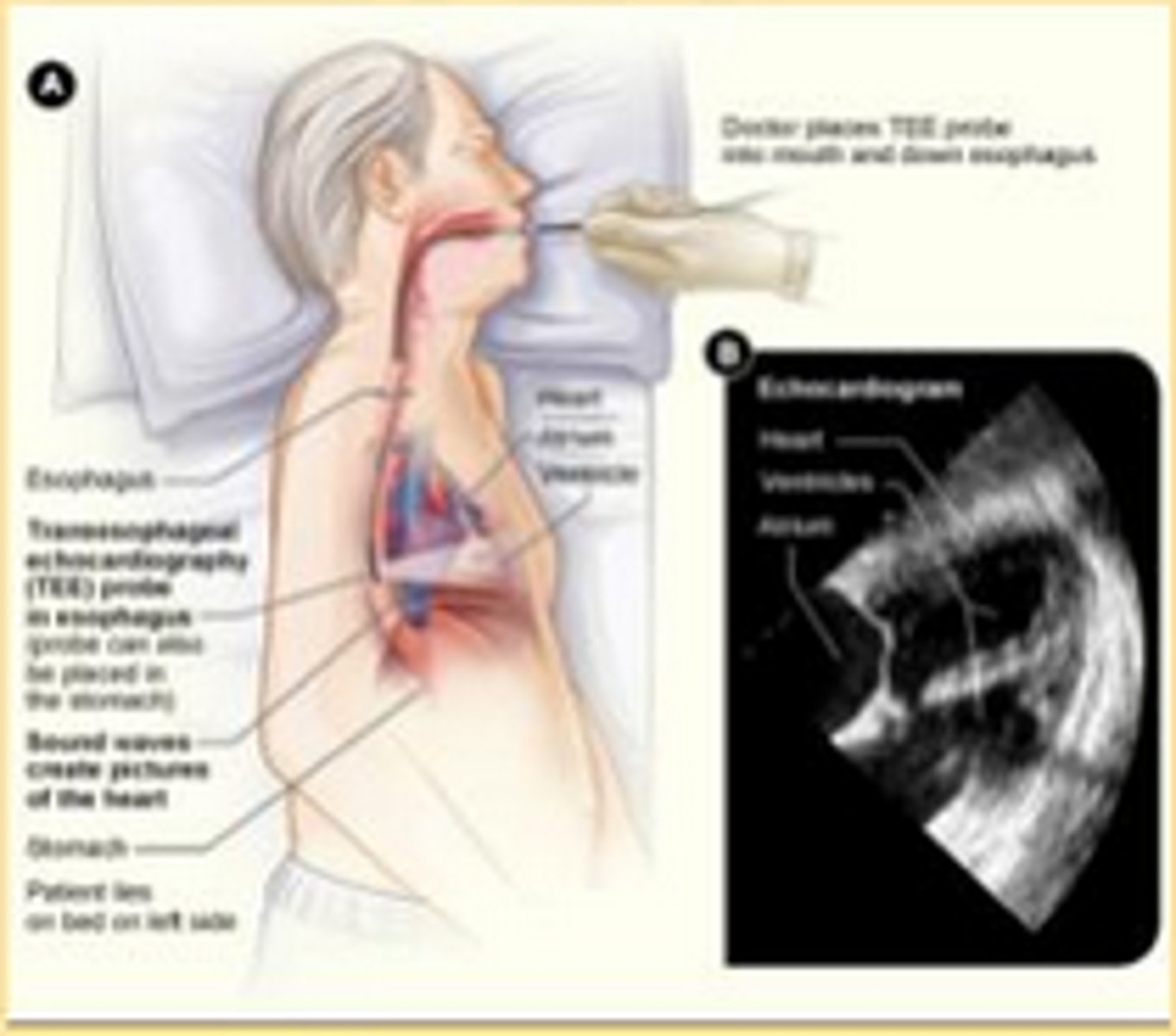
stress echocardiogram
an echocardiogram of the heart recorded during the induction of controlled physical exercise via treadmill or bicycle or administration of a pharmaceutical agent that produces the effect of exercise stress in patients unable to ambulate -- useful in detecting conditions such as ischemia and infarction
electrophysiological study
specialized cardiac cath procedure to identify conduction system paths and dysrhythmias
electrodes on the end of the catheter to record electrical activity
an ECG from the inside
50-70%
What is a normal ejection fraction?
cardiac ablation
procedure in which a catheter is inserted through a vein in the groin and threaded to the heart to correct structural problems in the heart that cause an arrhythmia
cardiac nuclear scanning with stress test
A cardiac nuclear scan with stress test is an imaging procedure that uses a radioactive substance to show how well blood flows through the heart muscle
thallium, Tc-sestamibi, Tc-myoview
What types of radioactive tracers are used during cardiac nuclear scanning with stress tests?
NPO 4-6 hours before test, hold beta blockers, no caffeine before the test
What are some important teaching points about cardiac nuclear scanning with stress test?
cardiac PET scan stress test
A radioactive tracer is injected into a vein, and a PET scanner detects the radiation energy released by the tracer. The scanner creates 3D computer images of the heart.
N13-ammonia
What kind of tracer is used for cardiac PET scan stress test?
PET
Which scan is shorter, cardiac PET scan stress test or cardiac nuclear scanning with stress test?
70-110
What is a normal MAP?
2-8
What is normal CVP or RAP?
20-30/8-15
What is normal PAP?
8-12
What is a normal PAOP?
60-80%
What is a normal SvO2?
4-8
What is normal CO?
2.5-4
What is normal CI?
800-1200
What is a normal SVR?
<250
What is a normal PVR?
60-100
What is a normal SV?
intima, tunica media, tunica adventicia
What are the three layers of the aorta?
aorta
What is the largest artery in the body?
aneurysm
a localized dilation of a blood vessel
heredity, hypertension, smoking, trauma, syphilis, infection, high cholesterol, gender (male), age, congenital (Marfan's Syndrome), connective tissue disease
What are risk factors for aneurysms?
true aneurysm
weakening of all 3 layers and complete stretching of the vessel wall
outpouching around the entire circumference of the aorta
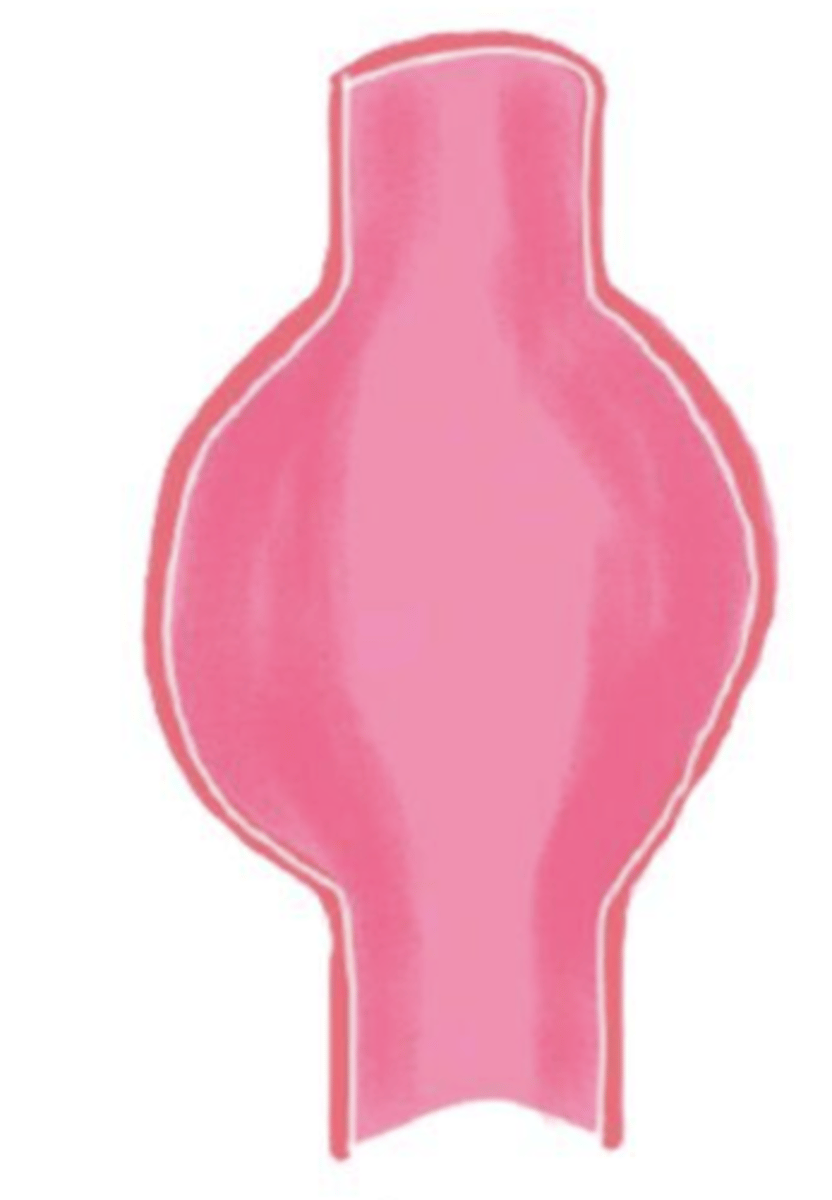
false aneurysm
break through all layers and surrounding tissue forms a false wall with a clot
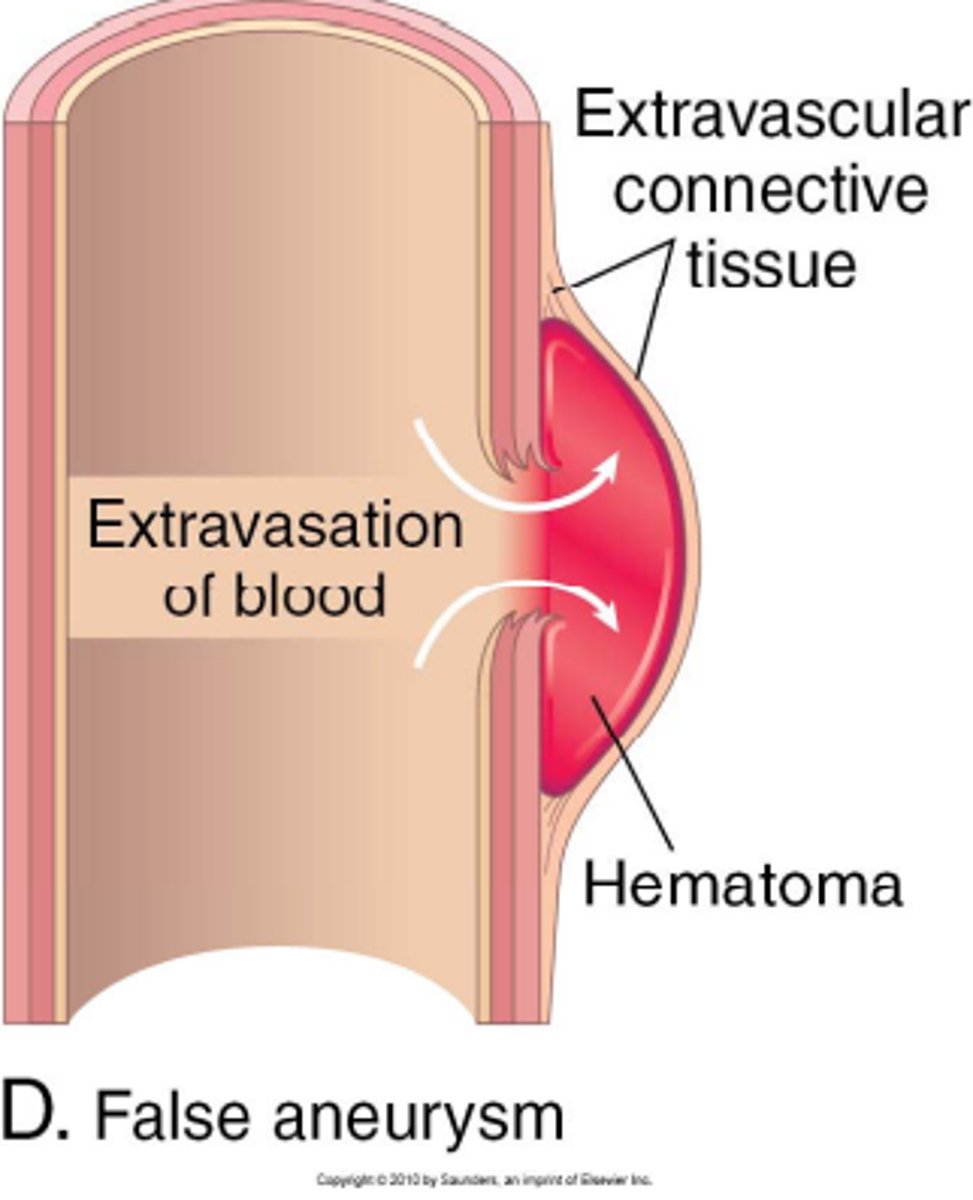
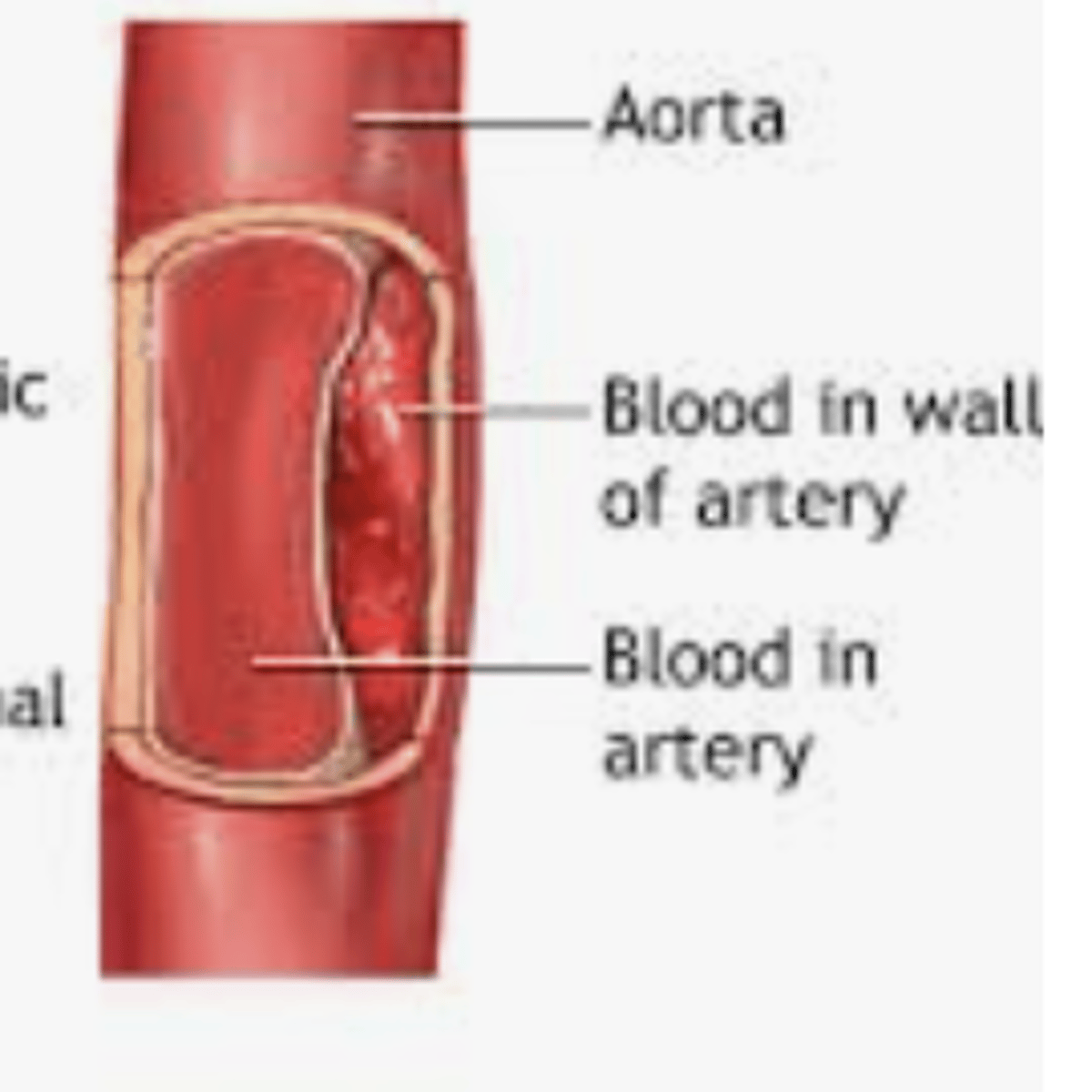
dissecting aneurysm
A condition in which the inner layers of an artery allowing blood (at high pressures) to flow between the layers.
severe ripping or tearing pain (can be abrupt and shuts off blood to distal circulation - SURGICAL EMERGENCY)
What is the classic sign of dissection of an aneurysm?
thoracic, abdominal, peripheral
Where are locations where aneurysms can occur?
tracheal deviation, tracheal tug, chest pain (deep and dull)
What are symptoms of thoracic aneurysms?
difficulty swallowing, difficulty speaking, chest pain, SOB, N/V, aortic murmur
What are symptoms of ascending thoracic aneurysms?
difference in brachial BP >20, pulse deficit from side to side, mimics stroke (hoarseness, cough dysphagia, cerebral ischemia)
What are symptoms of transverse thoracic aneurysms?
back pain, spinal stroke symptoms
What are symptoms of descending thoracic aneurysms?
abdominal
Where is the most common location for an aortic aneurysm?
abdominal pain and tenderness, abdominal bruit, wide abdominal pulsations, pain (abdomen, back, or pelvic), ankle-brachial index abnormalities, weak pedal pulses, lower leg ischemia
What are symptoms of an abdominal aneurysm?
avoid palpation once diagnosed
What is an important nursing action if a patient has an abdominal aortic aneurysm?
6 ps (pain, pallor, paraesthesia, poikilothermia, paralysis, pulselessness)
What are symptoms of a peripheral aneurysm?
Ankle SBP / Brachial SBP
How do you calculate Ankle Brachial Index (ABI)?
<0.5 = severe occlusion
0.5-0.8 = moderate occlusion
0.8-1 = mild occlusion
1-1.2 = normal
What do ABI values mean?
every 6 months (they grow fast >0.5 cm/year)
How often should patients with aneurysms have ultrasounds?
>/= 5 cm, grows >0.5 cm in a year, patient is symptomatic
When is surgery indicated for aneurysms?
abdominal surgical approach for aneurysm
patient is not placed on bypass during the procedure to fix the aneurysm
the aorta is cross-clamped (causes all flow to distal areas to stop - need to assess for signs of ischemia and organ damage post-op)
graft is placed and vessel is sewn around the graft
endovascular surgical approach for aneurysm
a minimally invasive procedure that treats aneurysms by placing a stent or coil inside the aneurysm or blood vessel
leaking of the graft site, rupture of aneurysm (EMERGENCY), dissection, organ ischemia, sexual dysfunction, arterial emboli from thrombi on graft (trash foot)
What are the complications of aneurysm repair?
trash foot
A condition resulting from occlusion of the small arteries of the foot by atherosclerotic debris
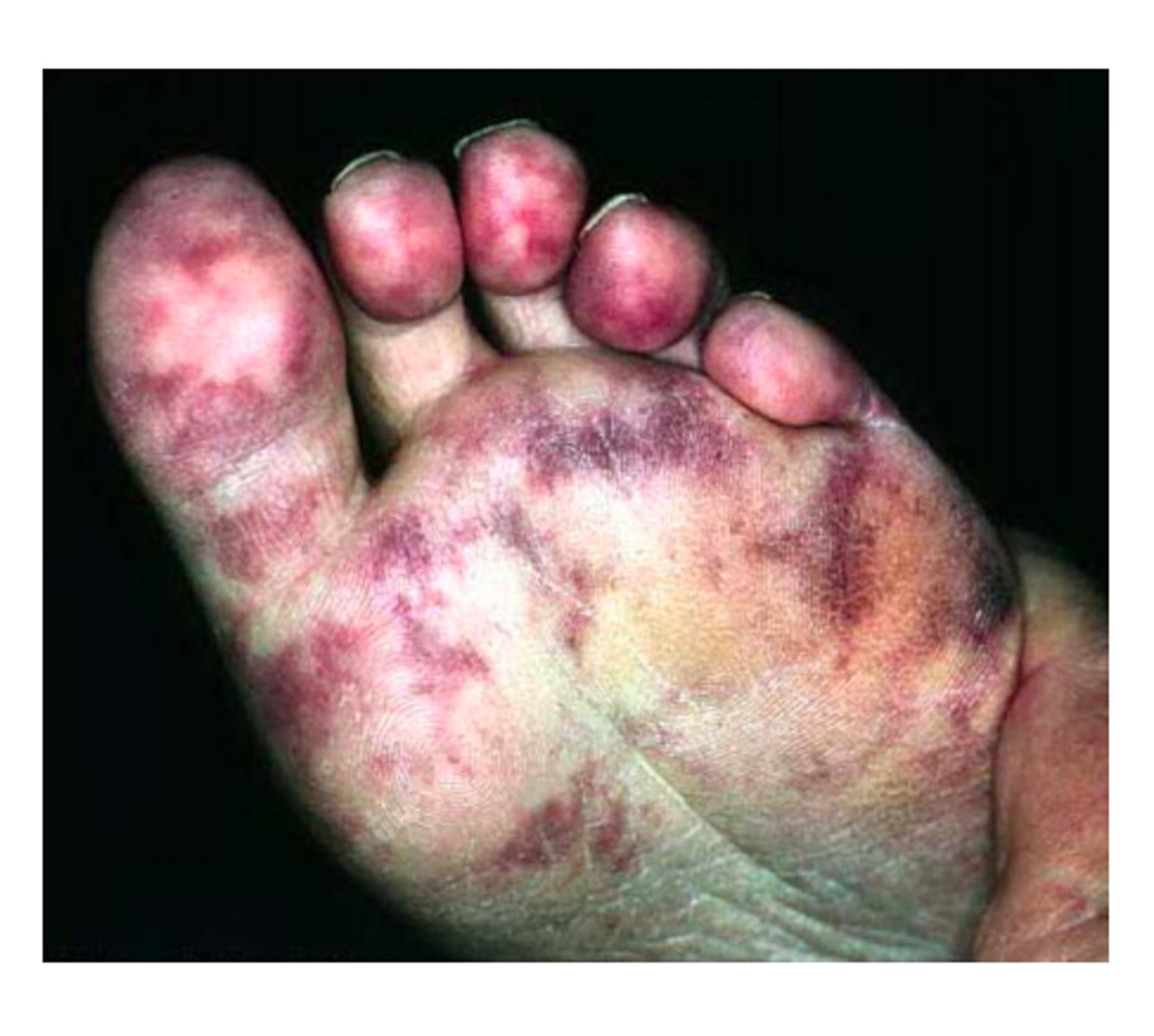
mark peripheral pulses, watch renal function, perform neuro status checks, monitor H&H, control BP
What is pre-operative care needed for patients who are going to have an aneurysm repair?
watch for s&s of bleeding, monitor H&H, monitor UO, monitor BP, 6 Ps, wound care, pulmonary toileting, pain management, hydration, infection, monitor for trash foot
What is post-operative care needed for patients who are going to have an aneurysm repair?
heart failure
heart can't pump enough blood to meet the body's needs
CAD, MI, ischemia, cardiomyopathies, valve disease, congenital defects
What are some causes of HF related to impaired cardiac function?
HTN, pulm HTN, fluid overload, anemia, thyrotoxicosis
What are some causes of HF related to excess work damands?
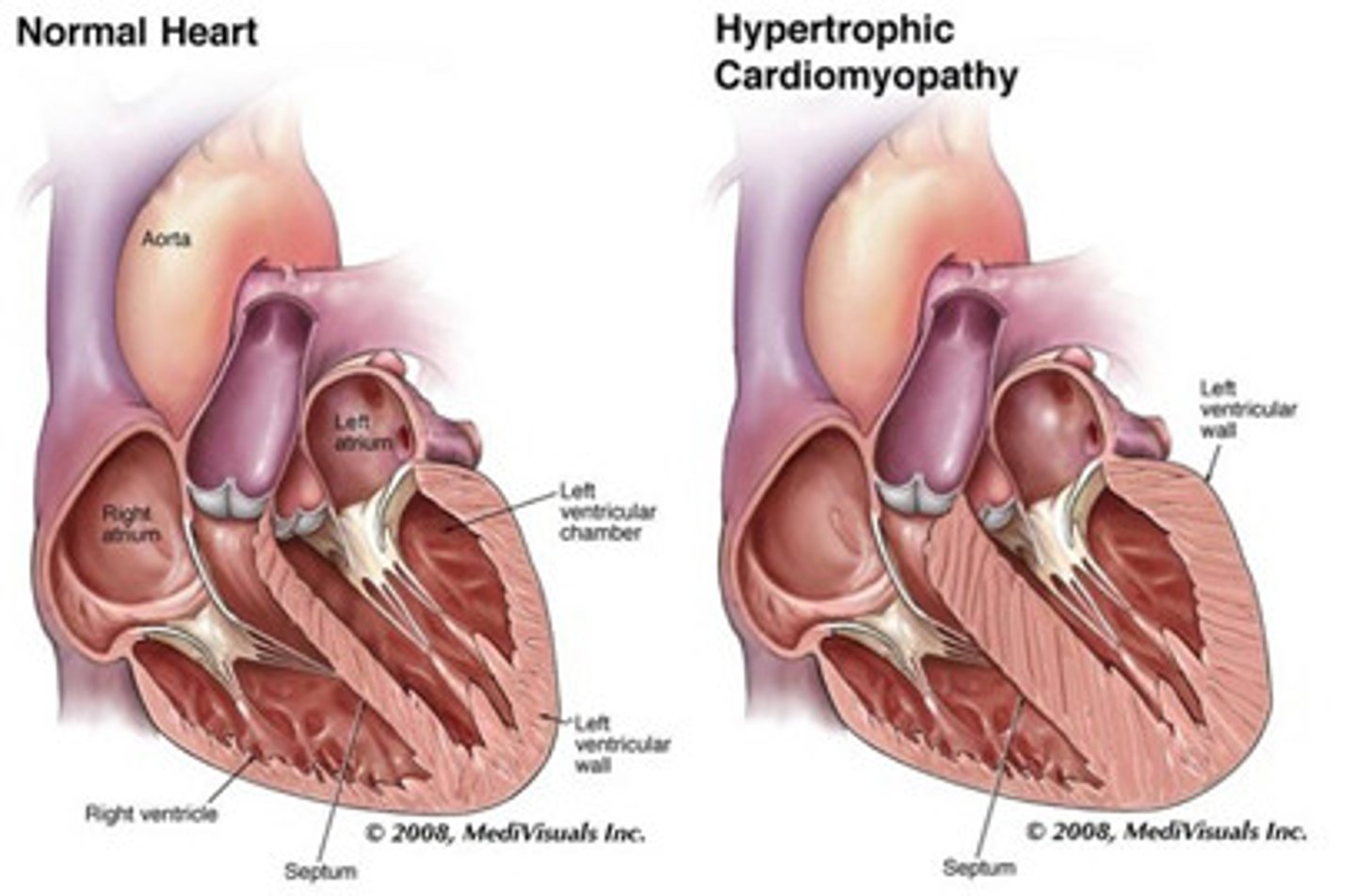
myocardial hypertrophy
enlargement of the cardiac muscle due to increased work
myocardial dilation
Myocardium stretches and becomes thinner and less elastic
Results from increased preload
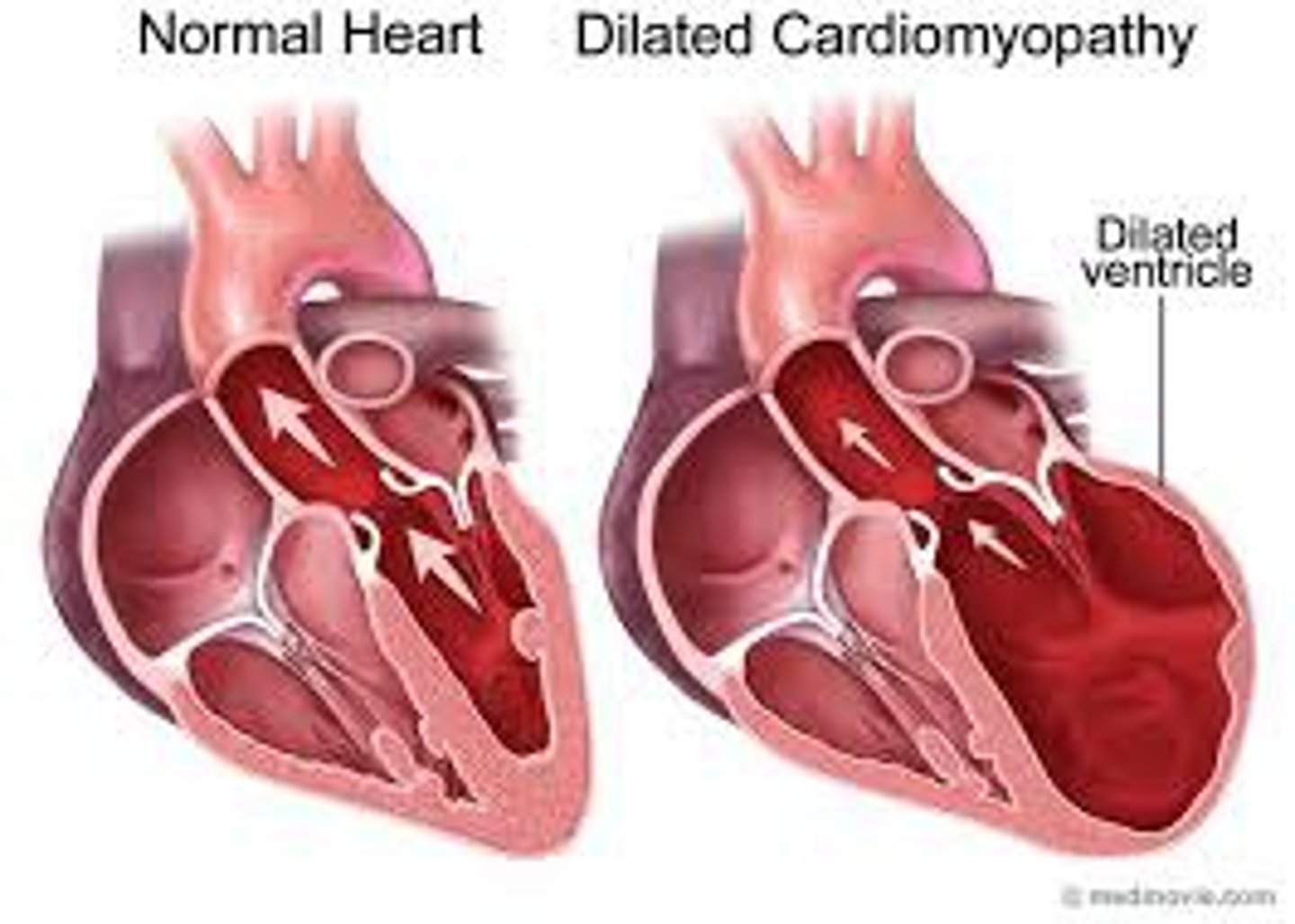
heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF)
a type of heart failure that occurs when the left ventricle of the heart is too weak to pump enough blood to the body (reduced contractility)
ejection fraction <40%
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF)
a type of heart failure where the heart's left ventricle still contracts normally (preserving its ejection fraction), but the heart muscle becomes stiff and less compliant. As a result, the heart has difficulty filling with enough blood during the relaxation phase (diastole)
ejection fraction is normal, but output is decreased because heart can't fill with enough blood
HFpEF
Which type of HF has a worse prognosis?
BODY (JVD, edema, ascites, increased CVP)
Where does fluid back up in right-sided heart failure?
LUNGS (crackles, decreased SpO2, increased RR and PAP, pulmonary edema, orthopnea)
Where does fluid back up in left-sided heart failure?
left and right ventricular MI or severe left-sided failure that was left untreated
What are causes of biventricular HF?
>2lbs/day or >5lbs/week
What is a concerning amount of weight gain for a heart failure patient?
renal failure (decreased UO)
What is an early sign of HF?
reduce ventricular remodeling, improve tissue perfusion, improve quality of life, reduce mortality and complications
What are the goals of HF management?
decrease fluid overload
Why are diuretics used for HF patients?
replenish volume if over-diuresis or dehydration
Why are IV fluids used for HF patients?
increase contractility and decrease O2 demands
Why are inotropes used for HF patients?
dopamine
Which inotrope is typically used for HF?
reduces oxygen demand and decreases anxiety
also vasodilates and reduces preload
Why is morphine used for HF patients?
increase contractility and decrease SVR (also increase HR and O2 demand of the heart)
Why are inodilators used for HF patients?
milrinone, amrinone
What are examples of inodilators used in HF patients?
reduces preload
Why is NTG used for HF patients?
decreases preload and afterload
Why is nitroprusside used for HF patients?
vasodilation, promotes natriuresis (sodium excretion), increases diuresis
Why are ARNIs used for HF patients?
decreases afterload, increase CO, reduces workload of the heart
Why are ACE inhibitors used for HF patients?
decrease afterload
Why are ARBs used for HF patients?
reduces contractility (reduces oxygen consumption of heart by decreasing the workload)
Why are beta-blockers used for HF patients?
biventricular pacing, internal cardiac defibrillator
What are examples of devices to treat HF?
replace valves, correct defects, partial ventriculostomy, heart transplant
What are surgical interventions for HF?
intraaortic balloon pump (IABP)
A mechanical assist device that consists of an inflatable balloon pump inserted through the femoral artery into the thoracic aorta. It inflates during diastole to improve coronary circulation and deflates before systole to allow blood ejection from the heart
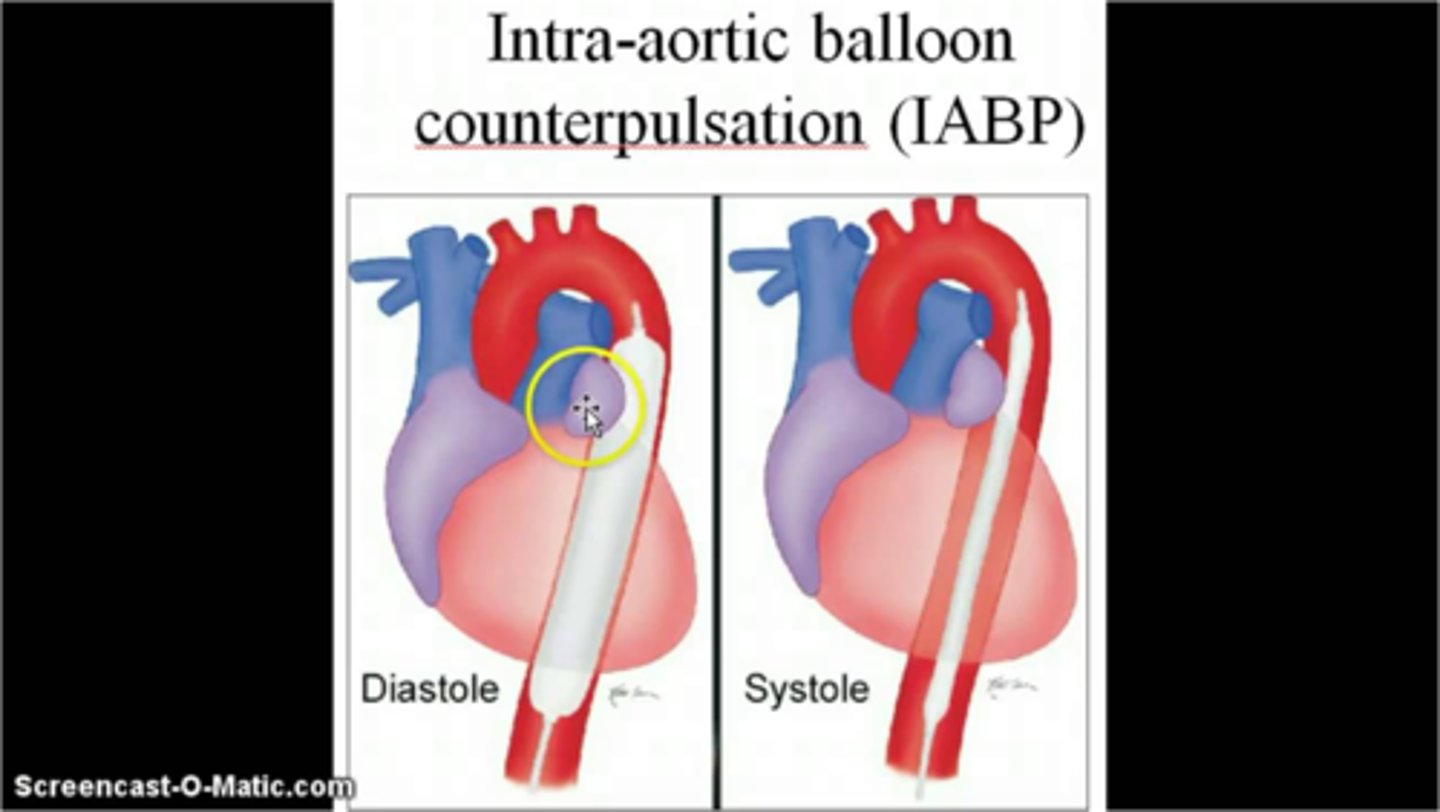
increased coronary perfusion and oxygen supply to the myocardium, decreased cardiac workload by decreasing afterload, increased contractility and increase CO by 8-10%
What are the desired outcomes of a IABP?
cardiogenic shock, bridge to transplant (to buy time), treat HF and MI
What are the uses a an IABP?
timing (must align with systole and diastole)
What is a critical component of IABP?
ischemia in leg the balloon pump is inserted in, bleeding at femoral artery insertion site, infection, decreased CO from improper synchronization, balloon rupture, balloon moving toward heart or backward
What are complication of an IABP?
gradually reduce assist ratio (1:1 -> 1:2 -> 1:3, etc) q4-6h while monitoring hemodynamic
How do you wean a patient off of an IABP?
ventricular assist device (VAD)
a mechanical pump used to support heart function and blood flow in patients with severe heart failure
left ventricular assist device (LVAD)
a type of mechanical pump designed to assist the heart's left ventricle in pumping blood to the rest of the body