A Level CIE Business: Human Resource Management
1/185
Earn XP
Description and Tags
304 up to 330
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
186 Terms
why is structure needed (2)
to know who does which job
to know who’s responsible for which decisions
what does structure allow (2)
division of tasks and responsibilities made clear to all
workers understand which manager they’re responsible to
functional structure
Departments are organised by specialist areas such as marketing, finance, human resources, or operations.
what does organisational structure indicate: (7)
who has overall responsibility for decision making
formal relationships between different people and departments
position of each individual in business and who their line manager is
way in which accountability and authority may be passed down the organisation
number of subordinates reporting to each more senior manager
formal channels of communication, both vertical and horizontal
identity of the supervisor or manager to whom each worker is accountable
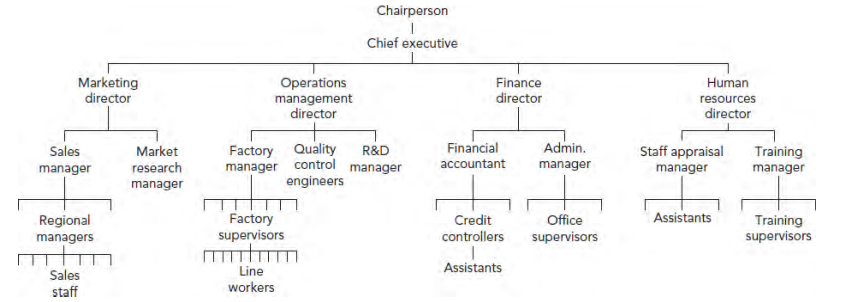
what does an organisation consist of
any number of individuals who work together to achieve the mission of the orgnaisation. each fills a certain role within the structure and does tasks to achieve objs set by management. each has specific role w/ certain amt of accountability to do tasks
how is internal structure designed
to help achieve its objectives so when objs change, structure may need to
why must structure change as a result of a more competitve market
needs quicker-acting more flexible structure
why must structure change as a business grows and develops
adapt and reduce pressure on entrepreneur/owner at the center if a small bus uses entrepreneurial structure
when grows, may need manager or supervisor because time consuming even if delegation used
if expansion achieved e.g. new areas then more ppl needed e.g. regional director
must be fliexble to meet changing needs
why might bus structure need to change
new competitors enter indsutry
growth and dev business
business objs change
intrapreneurship encouraged
why might bus structure change if bus objs change
e.g. obj = increase sales ino ther countries then must make regional mkting dept
e.g. obj = innovation then bus must have r&d dept
why might bus struc change if intrapreneurship encouraged
intrapreneurship = comp advantage, bureaucratic = poor innovation and inflexible as focused on top-down communication and don’t encourage teamworking betw depts so must encourage intrapreneurs
intrapreneurial teams or task forces from diff deps and divs created to help stimulate new ideas not focused on one dept
high levels of delegation and trust must be shown, w/ minimum direct management control on day to day basis
flexibility of team membership important. team should be able to call on specialist for short or long period to help w its project
3 most widely adopted types of organisational structure
functional
hierarchal
matrix
functional manager
A senior employee with authority over a complete organisational unit, leads departments.
3 advs of functoinal structure
employees display high level of departmental loyalty and pride in work of their dept
encourages employees to become specialists which can increase efficiency and productivity
depts led by managers who are specialists in functional area
4 disadv of functional structure
structure is vertical one and often doesnt allow for good connections betw depts
coordination betw depts is therefore difficult e.g. when developing new major project
communication flows thru department heads to top management, so employees may feel remote from senior management
might be competition betw depts which may not benefit whole organisation e.g. comp for financial resources is based on getting the most for the department and not necessarily considering what is best for bus as a whole
hierarchical structure
A structure with multiple levels, where all members except one are subordinate to someone else.
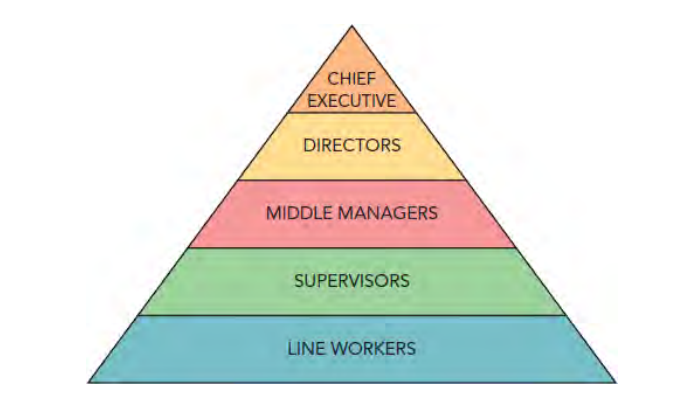
main features of hierarchical structure:
levels of hierarchy
chain of command
spans of control
levels of hierarchy
A stage in the organisational structure where all personnel share equal status and authority.
each level in hierarchy represents grade or rank of staff.
lower levels are subordinate to superiors on higher lvl
greater no. levels = greater no. diff grades or ranks in org
narrow or tall org has many levels
flat has few levels but wider spans of control
chain of commmand
a hierarchy of authority where those at the top of the organization direct and control the activities of the organizational members below them
taller org struc = longer chain of command = slower comms
3 main problems with tall/narrow having many lvls of hierarchy:
comms thru org slow, w messages becoming distorted or filtered in some way
spans of control likely to be anrrow as clear relationshisp between no. lvls in hierarchy and avg span of ctrl
those on lower lvls can feel remote from decision making power at the top
spans of control
The number of subordinates directly accountable to a manager.
can be wide w/ managers for many subordinates or narrow w/ manager direct respons for few subordinates
4 beenfits of flat org structure w/ wide spans of control
each worker delegated more authority as less direct control from manager who is respnosible for many other employees
employee empowerment can be an important motivational force
short chain of command results in better comms: clear link betw no. hierarchy lvls and spans of ctrl
few lvls of hierarchy so fewer middle managers needed, reducing bus costs, increasing avg size of each span fo ctrl helping to demonstrate clear link betw no. levels of hierarchy and spans of ctrl
advs of hierarchal structure
decision making power starts at top but may be passed dow to lower levels
role of each individual clear and well defined
clearly identifiable chain of command
most frequently used in role cultures where role determines position in hierachy
disadvs of hierarchical structure
indicates taht on way (top down) comms is standard practice, ineffective comm
no horizontal links betw depts or separate divisions = lack of coordination
managers accused of having narrow vision as don’t look at problems in other way than thru dept experience
inflexible and often = change to resistance as managers tend to defend their position in hierarchy and dept importance
divisional organisatoinal structure
Organises business activities around geographical areas or product groups. Each self contained, have own mkting, production and research teams and senior manager reports to head of product type. strategic decisoin making and finance still centralised
structure by product or geographical area
vert divisions in hierarchy do not have to be based in functional depts can be region, country or product category = divisional organisation structure
3 ways product structure and geog area structure can help bus
focus on specific market segments
repsond to consumer needs and market changes more quickly
measure performance and profitability of each division separately
3 potential disadvs of product structure and geog area structure:
duplication of roles e.g. each div has own sales team
rivalries between divisions might develop as they each focus on divisional objs
loss of overall central control over each div
delayering
Removing one or more levels of hierarchy from the organisational structure.
why does delayering happen
narrow hierarchical structures often have commm adn employee motivation issues so managers need to create shorter structures.
4 advs of delayering
delayering reduces bus costs
shortens chain of cmd and should improve comm thru org
increases span of ctrl and opps for delegation
can increase workforce motivation bdc less remoteness from top management and greater chance of having more responsible work to perform
3 disadvs of delayering
could be one-off costs of making managers redundant (e.g. redundancy payments)
managers who remain have more workloads = overwork and stress
fear that redundancies might be used to cut costs could reduce sense of security of whole workforce (maslow)
matrix structure
An organisational structure that creates project teams cutting across traditional functional departments. has team of specialists w/ obj of completing task or project instead of higlighting role or status of individuals. emphasis on individuals contirbution ability rather than position
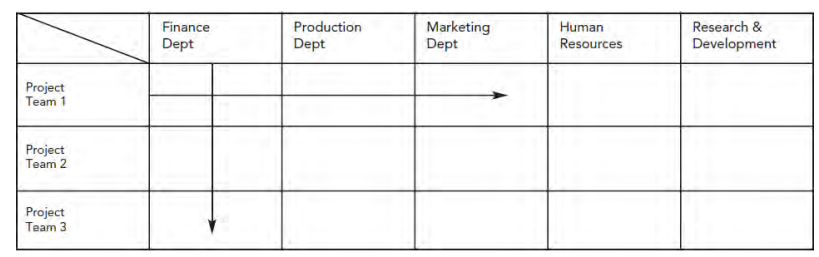
what did peters suggest that
organisatoins need flexi structures that remove as much bureaucracy as possible by getting rid of as many rigid rules and regulations as possible
use of project teams should lead to more innovative and creative ideas as employees will be more motivated to contribute
5 matrix structure advs
allows good comms betw all membs of team
cuts across traditional boundaries betw depts in hierarchy
less chance of people focusing on just what is good for their dept as the aim is to foucs on project and bus as a whole
crossover ideas betw people w specialist knowledge in diff areas tends to create more successful and innovative solutions
new project teams can be created quickly so this system is well-designed to respond to changing markets or technological innovations
4 disadvs of matrix structure
less direct control from senior managers as the teams may be empowered to undertake and complete project
passing down authority to more junior employees can be hard for some senior mgers to accept
reduced bureaucratic ctrl may be resisted by some senior mgers
team mbers may have 2 mgers to report to. if bus retains lvls of hierarchy for depts but allows cross-dept teams to be created, each team mber has 2 bosses and could cause conflict of interests.
delegation
Passing authority down the organisational hierarchy. wider span of control = more delegation
accountability
The responsibility to account for, explain, and disclose the results of one's work honestly. subordinates accountable to manager and can be held account and disciplined for inadequate performance
5 steps of accountability process
give clear expectations before employee starts job
make sure employee has appropriate skills providing training if necessary
establish 2 way comms to provide feedback on how employee is performing while doing job not just at end of task
agree a clear measurement of perf so that worker knows when theyll be assessed as having done a job well or poorly
consequences of good or poor perf need to be made clear to employee.
4 advs of delegation
gives senior managers more time to focus on strat roles
shows trust in subords = motivate and challenge them
develops and trains employees for more senior positions
helps employees achieve fulfillment thru work (self actualised)
3 disadvs of delegation
if task not well-defined or if inadequate training, than delegation is unlikely to succeed
delegation unsuccessful if insufficient authority (power) given to subord performing tasks
managers may only delegate boring jobs that they don’t want to do which wont be motivating
control
Measuring and supervising employee performance. fewer lvls of hierarchy = wider spans of control = more trust placed in each individual employee as there less direct supervision
authority
The power to give orders and make decisions. delegation gives authority to perform certain tasks. have power to undertake jobs and make decisions necessary for these jobs to be completed but overall responsibility remains w manager
auhtority, what does manager still do:
selects employee or delegatee to undertake task
allocates resources
arranges training
how is ultimate control over employees work achieved by:
setting and agreeing targets
regular appraisal
monitoring of performance against targets
control and trust
mgers dont like giving up control as feel less important and risky to give up control
conflict between showing trust in owrker and controlling workers efforts
effective delegation = slowly releasing management control in order to show more trust
trust allows worker to gain greater sense of achievement when work done well
delegation = empoewrment, allows them to show intiative and creativity, requires greater lvl of trust from managers as theres even less direct ctrl over work being carried
centralisation
Concentrating important decision-making powers within the head office or organisational centre (e.g. head office).
decentralisation
Distributing decision-making powers down the hierarchy to empower subordinates or area/product managers.
key differences between decen and cen
decen involves delegatton
cen insists on same procedures across business = uniforminty and consistency
head office exerts control over all operations
decen empowered employees and trust
centralised bus want to maintain exactly same image and product range maybe to save costs or retain carefully created bus identity in all markets
5 adv of cen
fixed set of rules nad procedures in all depts/divs of bus = rapid decision making as no opp for discussion
bus has consistent policies thru org preventing conflict between div and avoids consumer confusion
senior mgers take decisions in interest of whole bus not just one div of it
cen buying allows for greater eos
senior mgers at head office = experienced decision makers = reduced risk
4 adv of decen
more local decisions can be made that reflect diff conditions. mgers who take decision have local knowledge and likley to have closer contact with consumers
more junior mgers can develop their skills and this prepares them for more challenging roles
delegation and empowerment possible = good motivation
decisison making in response to changes (e.g. local market conditions) should be quicker and more flexible as head office won’t be involved in every decision.
line managers
Managers with direct authority over people, decisions, and resources in the organisational hierarchy. e.g. sales director and sales mgers, carry out line functions that directly impact core activities
staff manager
Specialists who provide support, information, and assistance to senior line managers. e.g. economists, specialist market researchers or specific experts advising. carry out staff function and support line mgers.
why may there be conflict between line and staff managers functions
staff managers very well paid bc experience and professional status but accused of haivng less loyalty to bus as services might be in great demand by wide range of firms so may be attracted by better rewards in other orgs
line mgers resent experts coming in and ordering them around.
staff have frequent comms/access to directors which can cause jealousy.
effective communication
The exchange of information between people or groups, with feedback, must have been received and understood by receiver
5 key features of effective communication
sender/transmitter of the message
message that is clear enough for the receiver to understand it
appropriate medium (the way in which the message is sent)
receiver of the message
feedback from the receiver to confirm receipt and understanding
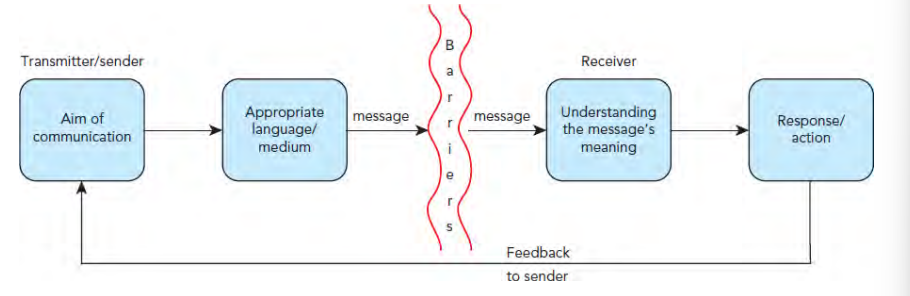
when is effective external communication essential for: 3
communicating with customers: new prods, variations, safety warnings, feedback, offers and promo
comms w suppliers: details of next order, delivery, discount, queries abt products
comms w shareholders: date of next agm, latest dividend payments, election of new directors, latest reports and accounts
effective internal communication essential for: 2
comm w employees: employ contract, training programmes, annual pay increases, performance appraisals, new working practices, new work sched and workplace problems when employee input required
comms between managers: coordinating activities and decisions of diff depts, reporting to senior mgment, passing decs and instructions to subordinate mgers, giving mgers opportunity to express opinion
communication methods
media used to communicate methods
methods of communication
have a significant impact on effectiveness
the media used to communicate messages
spoken
written
electronic
visual
visual communication
conveying information or ideas in forms that can be seen e..g maps, charts, posters, graphic design, animation, short films, diagrams, pics, charts, images
written communication
any type of message that uses written words e.g. use letters, memos, notices on boards, reports, minutes of meetings, diagrams for tech - most sent electronically
electronic communication
sending messages using media such as computers, email, or video conferencing e.g. dms, websites, blogs, texts, voicemail, video conferenc and video message
spoken communication
sending messages verbally between two or more people, e.g. one-to-one communication, interviews, appraisal sessions, group meetings or team briefings
information overload
receiving too much info, mkaing it difficult to identify and act upon important messages
strengths of spoken communication 5
allows for 2-way communication and feedback, and this should encourage good motivation. herzberg considered frequent feedback was a powerful motivational factor
instantaneous as theres no delay betwween sending and receiving the message
evidence of who attended a meeting and of who received the message delivered at the meeting, can be kept for future reference
if any pts not made clearly then receiver should be able to ask for immediate clarification
allows sender to reinforce msg with appropriate body language
weaknesses of spoken ocmmunication 4
some spoken communication can be ambiguous and, in a large group, some receivers may be reluctant to ask for further detail
there may be no written record of what was said so the message cannot be referred to again
might not be appropriate for complicated and technical matters, which would be better sent in written form
spoken communication, especially on a one-to-one basis, can be time-consumign
strenghts of written communication 3
written msgs can be referred to more than once to aid the receiver’s understanding
written comm allows detailed info, figures and diagrams to be sent
provides permanent record which might be useful legally e.g. employment contracts
weaknesses of written communication 3
non-verbal comm cant be used to support message
written comm doesnt allow for immediate feedback and clarification of msg cant be obtained quickly
evidence that msg has been sent but not that it has been recevied and/or understood
strenghts of electronic comm 6
messages transmitted rapidly as requires only a few secs to comm thru electronic media
global coverage is possible as the internet allows communication w potentially many millions of receivers all over the world
once hardware and training costs have been covered, electronic communication is low cost. can save time and money compared to more traditional methods (e.g. sms text messaging cheaper than letter and video conferences saves thousands of dollars bringing everyone to one spot)
electronic comms allow for instant exchange of feedback
improves flow of info for managers, enabling them to control a large, perhaps globally spread, business. useful for multinationals
most legal systems around the world now admit email as evidence and legal proof of contracts and transactions
weakness of ecomm 6
ecomm may require employees to be trained and the young are usually much more proficient in its use than older employees
reduces social contact and can create a sense of isolation. immportant social need may go unsatisfied
employees may use company time to send personal messages
direct interpersonal contact is lost and most ecomm doesnt allow use of body language to help convey msg
security and tech issues w computer tech and hard copies of important msg are often also kept in case of virus
increasing evidence that it can lead to information overload. too many msgs such as emails can prevent really important communications from being acted upon. too many msgs can cause emplotyee stress and feeling of overwork
strengths of visual comm 4
effective for receivers w poor skills in language being used for comms esp when exchanging info with ppl from several diff countries
supports spoken comm which becomes more meaningful if graphs, pics, diagrams used too. create real impact to support senders message
simple way of presenting complex info e.g. organisational chart
receiver can understand msgs presented in form more quickly than info is transmitted in pages of text
weaknesses of visual comms 4
viusal methods of comm can be costly and time conusming to produce
cannot be only method used when detailed tech data/accounting info needs to be transmitted
visual methods dont allow for nonverbal comm such as body language
visual images so dramatic that deflect receivers attention from key message
Formal communication channels:
The official communication networks and routes used within an organisation.
one way communication
Messages sent in one direction, from sender to receiver, with no feedback expected.
two way communication
Communication involving message transmission that encourages response and feedback.
4 problems with one way communication
receiver cant question meaning of message or ask further explanation
no discussion between sender and receiver
sender not sure message received, understood and acted upon
usually associated w authoritarian managers
2 problmes with two-way communication
time conusimng and employees may have to stop work to attend meetings
may be inappropriate for some msgs that give clear info that cant be argued w and requires no discussion
how is 2way better than 1 way
receiver can contribute to debate abt message or question sender. proves more morivating bc can participate and is essential for democratic leadership to opearte and meets some conditions for motivation mayo herzberg
2 links to employee miotivation and comm chanels:
motivation = effective comm: well motivated employees listen and respond positively to msgs resulting in better and more accurate 2 way comms
2 way comms leads to motivation: 2 way comms mean employees are more likely to feel involved and receive constant feedbakc. shorter comm channels reduce remoteness from top and lead to better-motivated workers.
important and could lead to virtuous circle.
vertical communication
Communication between people at different levels in a hierarchy. main direction
horizontal communication
Communication between people on the same level of hierarchy.
problems with vertical communication 4
nearly always down the org e.g. from senior mgers to production employees
usually used by authoritarian mgers using 1way comm
if many intermediaries in chain, msg may become distorted
msgs take time to be received by final person in the chain
leader gets control
problmes with horizontal 2
diff depts mayu not understand fculutre, ways of working, objs, porblems or tech language of others
outlook and objs of diff depts could conflict, e.g. spending money on ads that finance thinks is unecessary
communication barriers
Reasons why communication fails.
3 broad reasons why barriers to comm occur
failure in one of the stages of comm process
poor attitudes of senders or receivers
physical reasons
failure in one of the stages in comm process
method chosen might be inappropriate e.g. mobile w/ detailed tech langauge
if details of lengthy verbal msg likely to be forgotten, then written version more appropriate
misleading/incomplete msg results in poor understanding e.g. send goods soon, interpreted as ‘send tomorrow’ when in fact sender meant now or asap
excessive use of tech language/jargon may prevent receiver ftrom understanding what is required. msgs sent to branches or employees in another country may not be understoof unless translated into local lang
if too much info,. threat of overload = noise. unecessary info that prevents receiver from grasping the important elements of the message
if the channel of communication is too long, messages are slow to reach their intended receiver and may become distorted or have their meaning changed along the way. problem particularly signifiacnt in large orgs w long chain of cmd
poor attitudes of senders or receivers
if sender isnt trusted (bc before misleading msgs or unpopular decision) then the receiver may be unwilling to listen to or read the message carefully
unmotivated or alienated workers make poor receivers. if workers have never been consulted on immportant issues before, they may become very suspicious if management style seems to be changing toward a more participative one. worker with little interest in their work will not want to take trouble to ensure comm effective
intermediaries are people on the communication channel. sometimes, fi they are poorly motivated, they may decide not to pass on a message or to change it. could occur, e.g. if there has been a supplier query about an order or a customer complaint
the sender may have such a poor opinion or the receiver that no effort is made to ensure the message is clear or to check it has been understood.
physical reasons
noisy factories are not the best env for comm. so can limit effective comm
geographical distance can inhibit effective comm - interpersonal communication will certainly be very difficult. modern electronic methods, such as videoconferencing, designed to overcome some of these problems
overcoming communication barriers six steps
ensure msg clear and precise but adequately detailed
keep comm channel as short as possible
make sure channels of comm are understood by all involved
ensure feedback is part of comm process so problems w receiving or understanding msg can be checked quickly
establish trust betw senders and receivers. easy where bus culture is accepting all staff contributinos useful and important
ensure physical conditions appropriate for msgs to be received.
informal communication
Unofficial communication channels that exist between informal groups within an organisation.
3 lims of informal comms
could take up valuable working time
if used for gossip/rumous can be unsettling and lead to feelings of insecurity
may result in informal groups banding together to resist management decisions even tho they may not have been officially communicated yet
3 bens of informal comm
informal comm can create important feelings of belonging and social cohesion
management caan use this channel to test out new ideas and see what the unofficial reaction might be. if too negative might nvr make official announcement
can help reduce barriers betw depts and encourage dev of new ideas
how does effective external communication impact on business efficiency: 5
suppliers know which porducts to deliver and when, therefore reducing the chance of a halt in production
if loacl comms are made aware of bus plans that might affect them e.g. expansion, they are more likely to support them
creeditors (account payable) know when thye’re likely to be paid, encouraging them to supply on credit
debtors (accounts receivable) know when they should pay, helping to improve liquidity
investors in and lenders to bus will be more confident if bus keeps them regularly informed of performance
how does effective internal communication impact bus efficiency
increases employee motivation and labour prod. if workers encouraged to participate thru group discussion, then effective communication will aid motivation. workers will feel out of touch and isolated if poor comm
more and better ideas generated by employees. if workers asked for ideas then will assist w porblem solving
increases speed of decision making as up to date info is required for successful decisions to be made
increases speed of response to market chwnages if consumer preferences are comm quickly to operations dept
reduces risk of errors. incorrect understanding of a poorly expressed message will lead to incorrect responses. this could lead to many internal problems, such as wrong prods being made or incorrect prices being set
improves coordination betw depts especially if horizontal comm is encouraged.
what factors need analysis when making management decs to improve comm in bus situation : 8
importance of written record of msg that has been sent and received e.g. new legal contract
advs from employee participation thru 2-way comms. e.g. employee shift system proposal discussed before implementation
cost: electronic media requires expensive capital resources but once obtained ecomm cost effective. cost of management time in meetings shouldnt be overlooked. quicker and cheaper, maybe less effective to just email everyone at meeting
speed: electronic methods can be quick but time may be needed for discussion+opinions
quantity of data to be comm - longer and more detailed message less likely that oral comm effective
whether more than one method should be used for clarity to ensure that msg has been received. e.g. quick phone call + letter + order form achieve speed and accuracy
size + geographical spread of bus - regular and frequent meetings of senior regional managers may be impossible in multinational
actual content of msg to be communicated e.g. h&s info will need diff methods and channels to those used for comm a proposed change in production methods.
personal qualities in successful leaders: 8
desire to succeed and sufficient selfconfidence that they will succeed
ability to be innovative and think beyond the obvious, and to encourage others to do the same
multi-talented so that they can understand discussions about wide range of issues affecting their business
incisive mind to identify heart of an issue rather than unecessary details
being inspirational so others want to follow example and be part of success
complete honesty, integrity, and highest ethical standards
being good communicator so passion and vision transmitted to employees
empathy and emotional intelligence to better understand their followers
most significant leadership pos in bus:
directors
mgers
supervisors
workers representatives
informal leadership
directors
senior mgers elected into office by shareholders in limited company
head of major functional dept e.g. marketing/finance
responsible for delegating tasks, assisting in the recruitment of senior employees in the dept, meeting the depts objs set by the board of directors and communication these objs to their dept
mgers
any individual responsible for ppl, resources, or dec-making or all 3
have some authority over other employees below them in the hierarchy. they direct, motivate praise and, if necessary discipline workers in their section of dept.