4.1.8.5 Merit and Demerit goods
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
What is a merit good?
Good deemed to be beneficial for society, under-provided by the market.
When will a merit good operate?
social benefit is greater than private benefit.
positive externality from providing the good—> government is likely to intervene for the good of society and increase supply.
What do merit goods suffer from? What does this lead to?
under provision in the market
Consumers lack perfect information and would under-consume products that society believes would benefit them
leads to market failure
The government intervene in the market in order to increase the supply of this type of good or service
What are examples of merit goods?
Vaccinations: When individuals get vaccinated, they protect themselves from disease, but they also contribute to herd immunity, reducing the risk of disease transmission within the community.
Clean energy: The use of clean and renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, can be considered a merit good because it reduces carbon emissions and air pollution, benefiting society in terms of reduced environmental damage
Public libraries: While individuals benefit from using libraries, they also contribute to a more literate and informed society.
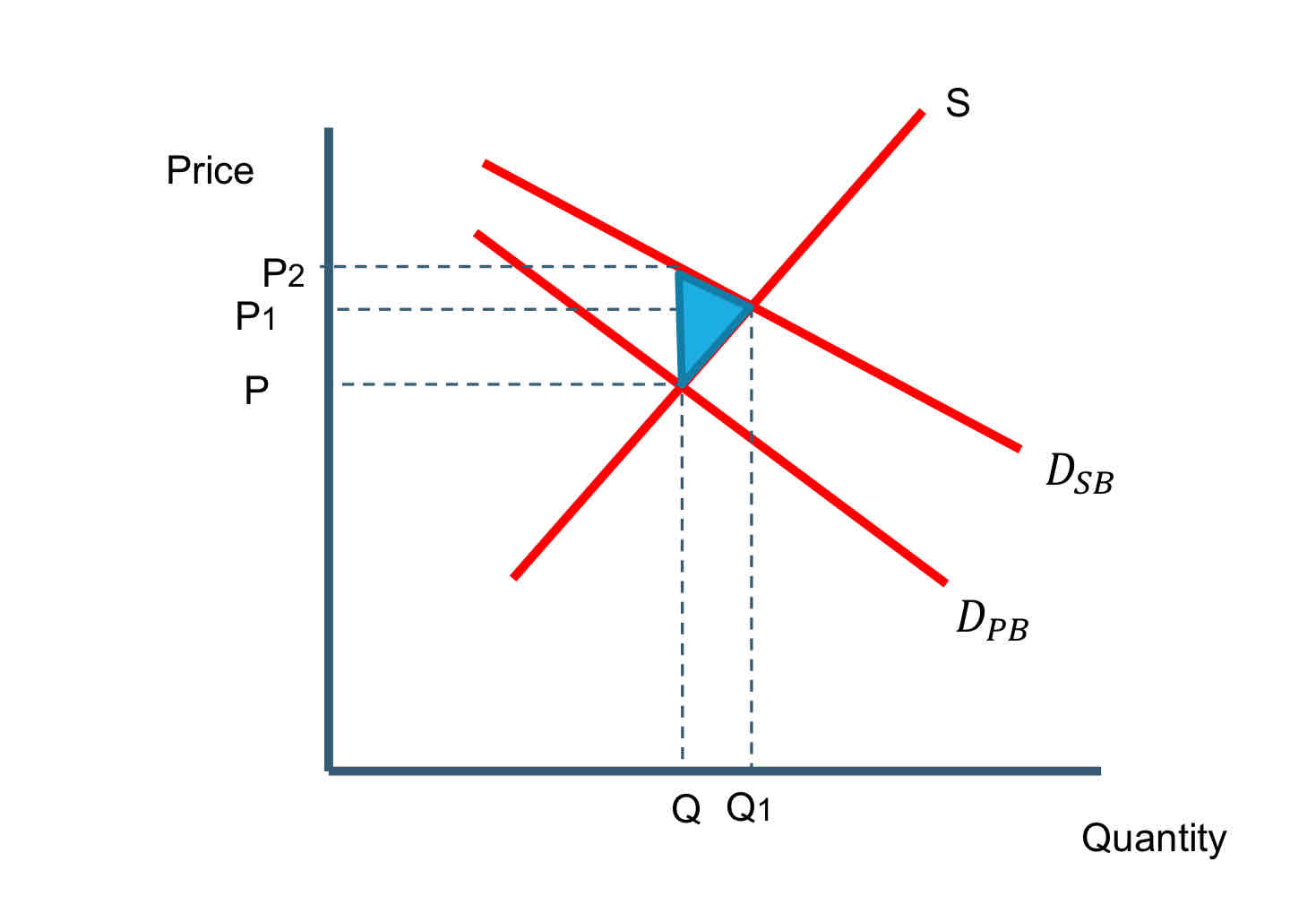
Draw the diagram for merit goods
The good/service is seen to provide benefits to society over and above those to the individual consumer i.e. there is an additional external benefit of providing the good.
Individuals will only consider their own private costs & benefits and demand Q of the good.
However, society would benefit to a greater extent if the demand for merit goods is higher leading to a quantity at Q1.
The additional benefit/positive externality can be measured by the blue shaded area.
Triangle across = deadweight welfare loss
What’s a demerit good?
one that is deemed to be bad for society but is over provided by the market.
will operate where private benefit is greater than social benefit.
leads to market failure
There is a negative externality from providing the good so the government is likely to reduce or eliminate the supply of the good for the benefit of society.
What are examples of demerit goods?
High Caffeine Energy Drinks
High-fat, high- sugar & high- salt foods
Violent films and games
Hands-free cell phones in vehicles
Alcohol fraud and binge drinking
Tobacco products
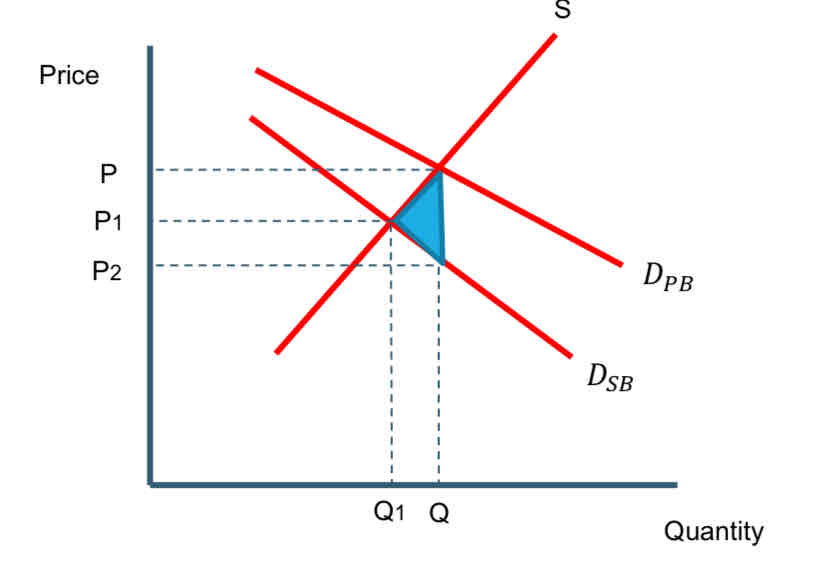
Draw the diagram for demerit goods
The good is seen to be bad for society and is over-consumed by the market.
Individuals will only consider their own private costs & benefits and demand Q of the good.
However, society would benefit to a greater extent if the demand for merit goods is lower leading to a quantity at Q1.
This negative externality can be measured by the blue shaded area.
What is Perfect knowledge or perfect information?
occurs when all consumers are fully aware of price, quantity available and all other relevant information for all products when making buying decisions
What is Information asymmetry?
when some parties in a transaction have more information regarding the product than others.
Example of perfect information
Gina goes to buy a diamond. She has perfect knowledge about diamonds: she knows how to test for originality, their price per carat, size, colour, and cuts.
In this case, the seller won’t be able to sell her a diamond at a supernormal profit, because Gina wouldn’t purchase it.
Gina will be able to rationally choose the right diamonds at the right price.
What is information failure?
market failure where consumers/ producers have asymmetric knowledge
it is difficult for consumers and producers to make decisions regarding price, quality and other relevant factors when buying and selling
What can imperfect information lead to?
under provision of merit goods
over provision of demerit goods as people