bio all
1/153
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
154 Terms
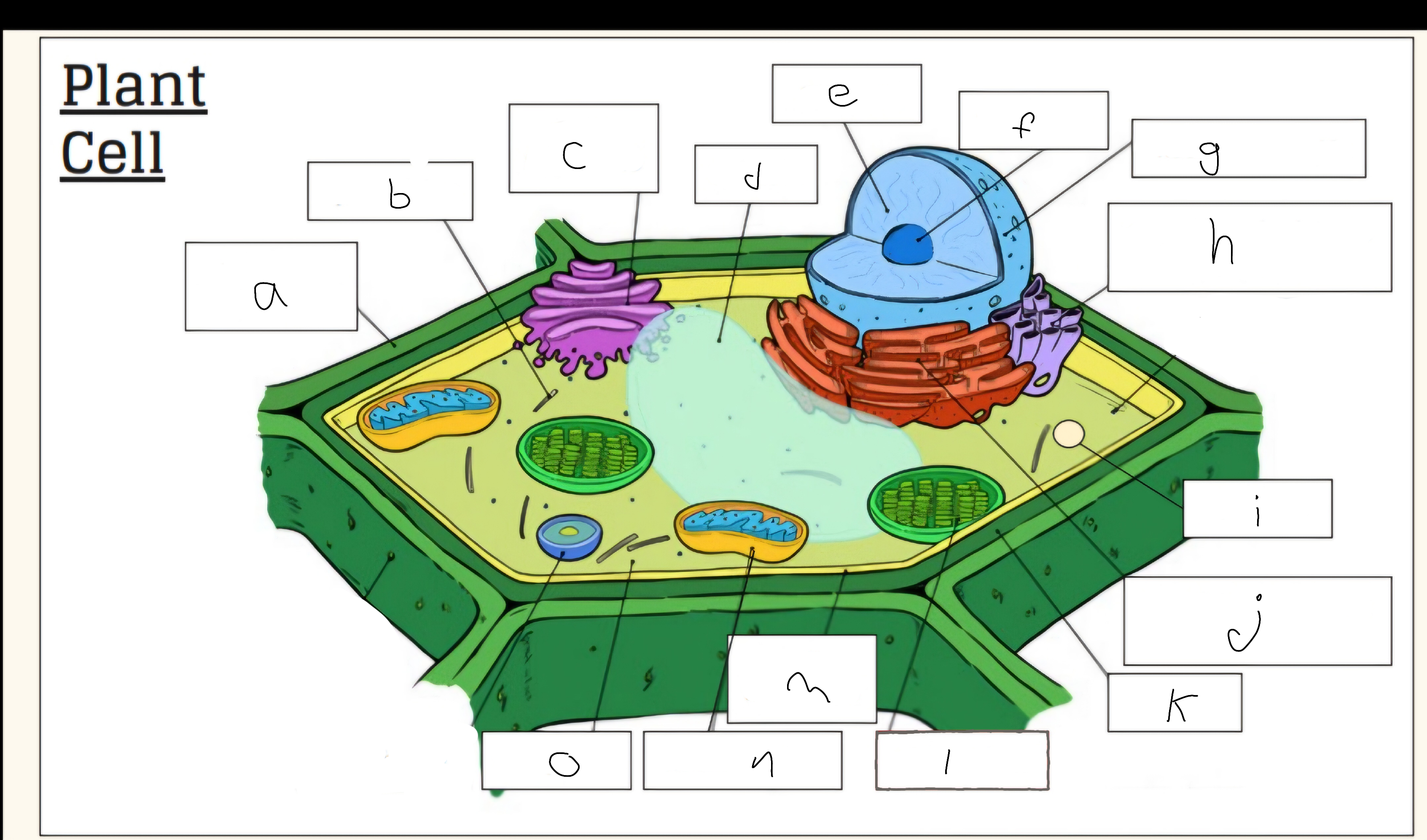
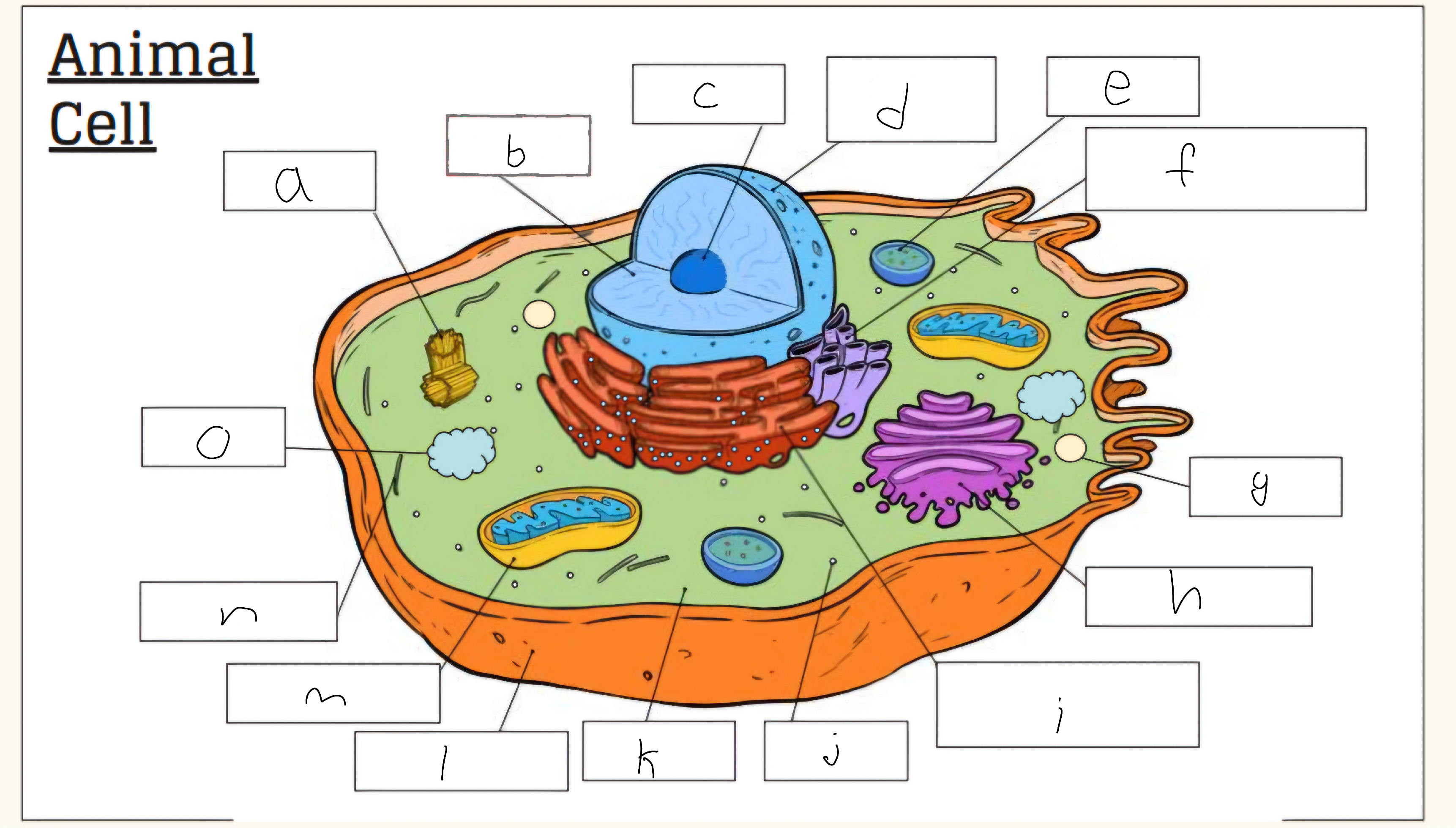
a
Cell wall
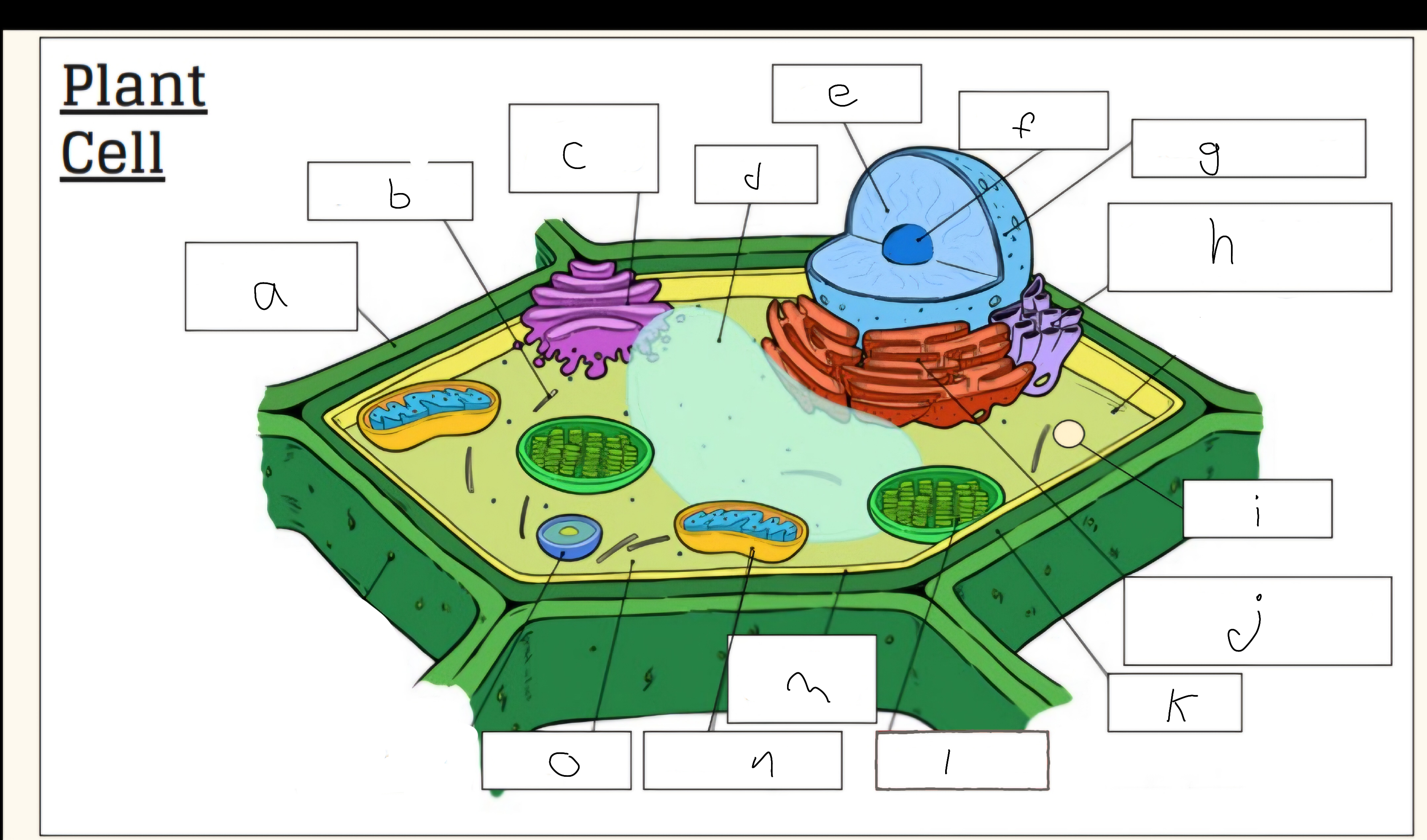
c
Golgi apparatus
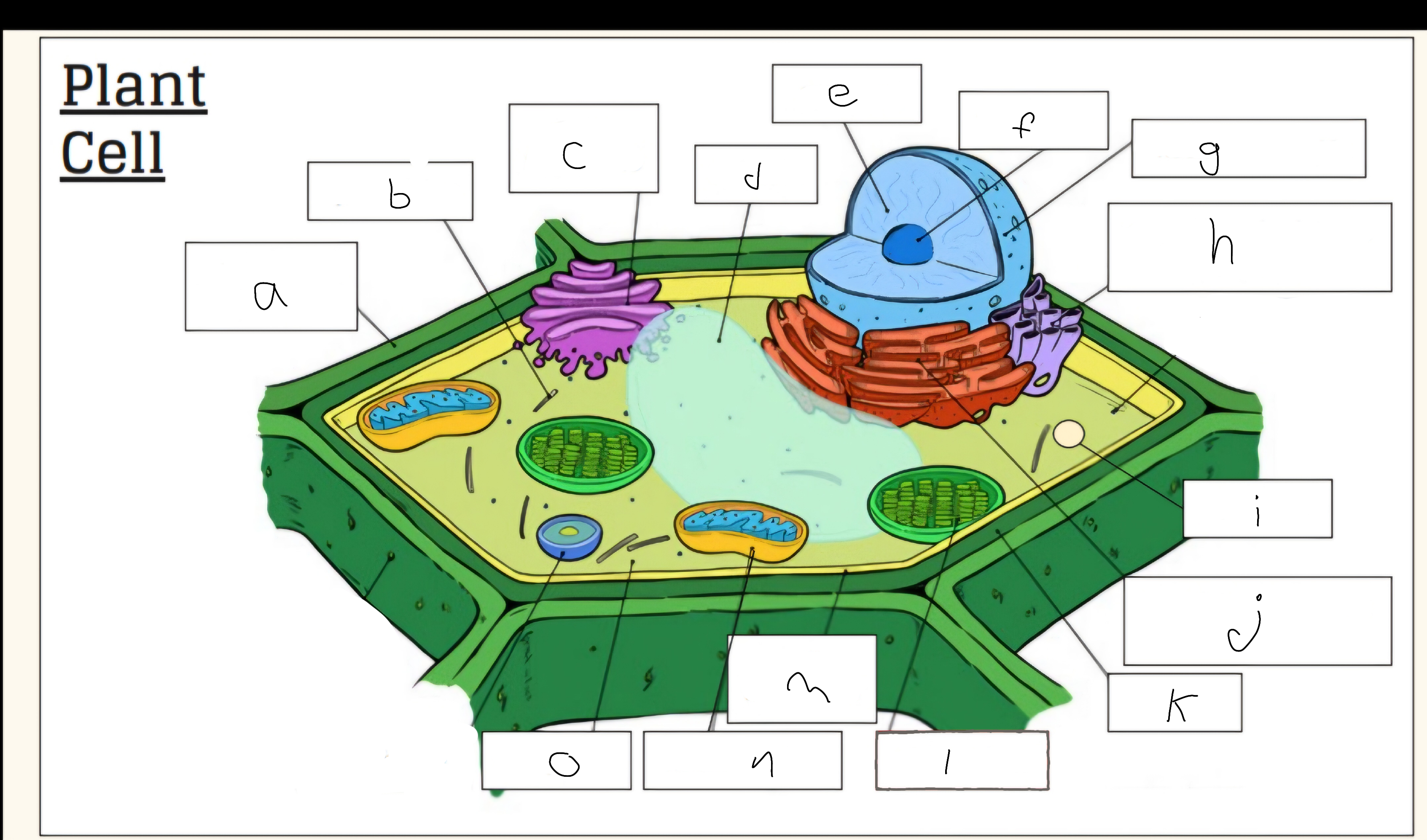
d
Vacuole
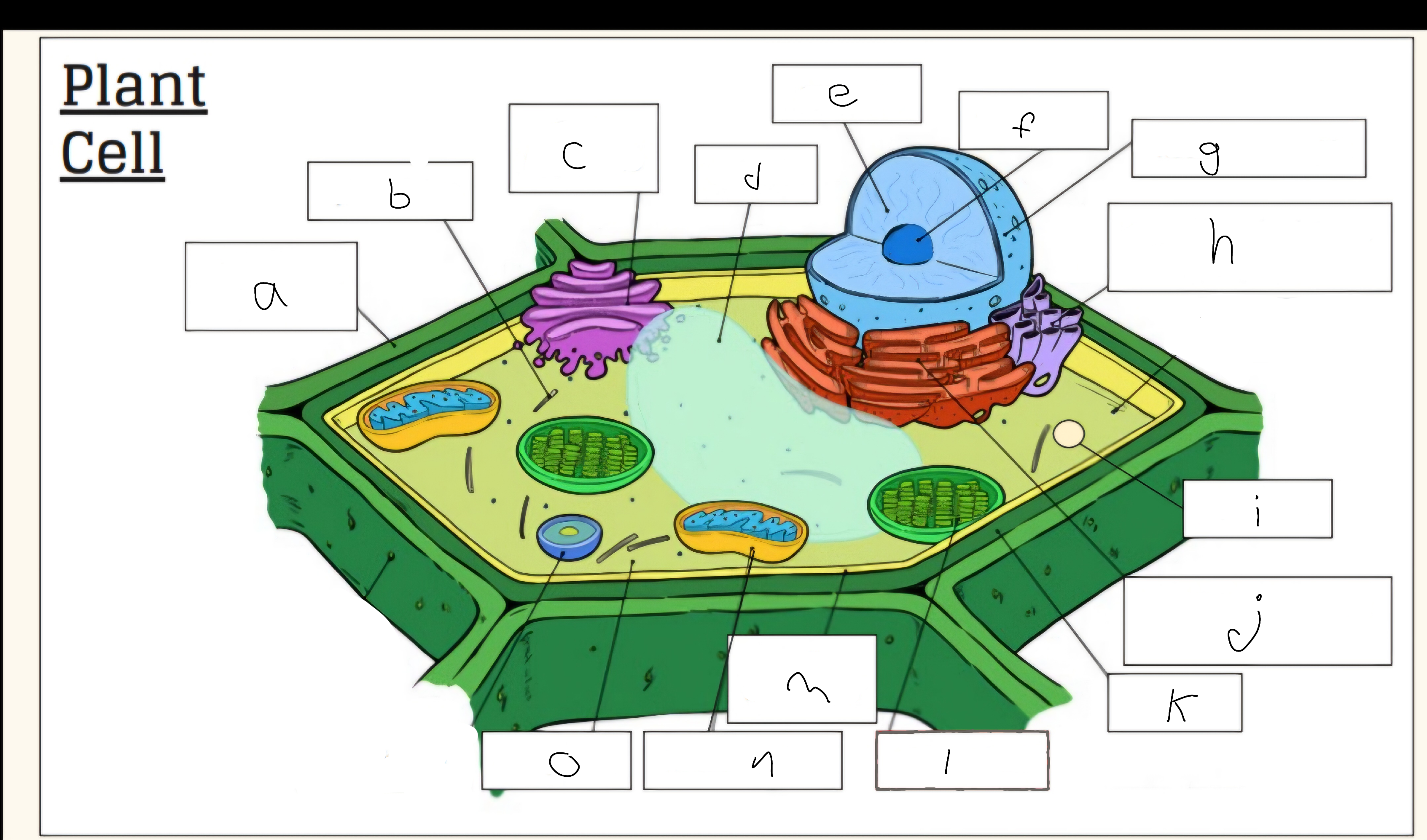
e
Nucleus
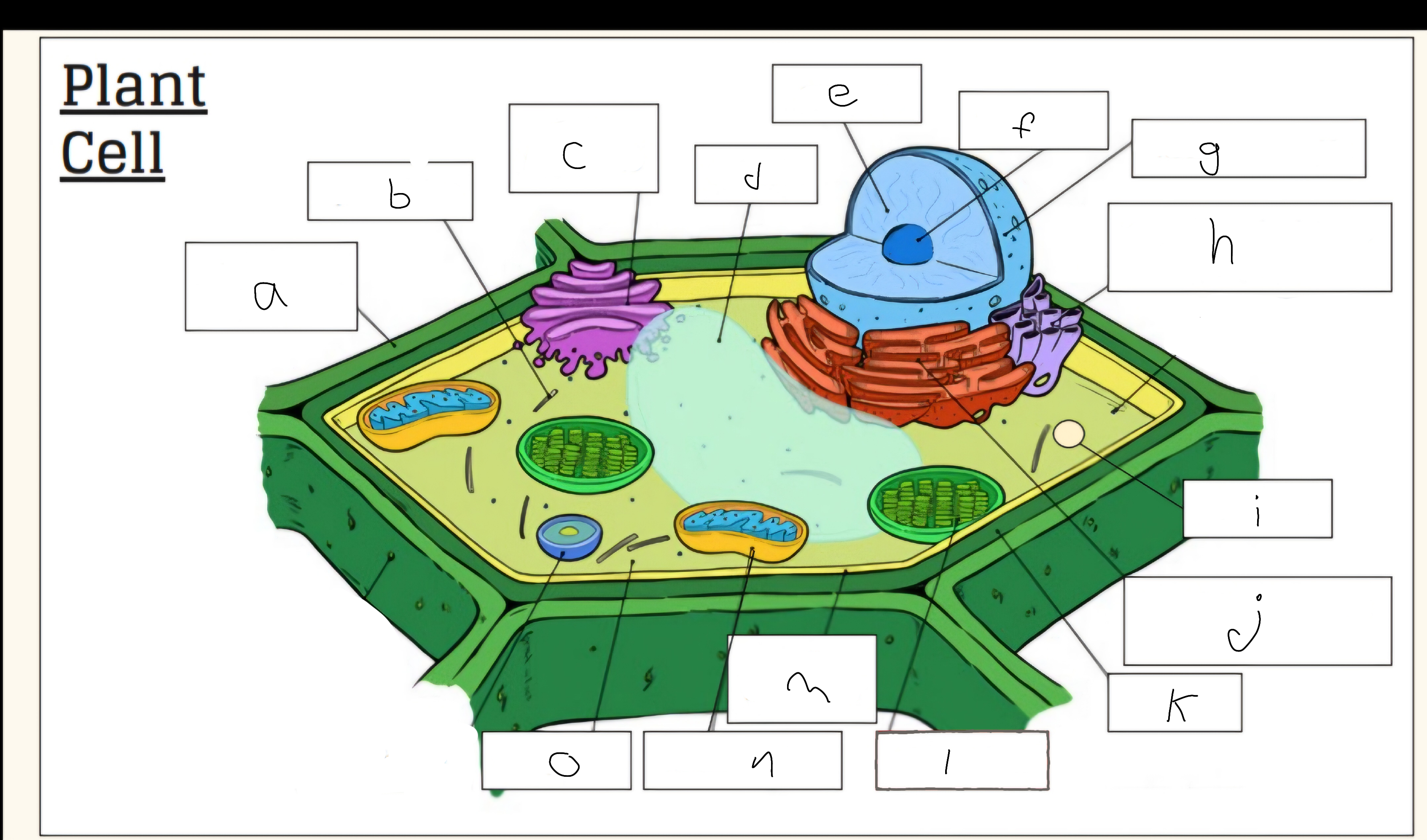
f
Nucleolus
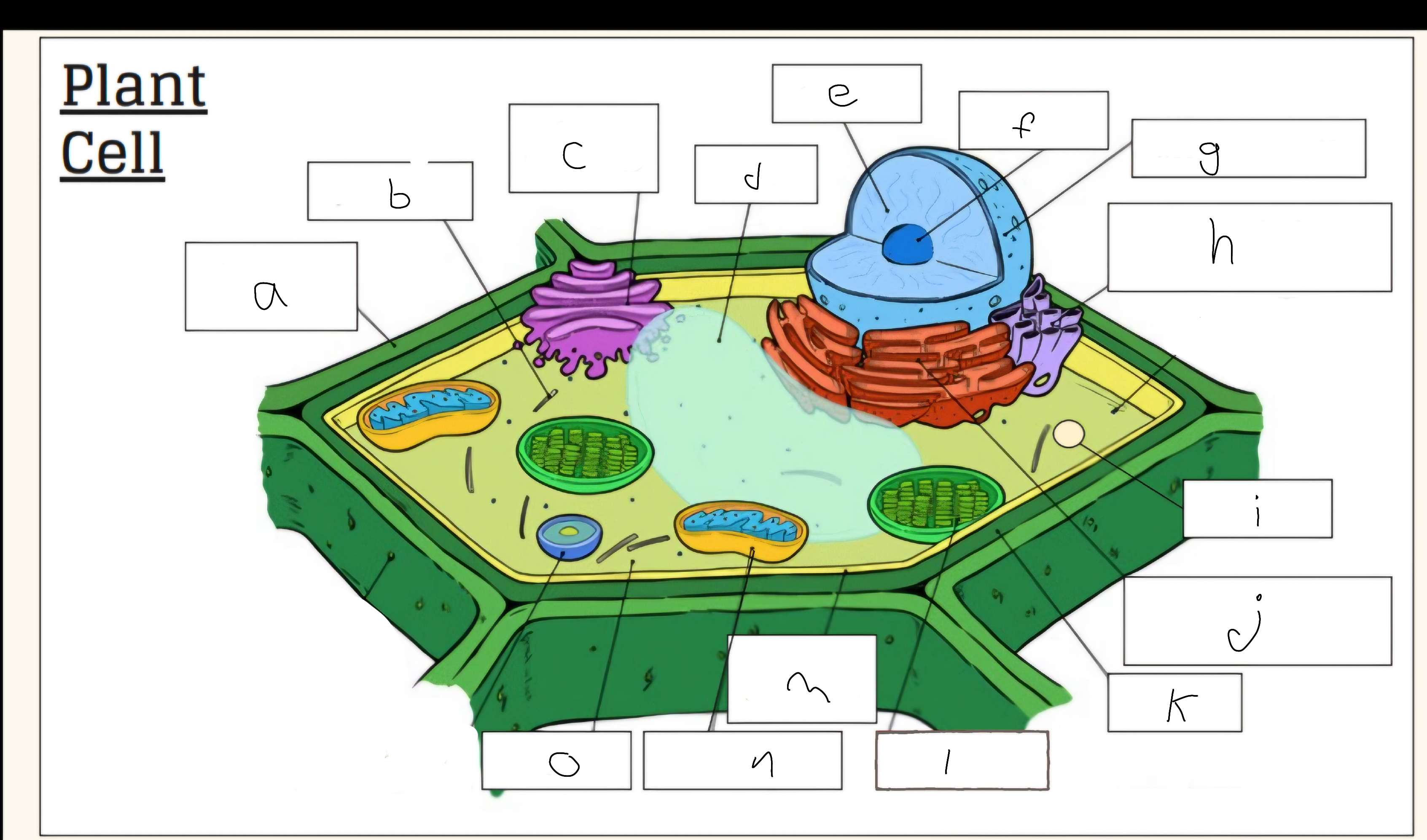
h
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
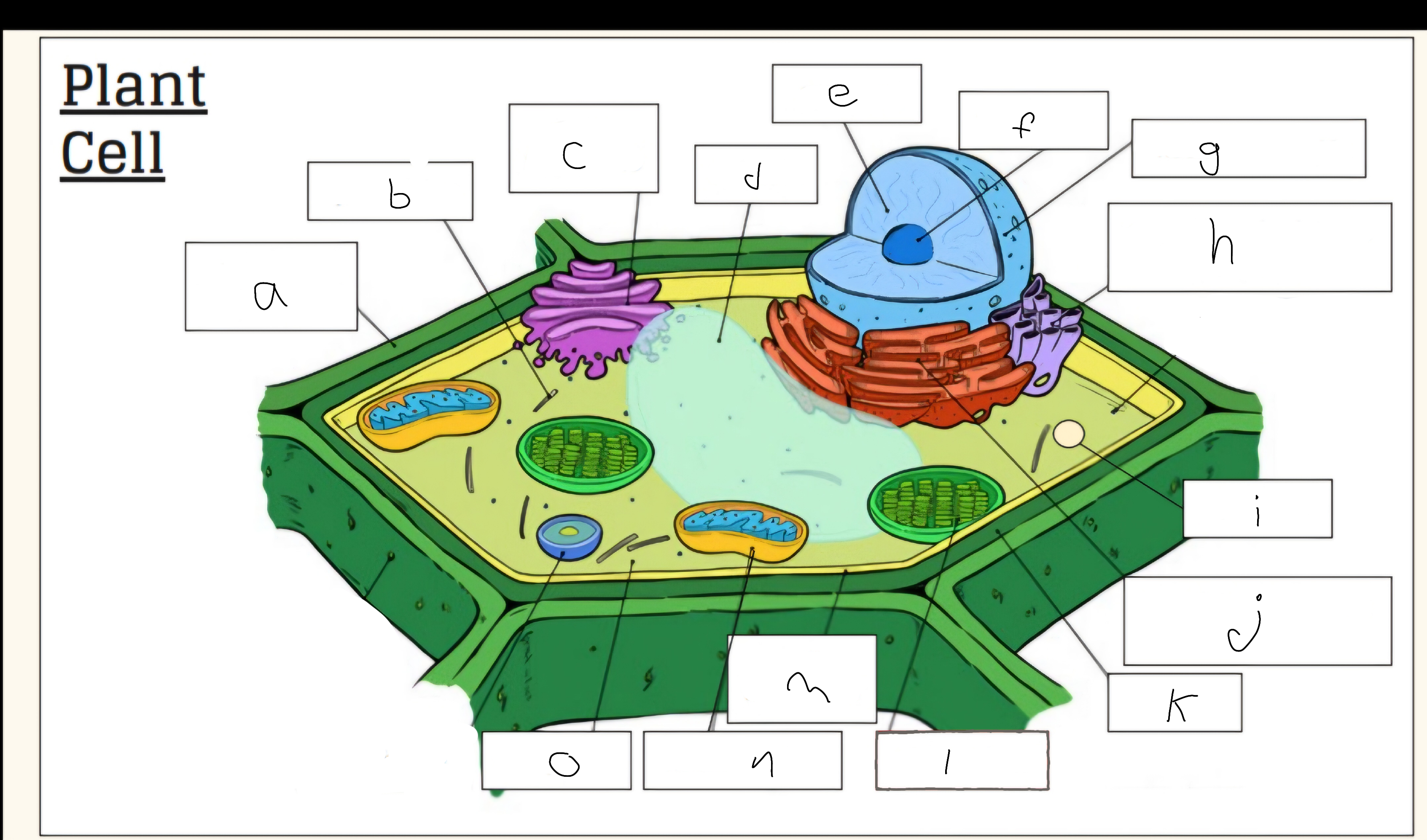
i
Vescicle
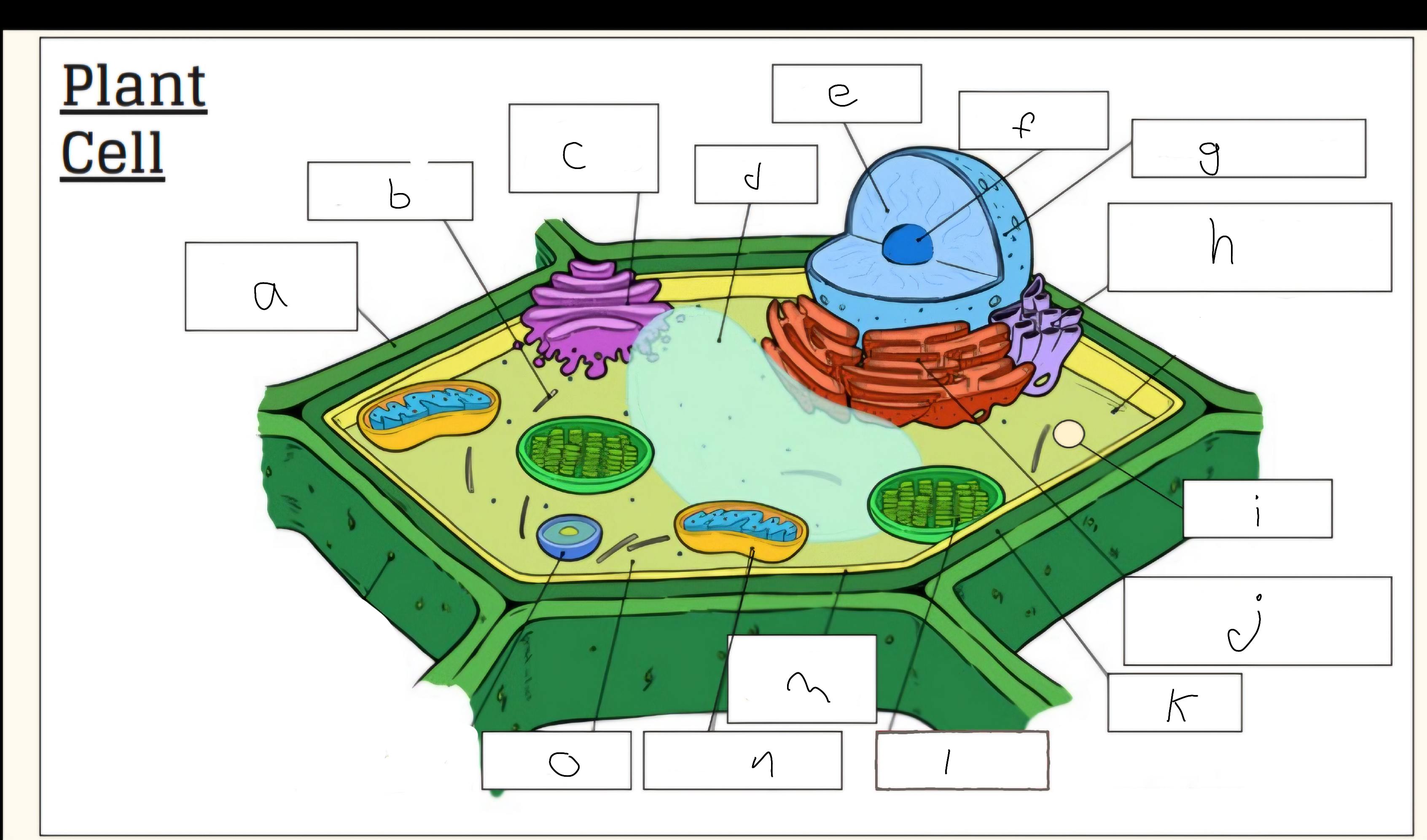
j
Tough endoplasmic reticulum
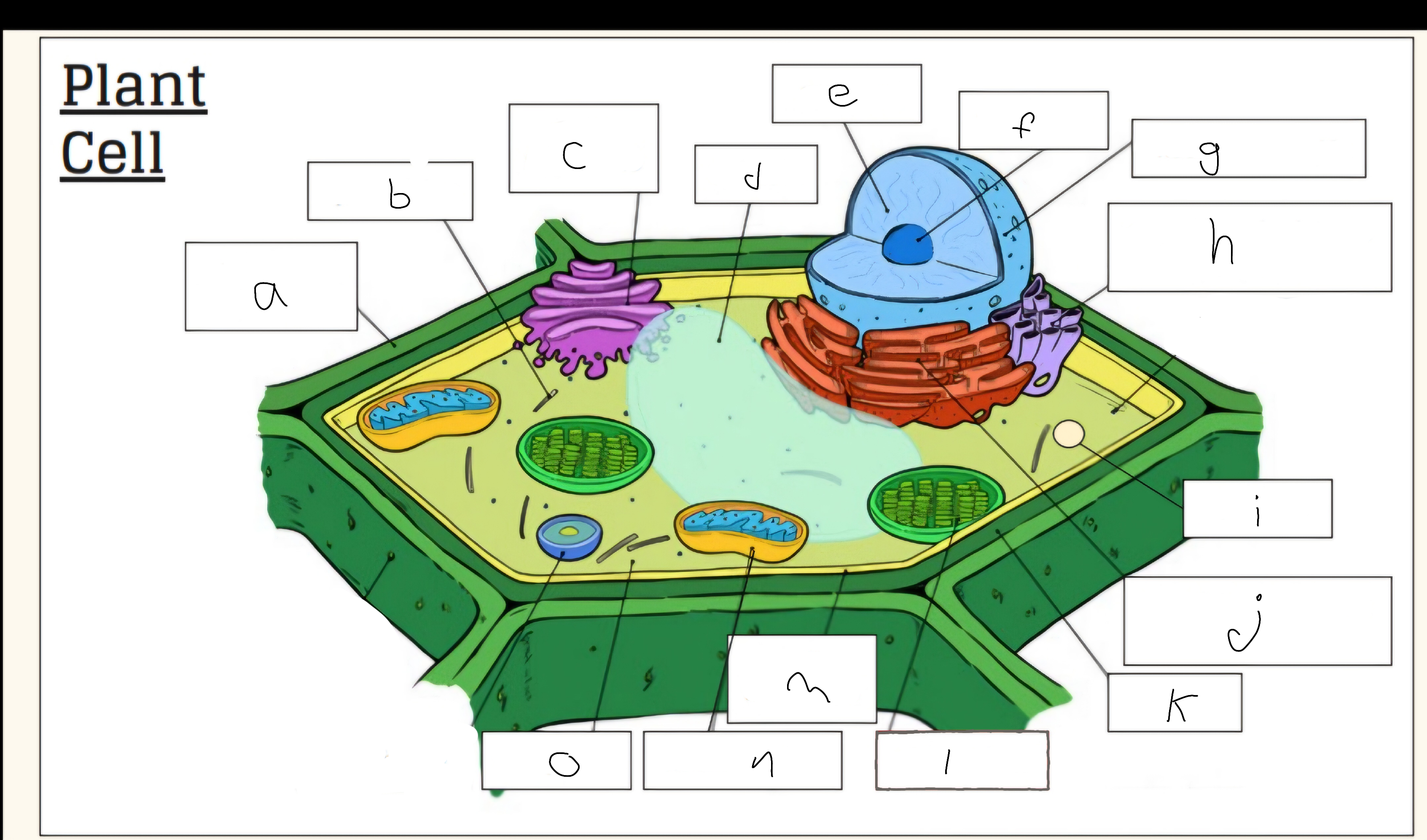
l
Chloroplast
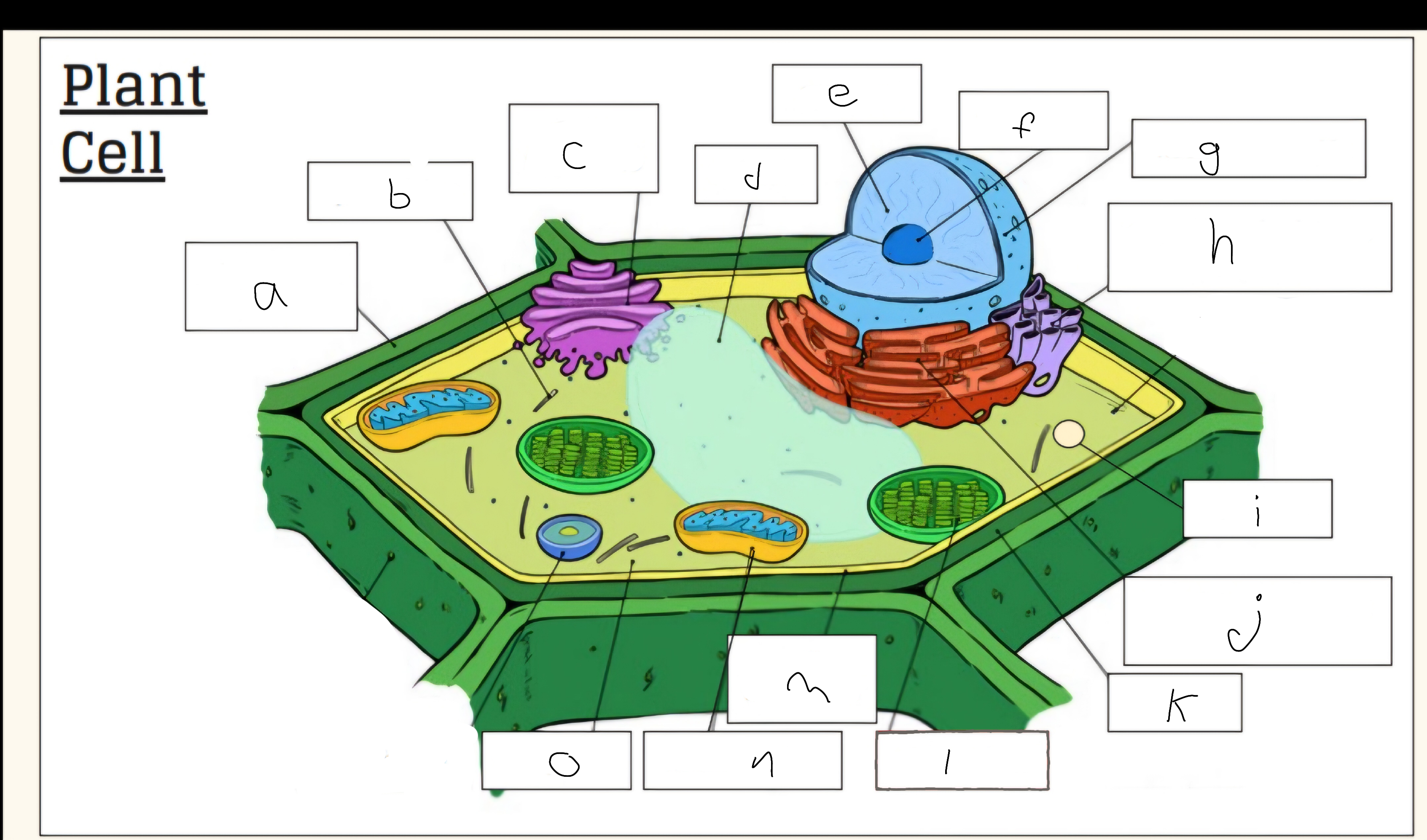
m
Cell membrane
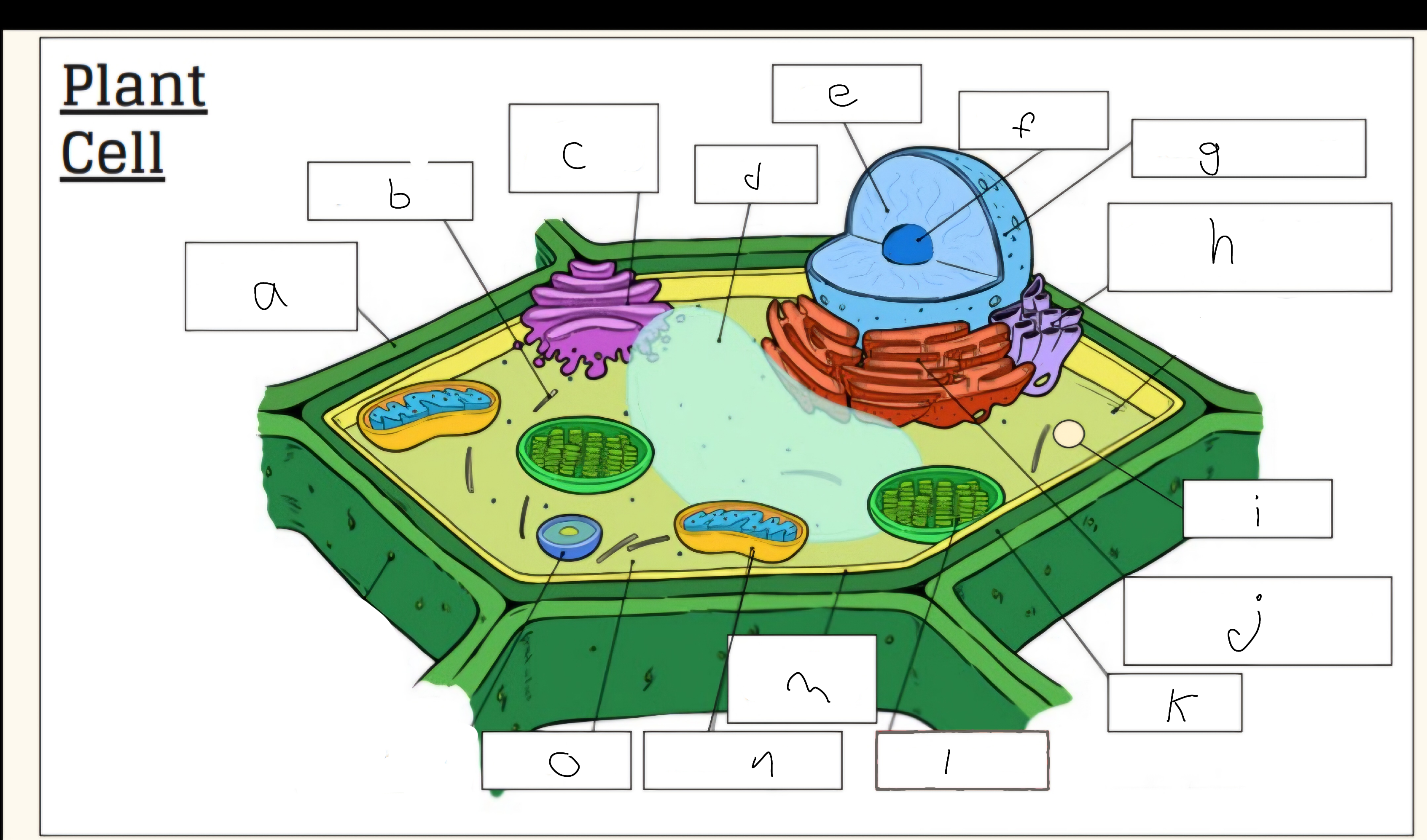
n
Mitochondria
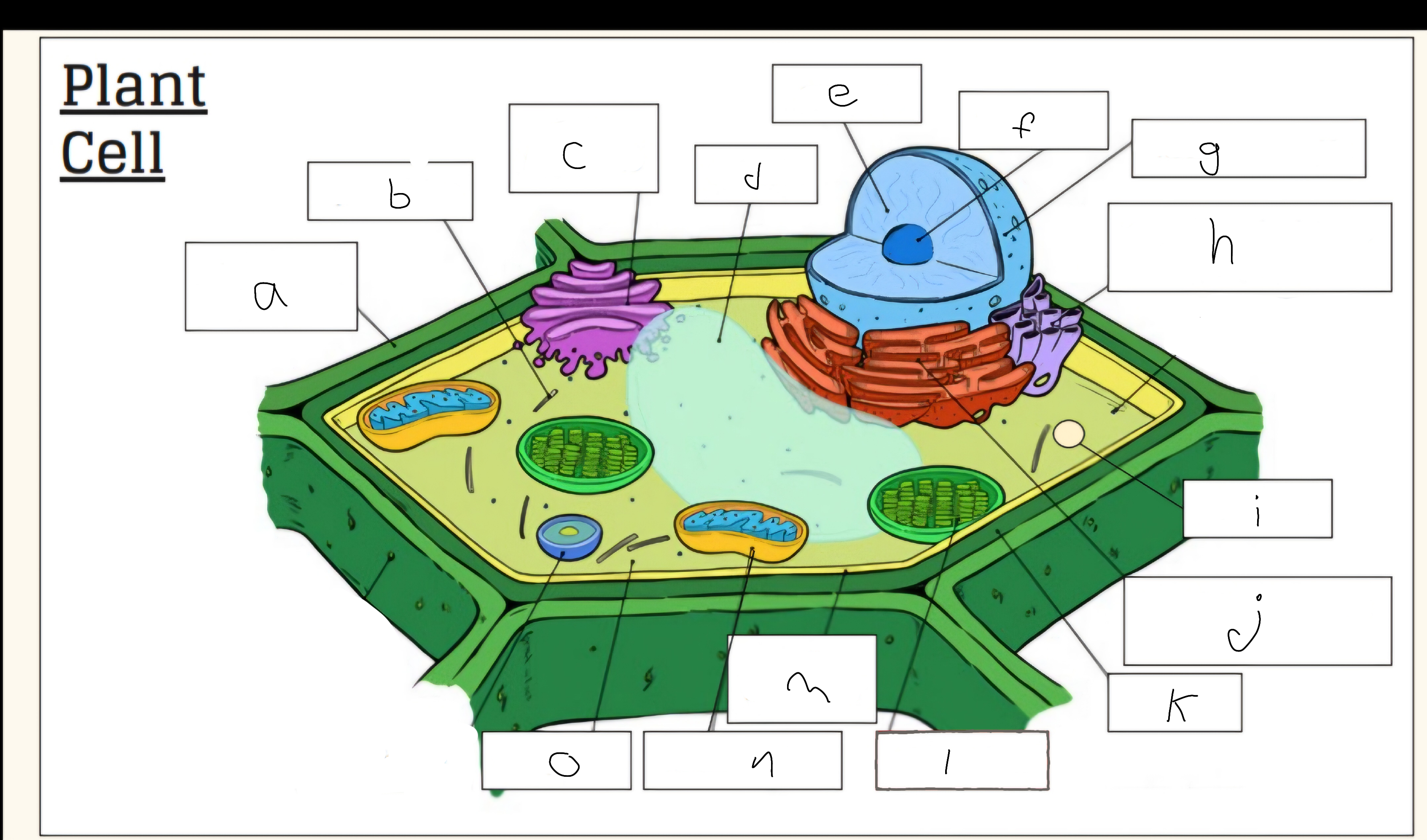
o
Cytoplasm
a
Centrioles
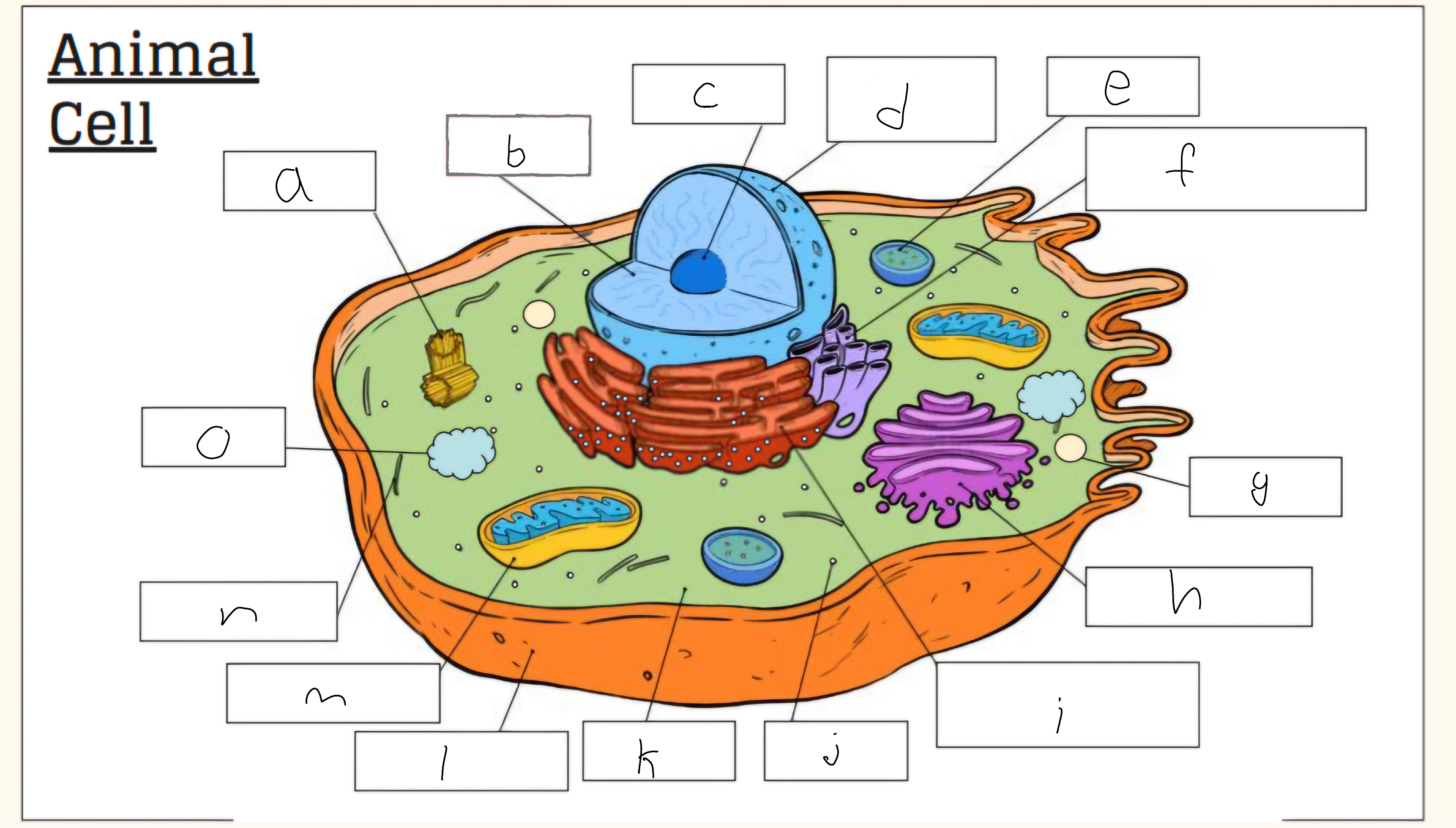
b
nucleus
c
nucleolus
d
Nuclear envelope
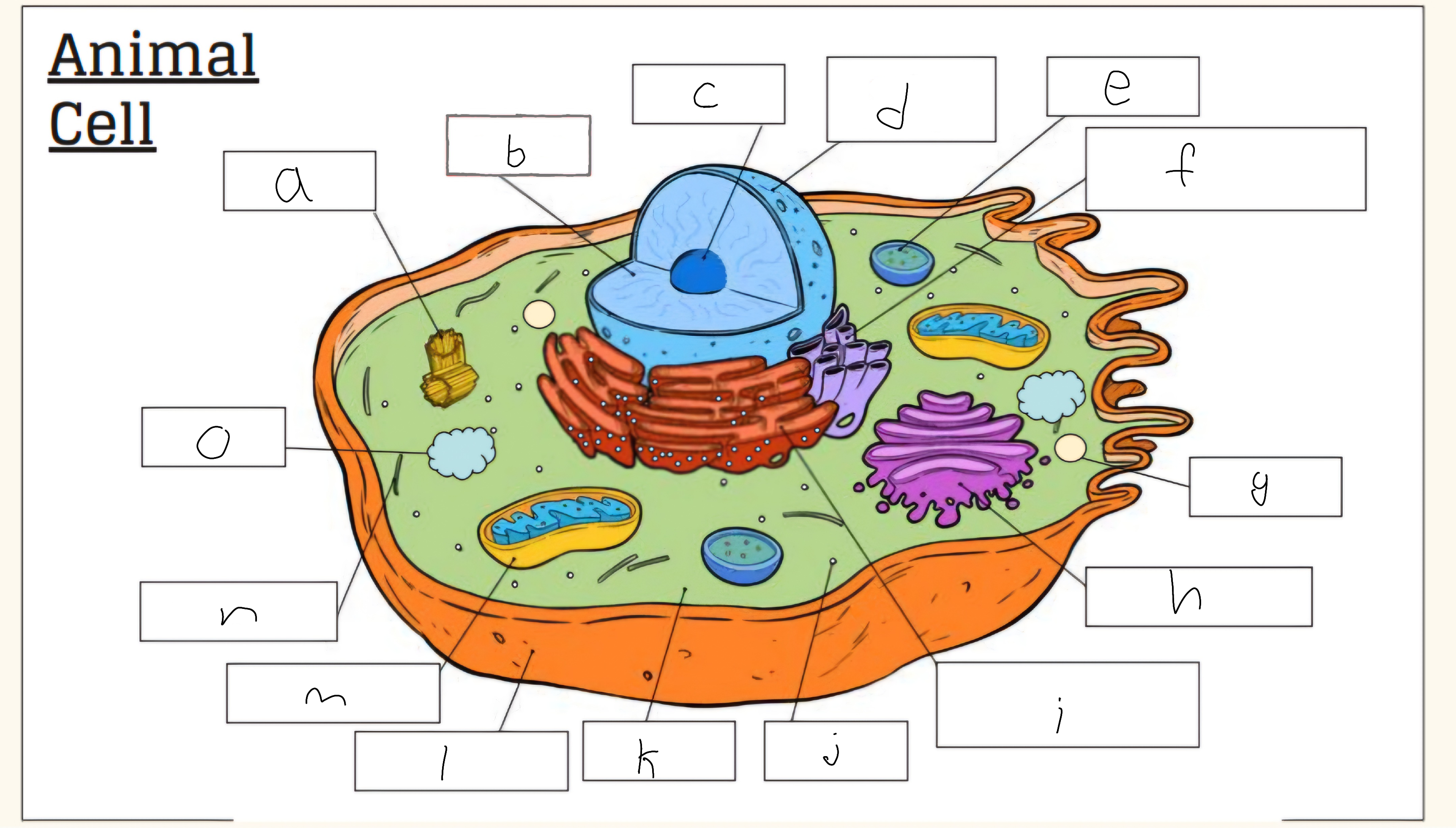
e
Lysosome
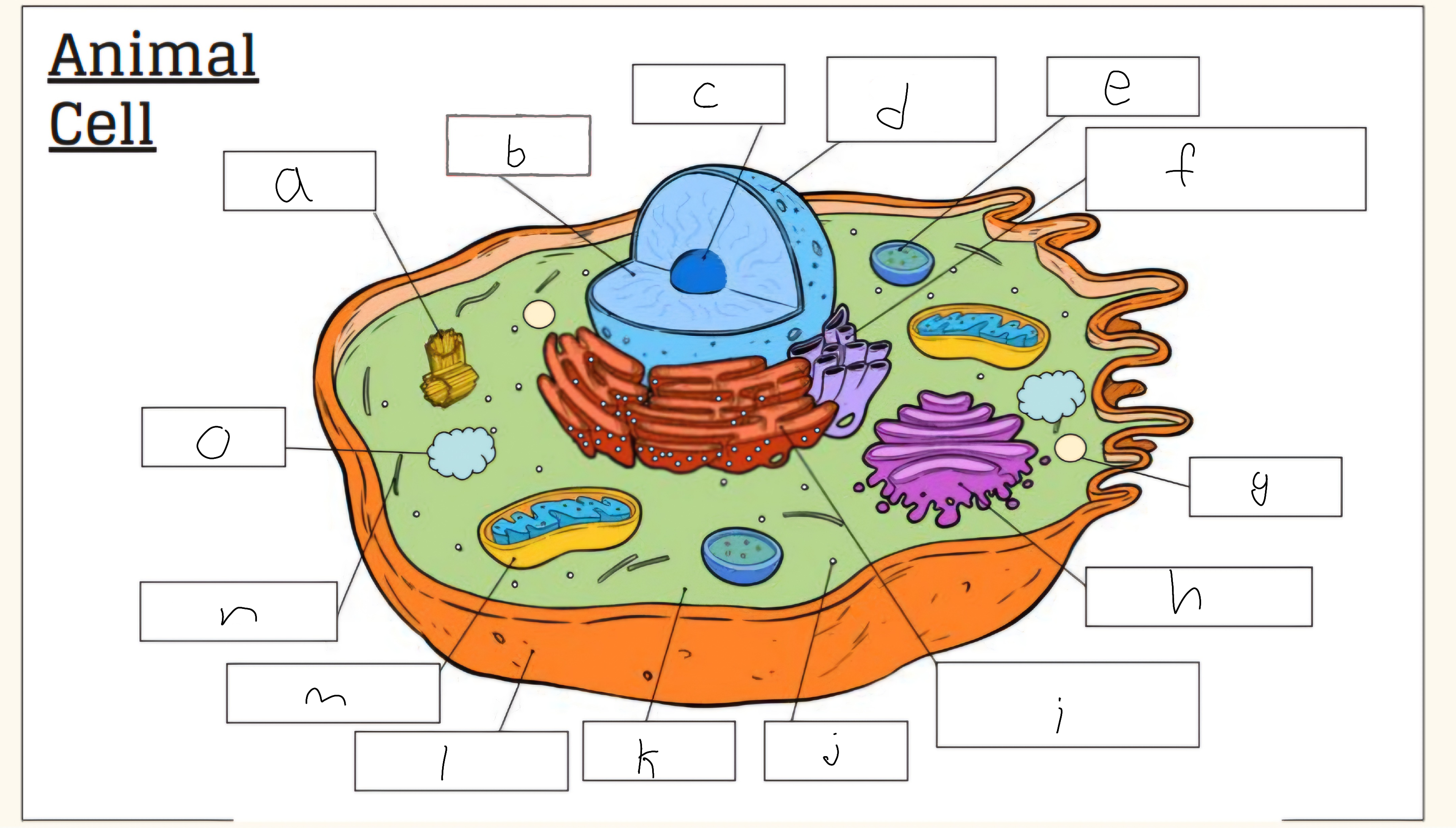
f
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
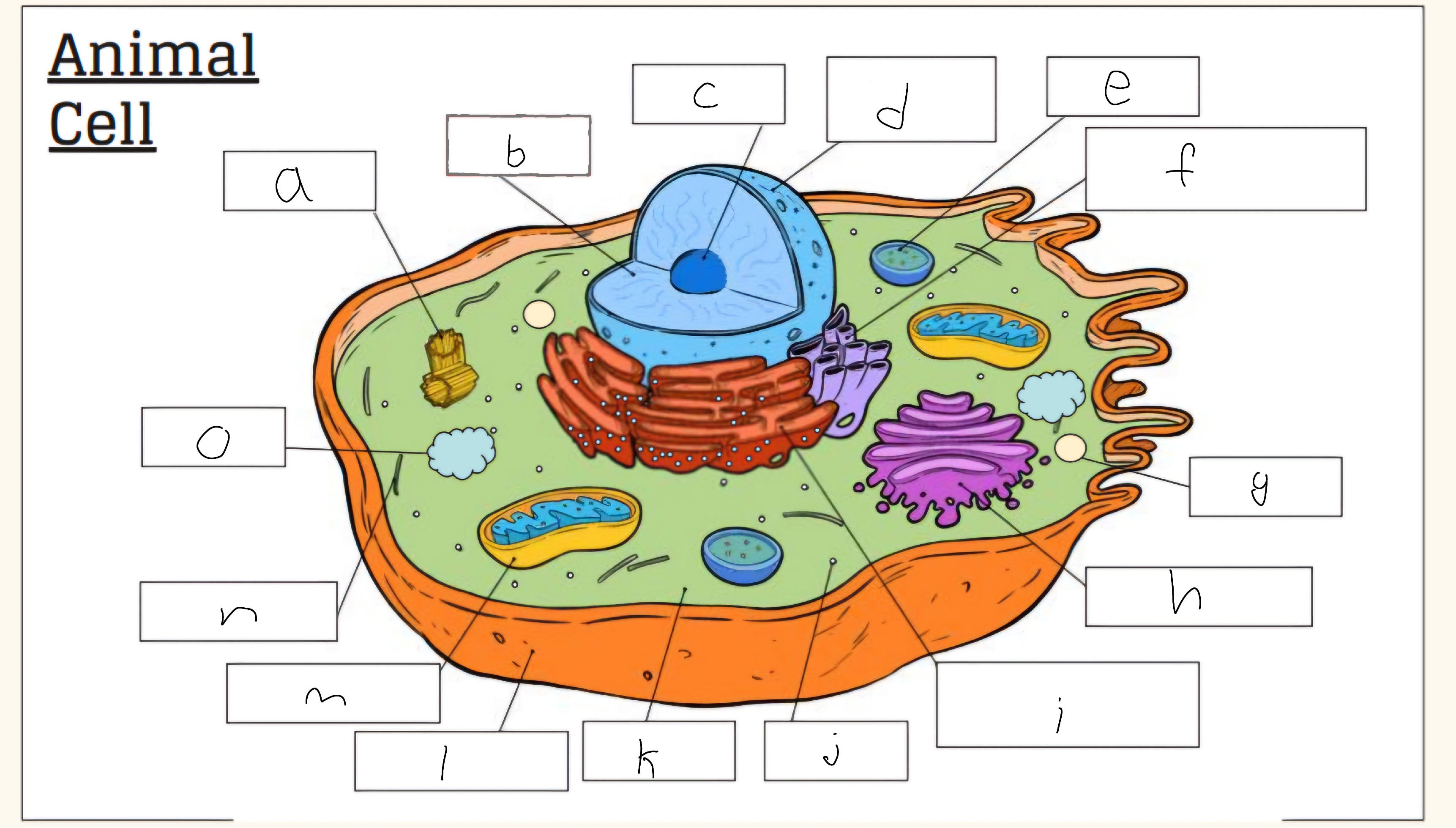
g
Vescicle
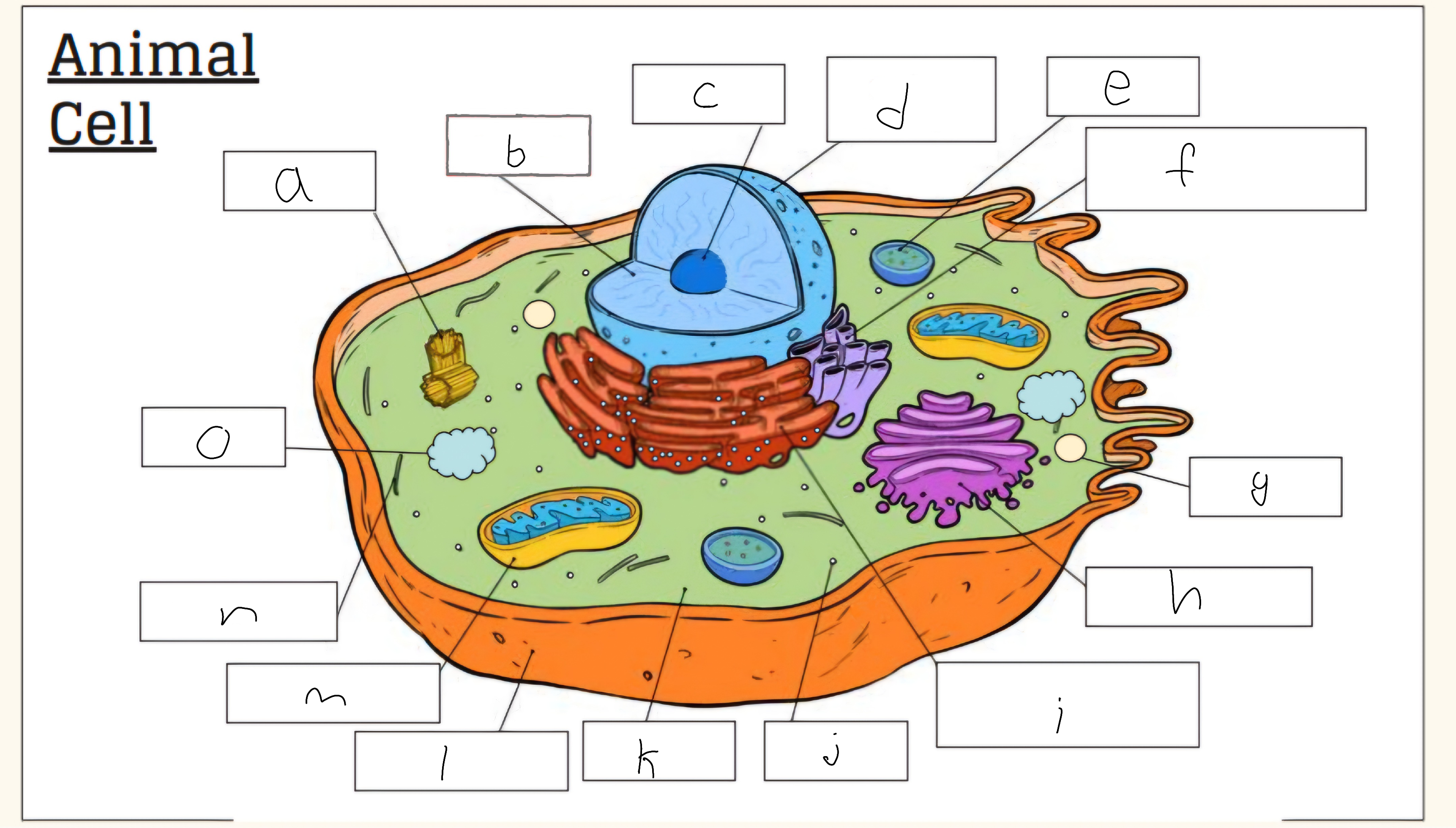
h
Golgi apparatus
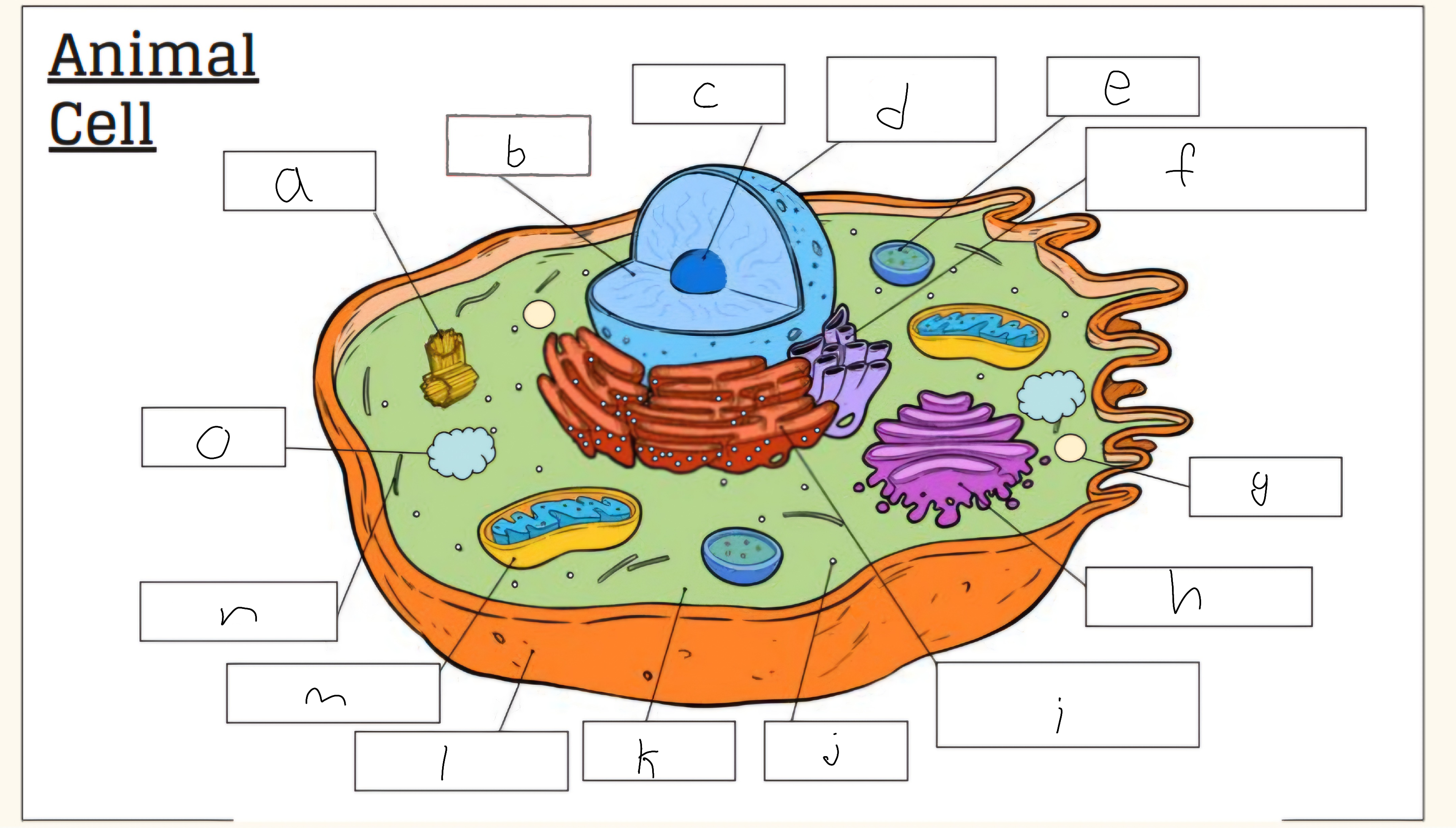
i
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
j
Cytoplasm
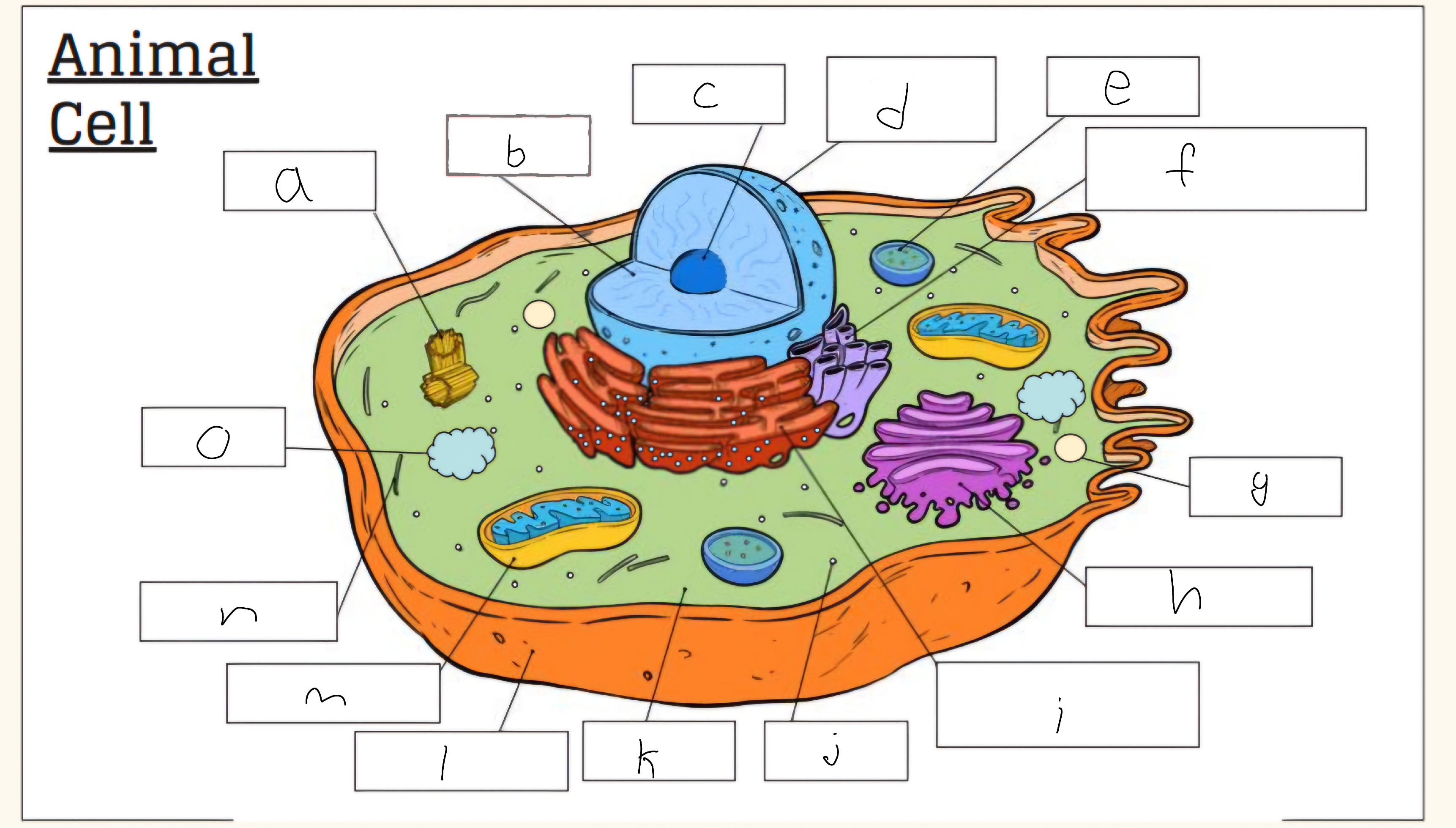
l
Cell membrane
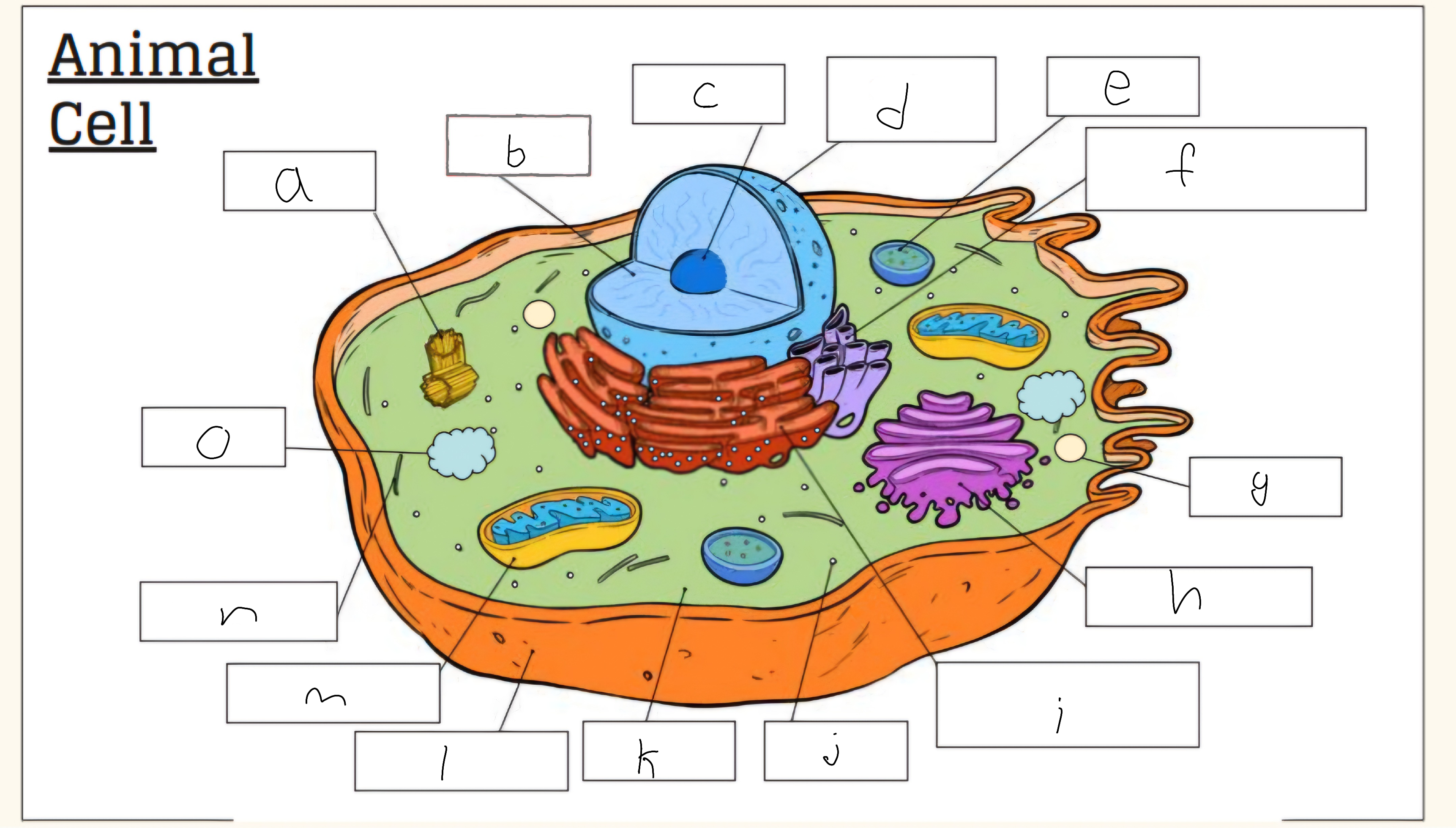
m
Mitochondria
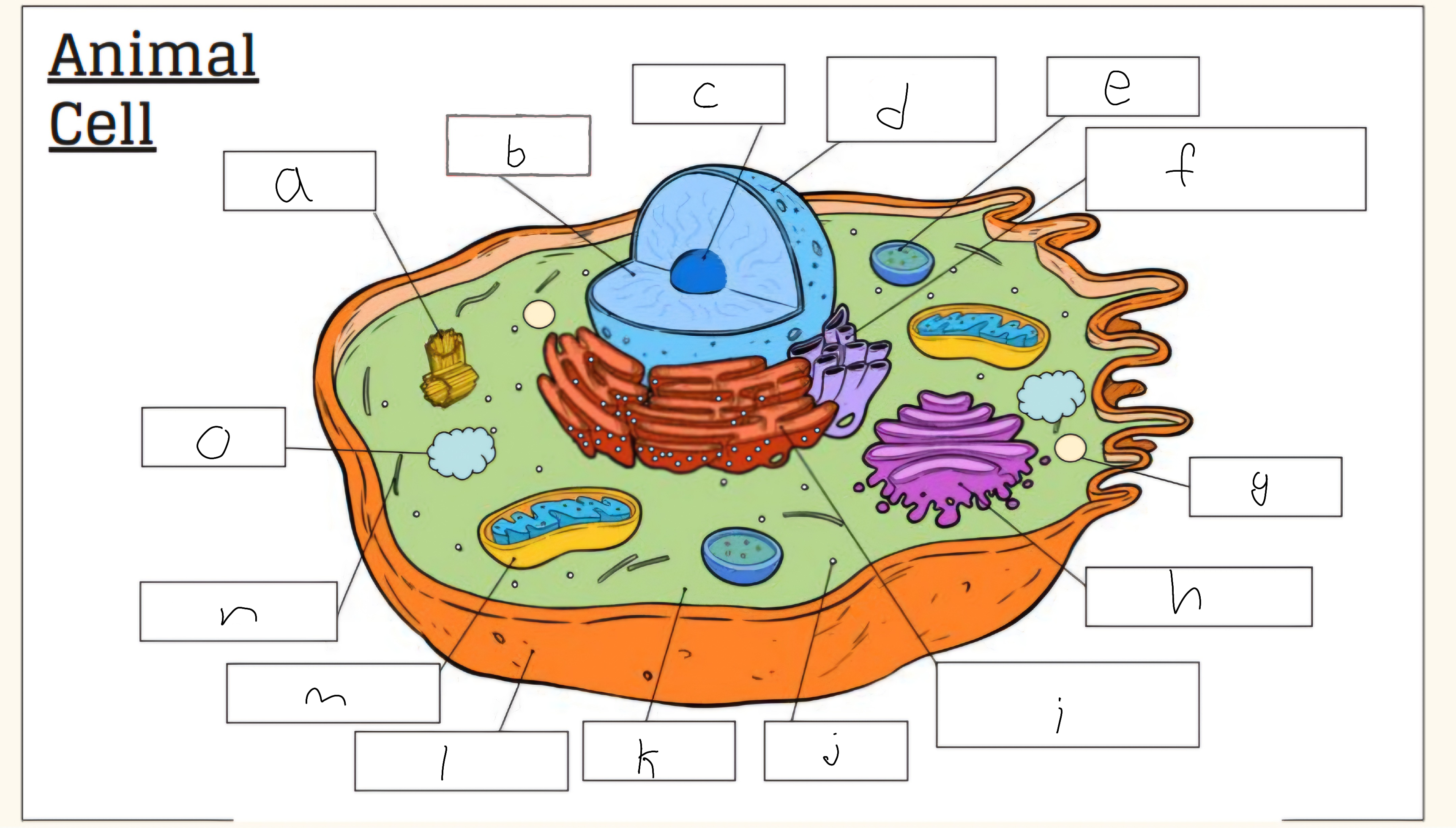
o
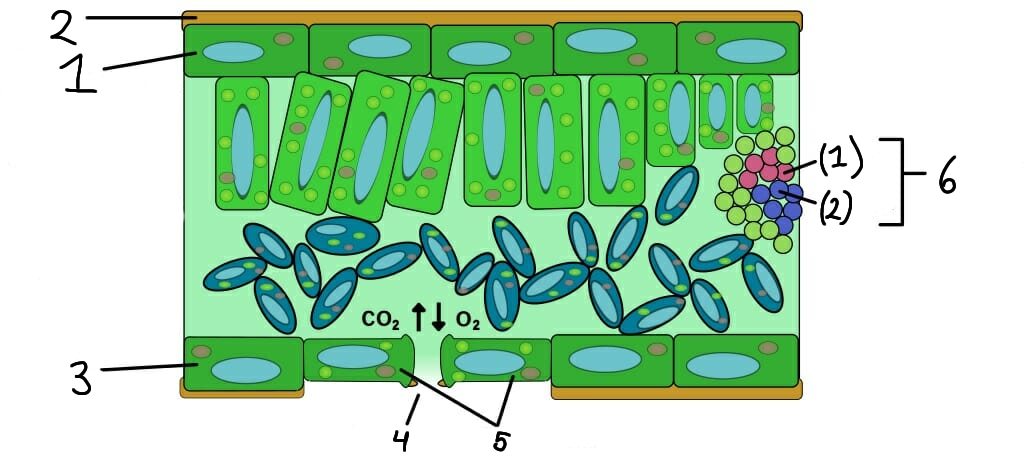
1
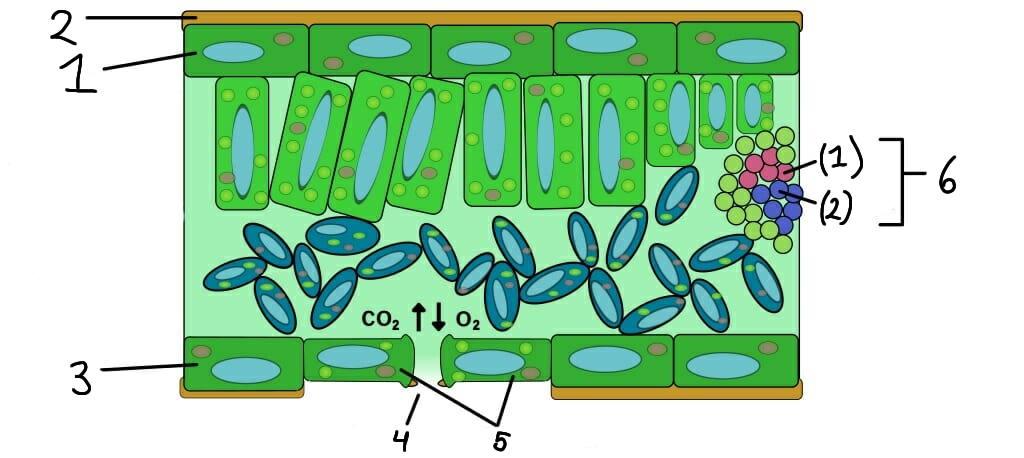
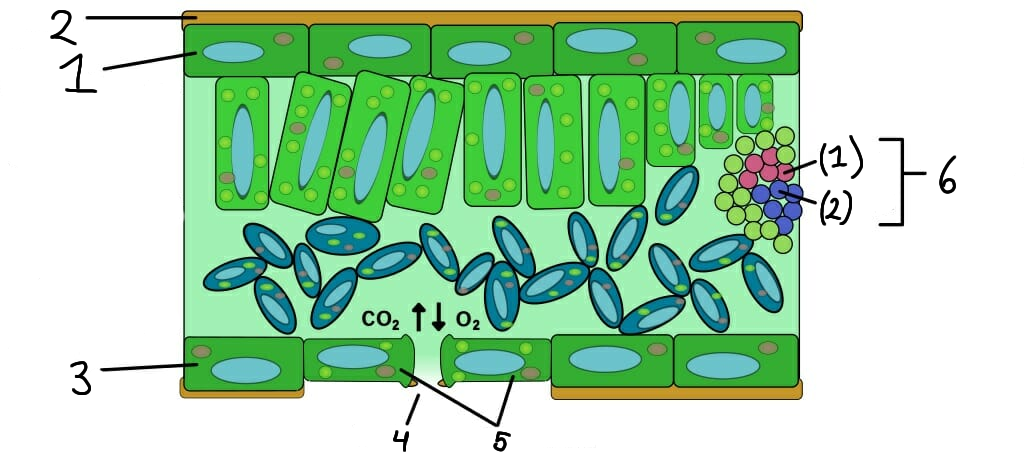
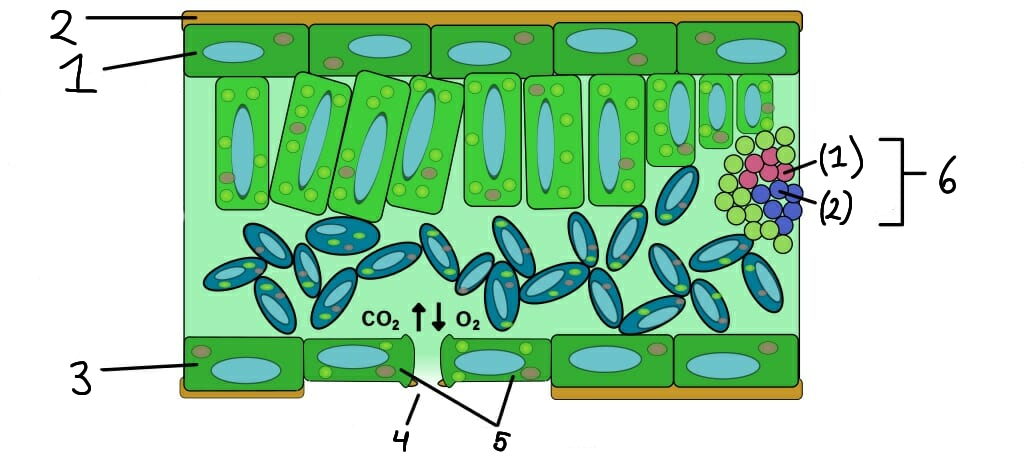
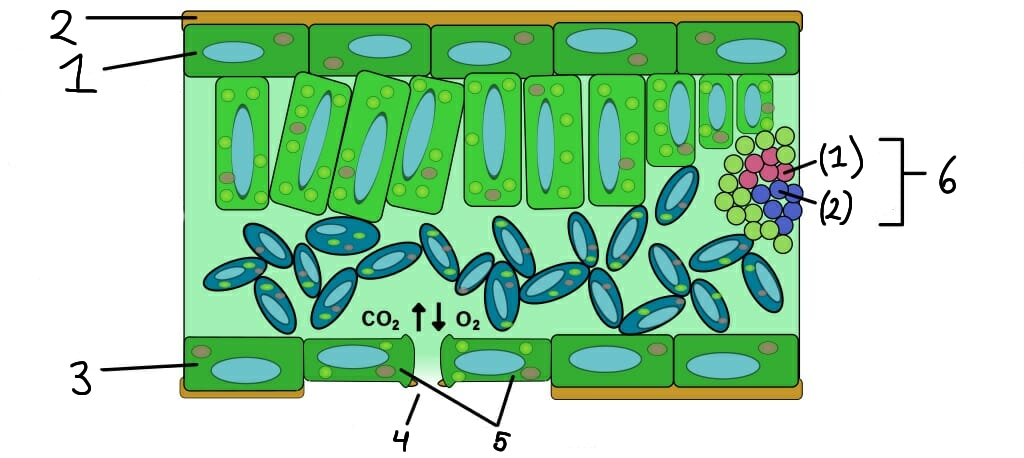
Upper epidermis
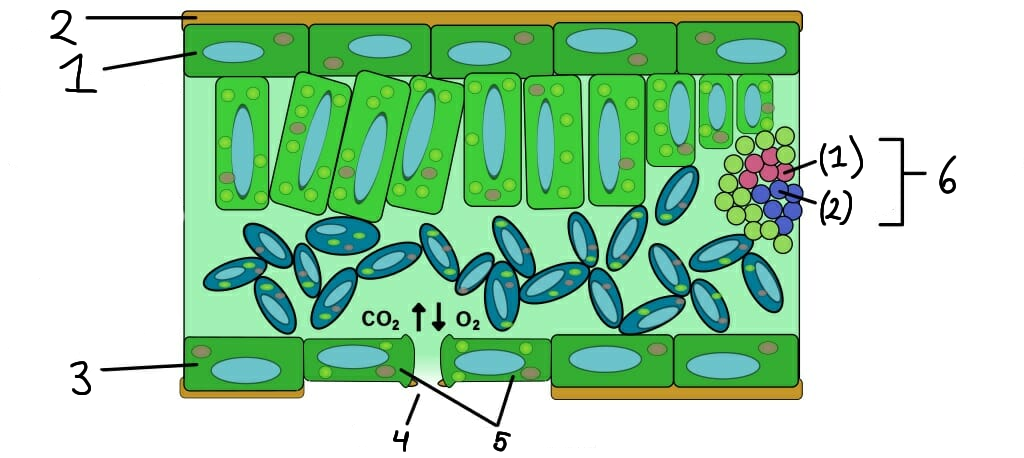
2
Cuticle
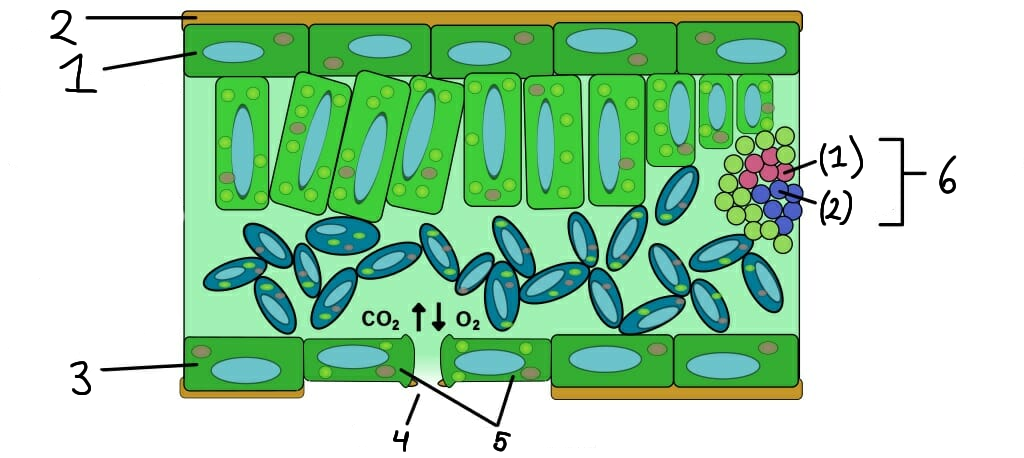
3
Lower epidermis
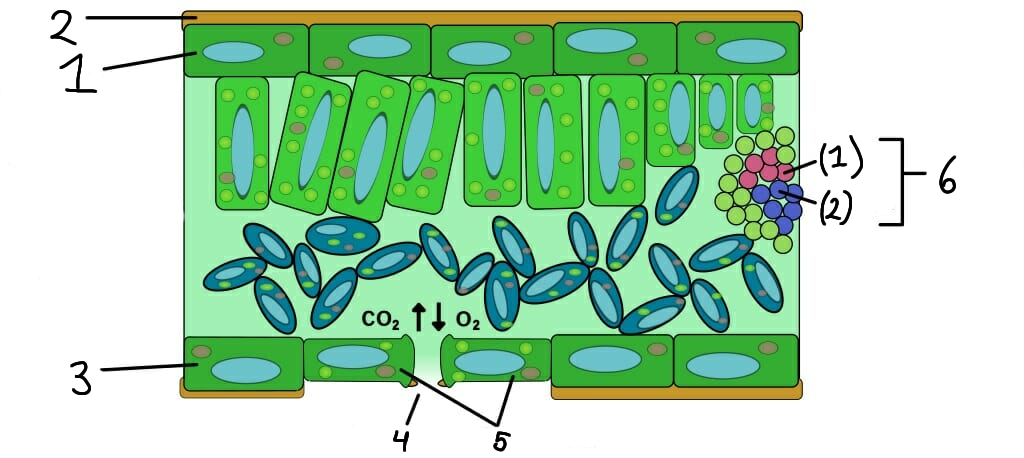
4
Stomata
5
Guard cells
6
Vascular bundle
(1)
Xylem
(2)
Phloem
What are climate graphs?
Climate graphs visually represent the average monthly temperature and precipitation of a location, helping to understand its climate pattern.
What is climate?
Climate refers to the long-term average of weather patterns in a particular area, including temperature, humidity, and precipitation.
What does a climate graph typically show?
A climate graph displays average monthly temperature and precipitation for a specific location.
What are biomes?
Biomes are large areas on the Earth’s surface that each have defining characteristics.
How do climate and biomes relate?
Climate influences the types of biomes that can exist in a region, as different organisms thrive under specific climate conditions.
What is an example of a biome characterized by high temperature and rainfall?
The tropical rainforest biome
What are the key biomes we need to know?
Tundra, desert, tropical rainforest, grasslands, deciduous forest, taiga,
What are the characteristics of the tundra biome?
Low temperature, low precipitation but highest in july-september
What are characteristics of the taiga biome?
Mostly low temperature, but increases significantly in the summer months. Varying precipitation
What are characteristics of the deciduous forest biome?
High and even precipitation, varying temperatures
What are characteristics of the grassland biome?
Low precipitation and temperature during the middle of the year
What are characteristics of the desert biome?
Very low precipitation, high temperature
What are characteristics of the tropical rainforest biome?
Very high precipitation, high temperature
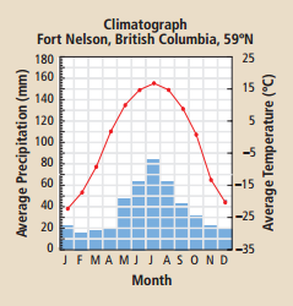
Which biome does this graph represent?
Taiga
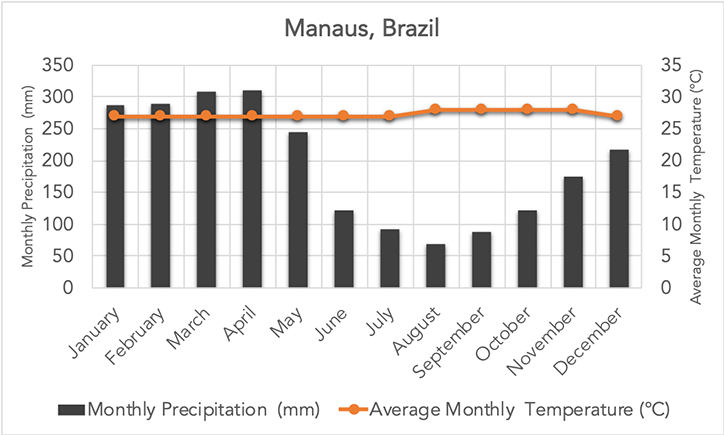
Which biome does this graph represent?
Rainforest
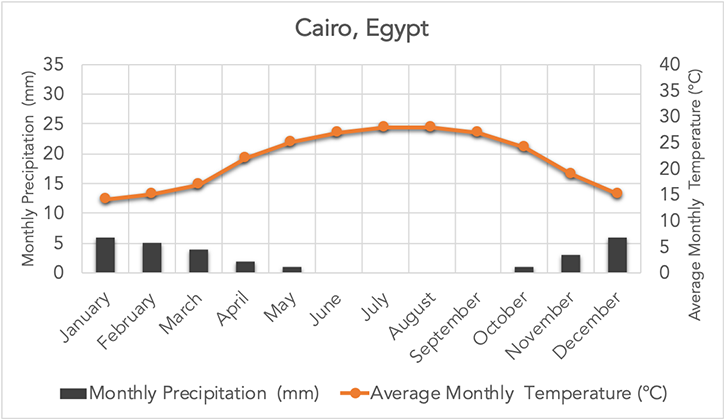
Which biome does this graph represent?
Desert
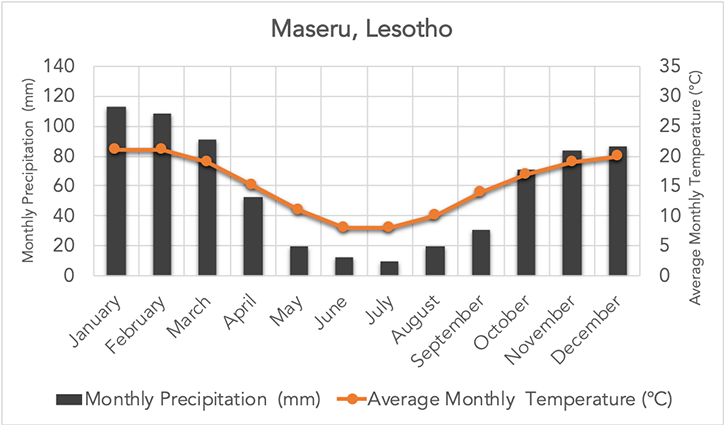
Which biome does this graph represent?
Grasslands
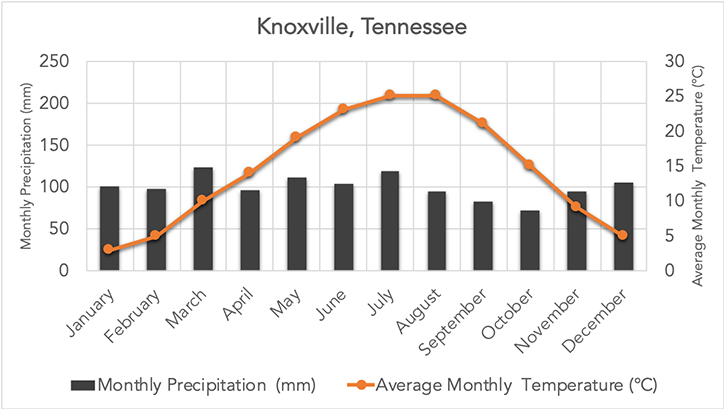
Which biome does this graph represent?
Deciduous forest
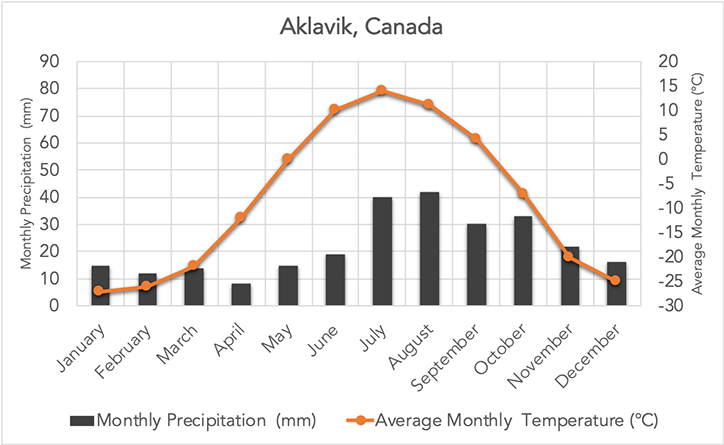
Which biome does this graph represent?
Tundra
What is the biosphere?
Thin layer of the earth that has conditions to support life
What are the three zones of the biosphere?
Atmosphere, lithosphere, hydrosphere
Describe the atmosphere
'air’ composed of gases: mainly nitrogen, less so oxygen, and a small amount of other gases.
Describe the lithosphere
'land’ solid, life is found up to 100km below the surface
Describe the hydrosphere
All water on earth. Mostly salt water, small amount of fresh water. The amount of water on earth always remains the same
Organisms found in the tundra
Polar bears, wolves, moss
Organisms found in the taiga
Moose, bears, coniferous trees
Organisms found in the deciduous forest
Deciduous trees, black bears, skunks
Organisms found in the grasslands
Buffalo, snakes, grass
Organisms found in the rainforest
Gorillas, frogs, vines
Organisms found in the desert
Camels, ostriches, cacti
What are the basic parts of a plant?
The basic parts of a plant are the roots, stem, and leaves.
What is the primary function of the roots?
The roots anchor the plant and absorb water and nutrients from the soil.
What is the role of the stem in a plant?
The stem supports the plant and transports water, nutrients, and sugars between roots and leaves.
What are leaves primarily responsible for?
Leaves are responsible for photosynthesis and gas exchange.
What is xylem?
Xylem is the tissue responsible for transporting water and dissolved minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant.
What is phloem?
Phloem is the tissue responsible for transporting sugars and nutrients produced during photosynthesis from the leaves to other parts of the plant.
What is turgor pressure?
Turgor pressure is the pressure of water inside the plant cells that helps maintain the plant's structure and rigidity. Helps water move against gravity
What role do stomata serve in plants?
Stomata are small openings on the leaf surface that allow for gas exchange (CO2 in and O2 out) and transpiration.
What is transpiration in plants?
Transpiration is the process of water vapor loss from the plant, primarily through stomata.
What are guard cells?
Guard cells are specialized cells that control the opening and closing of stomata, regulating gas exchange and water loss.
What is the function of the epidermis in plants?
The epidermis is the outer layer of cells that protects the plant and helps reduce water loss.
How does water movement occur in plants?
Water moves upward from roots to leaves through xylem via cohesion and adhesion.
How do nutrients move in plants?
Nutrients move through the phloem from leaves (where they’re produced) to other parts of the plant.
What is the relationship between transpiration and nutrient uptake?
Transpiration creates a negative pressure that helps draw water (and nutrients) upward from the roots through xylem.
What effect does turgor pressure have on plant health?
Adequate turgor pressure keeps plants firm and upright; low turgor can lead to wilting.
How do xylem and phloem work together?
Xylem and phloem work together to transport water, nutrients, and sugars, maintaining plant health and growth.
How does the structure of guard cells facilitate their function?
Guard cells change shape to open or close stomata by swelling with water or losing water.
What adaptations do plants have to minimize water loss through stomata?
Plants may develop fewer or smaller stomata, or have hairy leaves to reduce water loss.
What is cohesion?
The attraction of water molecules to other water molecules
What is adhesion
The attraction of water molecules to molecules from other substances
What is photosynthesis?
The process of a plant using oxygen, water, and sunlight to create glucose
What is cellular respiration
Occurs in both animals and plants, but significantly less in plants. Uses the created glucose and oxygen to create carbon dioxide so it can survive
What is the equation for temperature change? What does each variable represent?
Q=mc∆T Q= energy m= mass c= heat capacity ∆T= change in temperature
What is the equation for phase change? What does each variable represent?
Q=nH(fus) or Q=nH(vap) Q= energy n= amount in moles H= heat capacity
What is the difference between Q=nH(fus) and Q=nH(vap)
(Fus) is used when melting or freezing occurs, (vap) is used when evaporation or condensation occurs. The heat capacity is different
How do you combine temperature and phase change?
Add up the amount of energy determined in both equations
What is the unit of energy in the equations Q=mc∆T and Q=nH(fus) or Q=nH(vap)?
The unit of energy is joules (J).
Which equation would you use for boiling water?
You would use Q=nH(vap) for boiling water as it involves vaporization.
First
Aristotle
Second
Hooke
Third
Redi
Fourth
Brown
Fifth
Schwann and shleiden
Sixth
Pasteur
What did hooke do?
Coined the term ‘cellulae’ after looking at a cork under a microscope and seeing empty spaces
What did redi do?
Proved maggots did not come from meat, disproved spontaneous generation
What did pasteur do?
Further disproved abiogeneration through a broth experiment