Membrane Potentials part 1
1/70
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Membrane Properties, Transport Mechanisms
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
What is the General Properties of Cell Membranes?
Cell membranes are WALLS, Major lipid component: Phospholipids
What is the function of Major lipid component: Phospholipids?
only allow small, noncharge things to easily cross (gases”ghost example”: O2, CO2), lipid soluble molecules(SMALL)
Can Phospholipid bilayers be charged?
No, because they are a great wall like “brick”
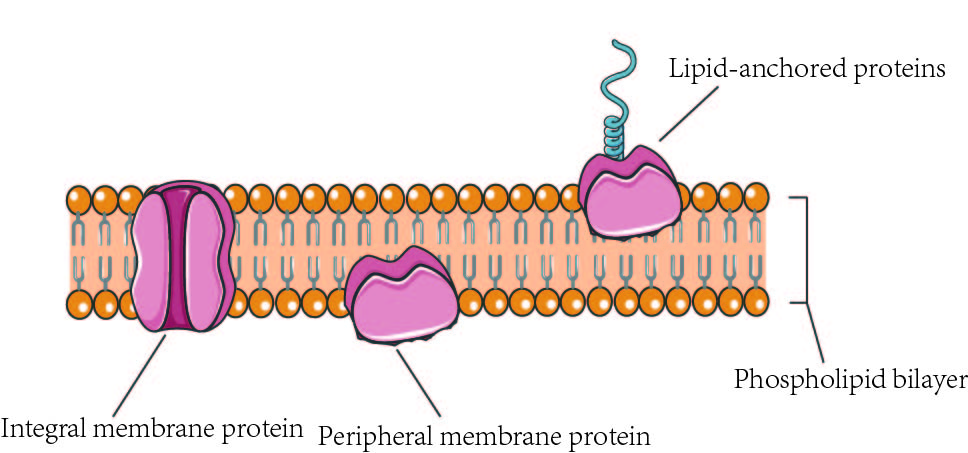
Membrane Proteins Provide Functions to Membranes in what two primary ways?
Spanning/ Transmembrane
Peripheral
Membrane Proteins Provide Functions to Membranes by?
the two primary ways
“Fluid” behavior bc they move laterally
anchored to PL (phospholipid bilayer)
anchored to other membrane proteins
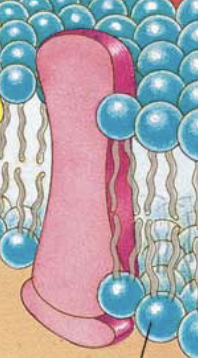
What is this called? & the Function of it
Spanning Membrane Protein & give a job to the membrane (ex: door/window) and also go through both lipid bilayer
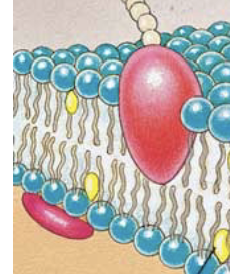
What is this called? & the Function of it
Two types of Peripheral Membrane Proteins (one leaflet)
T/F phospholipids move horizontally?
False, Laterally.
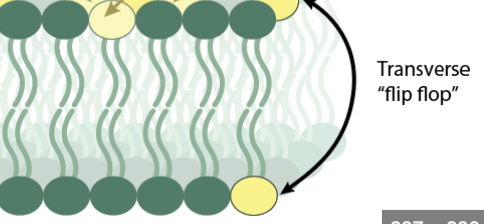
T/F: This is rare
True it is rare for this flip to happen because its energetically unfavorable
How many Membrane Protein functions are there?
5
4
7
5
What are the Names of the Membrane Proteins?
Ion Channels
Transporters
Adhesion/Anchors
Receptors
Enzymes
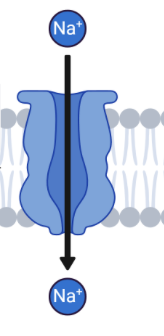
What do Ion Channels do?
Allow ion movement across membrane (ex: Na+, K+)
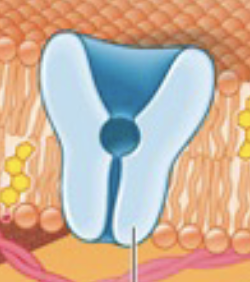
What do Transporters do?
Move ions, larger molecules (ex: glucose) and sometimes need energy
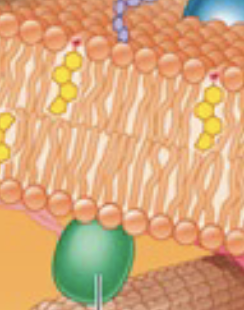
What do Adhesion/Anchors do?
Allow cells to stick to each other or force for transfer
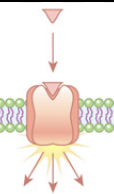
What do Receptors do?
*on cell* bind to signal molecule (ex: hormone, drug)
What do Enzymes do?
Catalyze(move ions w/ATP) chemical reactions (ex: move, digest something)
For a real cell, which of the following can cross cell membranes?
a. Gases such as CO 2
b. Water
c. Ions, such as K +
d. Lipid soluble molecules
e. ALL of the above should be able to cross the plasma membrane
a. Gases such as CO 2
What is Flux?
a Current in unassisted transport
What is Net flux?
Driven by concentration gradient and as it heats up is moves faster in unassisted transport
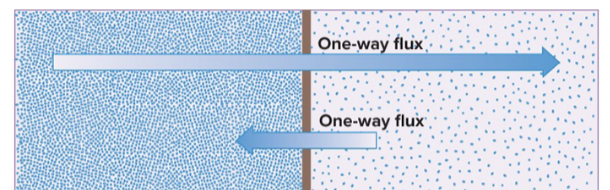
What is a one-way flux? Explain
Driven by concentration gradient and a small flux is still a flux in unassisted transport

What is Net flux gradient? Explain
Drive by concentration gradient and is the summation of flux in unassisted transport
What is Unassisted Transport?
Does NOT require a membrane protein to move the item, typically used by very small molecules non-polar molecules, gases, driven by gradients, passive
What is, NOT require a membrane protein to move the item, also known as? Also what is the idea of it?
Simple Diffusion and it is a region that goes from high to low concentration
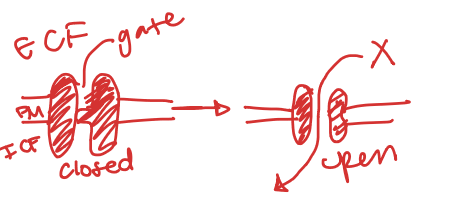
Describe a Ion Channel in terms of a Assisted Membrane Transport?
Specific
Moves charge ions across membrane
Channels are usually ion-specific
Create a water-filled pore
Do not change their shape while moving item
Uses Concentration Gradient Passively
Can exhibit GATING (door)
T/F, A Ion Channel can exhibit gating (door)
True
T/F, A Ion Channel uses concentration gradient actively
False, it uses concentration gradient passively
T/F, A Ion Channel cannot change their shape while moving item
True, they cannot change their shape while moving item
T/F, A Ion Channel is not specific
False, it is specific
T/F, A Ion Channel cannot move charge ions across the membrane
False, it can move charge ions across the membrane
T/F, A Ion Channel creates a water-filled pore
True it does create a water-filled pore
Ion Channel Gates
Open and Closed Gate
Explain an Assisted Membrane (carrier) Transport
Takes conformation
Binds
Carrier Changes Shape
Glucose gets released into interior of cell
REPEAT
Notes: Protein transporter changes shape
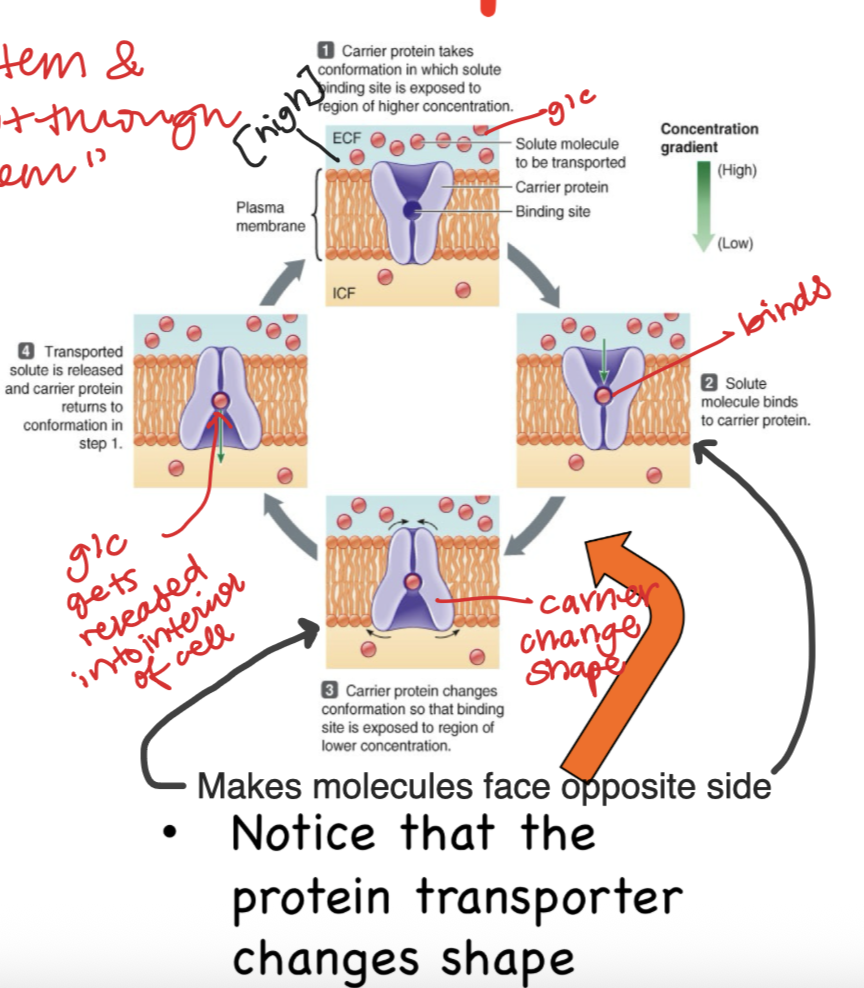
Carrier/Transporter
Contains speific binding sites for transported substance
Carrier changes shape as it transports the item
Uses Gradients—> Passive
Called facilitated Diffusion
A Carrier/Transporter contains ____ binding sites for ____ substance
specific, transported
A Carrier/Transporter carrier _____ shape as it ____ the item
changes, transports
A Carrier/Transporter uses ___ passively
gradients
A Carrier/Transporter is called a _____ diffusion
facilitated
A facilitated diffusion moves ___ molecules
big
A Carrier/Transporter takes _____ of a ______
advantage, gradient
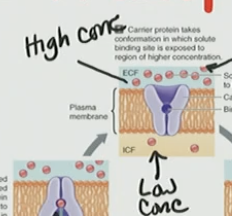
![<p>There is a [High] in ECF of a carrier and [Low] in ICF</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e2ab1d3b-f995-4cde-a9ed-746338ee4163.png)
There is a [High] in ECF of a carrier and [Low] in ICF
Ex: Glucose
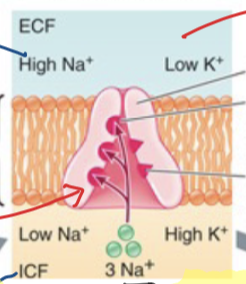
Primary Active Transport
always directly uses ATP—> ADP+Pi + energy
Na+/K+ ATPase transports 3Na+ out of cell & 2H+ into cell
Transporting both against concentration gradient
T/F the Primary Active Transport sometimes directly uses ATP—> ADP+Pi + energy
False, it always directly uses ATP—> ADP+Pi + energy
T/F: Na+/K+ ATPase transports 5Na+ out cell, 3K+ into cell
False, Na+/K+ ATPase transports 3Na+ out of the cell and 2K+ into cell as well as 1 ATP
T/F: there is [high] of Na+ outside (ECF) and [low] K+ outside (ECF)
True there is [high] of Na+ outside (ECF) and [low] K+ outside (ECF)
T/F: There is [high] of Na+ inside (ICF) and [low] of K+ inside (ICF)
False, there is a [low] of Na+ inside and a [high] of K+ inside
T/F: Does the Na+/K+ ATPase control the extracellular fluid [ ] of Na+
False, it does not
Secondary Active Transport
Na= flows into cell—> energy released
COUPLED w/transport at another item
Na+ moving w/[gradient] established by Na+/K+ pump → drives the transport of glc against its concentration gradient
![<ul><li><p>Na= flows into cell—> energy released</p></li><li><p>COUPLED w/transport at another item</p></li><li><p>Na+ moving w/[gradient] established by Na+/K+ pump → drives the transport of glc against its concentration gradient</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/135ece2a-7579-419e-bb6b-b36f6434e370.png)
Na+/K+ ATPase is part of Primary or Secondary Active Transport?
Primary Active Transport
Does Primary or Secondary Active Transport use ATP?
Primary Active Transport
There is a utilization of concentration gradient in Primary or Secondary Active Transport?
Both:
Primary Active Transport: uses energy like ATP to move molecules against their concentration gradient
Secondary Active Transport: uses energy stored in the electrochemical gradient created by primary active transport to move other molecules against their [ ] gradient
Na+/K+ ATPase _____ the concentration of ions inside of the cell
establishes
actively transporting Na+ and K+ ions against their [gradients]
In terms of the Secondary Active Transport: Na+ wants to flow into cell because of the ___(high/low) concentration ___ (outside/inside) since ___ (#) Na+ flow out and ___ (#) K+ flow in
low, inside, 3, 2
Membrane Potential implies that theres a voltage _____ between the extracellular fluid and the intracellular fluid
difference
bc there is a different in electrical charge between the inside and outside of a cell
T/F: the cell recycles/tosses the cells when they die
False, that would be energetically unfavorable because they actually regenerate the cells with energy
Electromotive Force (EMF) ____ a electrical current
drives
T/F: If the voltage goes to zero there is no current
True If the voltage goes to zero there is current
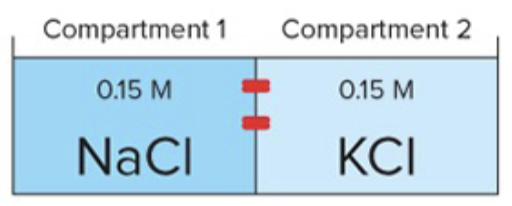
Two chambers are separated by a membrane permeable only to Na+. Which of the following will occur? Explain.
a) Na + flows from right to left
b) As Na + flows, a negative charge builds up in the left chamber
c) Cl - flows in the same direction as Na +
d) Na + flows until its concentration is IDENTICAL in both chambers
e) As Na + flows from Chamber 1 to 2, K + flows from 2 to 1
b) As Na + flows, a negative charge builds up in the left chamber, this occurs because this channel is only permeable to Na+ not Cl- or K+ ONLY Na+ so therefore only Na+ can go out which is from left to right and it leaves Cl- behind so that leaves a negative charge in compartment 1 (left)
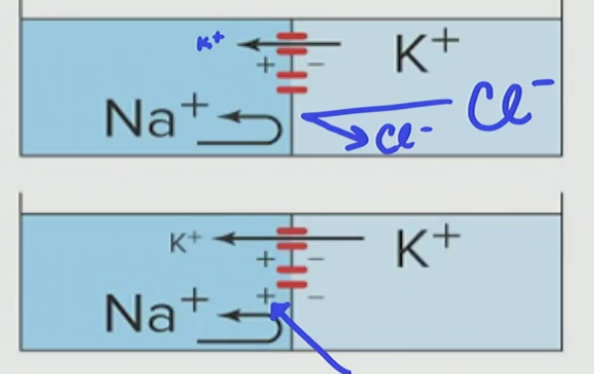
What kind of gradient is this?
Concentration gradient
How do you generate an electrical motive force?
voltage membrane potential in real cells by getting ion flux to occur, that’s how its established
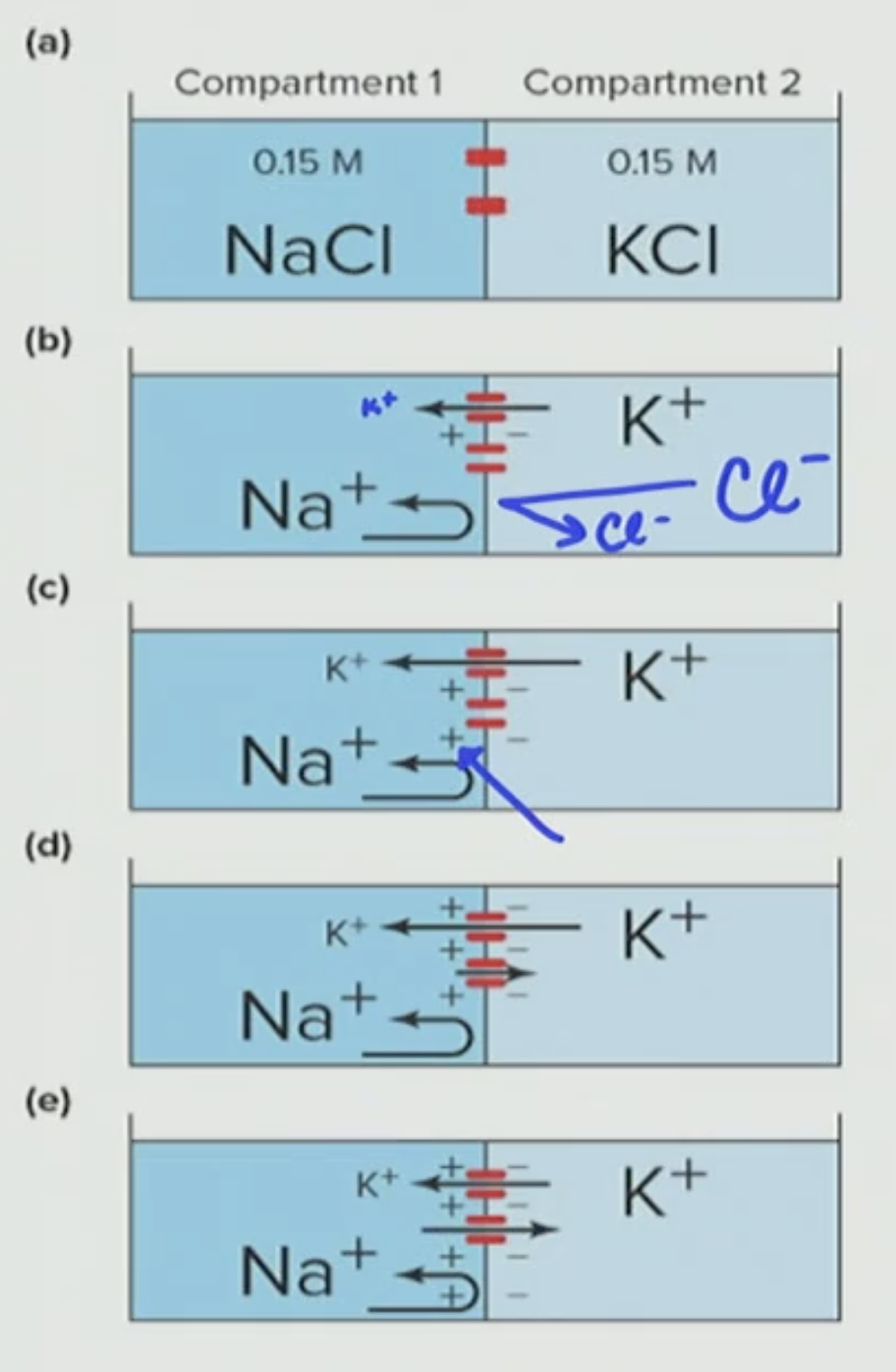
Explain this Concentration Gradient
First K+ flows to chamber #1 down its concentration gradient
As K+ flows, a positive charge builds up in chamber #1
Then a positive charge in Chamber #1 is strong enough that it repels K+ flux from Chamber #2—>Chamber #1
So it then becomes balanced (equal in magnitude) and generates an electrical motive force
When Equilibrium is reached forces are ____.
balanced
When Equilibrium is reached F___= F___
conc, elec; (Concentration gradient is equal in magnitude due to the force cause by the electrical gradient )
T/F: The Concentration gradient equals the electrical gradient when equilibrium is reached?
True, the Concentration gradient equals the electrical gradient when equilibrium is reached
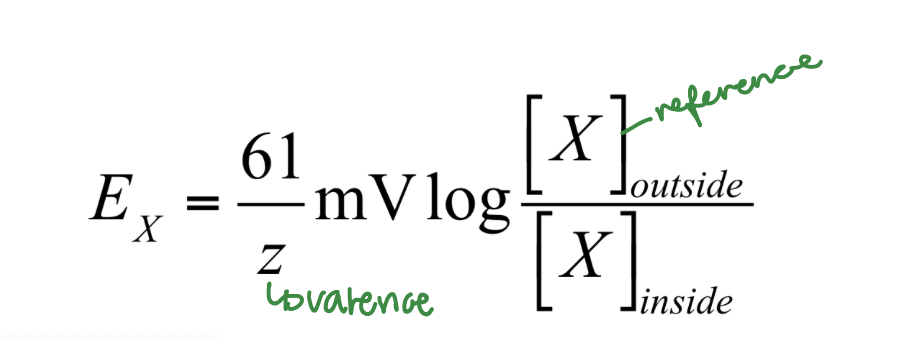
What equation is this?
The Nernst Equation
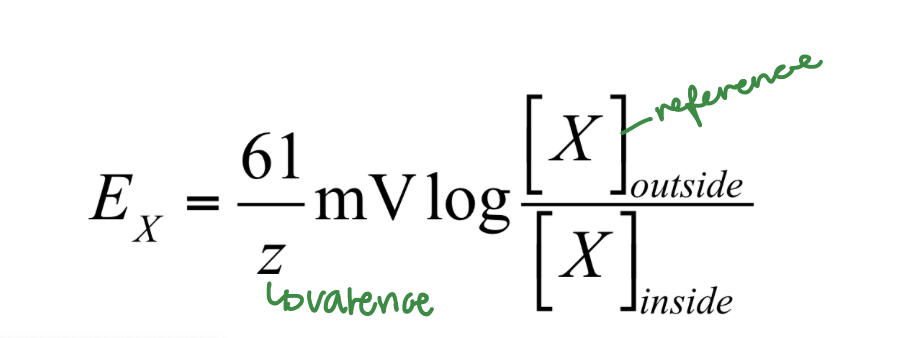
The Nernst Equation predicts the ____ at equilibrium.
potential
Permeability is how ___ it is for an ion to cross
easy
T/F: In living cells, ions are unequally distributed
True, in living cells ions are unequally distributed, this can be due to selective permeability
T/F: the membrane does not exhibit differences in ion permeability in Living Cells?
False, in living cells the membrane does exhibit differences in ion permeability
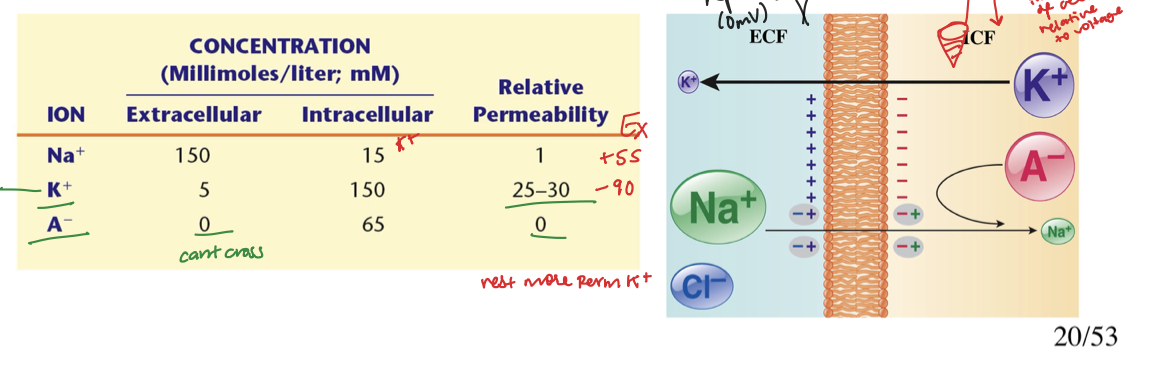
T/F: The interior of a Living cell is more electronegative?
True, the interior of a living cell is more electronegative, this can be because of unequal distribution of ions
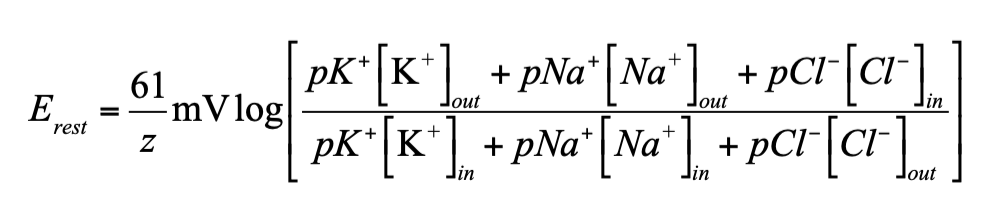
What equation is this?
the GHK (Goldman-Hodgkin-Katz) equation
What does the GHK equation calculate?
The GHK equation calculates the resting membrane potential of real cells