Knee Anatomy Biomechanics
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What are the functions of the LCL?
Checks varus stress of knee.
Limits ER of tibia (OKC)
Limits IR of femur (CKC)
What are the functions of the MCL?
Checks valgus stress at full extension and 25° extension and anterior translation
When is the anterior and posterior bundle of the ACL taut?
Anterior: taut through flexion
Posterior: taut in extension to 20* of flexion
Lachman test is more posterior bundle
Anterior drawer is more anterior bundle
Why is open chain movements not favored over closed chain movements for ACL rehab, especially in the first 6-8 weeks?
40°-0° of resisted knee extension puts largest strain on ACL
When is the anterior lateral and posterior medial bundles of the PCL taut?
Anterior lateral: taut in flexion
Posterior medial: taut in extension
When is the PCL as a whole most taut?
Full knee flexion
Which parts of the meniscus is considered the “red zone” and which is considered the “white zone?” Why is it called this?
Red zone (lateral 1/3rd): good blood supply allows for better prognosis
White zone (medial 2/3rd): poor blood supple leads to poor healing
What part of the medial meniscus attaches to the ACL and PCL respectively?
Anterior horn of medial meniscus attaches to ACL
Posterior horn attaches to PCL
Explain the asymmetry of the femoral condyles.
Lateral condyle is more anterior
Medial condyle extends further inferiorly
Which side of the patella is the add facet located?
Medially, contact with full flexion
What is patella baja and alta?
Patella baja: lower than normal patella position
Patella alta: higher placement of patella than normal.
Less efficient mechanically.
Function of the IT band?
Assists ACL to prevent posterior displacement of femur on tibia in terminal extension
Additional connections to patella which adds lateral force to patella
High Q angle has a higher risk for what?
Lateral patellar subluxations
Increased Q angle will cause what things?
genu valgum
Increased femoral anteversion
external tibial torsion
Right lateral retinaculum
How does the tibia rotate during swing/stance phase of gait?
Tibia IR in swing phase
Tibia ER in stance phase
Explain the screw home mechanism of the tibia in OKC and CKC.
OKC: tibia laterally rotates on femur during extension
CKC: femur medially rotates on tibia during extension
What is the main stabilizer of the patella that prevents in from moving outwards?
Medial patellofemoral ligament (MPFL)
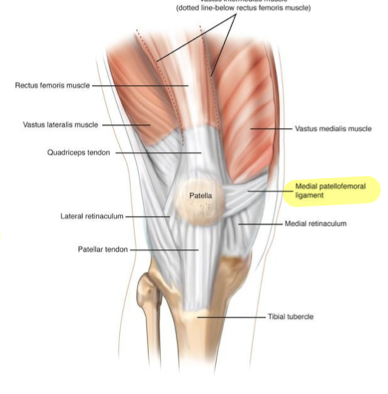
Where in knee ROM is the greatest area of contact between the patella and femur?
Between 90 and 60° of flexion
What is seen upon examination of a pt with quad tendon rupture?
Acute knee pain, swelling, palpable defect at location of tear
Loss of active extension and stability
Unable to perform SLR with varying degrees of extension of lag depending on size of tear
What is found upon exam of a pt with patellar fx?
Hematoma, edema, pain around involved area
Ottawa and Pittsburg Rules for determining appropriateness for radiographs
Tuning for test (significant pain)
What are the Ottawa and Pittsburg rules?

What would you see if a DVT is present?
Discoloration, warmth, swelling, and tenderness of the affected extremity