Combined LJM TBL 2
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
Which type of crystal is typically found in gout?
Monosodium urate crystals
Which type of crystal is typically found in pseudogout?
Calcium pyrophosphate crystals

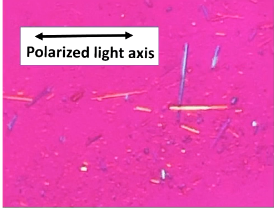
What is this
Positive birefringence
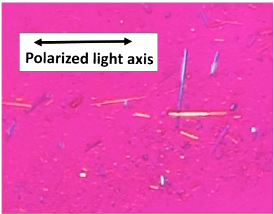
What is this
Negative Birefringence
What disease is this
Gout

What disease causes this
Pseudogout
What best describes a Grade 1 ligament sprain?
Mild stretching with microscopic tearing of fibers
Which of the following characterizes a Grade 2 ligament sprain?
Partial tear with some loss of function and moderate instability
How is a Grade 3 ligament sprain defined?
Complete tear resulting in joint instability and loss of function
Which of the following correctly lists components found in synovial fluid?
Hyaluronic acid, lubricin, water, proteinase, collagenase, prostaglandins
What best describes Grade 1 osteoarthritis?
Minor cartilage wear with possible osteophyte formation
Which describes Grade 2 osteoarthritis?
Moderate cartilage damage with definite joint space narrowing
What is characteristic of Grade 3 osteoarthritis?
Severe cartilage loss, joint space obliteration, and bone sclerosis
Which of the following best describes Grade 4 osteoarthritis?
Complete loss of cartilage with severe joint space narrowing and bone deformity
What is the primary function of a ligament?
Provides passive stabilisation to the joint
Which protein primarily composes ligaments?
Collagen
What is a sprain?
Injury to a band of collagen
What causes a ligament sprain or tear?
Joint movement outside its normal range
What describes a Grade I ligament injury?
Minor pull with microscopic tear
Which grade represents a complete ligament rupture?
Grade III
What does Grade II ligament injury indicate?
Partial tear of ligament fibres
Which structure produces synovial fluid?
Synovial membrane
Which of the following is NOT found in synovial fluid?
Clotting factors
What is one major role of synovial fluid?
Lubricating the articular surface
What typically triggers the onset of osteoarthritis?
Damage to the articular surface
Which process increases water in cartilage during OA?
Matrix disruption
What is the result of increased water content in cartilage?
Softened cartilage with loss of mechanical properties
What type of mediators worsen articular damage in OA?
Inflammatory mediators
What is the primary source of nutrients for articular cartilage?
Synovial fluid
What defines Grade 4 osteoarthritis?
Complete loss of articular surface
Which OA grade is characterized by more than 50% cartilage loss?
Grade 3
What is the earliest sign of OA on arthroscopy?
Softened cartilage
What is the primary goal of joint replacement?
Relieve pain and improve function
When should joint replacement be considered?
After failure of conservative measures
What is a common but usually non-serious surgical complication?
Wound healing delay
What is a serious risk associated with joint replacement surgery?
Deep infection
What is a potential vascular complication of surgery?
Deep vein thrombosis
What part is often replaced with metal and plastic in knee surgery?
Articular surface
What is extensor mechanism failure?
Rupture of quadriceps-patellar mechanism
Which lifestyle change has been shown to improve OA symptoms significantly?
Weight loss
What does the WHO pain ladder begin with?
Paracetamol
Which pain medication must be used cautiously in elderly due to kidney risks?
NSAIDs
Which intra-articular injection is most commonly used for OA pain relief?
Corticosteroids and local anaesthetic
How does pelvic rotation function as a determinant of gait?
It increases step length by rotating the pelvis forward on the swinging side
How does the knee moving towards the midline act as a determinant of gait?
It helps maintain balance by reducing lateral displacement of the body during stance
What is the role of knee flexion as a determinant of gait?
It helps shorten the limb during swing phase to aid foot clearance
How does pelvic tilt on the swing side help minimize the rise in the center of gravity during gait?
By lowering the pelvis on the swing side to reduce vertical displacement
What characterizes a hemiplegic gait?
Circumduction of the affected leg with decreased arm swing on the same side
What best describes unilateral foot drop gait?
Difficulty raising the front part of the foot on the affected side, leading to exaggerated hip and knee flexion to clear the toes during swing
Which of the following best describes Parkinsonian gait?
Small, shuffling steps with reduced arm swing and a stooped posture
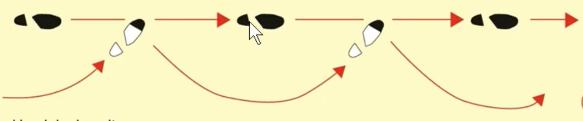
What kind of gait is this
Hemiplegic
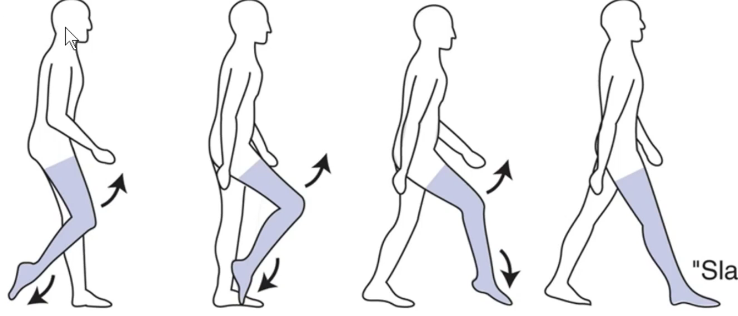
What kind of gait is this
Unilateral foot Drop

What kind of gait is this
Parkinsonian
Is there an aerial phase in gait in medicine
No
Which sequence correctly represents the 5 phases of the stance phase in the gait cycle?
Heel Strike → Foot Flat → Midstance → Heel Off → Toe Off
Which of the following correctly lists the 3 phases of the swing phase in the gait cycle?
Initial Swing → Midswing → Terminal Swing
Which of the following correctly lists the 3 primary muscle movements during the stance phase of gait?
Hip Extension → Knee Extension → Ankle Plantarflexion
Which of the following correctly lists the 3 primary muscle movements during the swing phase of gait?
Hip Flexion → Knee Flexion → Ankle Dorsiflexion
Which two muscle movements primarily control the lateral piston (side-to-side displacement) of the lower limbs on the trunk during gait?
Hip Abduction → Hip Adduction
What percentage of time is the stance phase time
60%
What percentage of time is the swing phase time
40%
What is the toe-out angle in gait analysis?
The angle between the line of progression and the long axis of the foot
What is the walking base in gait analysis?
The distance between the midpoints of the heels during two consecutive steps
What is stride length in gait analysis?
The distance between two successive placements of the same foot
Which of the following is the correct equation for power?
Power = Work ÷ Time
Which of the following is the correct equation for power in terms of force and velocity?
Power = Force × Velocity
Which of the following is the correct equation for stress?
Stress = Force ÷ Area
Which of the following are the three primary types of mechanical stress?
Tensile stress, compressive stress, shear stress
Which of the following is the correct equation for strain?
Strain = Change in length ÷ Original length
What is Ultimate Tensile Strength
The maximum stress a material can withstand before failure
What is extensibility as an ultimate material property?
The ability of a material to undergo significant deformation before failure
What is stiffness as an ultimate material property?
The resistance of a material to deformation under applied force
What is toughness as an ultimate material property?
The ability of a material to absorb energy before it breaks
What is the correct definition of mechanical stress in the context of deformable bodies?
Stress is the force applied to a material divided by the area supporting that force
In a biological system, why is calculating mechanical stress often challenging?
The magnitude of forces and the areas supporting them are highly variable
Which type of stress results from forces applied parallel to the supporting surface?
Shear stress
What does mechanical strain measure in a structure or tissue?
The change in dimension relative to the original dimension
Which of the following is NOT one of the four ultimate mechanical properties derived from stress-strain testing?
Flexibility
What does the slope of the stress-strain curve represent?
The stiffness or resistance to deformation of the material
In stress-strain experiments, what does the area under the curve represent?
Mechanical toughness
Why are dynamic imaging techniques like MRI significant in biomechanical studies?
They allow non-invasive observation of tissue deformation
What mechanical stress is involved when muscles like the quadriceps pull on tendons during knee extension?
Tensile stress
What is the primary external force acting on the musculoskeletal system according to the lecture?
Gravity
What characterizes a perfectly linear elastic solid in biomechanical testing?
A constant ratio of stress to strain up to failure
In the knee joint example, what combination of stresses may be present at the femur-tibia contact during motion?
Compression and shear
Which ultimate property is defined as the maximum strain a material can endure before failure?
Extensibility
What is the purpose of repeated loading and unloading experiments on biological tissues?
To simulate and study long-term mechanical performance
What does a high stiffness value indicate about a tissue’s mechanical behavior?
It resists deformation and requires large stress to stretch