Biology - Energy Transfer - Topic 11 & 12
1/12
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Outline the Light Dependent Reaction
Chlorophyll absorbs light and electrons become excited
Electron transport chain accepts excited electrons and they move down chain releasing energy
Photolysis of water occurs, producing electrons, protons and oxygen
Energy is used to pump protons from stroma to thylakoid membrane
H+ ions to facilitated diffuse through ATP synthase, causing it to catalyse ADP + Pi, forming ATP
Electrons reduce NADP forming NADPH
Describe the role of electron transport chains in LDR (6)
Electron transport chains accept excited electrons from chlorophyll
Electrons move down electron transport chain releasing energy
Energy is used to pump H+ from stroma to thylakoid membrane
Allows H+ ions to facilitatedly diffuse through ATP synthase which catalyses ADP+Pi forming ATP
Electrons reduce NADP to NADPH
Outline the Light Independent Reaction
CO2 combines with RuBP, catalysed by rubisco
forms GP
GP reduced by NADPH using energy from ATP
forming triose phosphate
1/6 triose phosphate forms hexose sugar
5/6 triose phosphate forms RuBP using ATP so all RuBP is reformed
One of the products produced from TP is hexose sugars. Give two uses for hexose sugars in plant cells. (2)
cellulose strengthens cell walls
respiration for ATP
conversion of starch for storage
Outline glycolysis
(1st stage of respiration, in cytoplasm)
Glucose is phosphorylated using 2 ATP
unstable intermediate forms, then splits into 2 triose phosphate
triose phosphate is phosphorylated then dephosphorylated
2 ATP form per triose phosphate, 4 per glucose
triose phosphate is oxidised, forming reduced NAD and pyruvate
what is the end result of glycolysis
net gain of 2 ATP
2 pyruvate
2 reduced NAD
Outline the Link Reaction
(in matrix)
pyruvate is oxidised forming acetate and releasing CO2
NAD is reduced forming reduced NAD
coenzyme A combines with acetate forming acetyl coenzyme A
Outline Krebs Cycle
(matrix)
2C Acetyl CoA combines with 4C oxaloacetate making 6C citrate
citrate is dehydrogenated, reducing NAD to NADH & decarboxylated releasing CO2 forming 5C intermediate compound
5C is dephosphorylated making ATP, dehydrogenated forming 2 NADH and 1 FADH2 and decarboxylated releasing CO2 and forming 4C oxaloacetate
Outline Oxidative Phosphorylation
(inner mitochondrial membrane)
FADH2 and NADH are oxidised forming FAD and NAD, releasing H+ ions and electrons
ETC accept electrons and they release energy as they move down
Energy is used to pump H+ ions from matrix to intermembrane space
H+ ions facilitatedly diffuse down electrochemical gradient via ATP synthase which catalysed ADP+Pi to ATP
Oxygen is the final electron acceptor
Explain why oxygen is needed for the production of ATP on the cristae of the mitochondrion
oxygen oxidises NADH and FADH2
ATP is formed as electrons move down transport chains
oxygen is the final electron acceptor
Outline anaerobic respiration in mammals
(lactate fermentation)
glycolysis occurs
pyruvate is reduced by NADH from glycolysis forming lactate
NAD regenerates which allows glycolysis to continue
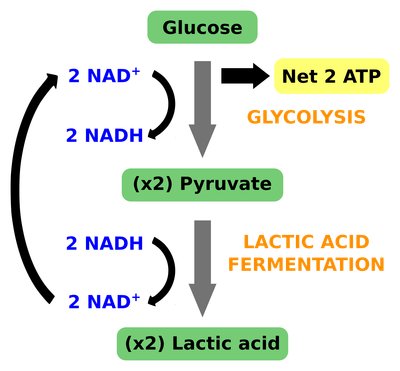
Outline anaerobic respiration in plant cells and yeast
(ethanol fermentation)
glycolysis occurs
pyruvate is decarboxylated, releasing CO2 and forming ethanal
ethanal is reduced by NADH from glycolysis forming ethanol
NAD regenerates which allows glycolysis to continue
Using a respirometer
oxygen diffuses into respiring maggots in aerobic respiration
CO2 produced and is absorbed by soda lime
this decreases volume and pressure so liquid moves left