Pregnancy
1/21
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
pregnancy
the time of development from conception to birth
how long is a pregnancy typically?
9 months
how long is each trimester typically?
3 months
how many trimesters are there in a pregnancy?
3 trimesters
what is the earliest the baby can be born prematurely and have a chance to live?
24 weeks, but they will need special medical care.
trimester 1 (weeks 1-12)
the mother and the baby experience lots of change. trimester 1 is the stage where miscarriages and birth defects are likely if the embryo is exposed to radiation, drugs, or alcohol.
week 5: a zygote has divided into a multicellular organism with a notochord (mesoderm), coelom (mesoderm), brain (ectoderm), spinal cord (ectoderm), limb buds, tail, and pharyngeal arches (that will eventually become the throat and middle ear — this cavity in your ear).
week 8: the embryo has developed all the basic parts to an actual human body. it has back and rib muscles. its limbs have fingers and toes. it can move its legs, arms, head, and make facial expressions
trimester 2 (weeks 13-26)
the fetus continues to develop and look more human. its eyes can open, teeth are forming, and the bones are hardening. the placenta releases progesterone to maintain the placenta. the corpus luteum is no longer needed to secrete the progesterone and degenerates.
week 14: the structures on the baby develop further, making the fetus look more like a human.
week 20: the baby now has eyebrows and eyelashes. the arms, legs, and fingers are all longer and have nails and some hair. they kick their mom. the mom’s belly is a lot more enlarged in this stage. the fetal position is seen in the baby since the space is little now in the mom.
trimester 3 (27-40)
the fetus is growing at a rapid pace now as it gets ready to be given birth to and exposed to the real world. the fetus squishes the mother’s organs causing an urge to pee a lot, digestive troubles, and back pain.
week 40: the newborn has its circulatory and respiratory systems develop to get ready to breathe in the air. the muscles thicken and the body hair is eliminated aside the head. the baby puts on weight and the head is down at the cervix.
typical size of baby
20 in/50 cm, 3-4kg/6-8 lb
labor
the process of giving birth to an infant in the uterus
what are the hormones involved in labor?
estrogen: a hormone at its highest levels in the last few weeks of pregnancy which is crucial to forming oxytocin receptors on the uterine cells.
oxytocin: a hormone released by the fetus as well as by the pituitary gland of the mother later in the pregnancy, allowing for the uterus to make coordinated contractions for labor
prostaglandins: chemicals that is made in the placenta stimulated by oxytocin to make the uterine muscles contract even more
induction of labor
the starting of labor using artificial means using positive feedback (a change that triggers an amplification of something)
may give the mom oxytocin and prostaglandins that will in turn lead to uterine contractions that will stimulate more of those hormones, that will allow the mom to push the baby out the uterus
the 3 stages of labor
Dilation: the cervix expands to about 10 cm in width. this is 6-12 hours, the longest stage.
Expulsion: the uterine contractions are strong at a frequency of every few minutes, giving the mother the feeling of wanting to push. after some time, the baby is pushed out. The umbilical cord is clamped to stop the blood flow from the placenta to the baby and is cut.
Delivering the Placenta
after pregnancy
progesterone and estrogen levels decreasing allow the uterus to return to how it was before the pregnancy.
as the baby sucks on the mother’s nipple and progesterone levels fall, the pituitary is stimulated to release prolactin and oxytocin, releasing milk (lactation) to the mammary glands (breastfeeding)
first few days colostrum is made with lots of protein and antibodies.
later on regular milk is made.
infertility
the inability to conceive
what problems may the male have that cause infertility?
low sperm count
defective sperm
impotence
solutions for male infertility
switch from briefs that hold the scrotum close to the body causing it to be too warm to produce enough or proper sperm to wearing boxers
take the man’s sperm and concentrate it to inject into the uterus
use another man’s sperm in the sperm bank (donated of course)
what problems may the female have that cause infertility?
lack of eggs
blocked oviduct
failure to ovulate
solutions for female infertility
hormones are injected to start ovulation (typically ends up with 2+ more babies)
get an egg donated and injected into the uterus
use a surrogate mother to carry a couple’s baby and give birth to it if the mother is unable to support the baby in her uterus
miscarriage
the death of a baby before 20 weeks of pregnancy since the uterus can’t support the growing embryo
assisted reproductive technologies
hormones are given to the woman in big quantity
secondary oocytes are collected surgically
externally fertilized in the lab
the embryo is returned to the female’s body
many of the gametes are taken out and many embryos may be made for future use.
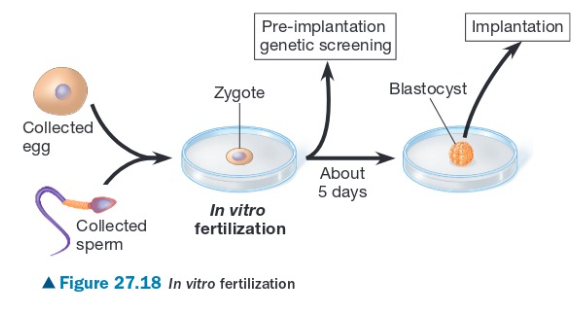
IVF (in vitro fertilization)
an ART in which the egg and sperm are fertilized on the culture dish and grown on a culture dish for around 5 days until it grows into a blastocyst
the blastocyst is screened to ensure it’s normal
blastocyst is inserted into the uterus at the right time as the regular ovarian cycle