ARC 1013 msstate test 3
1/147
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
148 Terms
Renaissance has
symmetry
circle and square pure form
mathematics, rational, proportions, universal order
renaissance architecture
Not aspire to heavens, grounded to earth, human reason are all parts of what?
Renaissance architecture
Gothic architecture
A-historical, asymmetrical
Architecture in service to God
governed by specific context

Renaissance 15th Century began in__________.
Florence, Italy
Renaissance 15th Century
Authentic re-use of classicism, based in
understanding of perspective, change size and proportion of columns, pediments, etc.
- Represent human intellect as much as the power of God
Humanism
philosophical system based upon the capacity of humankind for rational, objective thought, and action; stresses human reason and is centered in human nature, interests, and ideals, as distinct from religious philosophies based in a higher God
Renaissance
the activity, spirit, or time of the great revival of art, literature, and learning in Europe beginning in the 14th century and extending to the 17th century, marking the transition from the medieval to the modern world.
Renaissance Architecture
The various adaptations of Italian Renaissance architecture that occurred throughout Europe until the advent of Mannerism and the Baroque in the 16th and 17th centuries, characterized by the use of Italian Renaissance forms and motifs in more or less traditional buildings.
"Renaissance Man"
a person with many talents or areas of knowledge.
Brunelleschi was an
architect, painter, sculptor, goldsmith
Humanism (renaissance)
human achievement separate from religious dogma
Humanism : Reconcile the classical view of human potential with Christian believe in divine intention
wanted excellence in human achievement - all was possible
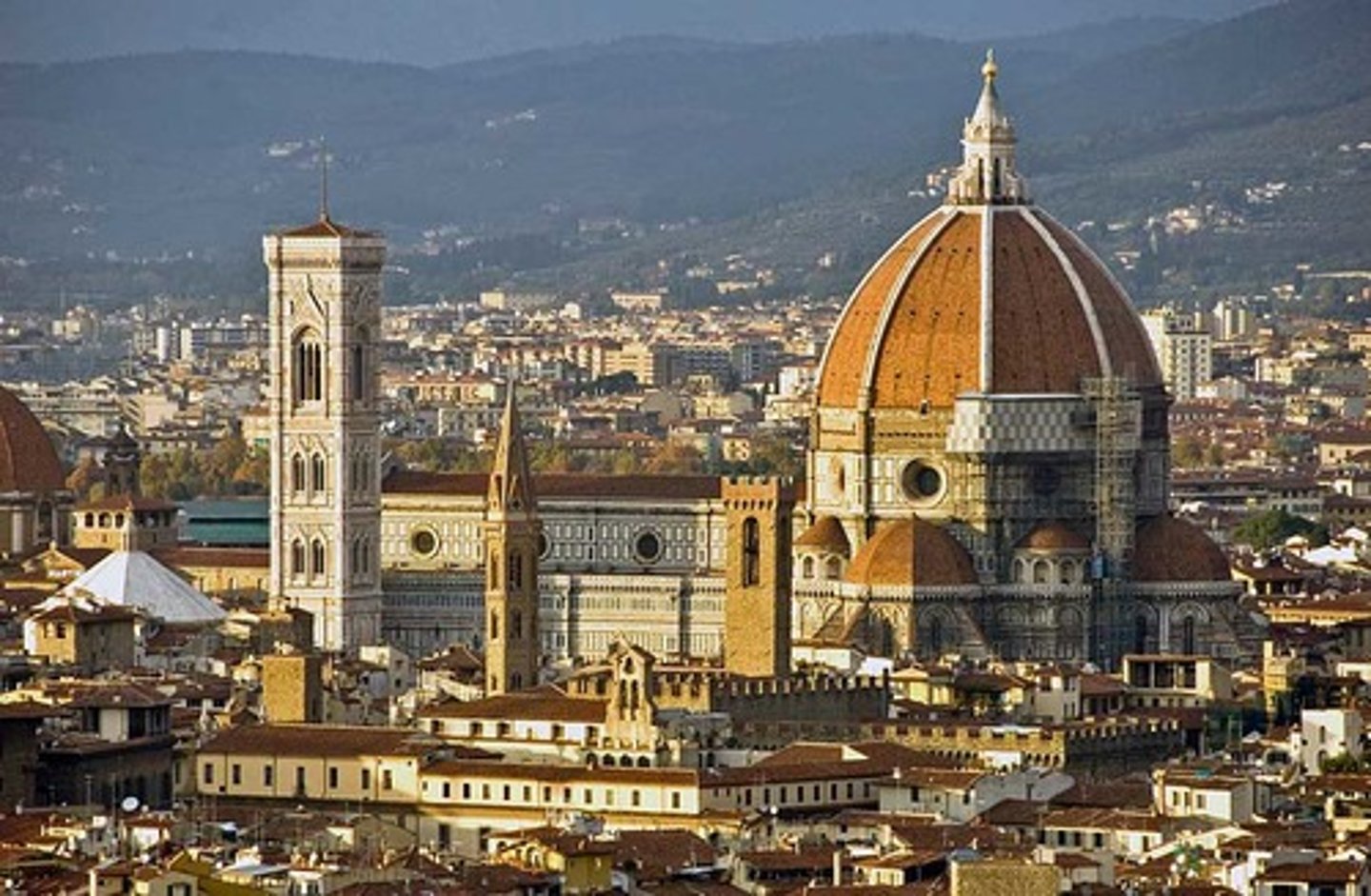
Cathedral in florence
dome is witness to human achievement
employed ribs and double shells

Early Renaissance
a style of Italian Renaissance art and architecture developed during the 15th century, characterized by the development of linear perspective, chiaroscuro, and in buildings, by the free and inventive use of classical details
Chiaruscuro is a
style of painting using only light and shadow
Brunelleschi: Father of the Renaissance
symmetrical forms; proportions relate one element to another; application scientific perspective
First Renaissance building
-Brunelleschi
-Foundling Hospital (orphanage) - Florence, Italy 1422
-symmetrical forms
-proportions relate one element to another
-application scientific perspective

The "Duomo", Dome of the Cathedral of Florence (1418-36)
largest dome built since Romans
technical achievement in its construction
-no "centering" - built to be self-supporting as it was constructed
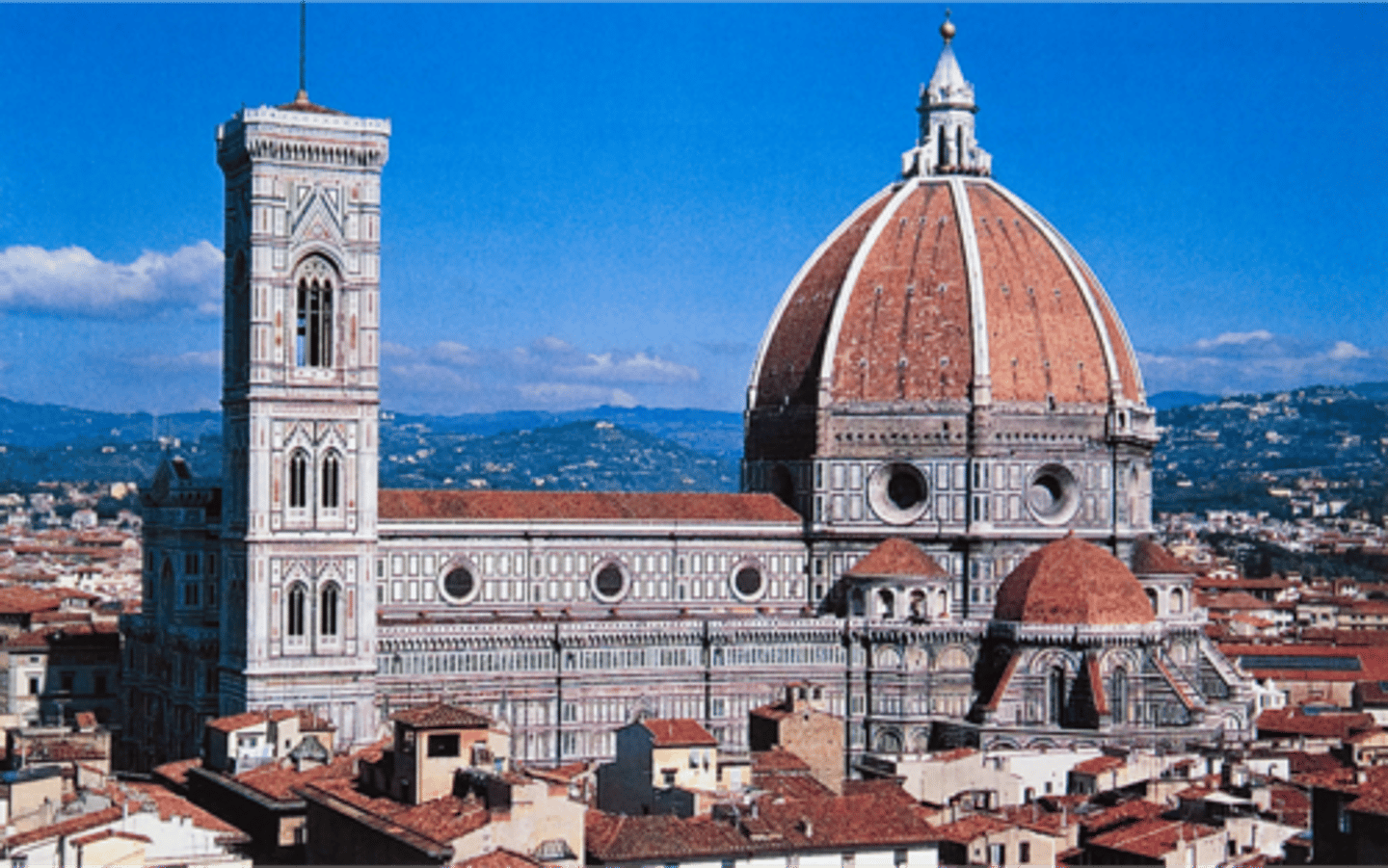

Cathedral in Florence
employed ribs and double shells
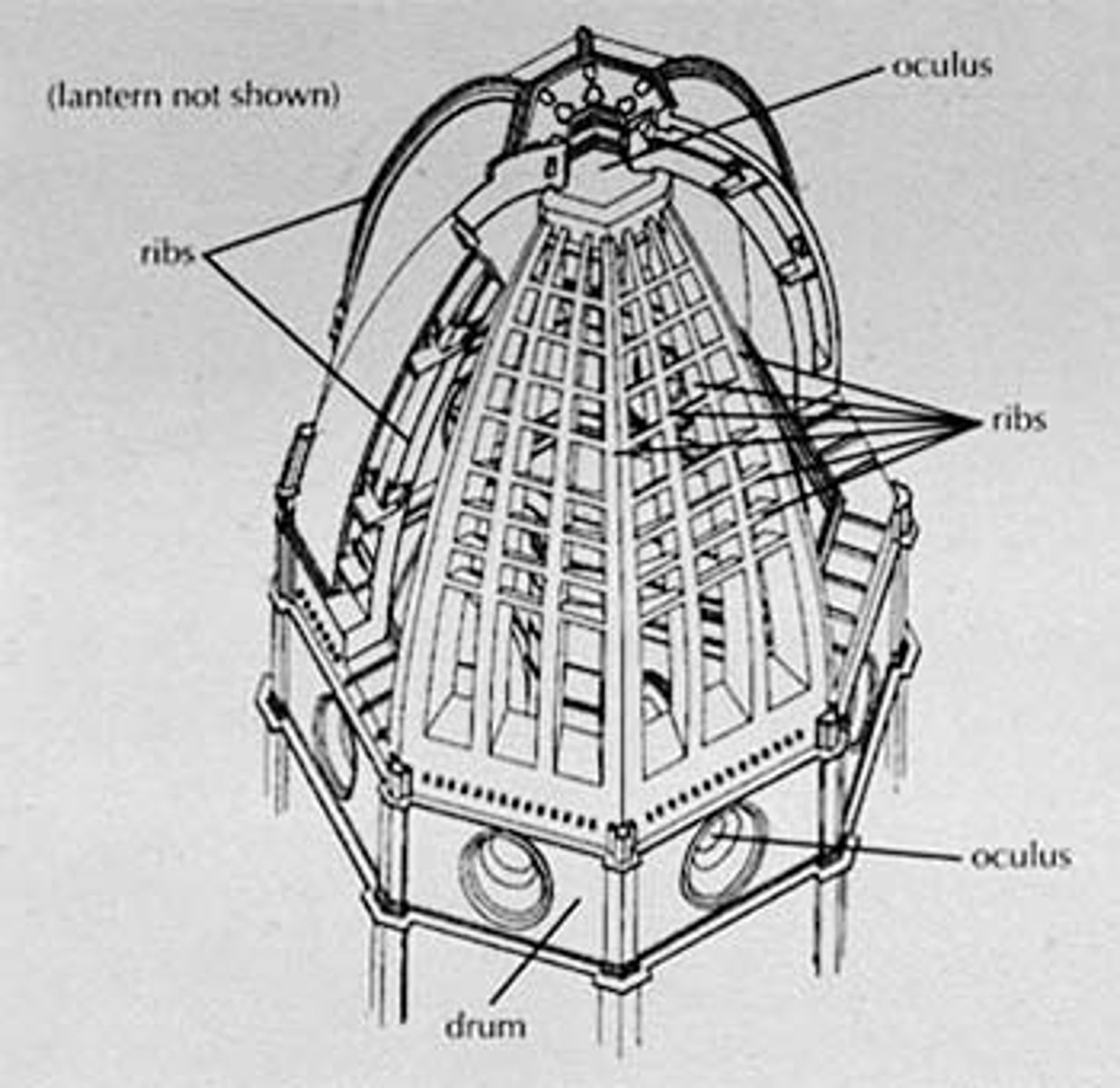
The dome for the Cathedral in Florence began in
Renaissance
the tower for the Cathedral in Florence began in
Gothic
Church of San Lorenzo (1418-46)
Filippo BRUNELLESCHI

Who hired Brunelleschi to rebuild the church of San lorenzo?
medici
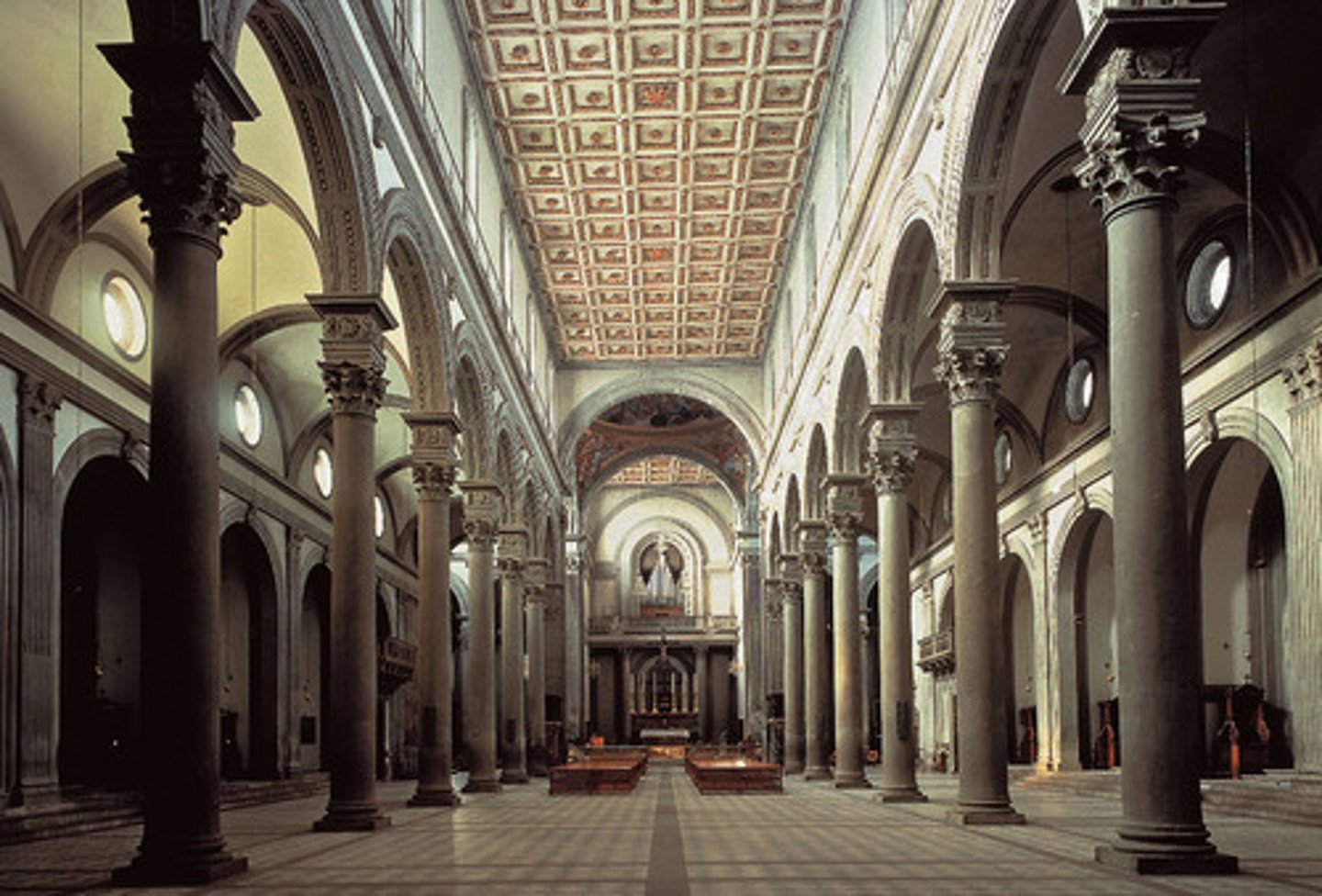
Church of S. Spirito (1436-82)
Filippo BRUNELLESCHI
proportions and style fully realized
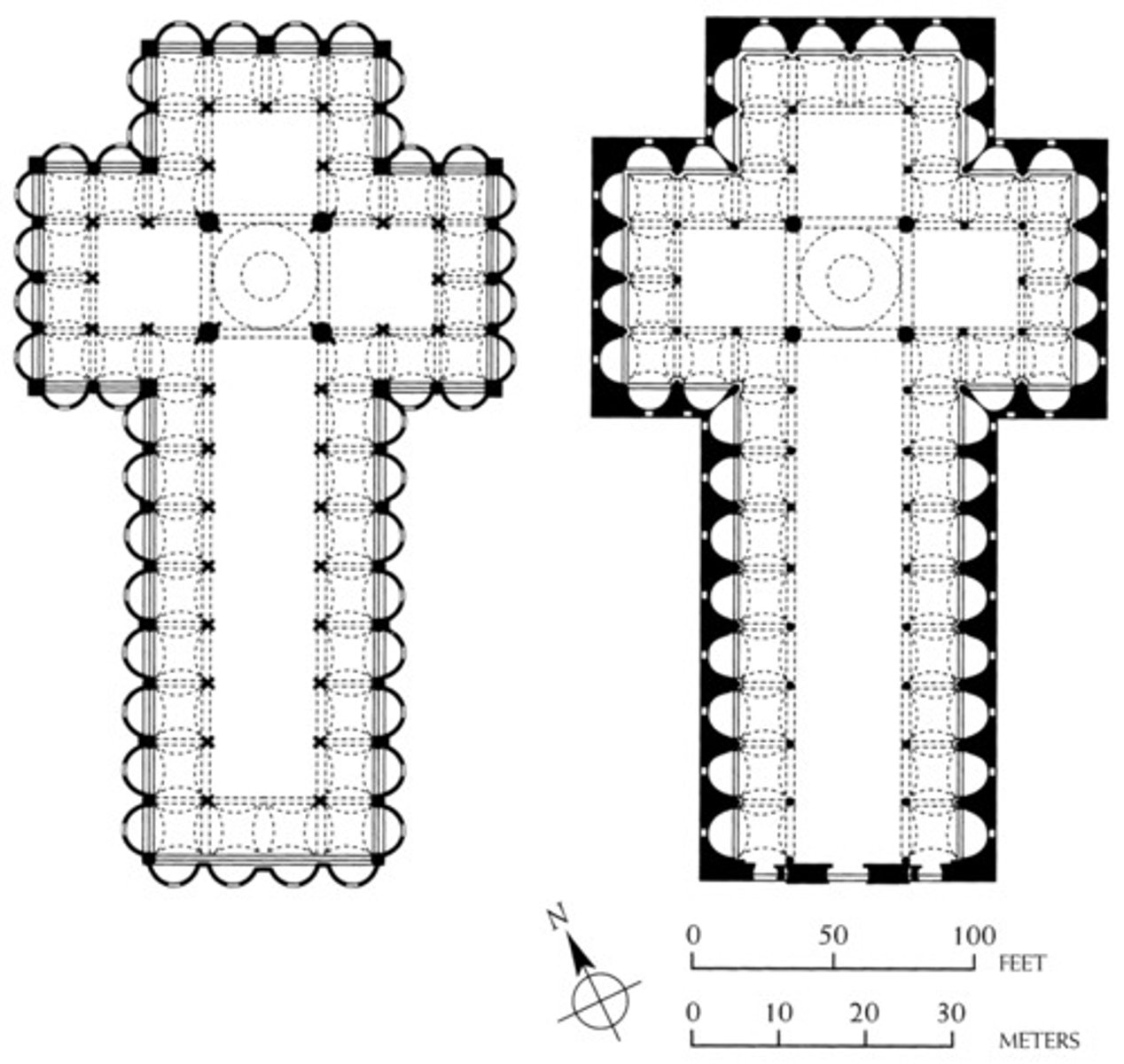
Volumes were ________ in the church of S. Spirito
CUBES
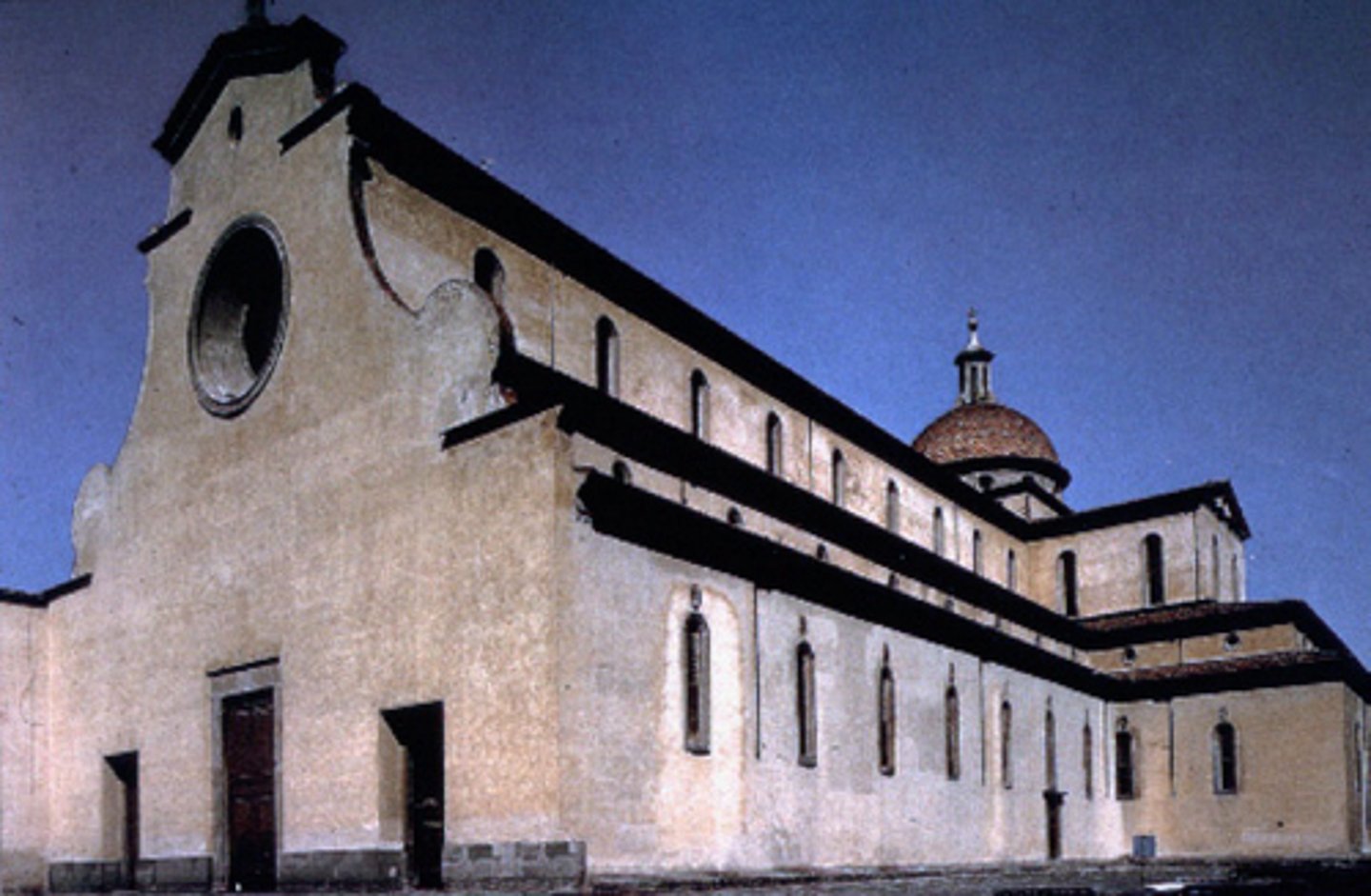

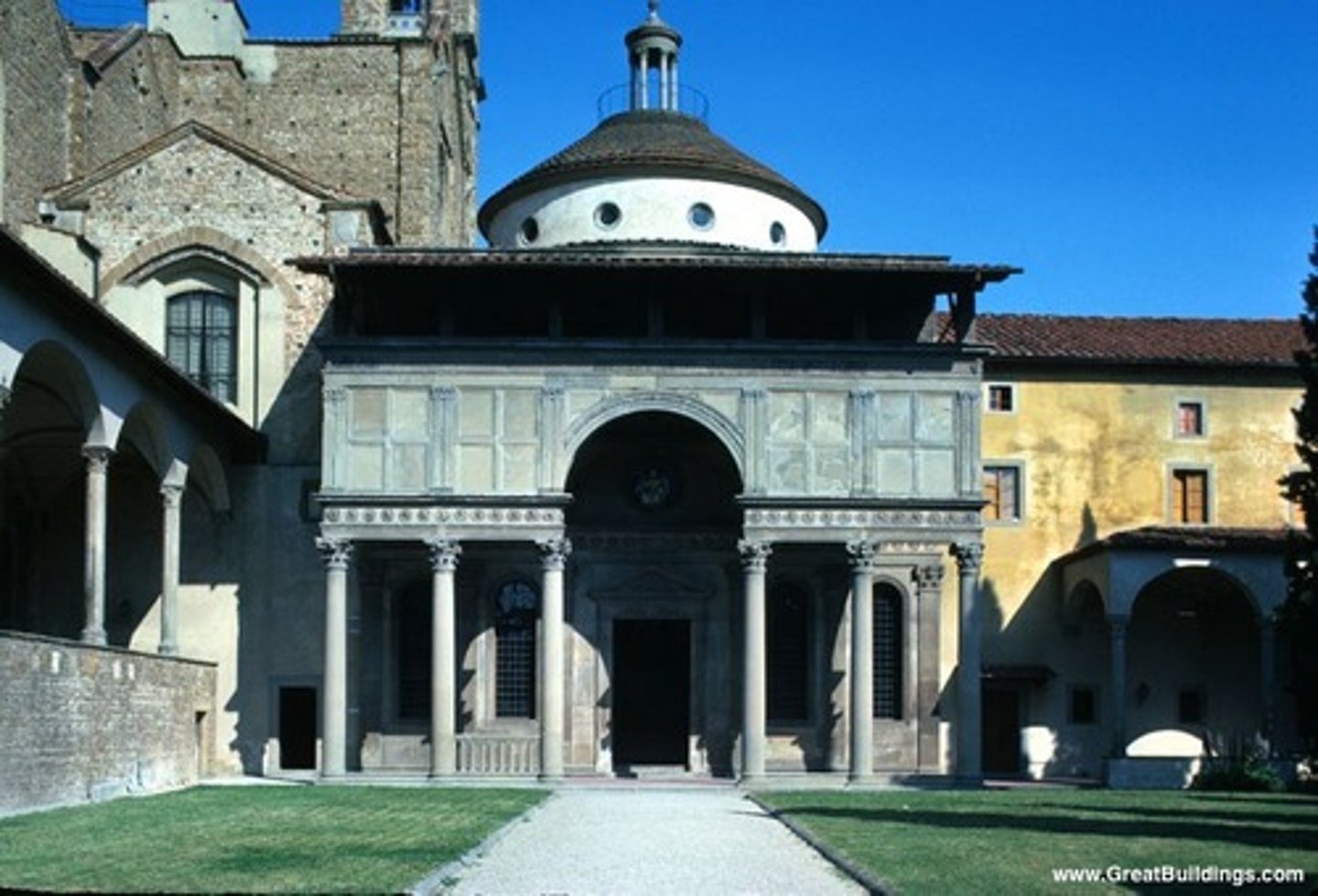
Picture of
Pazzi Chapel

Vitruvius: wrote "bible" for Renaissance architects
Roman architect and theorist, active -46 to -25 "the TEN BOOKS ON ARCHITECTURE"
-the only complete book on architectural design and theory to survive from the ancient world
-had enormous influence on Renaissance architecture
Two thoughts from Vitruvius
1. "Firmness, Commodity, and Delight
2. Vitruvian figure
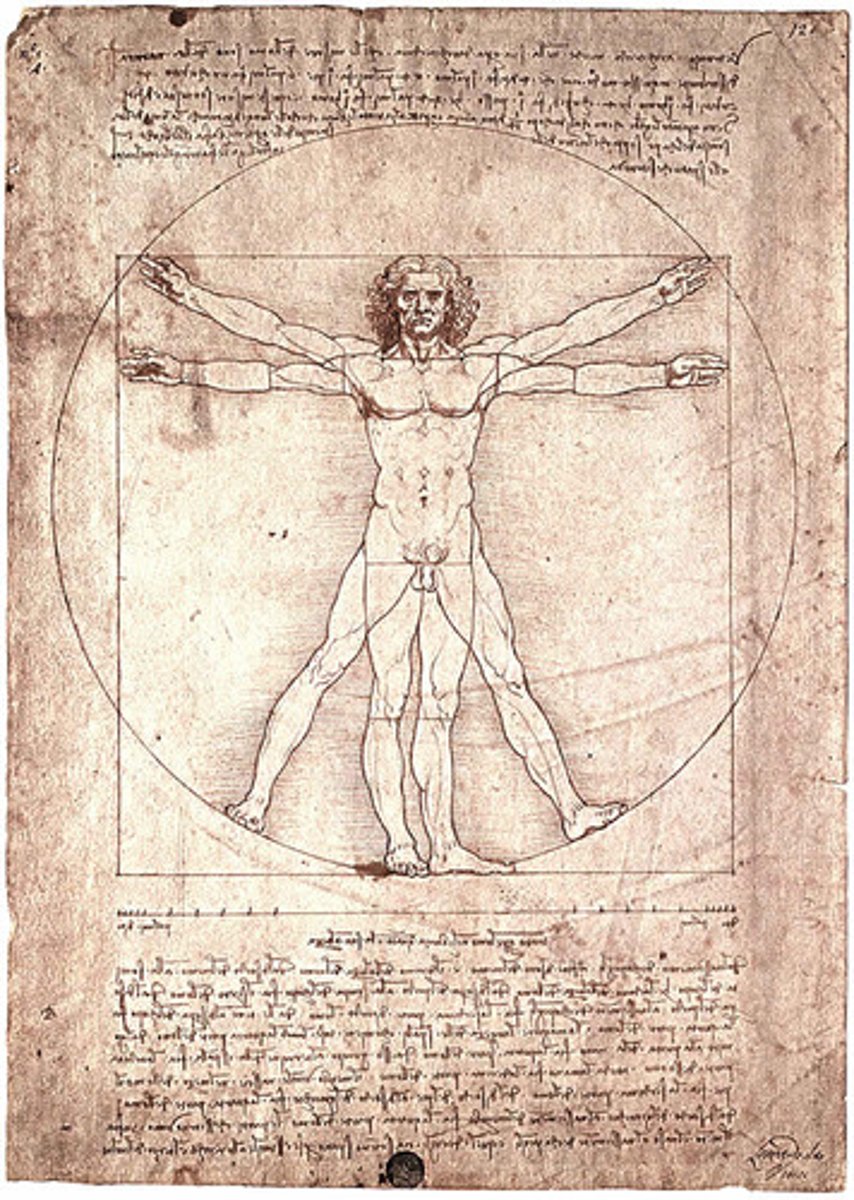
What is the center of humanism?
man
Church of Sant' Andrea
Leon Battista Alberti (theorist, historian, scientist, and architect) another TEN BOOKS on architecture modeled on Vitruvius' books
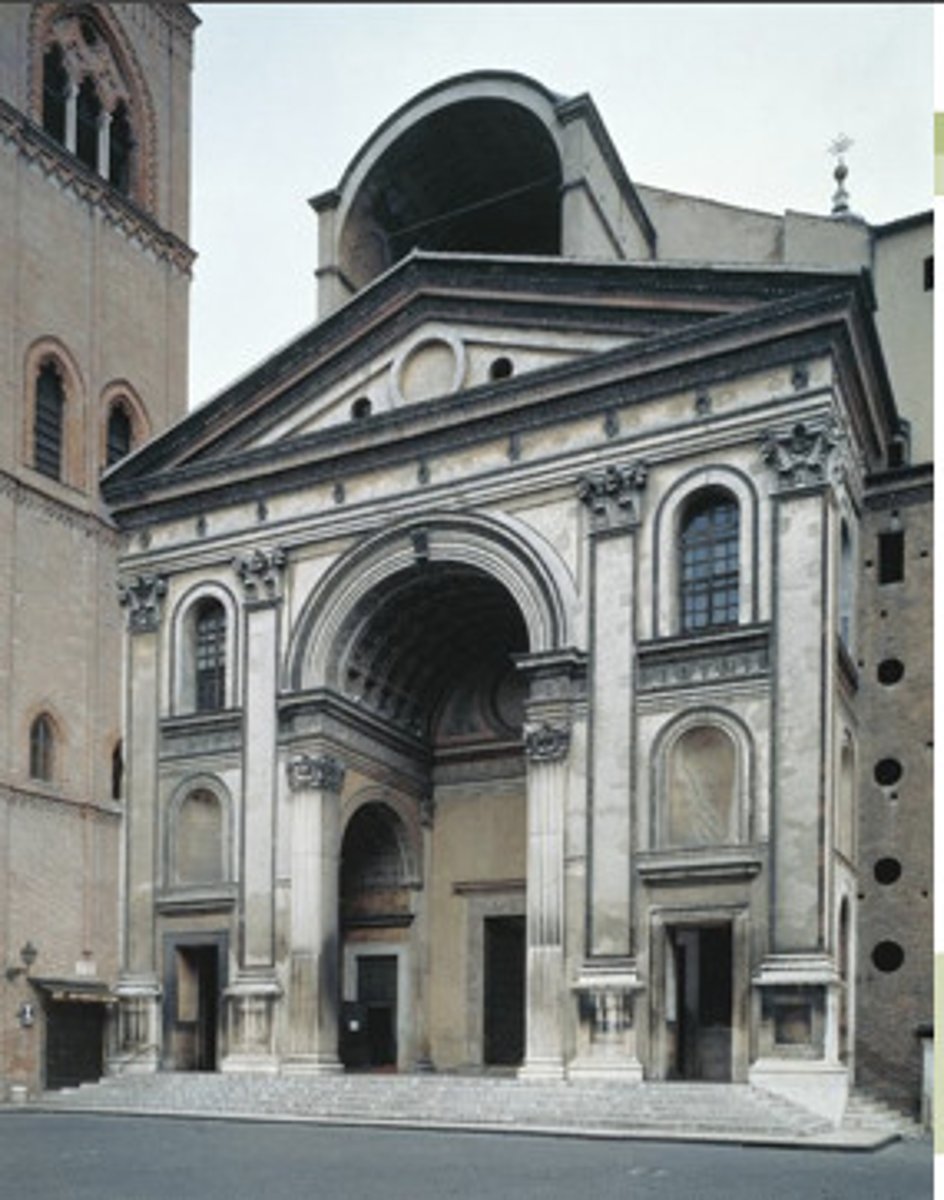

What promoted architecture as an intellectual activity?
Ten Books on architecture modeled on Vitruvius' books - Church of Sant' Andrea
Church of Sant' Andrea
note representation of pure geometric form
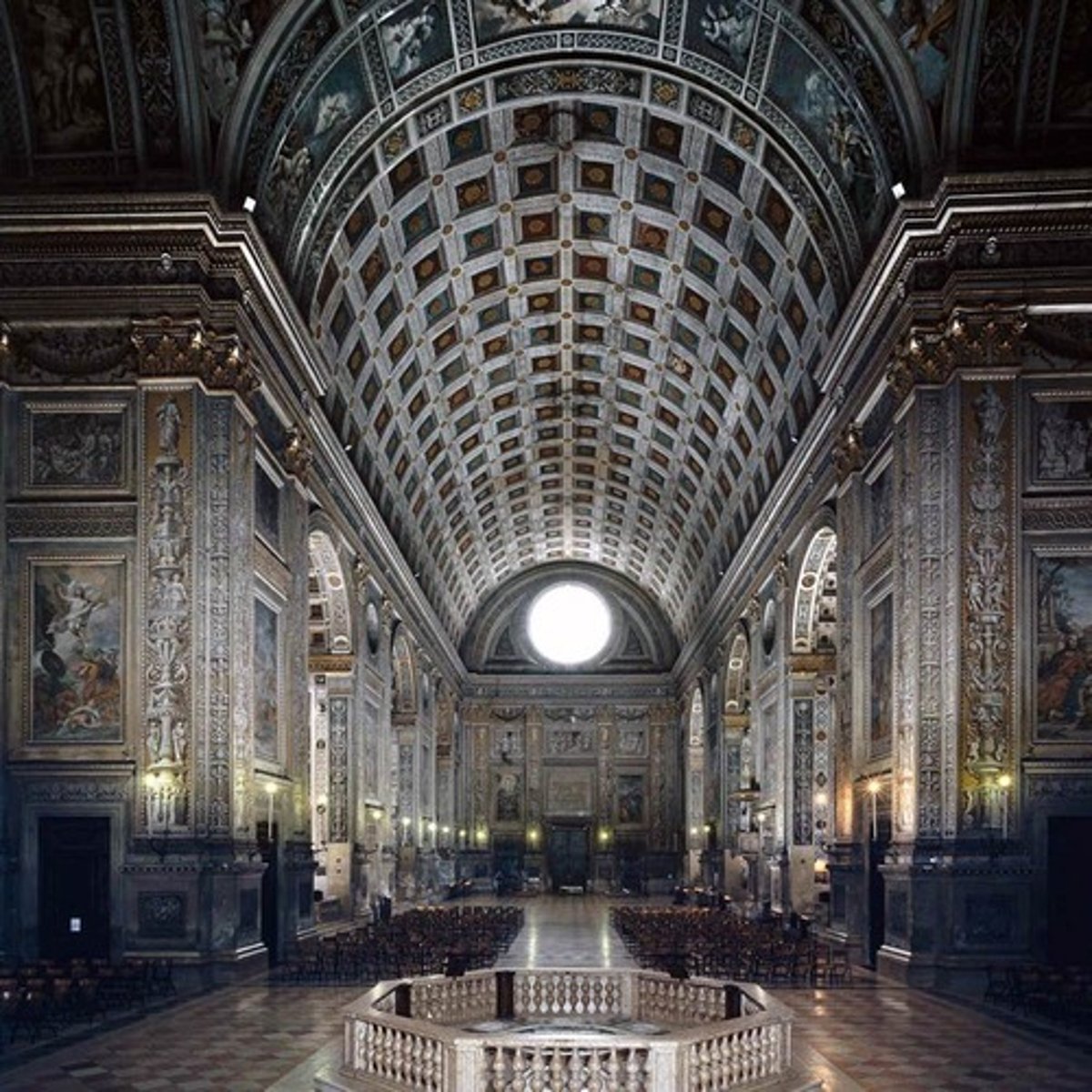

Ideal city of Sforzinda - geometric purity of the "circle plan" for a city
man is the center
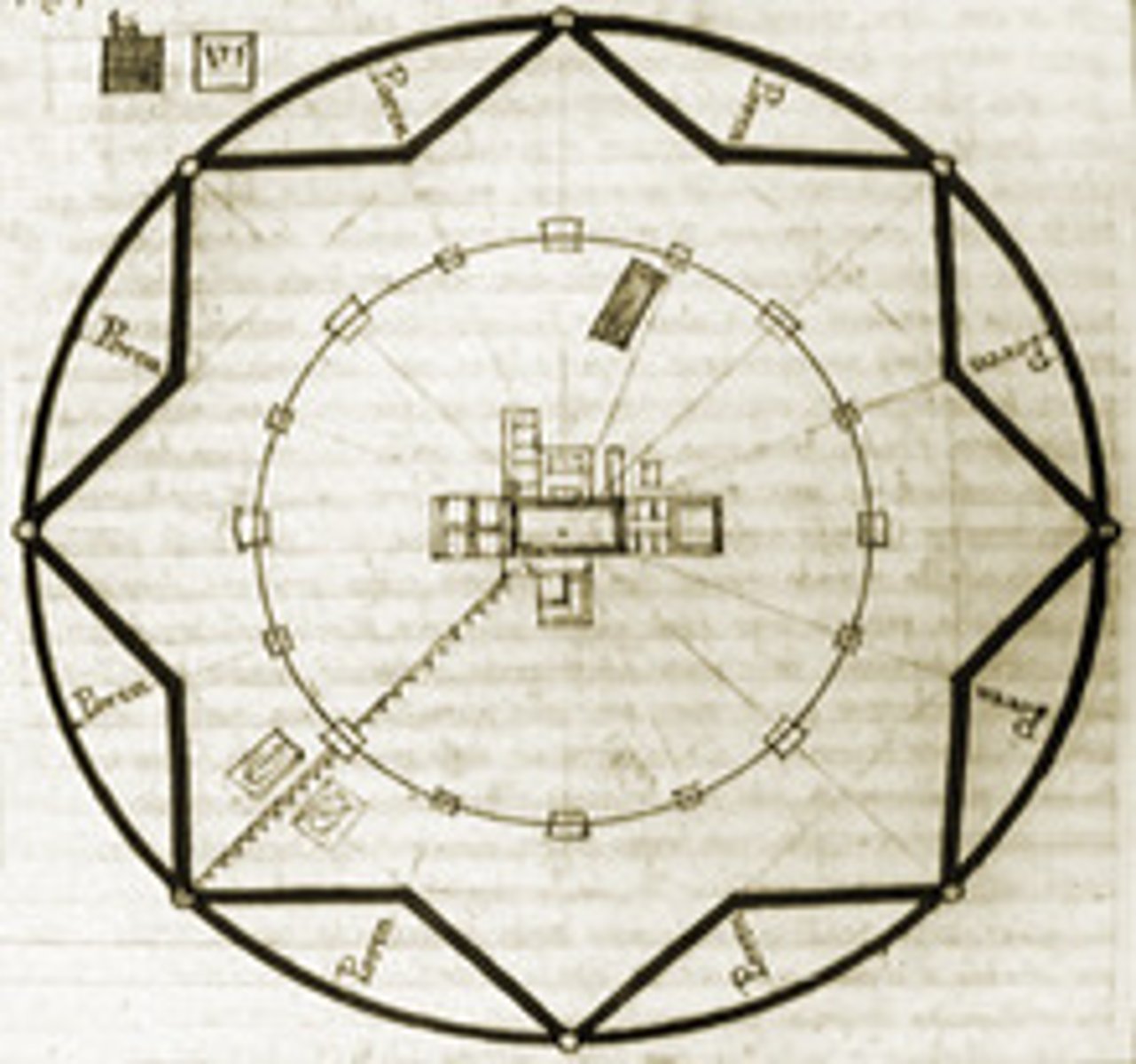
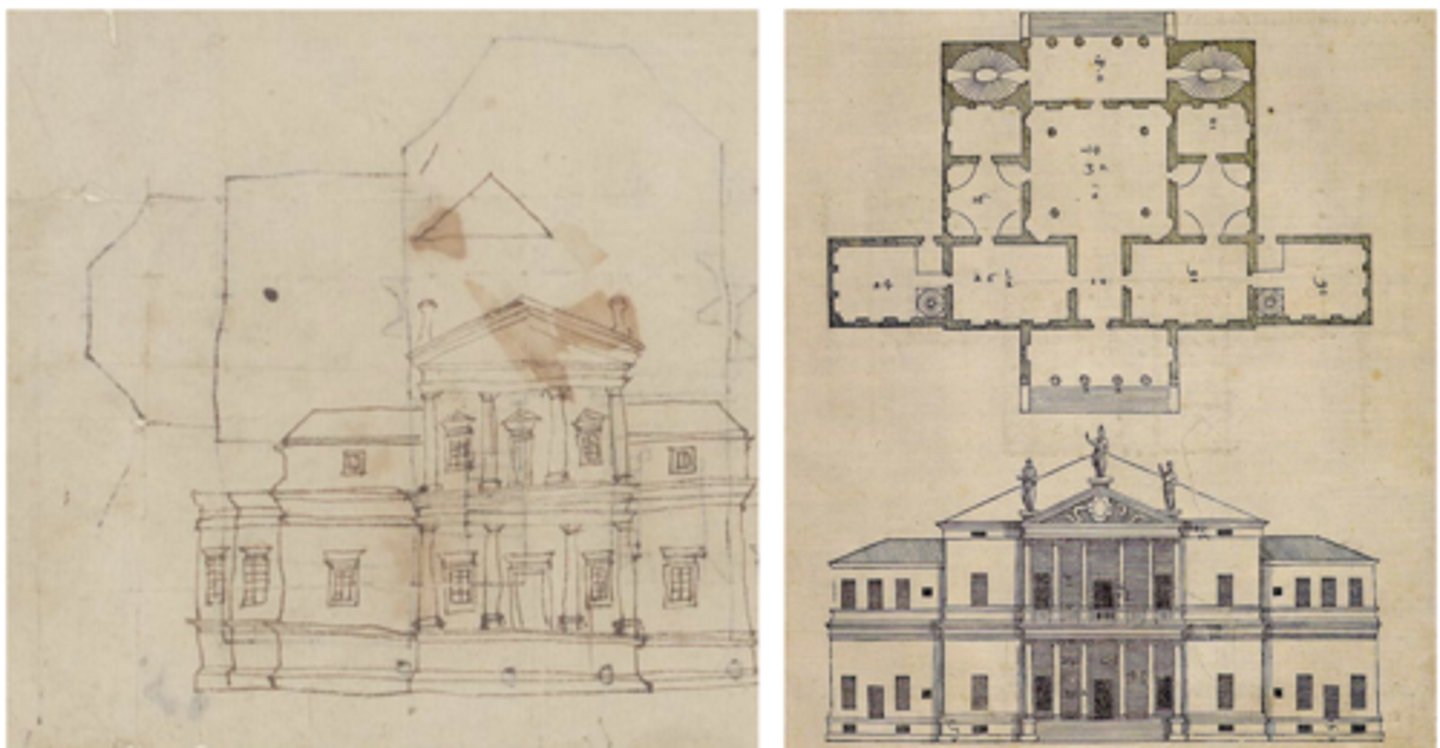
VILLA ROTUNDA c. 1500 Vincenza Italy
Andrea PALLADIO
Supreme example of theoretically inspired design
Completely symmetrical
Elements all governed by proportional relationships
Turned house into temple
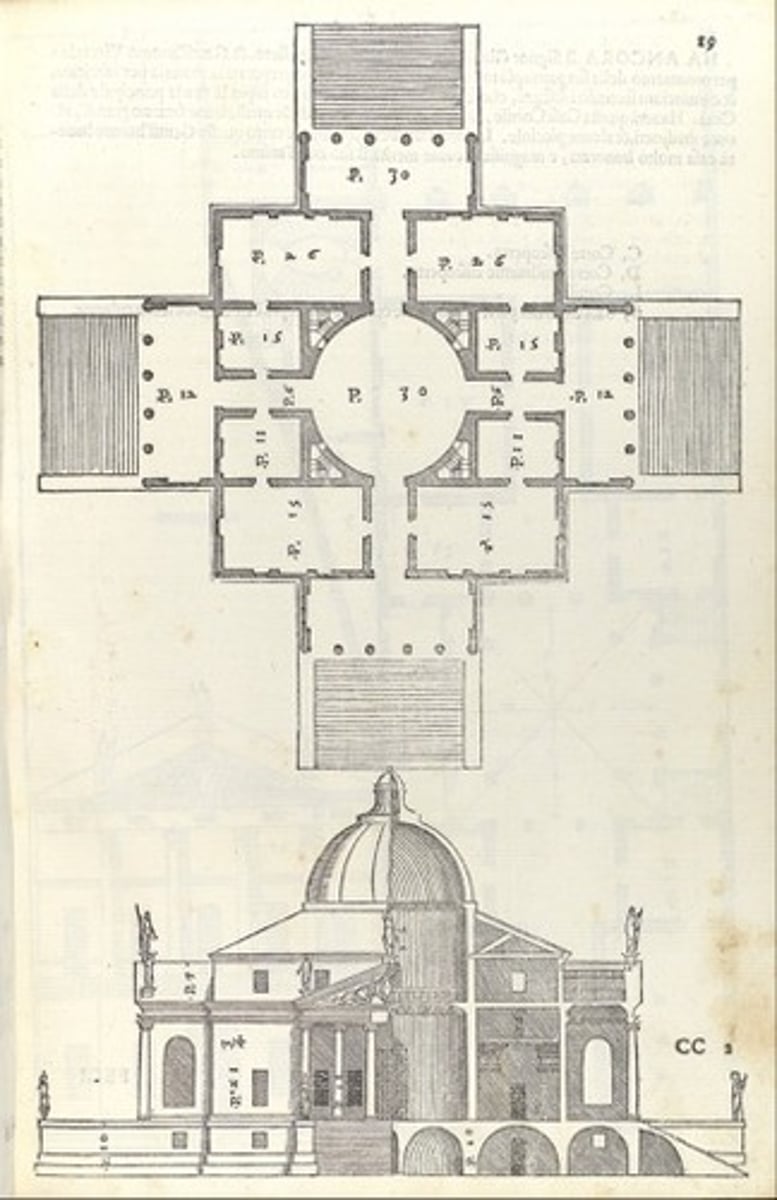
What is the supreme example of theoretically inspired design?
villa rotunda c. 1500 Vicenza, Italy
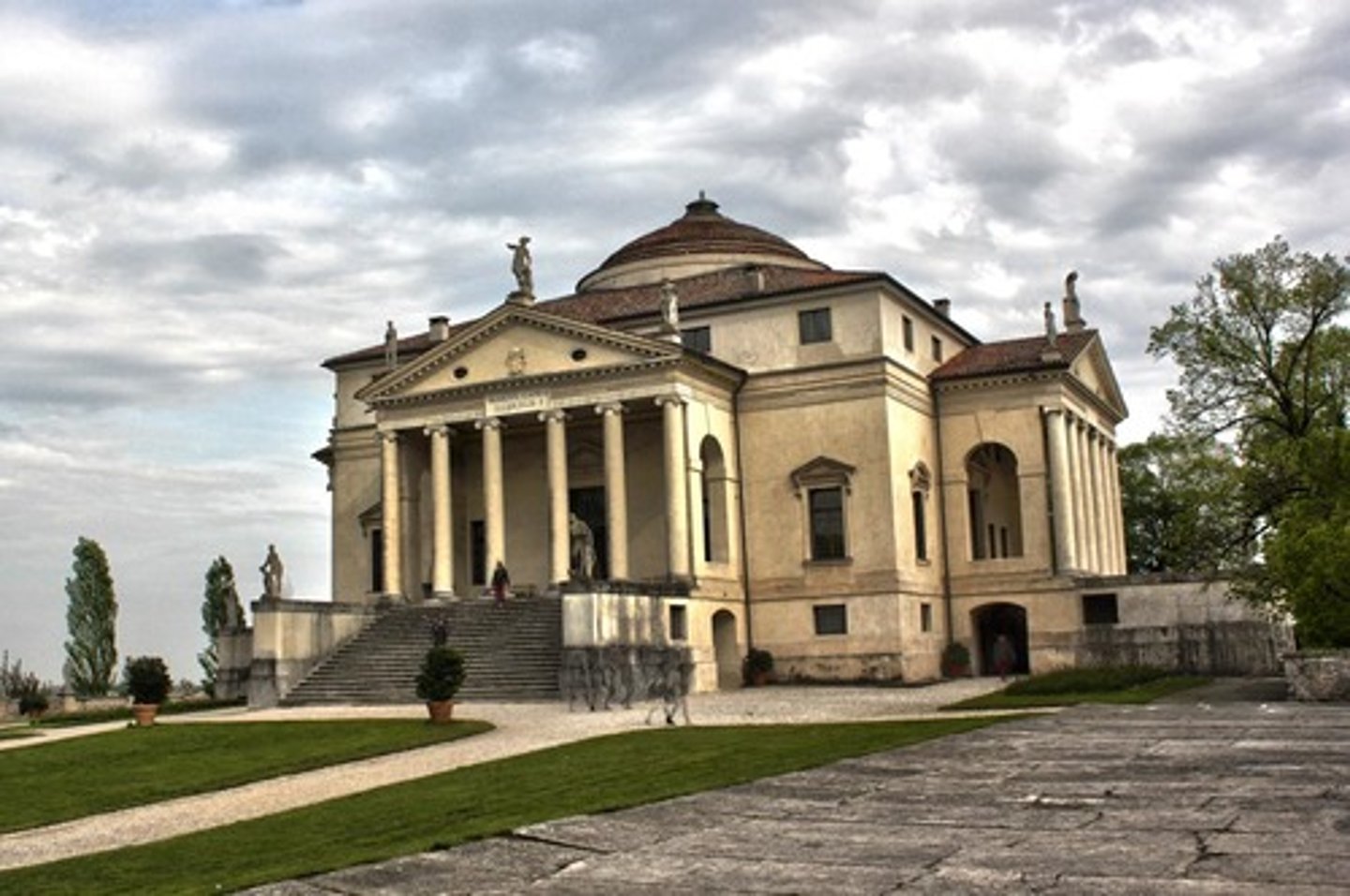

Palladio wrote treatise on architecture - THE FOUR BOOKS OF ARCHITECTURE
constructed villas between Venice and Vincenza 1550
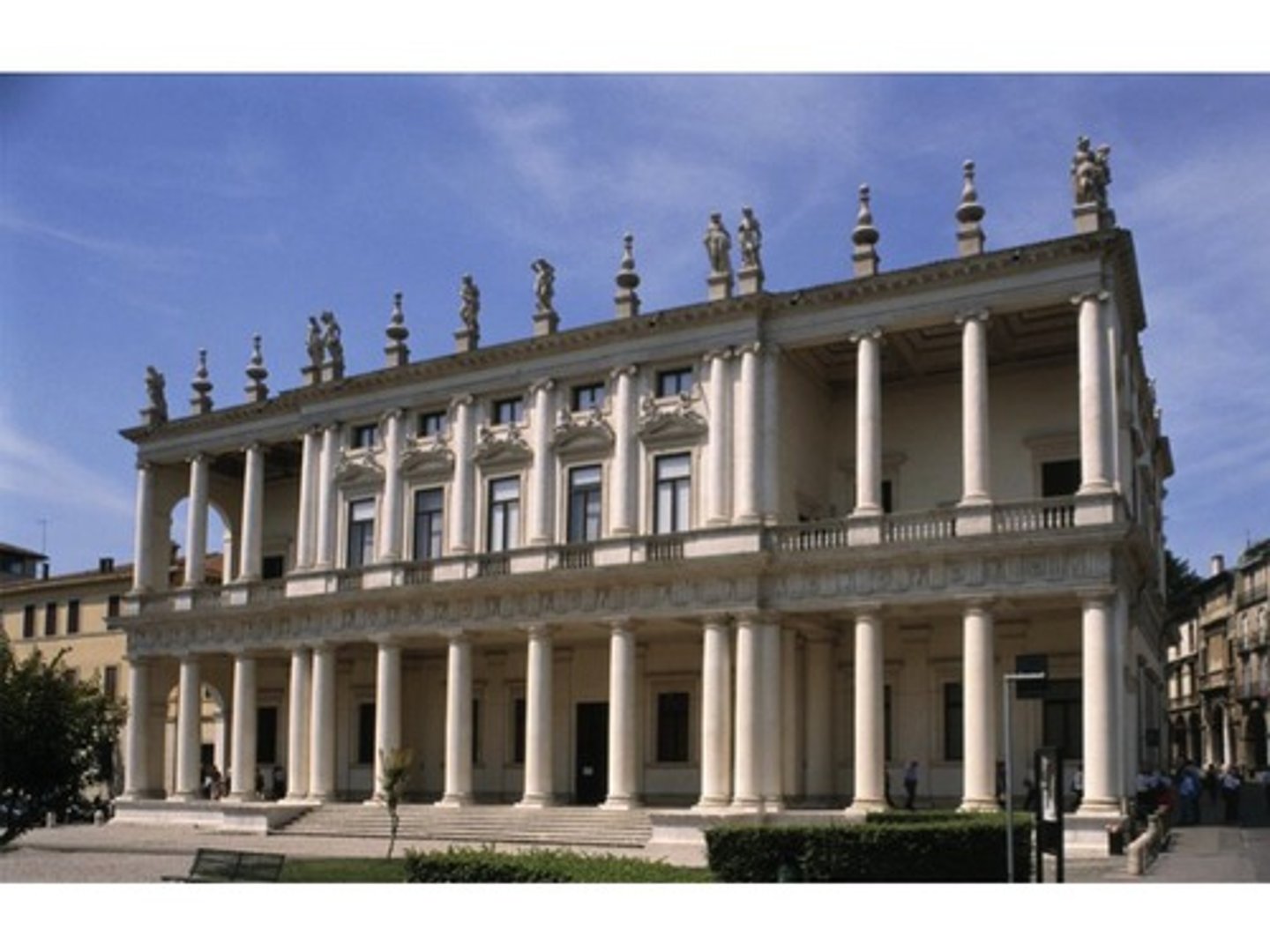
Palazzo
city house - built to street and for wealthy families

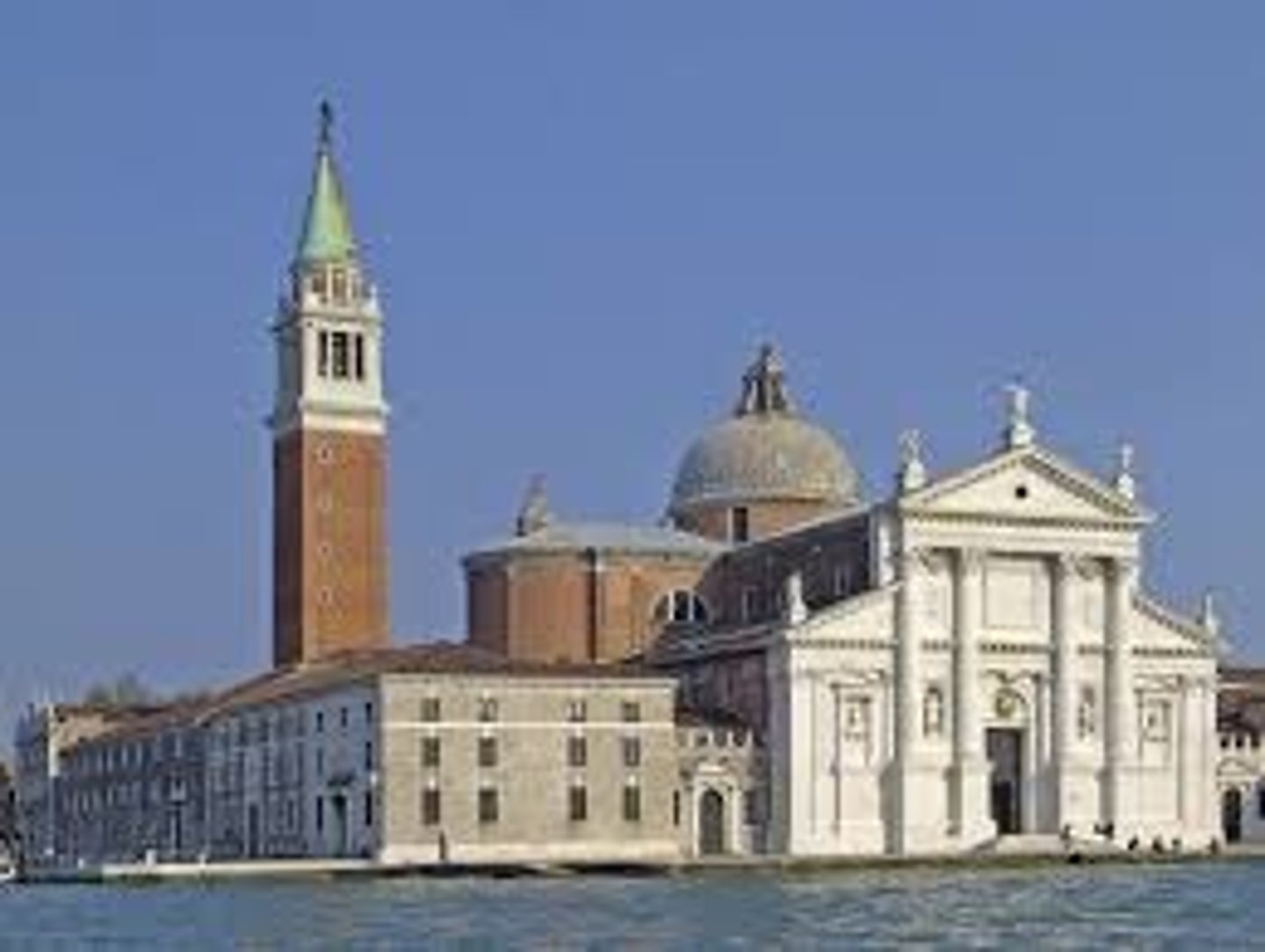
San Giorgio Maggiore - white façade faces across the basin of San Marco
scaled to present a public face to the town of Venice

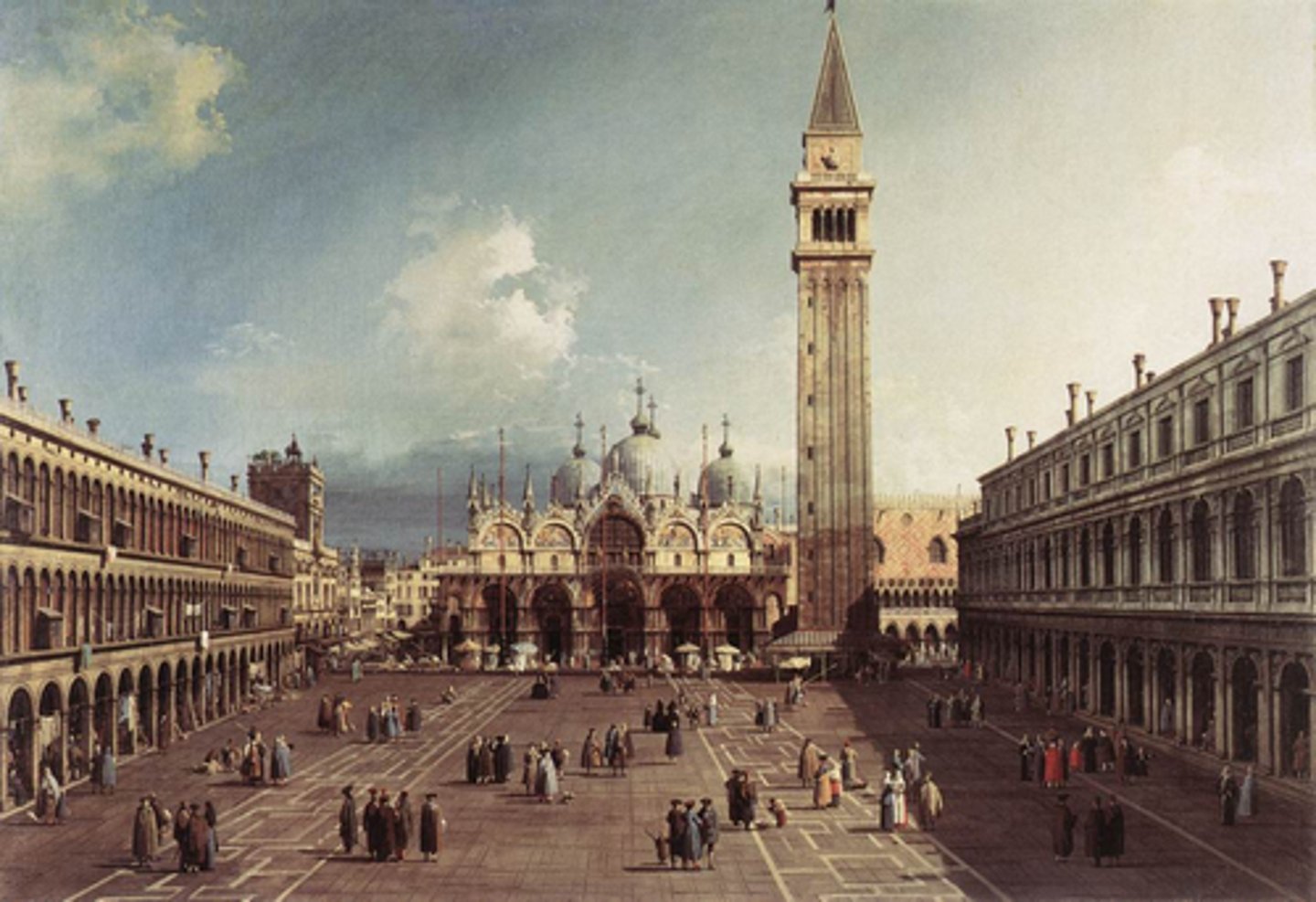
Piazza
a public square or marketplace, especially in an Italian town.

High Renaissance
a style of Italian renaissance art and architecture developed in the late 15th- and early 16th centuries characterized by an emphasis on draftsmanship, the illusion of sculptural volume in painting, and in building , by the imitative use of whole orders and compositional arrangements in the classical style, with great attention to the formulation of compositional rules after the precepts of Vitruvius and the precedents of existing ruins.
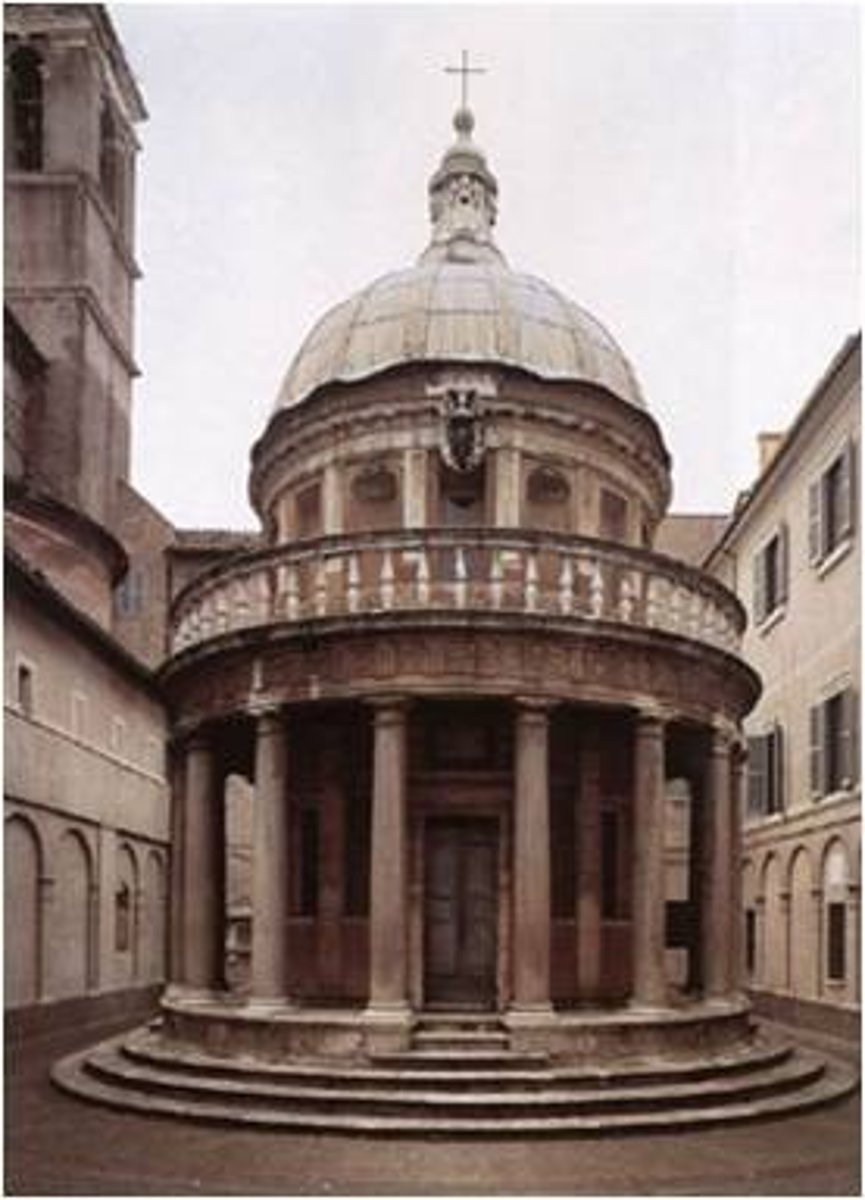
The "Tempietto" of San Pietro
Donato Bramante
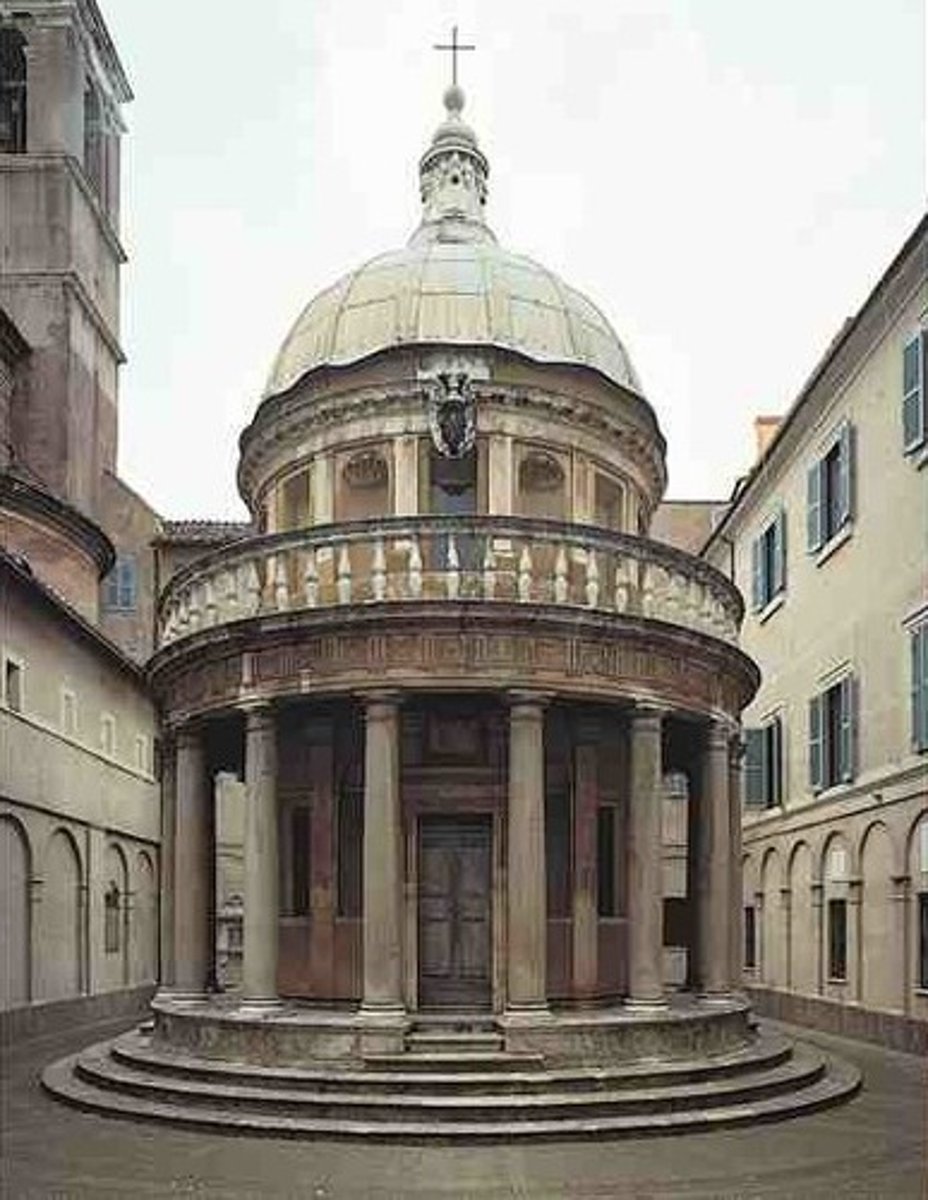

dome
outward manifestation of the centrally organized plan - donato bramante
Donato Bramante (1444-1514)
Tempietto, Rome - begun 1502
Bramante was close associate of Leonardo DaVinci
Early Work in Milan
Moved to Rome after French sack of Milan in 1499
Who was a close associate of Leonardo DaVinci who moved to Rome from Milan after the French sack in 1499?
Donato Bramante
Circle and square represent the perfection of the divinity
Tempietto, Rome - Donato Bramante
Believe religious figure "Saint Peter" was killed (martyred) here
meant to be an object, a picture, a marker - Tempietto, Rome

Pope Julius II 1503 - humanist ideals introduced into the Papal court
Rome Queen city - consolidate temporal power
Return to glory from Roman antiquity
Saint Peter's 1505-1612
Michaelango changed it
- magnificent new church over the crypt of St. Peter
- dome becomes an icon of dome often repeated

Bramante Plan
plans for St. peters
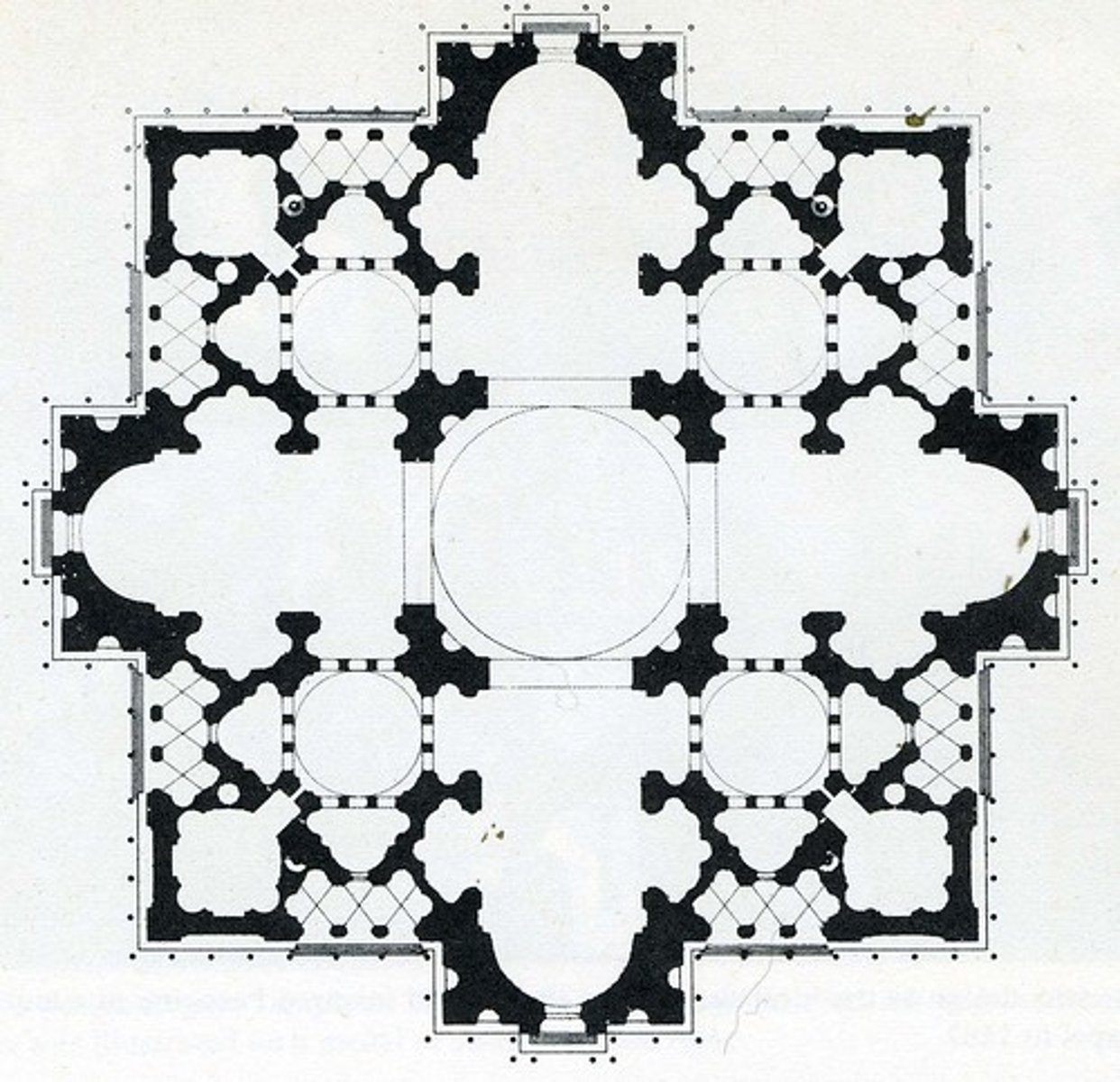
Michelangelo Plan
plans for St. peters
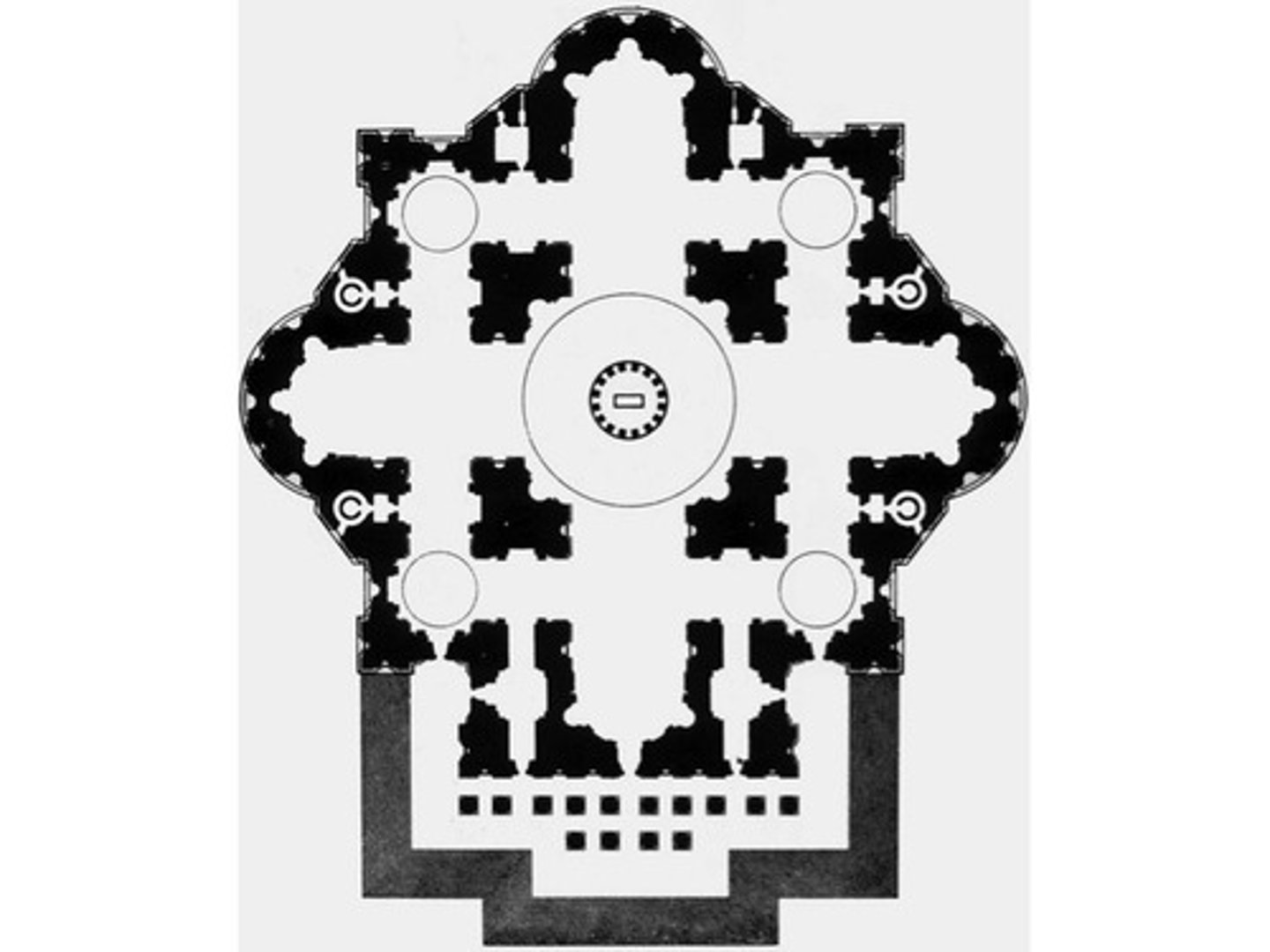
Peruzzi Plan
plans for St. Peters
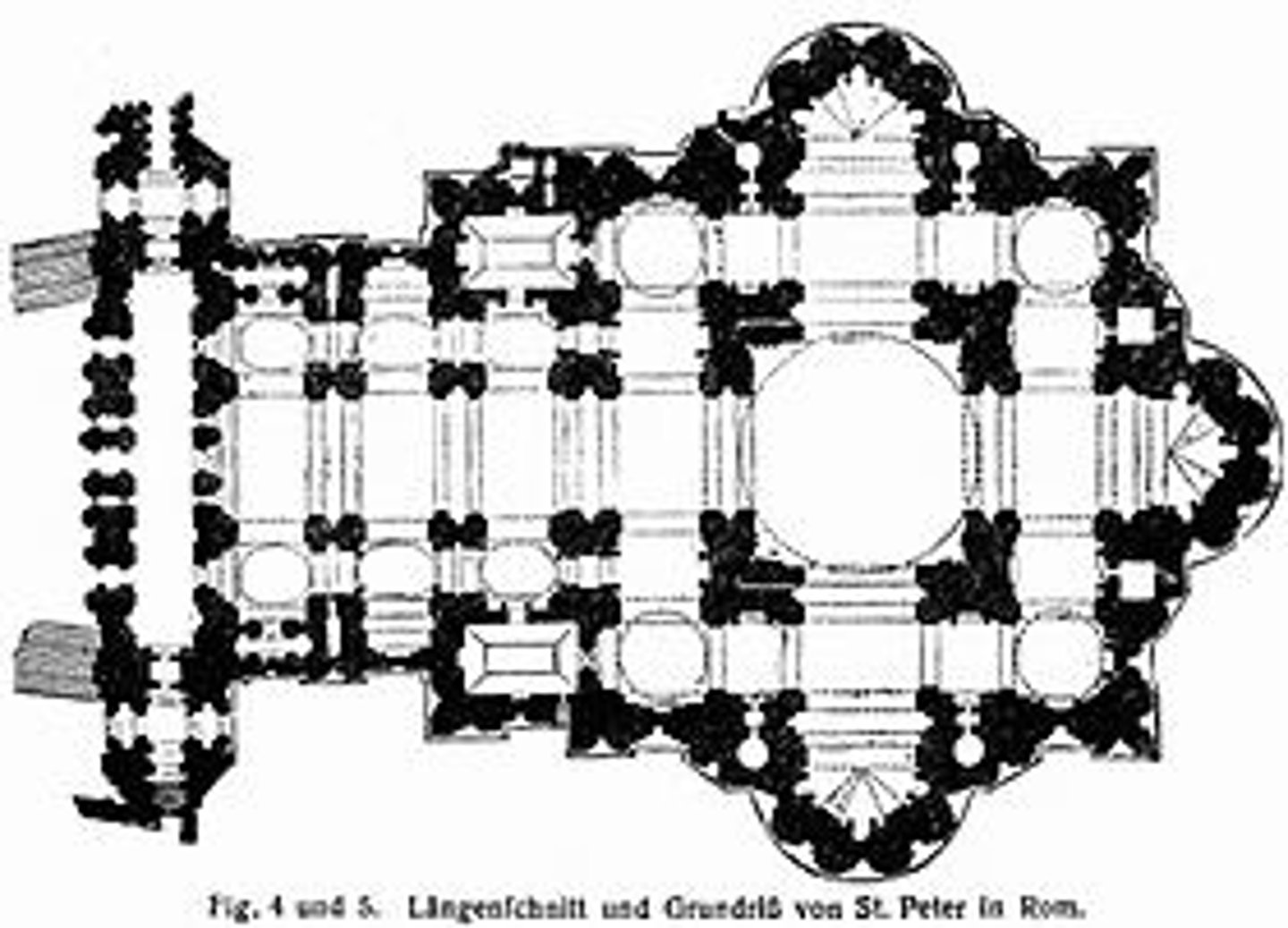
Saint Peter's (1505-1612) tomb for Pope Julius II would not fit in the old basilica (almost 1100 years old in 1505)
Bramante's scheme was on a scale grander than any Roman structure
Building about the size of the Baths of Diocletian
-Dome comparable to the Pantheon
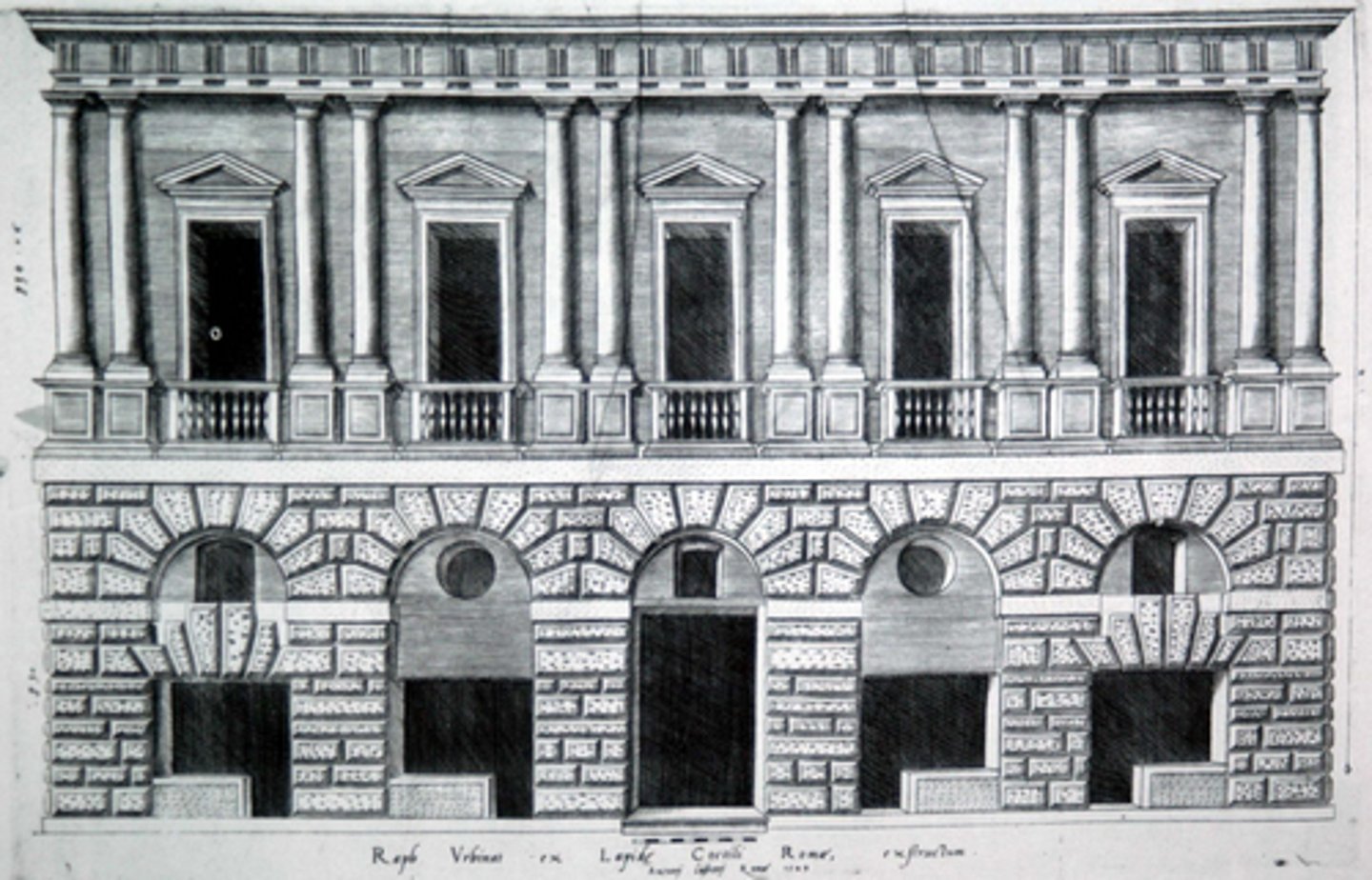
Bramante, Palazzo Caprini
- Rome, ca. 1512 (demolished)
Mannerism (high Renaissance)
Inventive combinations of elements of purposefully play with classical rules
proportions-exaggerated
Michelangelo (1475-1564)
rebelled against Renaissance decorum
Painter: ceiling of Sistine Chapel
Sculpture: David, thee Pieta
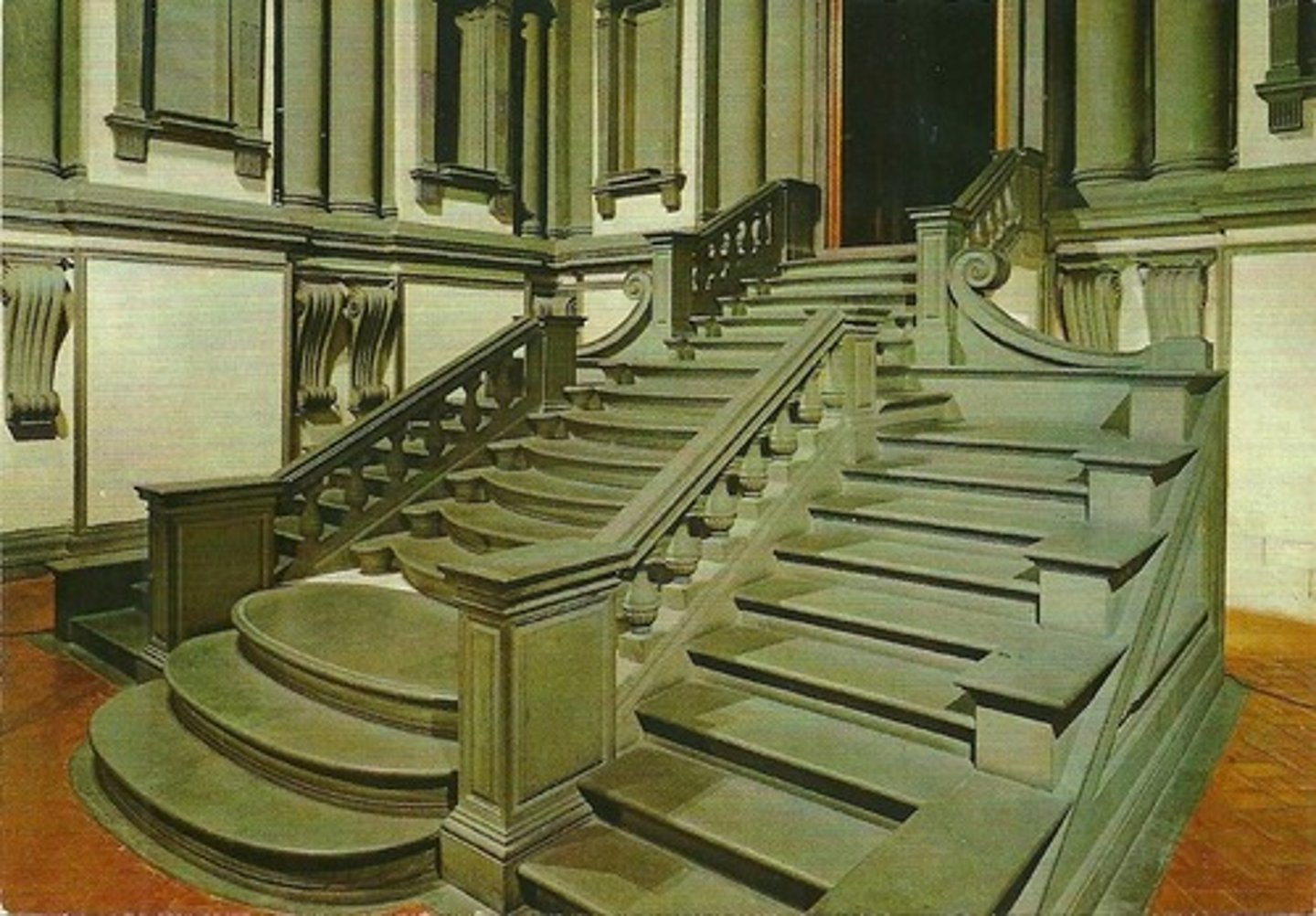
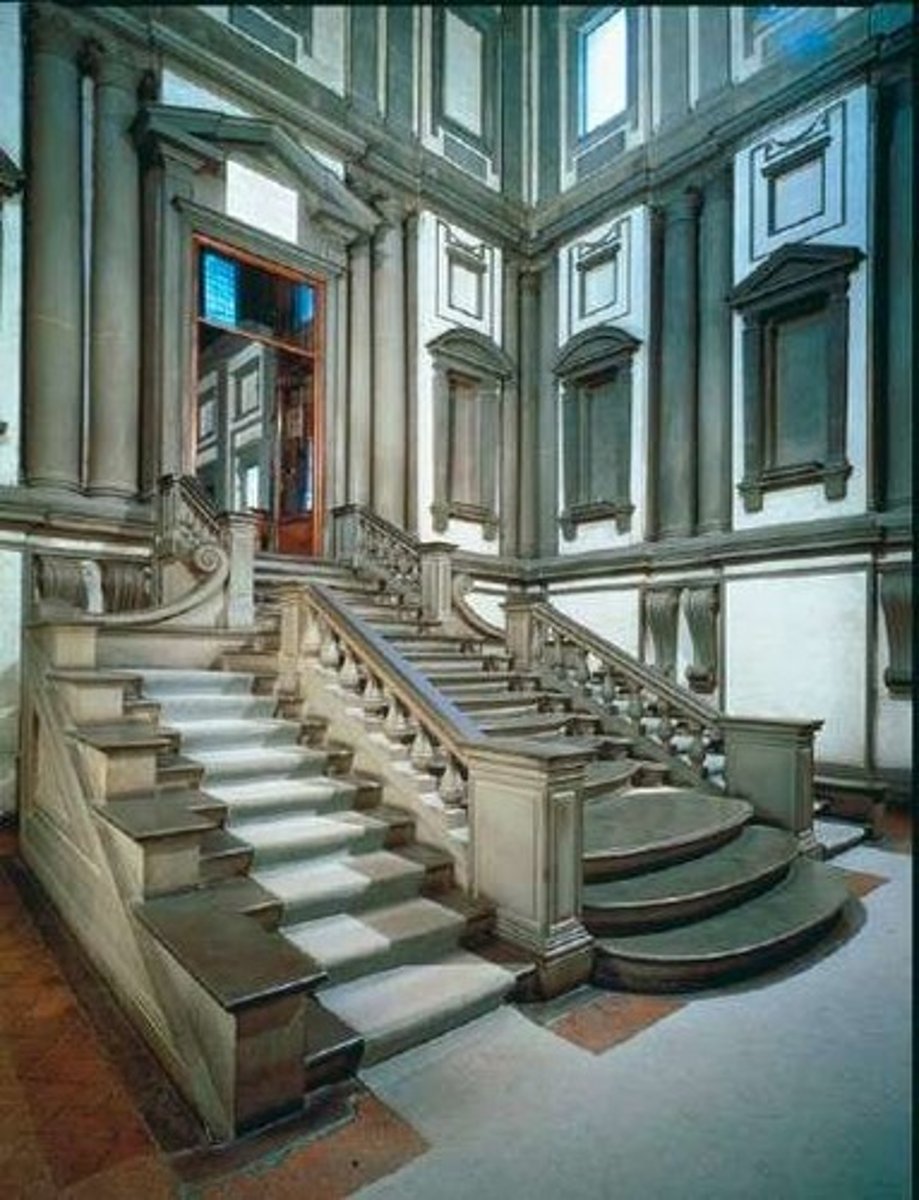
Architecture: Laurentian Library, started at age 70
Mannerism
a transitional style in European Architecture in the late 16th century, particularly in Italy, characterized by the unconventional use of the classical elements
Michelangelo adjusted proportions, details to suit his purpose
often made up his own details
Complete challenge to Renaissance rules of order, proportion, and use of historic elements
Goal: to heighten the physical experience of moving through space
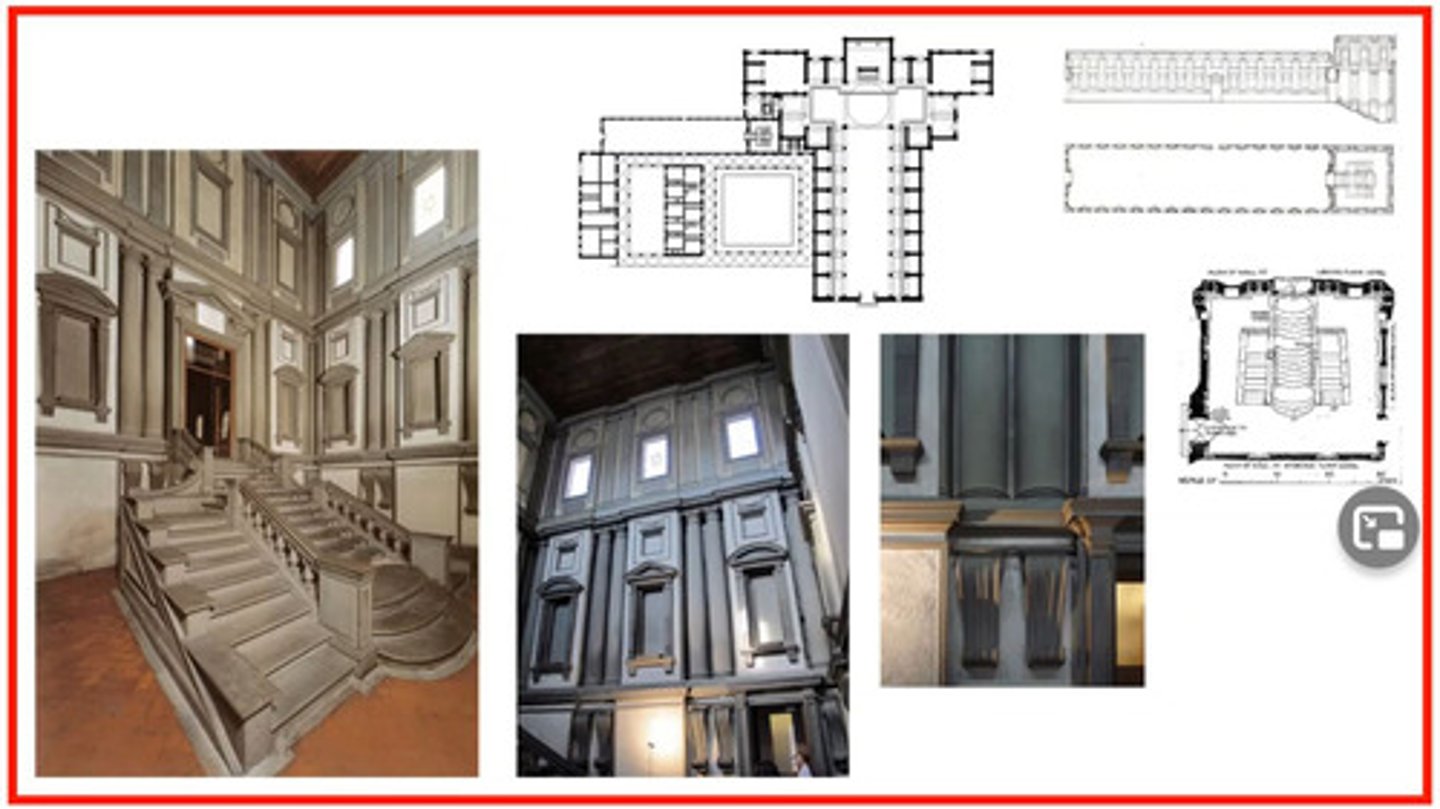
What design appears out of place with other Baroque Architecture?
Laurentian Library (1524) - stairs relentlessly flow downward, niches around staircase are blank
-complete challenge to renaissance rules of order, proportion and use of historic elements

Michelangelo essentially manipulated classical architecture
as elements in gigantic sculpture

The "Campidoglio", Capitoline Hill (1536)
Michelangelo Buonarroti
-Organization deviates from purity of renaissance geometry subtle tension of angled plan and oval plaza
-Ideas beginning to become "Mannerism"

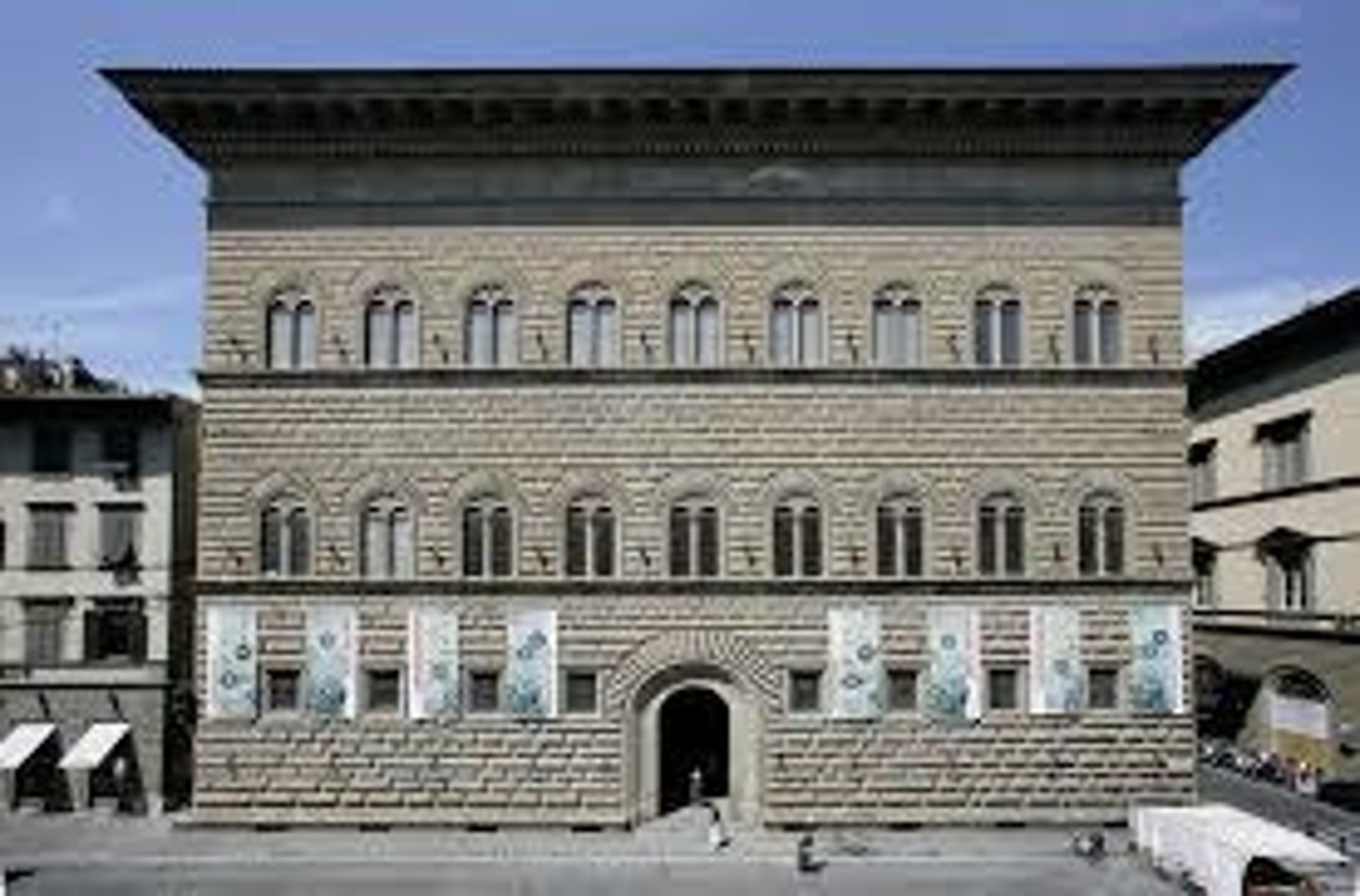
Pallazo Strozzi (begun 1489)
Florence, Italy

Palazzo Farnese, Caprarola (north of Rome) 1559
Giacomo Barozzi da Vignola
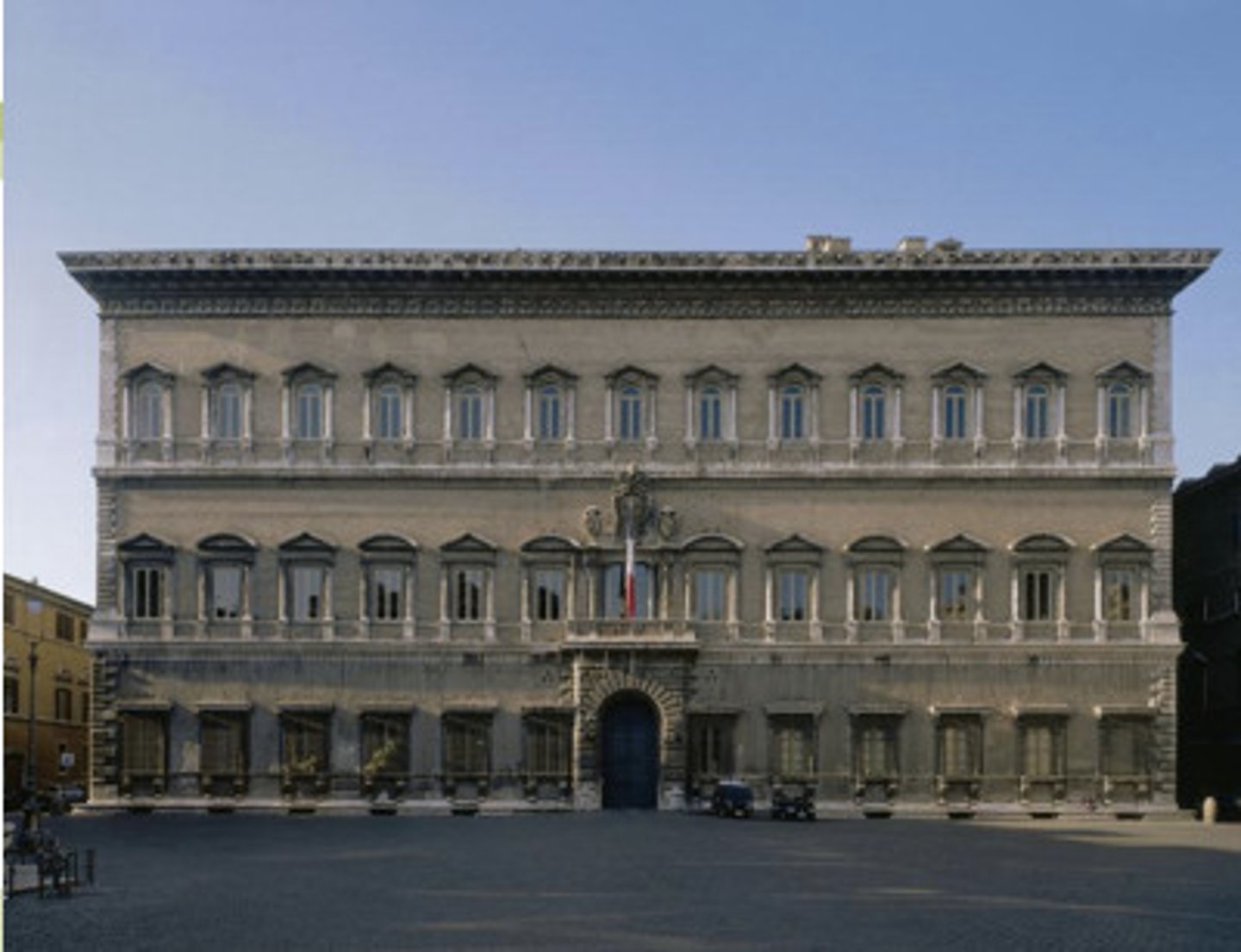

Inigo Jones (1573-1652) Renaissance Architecture in Britain
a notable ENGLISH architect of the Banqueting House in Whitehall
-two trips to Italy, studied Palladio's work
self-taught (son of clothmaker)Banque
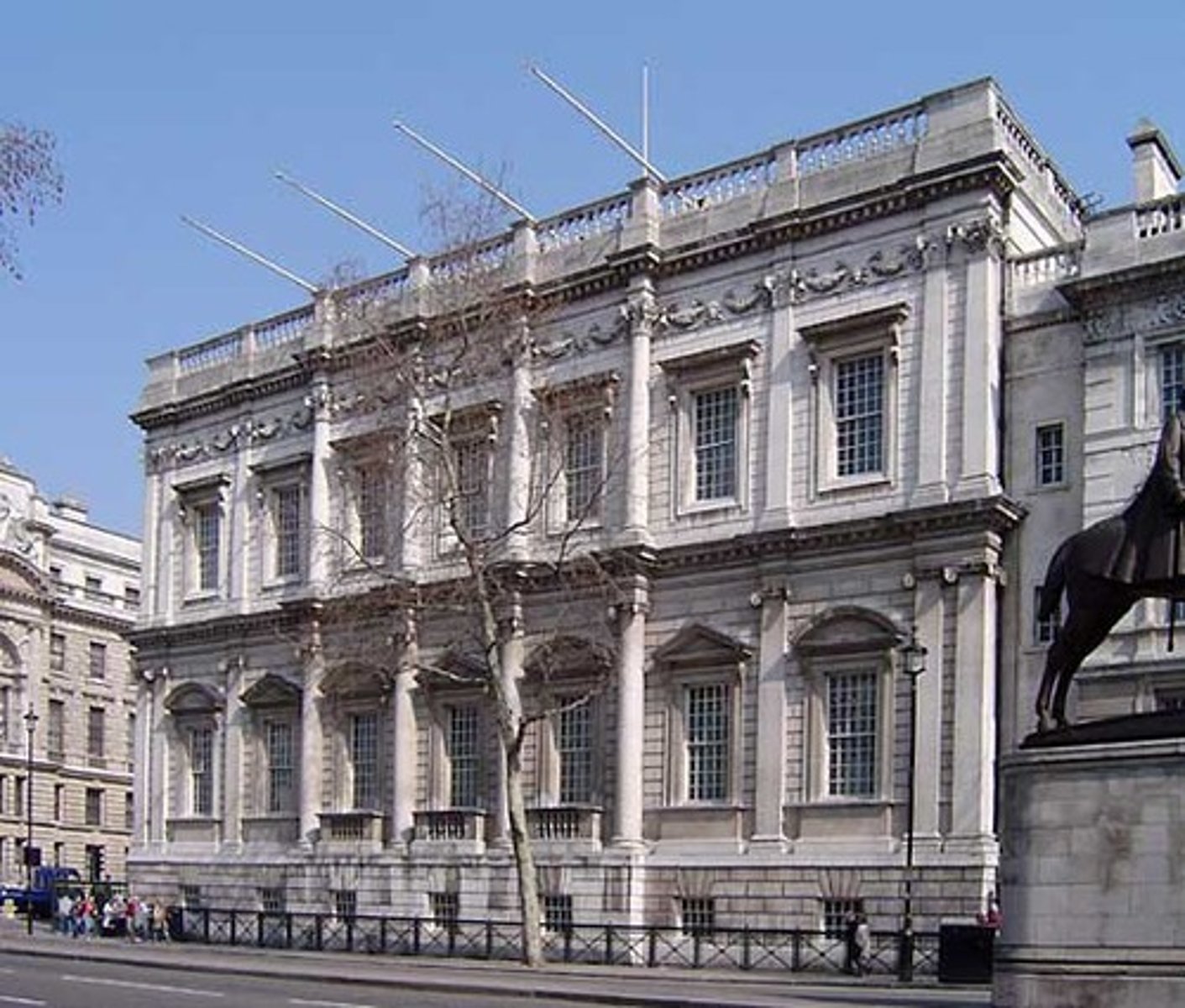

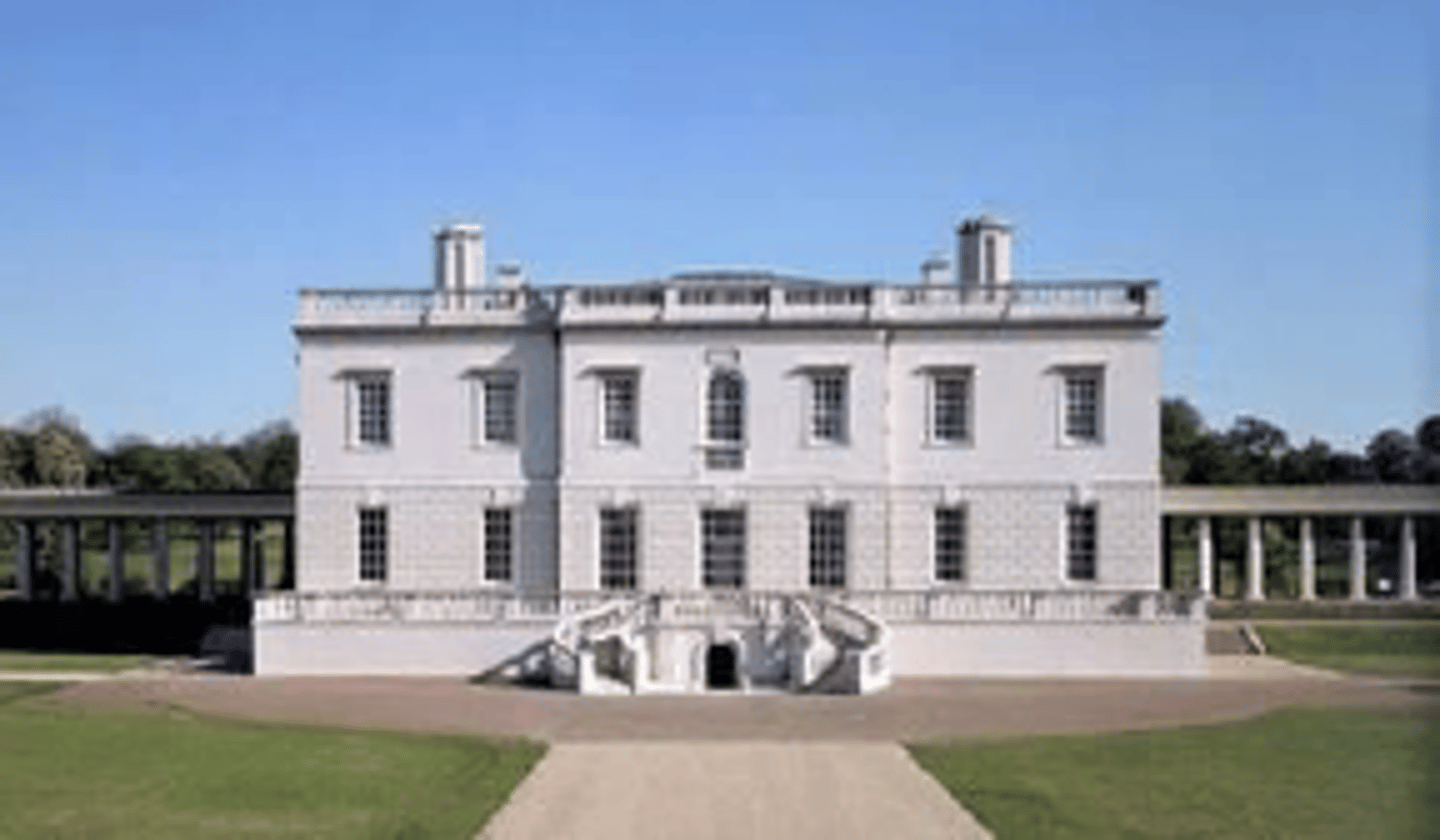
Inigo Jones designed the
Queen's House in Greenwich - begun 1616

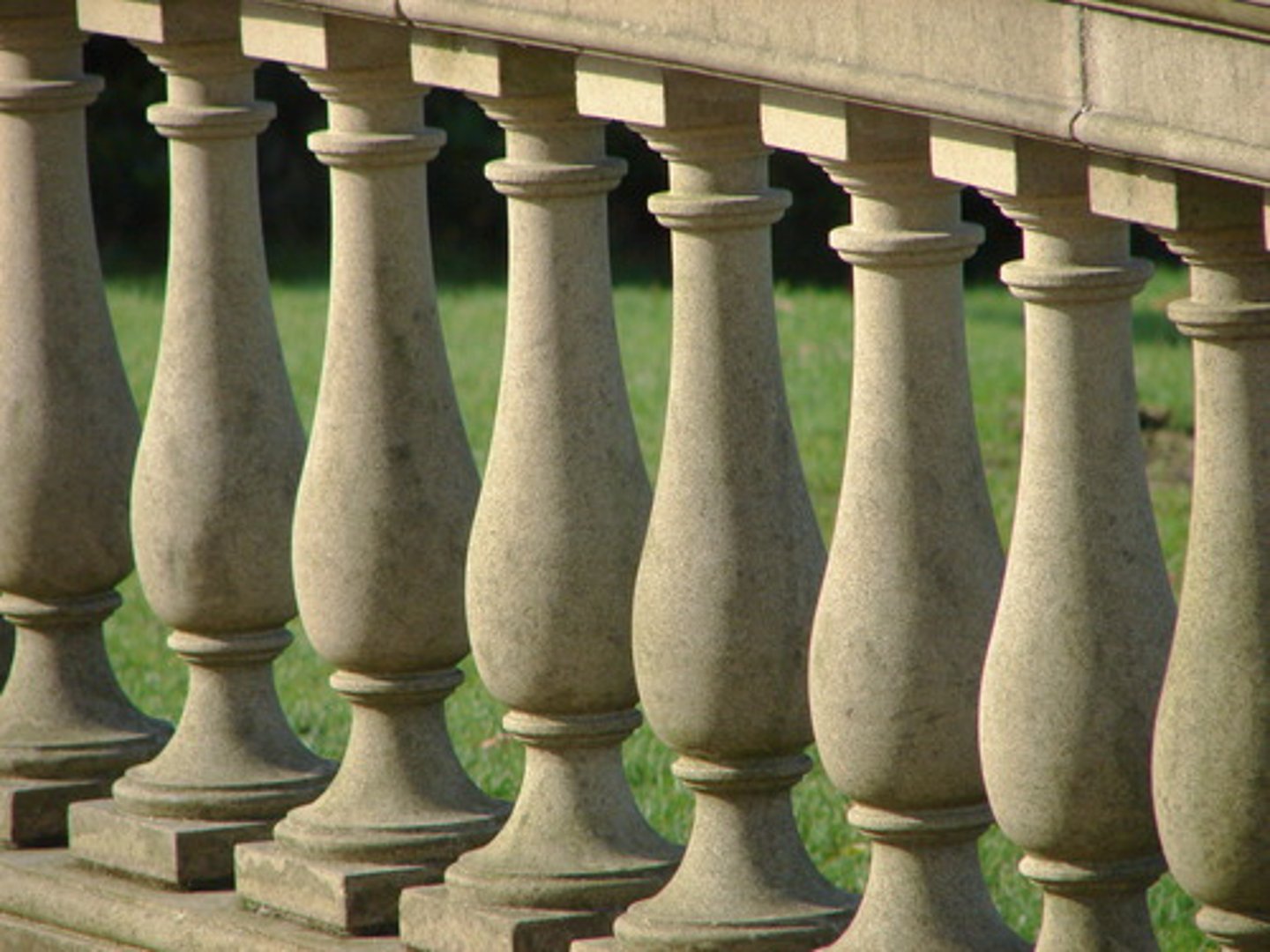
Balustrade
railing supported by balusters

Banqueting Hall in Whitehall, London 1619-
inigo jones
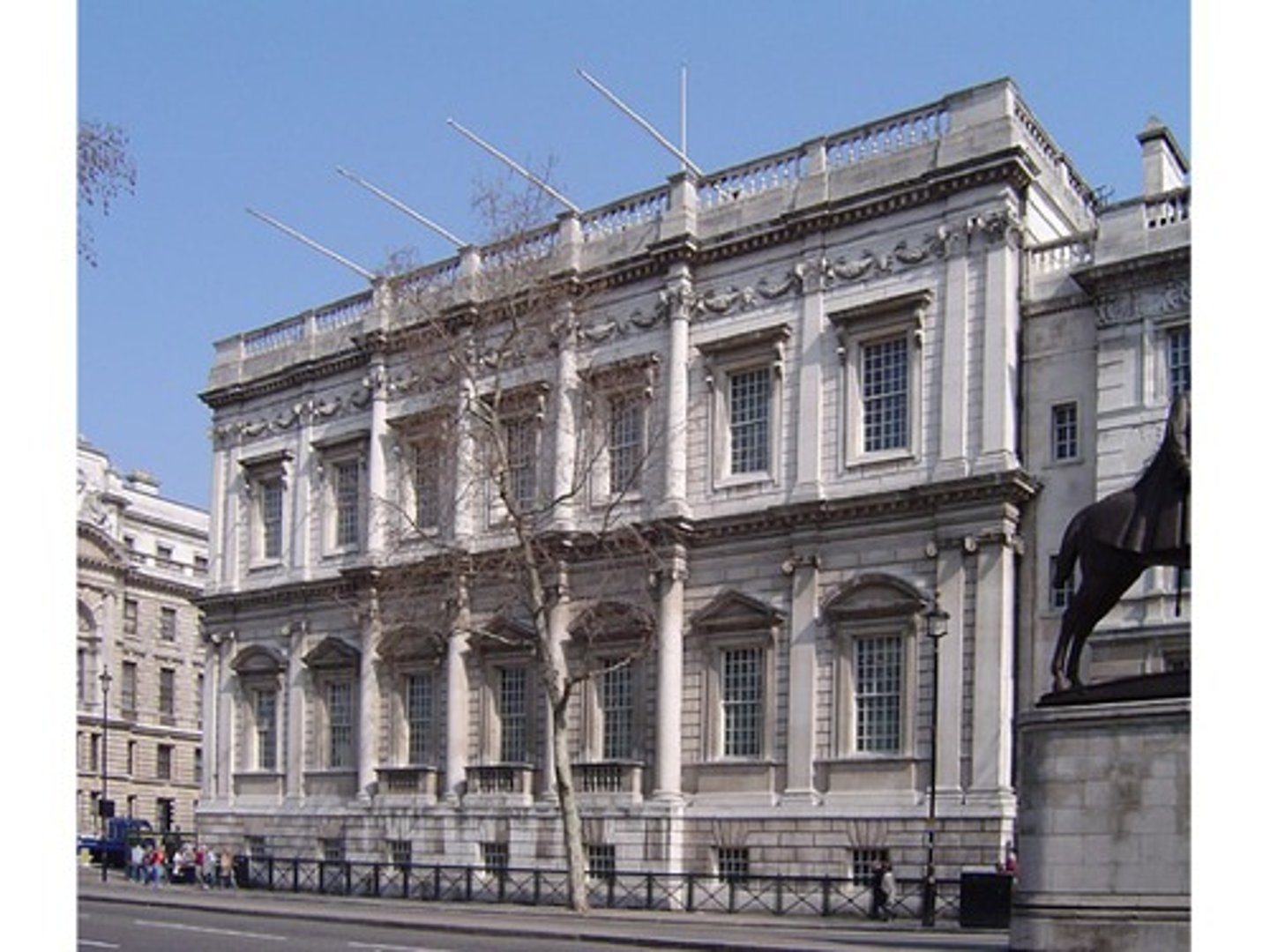

Renaissance Characteristics
engage intellect
pure forms
emphasize individual in isolation
architecture for wealthy
individual isolated buildings
Baroque (ill formed pearl) 17th century
engage the emotions
illusionary effects
emphasize individual as part of society
architecture for all social classes
buildings design to fit context
Baroque Architecture
a style of architecture originating in Italy in the early 17th century and variously prevalent in Europe and the new world for a century and a half characterized by free and sculptural use of the classical orders and ornament dynamic opposition and interpenetration of spaces, and the dramatic combined effects of architecture, sculpture, painting and the decorative arts.
Bernini and Borromini the Baroque in Rome
Reaffirmation of Catholic Church after the Protestant led Reformation
Buildings to awe, convert
Counter reformation: reintroduce spiritual values
Something greater than the individual
2 famous architects in Baroque period building to awe and convert counter reformation-reintroduce spiritual values something greater than an individual reaffirmation of the Catholic Church after the protestant reformation
Gianlorenzo Bernini and Francesco Borromini
Bernini and Borromini
S. Carlo alle Quattro Fontane Rome, begun 1634 Franscesco Borromini
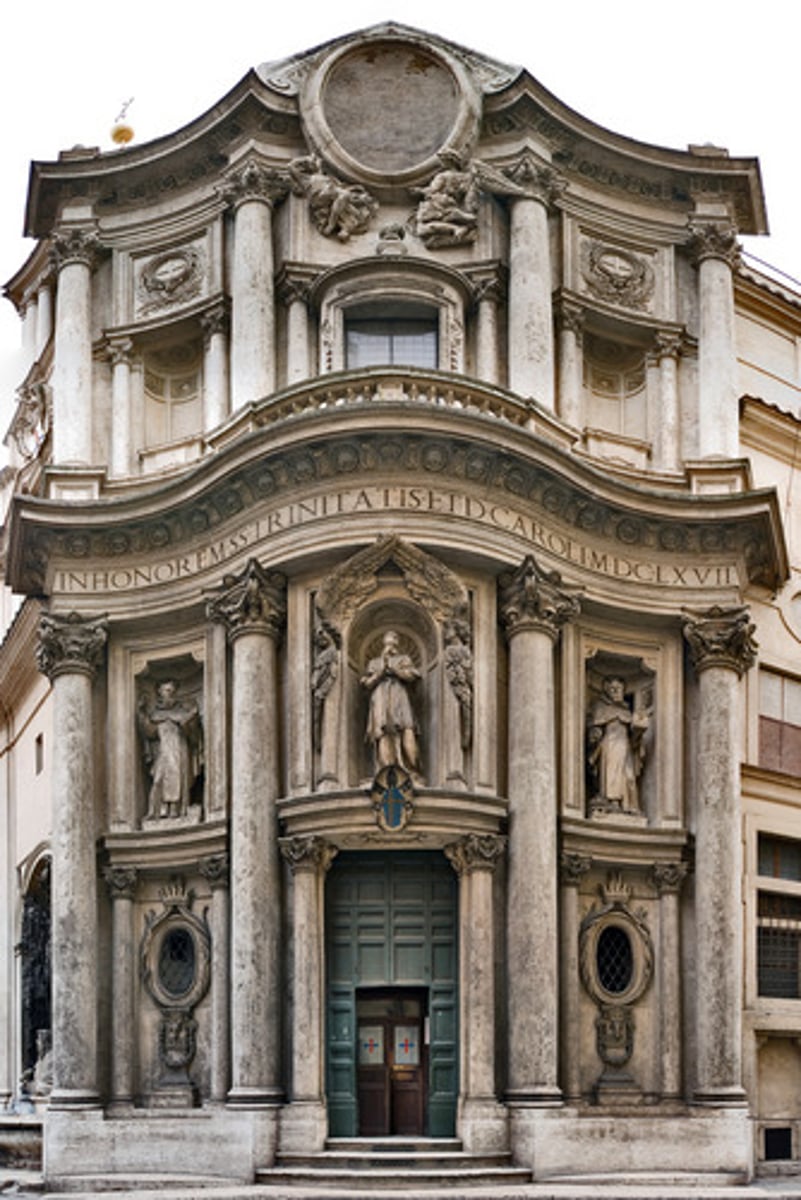

Bernini
added collonade - elliptical space
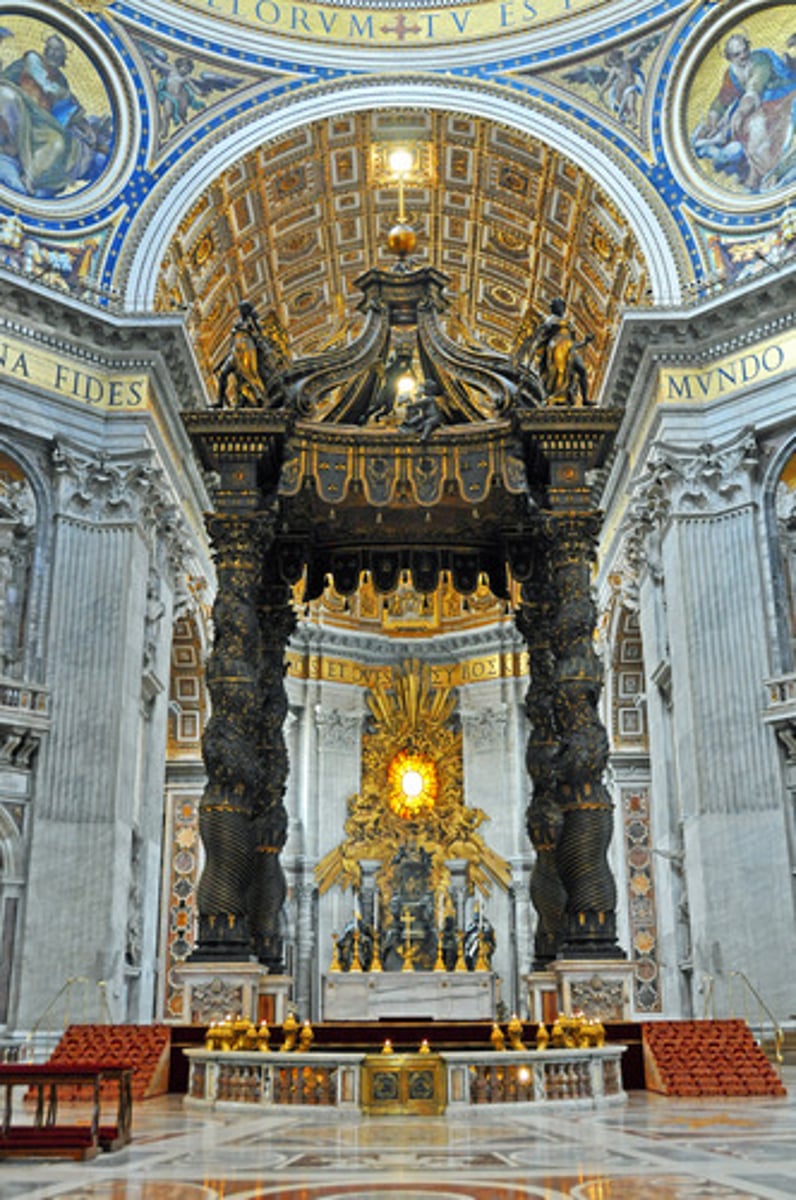
St. Peter's Rome 1624-1633
Baladacchino
built by Bernini

Piazza of St. Peter's
Begun 1656
Gianlorenzo Bernini
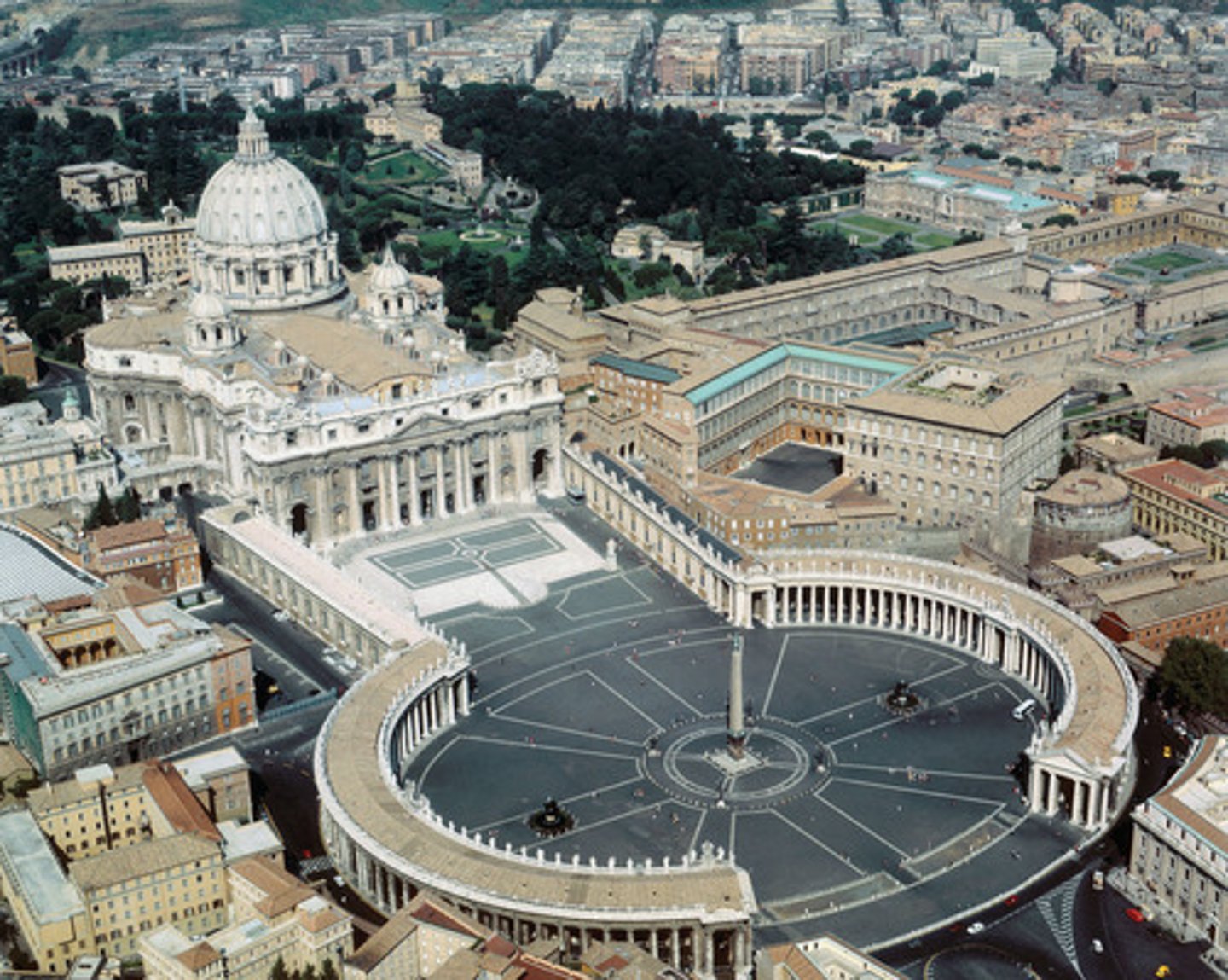

Bernini = ______________ ; Borromini = ______________
St. Peter's piazza and building; S. Carlo alle Quattro Fontane
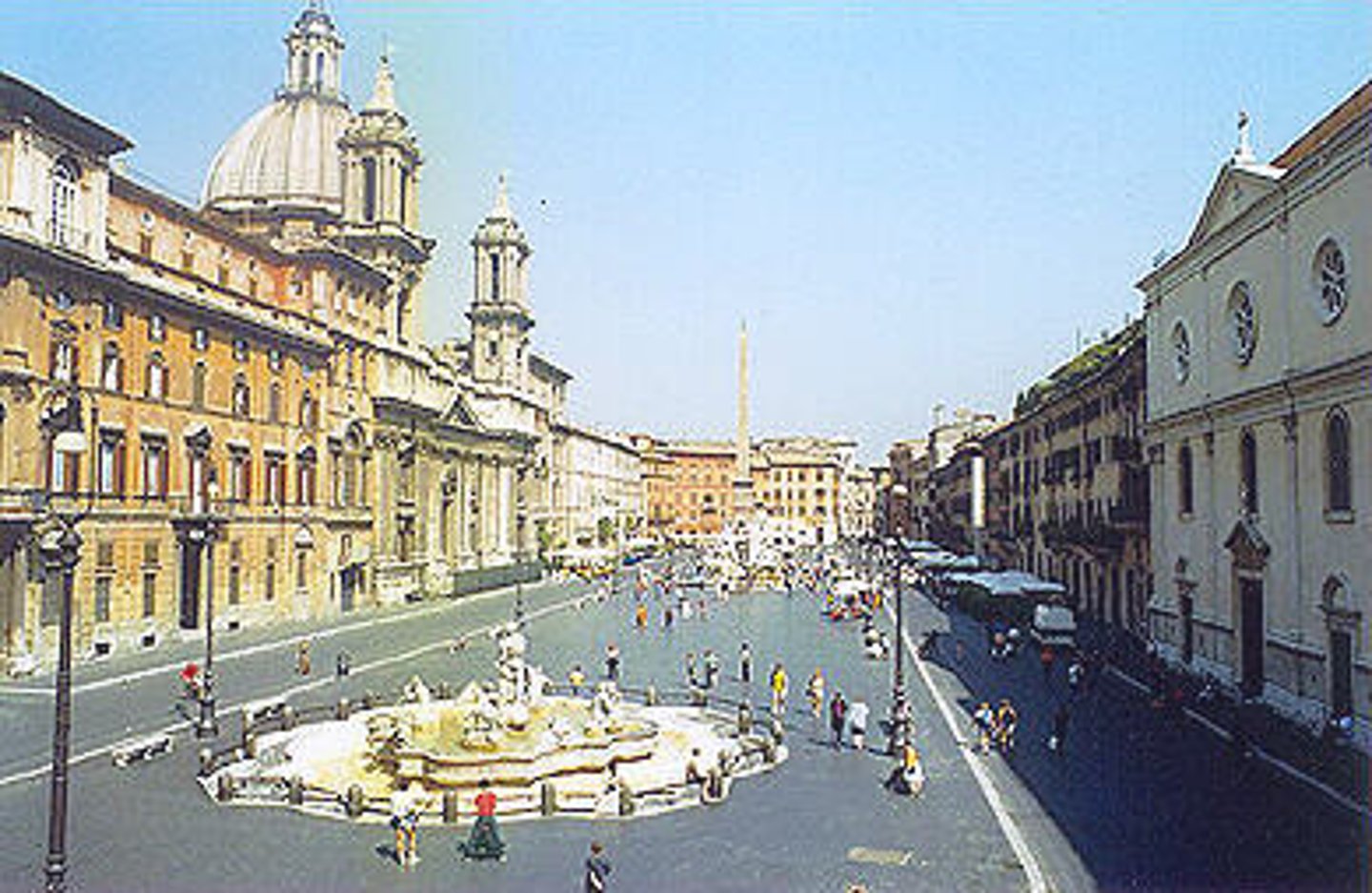
Piazza Navona, Rome
Bernini and Borromini, begun 1644
Space dates to ancient Roman Circus

London Fire of 1666
act of rebuilding the city of London; example of an early building code; Sir Christopher Wren redesigned St. Paul's Cathedral and over 50 other churches in London
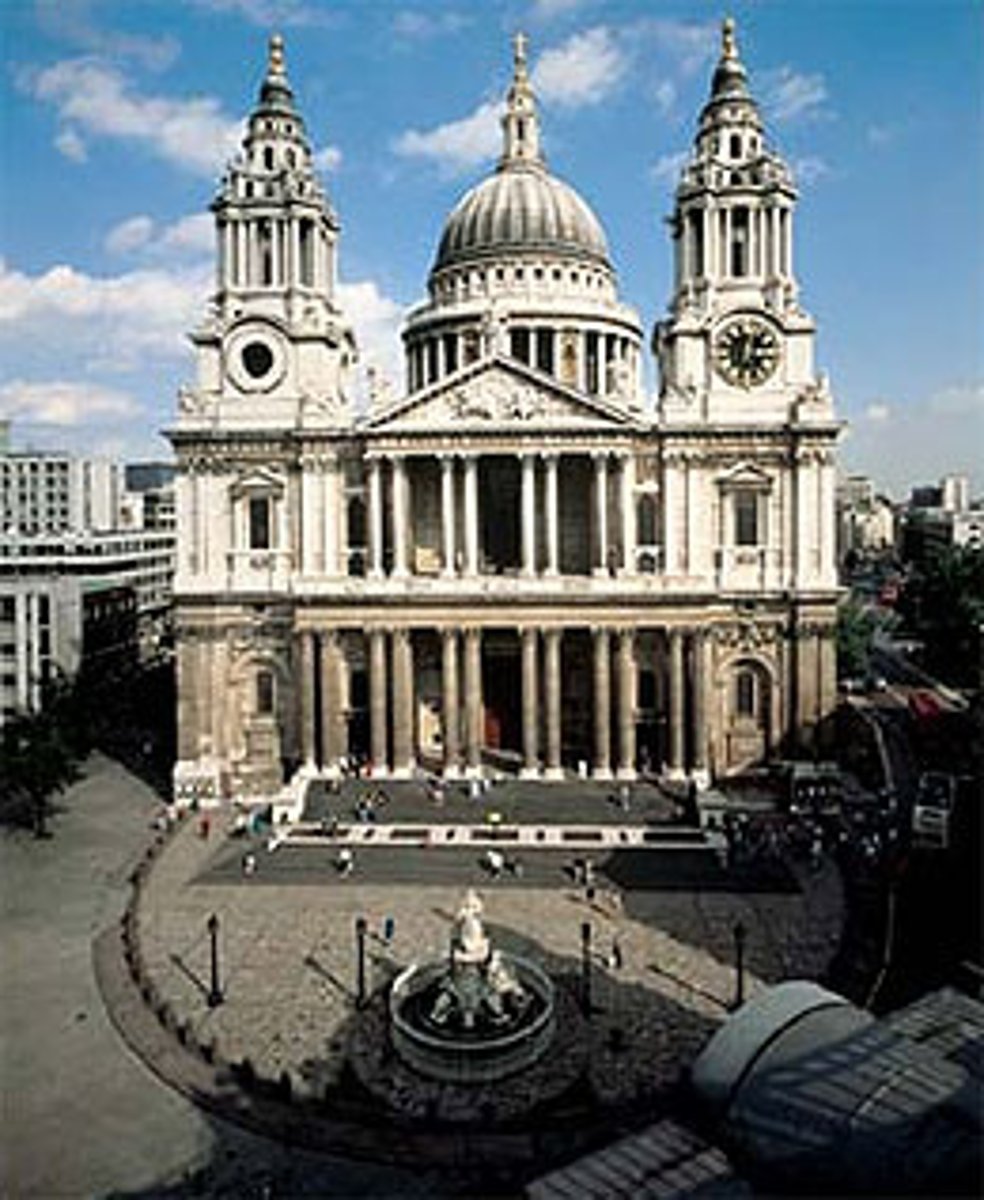
Sir Christopher Wren
St. Paul's Cathedral - London 1675-1709
rebuilding after fire

Sir Christopher Wren, London
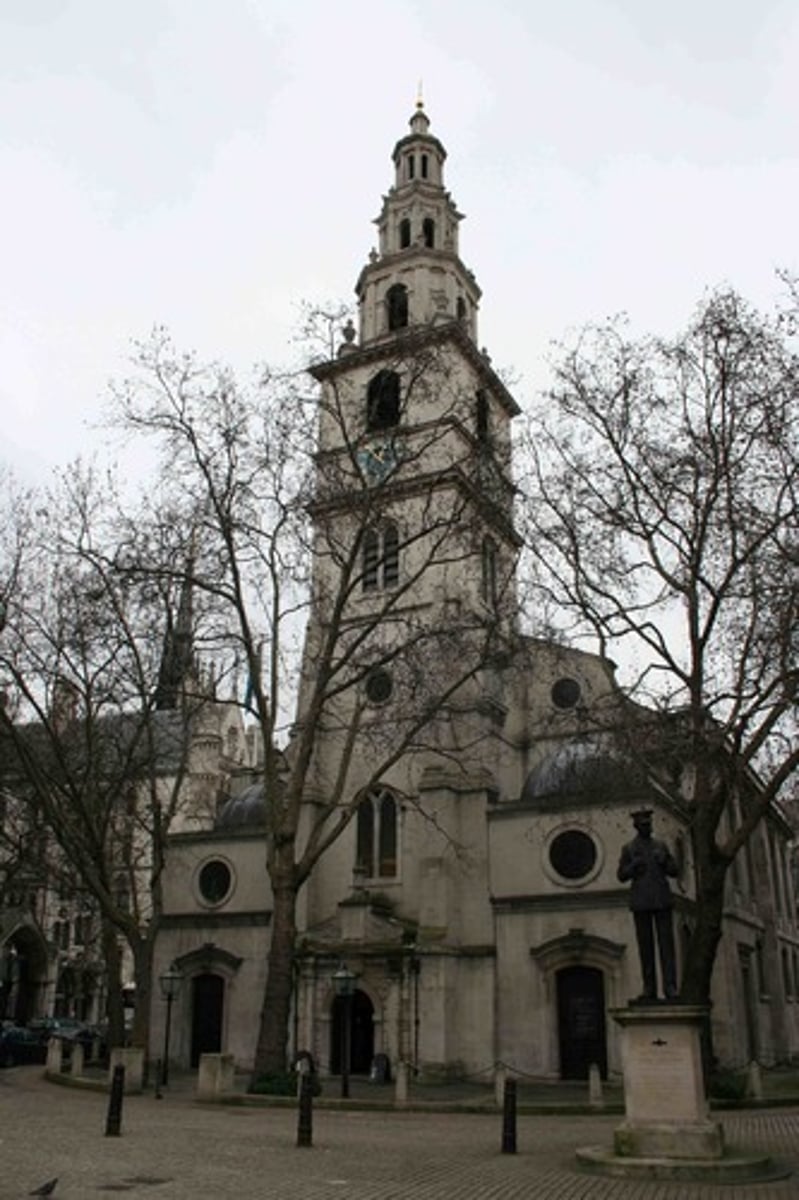
St. Clementine's Dane

Who redesigned St. Paul's Cathedral and over 50 other churches in London
St. Christopher Wren
Sir Christopher Wren, London 1672-79
St. Stephen Walbrook
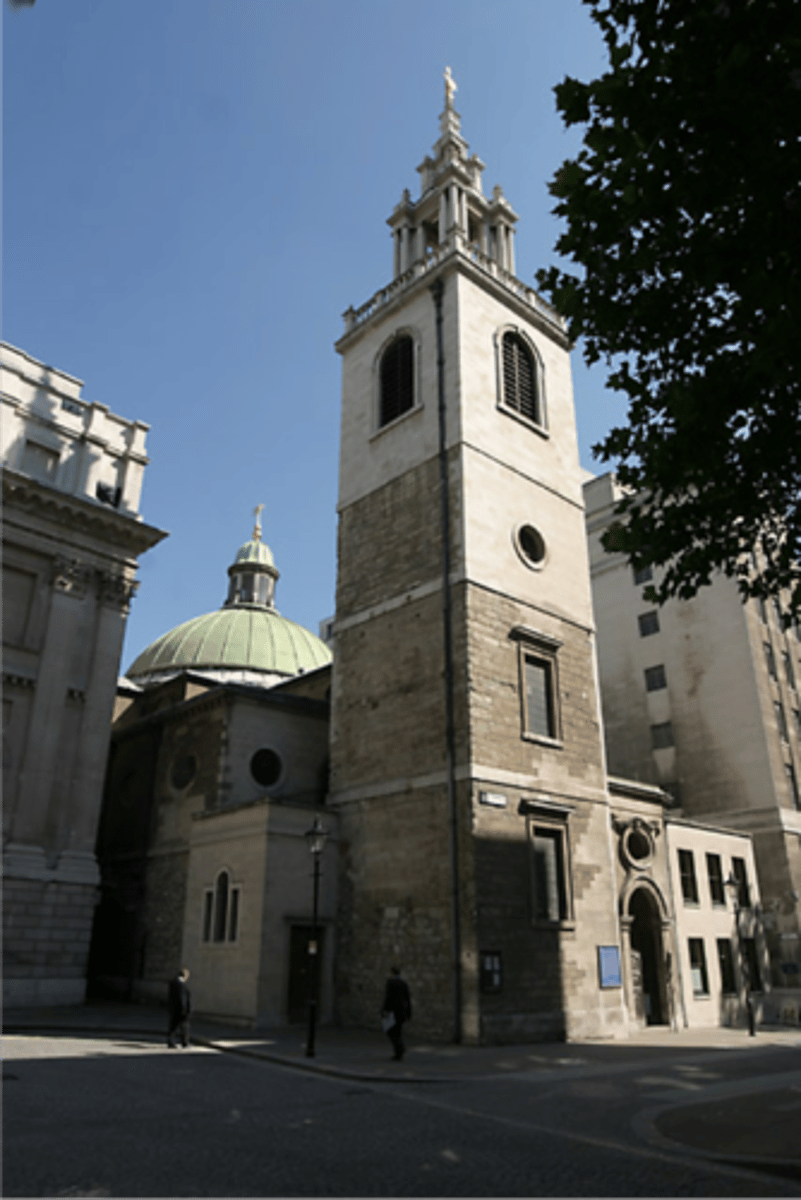

Christ Church in London
Nicholas Hawksmoor (1714-1729)
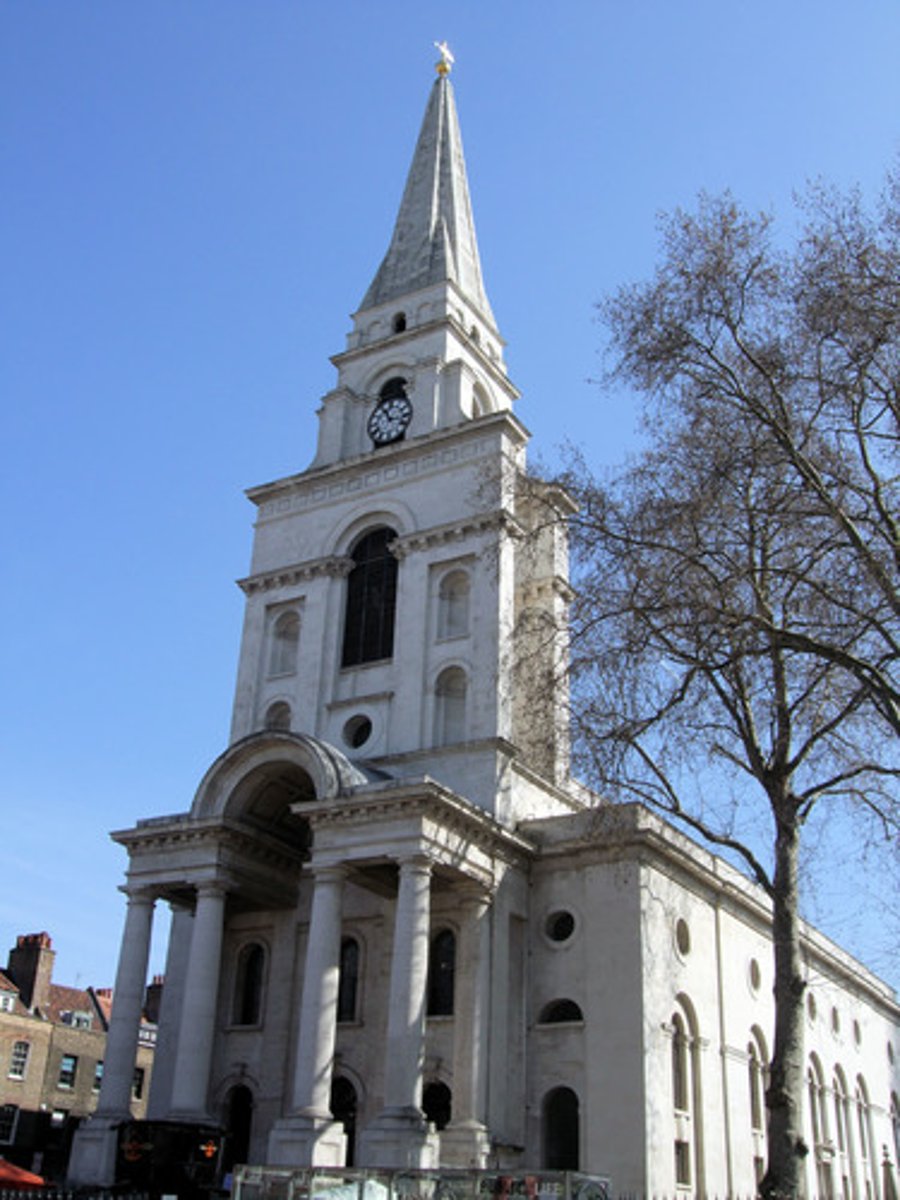

St. Mary Woolnoth London
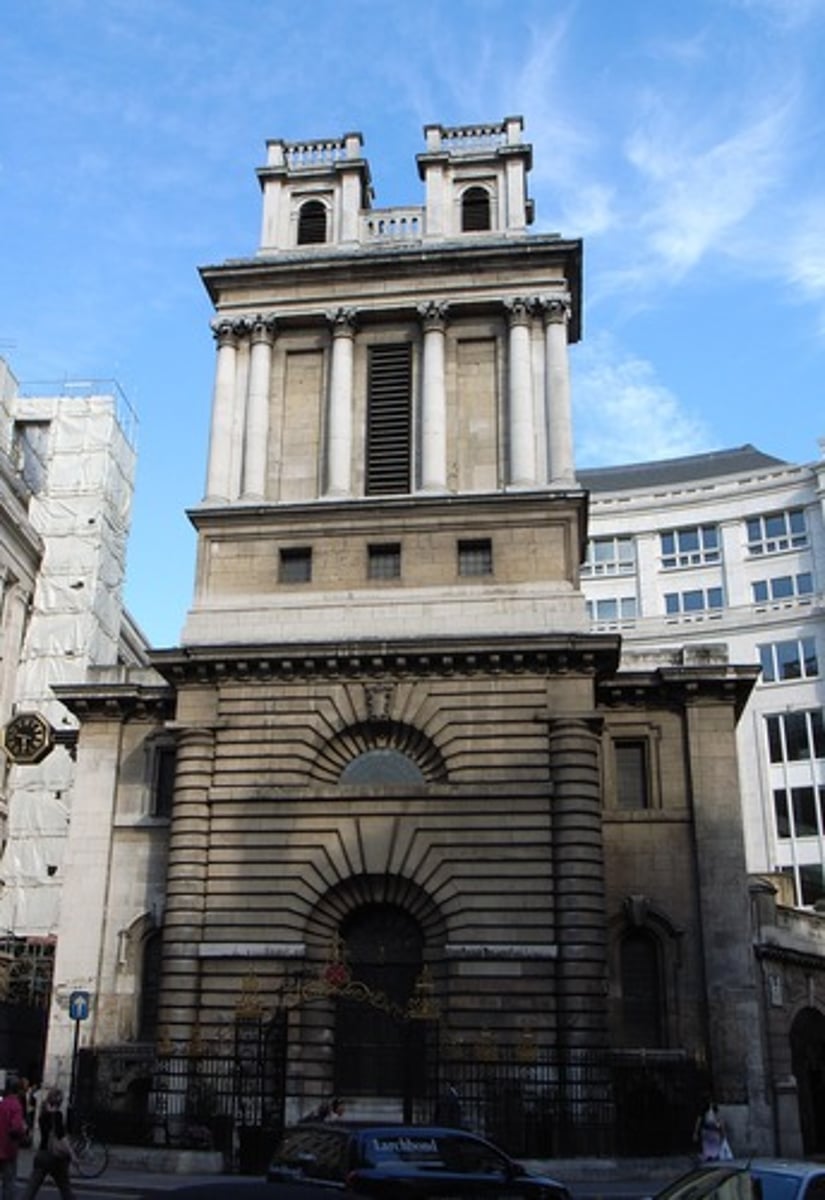
Nicholas Hawksmoor (1716-1724)

Versailles - outside Paris
Baroque
Louis 14th - a hunting lodge
begun 1661
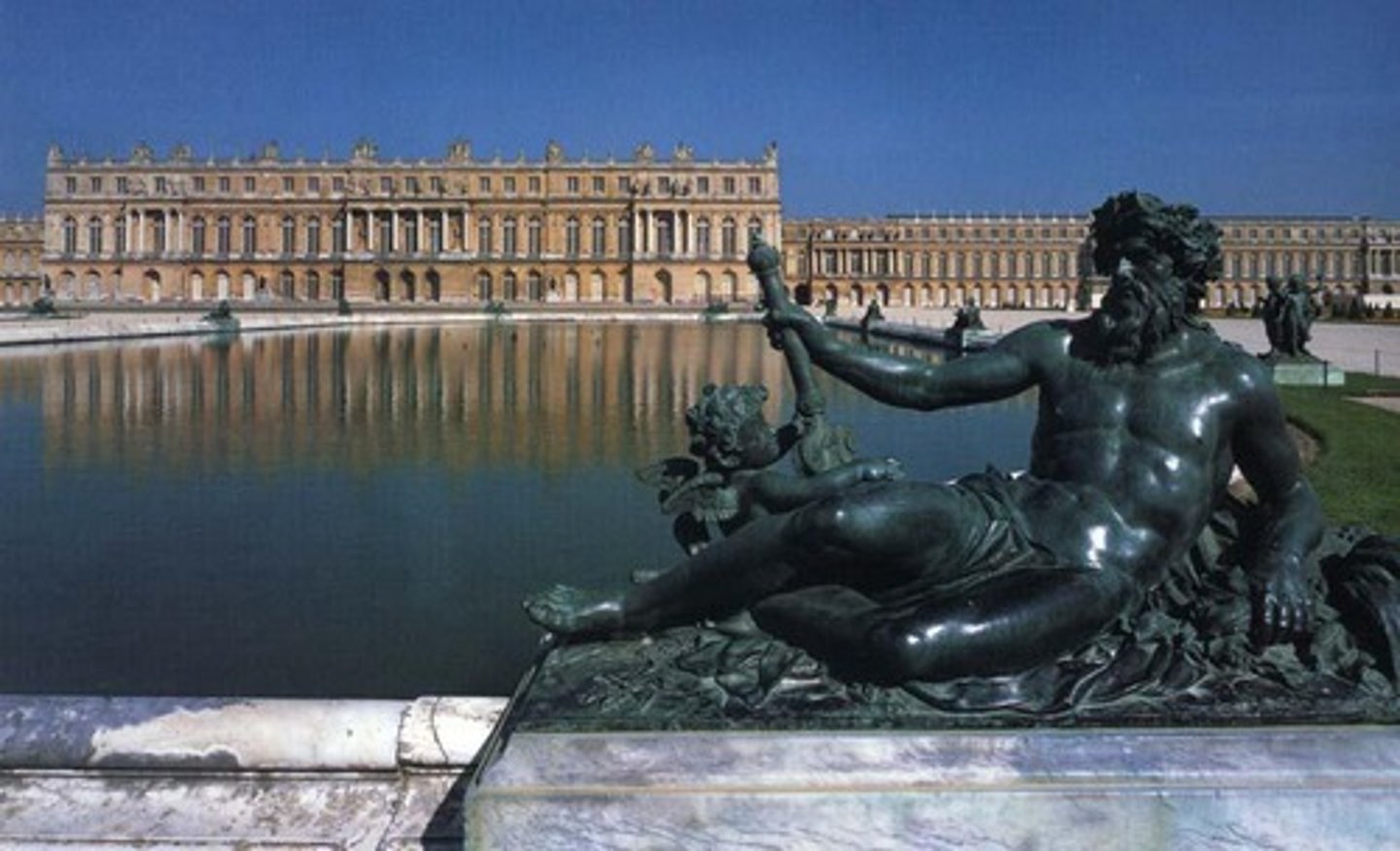

Versailles (gardens)
gardens included roughly 1400 fountains, using water pumped up from the Seine
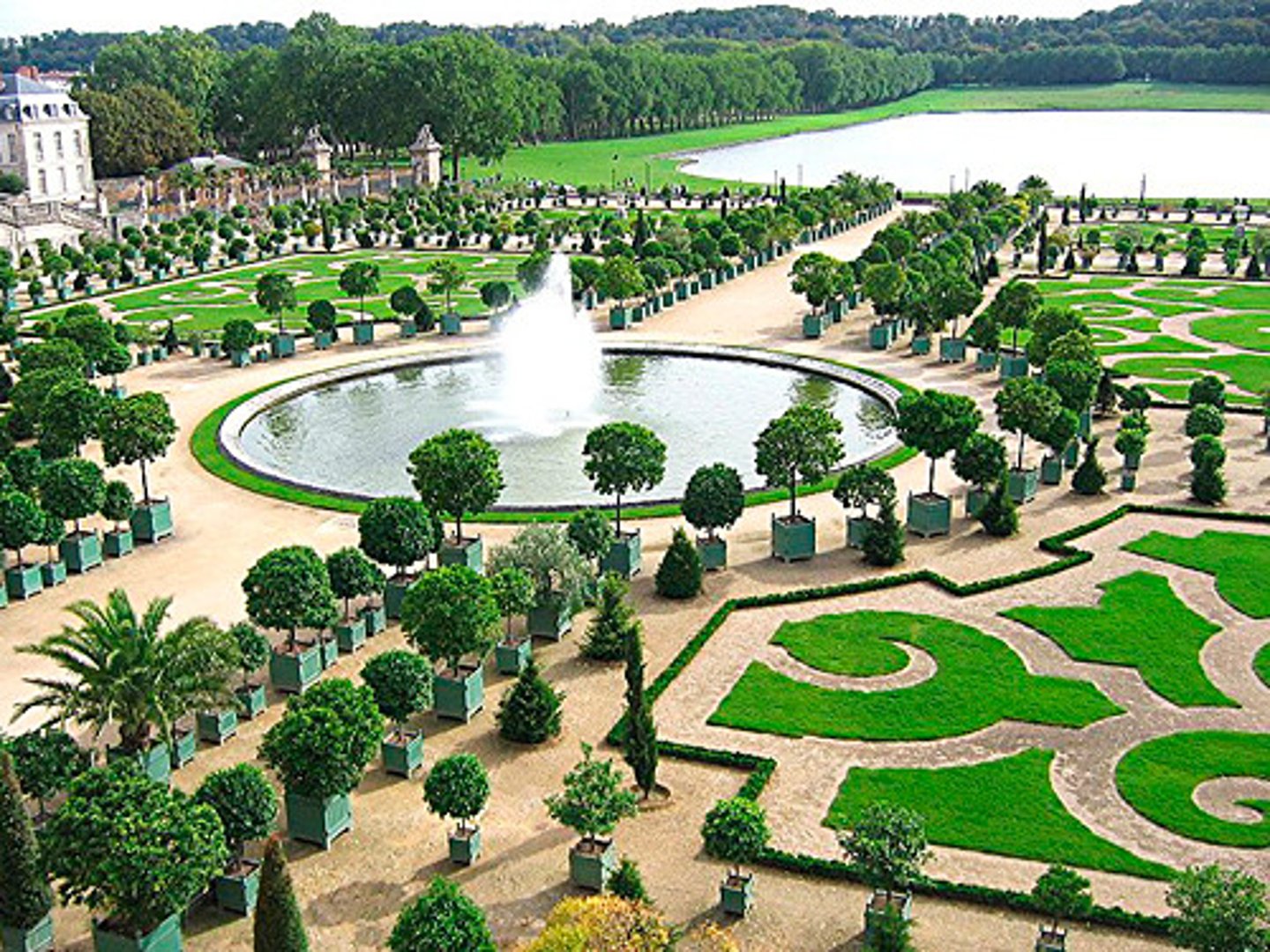

Parterre
gardens geometrically organized
extended baroque design of palace rooms into the landscape
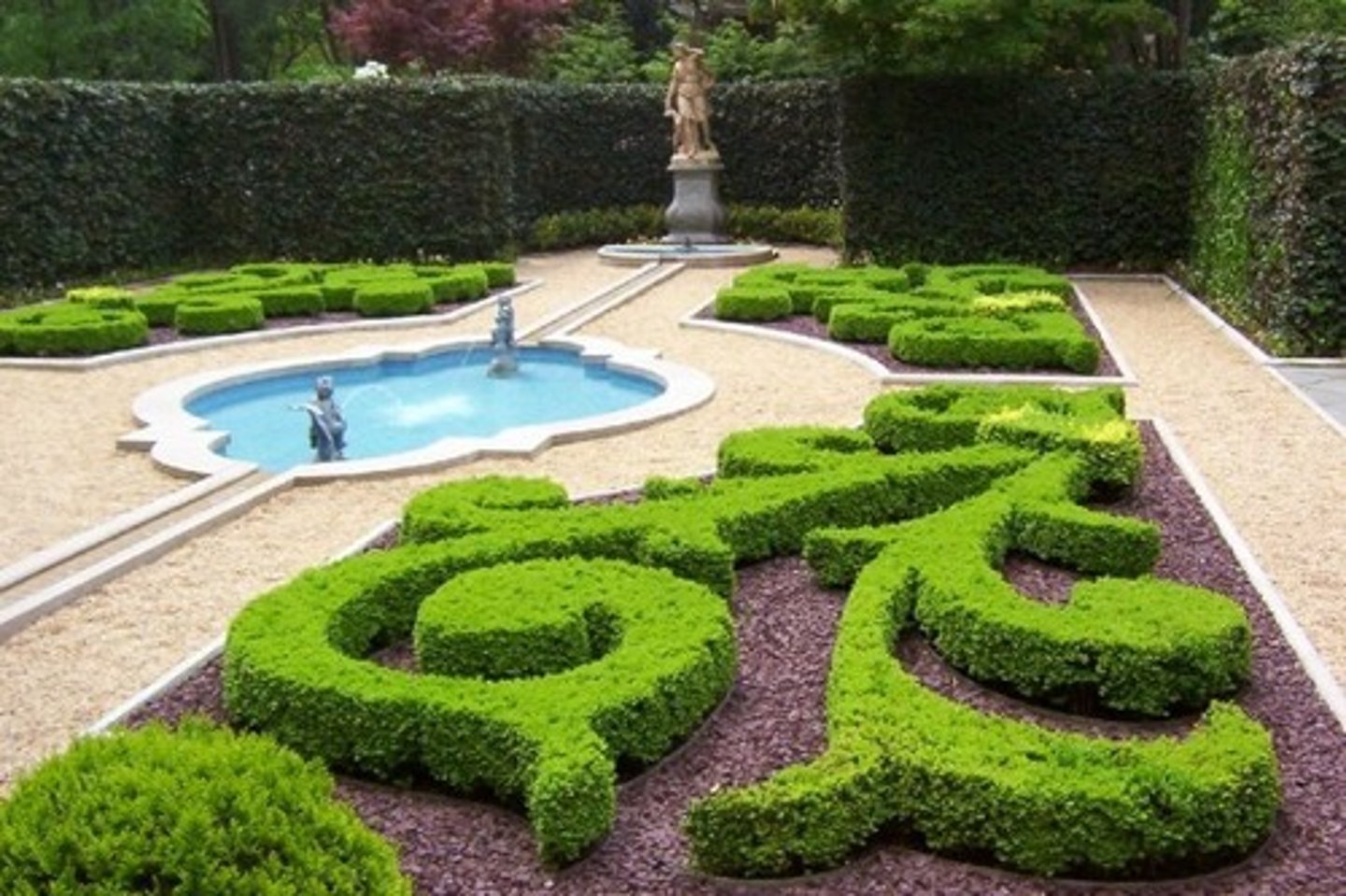

Vegetation
exotic to the region in baroque gardens
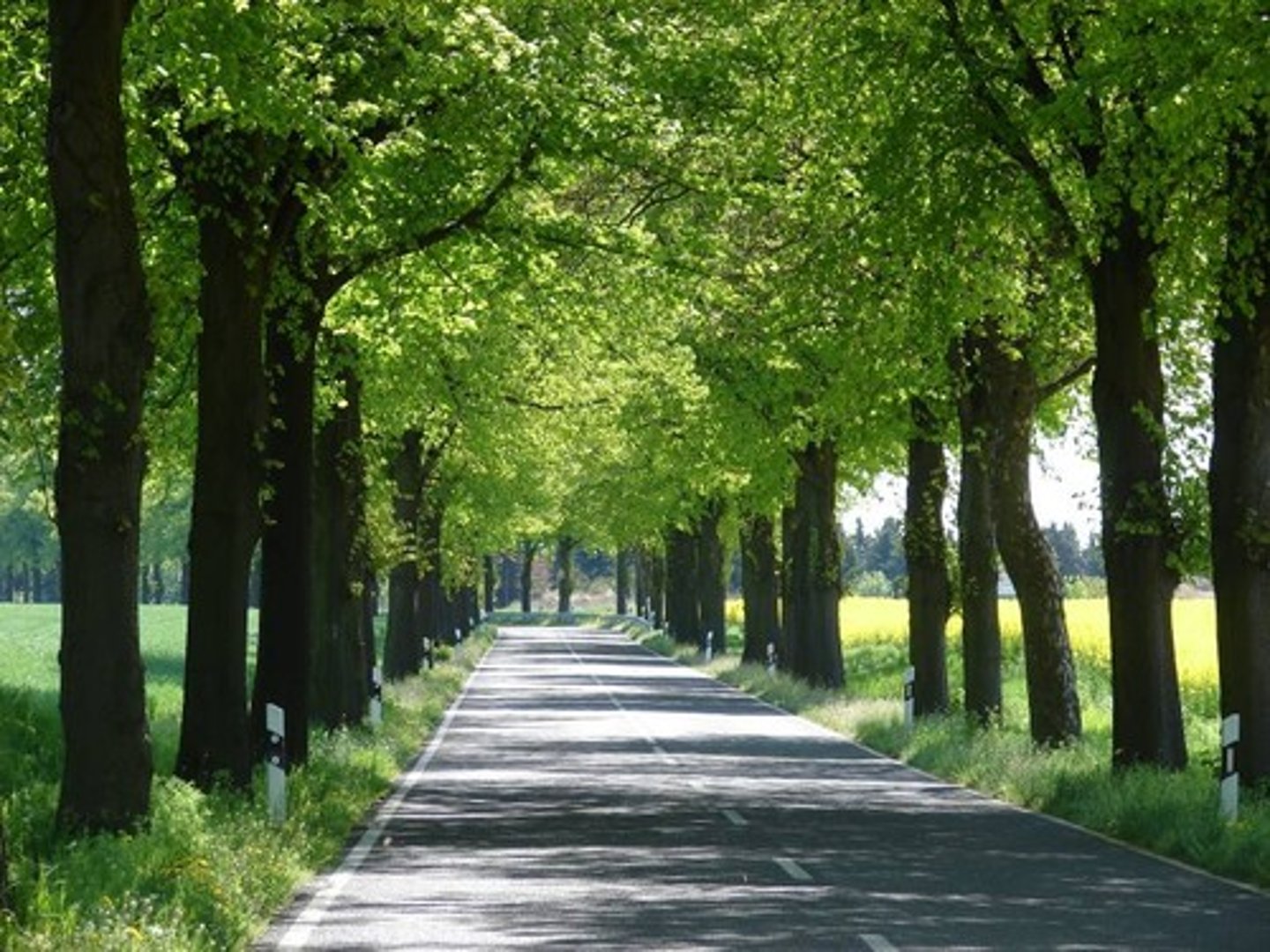
Allees
pathway lined with trees

rococo
a style of decorative art that evolved from the Baroque, originating in France about 1720 and distinguished by fanciful, curved spatial forms and elaborate, profuse designs of shellwork and foliage intended for a delicate overall effect

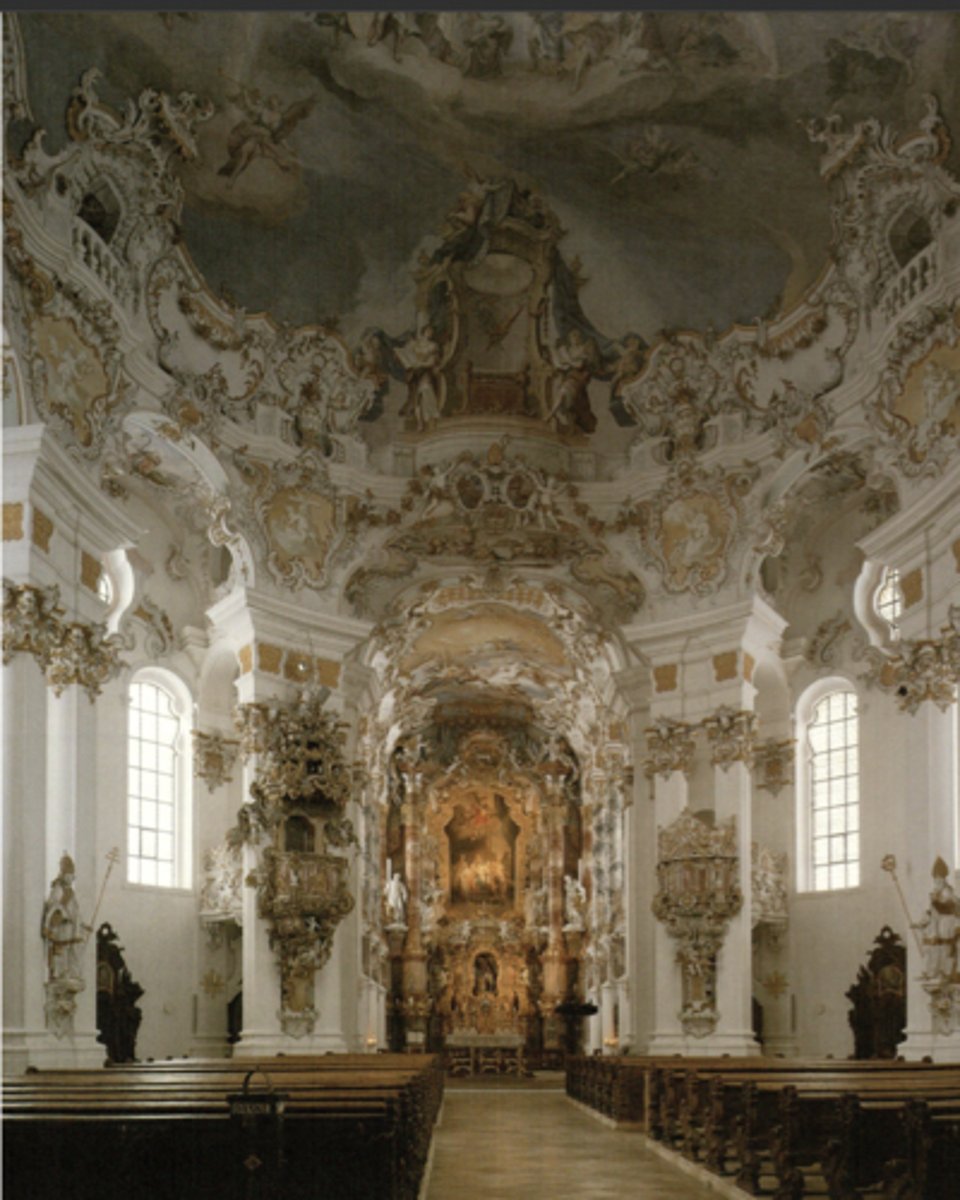
Dominikus Zimmerman
Die Wies, near Munich: 1746-54
-church in rural Bavaria
-Zimmerman brothers design structure disappears behind decoration outside place facades intricate detail on interior

Spanish Steps
Rome, 1723-25
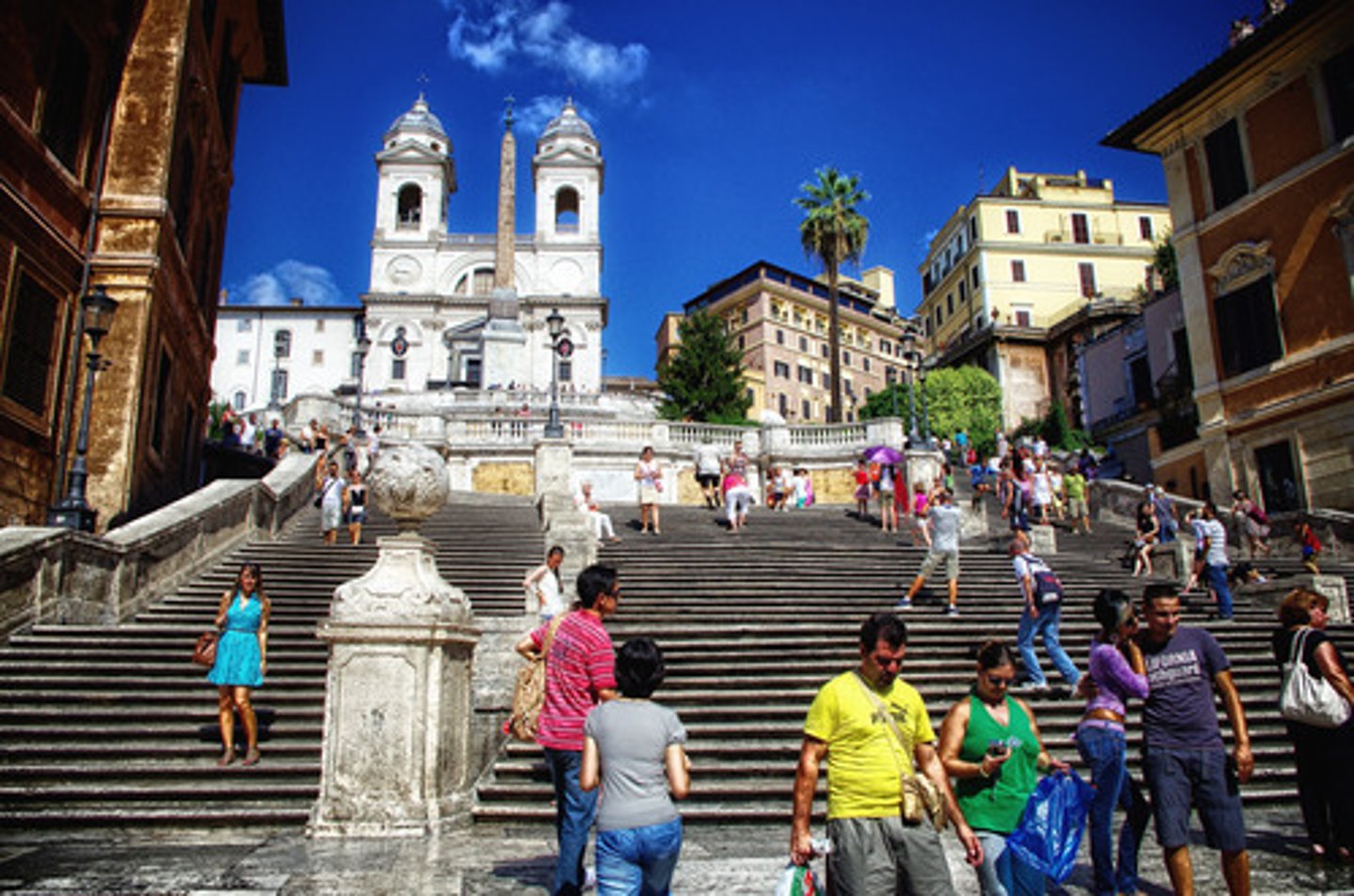

Revivals: Enlightenment
industrial revolution
new building types
architects respond by looking back: borrow styles from all eras and continents
anti-Baroque go classical: motivated by archeological digs too
the innovative architecture was designed by engineers
economic, political, cultural, social CHANGE
US and French Revolutions
Urban centers
Science rules
Industrial Revolution (middle class emerges) : cast iron building material
This was James Gibbs' design that was copied in the US
St. Martins in the field
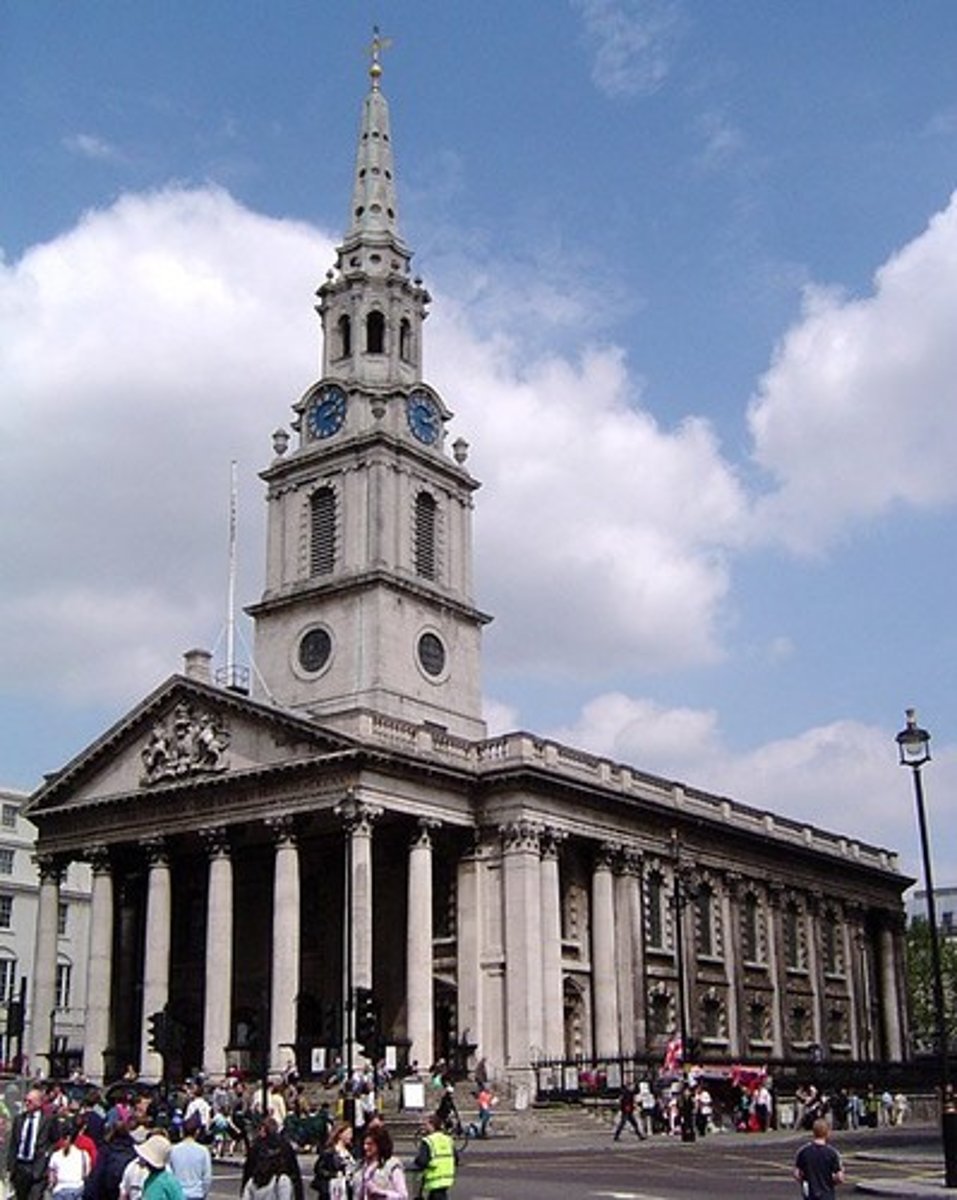

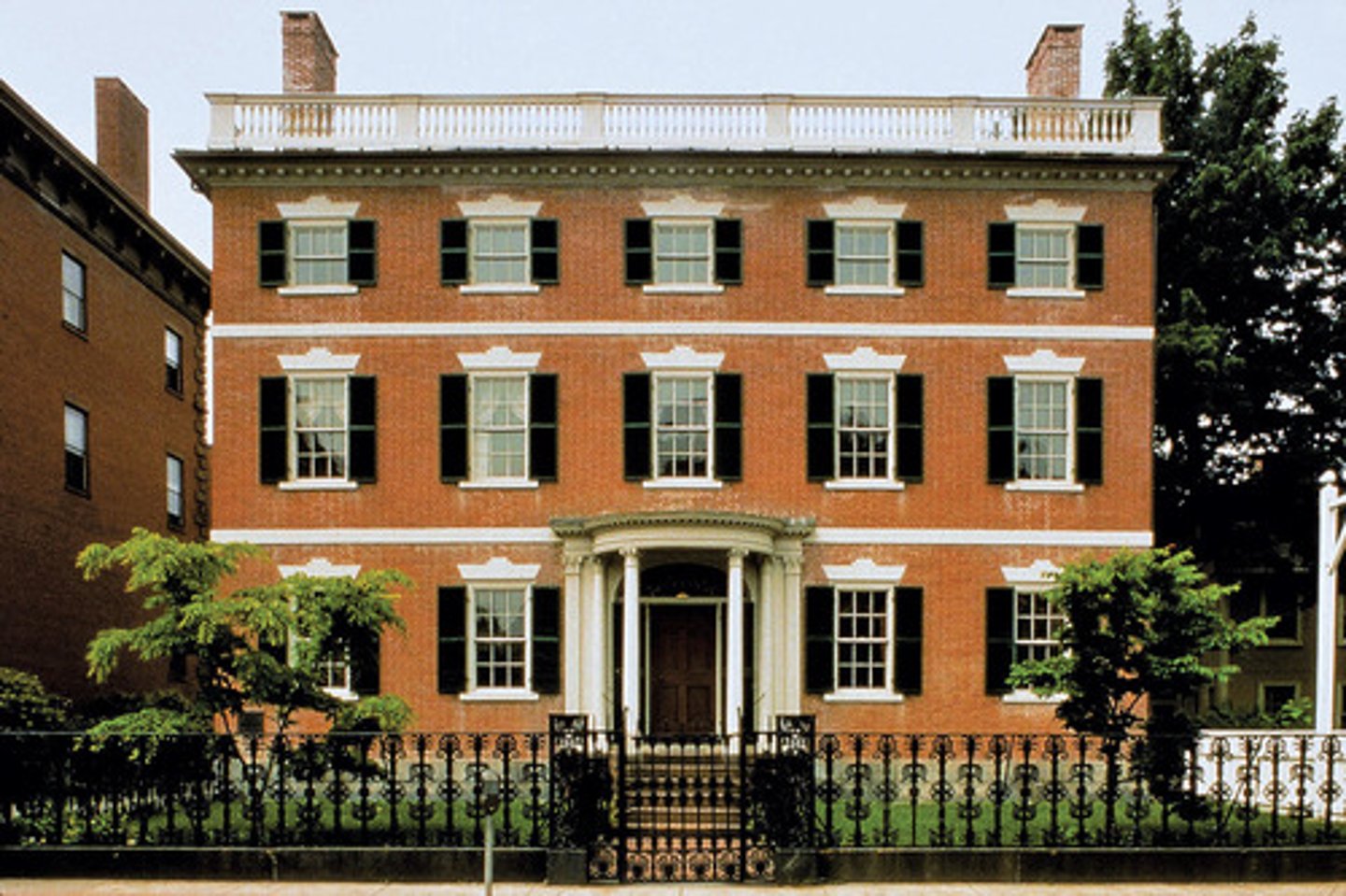
Developed after American revolution copied from British architect Robert Adam
federal style

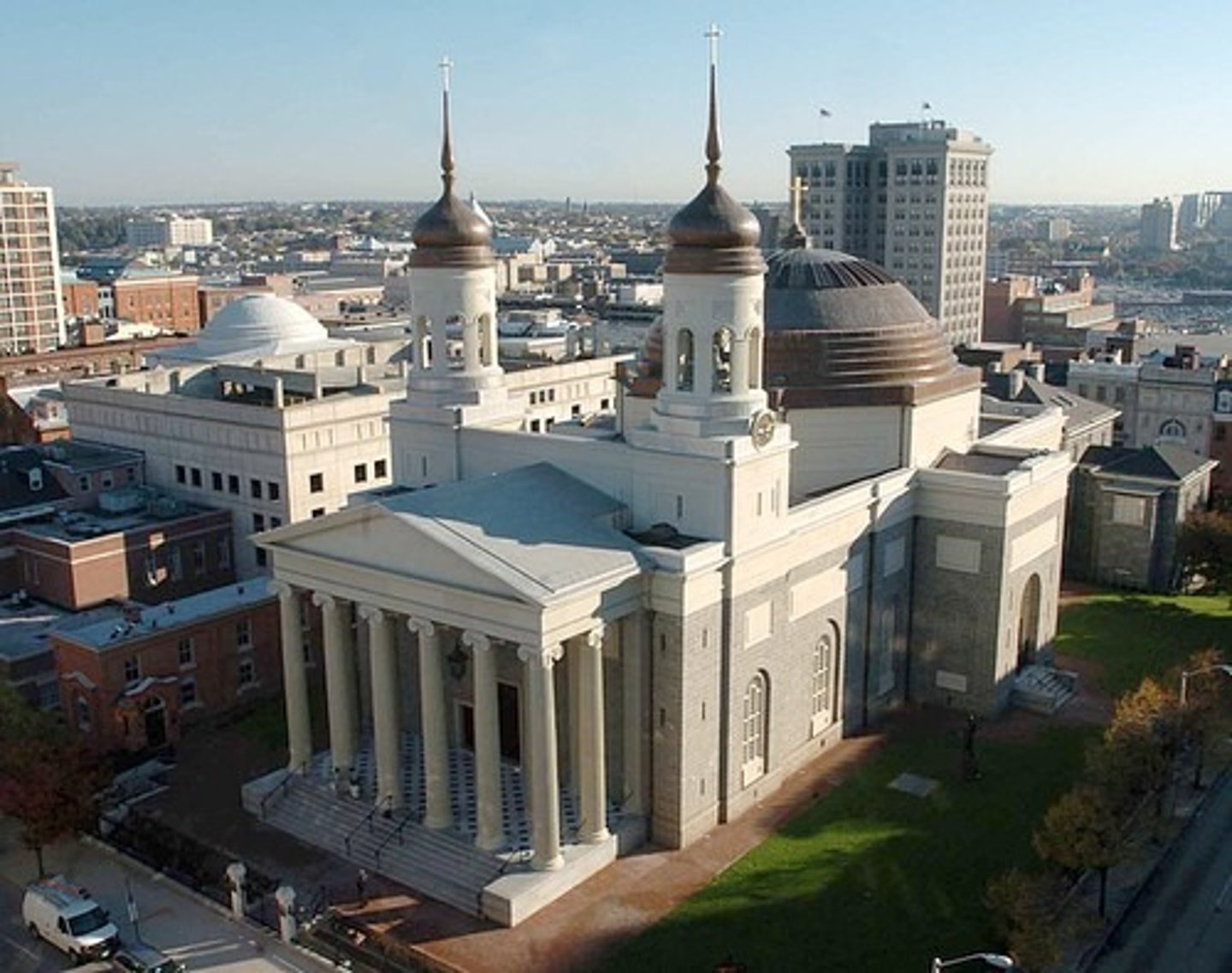
Who built the Baltimore cathedral and acknowledged as 1st professional architect?
Benjamin Latrobe

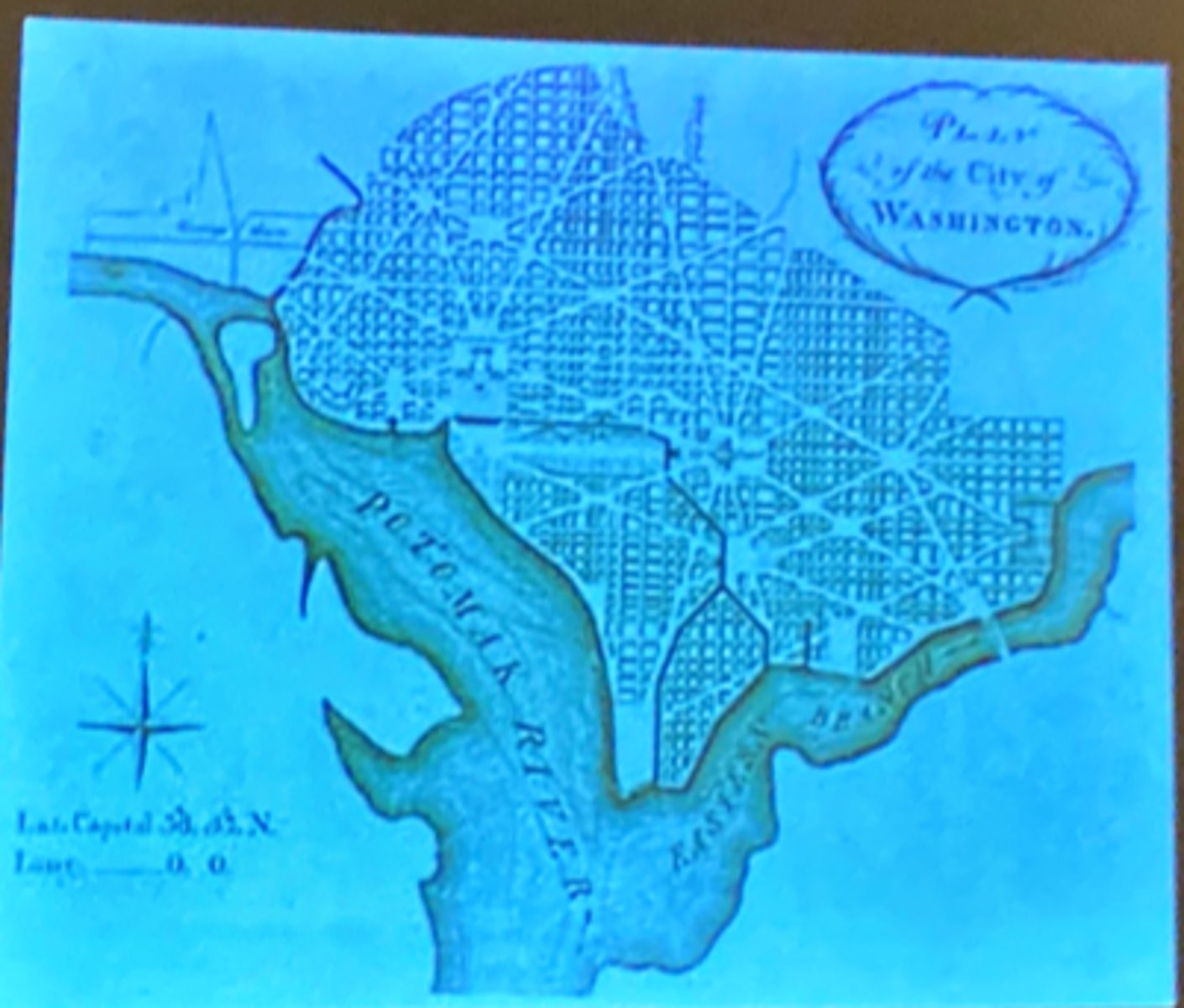
Who designed the plan of Washington DC?
Pierre Charles L'enfant