Marine Science Ch 3 Part 2 Test
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Downwelling
The sinking of surface water that is denser than underlying water layers.
Thermocline
A zone in the water column that shows a rapid decline in temperature with depth.
Deep & Bottom Layers
The layer of the ocean that is uniformly cold.
Thermohaline Circulation
Movement patterns of water passes (allows for ocean circulation) over great distances driven by differences in salinity and temperature.
Upwelling
The process by which colder water rich in nutrients rise from lower to higher depths.
Intermediate Layer
The layer of the ocean with the main thermocline.
Pycnocline
The zone in the water column in which the density rapidly increases with depth.
Halocline
The zone in the water column that shows a rapid increase in salinity with depth.
Surface Layer
The layer of the ocean that is mixed by wind, waves, and currents.
Ekman Spiral
The change in the direction of water movement (spiral motion) as you descend the water column.
Trade Winds
Steady winds that blow from east to west in the Tropics.
Gyre
A very large nearly circular system of wind driven by surface currents.
Equatorial Currents
Major ocean current that moves parallel to the equator.
Westerlies
Winds that move west to east in the middle latitudes.
Easterlies
Variable winds that move east to west in high latitudes.
Coriolis Effect
The tendency of objects moving large distances on the Earth’s surface to bend.
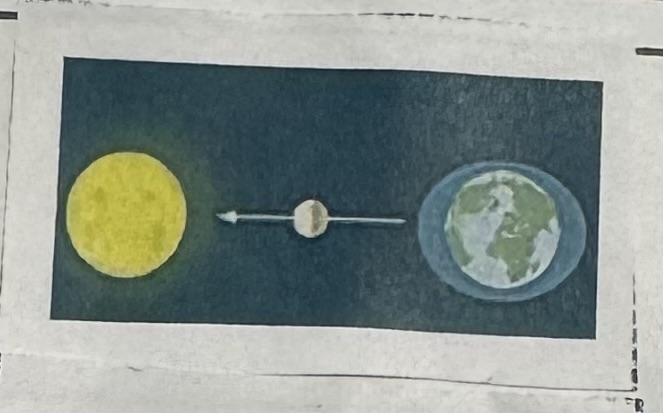
Spring Tides Picture
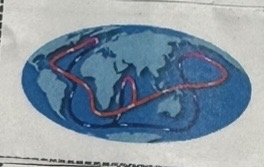
Deep Currents Picture
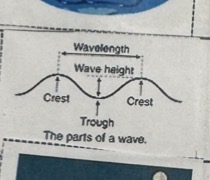
Parts of Wave Picture
Neap Tides Picture

Water Bulge Picture

Tides Picture

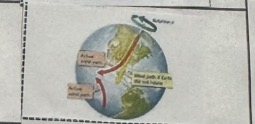
Coriolis Effect Picture
Tidal Range Picture
Surface Currents Description
Move on or near the surface of the ocean.
Controlled by factors such as air currents, Earth’s rotation and location of continents.
Affected by winds.
High Tides Description
Periodic rise and fall of the sea level.
Water level at its highest.
Affected by gravity of Sun and Moon.
Waves Description
Caused by wind, earthquakes, gravitational force of the Moon and Sun.
Has a rhythmic movement with definite wavelength.
Water molecules move up and down without moving forward and backward.
Neap Tides Description
Occurs when the sun and moon are at right angles to the Earth.
Total gravitational pull is weak.
Occurs during quarter moons.
Deep Currents Description
Driven by density and temperature gradients.
Flow under the surface of the ocean.
Travel with a much slower speed.
Spring Tides Description
Occurs when the Earth, the Sun, and the Moon are in line.
Total gravitational pull is stronger.
Occurs during the full moon and the new moon.
Tides Description
Affected by the declination of the Moon.
Also affected by local geography of the coastline, topography of the ocean floor, depth of the water.
Bulge of Water Description
Slight upward movement of water on the side of the earth facing the moon.
Caused by gravity of the moon.
Created on opposite sides of the earth.
Low Tides Description
Water level is at its lowest.
Affected by gravity of sun and moon.
Tidal Range Description
Difference in ocean level between high-tide and low-tide.
It is not constant, but changes depending on the relative position of the earth, sun, and moon.
Tide Timings Description
Periodic rise and fall of the sea level.
It is of two types: high and low.
Cycle takes place at every 12 hrs and 25 min.
Coriolis Effect Description
Known as curving path of oceans & winds due to Earth’s rotation.
Deflects air towards the right in the N-Hemisphere and toward the left in the S-Hemisphere.