BIOSC 139 EXAM 3
1/217
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering muscle tissue, axial and appendicular muscles, and nervous tissue.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
218 Terms
What are the properties of muscle tissues?
remember CEEE
C: contractility
E: excitability
E: extensibility
E: elasticity
What are the three functions of skeletal muscles?
movement, posture, and temperature regulation
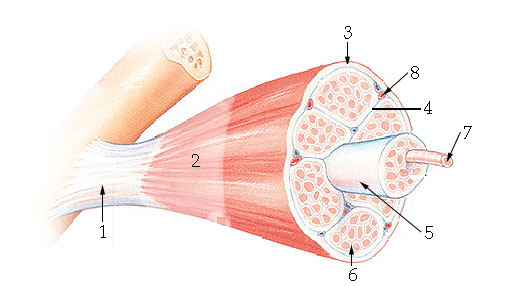
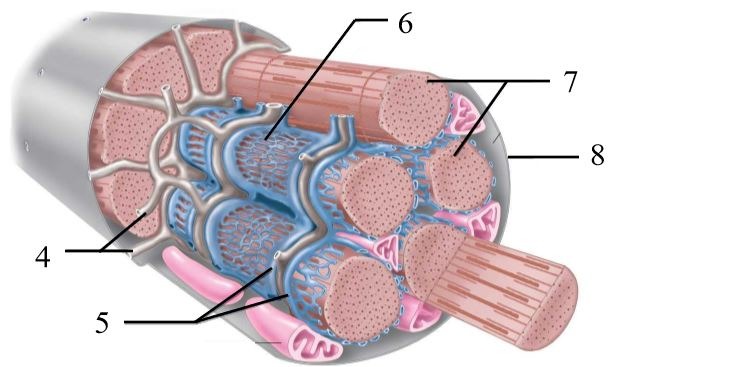
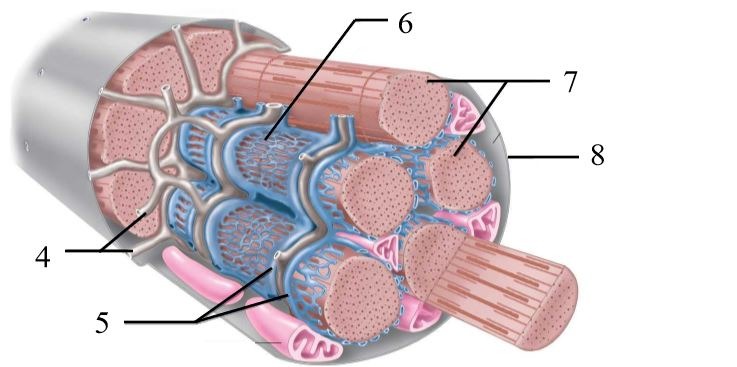
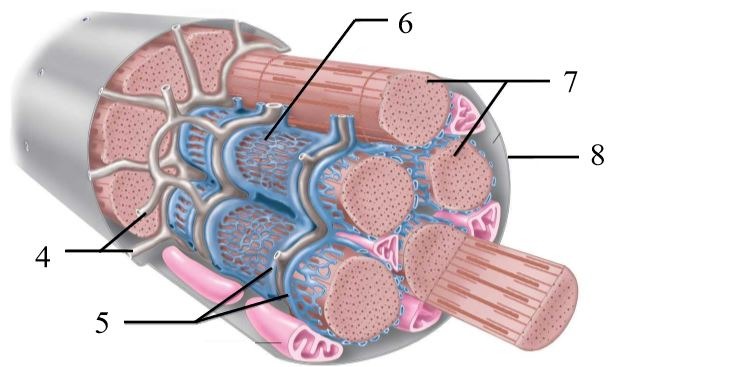
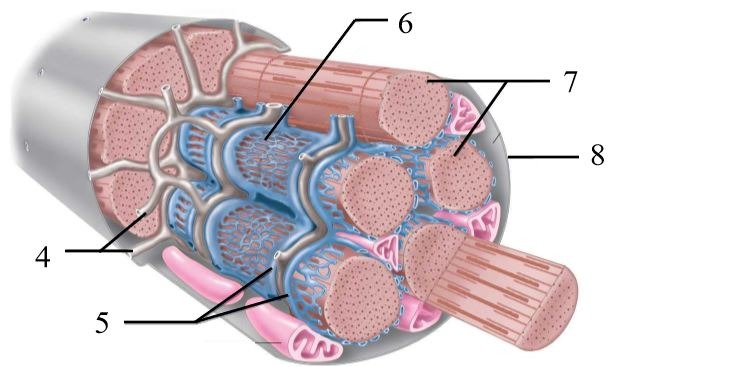
What structure is #6 indicating?
endomysium
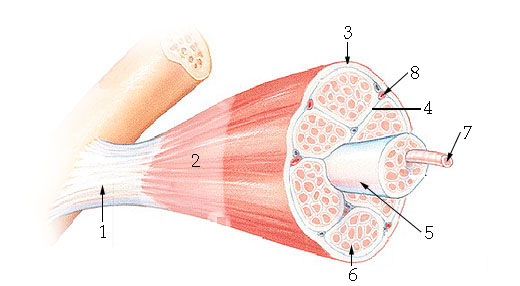
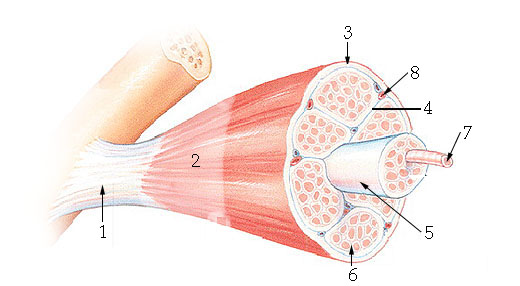
What structure is #4 indicating?
perimysium
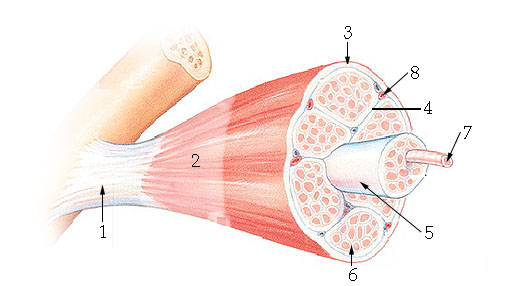
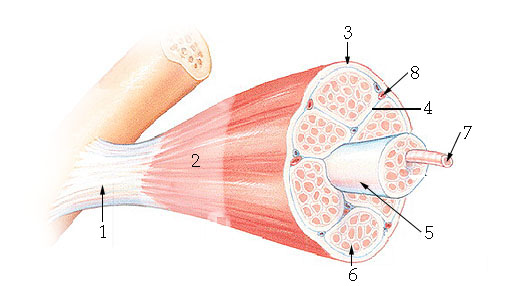
What structure is #3 indicating?
epimysium
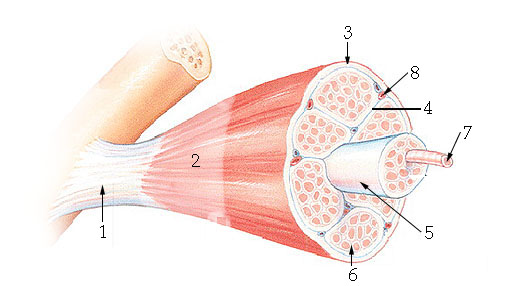
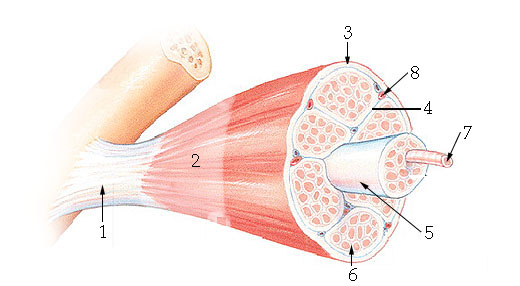
What structure is #2 indicating?
deep fascia
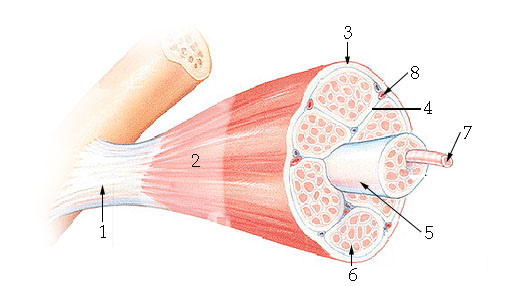
What are the three sheathes in skeletal muscle?
epimysium: outermost layer
perimysium: middle layer around fascicle
endomysium: inner most layer around individual muscle fibers
What is the term for a flat tendon?
aponeurosis
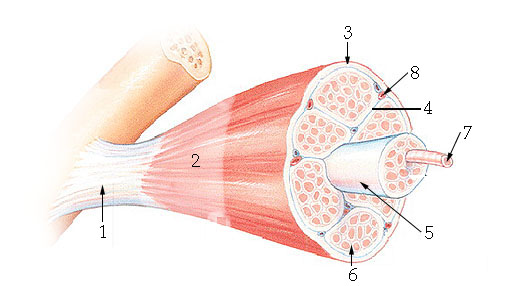
What structure is #7 indicating?
myofibril
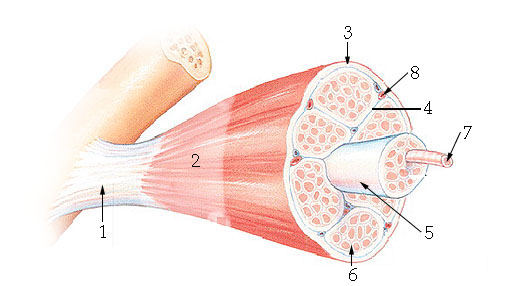
What is the cell membrane of a skeletal muscle called?
sarcolemma
What is the cytoplasm of a skeletal muscle called?
sarcoplasm
What do the transverse tubules do?
carry electrical impulses into the muscle cell
What structure does #4 indicate?
transverse tubule (T tubule)
What structure is indicated by the blue on the diagram?
sarcoplasmic reticulum (stores calcium)
What are the three types of myofilaments?
actin (thin filament), myosin (thick filament), titin
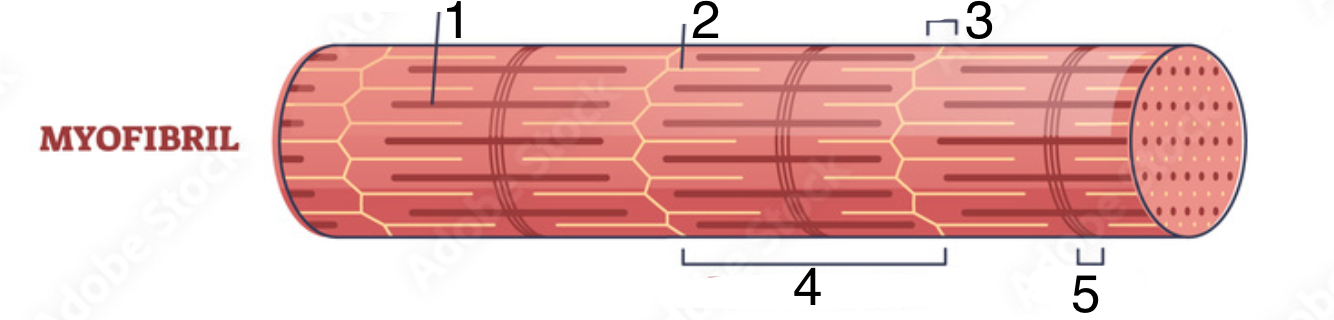
What structure does #1 indicate?
myosin (aka thick filament)
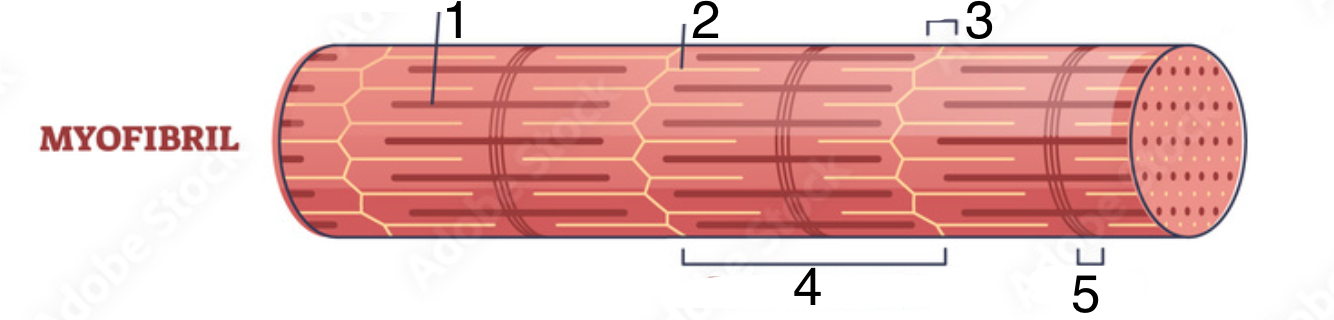
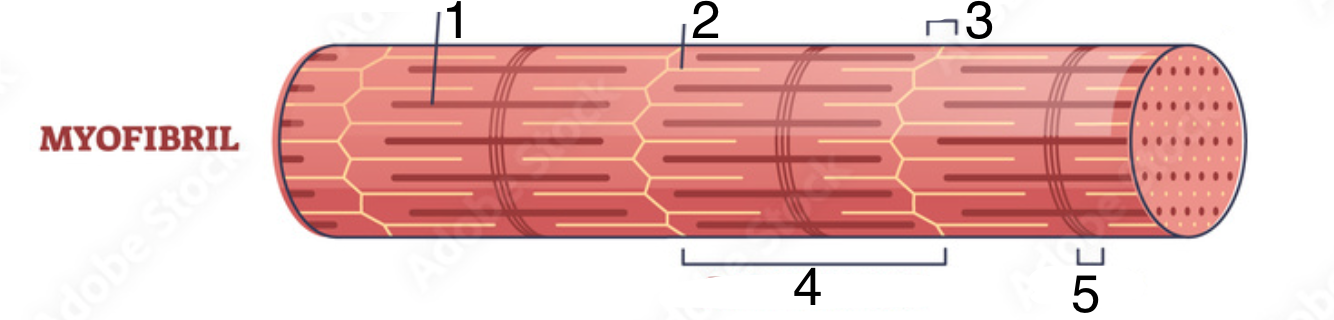
What structure does #2 indicate?
actin (aka thin filament)
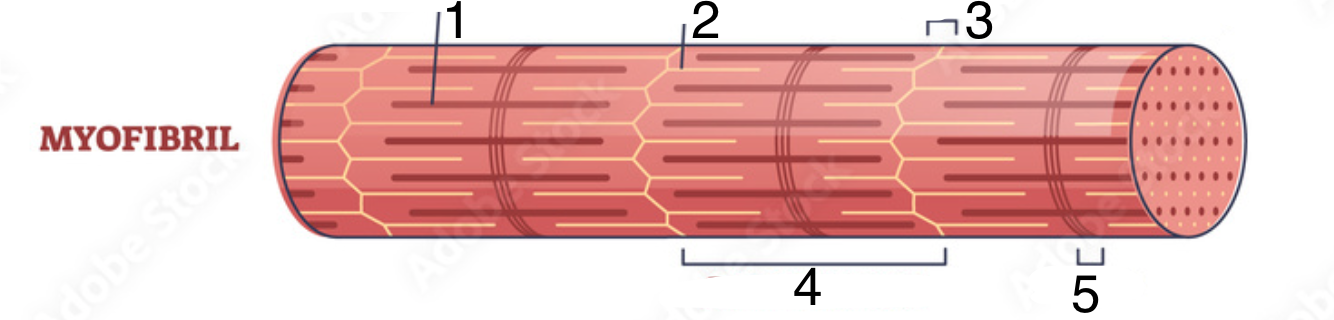

What are the two notable structures in myosin?
Heads (aka crossbridges) - site for ATP to bind
Tails

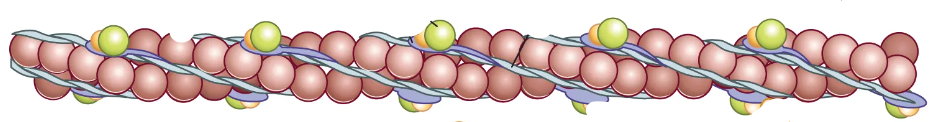
How many strands does actin filament have?
2
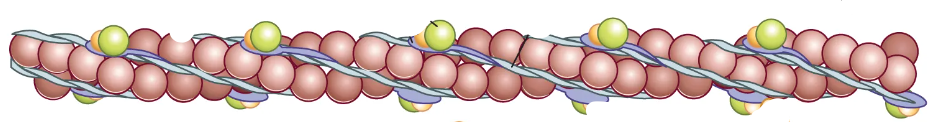
What associated proteins are in actin filament?
troponin and tropomyosin
What does troponin do?
binds calcium
What does tropomyosin do?
covers over the myosin binding sites (aka active sites) on actin until muscle contraction is prompted
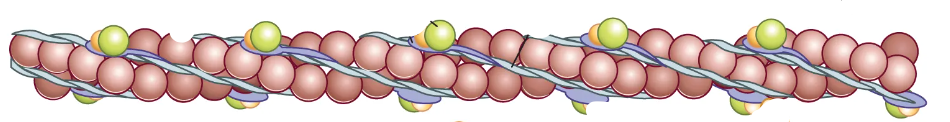
What are the notable structures in actin filament?
2 actin strands wrapped around each other (look like beads), troponin, tropomyosin, and active sites
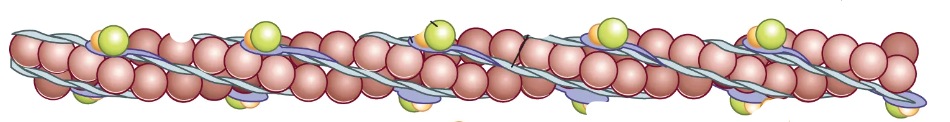
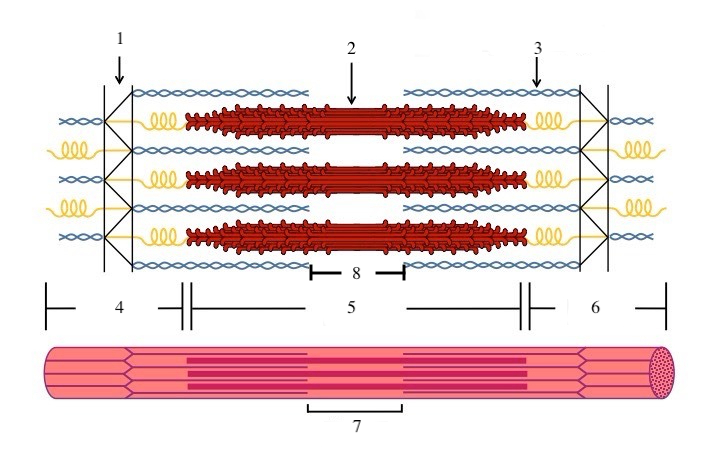
What is a sarcomere?
the functional unit of a muscle fiber (a section of the myofibril)
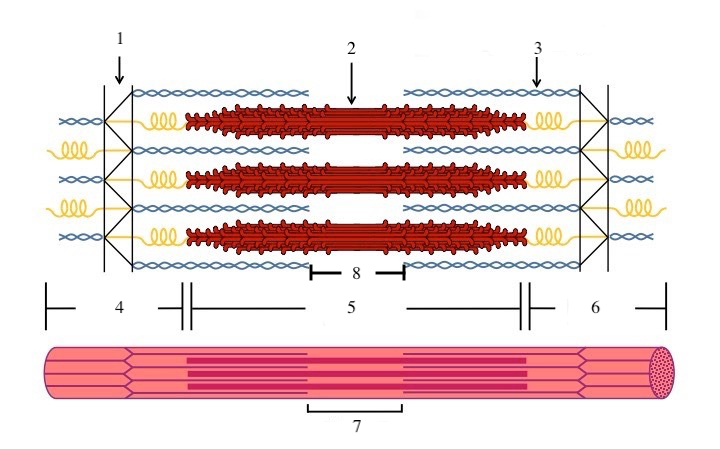
What zone/line is indicated by #1?
Z disc
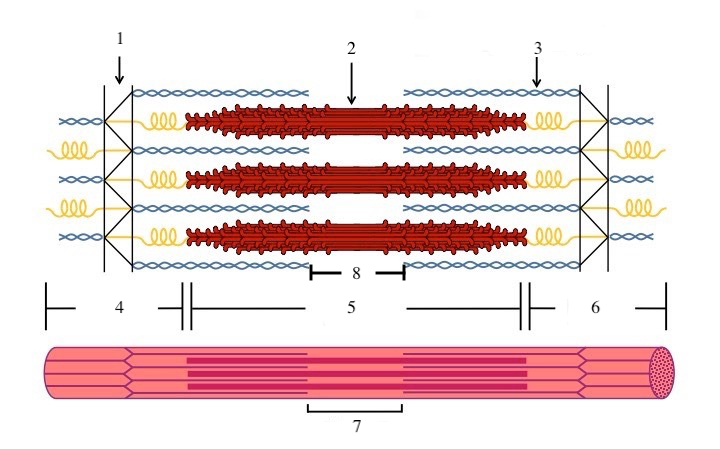
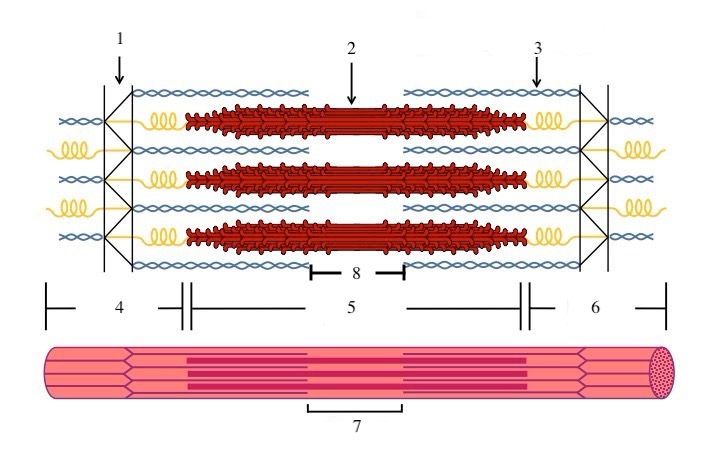
What zone/line is indicated by #2?
M line (or midline)
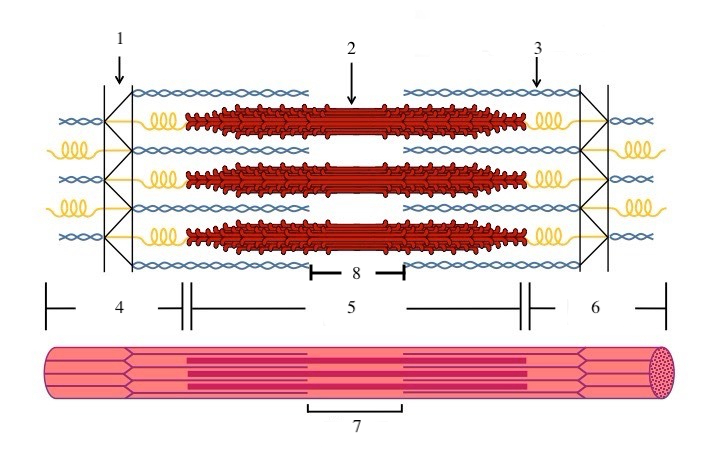
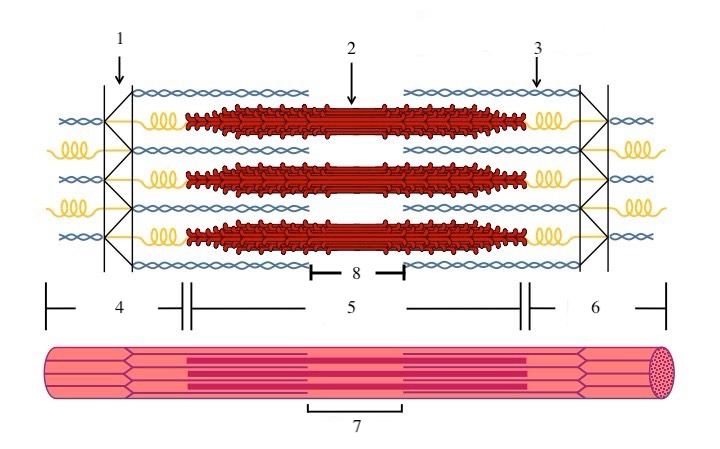
What zone/line is indicated by #5?
A band (runs the entire length of myosin filament)
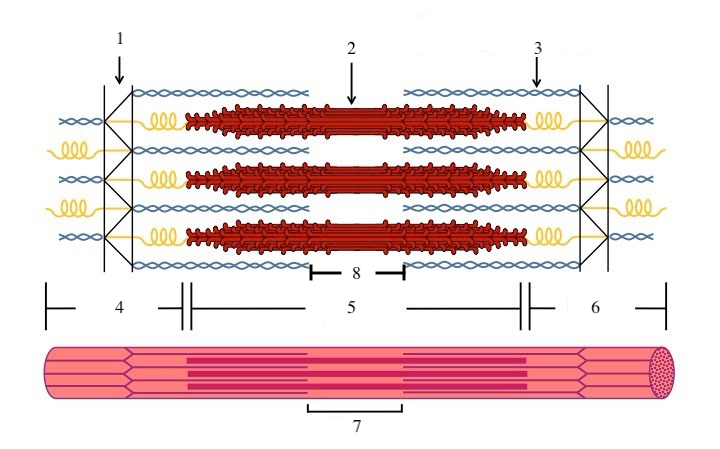
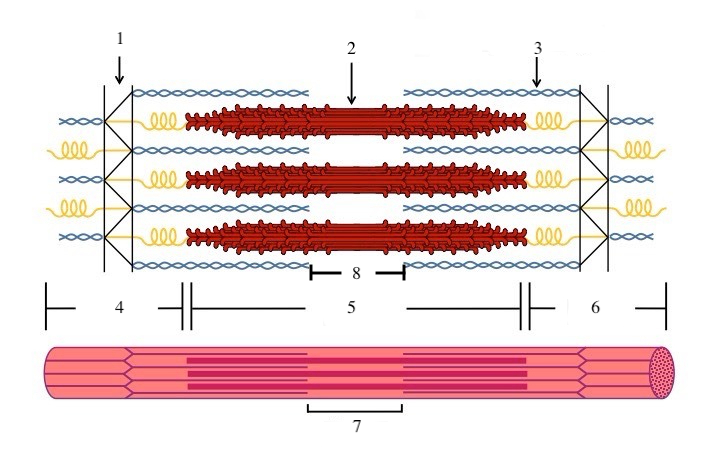
What zone/line is indicated by #8?
H zone (area where there is myosin but no actin)
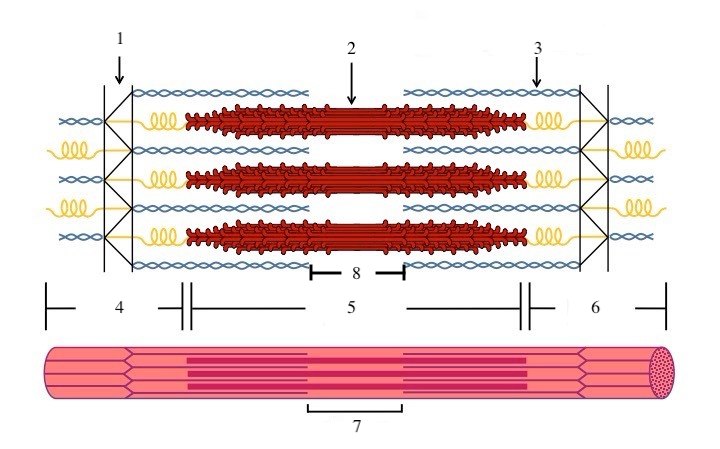
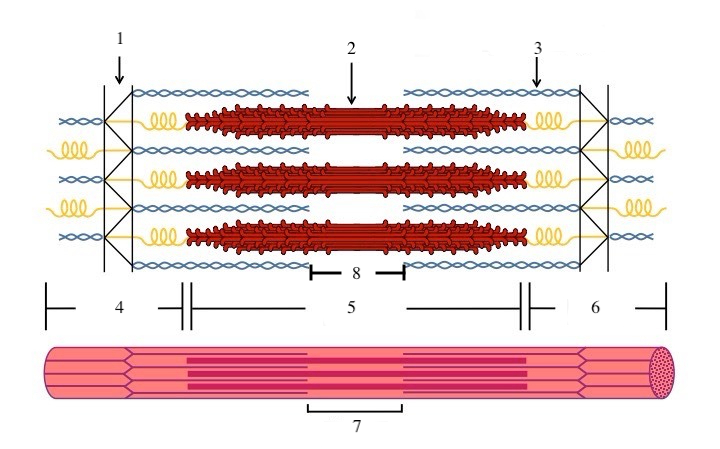
What zone/line is indicated by #4 and #6?
I band (area where there is actin but no myosin)
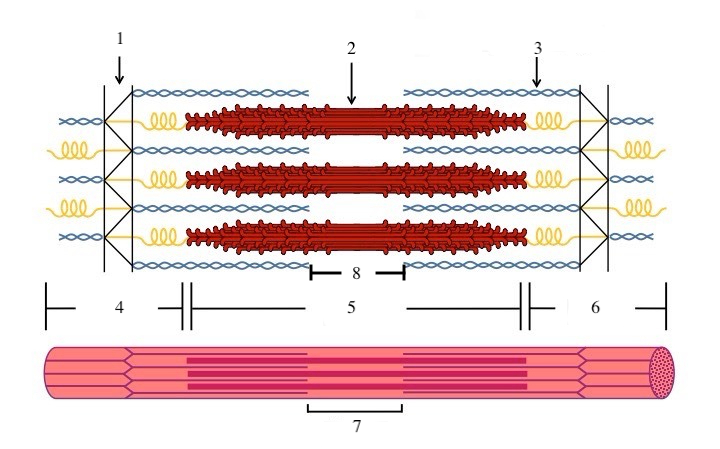
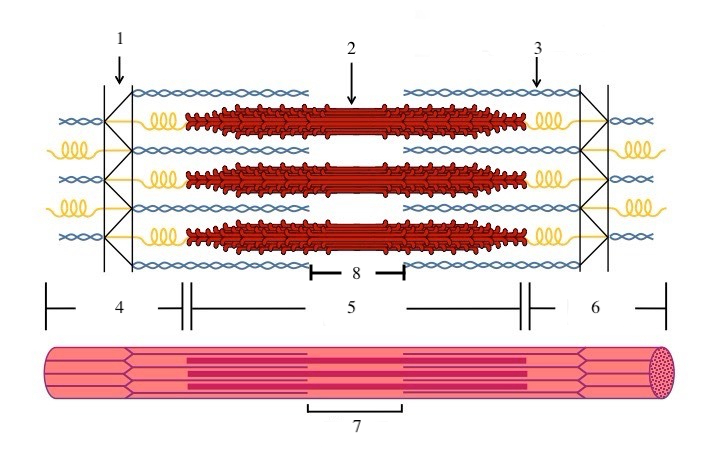
What is indicated by #7?
sarcomere
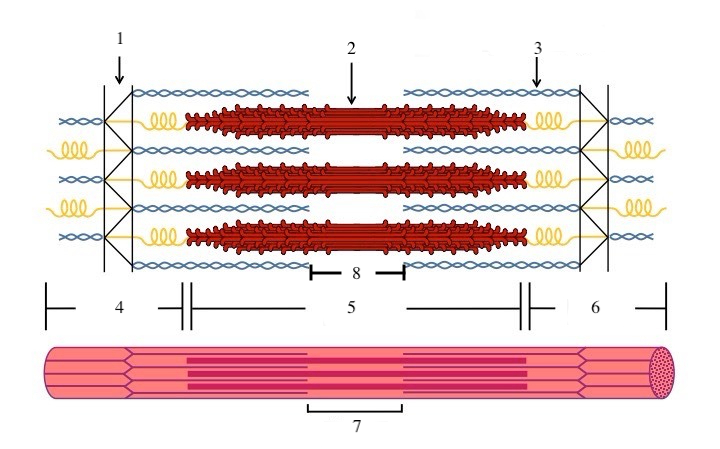
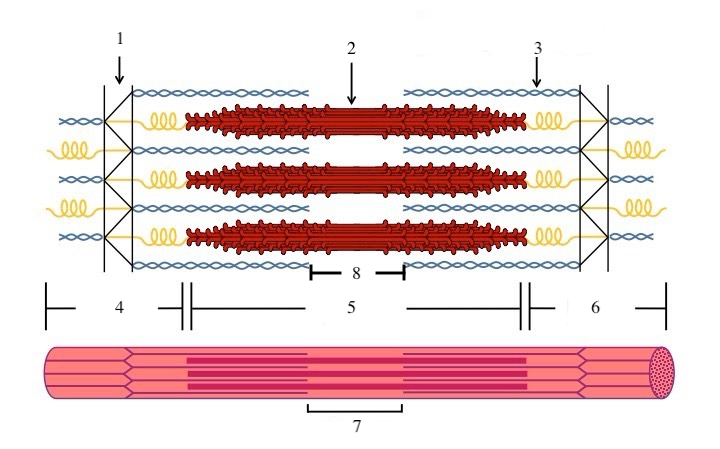
What does titin do?
provides structural support and elasticity to sarcomere (indicated by the spring in diagram)
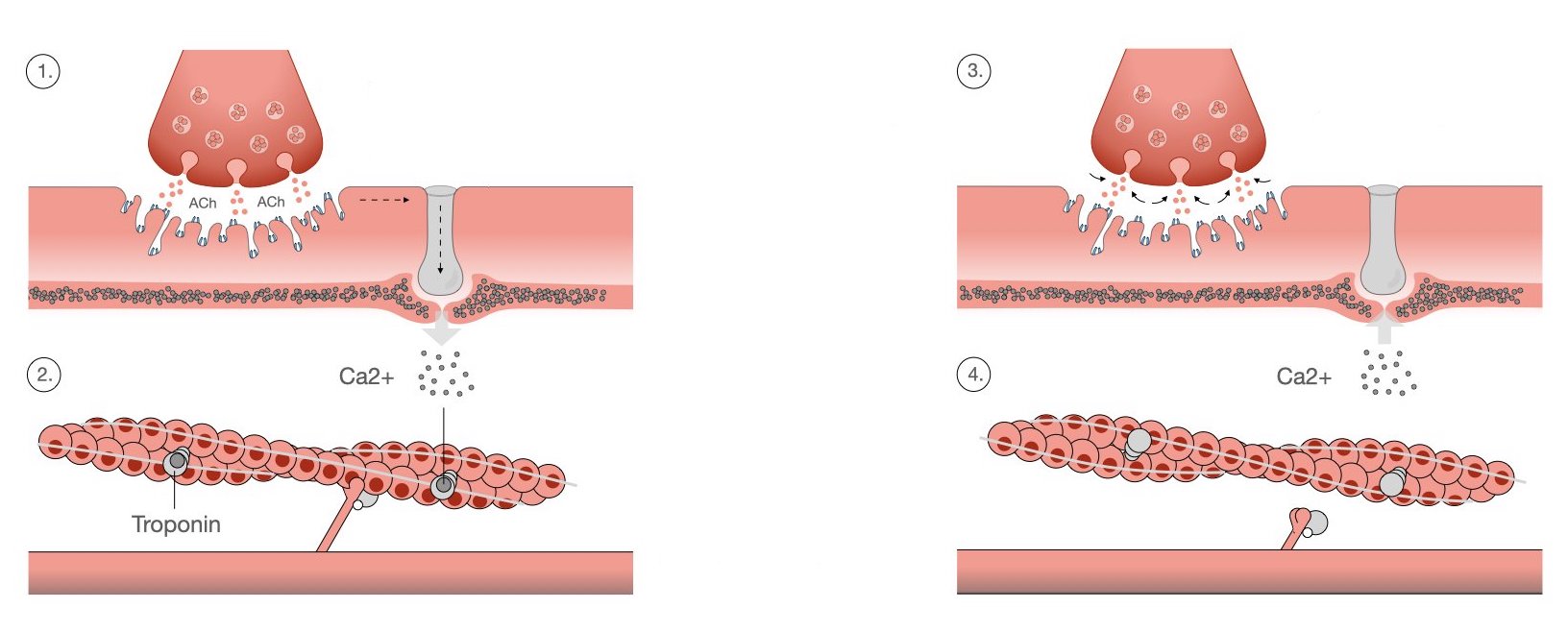
What is a neuromuscular junction? (NMJ)
site where motor neuron meets a muscle fiber
What is a motor unit? (MU)
One nerve fiber (cell) and all of the muscle fibers it innervates. All fibers within MU are the same type. Have both large and small MU.
What is the theory that describes how skeletal muscles contract?
Sliding Filament Theory
What is the cross-bridge cycle?
cross bridges (heads) of myosin bind to actin at active sites and pull on the actin to made the filaments slide by each other. ATP provides energy for process.
What happens to the sarcomeres’ length during the cross-bridge cycle?
they shorten
What is it called when the myosin rotates to pull the actin?
a powerstroke
What are the steps of excitation-contraction coupling?
action potential on neuron reaches neuromuscular junction, thacetylcholine (ACH) is released
ACH binds receptors to muscle fiber and releases action potential on sarcolemma
when action potential reaches the transverse tubules (t-tubules), it goes into the muscle fiber
this prompts the release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum
calcium binds to troponin on actin filament
troponin moves tropomyosin out of the way of the active sites so myosin can react with actin filament
What are the two main types of muscle contractions?
dynamic and static (aka isometric)
What is it called when the muscle shortens during contraction?
concentric contraction
What is it called when the muscle lengthens during contraction?
eccentric contraction
What is it called when the muscle is contracting, but not lengthening or shortening?
static (aka isometric) contraction
What are the three major types of muscle fibers?
Type I (slow oxidative)
Type IIa (fast oxidative glycolytic)
Type IIb (fast glycolytic)
Type I Muscle Fibers (slow oxidative)
red fibers
ATP mainly made aerobically
high # of mitochondria
high # of capillaries
slow contractions
moderate force production
high fatigue resistance
typically utilized in endurance (ex. posture control)
Type IIa Muscle Fibers (fast oxidative glycolytic)
off-white fibers
ATP mainly made aerobically, but can also be made anaerobically if needed
high(er) # of mitochondria than Type IIb
high(er) # of capillaries than Type IIb
fast contractions
high force production
medium fatigue resistance
typically found in the arms
Type IIb Muscle Fibers
white fibers
ATP mainly made anerobically
low # of mitochondria
low # of capillaries
contract fast
high force production
low fatigue resistance
typically utilized in power activities (ex. sprints)
What is it called when muscles get smaller?
atrophy
What is it called when muscles get bigger?
hypertrophy
What is it called when muscle cells increase? NOTE: doesn’t apply to humans
hyperplasia
What is the muscle role called for a muscle that does the bulk of the work for a movement?
agonist (prime mover)
What is the muscle role called that acts as the opposite of the most-working muscle?
antagonist
What is the muscle role called for muscles that assist the main working muscle in a movement?
synergist
What is the muscle role called where muscles work to reinforce around joints during a movement?
fixator/stabilizer
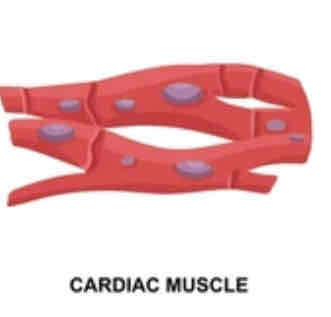
What are some notable things about cardiac muscle?
striated (striped) appearance
1-2 nuclei
y-shaped branches
intercalated discs (gap junctions)
auto-rhythmic (generates own action potential)
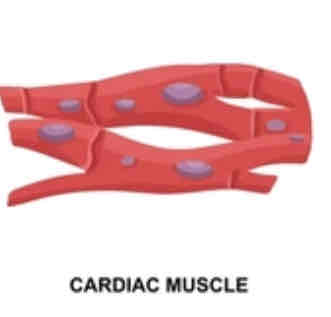
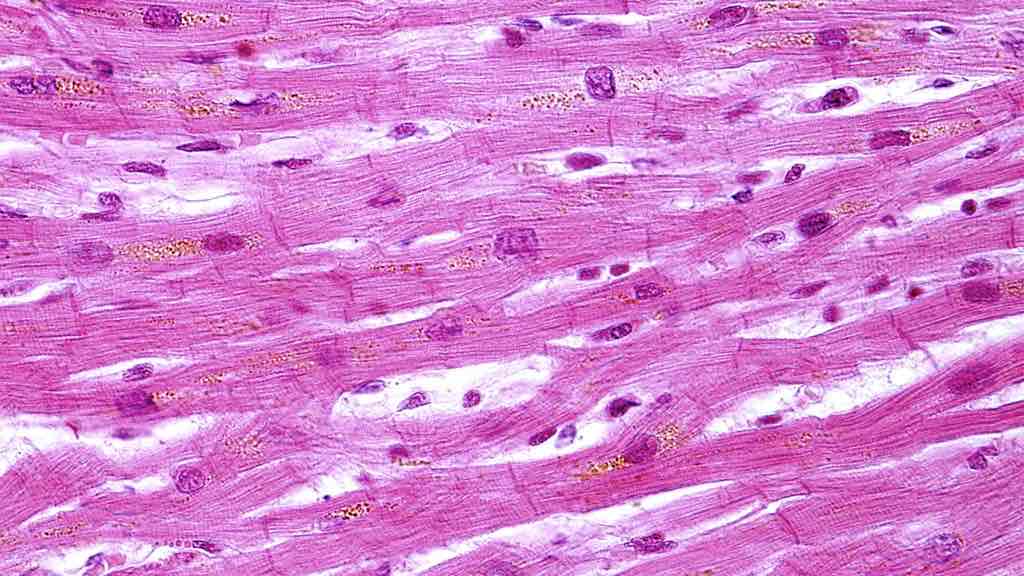
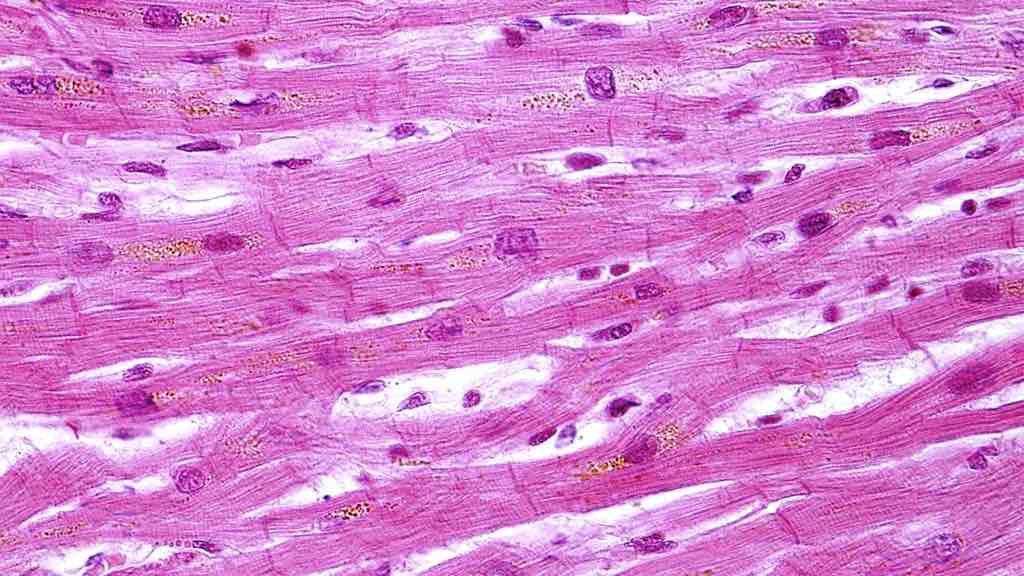
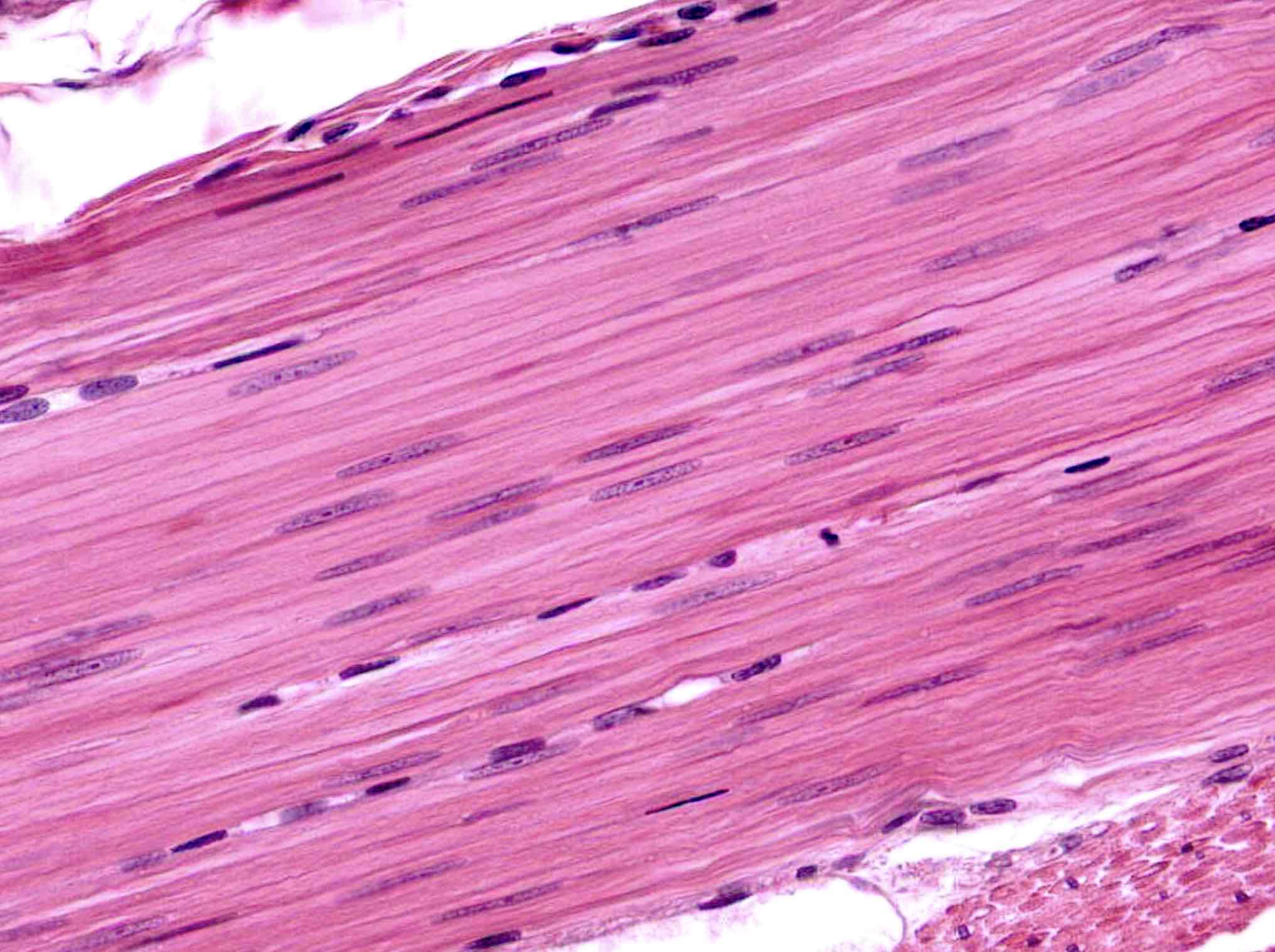
What is the histology pictured?
cardiac muscle tissue
What are some notable things about smooth muscle tissue?
1 nuclei
fusiform appearance (tapers at ends, fat in middle)
nonstriated (not striped)
involuntary
fatigue resistant
dense body proteins attached to actin and myosin
twisting contraction due to dense body proteins
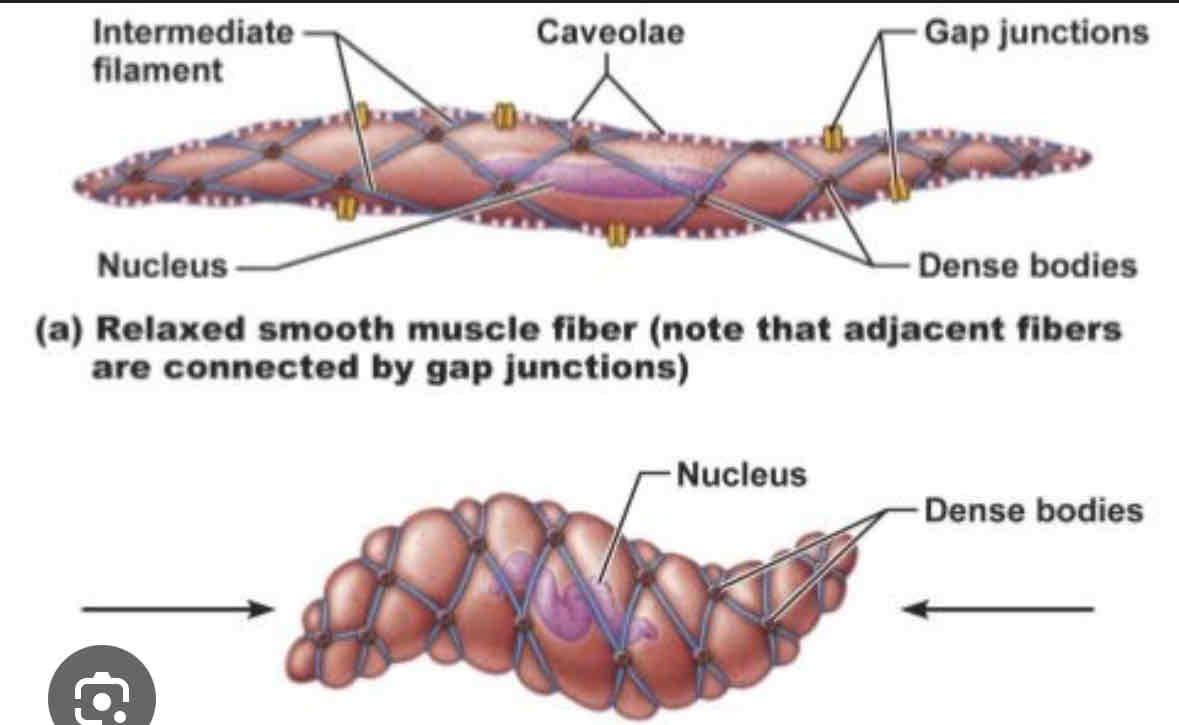
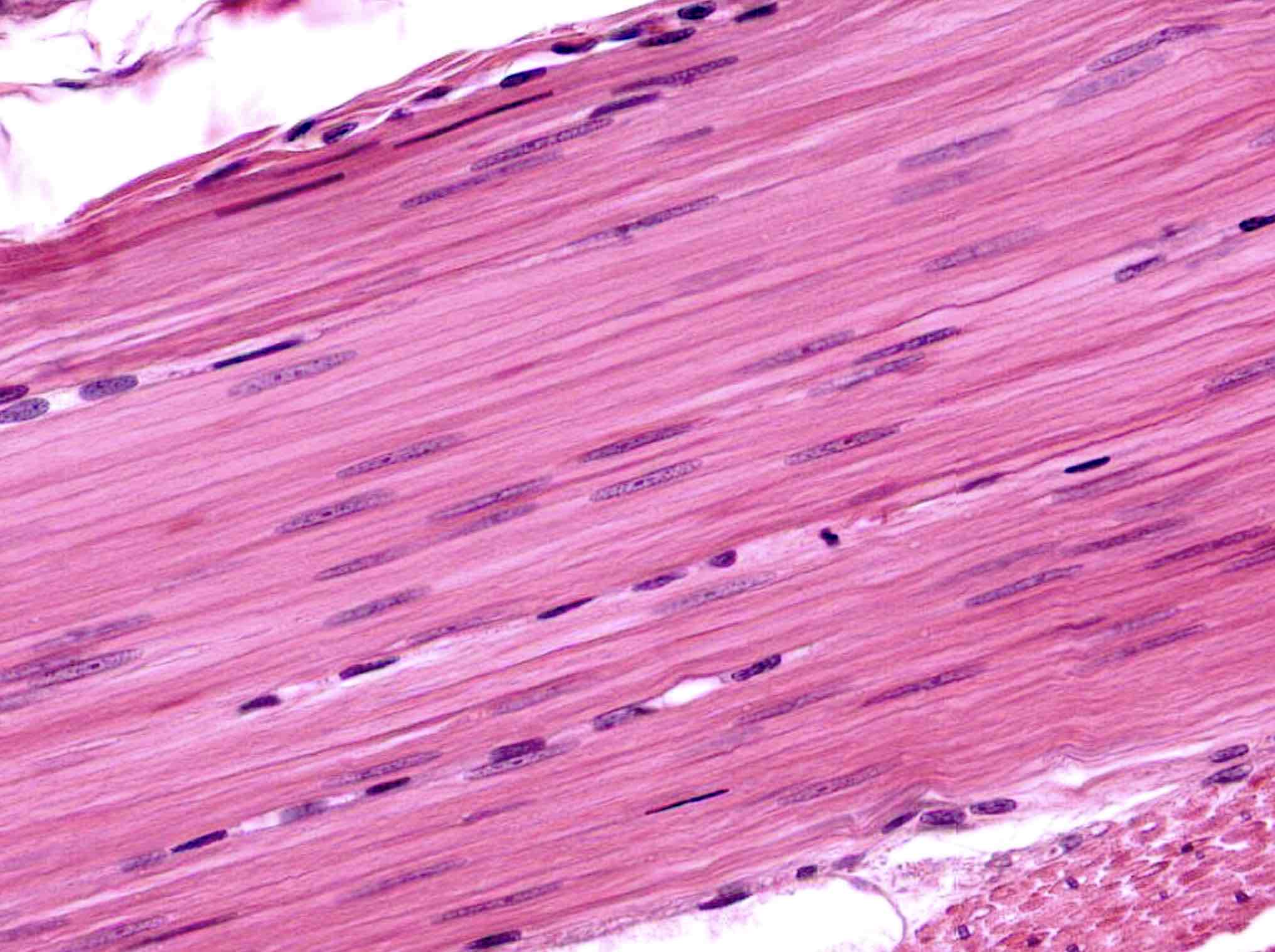
What is the histology pictured?
smooth muscle
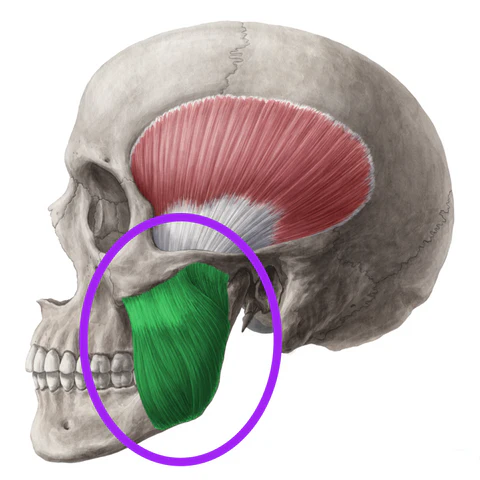
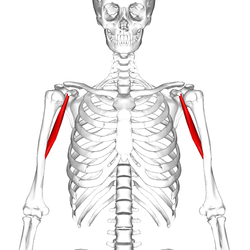
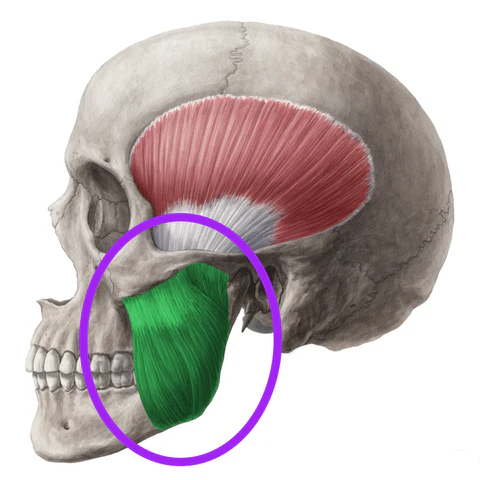
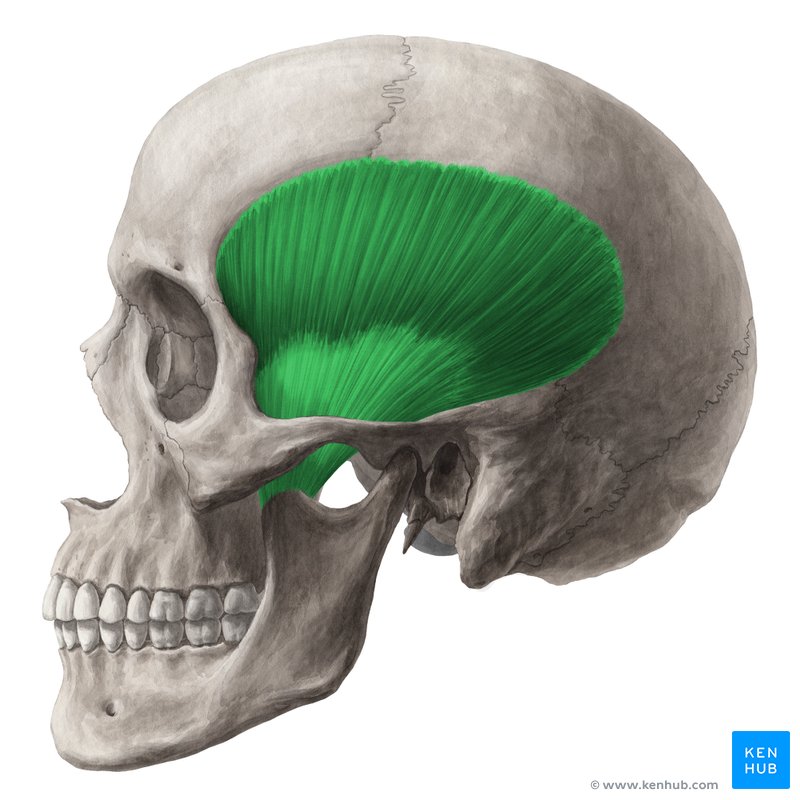
What is the structure pictured?
masseter
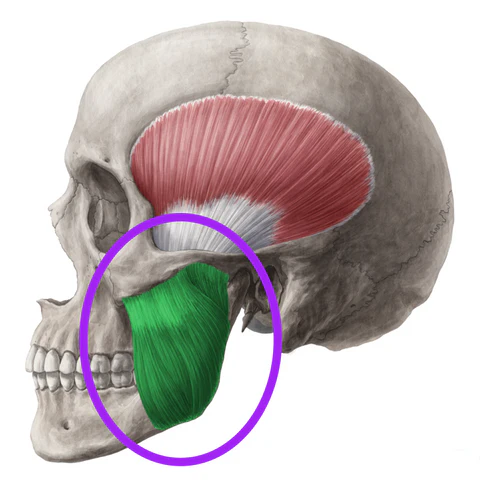
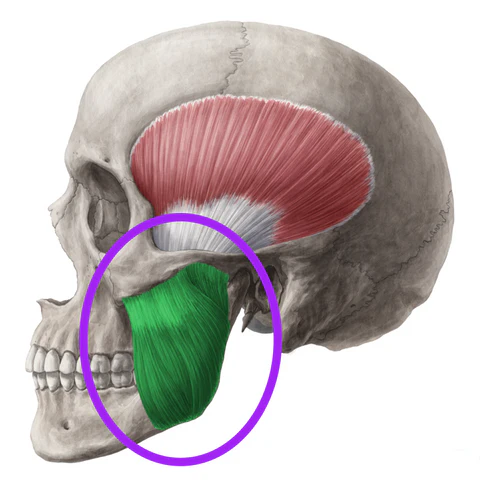
What are the origin and insertion points of the masseter? What is it’s action?
Origin: zygomatic arch
Insertion: coronoid process, lateral surface and angle of mandible
Action: elevation and protraction of the jaw
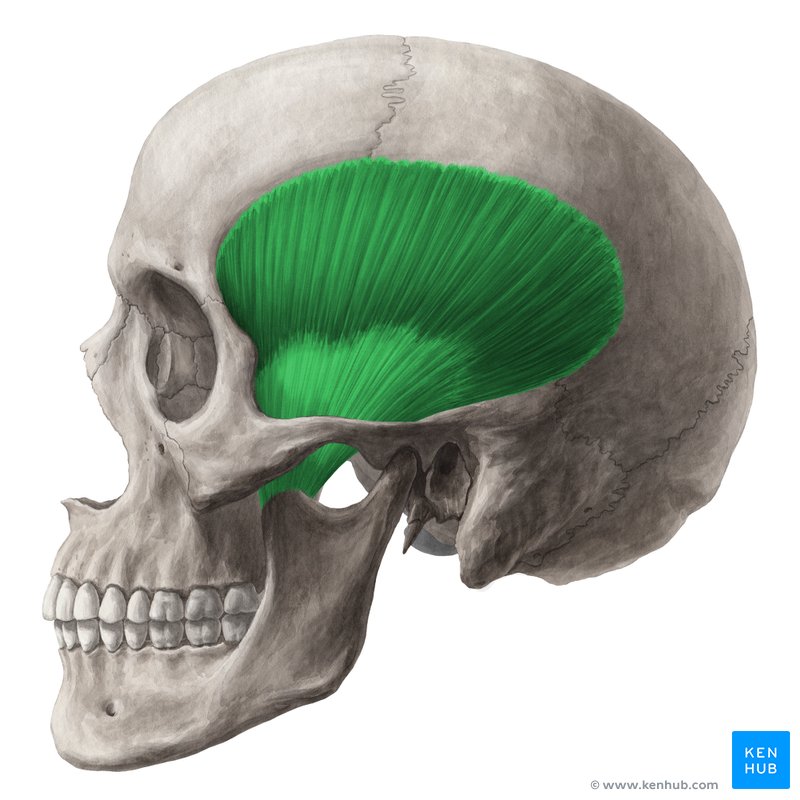
What is the structure pictured?
temporalis
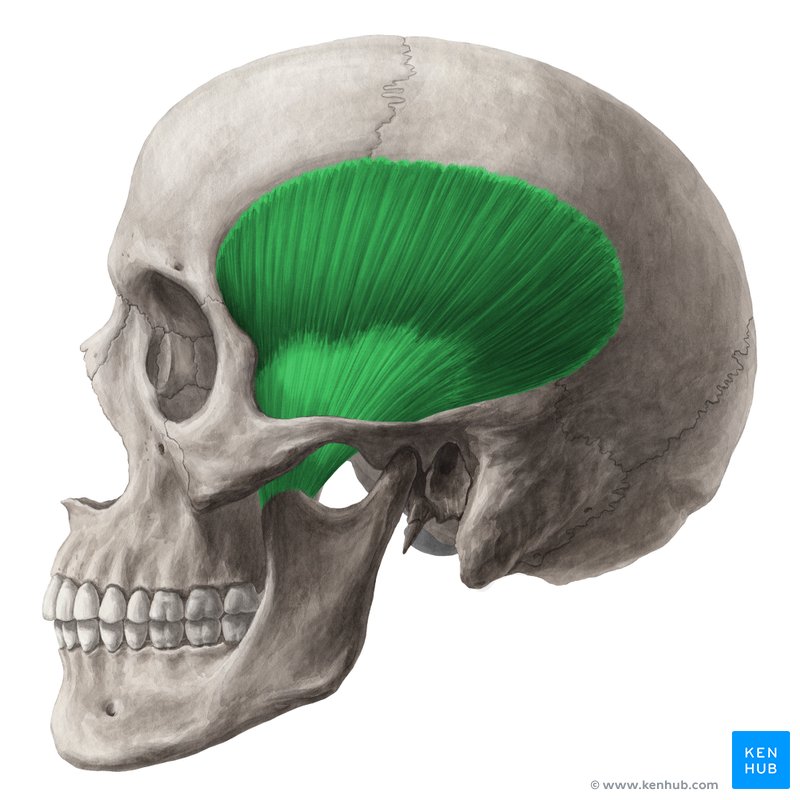
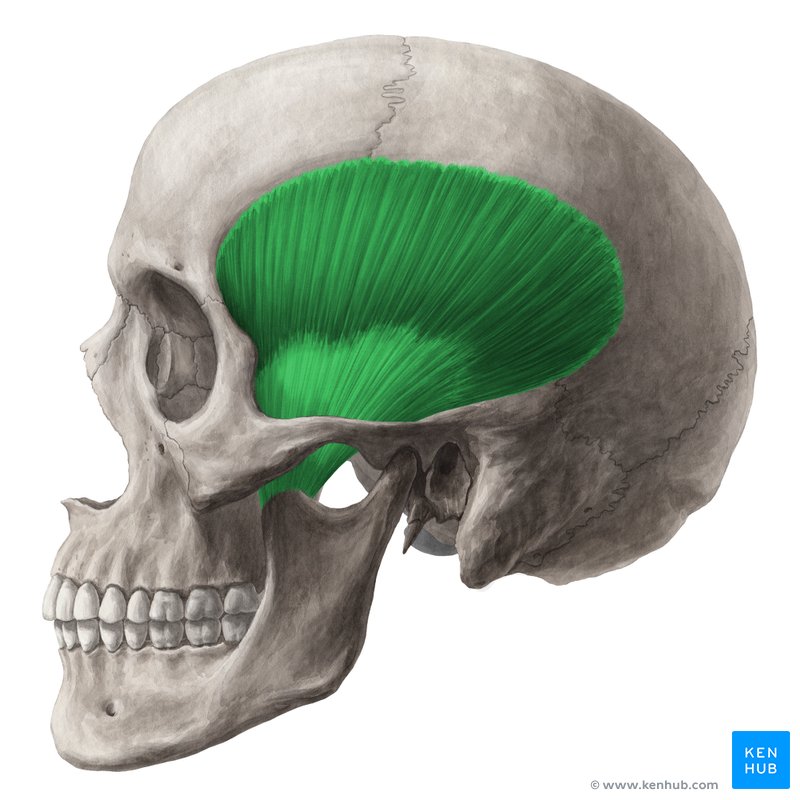
What are the origin and insertion points of the temporalis? What is it’s action?
Origin: temporal bone
Insertion: coronoid process of the mandible
Action: elevation and retraction of the jaw
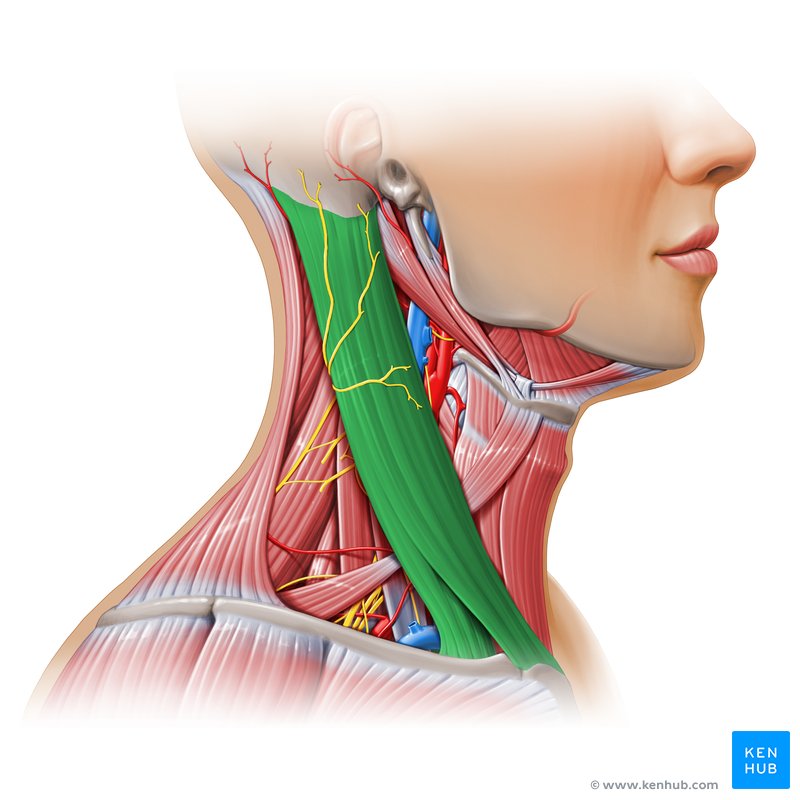
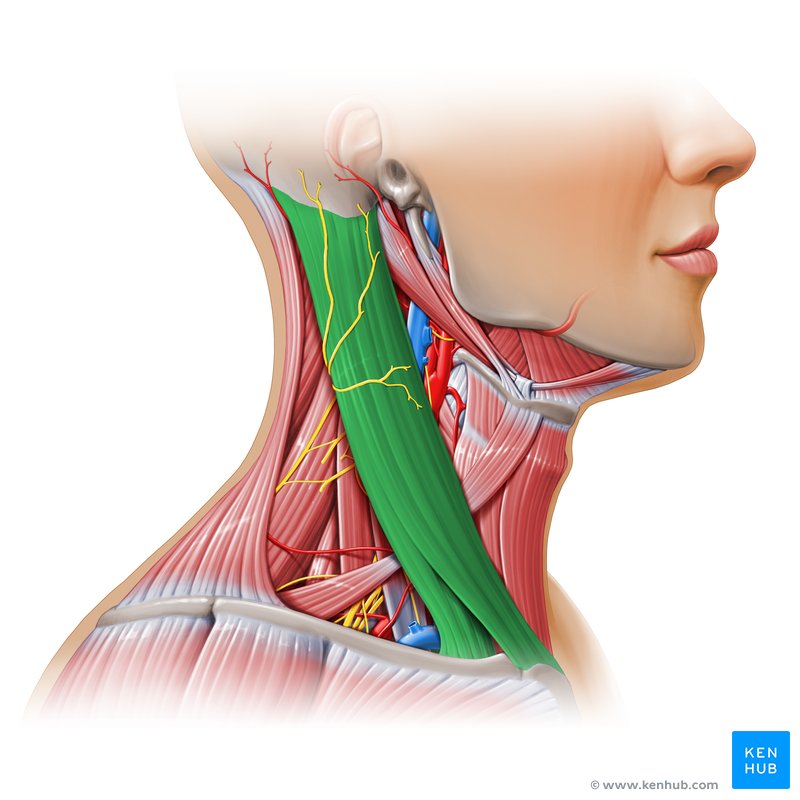
What is the structure pictured?
sternocleidomastoid
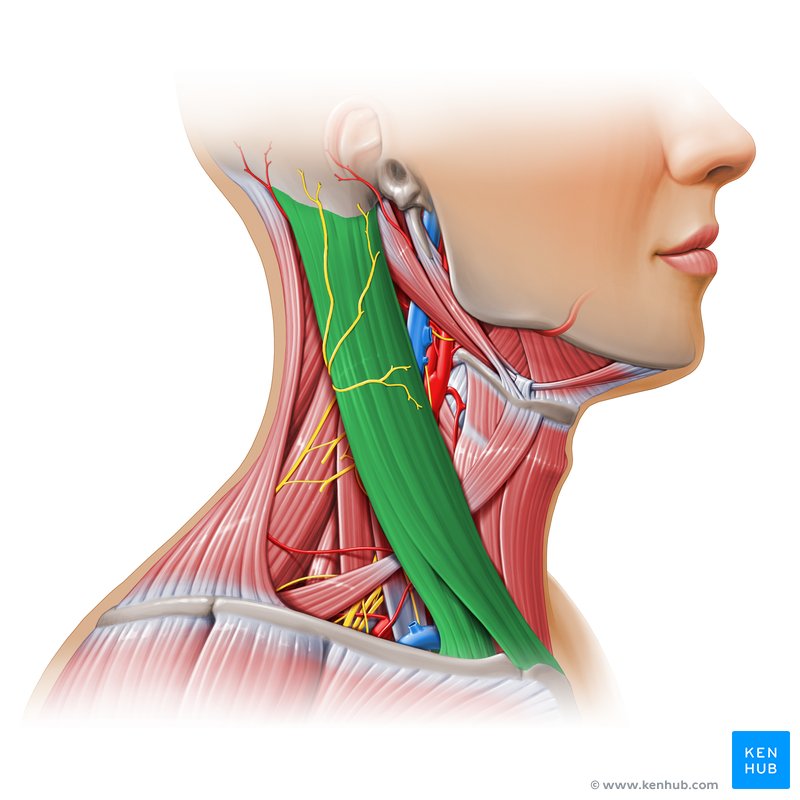
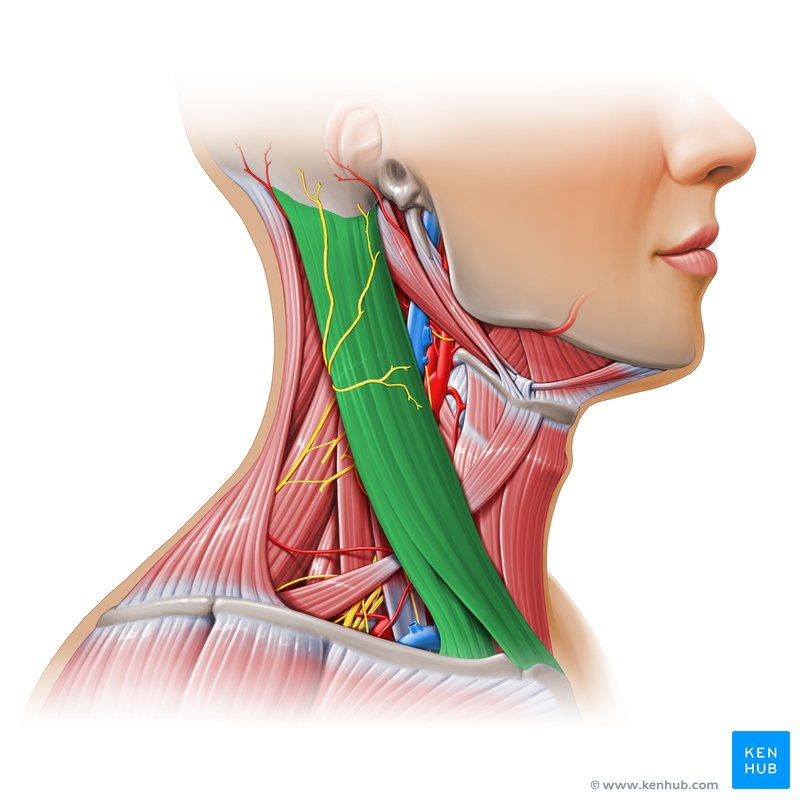
What are the origin and insertion points of the sternocleidomastoid? What is it’s action?
Origin: manubrium and clavicle
Insertion: mastoid process
Action: (bilateral) neck flexion, (unilateral) lateral flexion and rotation to the opposite side
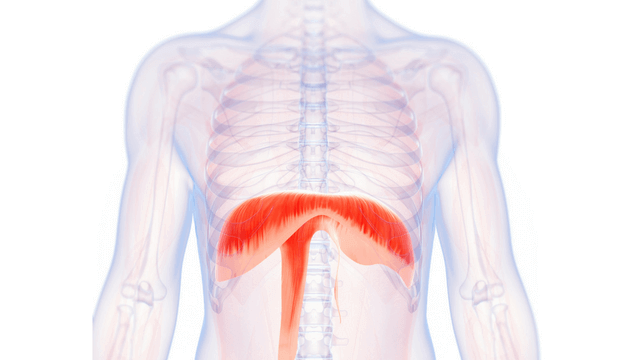
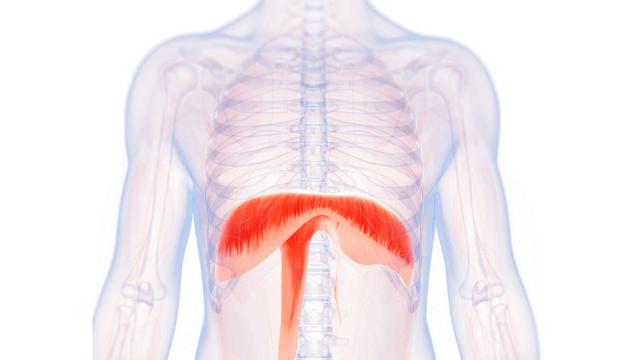
What is the structure pictured?
diaphragm
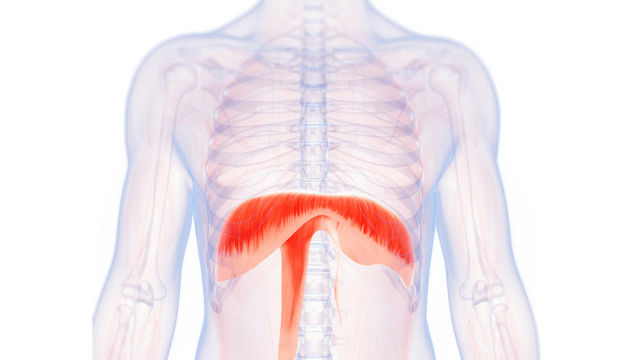
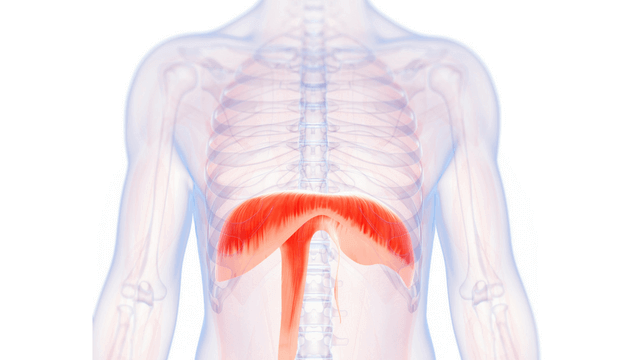
What are the origin and insertion points of the diaphragm? What is it’s action?
Origin: xiphoid process, costal cartilage of lower 6 ribs, lumbar vertebrae
Insertion: central tendon
Action: flattens downward
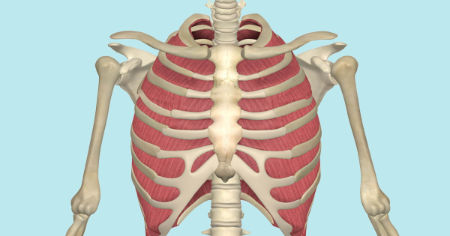
What is the structure pictured?
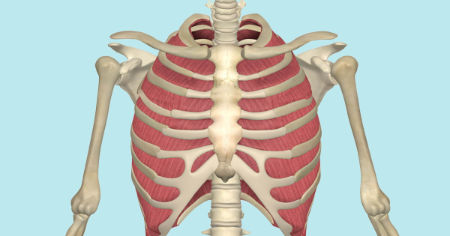
external intercostals
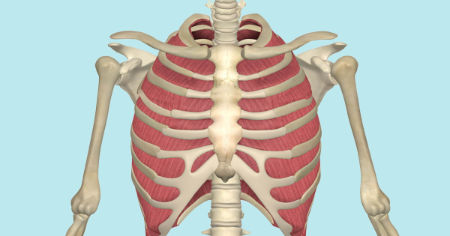
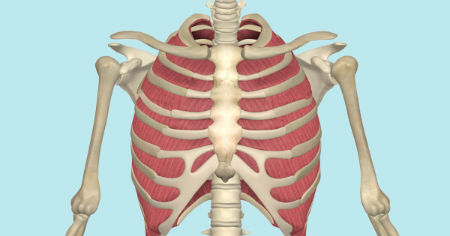
What are the origin and insertion points of the external intercostals? What is their action?
Origin: inferior border of whatever rib is above
Insertion: inferior border of whatever rib is above
Action: depression
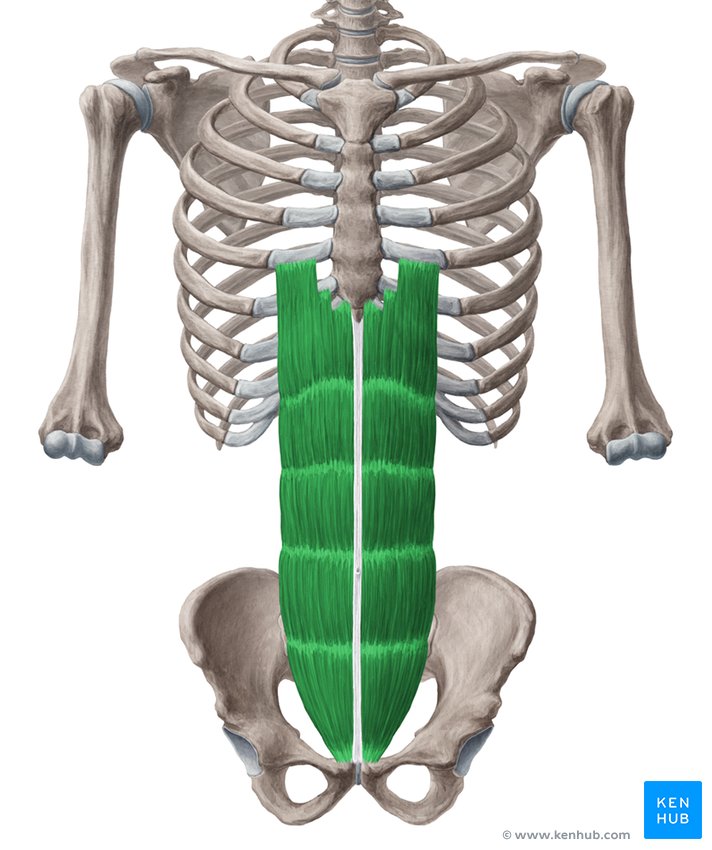
What is the structure pictured?
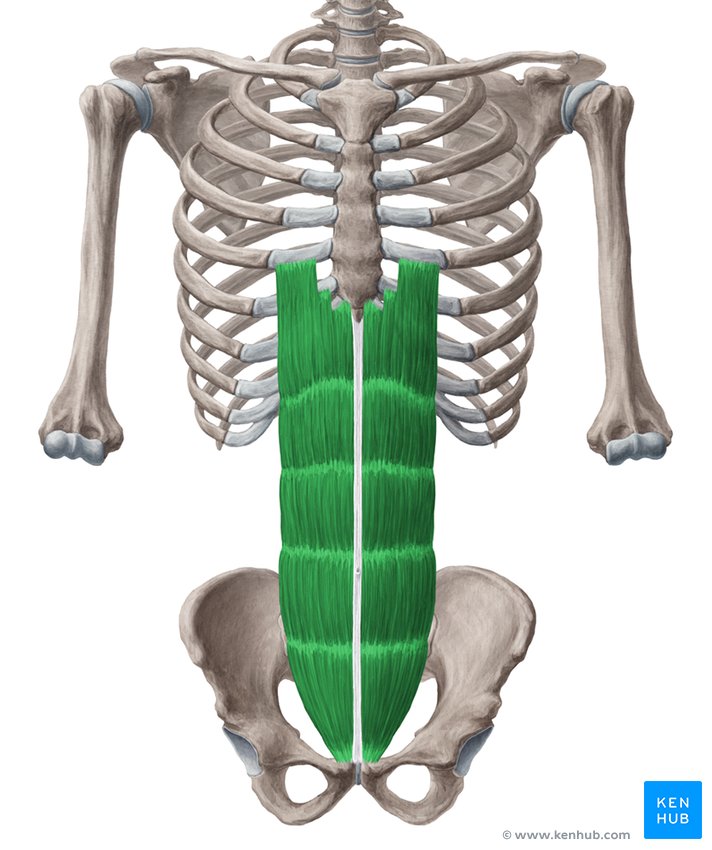
rectus abdominis
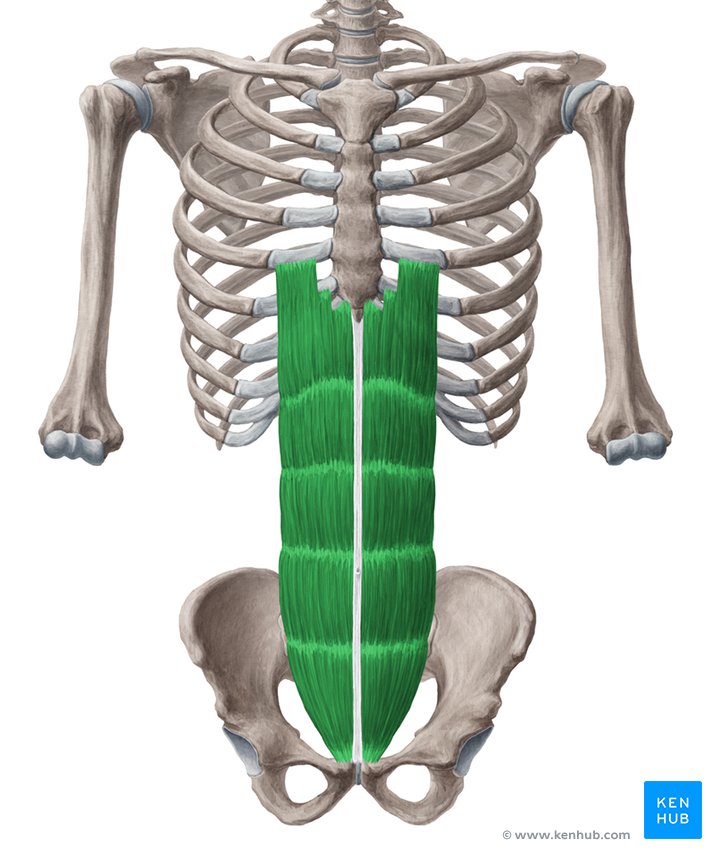
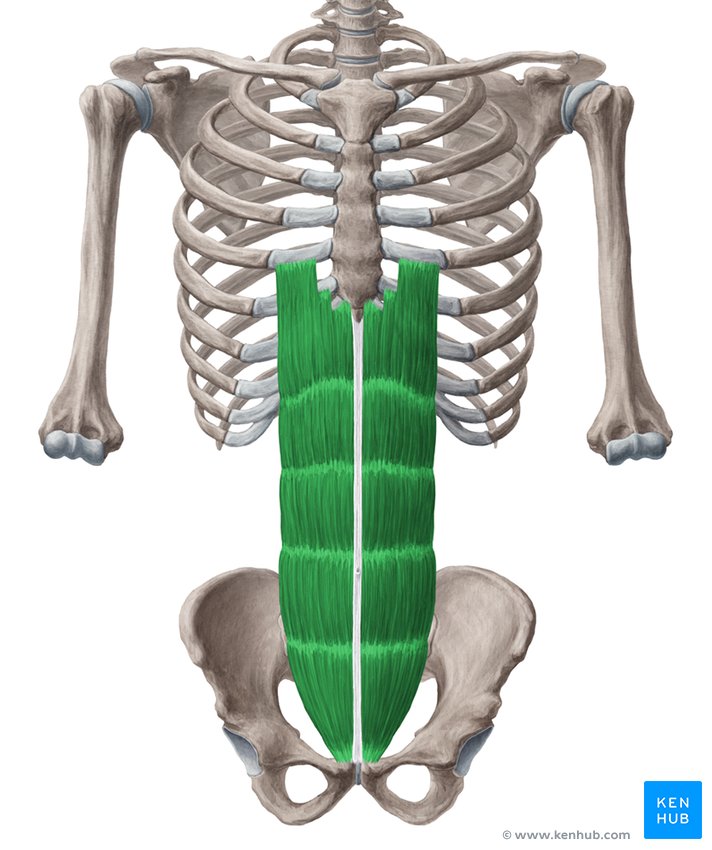
What are the origin and insertion points of the rectus abdominis? What is its action?
Origin: pubic crest and symphysis
Insertion: costal cartilage of ribs 5-7 and the xiphoid process
Action: flexion and compression
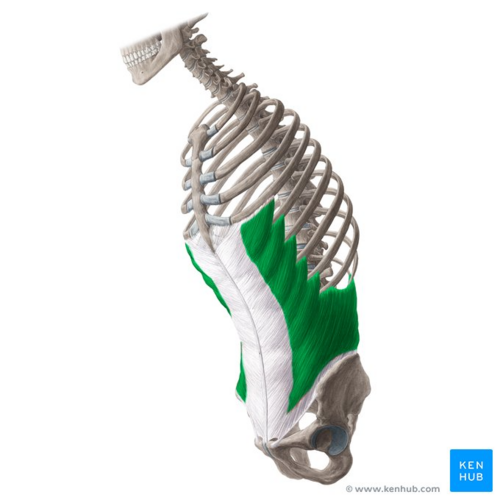
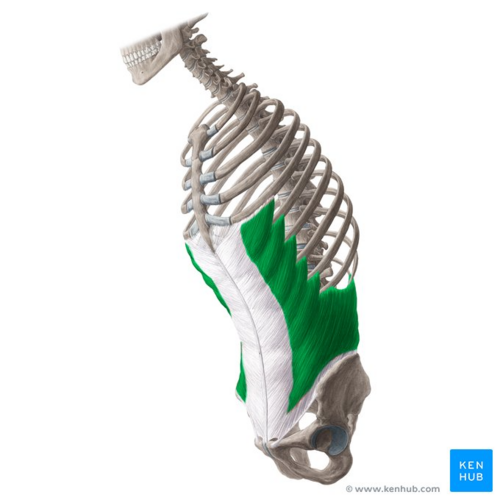
What is the structure pictured?
external oblique
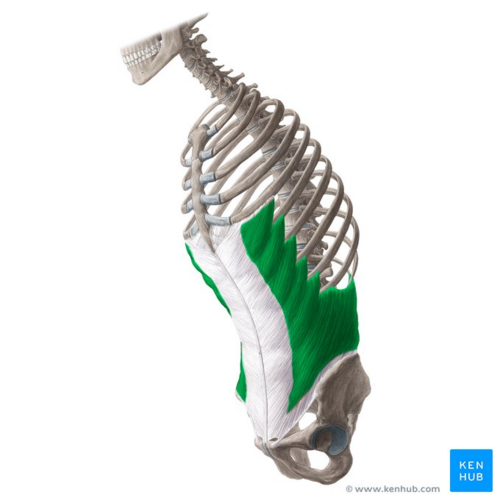
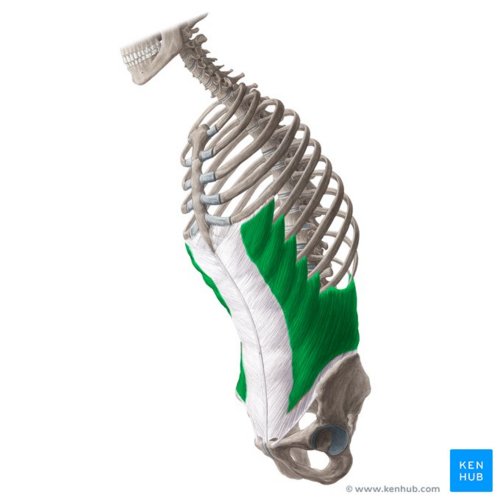
What are the origin and insertion points of the external obliques? What is their action?
Origin: inferior 8 ribs
Insertion: iliac crest and linea alba
Action: (bilateral) flexion, compression. (unilateral) lateral flexion and rotation to opposite side
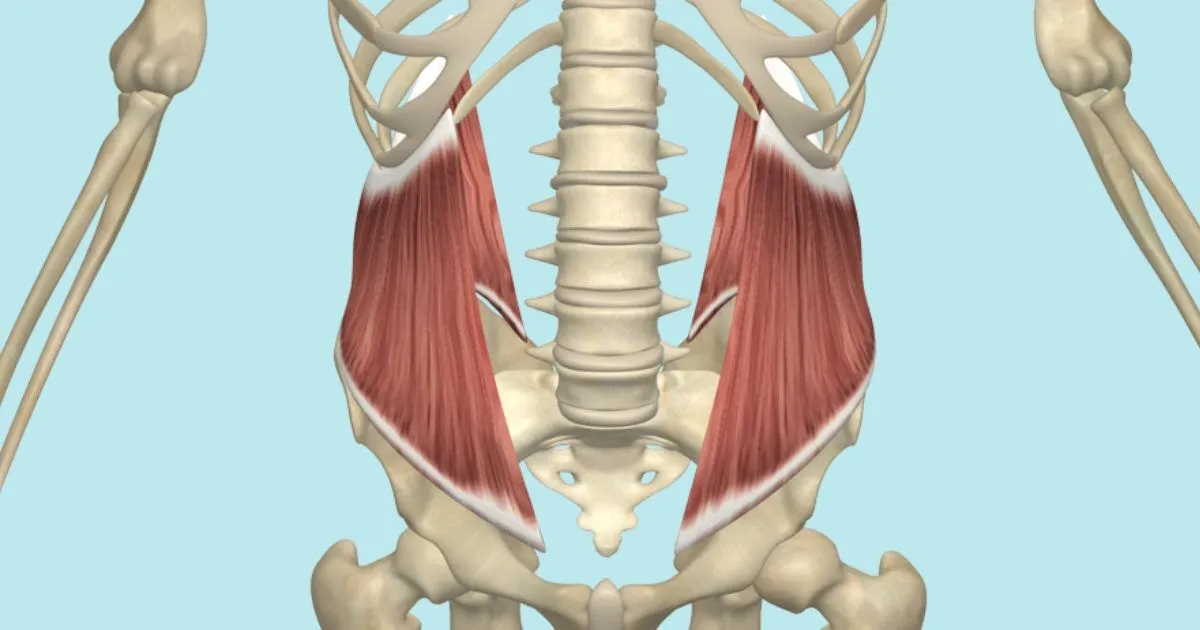
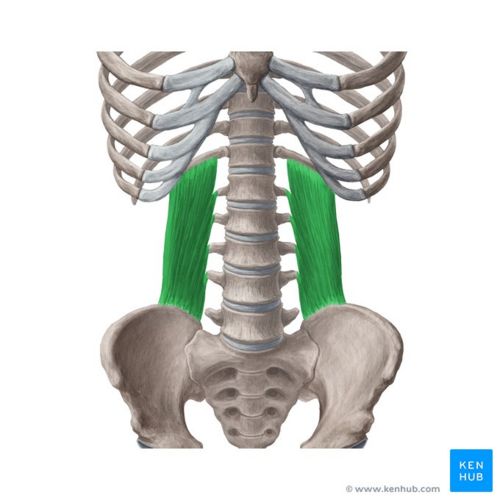
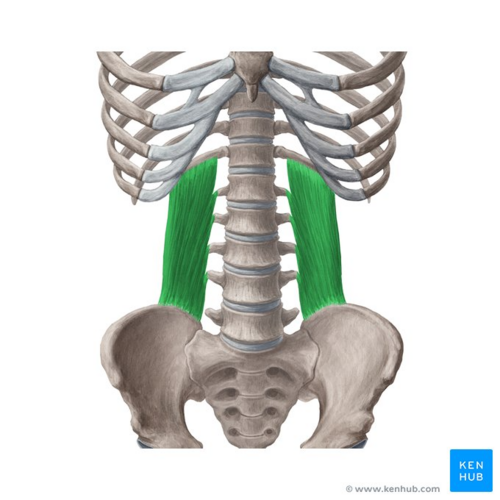
What is the structure pictured?
internal oblique
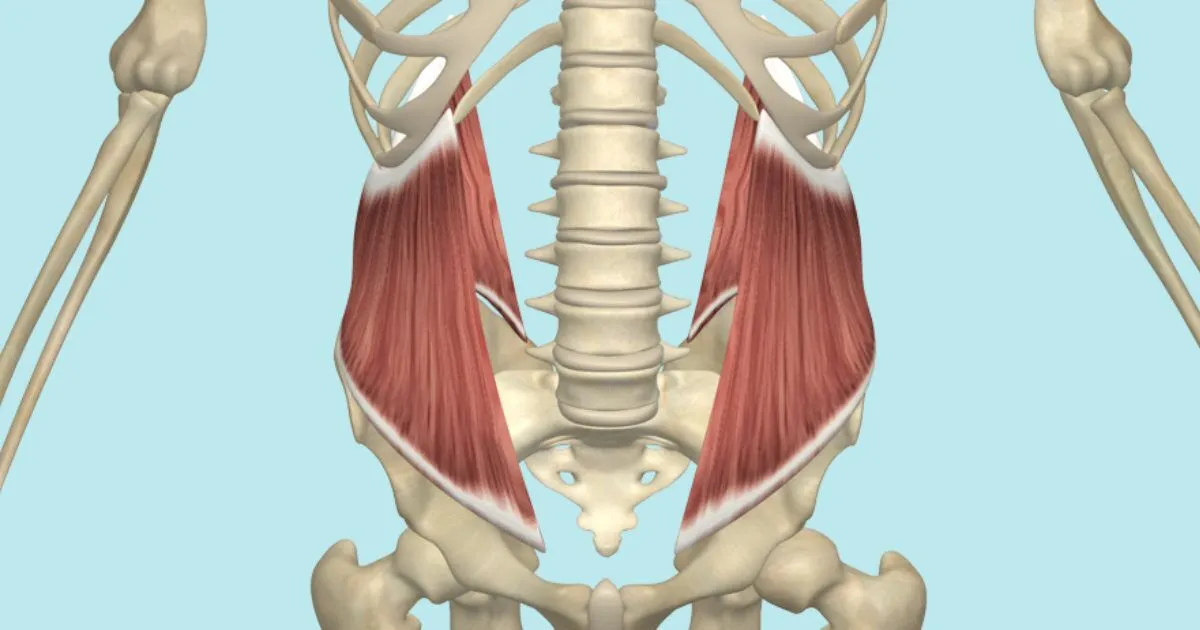
What are the origin and insertion points of the internal obliques? What is their action?
Origin: iliac crest, inguinal ligament, lumbar fascia
Insertion: linea alba, pubic crest, costal cartilage of lower 4 ribs
Action: (bilaterally) flexion, compression. (unilaterally) lateral flexion and rotation to the same side
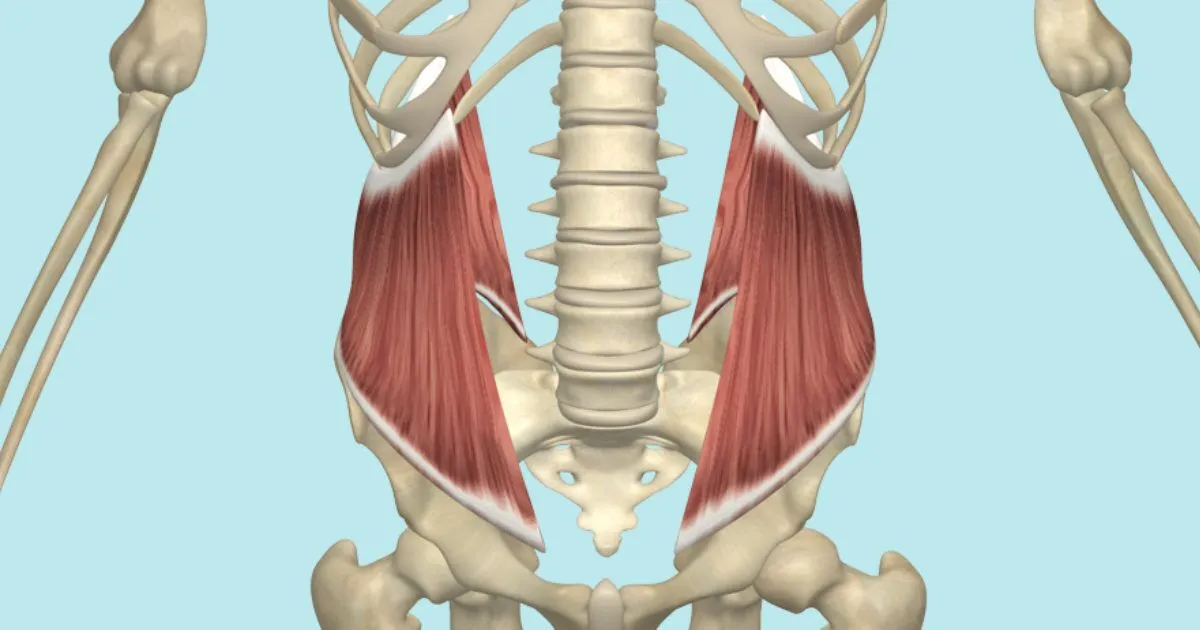
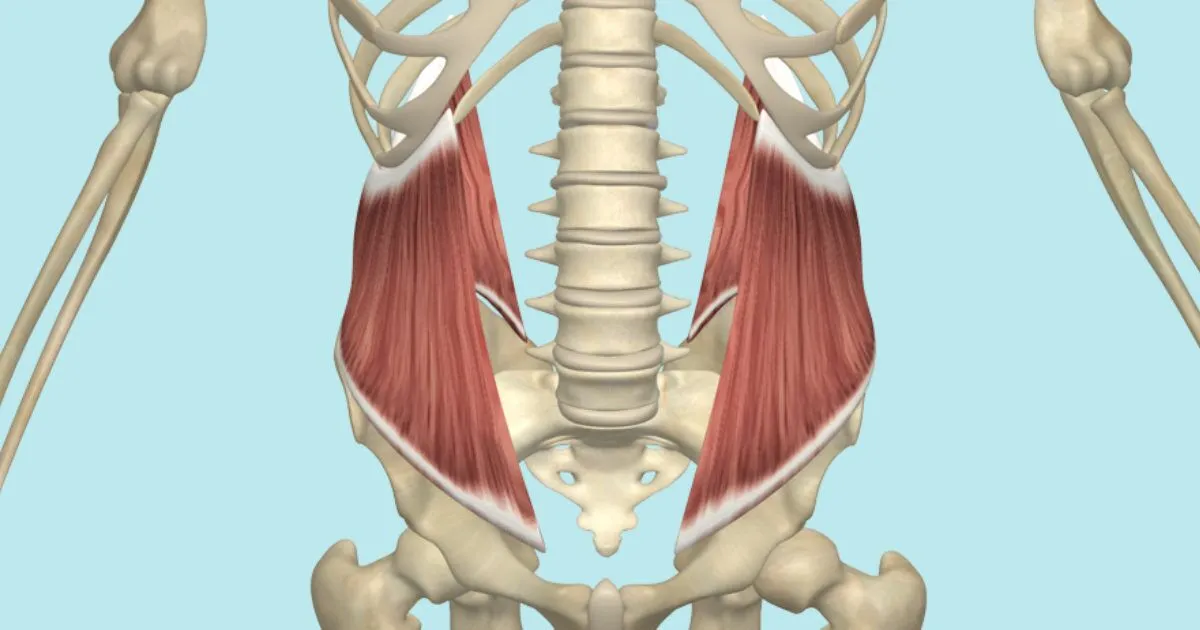
What is the structure pictured?
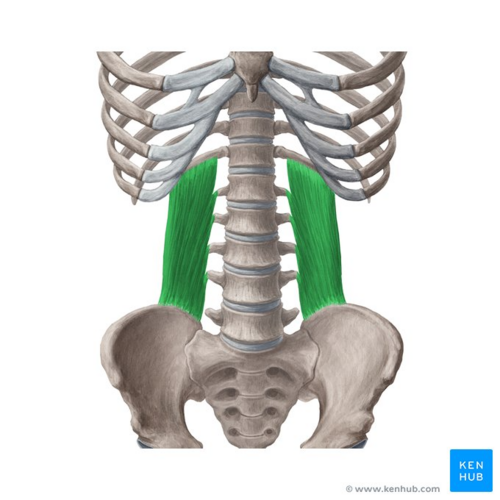
quadratus lumborum
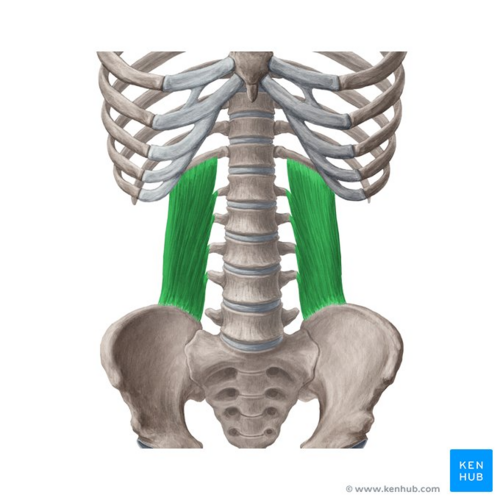
What are the origin and insertion points of the quadratus lumborum? What is their action?
Origin: iliac crest, iliolumbar vertebrae and 12th rib
Insertion: TP of lumbar vertebrae and 12th rib
Action: (bilaterally) extension. (unilaterally) lateral flexion
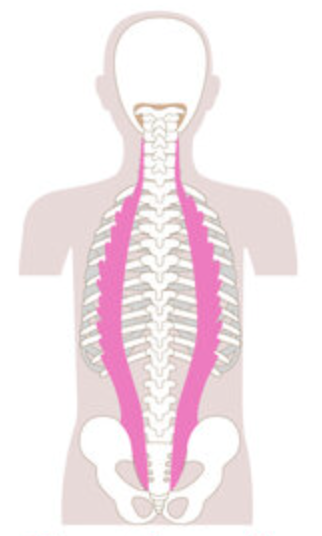
What is the structure pictured?
iliocostalis group
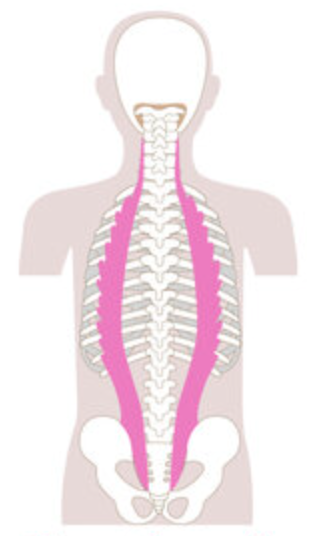
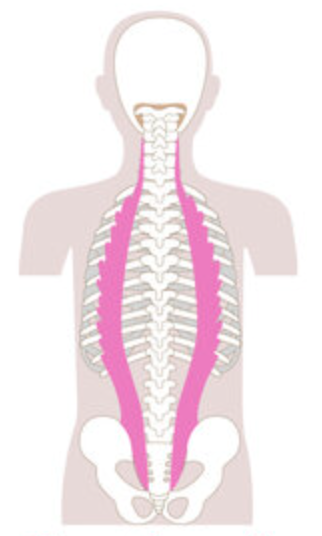
What are the origin and insertion points of the iliocostalis group? What is their action?
Origin: ribs, iliac crest
Insertion: TP of cervical vertebrae, ribs
Action: (bilaterally) extension. (unilaterally) lateral flexion
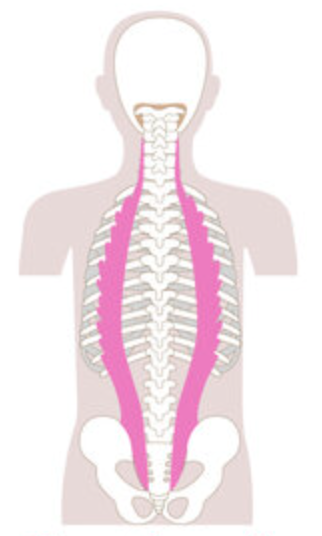
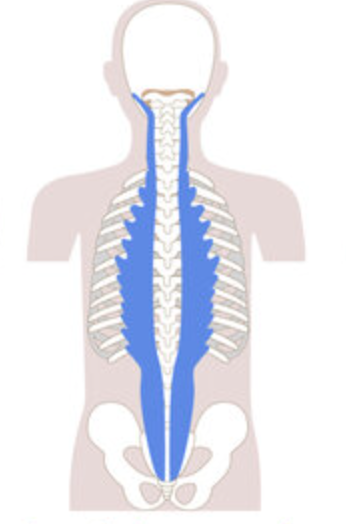
What is the structure pictured?
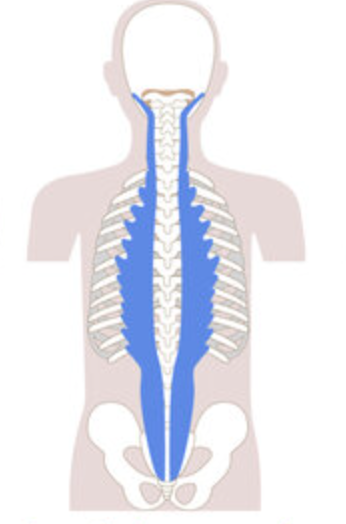
longissimus group
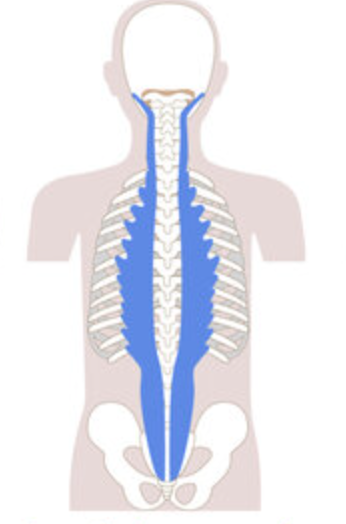
What are the origin and insertion points of the longissimus group? What is their action?
Origin: Tp of cervical, thoracic, and lumbar vertebrae
Insertion: mastoid process, TP of cervical and thoracic vertebrae
Action: (bilaterally) extension. (unilaterally) lateral flexion
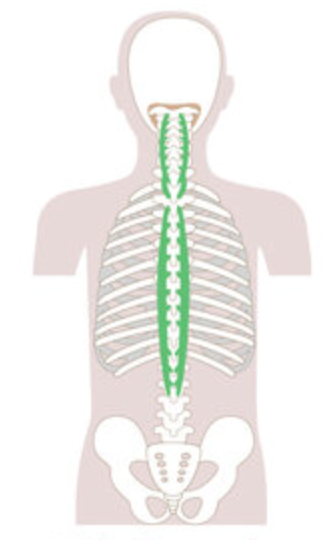
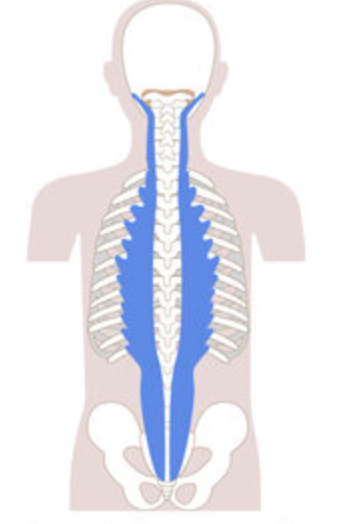
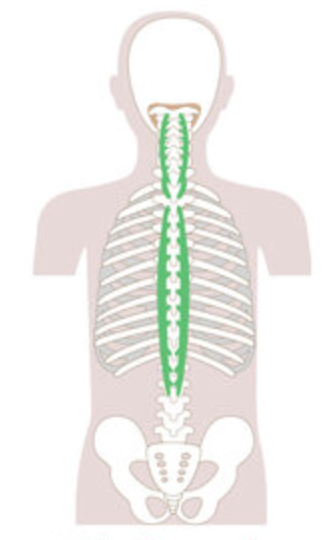
What is the structure pictured?
spinalis group
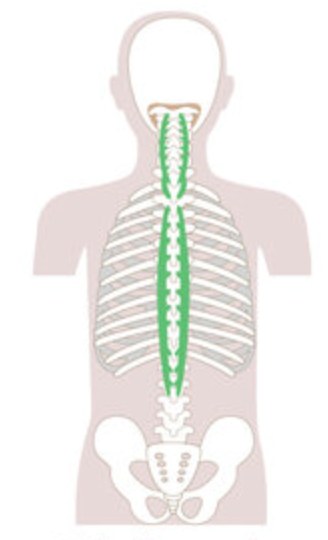
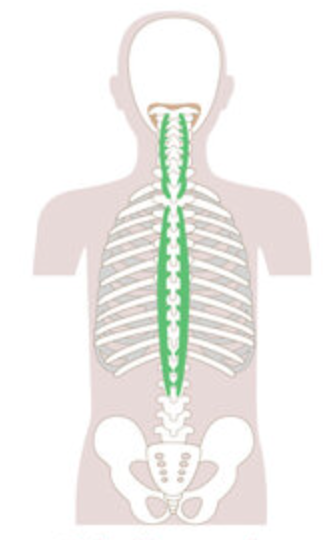
What are the origin and insertion points of the spinalis group? What is their action?
Origin: SP of C7-lumbar vertebrae
Insertion: SP of axis and thoracic vertebrae
Action: (bilaterally) extension. (unilaterally) lateral flexion
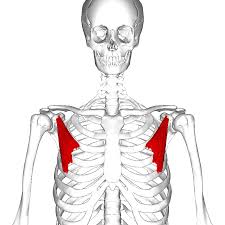
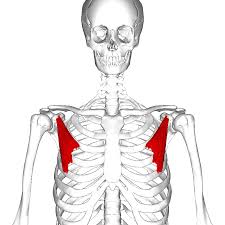
What is the structure pictured?
pectoralis minor
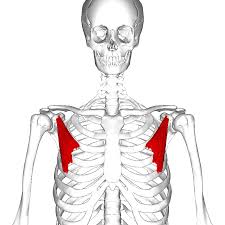
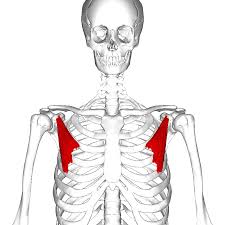
What are the origin and insertion points of the pectoralis minor? What is their action?
Origin: ribs 3-5
Insertion: coracoid process of the scapula
Action: depression, protraction, downward rotation
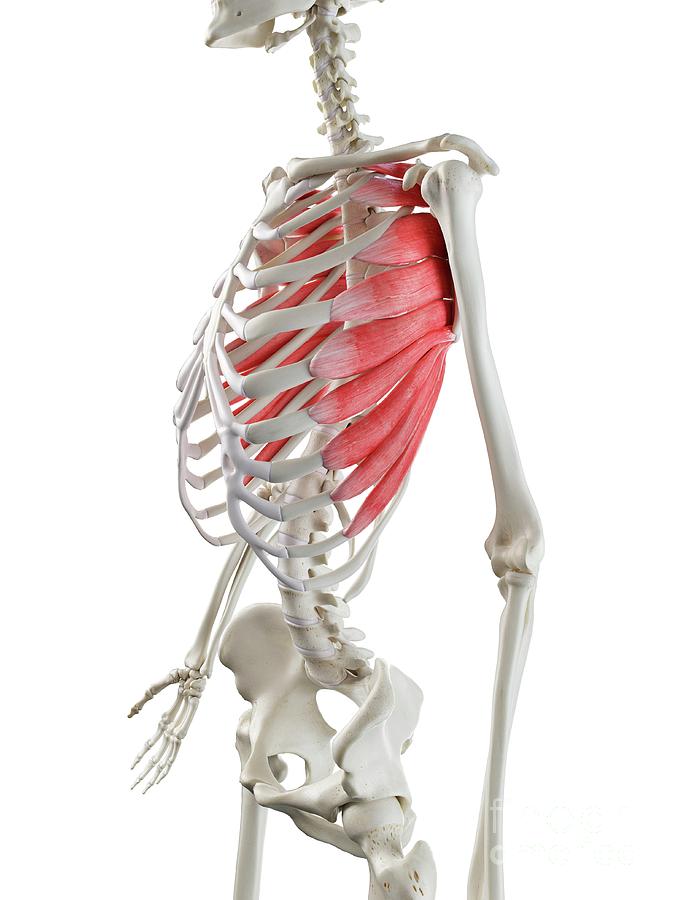
What is the structure pictured?
serratus anterior
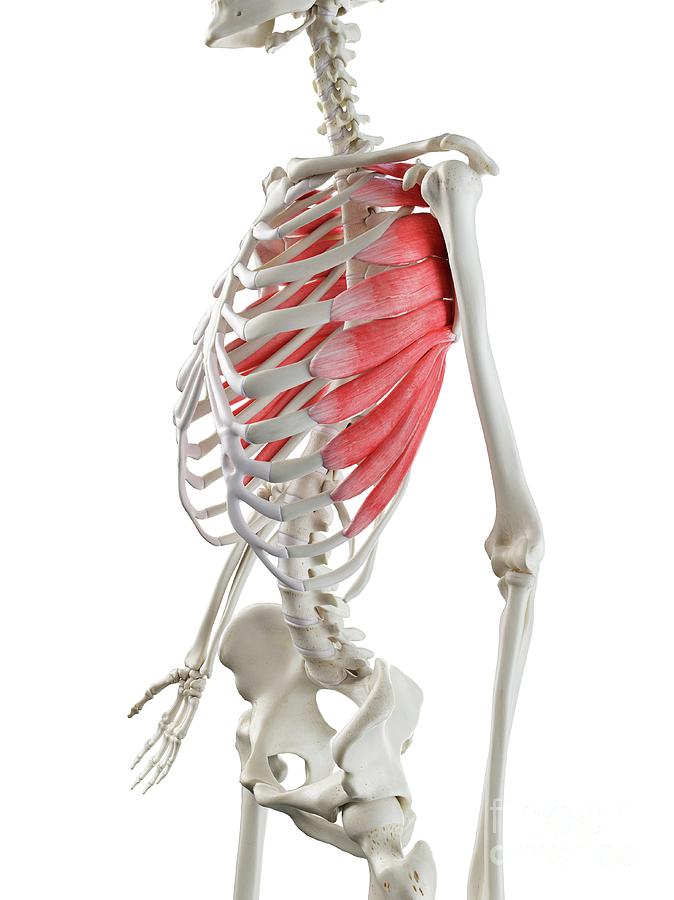
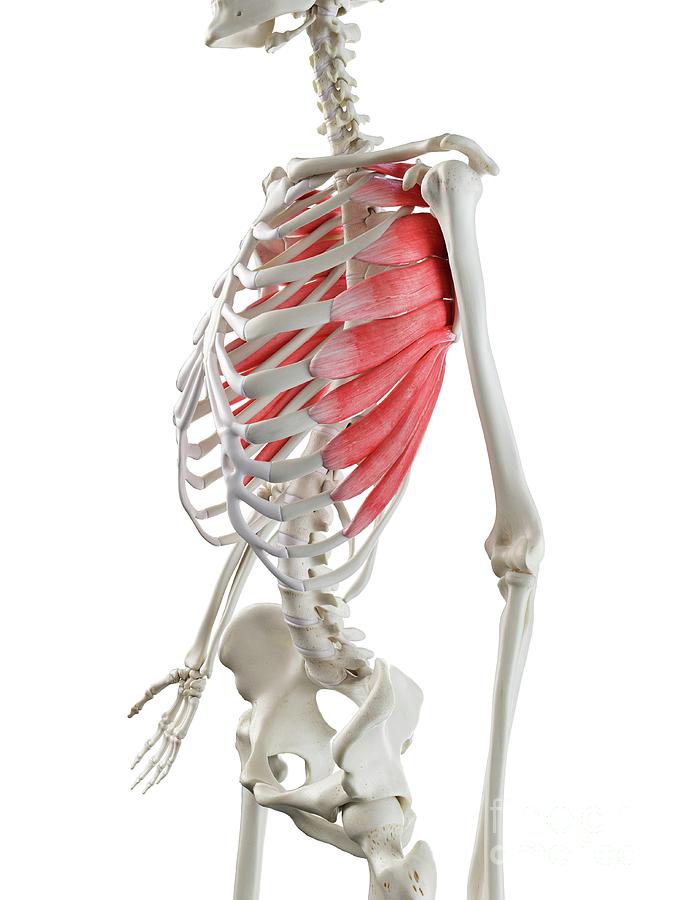
What are the origin and insertion points of the serratus anterior? What is their action?
Origin: ribs 1-8
Insertion: anterior medial border of the scapula
Action: protraction, upward rotation, “boxers muscle”
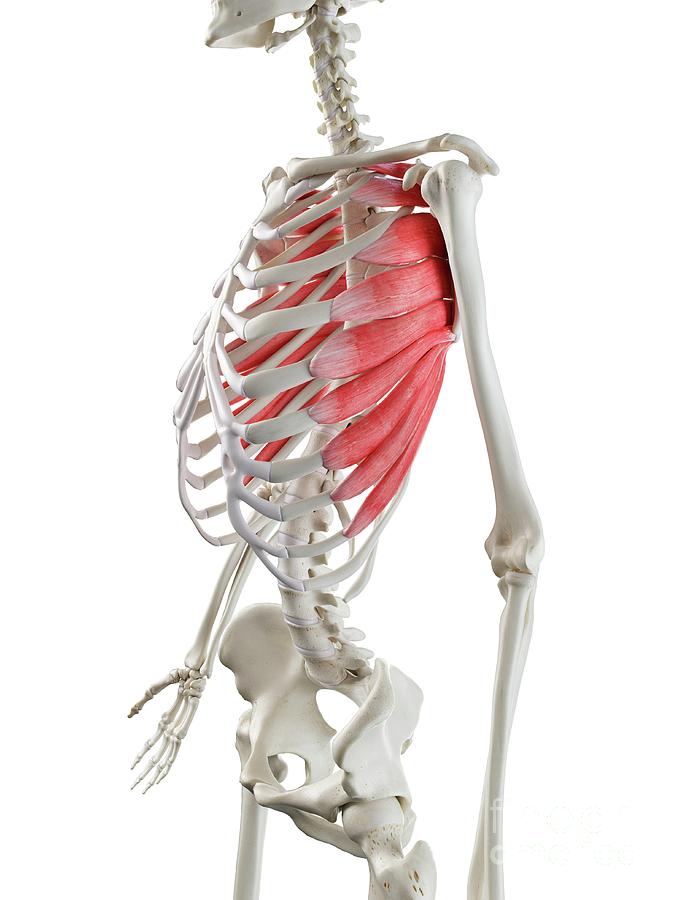
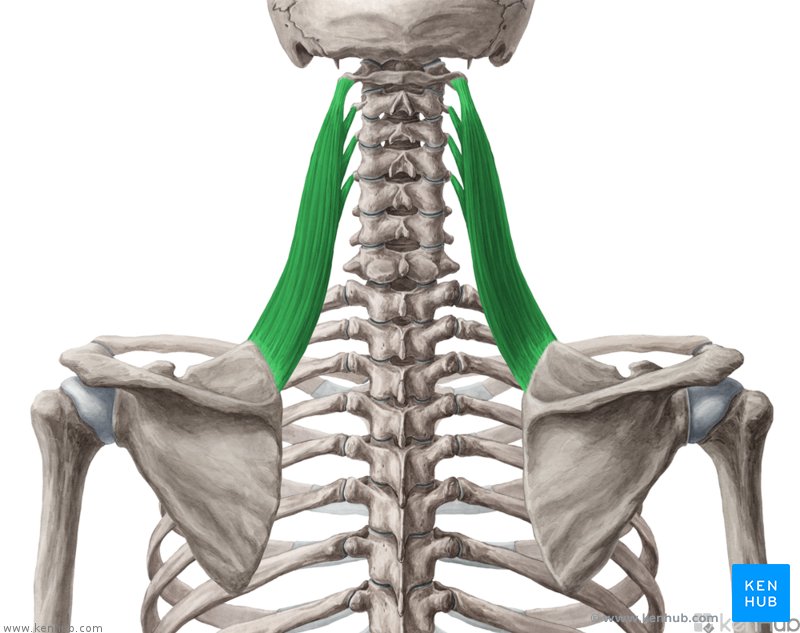
What is the structure pictured?
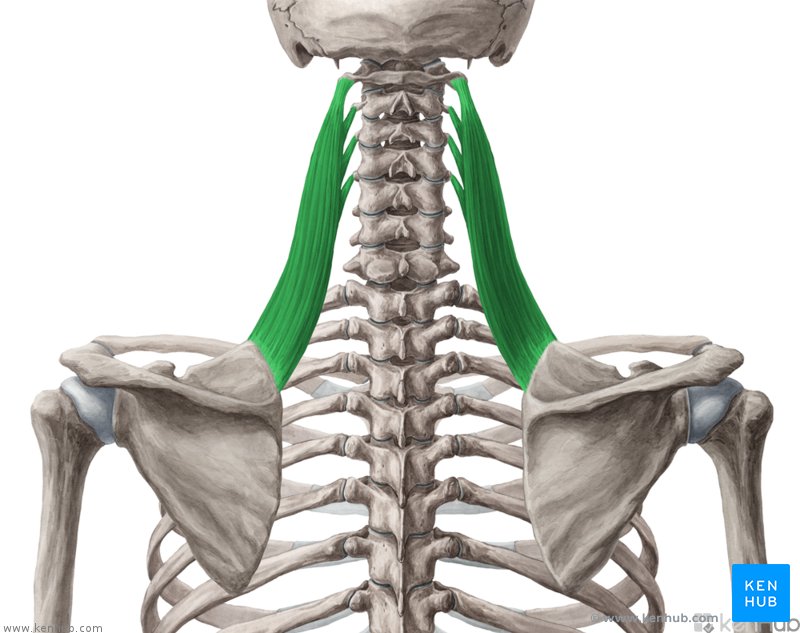
levator scapulae
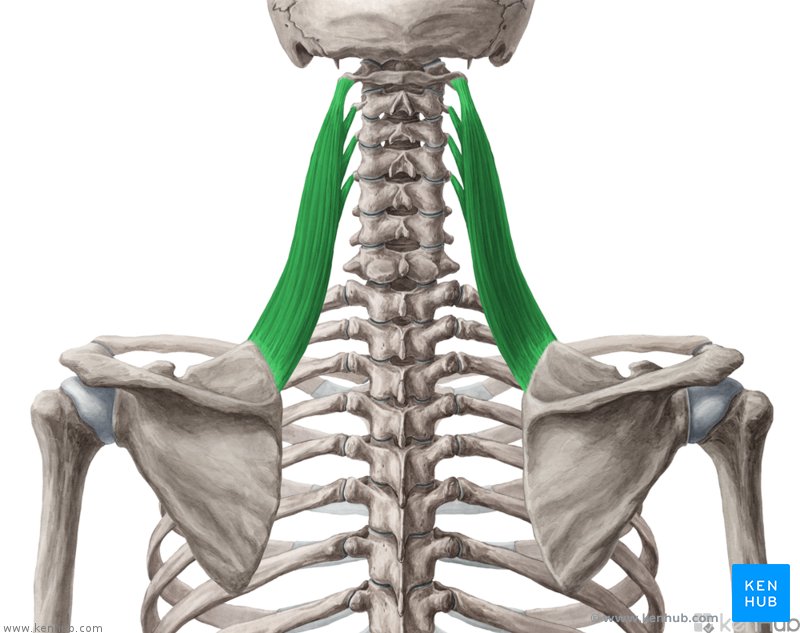
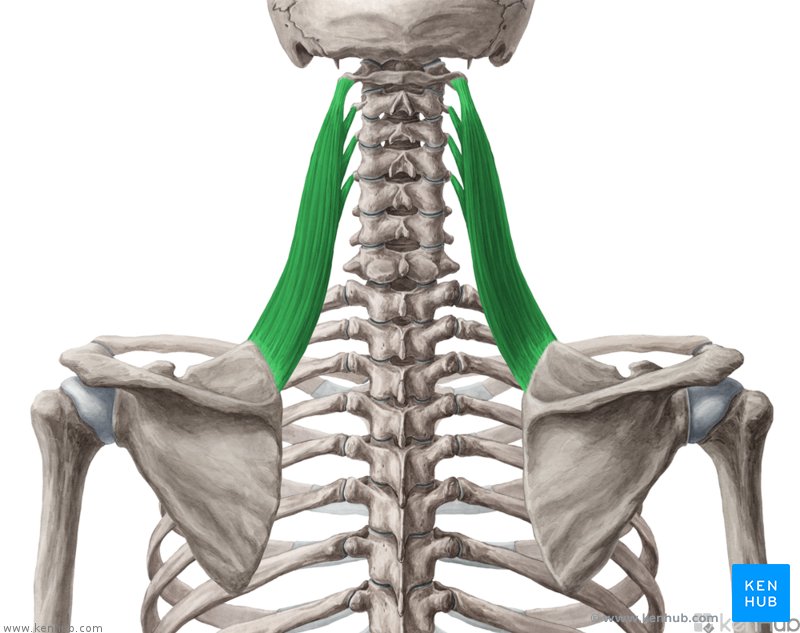
What are the origin and insertion points of the levator scapula? What is their action?
Origin: TP of C1-C4
Insertion: superior medial border of scapula
Action: elevation, retraction, and downward rotation
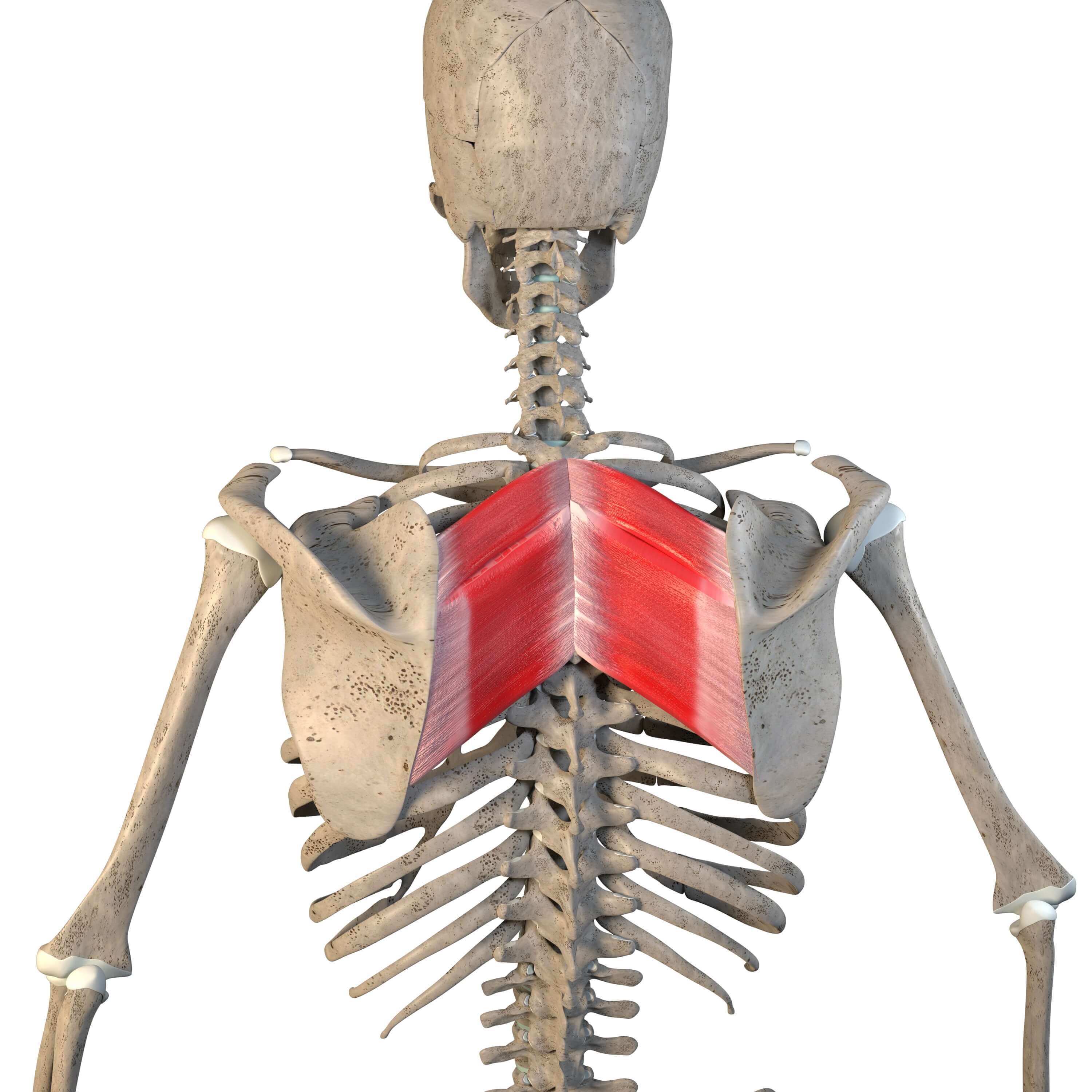
What is the structure pictured?
rhomboid major
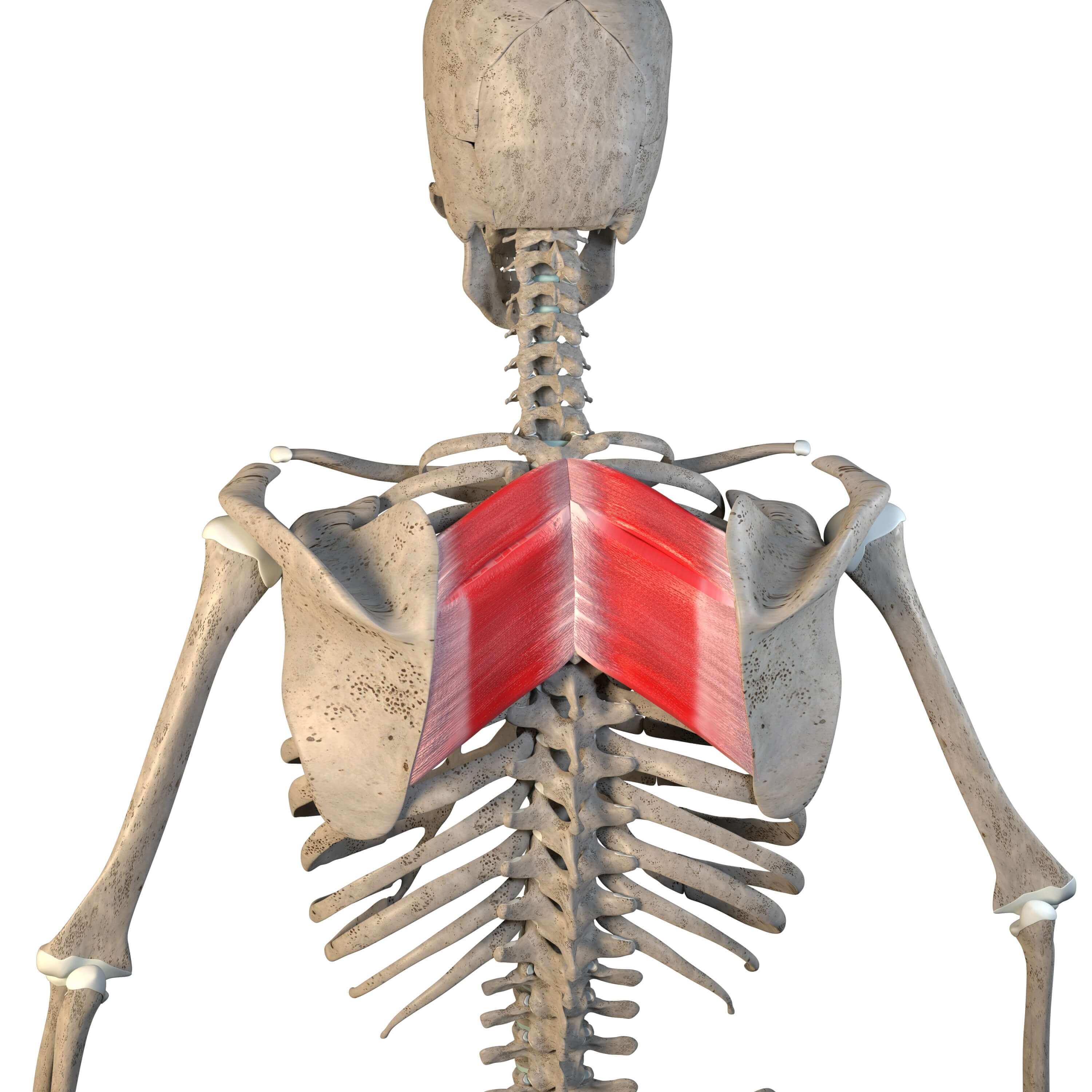
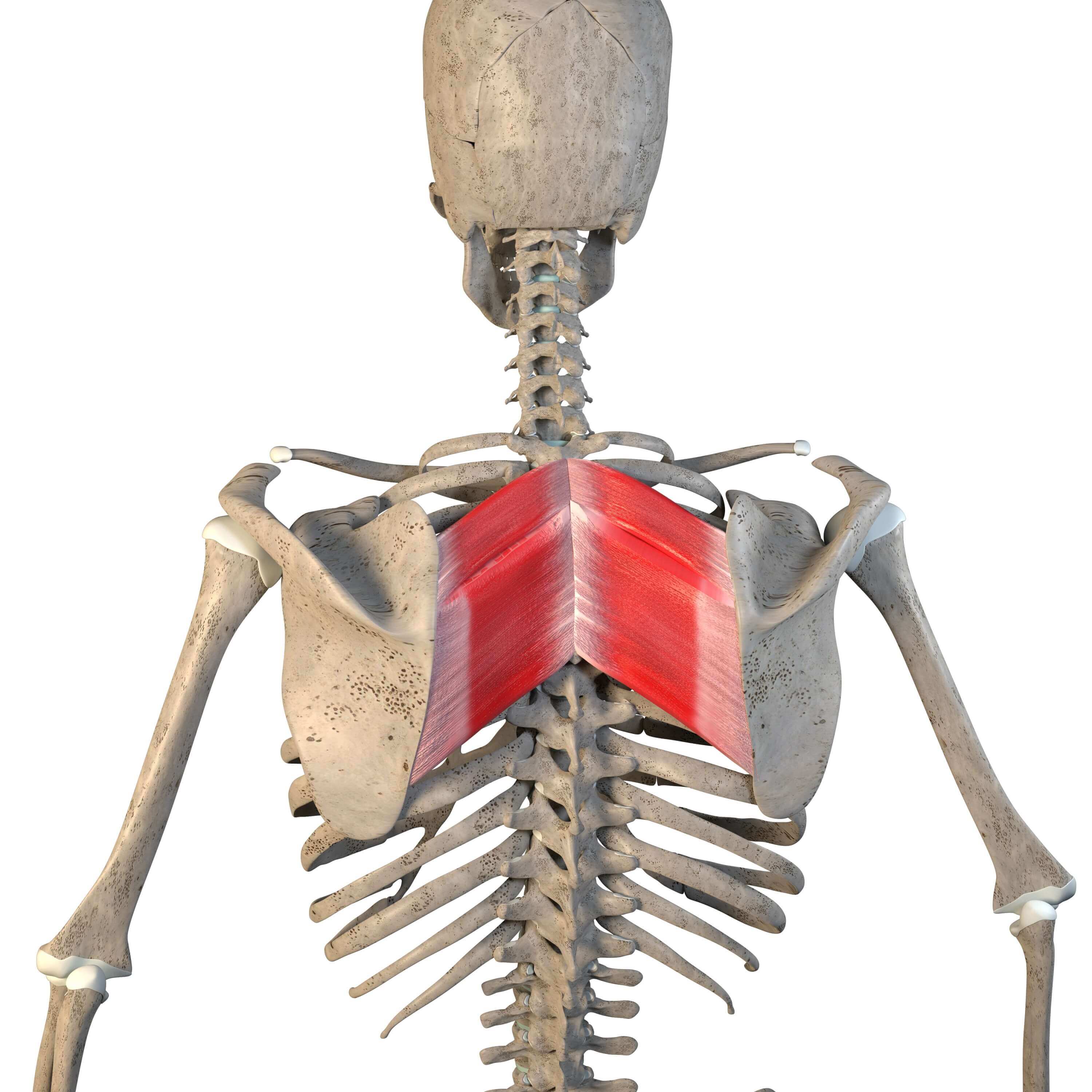
What are the origin and insertion points of the rhomboid major? What is their action?
Origin: SP of T2-T5
Insertion: medial border of the scapula
Action: elevation, retraction, and downward rotation
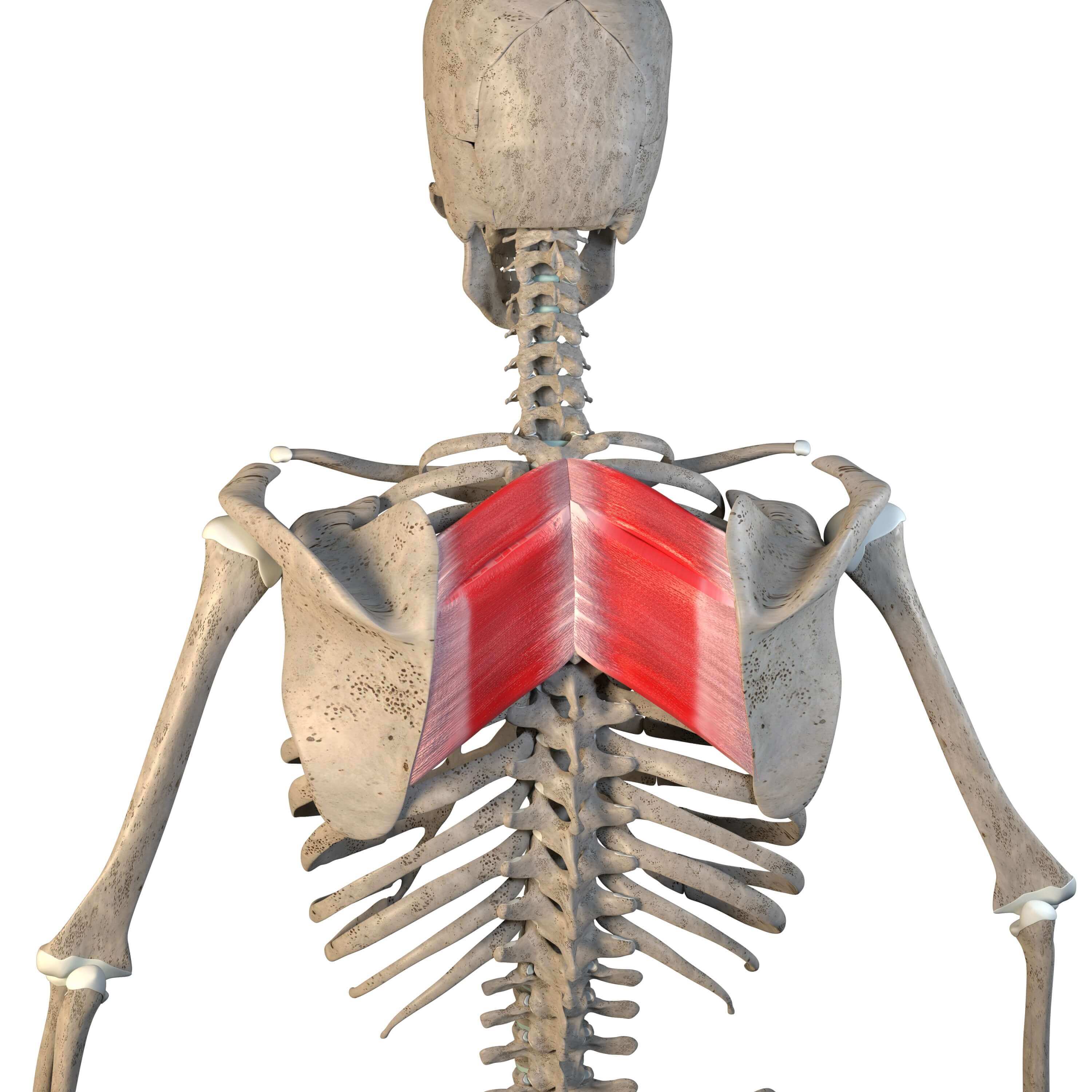
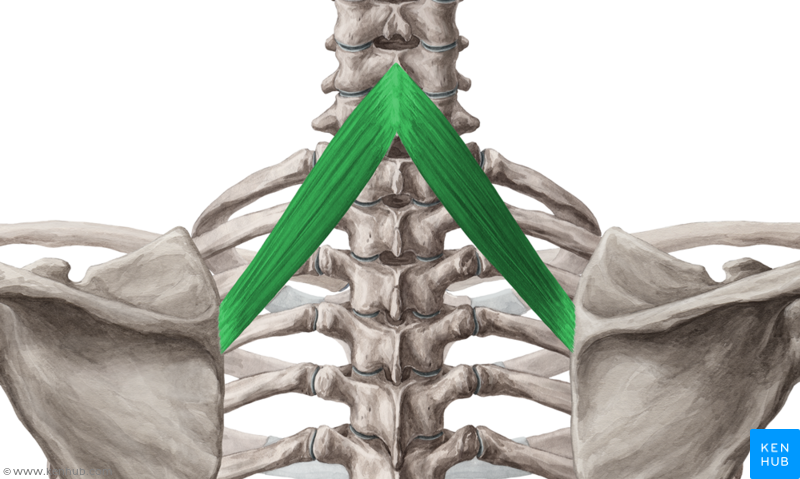
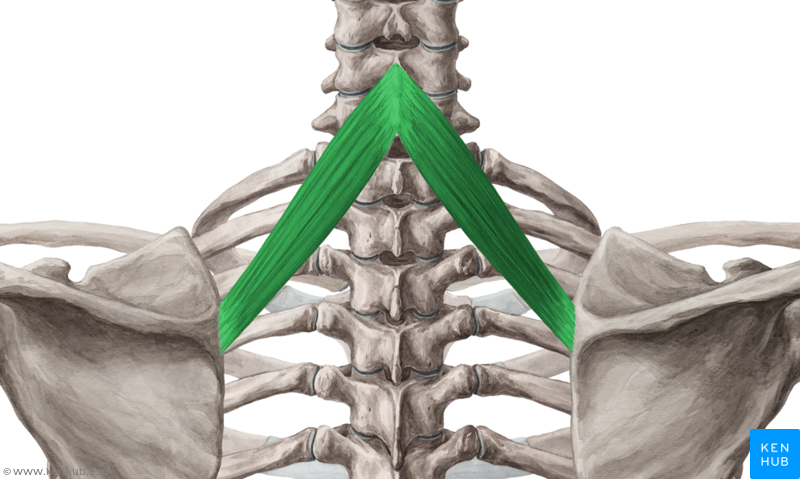
What is the structure pictured?
rhomboid minor
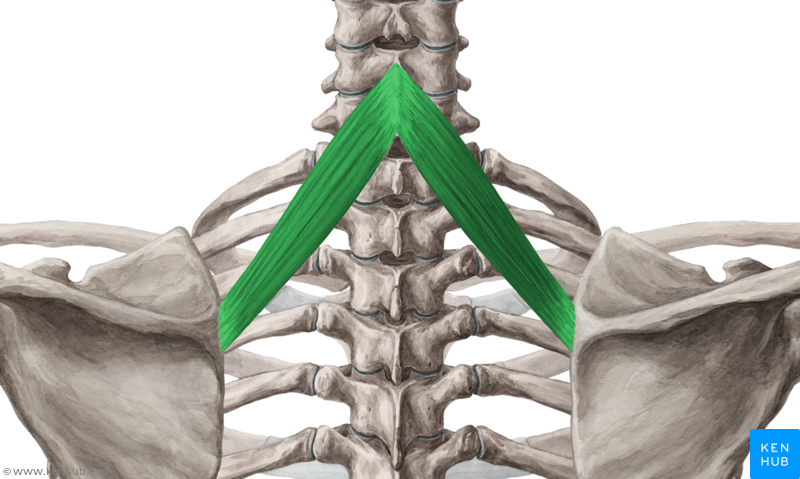
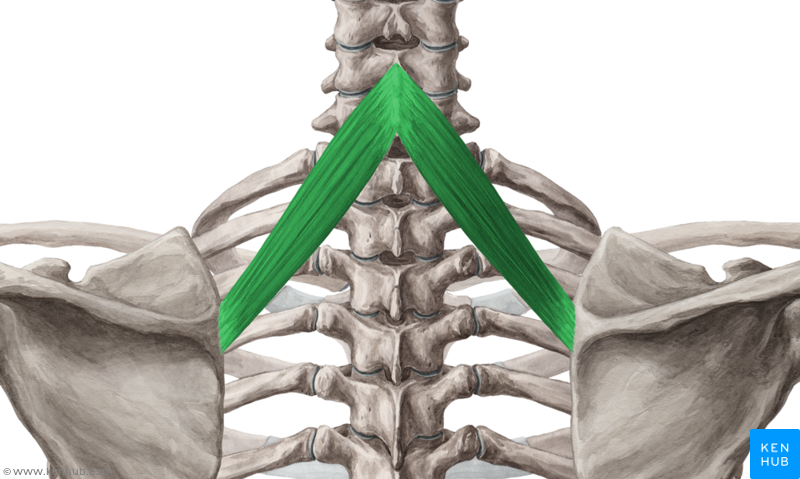
What are the origin and insertion points of the rhomboid minor? What is their action?
Origin: SP of C7-T1
Insertion: medial border of the scapula
Action: elevation, retraction, and downward rotation
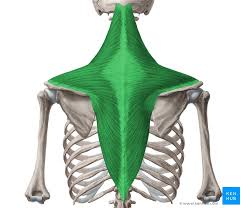
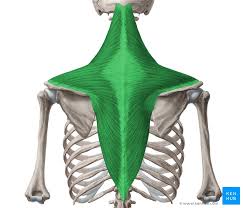
What is the structure pictured?
trapezius
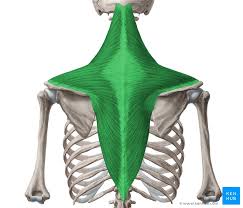
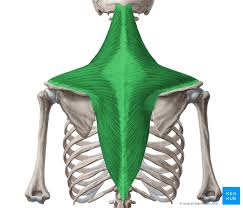
What are the origin and insertion points of the trapezius? What is their action?
Orign: (up) occipital bone. (mid) SP of C7-T4. (low) SP of T5-T12.
Insertion: (up) clavicle, acromion. (mid and low) scapular spine
Action: (up) elevation, upward rotation. (mid) retraction. (low) depression, downward rotation
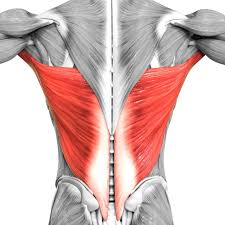
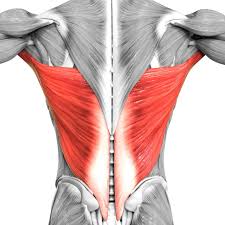
What is the structure pictured?
latissimus dorsi
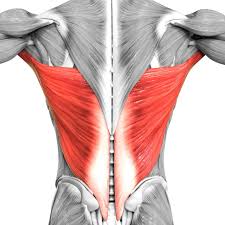
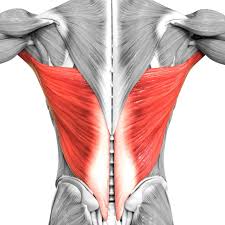
What are the origin and insertion points of the latissimus dorsi? What is their action?
Origin: SP of T7-T12, lumbar vertebrae, iliac crest, ribs 8-12, thoracolumbar fascia
Insertion: intertubercular groove of humerus
Action: extension, adduction and medial rotation
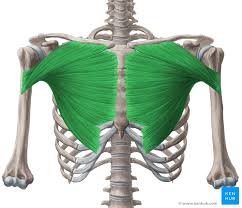
What is the structure pictured?
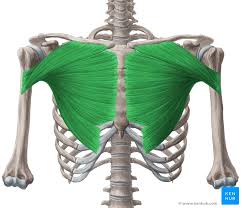
pectoralis major
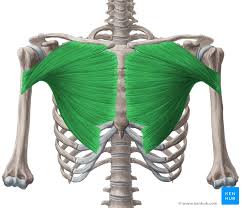
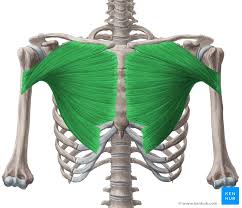
What are the origin and insertion points of the pectoralis major? What is their action?
Origin: medial clavicle, body of sternum, cartilage of ribs 2-6
Insertion: greater tubercle, intertubercular groove
Action: flexion, horizontal adduction, medial rotation
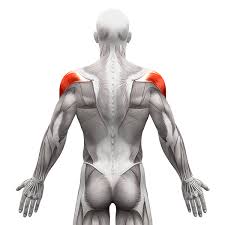
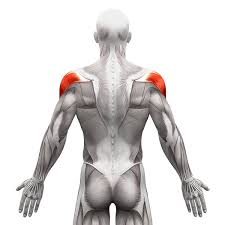
What is the structure pictured?
deltoids
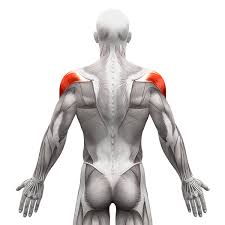
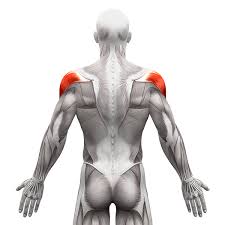
What are the origin and insertion points of the deltoids? What is their action?
Origin: (ant) lateral clavicle. (mid) lateral acromion. (post) spine of scapula
Insertion: (all) deltoid tuberosity of the humerus
Action: (ant) flexion, medial rotation. (mid) abduction. (post) extension, lateral rotation.
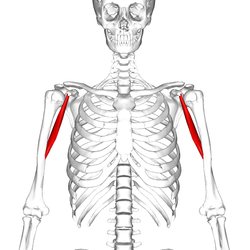
What is the structure pictured?
coracobrachialis