unit 1 introduction to anatomy
1/161
Earn XP
Description and Tags
12th grade honors anatomy/physiology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
162 Terms
biology
study of life
organisms
- all living things
- made of cells
- respond to stimuli
- able to grow and develop
- reproduce
- use energy (have a metabolism)
- contain DNA or RNA
- maintain homeostasis
- evolve/change over time (adapt to environment)
cells
- the most basic structural and functional unit of life
- smallest part of an organism that is still capable of all of life's processes
- very diverse (prokaryotic, eukaryotic, specialized)
- made up of organelles
organelles
- cytoplasm
- cell (plasma) membrane
- cytoskeleton
- centrioles
- cilia and flagella
- nucleus
- ribosomes
- rough endoplasmic reticulum
- smooth endoplasmic reticulum
- golgi apparatus
- lysosomes
- vacuoles
- mitochondria
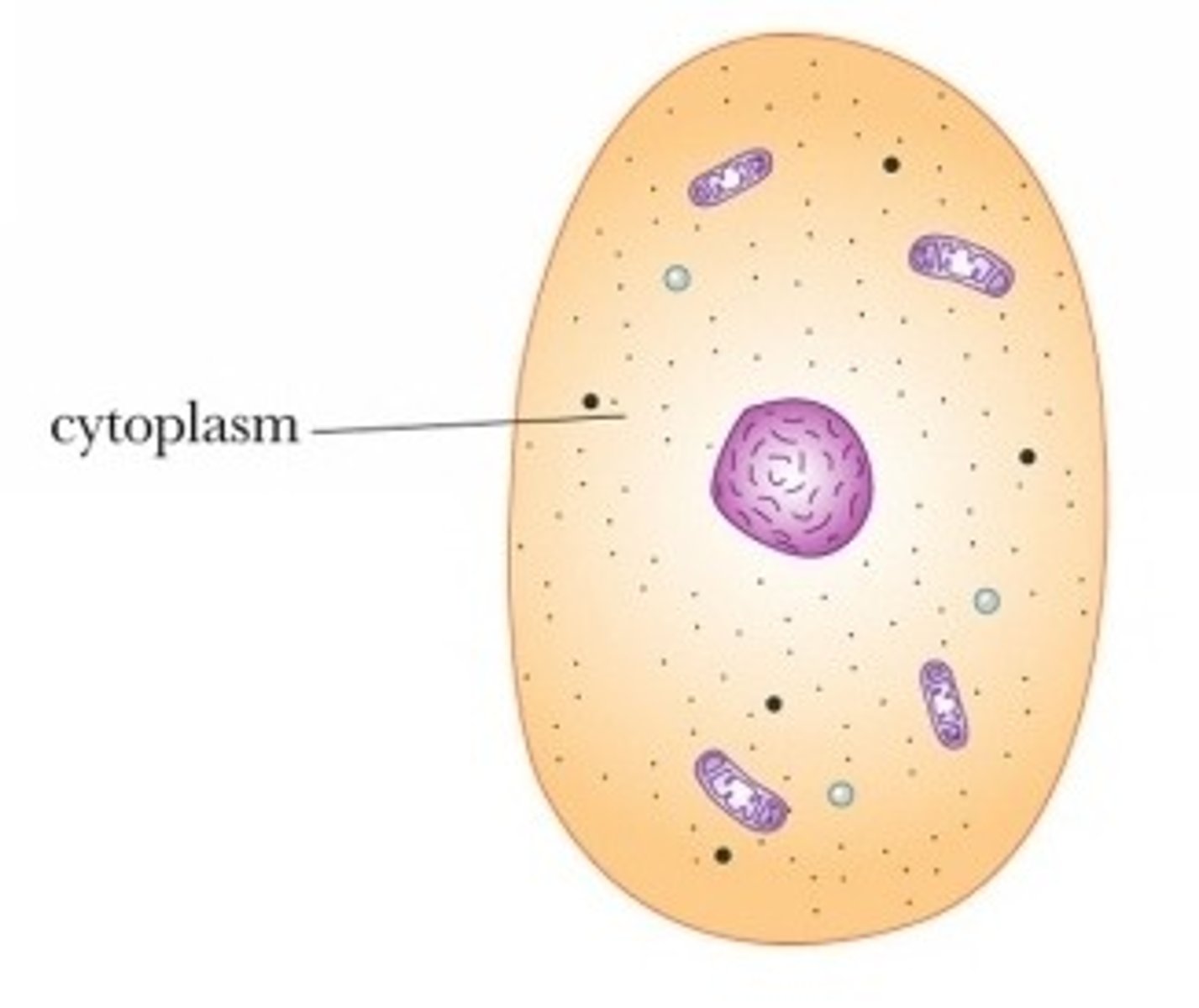
cytoplasm
- structure: jelly-like fluid, mainly made up of water
- function: holds everything in place
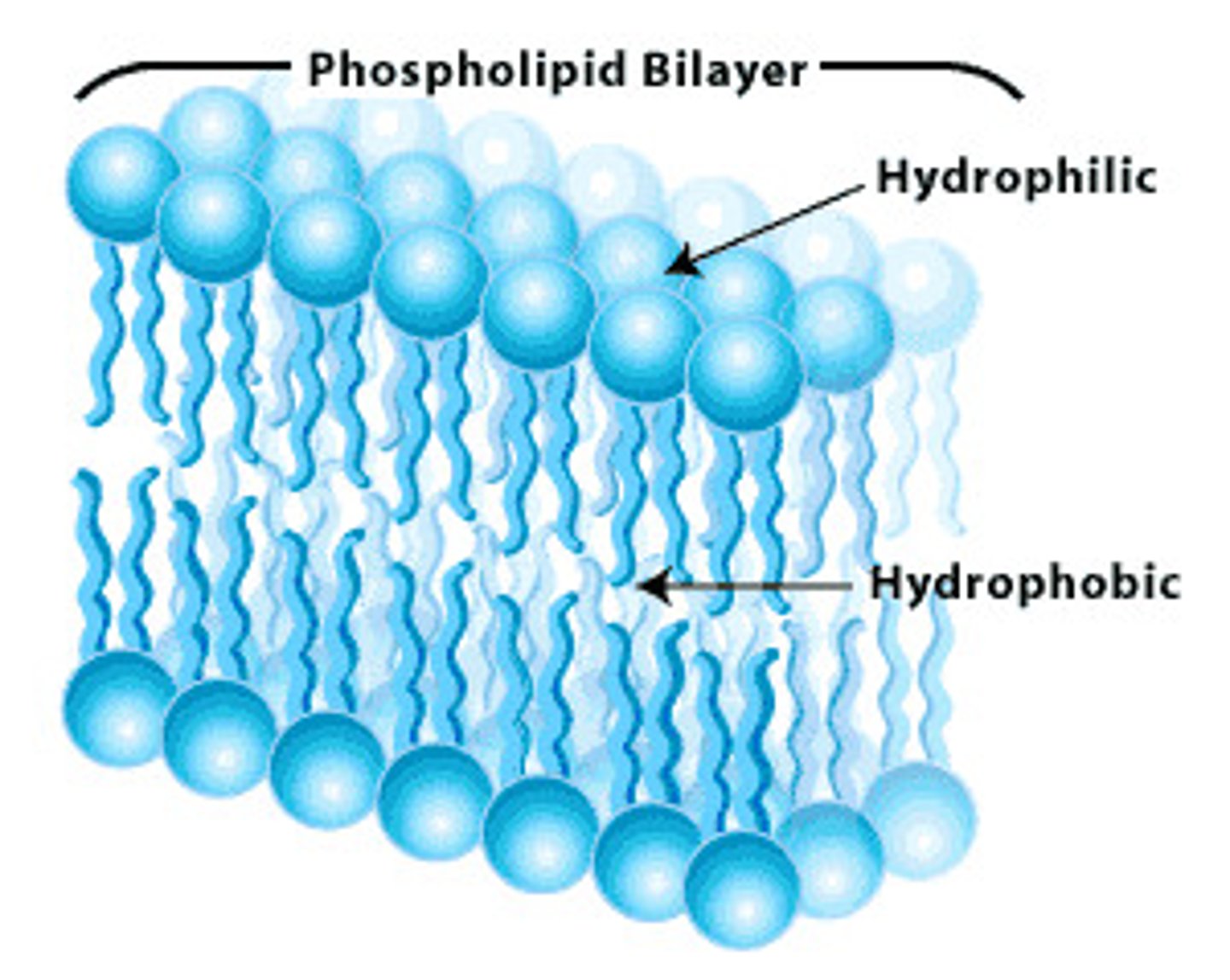
cell (plasma) membrane
- structure: selectively permeable barrier, phospholipid bilayer (hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails)
- function: control what goes in and out of the cell, communication, maintaining homeostasis
cytoskeleton
- structure: threadlike fibers, made of proteins, 3 types (microtubules, intermediate filaments, microfilaments)
- function: support, maintain shape, motility, regulate biochemical activities
centrioles
- associated with cytoskeleton
- structure: made of microtubules, 2 centrioles = centrosome
- function: appear during cell division, help cell divide by pulling chromosomes apart during anaphase
cilia
- associated with cytoskeleton
- structure: shorter, more numerous, tiny oars
- function: move fluid across cell's surface
flagella
- associated with cytoskeleton
- structure: longer, fewer (1-3)
- function: move entire cell through extracellular fluid
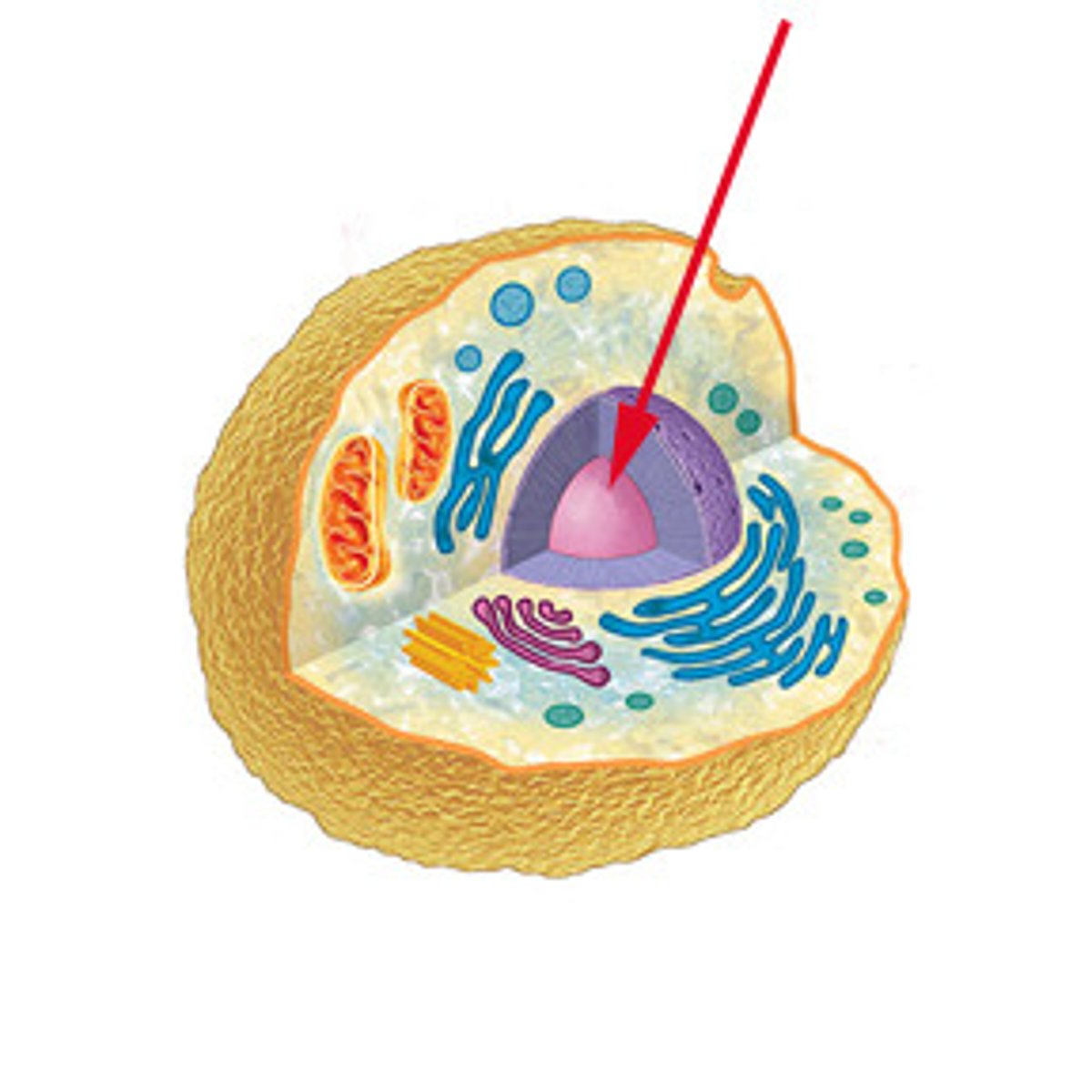
nucleus
- structure: contains DNA, nucleolus in the center, surrounded by a nuclear envelope/membrane with pores that control what goes in and out
- function: protects the DNA that controls the activities of the cell, nucleolus is where ribosomes are formed
ribosomes
- structure: made of proteins and rRNA, located on rough er and cytoplasm
- function: make proteins (rough er = proteins to export, cytoplasm = within cell)
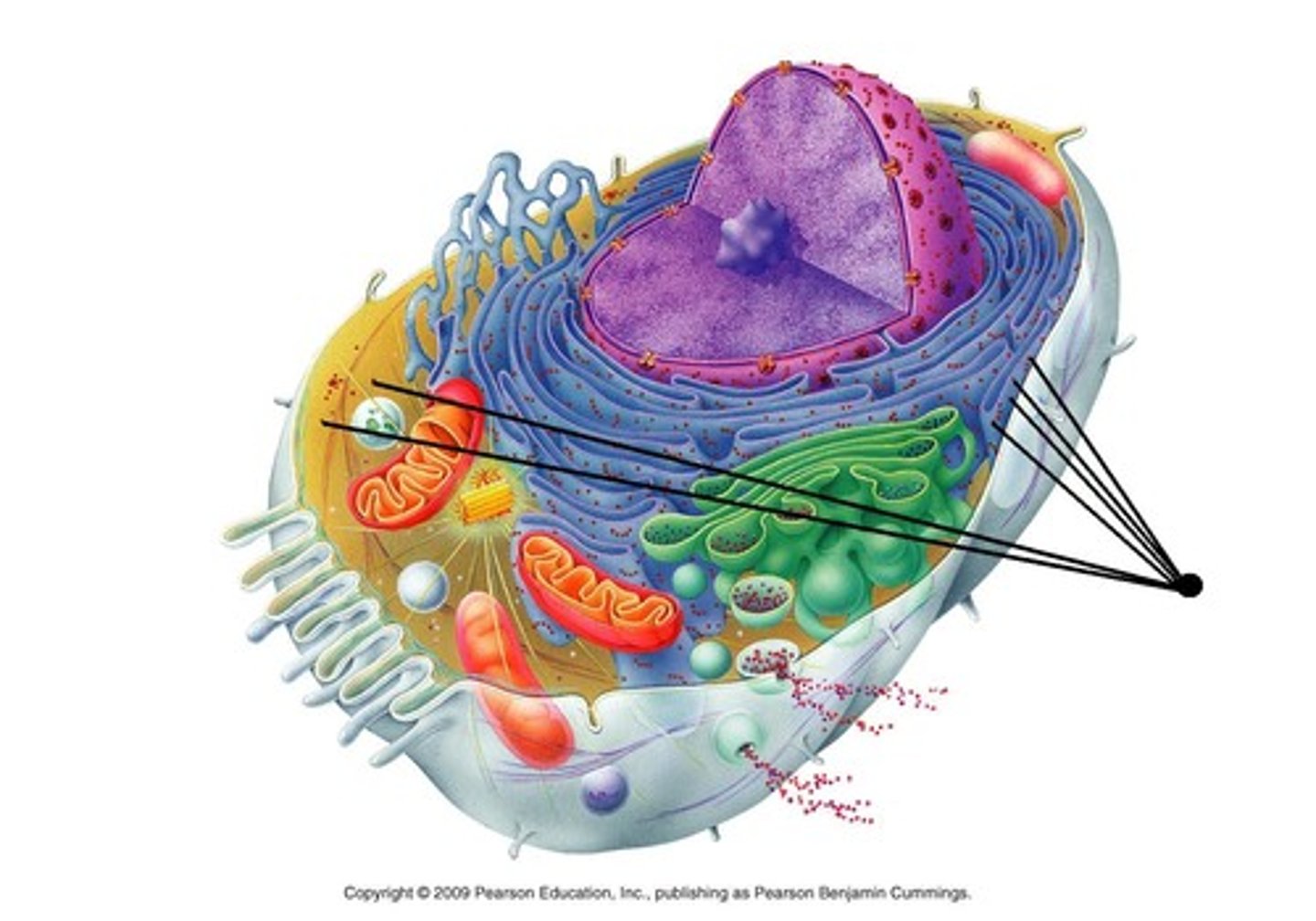
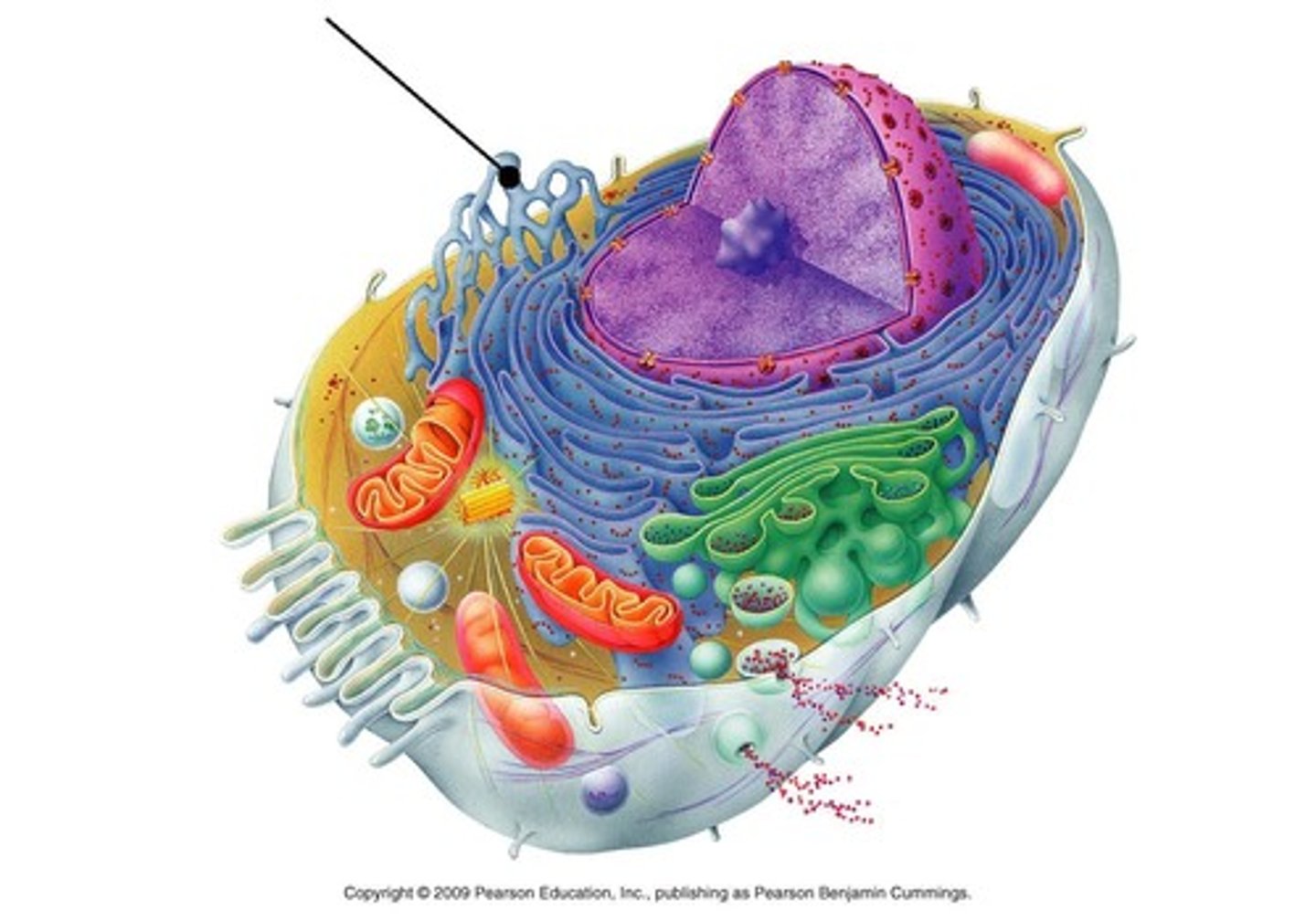
rough endoplasmic reticulum
- structure: ribosomes on surface, hugs the nucleus, network of membranes and sacs
- function: make proteins, package them for secretion, send transport vesicles to golgi apparatus
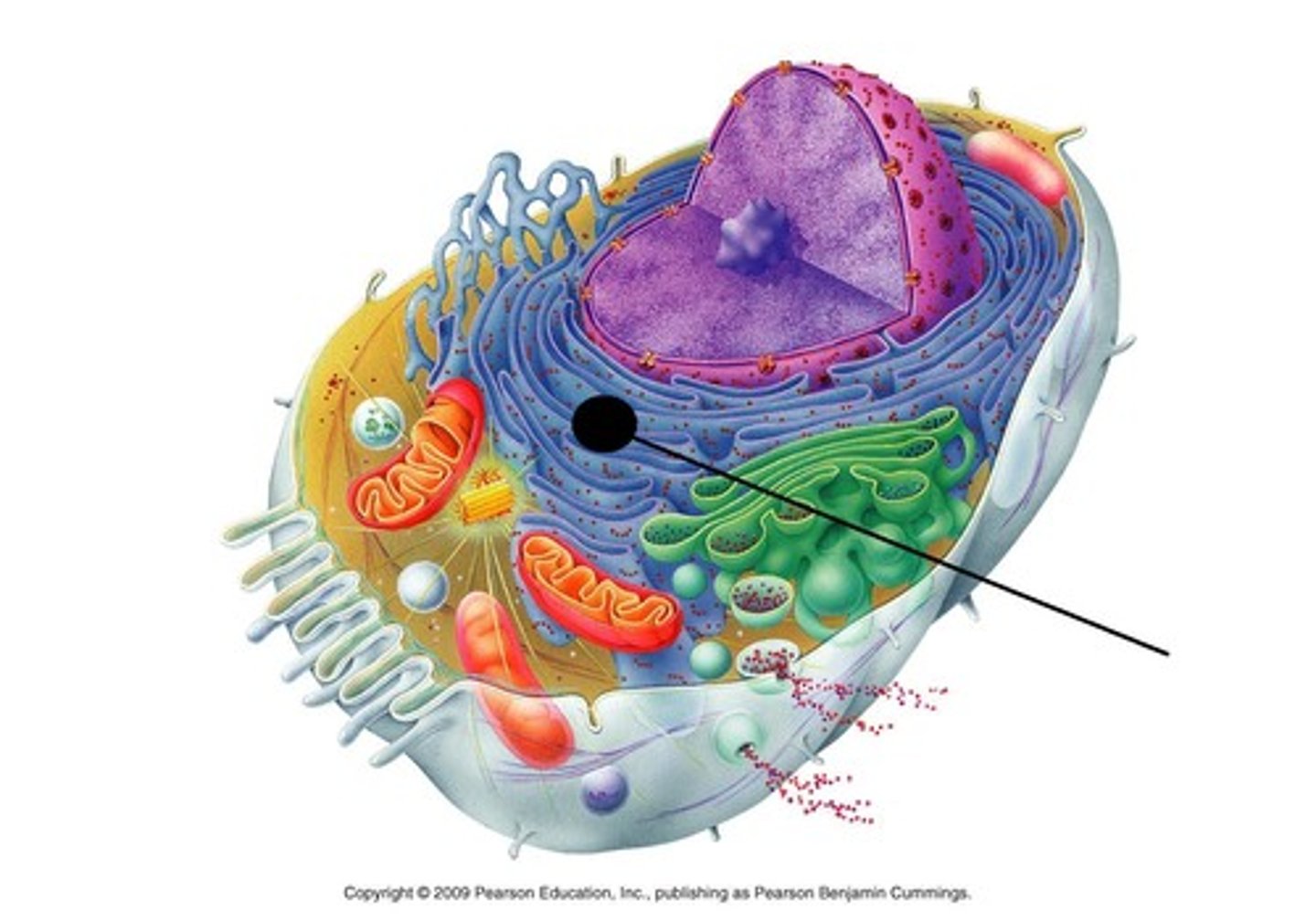
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
- structure: no ribosomes on surface, attached to rough er, network of membranes and sacs
- function: make lipids (membrane), chemically modifies small molecules, site of glycogen degradation, store Ca⁺²
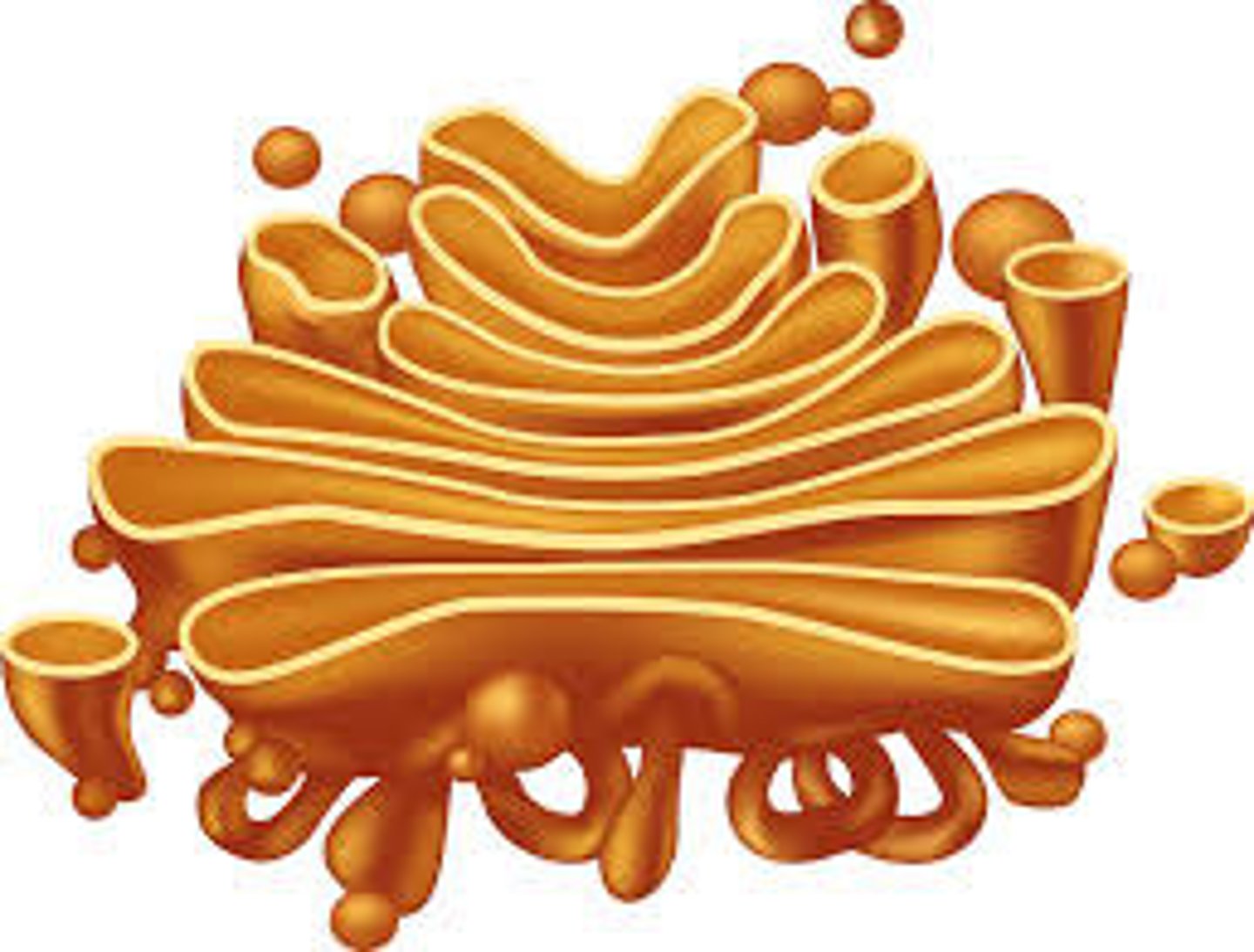
golgi apparatus
- structure: folded/flattened membrane sacs
- function: processes, sorts, and ships proteins

lysosomes
- structure: contain hydrolytic enzymes for breaking stuff down
- function: breakdown dead stuff (food, bacteria, old parts of cell), programmed cell death (apoptosis)
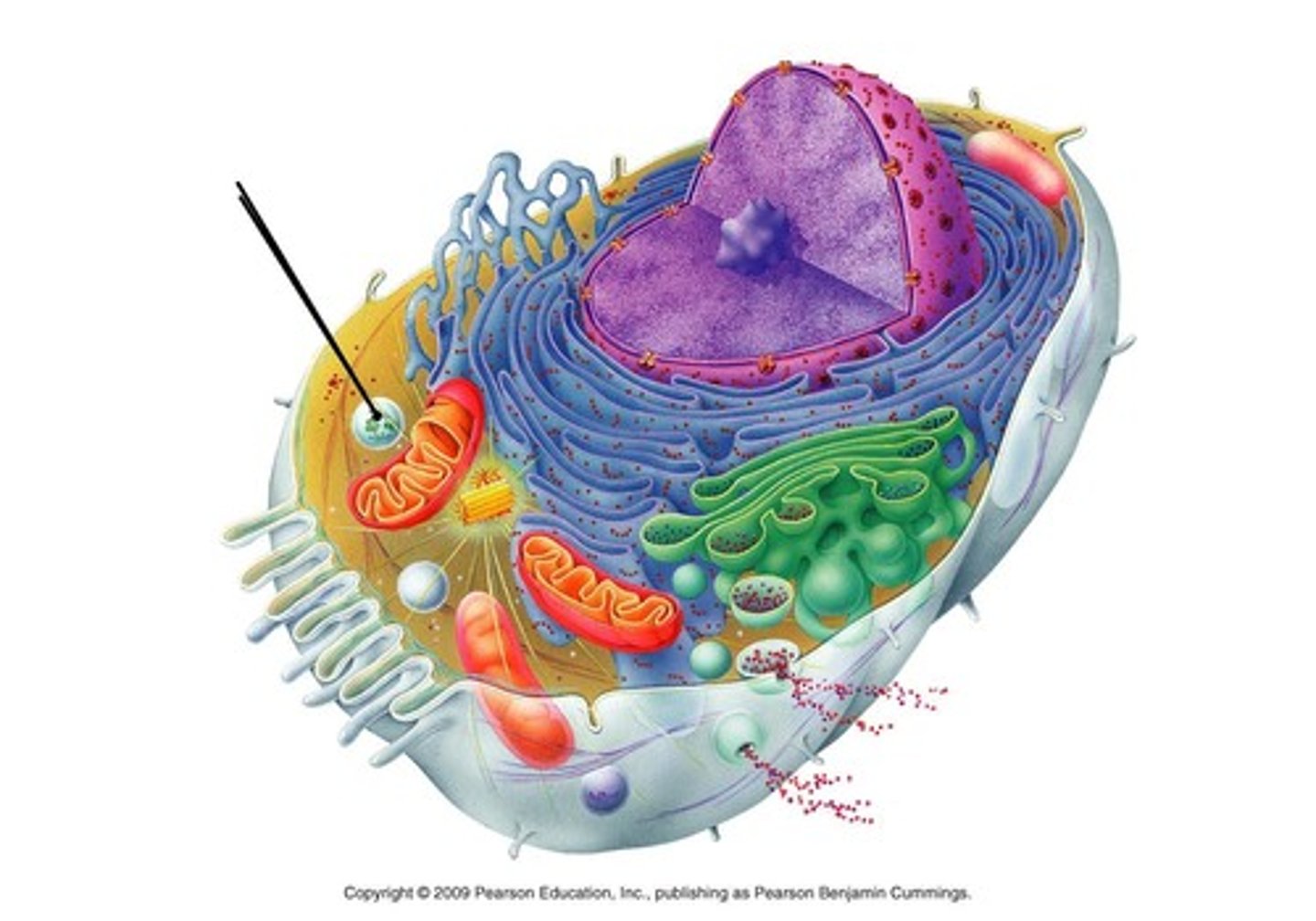
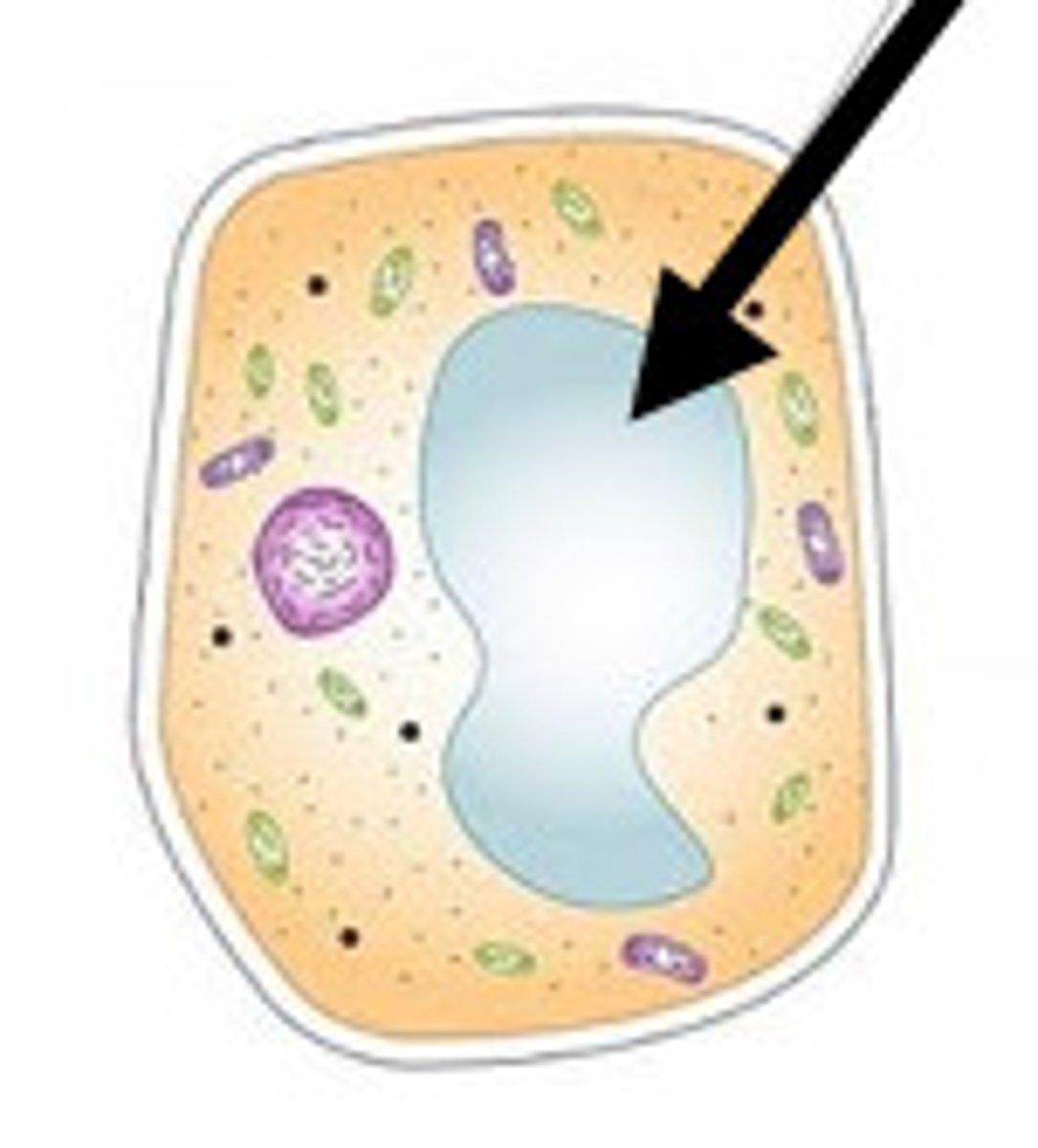
vacuoles
- structure: smaller, more numerous in animal cells
- function: storage (water, nutrients, waste)
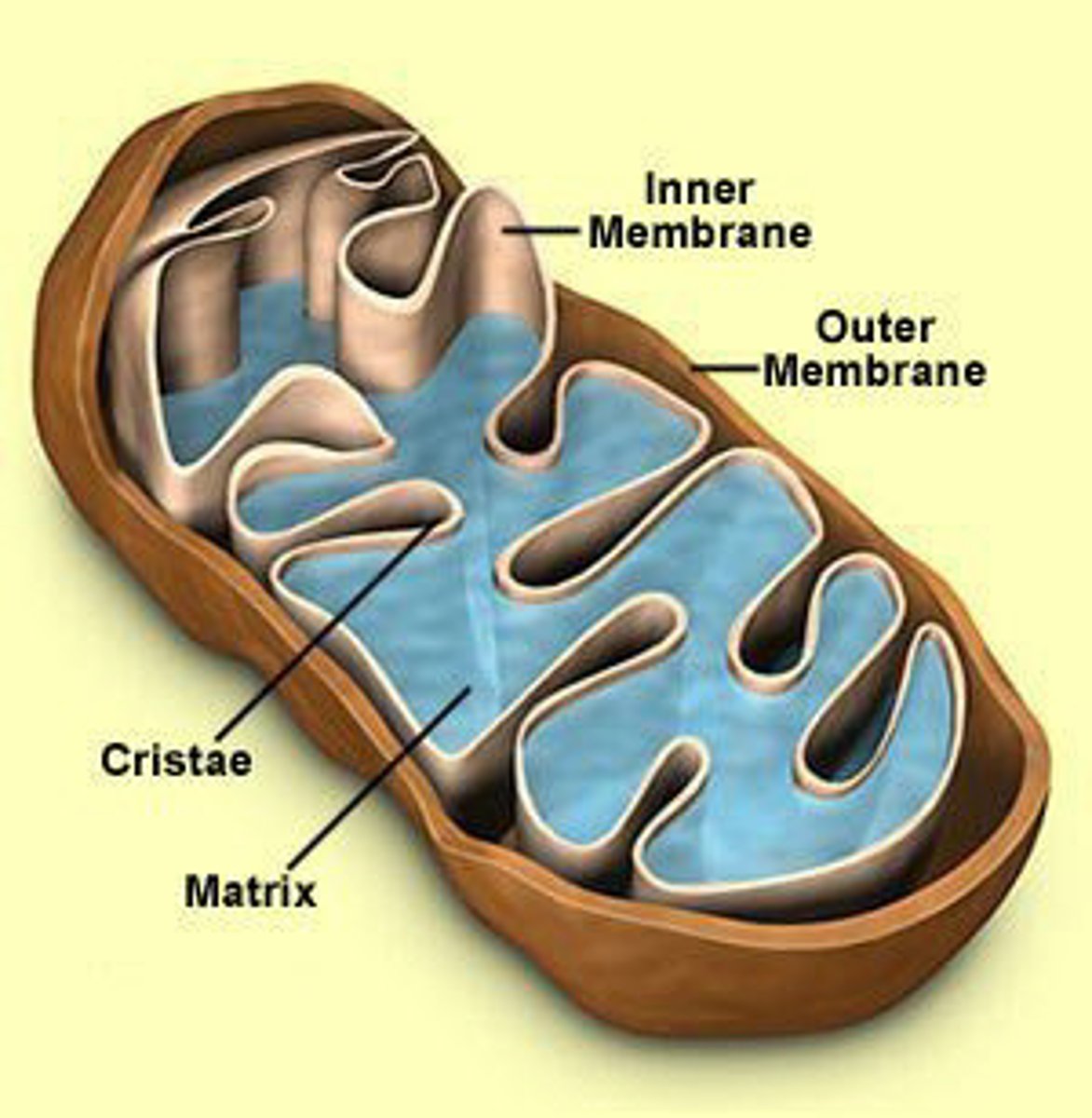
mitochondria
- structure: folded inner membrane (cristae), enzyme-packed fluid (matrix)
- function: cellular respiration (breaks down chemical energy in food to release it as usuable energy in the form of ATP)
living tissue composition
- about 70% is made of water
- about 26% is composed of macromolecules
- rest is ions
macromolecules
- larger molecules (polymers) made of smaller molecules (monomers) typically linked together through covalent bonds
- critical for regulation of life processes
- nucleic acids, lipids, carbohydrates, proteins
nucleic acids
- monomer: nucleotides
- function: information (stores, transmits, and expresses our genetic information), blueprint for life
- ex: DNA (A, T, C, G), RNA (A, U, C, G)
lipids
- monomer: fatty acids, glycerol
- function: long term energy, structure in cell membrane for protection and insulation
- ex: fats, oils, steroids, phospholipids
carbohydrates
- monomer: monosaccharides
- function: short term energy, used structurally to transport stored energy, recognition in signaling pathways
- ex: glucose, fructose, glycogen
proteins
- monomer: amino acids
- function: everything else (enzymes, signaling, receptors, structural, regulatory, contractile, protection against disease, transport, storage)
- ex: enzymes, hormones, motor proteins, transport proteins
enzymes
proteins that are biological catalysts
catalysts
speeds up biochemical reactions
levels of organization
SMALLEST
1. chromosome
2. macromolecule
3. organelle
4. cell
5. tissue
6. organ
7. organ system
8. organism
LARGEST
cell division
1. interphase
2. mitosis
3. cytokinesis
interphase
where the cell spends most of its "life"
mitosis
where the cell begins to divide
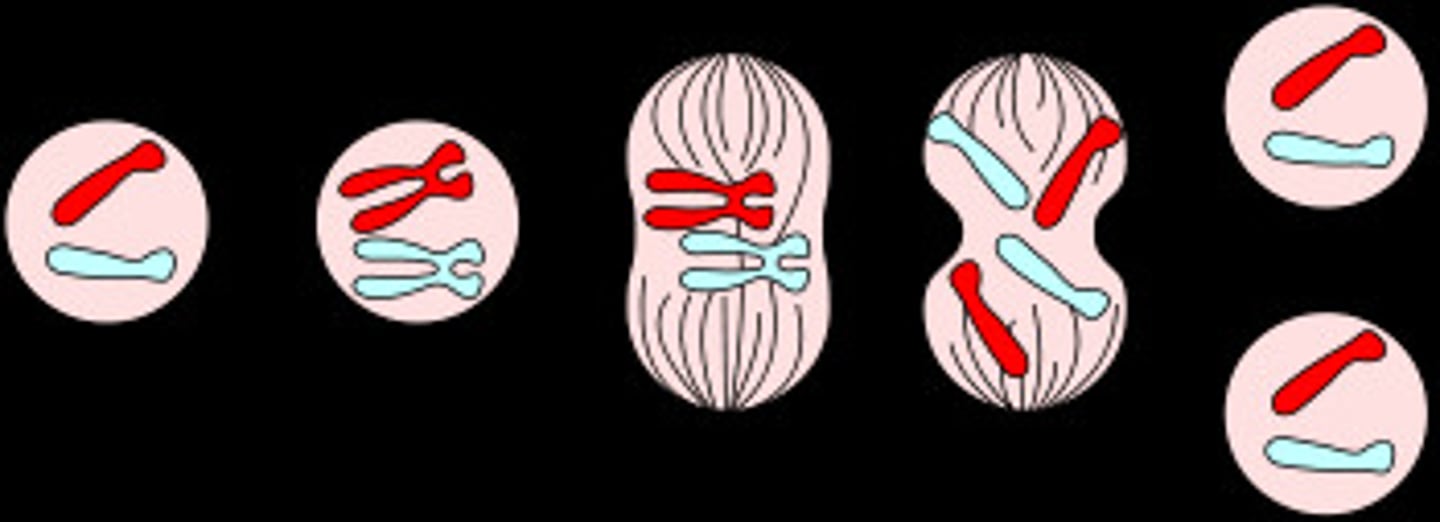
cytokinesis
where the cytoplasm splits forming 2 identical daughter cells
differentiation
- process of stem cells, or undifferentiated cells, undergoing specialization to become specific types of cells with different functions
- gene expression determines what a cell becomes
- form (structure) dictates function
homeostasis
- stability of the internal environment and the mechanisms that maintain stability
- maintained through regulation at the organ system level all the way down to the cellular level
- feedback mechanisms evolved to help maintain
positive feedback mechanisms
- output/product of a system intensifies the response
- ex: human child birth, fruit ripening
negative feedback mechanisms
- output/product of a system causes a counter response to return to a set point (normal)
- ex: human body temperature, water concentration, blood sugar regulation
feedback loops
- receptor: sensory organ that receives the stimulus (ex: skin)
- stimulus: action that evokes a response (ex: hot or cold)
- effector: organ that does the response (ex: sweat glands or muscles capillaries)
- response: the effect caused by the stimulus (ex: sweat dilate or shiver constrict)
passive transport
- requiring no extra energy
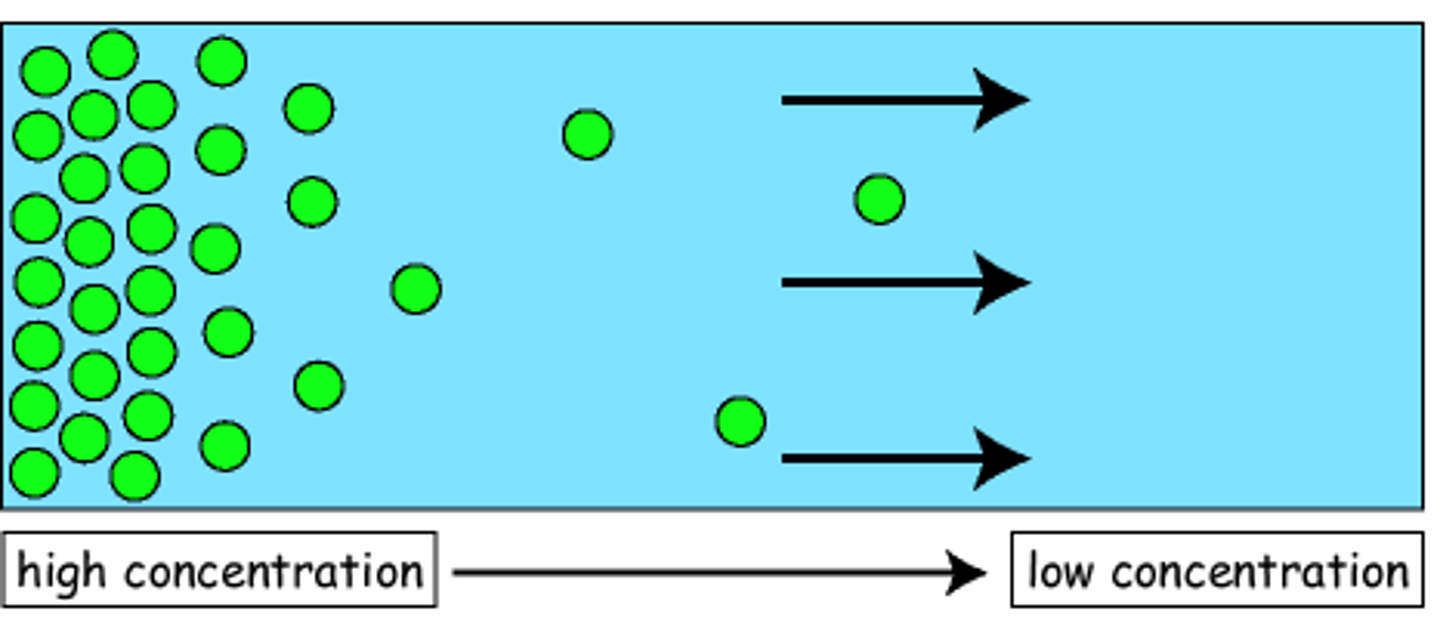
- high to low concentration
- simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis
simple diffusion
- spreading out of molecules across the membrane until equilibrium is reached
- ex: O₂, CO₂, small nonpolar lipid-soluble molecules
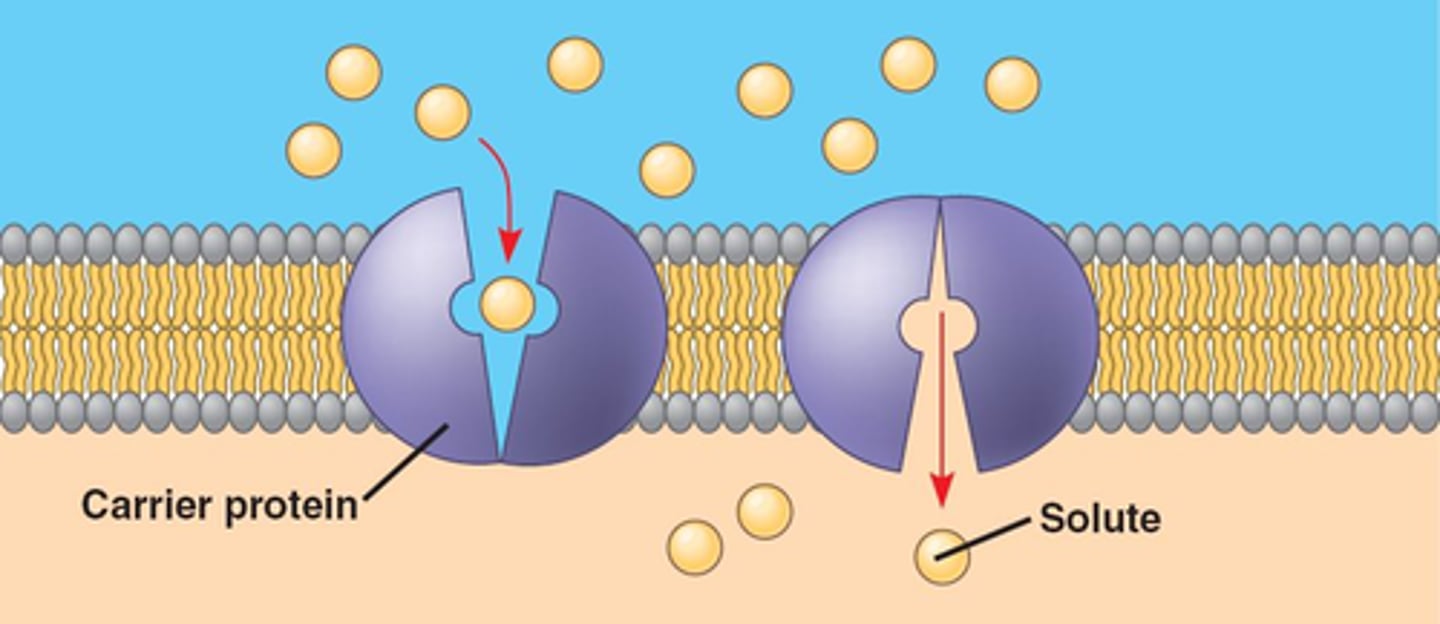
facilitated diffusion
- transport protein acts to help the diffusion of molecules that normally couldn't pass through the cell membrane (large and polar molecules)
- transport protein acts a channel and carrier
osmosis
- diffusion of water
- high water concentration (low solute) to low water concentration until equilibrium
- hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic solutions
hypertonic solution
- water is lower than the cell's cytoplasm
- high solute
- water moves out of cell (cell shrivels)
hypotonic solution
- water is higher than the cell's cytoplasm
- low solute
- water moves into cell (cell swells)
isotonic solution
- identical water to cell's cytoplasm
- cell stays the same
active transport
- requiring extra energy to move molecules against the gradient
- low to high concentration
- molecular pumps, endocytosis, exocytosis
molecular pumps
- when a cell uses energy to pump molecules across the membrane against the gradient, through a protein channel
- ex: sodium-potassium pump
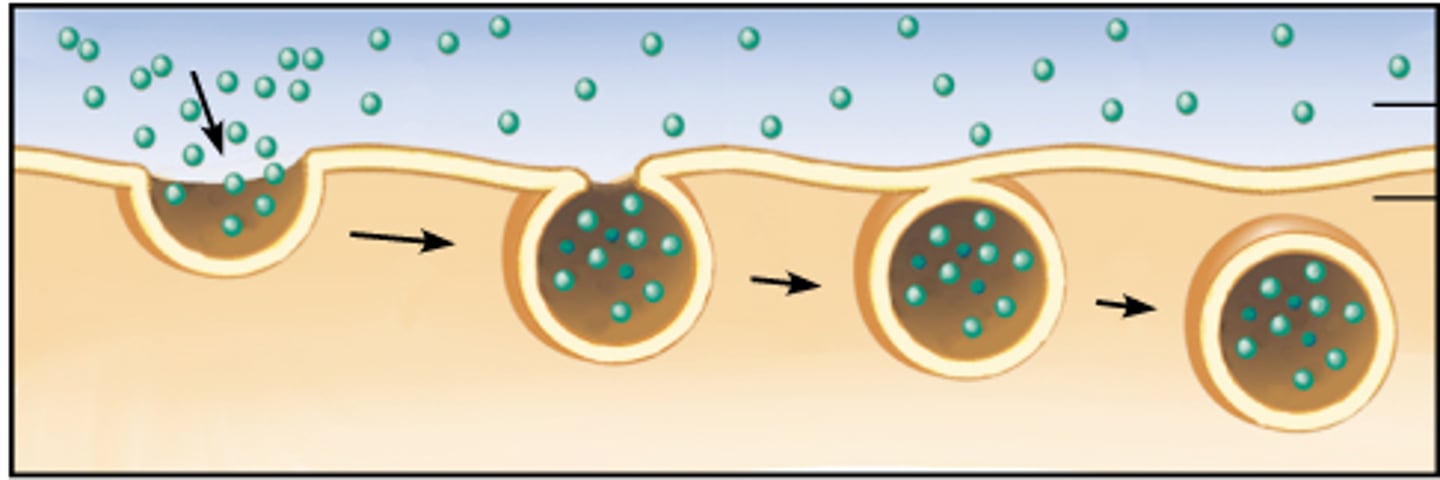
endocytosis
- uses vesicles to move large particles into the cell
- ex: white blood cells engulf bacteria to fight infection
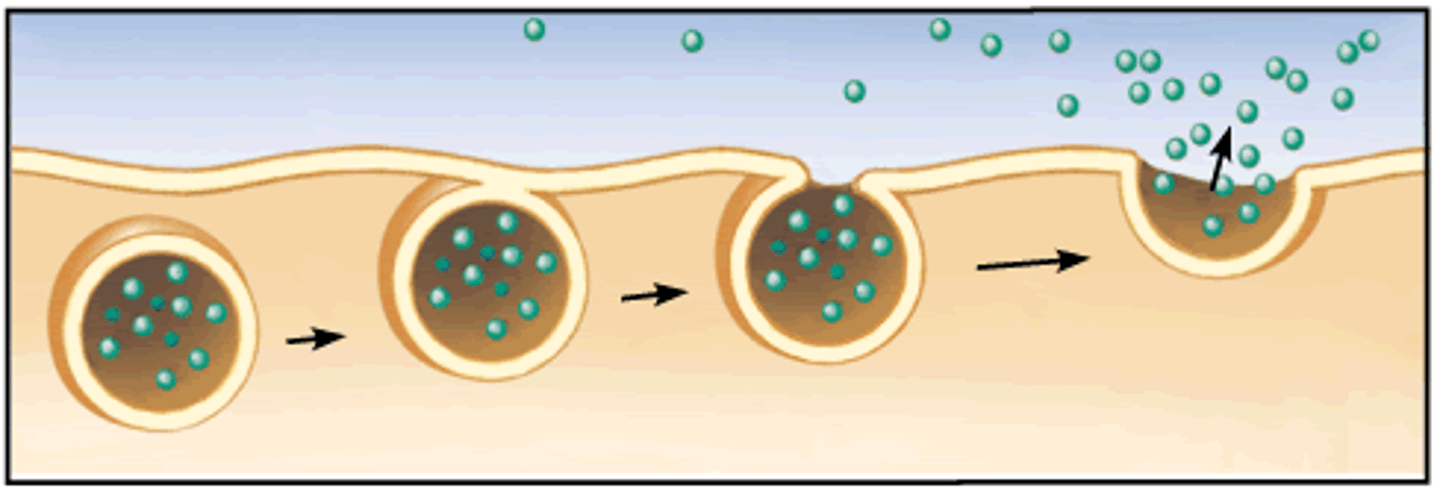
exocytosis
uses vesicles to export materials out of the cell
- ex: nerve cells secrete neurotransmitters
cell signaling
- allows cells to process information from their environment (stimulus) and communicate to other cells
- signals can be physical or chemical stimuli
ligands
molecules that bind to other molecules (receptor proteins) for signaling purposes
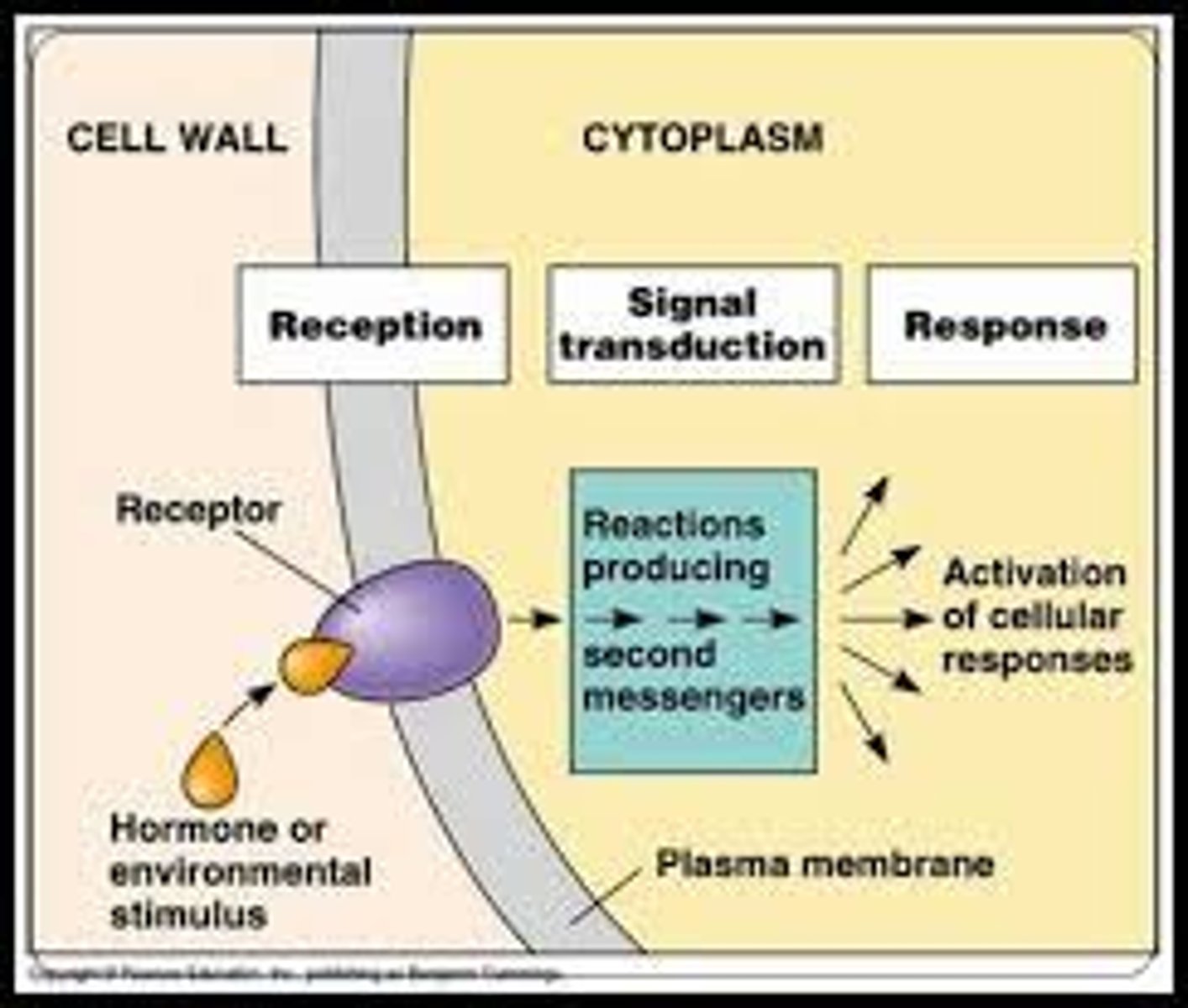
signal transduction pathway
- sequence of events initiated by a signal that leads to a cellular response
- signal -> message transduced -> desired response
chemical signals
- autocrine
- paracrine
- juxtacrine
- hormones
autocrine signals
- "self"
- affect the same cell that releases them
paracrine signals
diffuse to nearby cells
juxtacrine signals
require direct contact between the signaling cell and the receiving cell
hormones/endocrine signaling
signal travels to distant cells
receptors
- protein where the signal is received on the target cell
- intracellular and membrane
- highly specific and 3D (only certain ligands bind certain receptors)
intracellular receptors
located inside a cell
membrane receptors
located on surface of the cell
transduction
the passing along of the signal until the desired response is reached
responses
transduction pathway eventually triggers a response (opening of ion channels, alterations in gene expression, alteration of enzyme activities)
disease
disorder of structure or function that produces specific signs or symptoms or that affects a specific location
sign
- definitive and objective
- can be measured (usually a number)
symptom
- subjective
- more difficult to diagnosis
syndrome
specific group of signs and symptoms
diagnosis
- signs and symptoms lead to this
- an identification of a disease determined by studying a patient’s sign, symptoms, history, and results of a diagnostic test
prognosis
prediction of the outcome of the disease
etiology
cause of the disease
skeletal system
- support, protection for internal organs, and aid in movement
- bones, tendons, ligaments, and cartilage
muscular system
- movement and stabilization
- skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles
nervous system
- collect, process, and respond to sensory information (control voluntary and involuntary actions)
- brain, spinal cord, all connected nerves and sensory organs
endocrine system
- production and secretion of hormones for regulation of the body (growth, metabolism, and sexual development)
- hypothalamus and glands
cardiovascular system
- gas exchange and nutrient transport to and from cells throughout the body
- heart, blood, vessels, and blood
respiratory system
- gas exchange (taking in oxygen and getting rid of carbon dioxide)
- lungs, nose, mouth, trachea, and diaphragm
digestive system
- break down of food and absorption of nutrients
- mouth, stomach, and intestines
urinary system
- maintains water balance, gets ride of waste, regulates blood volume and pressure, filters blood
- kidneys and bladder
integumentary system
- acts as a barrier to protect the body from the outside world, as well as regulates temperature and controls water loss
- skin, hair, nails, and associated glands
immune and lymphatic systems
- defend, deflect, and destroy infectious agents that make their way into the body
- lymph nodes, blood vessels, thymus, bone marrow, and spleen
reproductive system
- allows animals to reproduce by producing egg and sperm, hormones, and nurturing developing offspring
- male: testes and penis
- female: vagina, uterus, and ovaries
anatomical position
- where a person is standing up with feet slightly apart and arms at their sides
- right and left are from his perspective
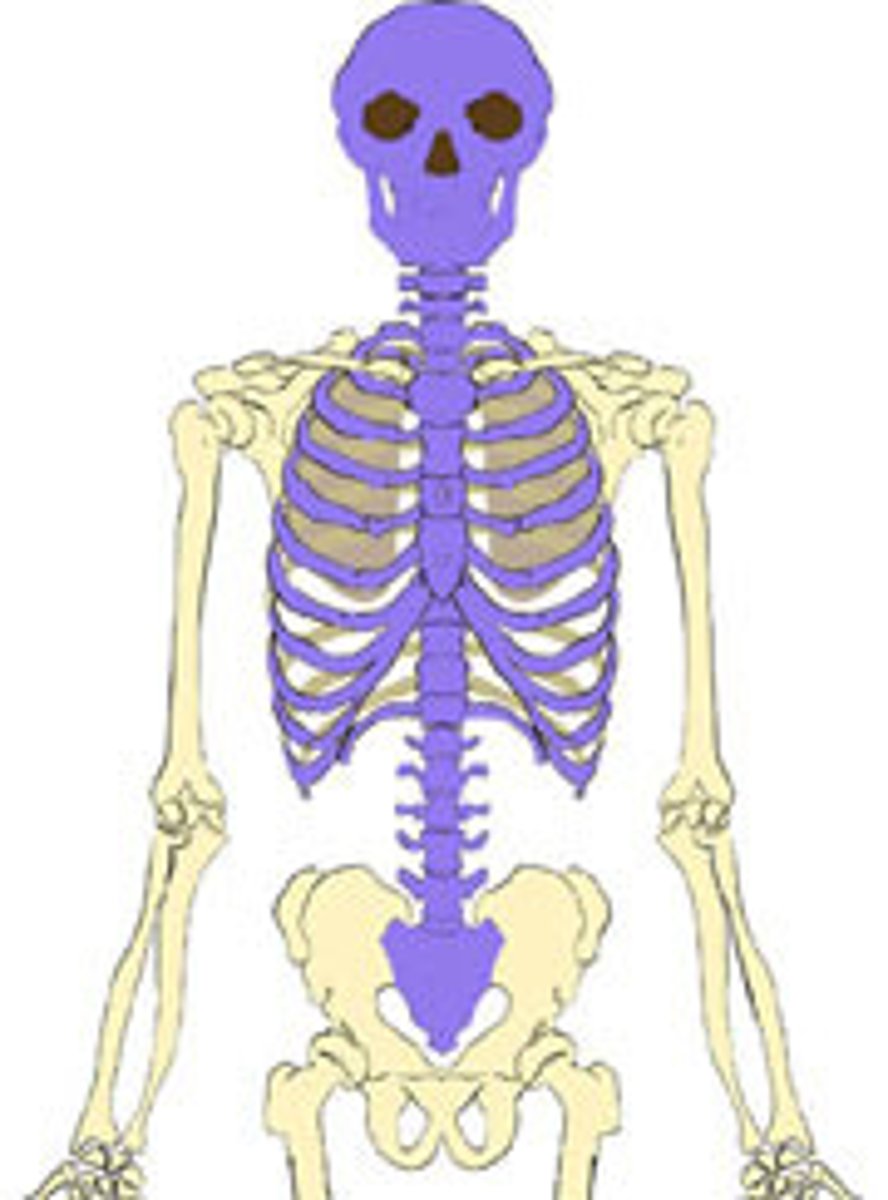
axial
head, neck, and trunk
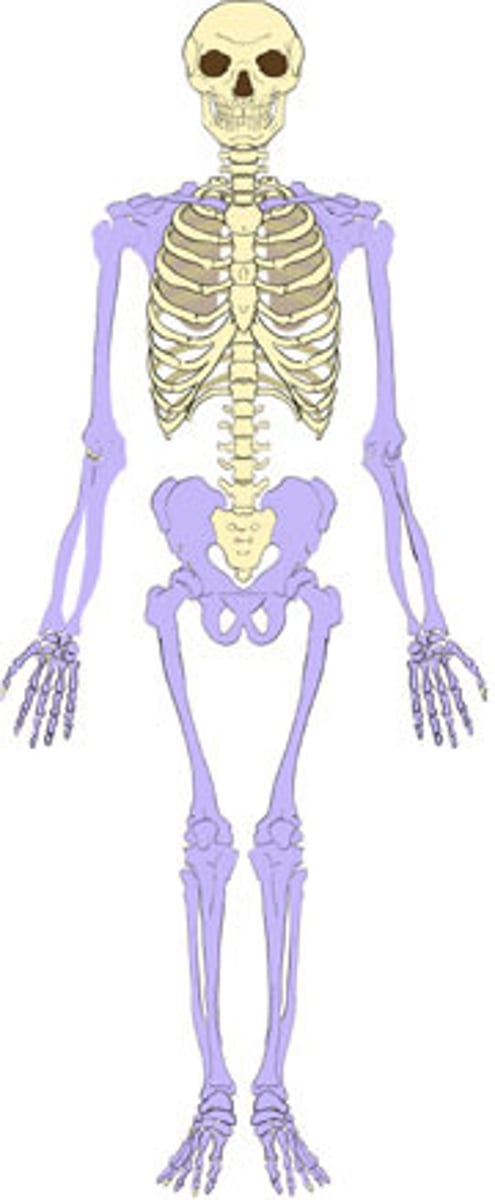
appendicular
- appendages (limbs)
- attached to the axis
superior (cranial)
- toward the upper part; above
- ex: chin is superior to the abdomen
inferior (caudal)
- toward the lower part; below
- ex: knees are inferior to the naval
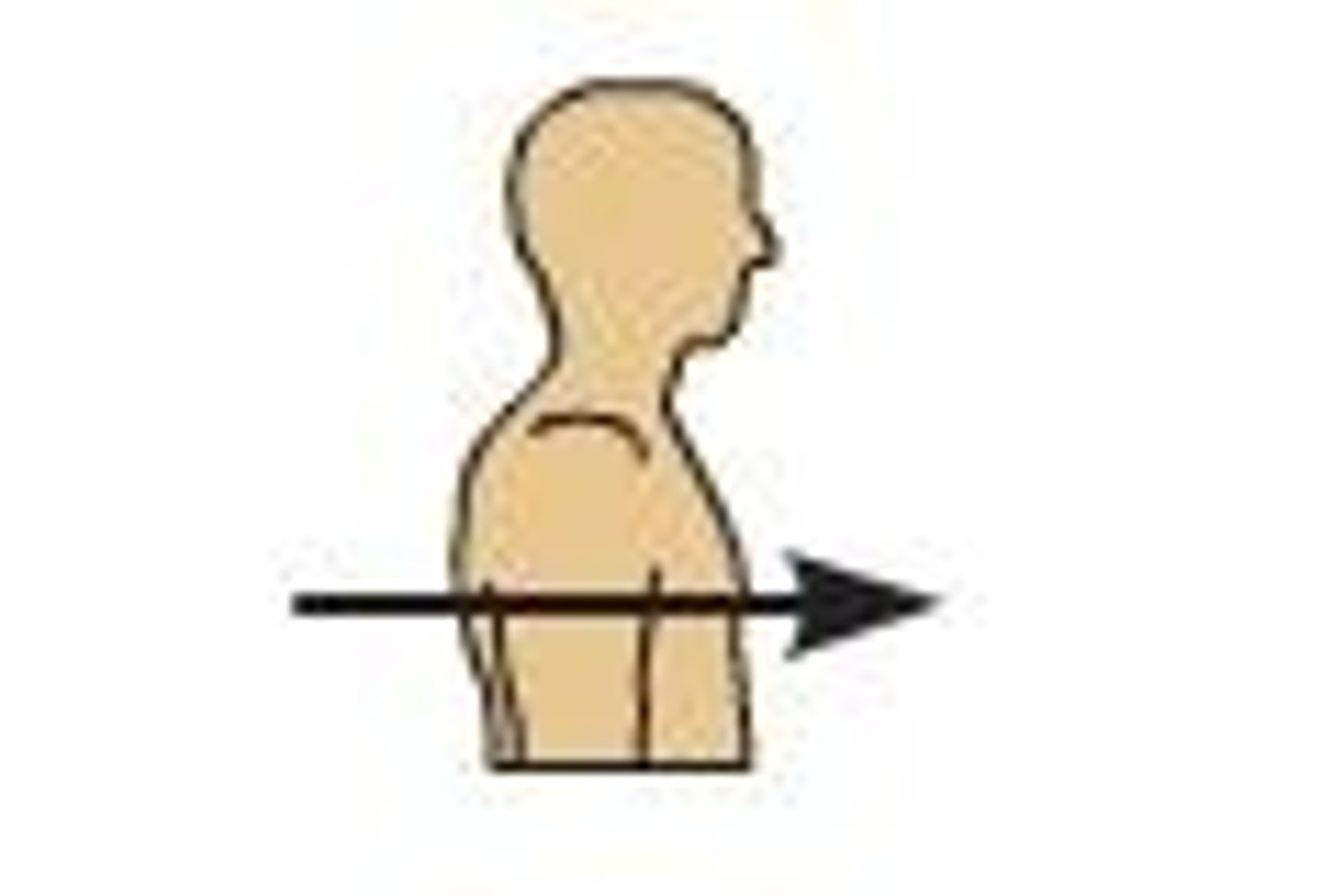
anterior (ventral)
toward or at the front of the body; in front of
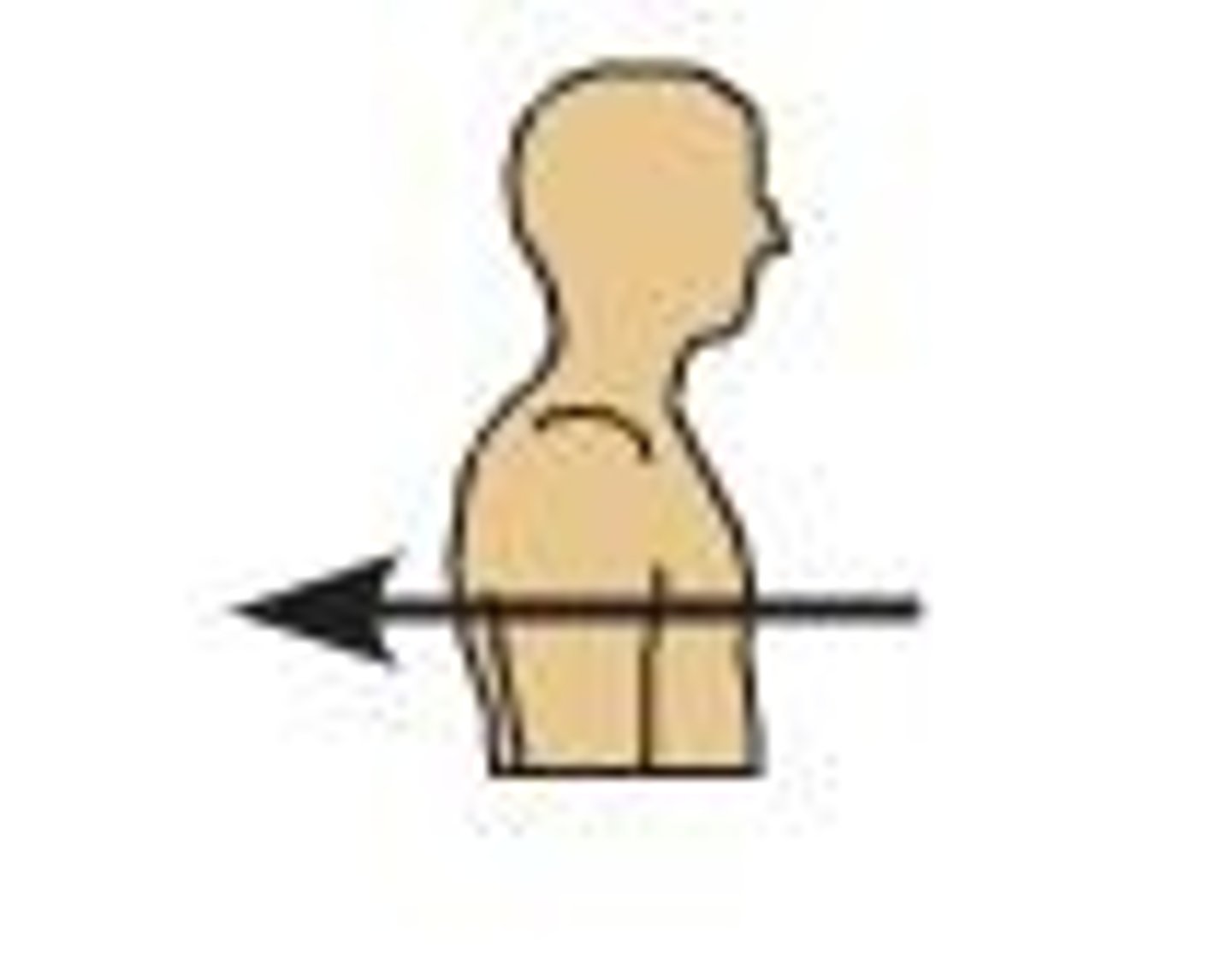
posterior (dorsal)
toward or at the back of the body; behind
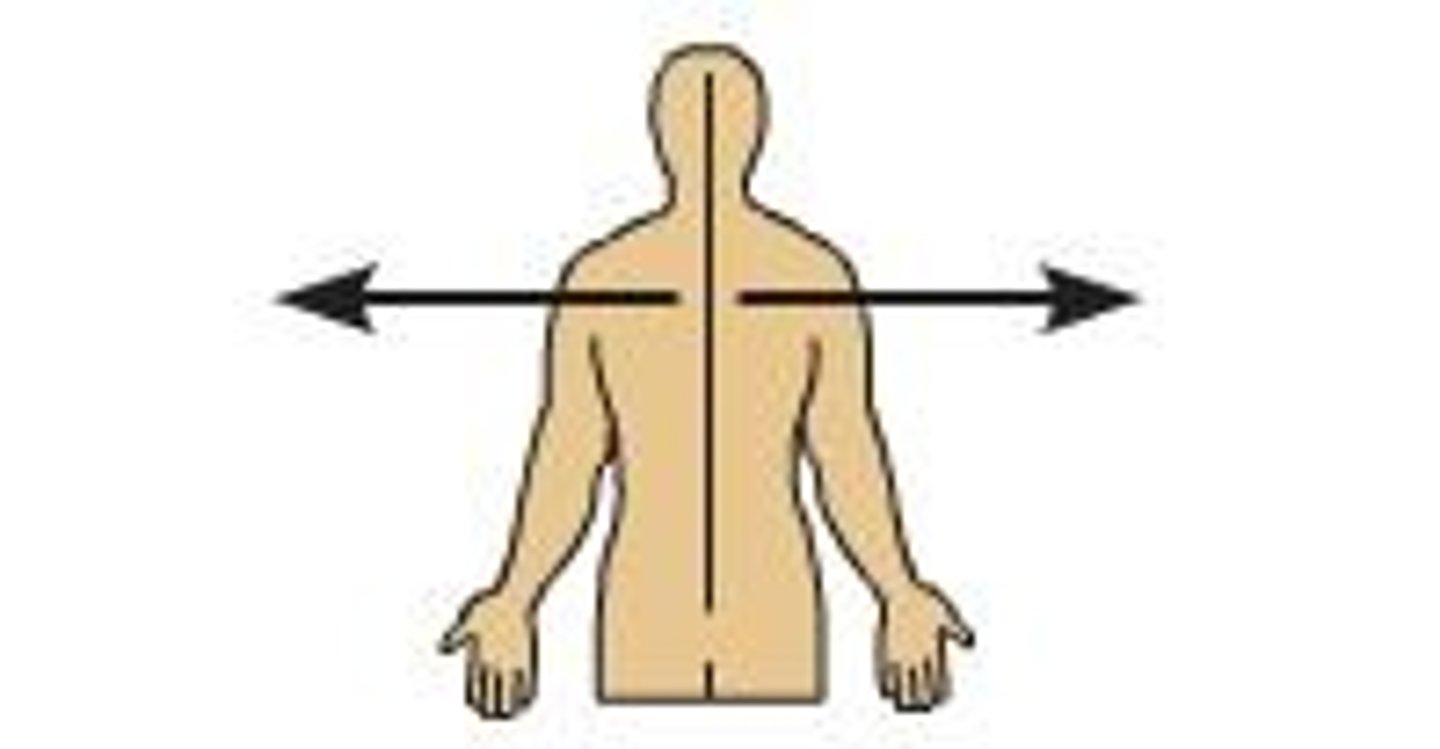
medial
toward or at the midline of the body; on the inner side
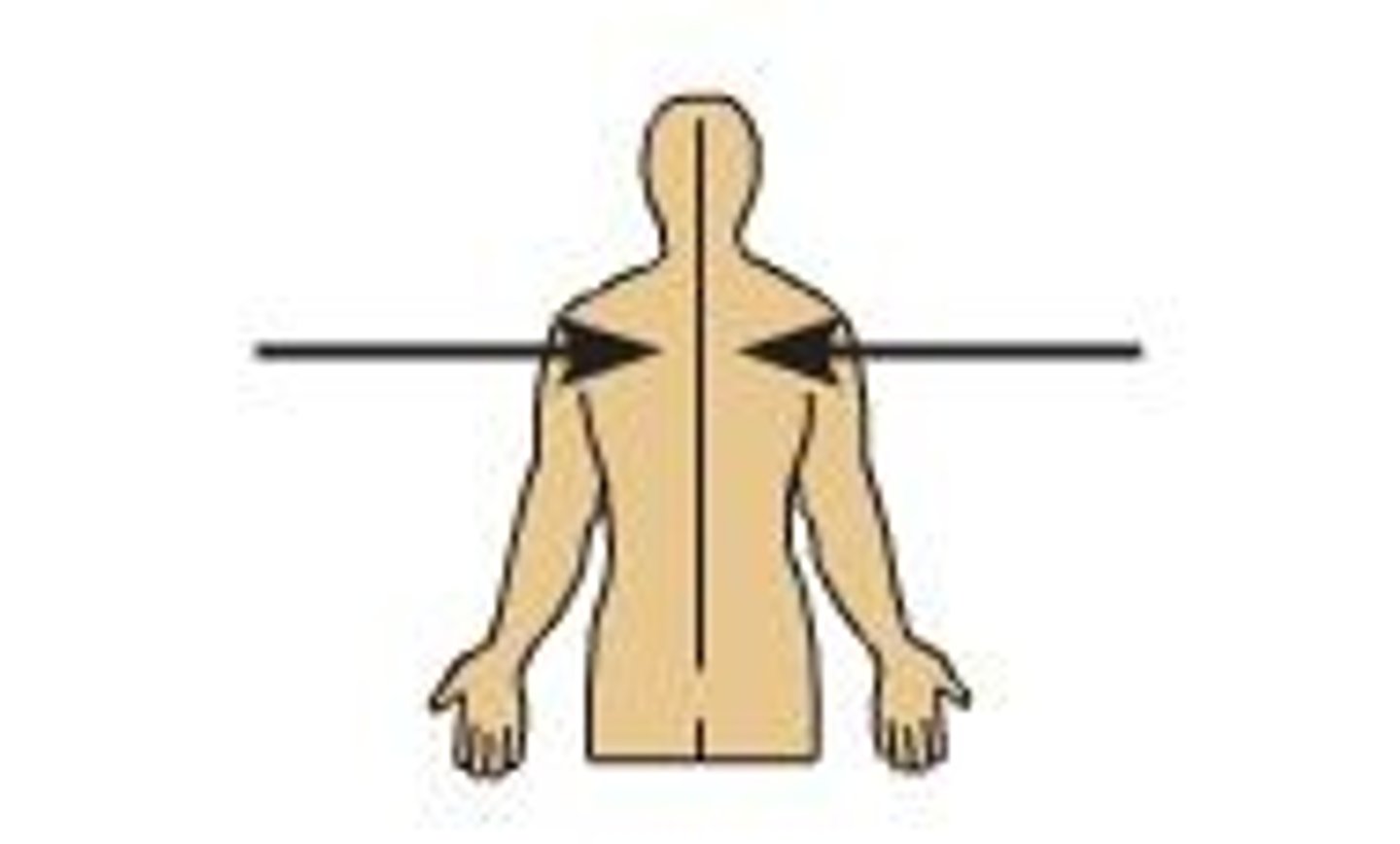
lateral
away from the midline of the body; on the outer side
intermediate
inbetween
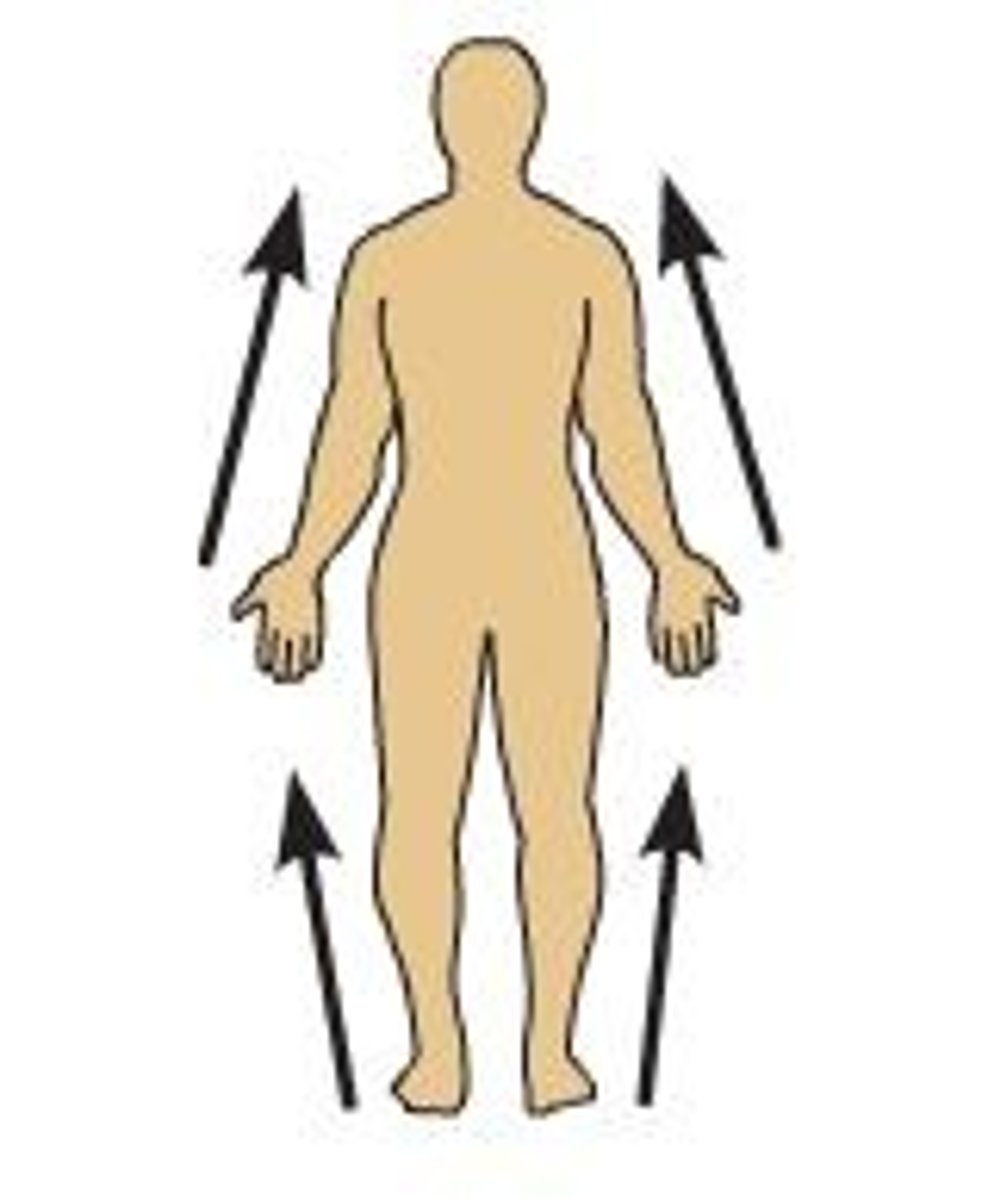
proximal
closer to the point where a limb attaches to the body trunk
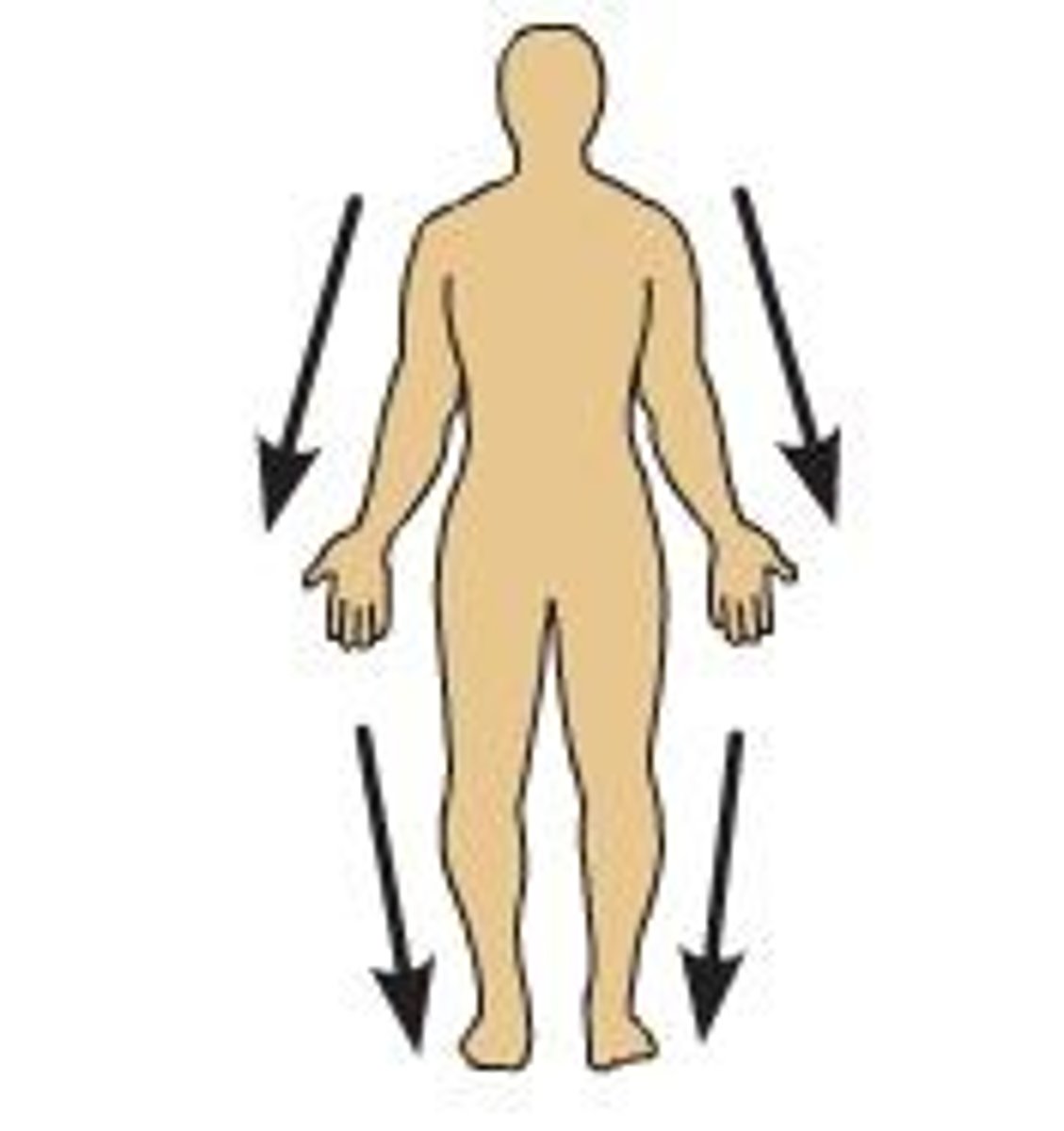
distal
farther from the point where the limb attaches to the body trunk
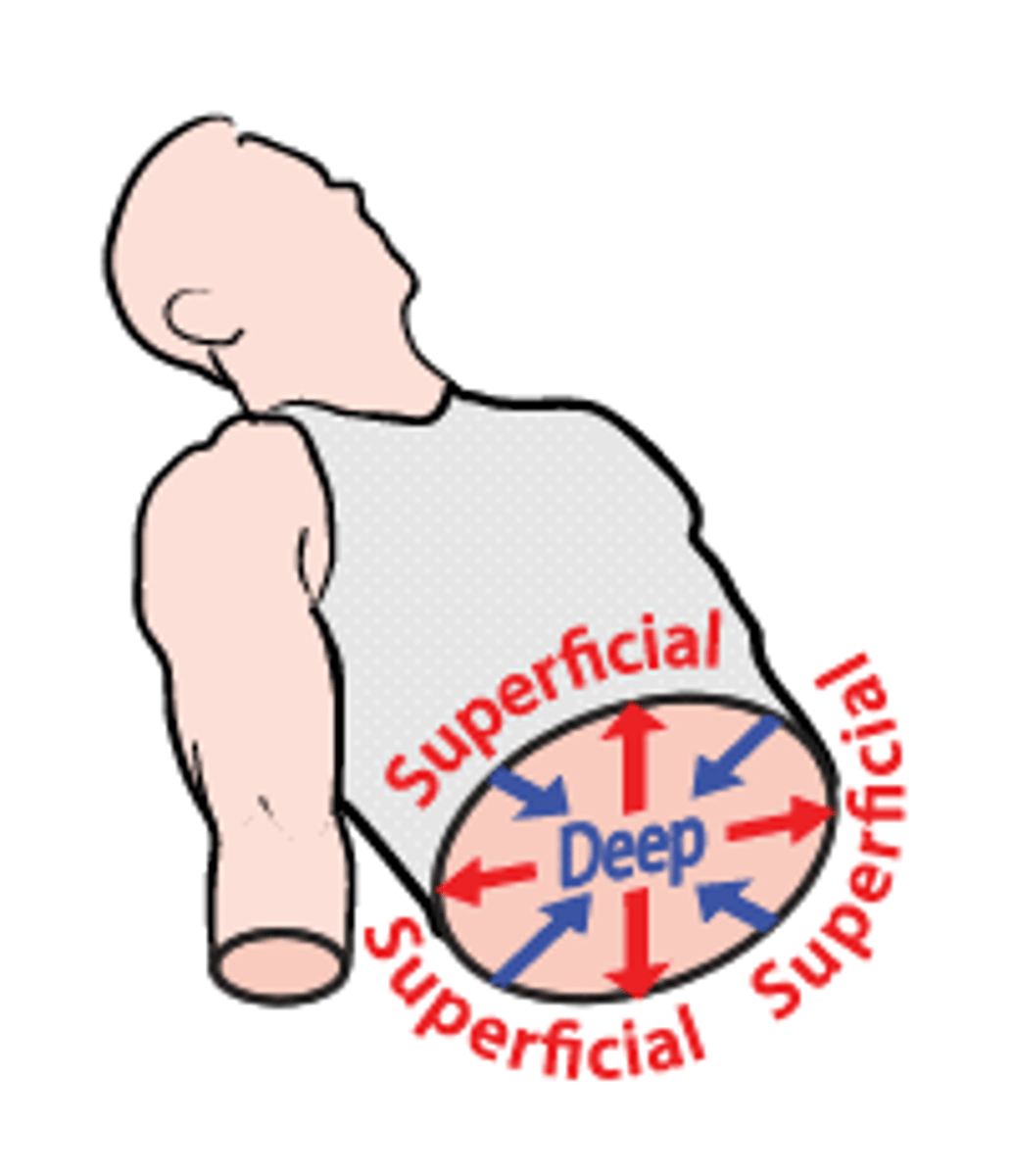
superficial (external)
toward or at the body surface
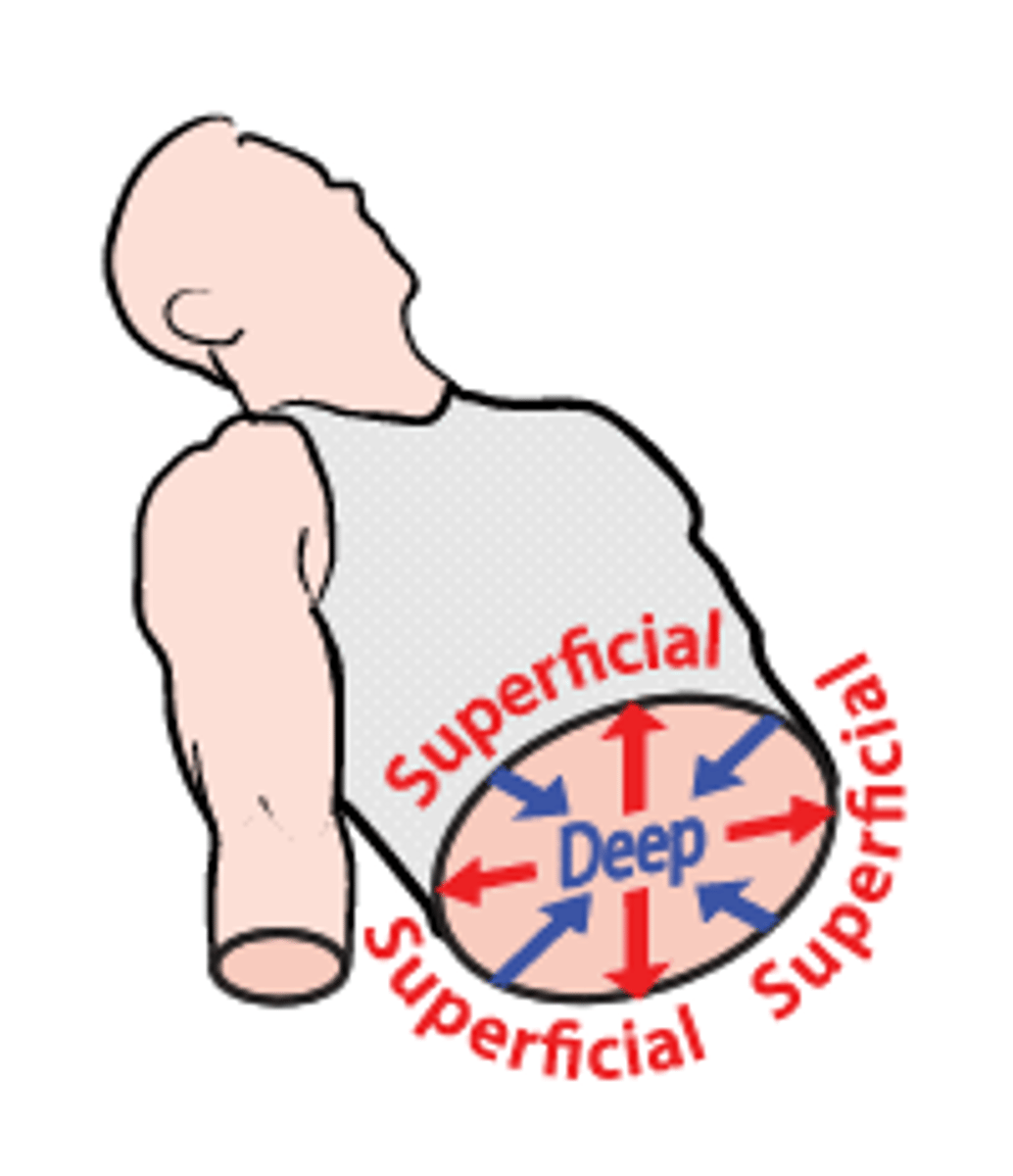
deep (internal)
away from the body surface
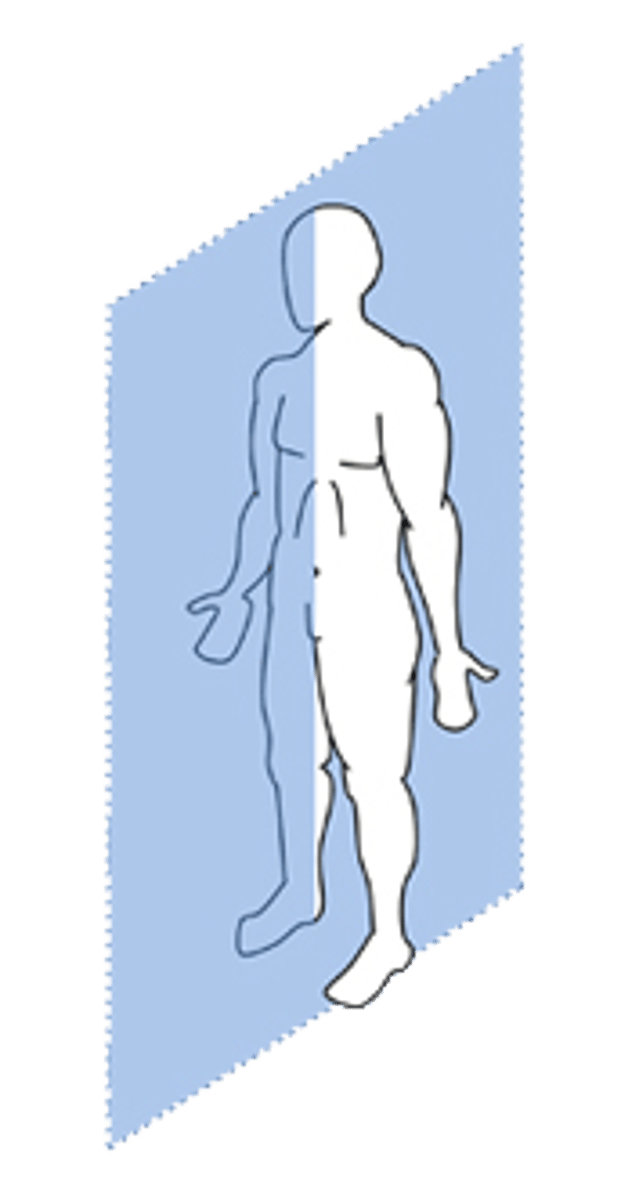
sagittal
- a vertical plane that divides the body into left and right sections
- midsagittal: equal left and right
- parasagittal: unequal left and right
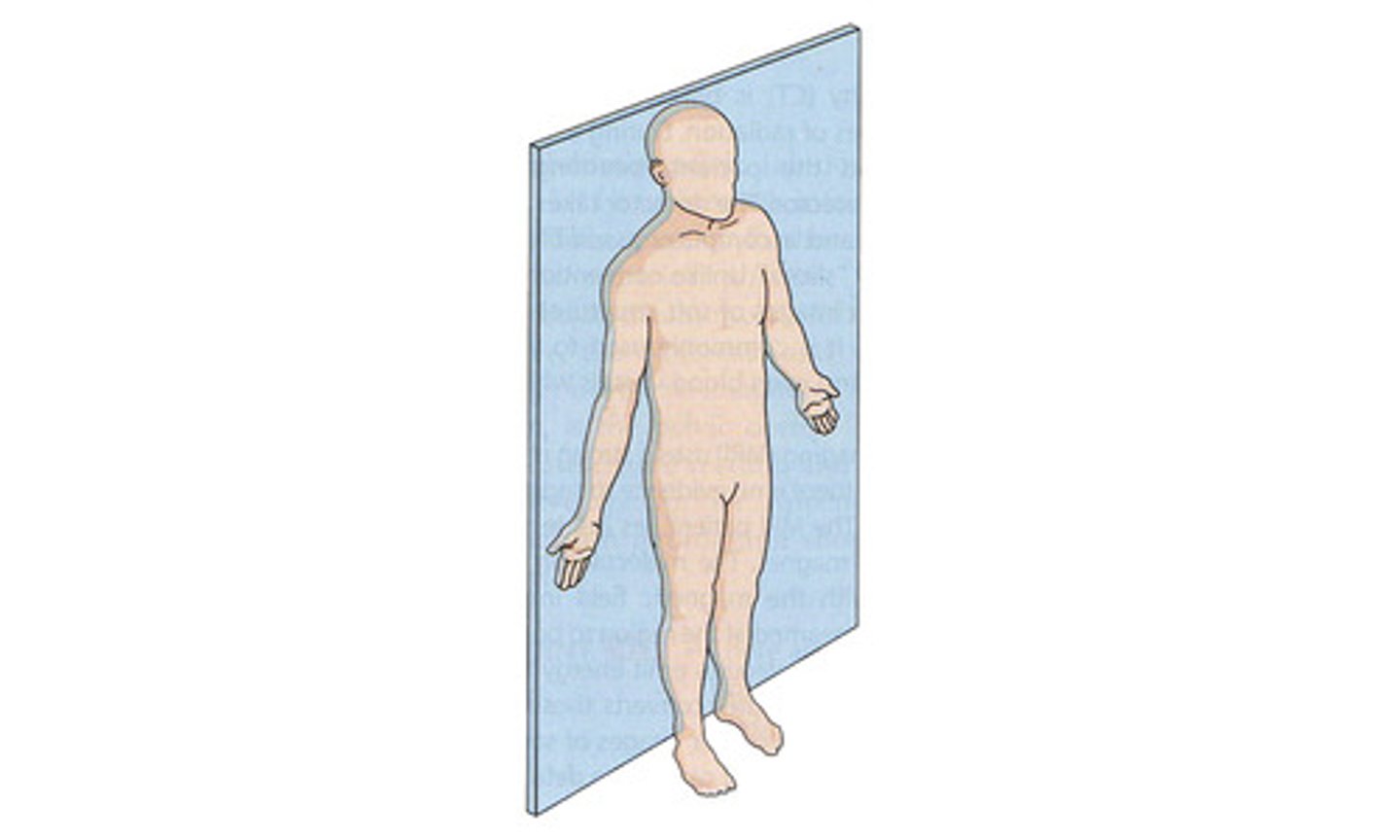
frontal (coronal)
a vertical plane that divides the body into anterior (front) and posterior (behind) sections
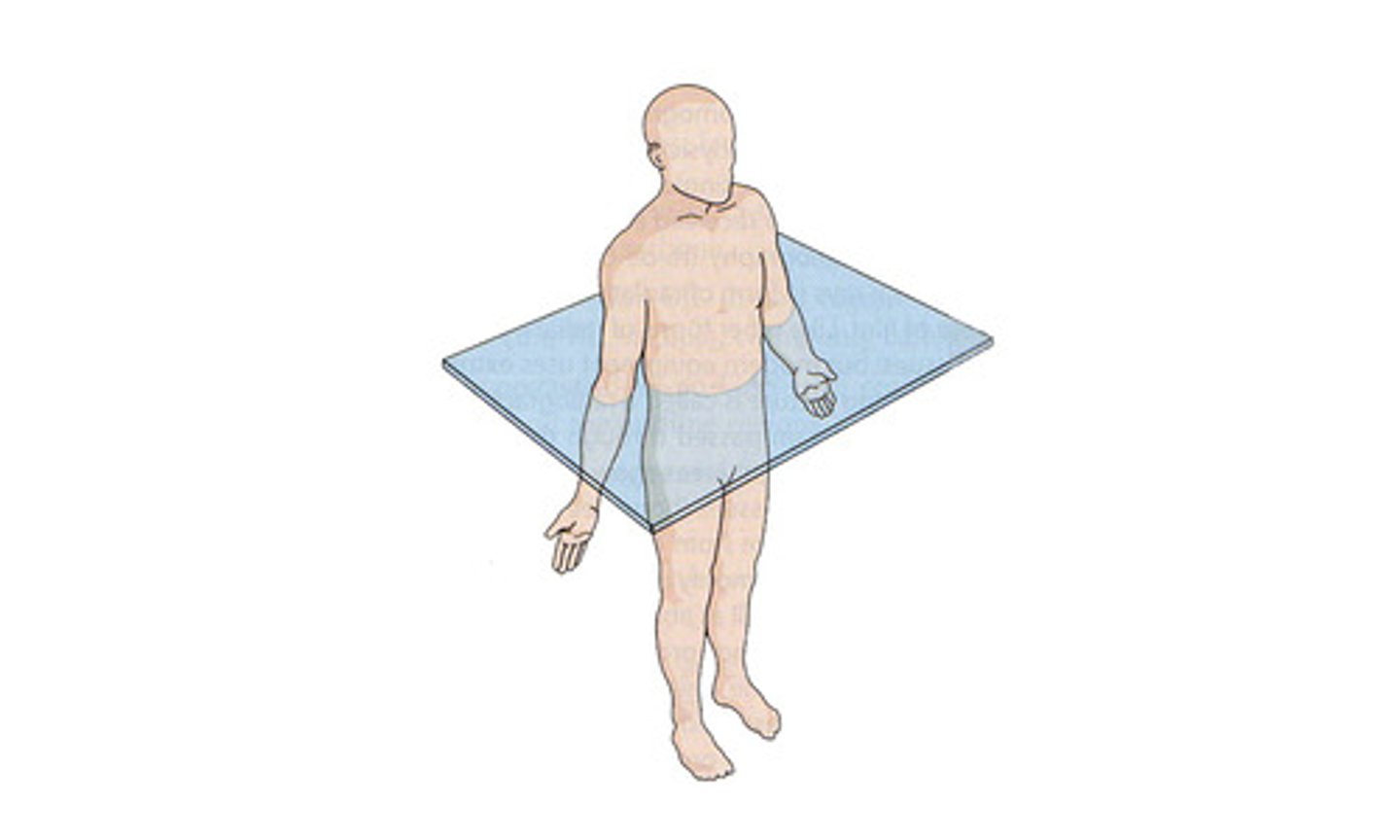
transverse (cross section)
a horizontal plane that divides the body into superior (above) and inferior (below) sections
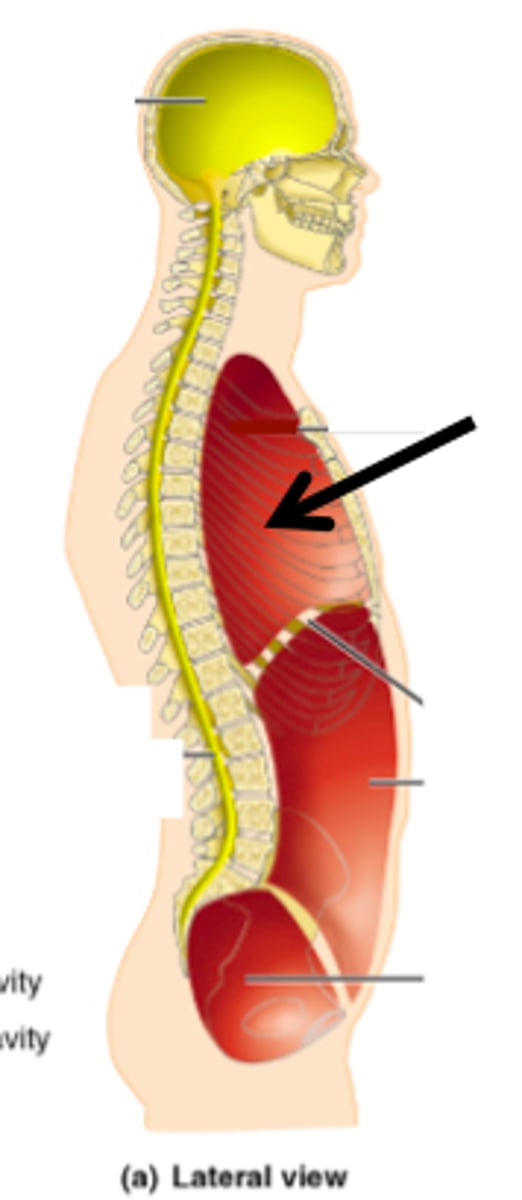
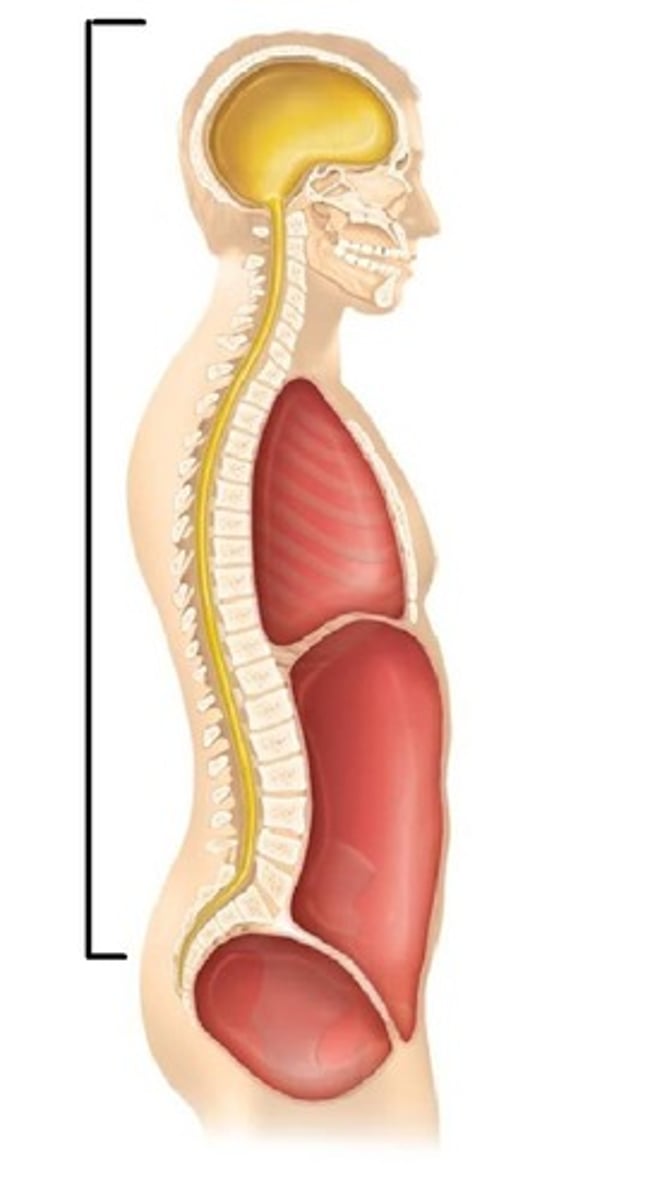
dorsal body cavity
- part of the axial portion of the body encased in bony structures for protection
- houses the fragile nervous systems organs
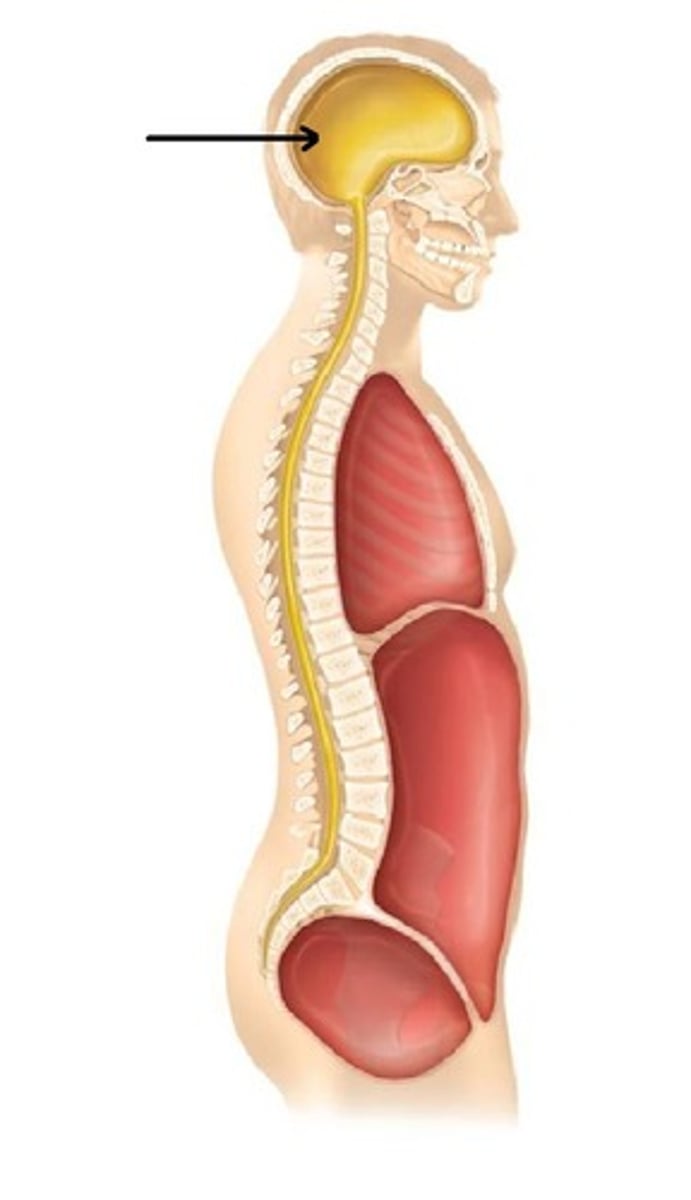
cranial cavity
holds the brain (encased by the skull)
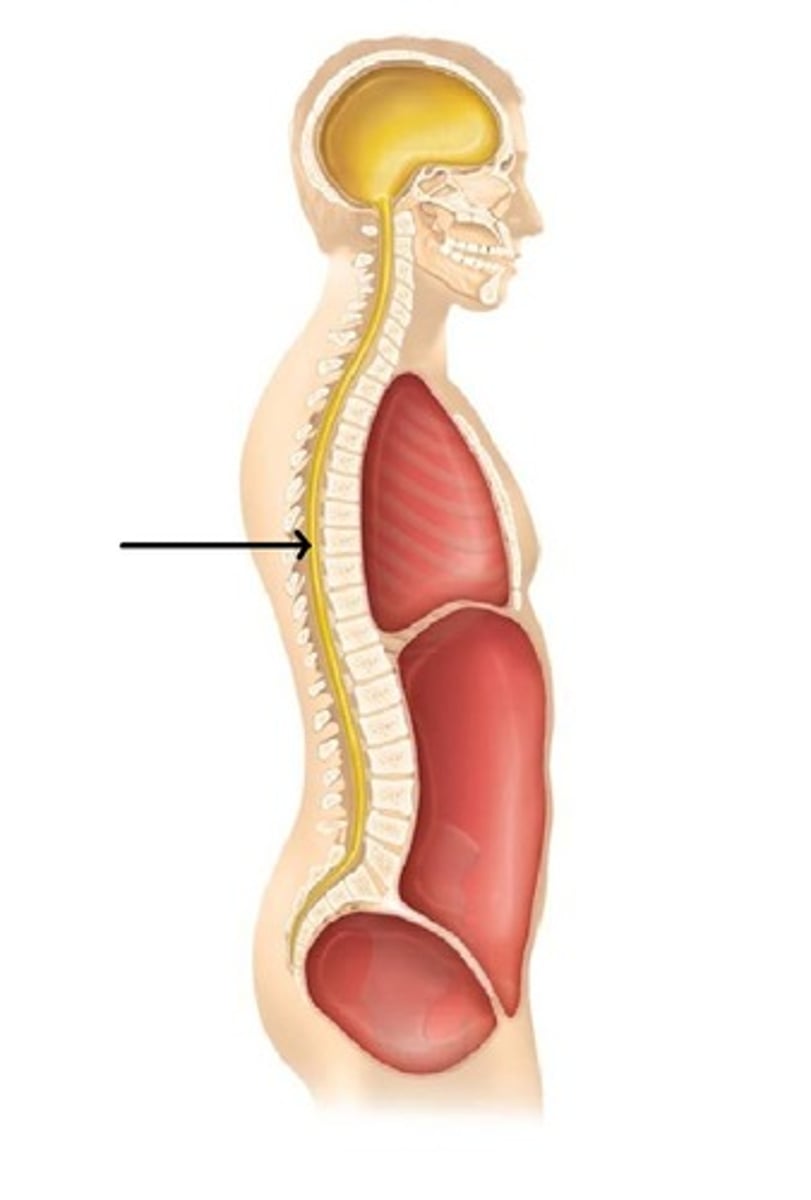
vertebral (spinal) cavity
holds the spinal cord within the body vertebrate
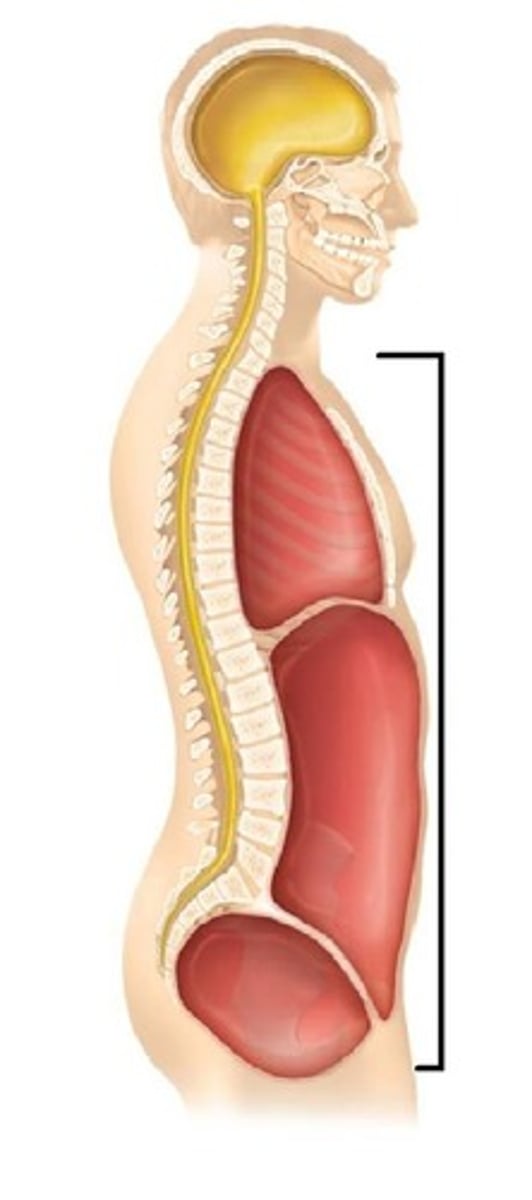
ventral body cavity
- part of the axial portion of the body, less protected but allows more mobility
- houses the visceral organs
thoracic cavity
- holds the heart and lungs (protected by ribs and chest muscles)
- pleural cavities: holds the lungs
- pericardial cavity: holds the heart, esophagus, and trachea