Dr. Dan review sheets for rabbits, guinea pigs, chinchilla, small rodents, sugar gliders, hedgehogs, degu, gerbil, ferret, primates,
1/224
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
225 Terms
open rooted teeth are termed
elodont
the root of the teeth is the ____? which contains
apex: contains germ cells (germinal tissue) for continual tooth growth
clinical signs of dental disease
hypersalivation, reduced food intake, selective food intake, reduced fecal output, or fecal pellets that are smaller than normal; patient may go to food and show initial interest but refrain from eating due to difficulty or pain
rabbits and rodents are obligate ____
nasal breathers
maloccluded, overgrown teeth require
repeated trimming
trimming of maloccluded teeth is only ___
temporary
acquired dental disease is
progressive and nonreversible
goals of treatment are
provide food quality of life, minimizing discomfort, maintaining body condition, and enabling the pet to eat on its own if possible, however lifelong syringe feeding is also acceptable for many small herbivore patients
the best prevention is to encourage dental wear through a ___
course low energy high fiber diet that is necessitates constant grazing activity and containing vitamin C (guinea pigs)
rabbits, guinea pigs, and chinchillas are
hindgut fermenters with an active cecum
hind gut fermentors rely on
cecal microorganisms to break down cellulose and convert it to volatile fatty acids for energy
VFAs have a positive effect on
appetite and gut motility
GI stasis, dysbiosis, bloat, diarrhea, and lack of feces are collectively called
gastrointestinal syndrome
GIS is a ____ not a _____
symptom not a disease
GIS can be triggered by any event leading to
inappetence or anorexia or dehydration ( pre sx, fasting, sudden change in diet, concurrent illness, extreme pain, starvation, sipper malfunction, bas tasting water, careless mistake)
long stemmed hay fiber and course roughage promote
gut motility in a way (scratch factor) that finely ground hay fiber does not
lack of fiber, excessive carbs, certain antibiotics can threaten favorable microorganisms and promote opportunistic pathogens and toxin productions is called
bacterial dysbiosis
stress has a ___ effect on the GI motility
negative; ex: include pain (dental dz, post op), concurrent dz, anxiety, and almost anything that you could call “inappropriate husbandry”
clinical signs of GIS
signs of GIS
decreased appetite, patients will often initially stop eating pellets, hay, but will continue to eat treats, followed later by complete anorexia. fecal pellets may have become scant, firm, or smaller than normal, will complete GI stasis there may be no fecal production at all
bruxism, hunched posture, failure to groom, and reluctance to move. affected animals may stretch out or roll while attempting to relieve pain
if no feces are produced, clients may incorrectly assume that their pet is
constipated
firm ingesta in the stomach of a patient with a hx of anorexia for 1-3 days prioe to presentation suggests
gut stasis
treatment of GIS includes
fluid therapy, syringe feeding, pain management, antinausea treatment (maropitant), and prokinetics (metoclopramide, cisapride)
domesticated rabbit (european rabbit)
oryctolagus cuuniculus
langomorphs are? how many incisors?
(rabbits, hares, pikas) 6 incisors (2nd set on top called peg teeth or auxiliary incisors)
rabbits have fragile skeleton, if mishandled a rabbit may kick and cause a
spinal fracture at the 7th lumbar vertebra
rabbits ovulation is
induced
rabbit kits are born
blind and hairless (altricial)
normal rabbits can carry ________ and may trasmit it to other pets like
Boredetella bronchispectica and guinea pigs
rabbits GI transit time is only
4-5 hrs
rabbits produce ______: they periodically excrete and consume cecal contents called “_____” which is a specific kind of coprophagy
cecotrophy, pseduorumination,
the basis of an adult rabbit diet should be
grass-hay and water, should always be available, limited pellets and mixed greens should make up the rest
unspayed rabbits are prone to
uterine adenocarcinomas
rabbits cant ____ or ___ and are thus prone to gastric tympany
vomit or eructate
with dental dz, sharp points and edges tend to develop on the _____ aspect of the upper arcades and on the ____ aspect of the lower arcades
buccal (maxillary); lingual (mandibular)
“Snuffles” is a common term for ____. often attributed to ______ but other ___ may be involved
URI; pasteurella but other bacteria may be involved
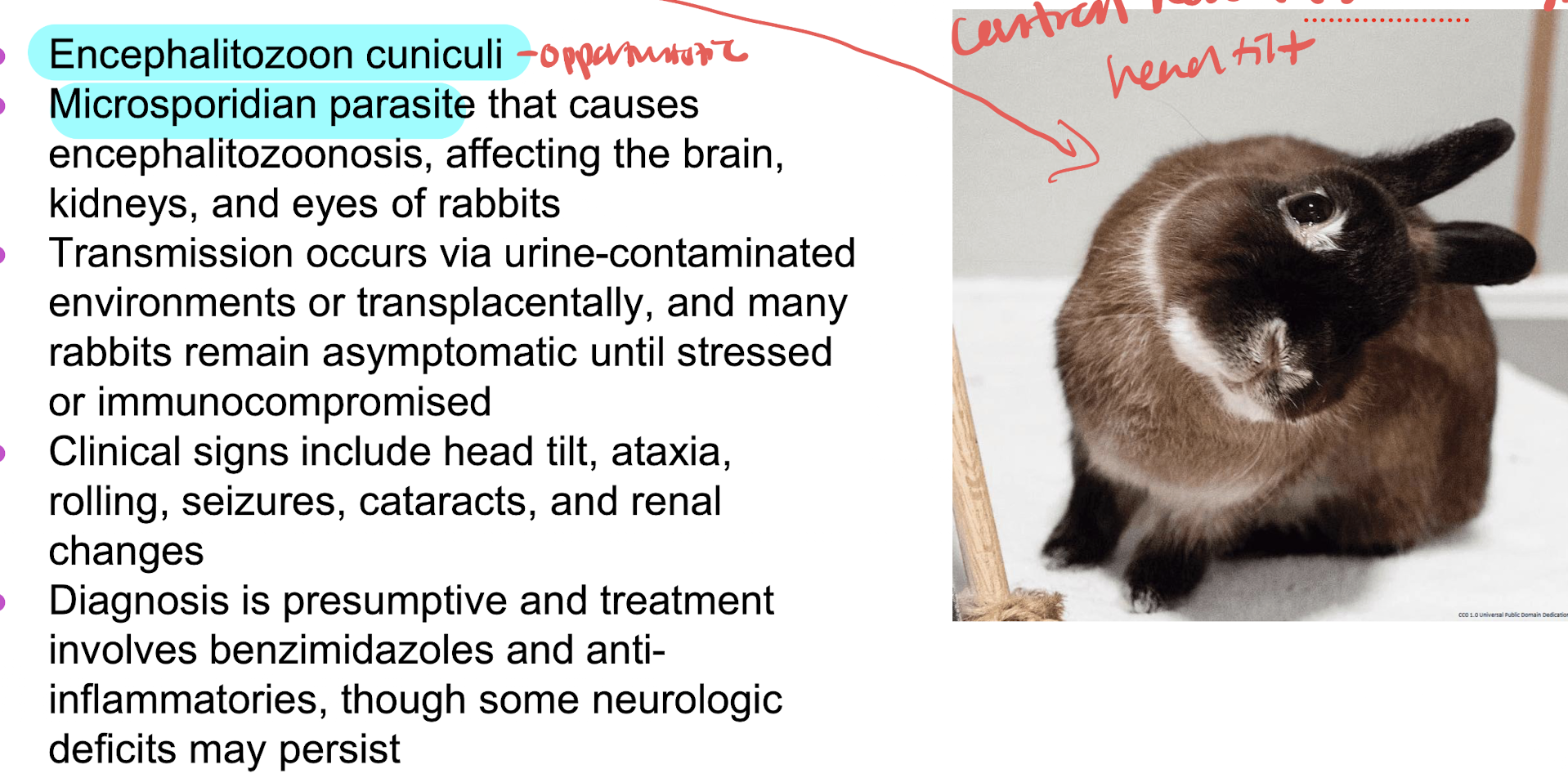
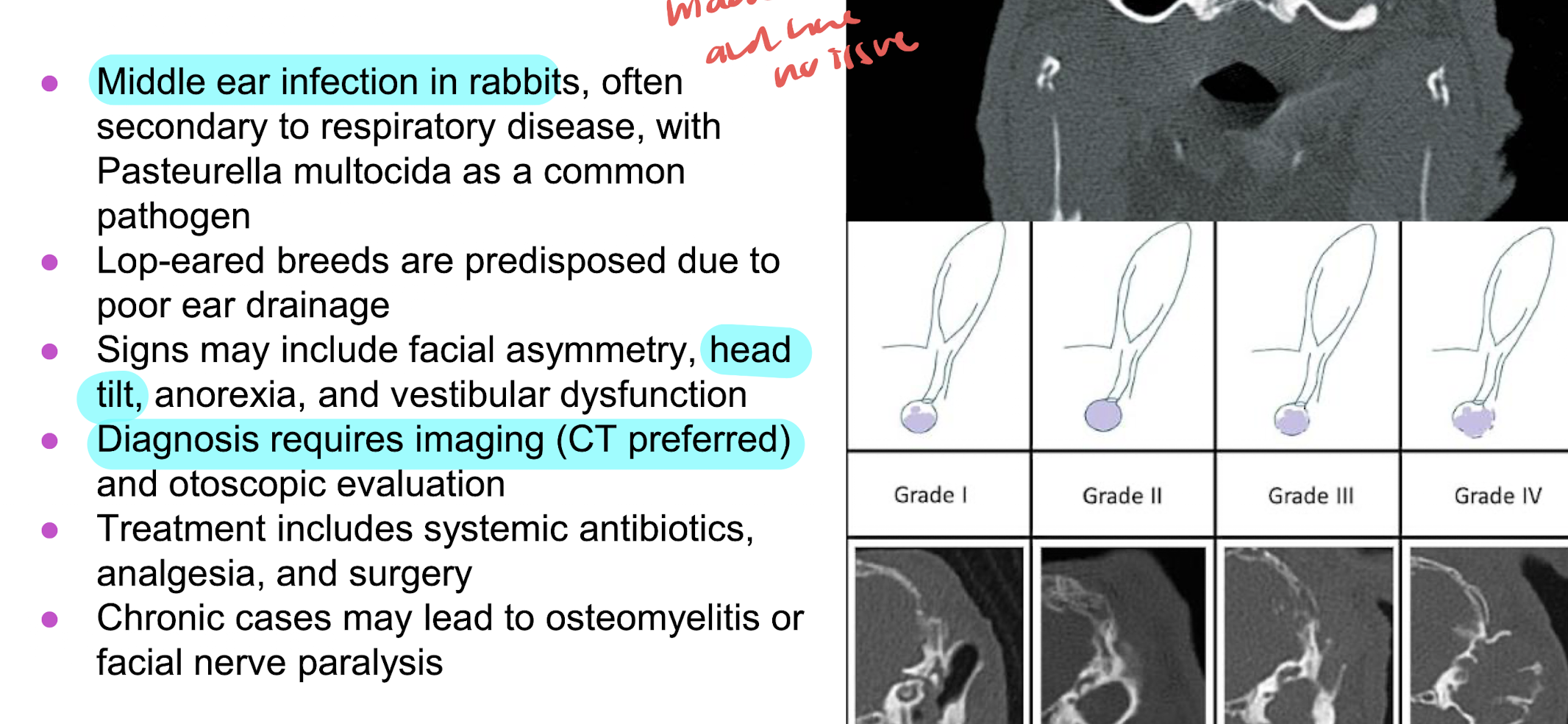
heat tilt (torticollis, wry neck) suggest either
otitis due to pasturella multocida or CNS infection by Encephalitozoon cuniculi (microsporidian parasite)
“sore hock” is ___________, caused by
ulcerative pododermatitis; caused by pressure, mostiture, abrasion, and unsanitary conditions
stap aureus infection is typical with this
pododermatitis is prevented by
providing soft dry clean bedding
Rabbit hemorrhagic Disease Virus is
highly transmissible and fatal calicivirus that has recently been reported in the US; vaccine is available
cuterebriasis
a parasitic infestation caused by cuterebra fly larvae, typically found in rodents and rabbits, leading to swelling, tissue damage, and a draining wound

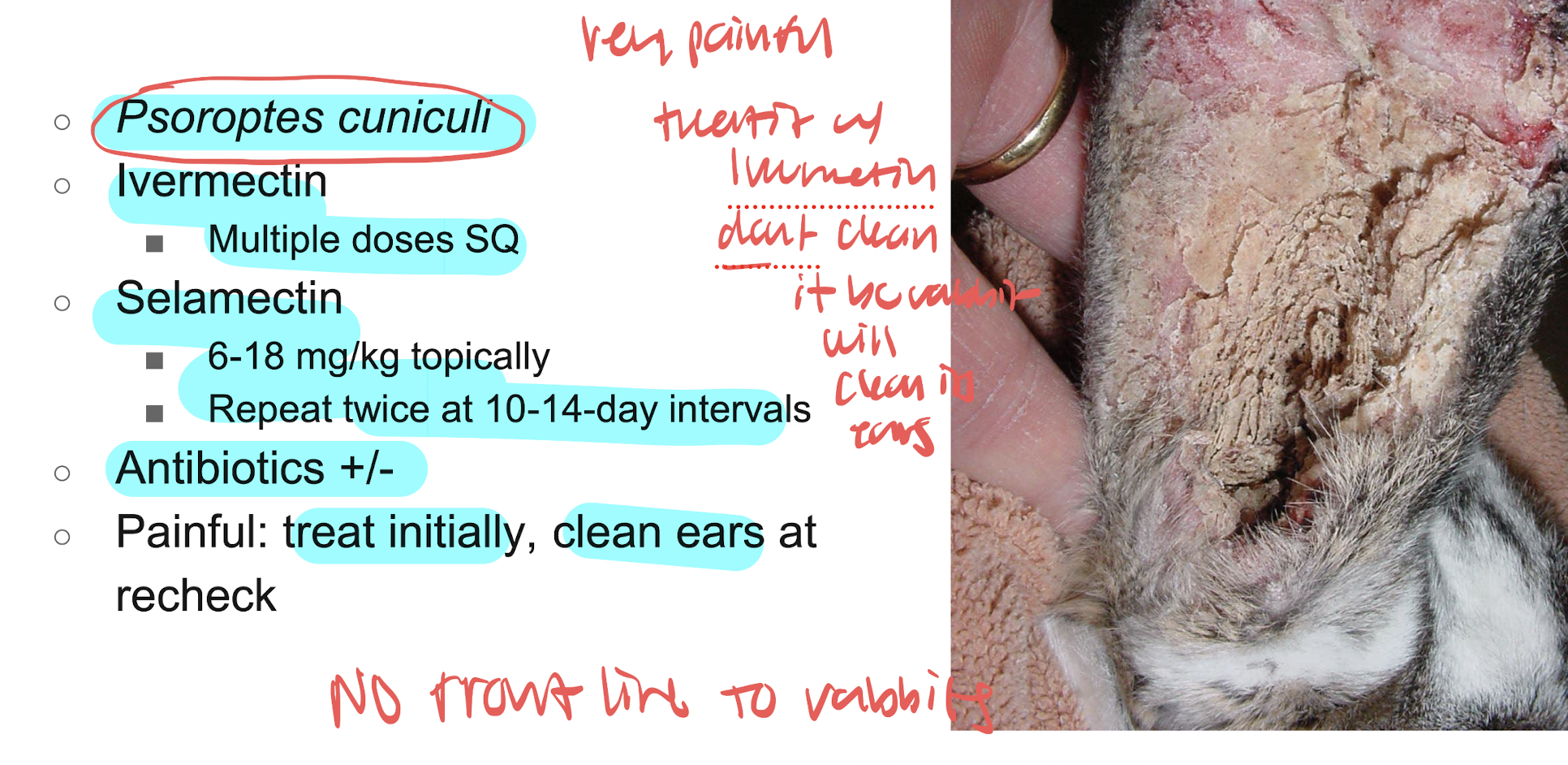
otacariasis
an ear condition caused by psorptes cuniculi mites, commonly seen in rabbits resulting in itching inflammation and crusting
pasteurellosis
a bacterial infection caused by pasteurella multocida often affecting the respiratory tract of rabbits and potentially leading to abscesses or systemic illness

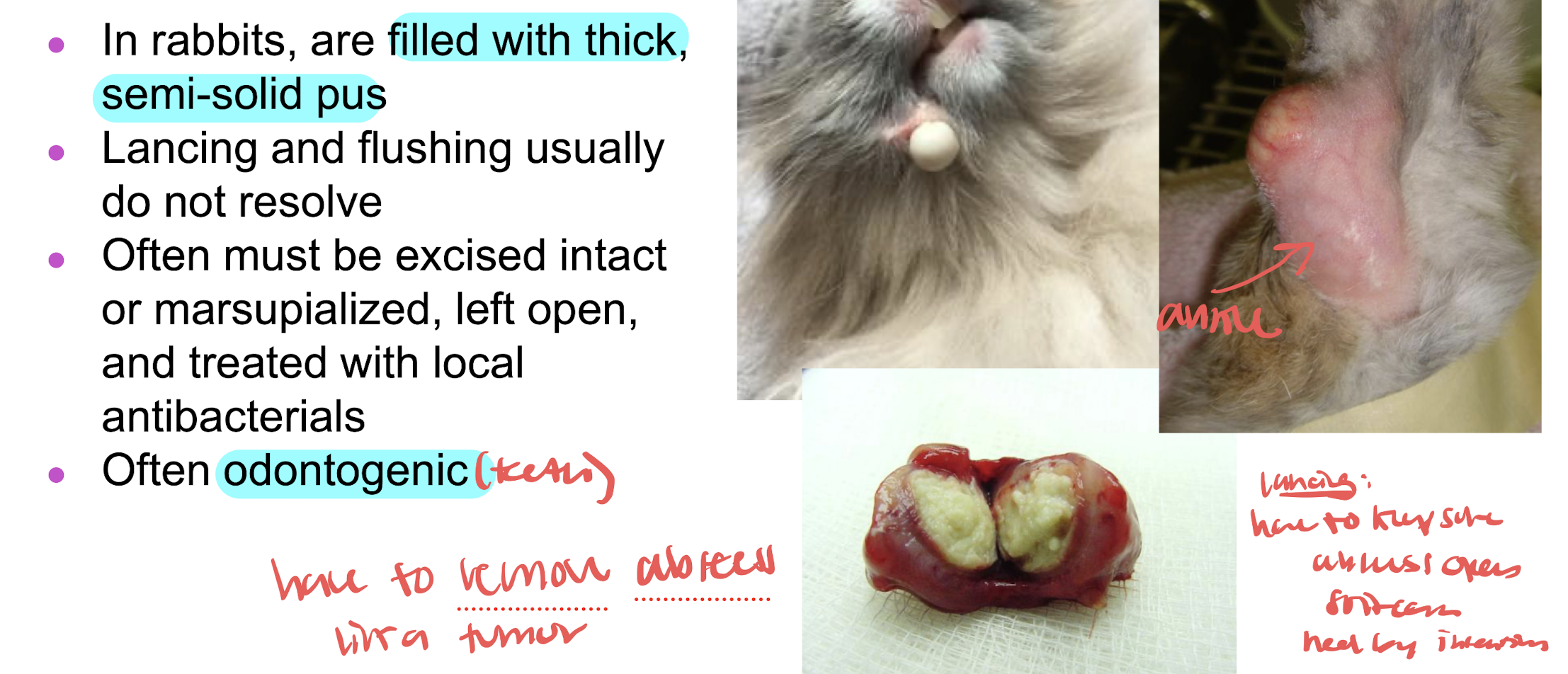
rabbit abscesses
localized collections of pus caused by infection, frequently seen in rabbits due to dental dz trauma or bacterial spread
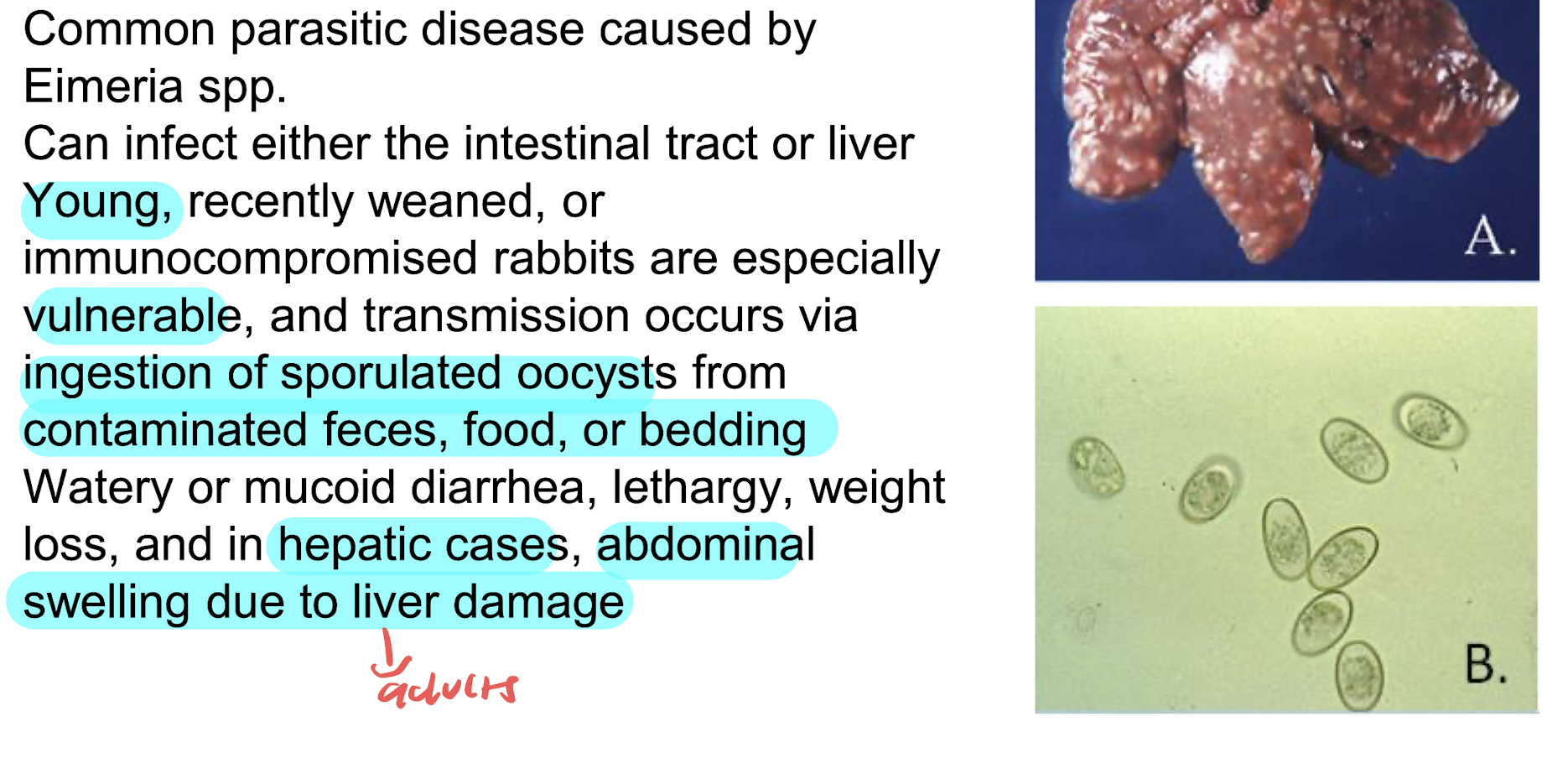
coccidiosis
disease caused by eimeria spp. affecting the liver and/ or intestinal tract and leading to diarrhea, weight loss, and poor growth in young animals
E.cuniculi (encephalitis)
zoonotic
otitis media
rabbit pneumonia

RHDV2

genius and order name of guinea pig
cavia porcellus
guinea is pig a ______ rodent
hystricomorph (“porcupine-like”)
diastema
the space between the incisors and cheek teeth
male guinea pigs (boars) have a _____ on the rump that produces a waxy substance causing a “grease trail”
scent gland
Boars (male guinea pig) have large ______ that resemble a uterus and also have a ____ ____ within the similar to dogs
seminal vesicles; os penis
guinea pigs have ____ offspring
precocial offspring; (fully furred, eyes open, able to graze)
guinea pigs require a dietary source of _______ or scurvy (scorbutus) will result
vitamin C (ascorbate, ascorbic acid)
symptoms of scurvy
loosening or loss of incisors, swollen joints, lameness, and general unthriftiness
guinea pigs, like all rodents, practice ____
coprophagy
Vitamin C rich food
parsley, mustard greens, turnup greens, kale, cabbage, tomato, bell pepper, broccoli, califlower, citrus fruits
not good: carrots, lettuce, celery
guinea pigs is prone to respiratory infections caused by _______ and _______
bordetella bronchiseptica and streptococcus pneumoniae
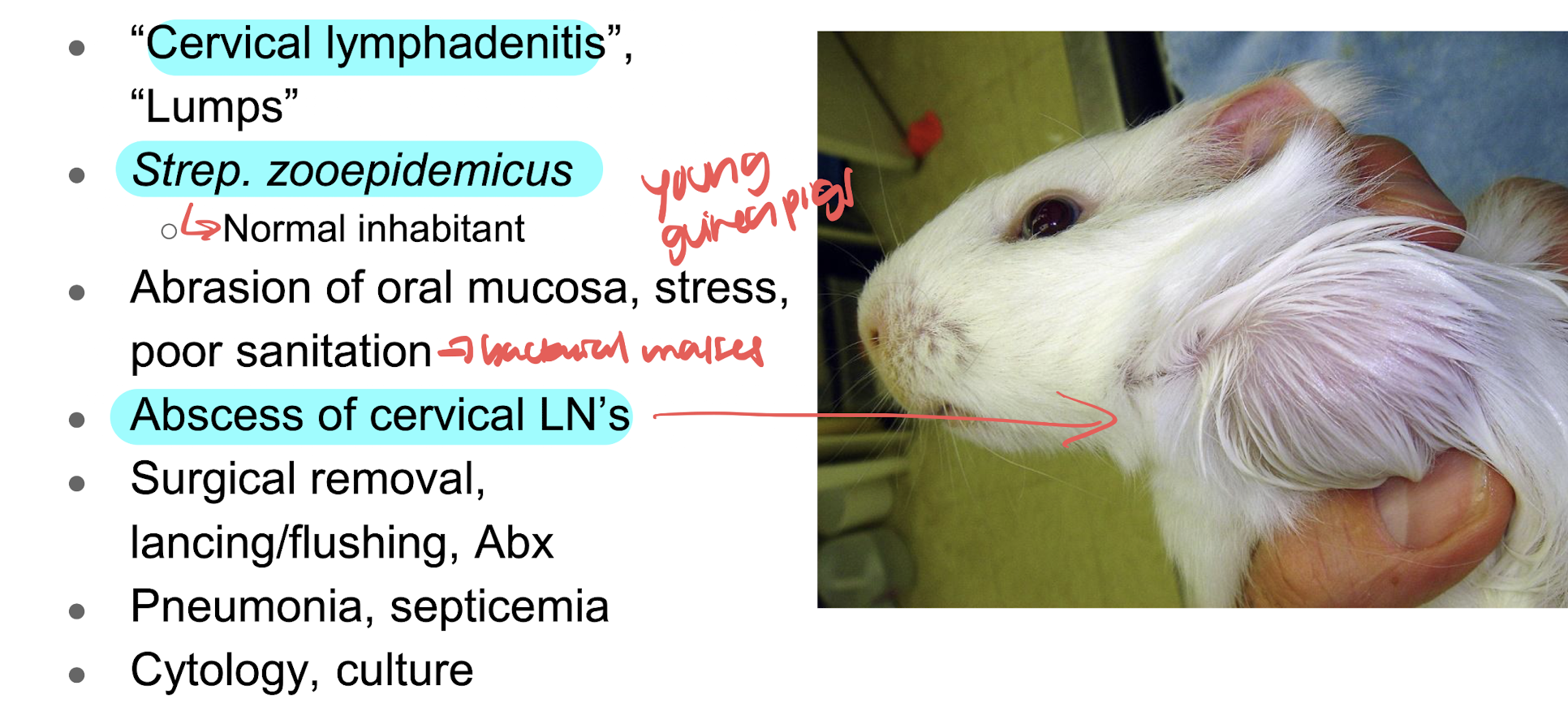
cervical lmphadenitis (lumps) is
cervical abscessation usually caused by strep. zooepidemicus
Antibiotics to avoid
amoxicillin, ampicillin, erythromycin, clindamycin, lincomycin
in guinea pigs they are good at cheek tooth crowns growning until
tongue becomes entrapped, mouth cannot fully close and incisors get too long
guinea pigs are prone to pododermatitis secondary to:
scurvy, obesity, and/or poor sanitation
Trixacarus caviae
mite infestation results in scabbing, alopecia, self trauma, and pruritus so intense that it may be mistaken for seizures
guinea pig _______ infection is a frequent zoonosis
dermatophyte
guinea pigs _____ is common: diagnosis is by radiographs, ultrasound, and urinalysis: surgical removal is usually indicated and recurrence common
urolithiasis
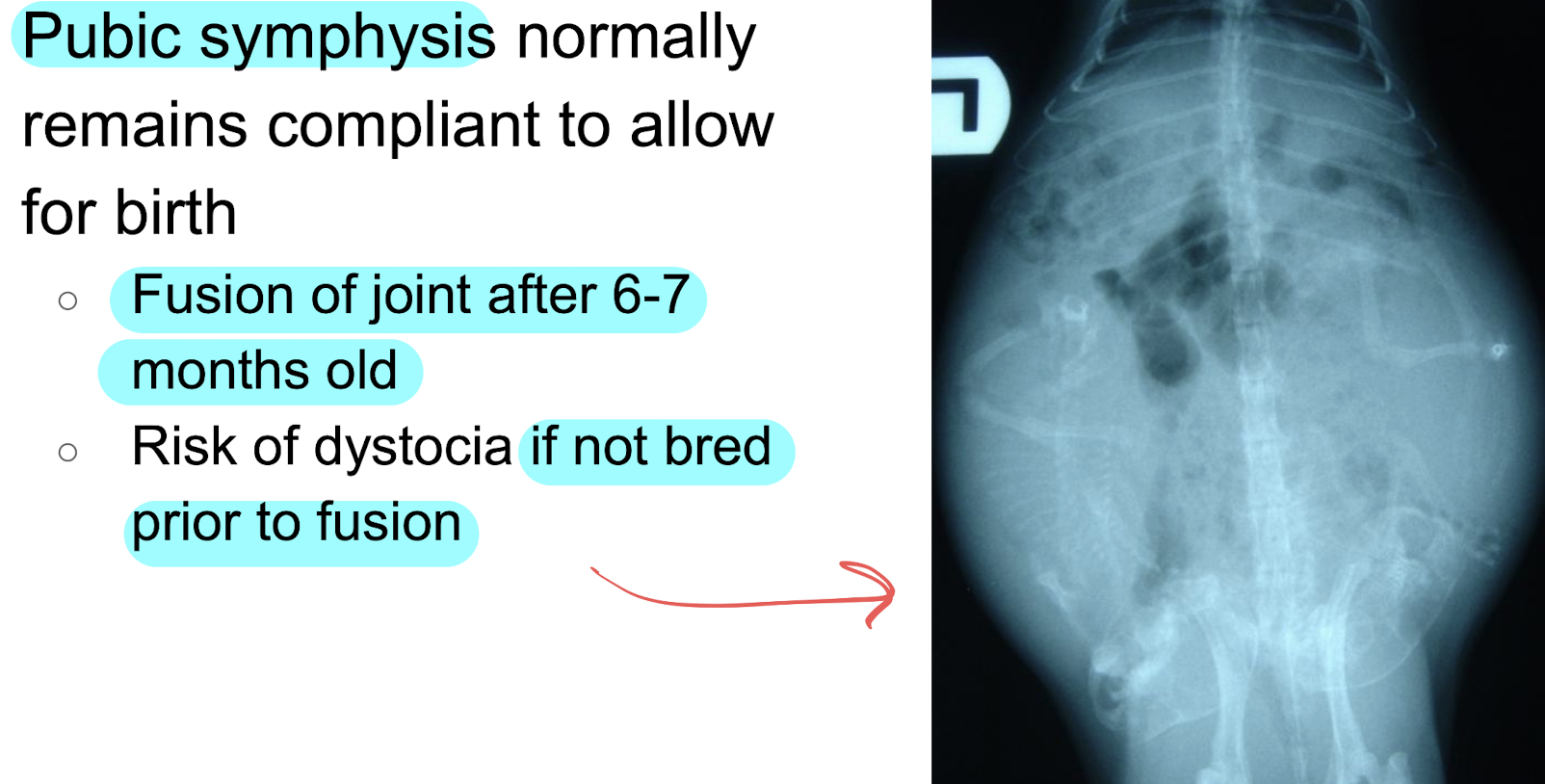
in guinea pigs the ________ of the young female cavy remains compliant to allow for parturition until _____ months of age
pubic symphysis, 6-7
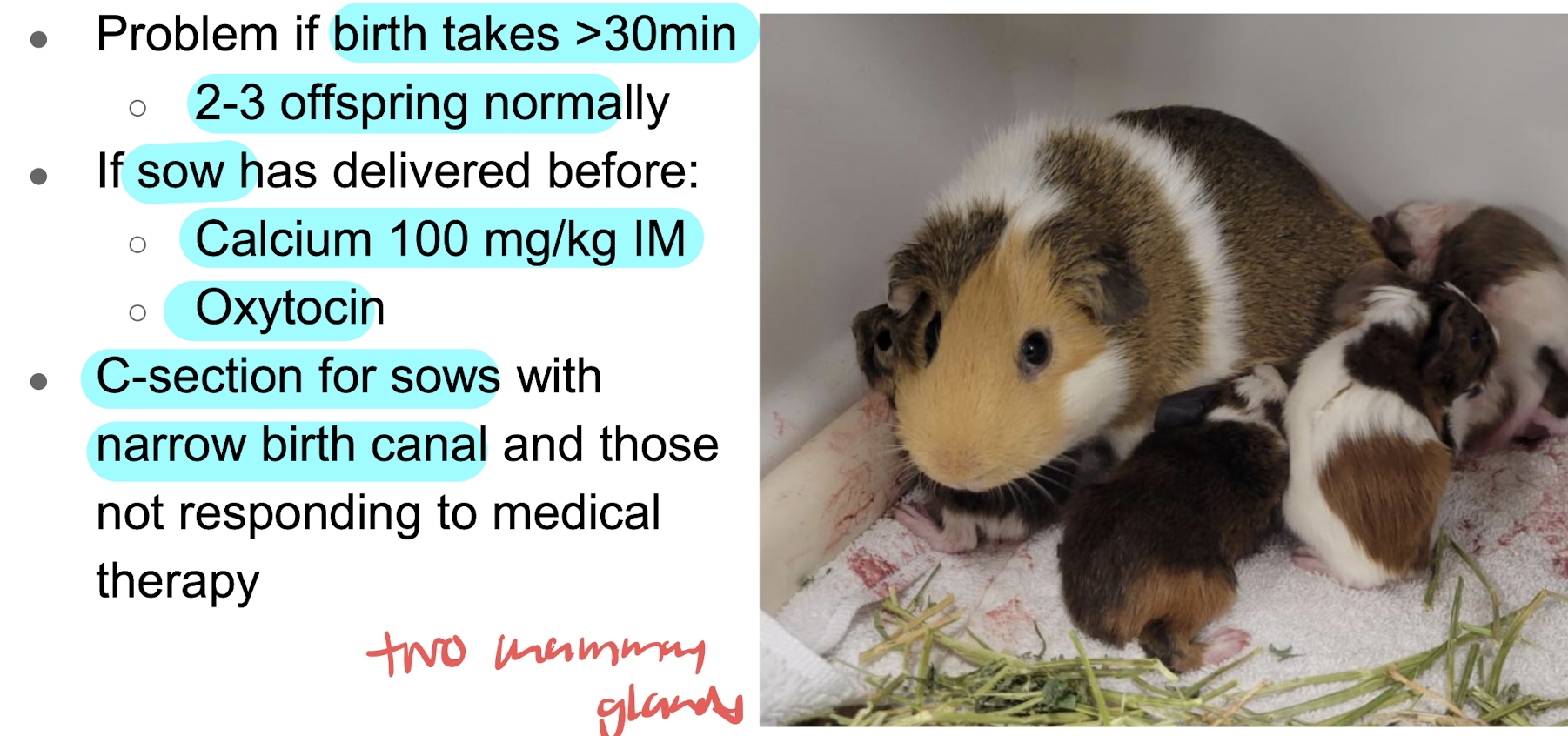
female guinea pigs (sow) bred after fusion of symphysis are at risk for ____
dystocia
cystic ovarian disease can cause
bilateral alopecia over the flanks, abdominal distension, anorexia, fatigue, and depression
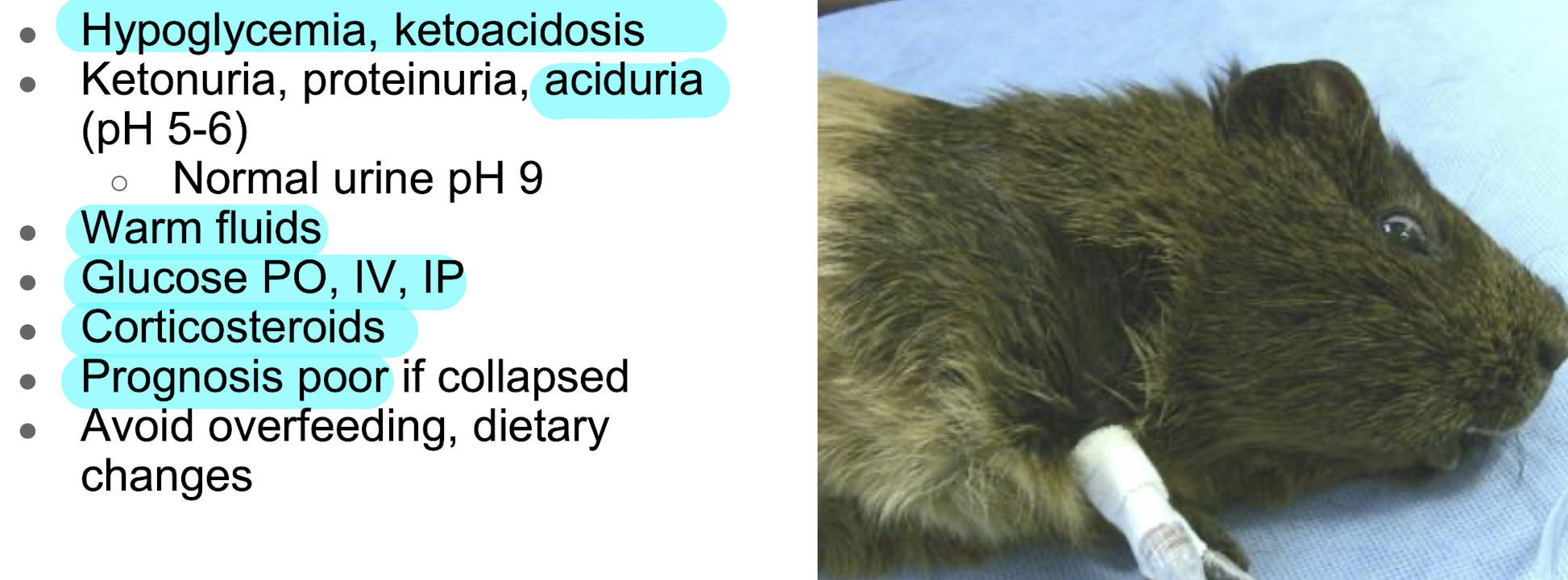
obese expectant female guinea pigs are prone to _______
pregnancy toxemia
bacterial enteritis

streptococcosis
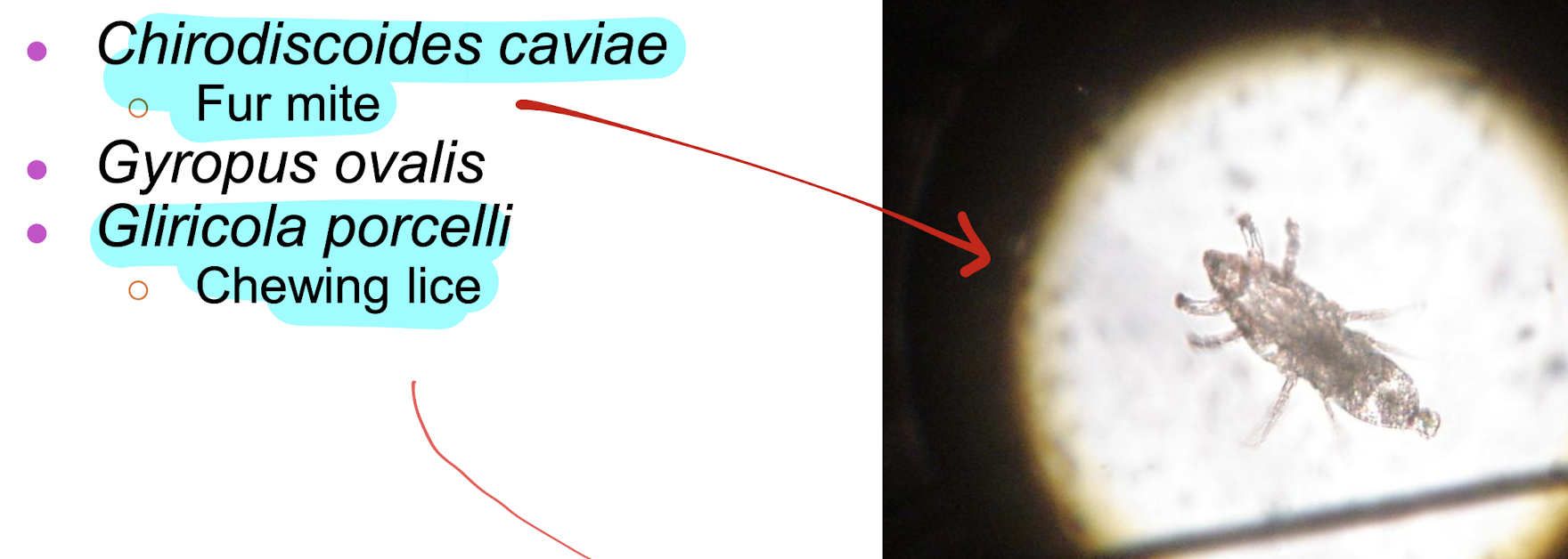
parasites, internal and external

case example




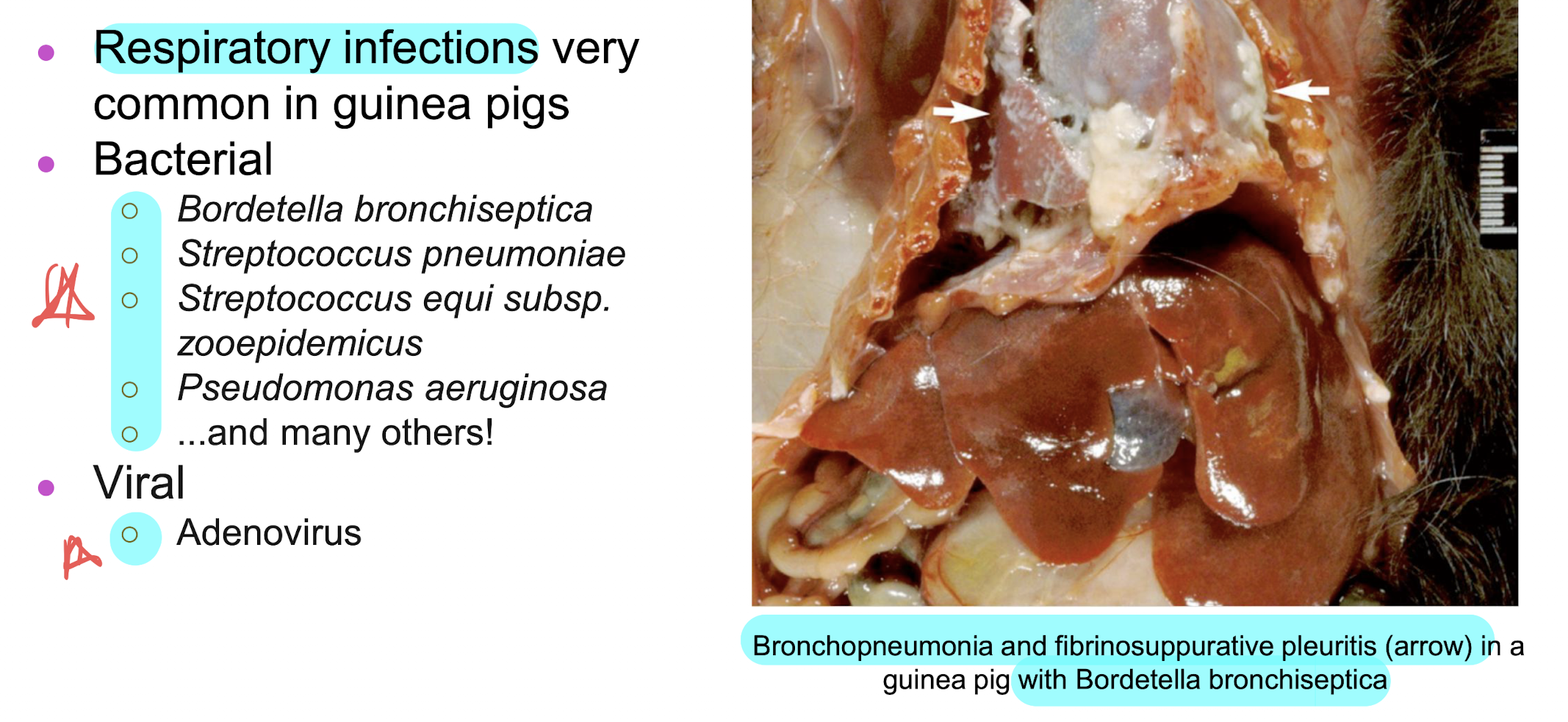
pneumonia
pregnancy toxemia

dystocia
trixacarus caviae

Chinchillas are adapted to a _____, _____ climate
cool, dry
chinchillas are susceptible to ____ and _____bc of their coat
heat and humidity
chinchillas have ______ rather than claws typical of most rodents
fingernails
female chinchillas are ___ than males
larger
chinchillas have exceptionally large _______
auditory bullae
chinchillas are long- lived and live up to ____
20 years old
chinchilla off spring are _____
precocial
female chinchillas are generally ____ to males
dominant
chinchillas need _____ where individuals can take refuge should an altercation occur
hiding places
chinchillas need dust bath offered for ___ every ____ with commercial chinchilla dust
10-15 min q day or two
if chinchillas are handled roughly then _____ may result
fur slip
in chinchillas ________ can be an incidental finding
heart murmur
Ptyalism “slobbers” can be a sign of ____ in chinchillas
dental disease or overheating
chinchillas are prone to ________ with advanced dental disease
apical elongation
in chinchillas blepharospasm may be caused by
apical elongation, duct in the eye, bacterial infection (pseudomonas→ precursor to pneumonia)
in chinchillas enteropathy can lead to
rectal prolapse
Male chinchillas often develop ______. can cause injury, paramphimosis, and dysuria in extreme cases, thus must males should be checked as part of the vet. exam
fur rings around the base of the penis
In small rodents avoid ____ and ____ shavings because they release volatile hydrocarbons
cedar and pine
Degus are closely related to chinchillas and guinea pigs. All are____ and all have___ incisor and cheek teeth all have a ____ adapted to a high fiber diet.
hystricomorphs, elodont, functioning cecum
Hamsters mice rats and gerbils are closely related. All are _____ have _____ incisors and _____ cheek teeth. all have a ______ tract adapted to a high energy diet
myomorphs, open rooted incisors, closed rooted (brachydont) cheek teeth, simple GI tract
Rodent pellets and blocks (formulated diets) are preferred over _______
seed-based diets
all rodents have __ chisel like incisors, the lower incisors are normally ___ the length of the uppers
4 incisors and 3X
In small rodents, there are____within the orbits, they produce porphyrin (red pigment) which can collect around the eyes and ears and can be mistaken for blood
Harderian glands