The Universe - 2023
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 2:10 PM on 5/10/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
1
New cards
what is a star
a large celestial body composed of gas and emits light
2
New cards
what is a galaxy
stars grouped together in a structure
3
New cards
what are galaxies made up of
large collection of stars, gas, and dust
4
New cards
list the 6 types of galaxies
barred spiral, irregular, spiral, peculiar, elliptical, lenticular
5
New cards
estimate amount of galaxies
100 billion
6
New cards
what does the universe contain
space and all the matter and energy
7
New cards
what is the ozone layer
layer in the atmosphere which absorbs harmful solar radiation + other gases (keeps the earth toasty)
8
New cards
what is a solar system
collection of stars and small bodies that orbits our sun
9
New cards
another name for bodies
planets
10
New cards
what is a planet
a spherical body which orbits the sun
11
New cards
name the terrestrial planets
mercury, venus, earth, and mars
12
New cards
qualities of the terrestrial planets
orbit nearest to the sun - rocky, dense, and relatively small
13
New cards
name the gas planets
jupiter, saturn, uranus, neptune
14
New cards
qualities of the gas planets
orbit farthest from the sun - thick, gaseous atmosphere; small, rocky cores; ring system of ice, rock, and dust
15
New cards
what are most stars made of
hydrogen and helium
16
New cards
life cycle of the star
RAHHHHHH
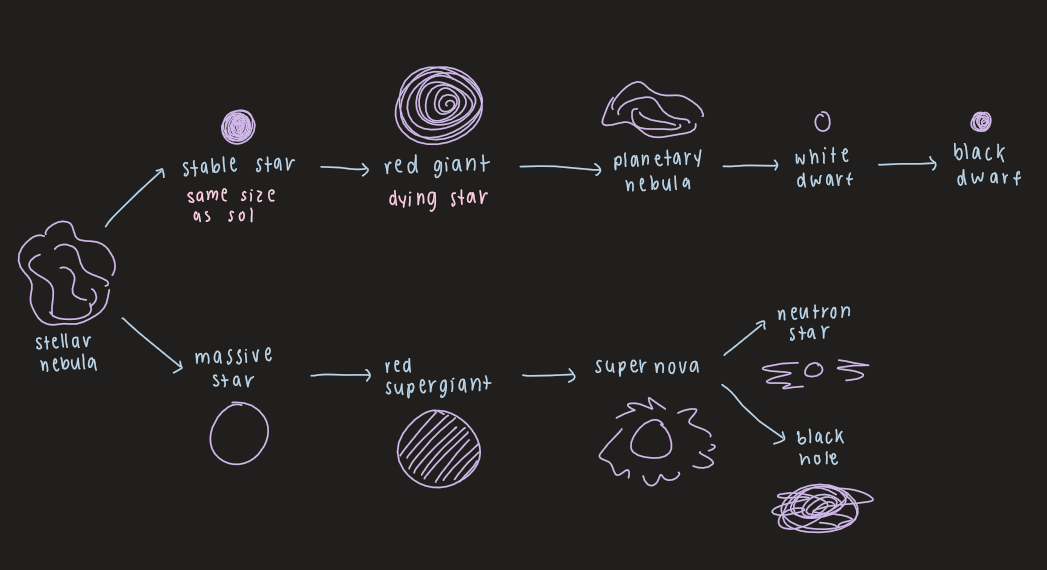
17
New cards
name the process which energy produced in the core of a star
nuclear fusion
18
New cards
what are galaxies
large collection of stars, gas and dust held together by gravity
19
New cards
how many stars do dwarf galaxies contain
few billion stars
20
New cards
how many stars do giant galaxies contain
hundreds of billions
21
New cards
where is our solar system located
Milky Way
22
New cards
why type of galaxy is the milky way
spiral galaxy
23
New cards
spiral galaxy
shaped like a pinwheel, central bulge which two or more spiral arms extend
24
New cards
elliptical galaxies
looks like spheres or ovals and do not have spiral arms
25
New cards
irregular galaxies
splotchy, irregularly shaped - blob
26
New cards
what is period of rotation
the amount of time taken for an object to rotate once (1 day)
27
New cards
what is period of revolution
the time taken for an object to revolve around the sun once (1 year)
28
New cards
what is gravity
a force that pulls all objects towards each other
29
New cards
what is inertia
the tendency of an object to stay either at rest or in motion along a straight path
30
New cards
what would happen if inertia was stronger than gravity
the objects would stay on their straight path and fly off into space
31
New cards
what would happen if gravity was stronger than inertia
the objects would crash into the earth
32
New cards
what do inertia and gravity do
work together to keep the moon orbiting the earth and to keep planets orbiting the sun
33
New cards
what is a comet
small body made out of dust, rock, gas, and ice
34
New cards
name parts of comets
nucleus, coma, ion tail, dust tail.
35
New cards
what are astroids
large pieces of space rock with irregular shapes
36
New cards
where do most asteroids orbit
sun in the asteroid belt located between mars and jupiter
37
New cards
what is a meteoroid
pieces of rock or dust that are smaller than asteroids
38
New cards
what is colour a clue about a star
the stars tempurature
39
New cards
what is a binary star
pairs of stars, pulled together by gravity, that orbits each other
40
New cards
what are binary star use to
determine the stars property
41
New cards
light year
units used to express stellar distance → distance light travels in one year
42
New cards
apparent magnitude
a stars brightness as it appears on earth
43
New cards
absolute magnitude
how bright a star actually is
44
New cards
what does the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram show
the relationship between the absolute magnitude and temperature of stars
45
New cards
what is Cepheid variable
a stars whose brightness varies periodically because it expands and contracts
46
New cards
list the ways a star can be classified
size, temperature, brightness and magnitude
47
New cards
size meaning (star)
how massive the star is
48
New cards
what colour do cooler stars have
red stars
49
New cards
what colour do warmer stars have
blue stars
50
New cards
what colour do medium stars have
yellow
51
New cards
what does a H-R diagram do
compares the temperature, colour and luminosity of a star on a graph
52
New cards
where is the temperature on the H-R diagram
horizontal (bottom axis) - hotter at left, cooler at right
53
New cards
where is the brightness on the H-R diagram
vertical axis (left side) - brightest near top, dimmer near bottom
54
New cards
name the two most common measurement for distance
* astronomical unit - AU
* light year
* light year
55
New cards
what does the astronomical unit measure
the average distance from the earth to the sun (used when discussing distance within **our** solar system)
56
New cards
who discovered redshift
Edwin Hubble
57
New cards
what did Hubble’s discovery tell us about the universe
almost all galaxies were moving away from each other
58
New cards
how does redshift work
shows how light moves towards longer or shorter wavelengths as galaxies and stars move closer or farther away
59
New cards
what does it mean if a star is moving closer to the red side of the spectrum
it is moving farther away from the earth
60
New cards
what does it mean if a star is moving closer to the blue side of the spectrum
it is moving closer to the earth
61
New cards
what is cosmic microwave background radiation
shows that when the universe was young it was very hot and as it expanded it grew cooler
62
New cards
who discovered the composition of the universe
Cecilia Helena Payne
63
New cards
what did Payne discover
stars were mostly made of hydrogen and helium
64
New cards
who discovered dark matter
Fritz Zwick
65
New cards
what are space technologies used for
to enter and retrieve objects or life forms from space
66
New cards
name the 3 present day space technologies
* hubble space telescope
* curiosity rover
* kepler spacecraft
* curiosity rover
* kepler spacecraft
67
New cards
name the 3 future space technologies
* antimatter-powered rockets
* laser and microwave-powered rocket
* sun powered rocket
* laser and microwave-powered rocket
* sun powered rocket
68
New cards
what did Sir Isaac Newton discover
gravity, laws of motion, and the light spectrum
69
New cards
what is gravity
an invisible force that pulls everything towards the centre of earth
70
New cards
how is gravity measured
metres per second squared
71
New cards
how is mass measured
measured by how much matter is in an object
72
New cards
what is weight
weight is the force of a mass pushing down on the surface on which it is standingho
73
New cards
how is weight neasured
in newtons