Biology 101 Exam 2
1/368
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
369 Terms
Mitosis
The division of a cell into two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell
eukaryotic cell division
division of nucleus
production of somatic cells
Meiosis
A type of cell division that reduces the number of chromosomes in the parent cell by half and produces four gamete cells
eukaryotic cell division
production of gametes
Binary Fission
Main type of cell division in prokaryotes
how mitochondria and chloroplasts divide
Copy DNA
Separate DNA
Cytokenesis
Division of cytosol and other organelles after segregation of the genetic material into two daughter cells.
Functions of Mitosis
Growth
Repair/Replacement
Asexual Reproduction
Asexual Reproduction
Reproductive process where egg and sperm aren’t needed
Chromosome
Structure carrying genetic material (genes and non-coding DNA) found in nucleus
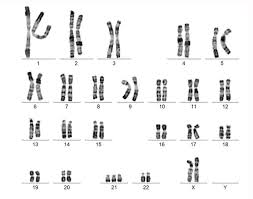
Karyotype
an individual's complete set of chromosomes. Also refers to a lab-produced image of a person's chromosomes arranged in numerical order
Diploid (2n)
Cells/organisms with paired chromosomes
1 chromosome from each parent
Haploid (1n, n)
Cells/organisms with unpaired chromosomes
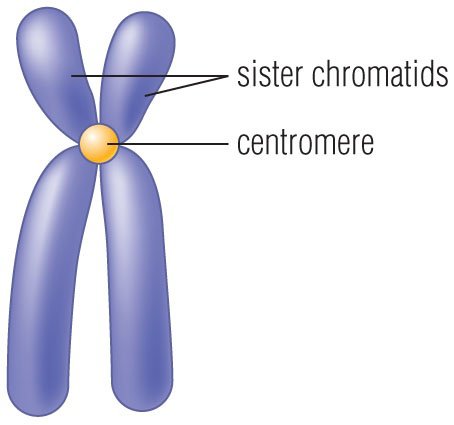
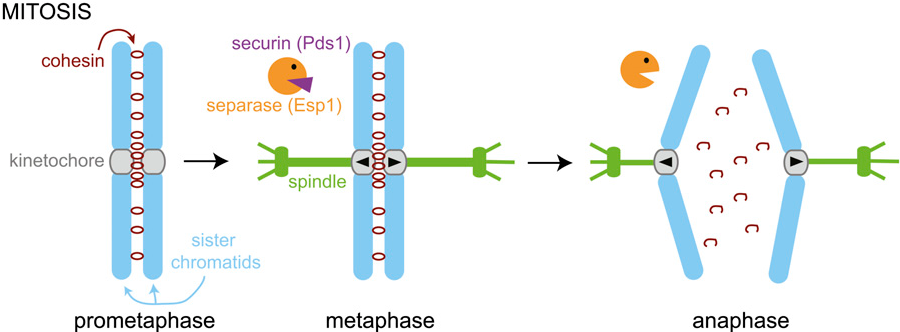
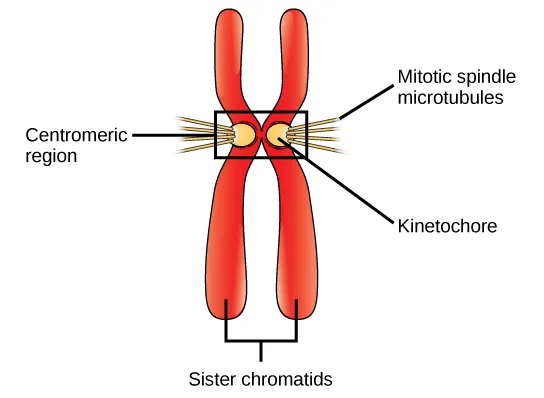
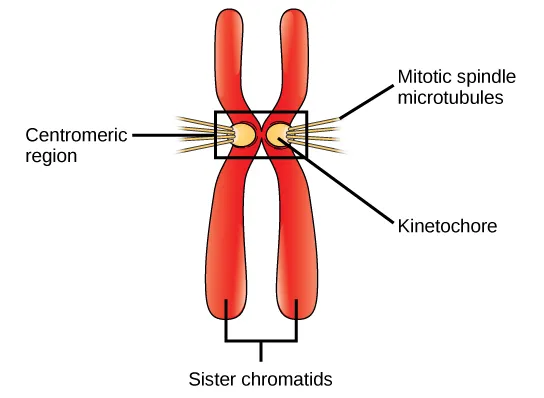
Centromere
The region of the chromosome to which the spindle fiber is attached during cell division
where sister chromatids attach
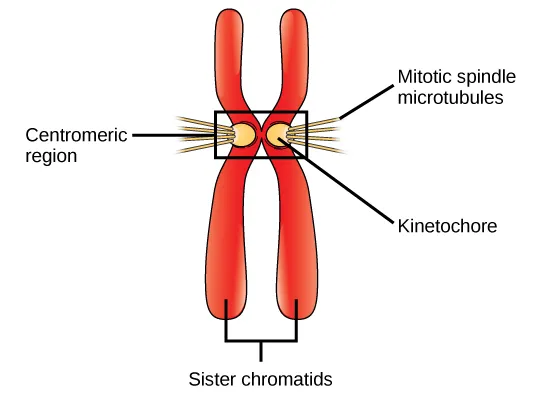
Kinetochore
Protein structure (that forms on a chromatin during cell division) where microtubules attach during mitosis
Sister Chromatids
The identical copies formed by the DNA replication of a chromosome, with both copies joined together by a common centromere
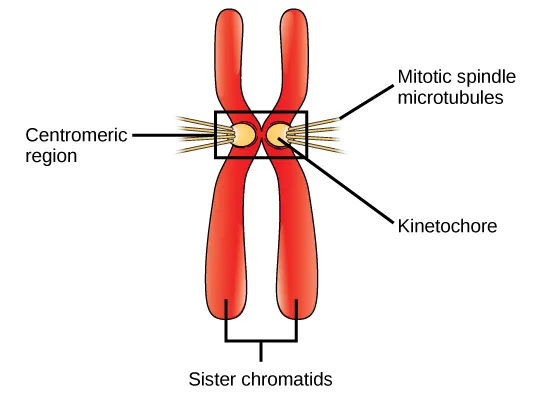
Cohesins
Chromosome-associated protein complex that is critical for chromosome separation during cell division.
connects sister chromatids
Cell Cycle
Life cycle of a cell, a series of events that takes place in a cell as it grows and divides
G1 - S - G2 - M
G1 Stage
Cell cycle stage that consists of:
Cell growth
Transcription/Translation
Duplication of organelles
Preparation for DNA replication
S stage (Synthesis)
Cell cycle stage where DNA replication occurs
G2 Stage
Cell cycle stage that consists of:
More growth
Transcription/Translation
Prepare to divide:
Centrosomes appear
M stage (Mitotic)
Cell cycle stage when the cell divides its copied DNA and cytoplasm to make two new cells.
two distinct division-related processes: mitosis and cytokinesis.
Fate of organelles
Endomembrane system
fragments into vesicle structures
reforms in daughter cells
Mitochondria
split between two daughter cells
divide by binary fission to reproduce in new cell
Contractile Ring
A ring of actin filaments located below the cell membrane which constricts the middle of a dividing cell
Gametes
a reproductive cell of an animal or plant
Somatic Cells
the cells in the body other than sperm and egg cells
Zygote
Diploid cell resulting from the fusion of two haploid gametes; fertilized egg
Condense
What chromosomes do at the start of mitosis
Replicate
What chromosomes do prior to mitosis
Mitotic Spindle Microtubulues
During mitosis, they form a macromolecular structure known as the mitotic spindle that is responsible for the accurate segregation of chromosomes between the two daughter cells
Homologous Chromosomes
Pairs of chromosomes in a diploid organism that have similar genes, although not necessarily identical
Sex Chromosome
A type of chromosome involved in sex determination. Humans and most other mammals have two sex chromosomes, X and Y, that in combination determine the sex of an individual.
Autosome
Any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome
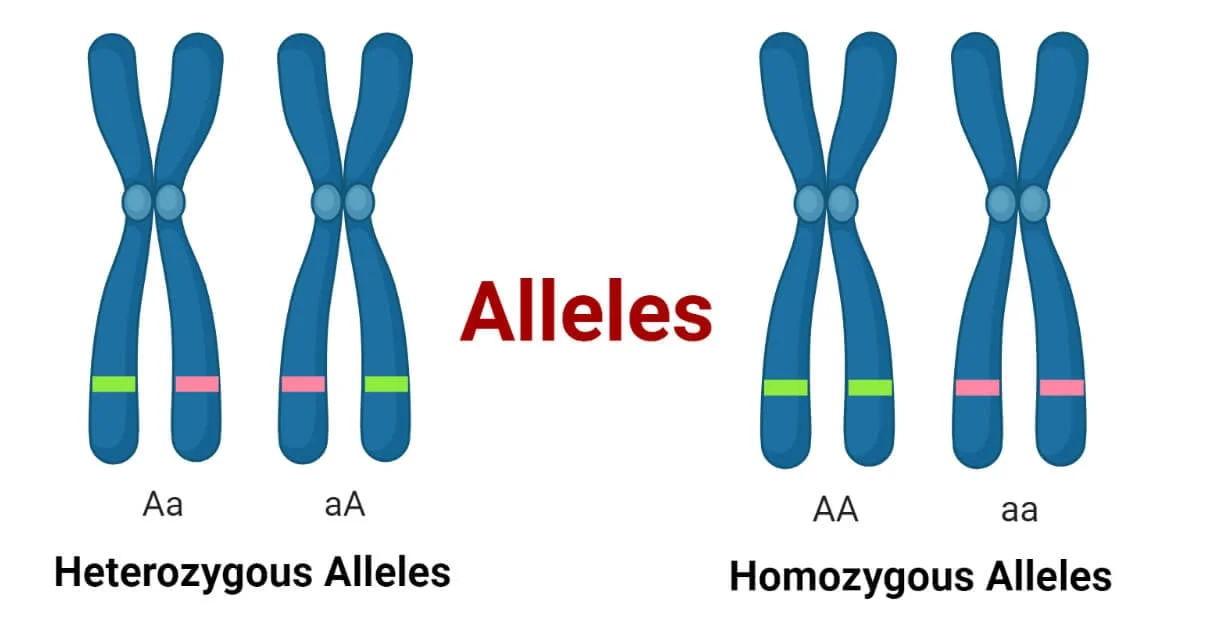
Alleles
Alternate forms of a gene ; found at the same place on a chromosome
Fertilization
The joining of an egg cell and a sperm cell
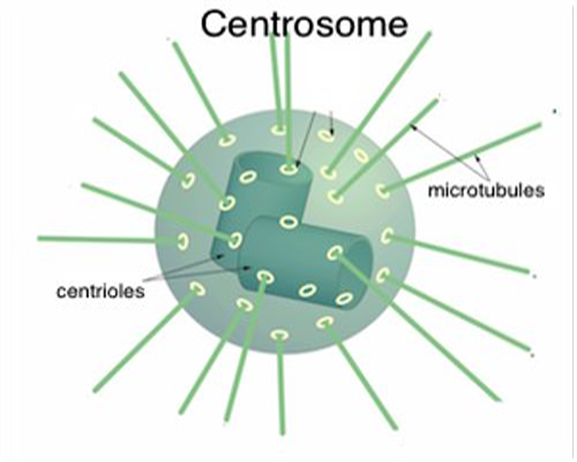
Centrosomes
Where microtubules grow from
Microtubule Organization Center (MTOC)
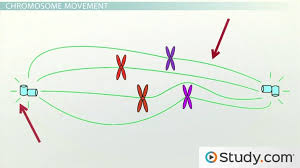
Mitotic Spindle
A structure made up of microtubules that forms during cell division and separates duplicated chromosomes and moves them from the parent cell into the daughter cells
XX
Sex chromosomes that indicate a female
XY
Sex chromosomes that indicate a male
Daughter Cells
The cells that are formed after cell division
In Mitosis: 2 diploid cells that are identical to each other and the parent
In Meiosis: 4 haploid cells that are not identical to each other or the parent
Sexual Life Cycle
Gamete formation (meiosis)
Fertilization
Growth (mitosis) & development
Stages of Meiosis
Prophase I
Metaphase I
Anaphase I
Telophase I
Cytokinesis
Prophase II
Metaphase II
Anaphase II
Telophase II
Cytokinesis
Prophase I (Meiosis)
Chromosomes condense
Nuclear envelope fragments
Centrosomes migrate
Meiotic spindle forms
Synapsis occurs
Crossing over occurs
Synapsis
Pairing of homologous chromosomes that happens during Prophase I of Meiosis
Crossing Over
Exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids that occurs during Prophase I of Meiosis
Synaptonemal Complex
Protein lattice between homologous chromosomes
Recombinant Chromatids
Two of the four chromatids present early in meiosis (prophase I) are paired with each other and able to interact
new combination of alleles
Non-Recombinant Chromatids
There is no genetic recombination; It is more akin to the original or parent DNA.
Metaphase I (Meiosis)
Homologous Pairs align on the metaphase plate
random assignment/independent assortment
Independent Assortment
A genetic principle that states that the alleles of two genes will segregate into daughter cells independent of one another. That means that the allele a cell receives for one gene is not influenced by an allele it receives for another gene.
Occurs in meiosis
NOT in mitosis
Anaphase I (Meiosis)
Kinetochore MTs shorten
Synaptonemal Complex degrades
Homologous chromosomes separate and move to the opposite poles of the cell
Sister chromatids stay attached
Non-kinetochore MTs lengthen and cell elongates
Telophase I/Cytokinesis (Meiosis)
Each half of cell has complete 1n set of replicated chromosomes
Each chromosome consists of 2 sister chromatids
Interkinesis (intermission)
NO DNA REPLICATION
Prophase II (Meiosis)
Same at Mitosis
Chromosomes condense
Metaphase II (Meiosis)
Chromosomes aligned on metaphase plate
Anaphase II (Meiosis)
Sister chromatids separated and moved to opposite poles of cell
Telophase II/Cytokinesis (Meiosis)
Chromosomes decondense
Nuclei reform
n=3
Haploid with three chromosomes
Genetic Variation in Offspring
Due to:
Mutation
Random assignment of chromosomes on metaphase I plate
Crossing over (>8.4m gametes)
Fertilization (random egg & sperm)
Disjunction
Disjoining DNA or chromosomes; the normal separation or moving apart of chromosomes toward opposite poles of the cell during cell division
Nondisjunction
Disjunction doesn’t work; homologous or sister chromatids don’t separate from each other
Aneuploid
The occurrence of one or more extra or missing chromosomes in a cell or organism
Trisomy
occurs when you have an extra copy of a chromosome
Monosomy
Occurs when you are missing a copy of a chromosome
Stages of Mitosis
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase/Cytokinesis
Prophase (Mitosis)
Chromosomes condense and become metaphase chromosomes
Nuclear envelope degrades and disappears
Mitotic spindle forms
Kinetochore Microtubules
Attached to kinetochores; connect chromosomes to microtubules of the mitotic and meiotic spindles in order to distribute the replicated genome from a mother cell to its daughters.
Non-Kinetochore Microtubules
Don’t attach to kinetochore; the aspect of the mitotic spindle that does not interact with chromosomes
Metaphase (Mitosis)
Chromosomes line up on the metaphase plate
Twice as many sister chromatids as chromosomes
Anaphase (Mitosis)
Separation of DNA
Cohesions degrade
Kinetochore Mts get shorter
Separate sister chromatins from each other and move them to opposite poles of the cell
Non-kinetochore MTs lengthen - elongates the cell
Telophase/Cytokinesis (Mitosis)
Opposite of prophase
Chromosomes de-condense
Nuclear envelope reassembles
Mitotic spindle disassembles
Microfilaments shorten
Checkpoints
Regulatory molecules at each cell cycle checkpoint “decide” if division should proceed
problems here = could become cancerous
G1 Checkpoint
Is growth factor present?
Is cell big enough?
Is DNA undamaged?
G2 Checkpoint
Is DNA replication complete?
Metaphase (M) Checkpoint
Are chromosomes attached to kinetochore microtubules?
Growth Factor
Stimulate cells to divide
each has a specific receptor
cells start & stop reproducing at the right time
Apoptosis
Occurs when a problem in cell division is not fixed; A type of cell death in which a series of molecular steps in a cell lead to its death
Tumor
Group of proliferating cancer cells that forms when a problem in cell division is not fixed but goes past the checkpoint anyway
cells can be immortal
Signal Transduction
The mechanism by which a cell leads an external signal through a cell, transforming it biochemically into a series of discrete entities (internal response) with specific biochemical properties.
Reception
Transduction
Response
Reception
Stage in signal transduction when a cell detects a signaling molecule from the outside of the cell.
Transduction
Stage in signal transduction where receptors are activated in succession, relying molecules in signal transduction pathway
Response
Stage in signal transduction when activation of cellular response occurs
Anchorage Dependence
Cells have to connect to the right thing to divide
Contact Inhibition
The concept that crowded cells stop dividing
Stages of Cancer Cells
A tumor grows from a single cancer cell
Cancer cells invade neighboring tissue
Cancer cells spread to other parts of the body
Cancer cells may survive and establish a new tumor in the body
Benign
Non-cancerous tumor
Malignant
Cancerous tumor
Metastasis
The spread of cancer cells from the place where they first formed to another part of the body
Properties of Cancer Cells
Cells divide with no growth factor
Cells ignore contact inhibition
Cells ignore anchorage dependence
Proto-oncogenes
Genes that encode signals, receptors, signaling molecules, and control proteins
normal
Oncogenes
Cancer-causing genes
always active
tells cell to divide when they aren’t supposed to
Point Mutation
A genetic alteration caused by the substitution of a single nucleotide for another nucleotide
leads to hyperactive or degradation-resistant protein
Gene Amplification
Multiple copies of the gene made, leads to normal growth-stimulating protein in excess
Translocation
Gene moved to a new locus, under new controls, leads to normal growth-stimulating protein in excess
Tumor Suppressor Proteins
Shut down cell division if conditions are not favorable
if mutated:
cell cycle checkpoints ignored
damage cells proliferate
BRCA 1 and BRCA2
Work in concert to protect the genome from double-strand DNA damage during DNA replication
Recognize DNA damage
Recruit repair enzymes
BRCA Mutation
Damaged DNA still goes through Mitosis
Increased risk for breast & ovarian cancer
p53
Tumor-supressor protein that is activated whenever DNA damage or cell cycle abnormalities occurs
Cycle cycle arrest, DNA repair, and cell cycle re-start
OR
Apoptosis
p53 Mutation
Damaged DNA/cells go through mitosis
Risk of colon, breast, lung, and other cancers
Apoptosis
The process of programmed cell death. It is used during early development to eliminate unwanted cells
Hyper-methylation
Too much methylation, leads to gene being turned OFF (epigenetic phenomenon)
Telomerase
Maintains telomere length; chromosomes don’t shorten
over-expressed = immortal cells
activity detected in tumors
HeLa Cells
Immortal cell line commonly used in biological research; have active telomerase
Traditional Chemotherapy
Injection of chemicals into bloodstream to kill dividing cells
non-selective