21. Neoplasia: Classification of Tumors
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
What are the four broad categories of tumors?
E
M
N
O
epithelial cells
mesenchymal cells
neural crest cells
other
What give rise to epithelial tissues and tumors?
all three embryonic layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm)
What do epithelial cells have? What is their function?
cell to cell junctions; line surfaces (epidermis, mucosa), form glands, cords, or tubules
How are epithelial tumors typically described grossly?
off white and firm
What are examples of benign epithelial neoplasms?
A
P
P
adenoma
papilloma
polyp
benign epithelial tumor with glandular or tubular differentiation
adenoma
benign exophytic (growing outwards) tumor that is typically arising from a cutaneous or mucocutaneous surface
papilloma
What are examples of malignant epithelial neoplasms?
A
C
adenocarcinoma
carcinoma
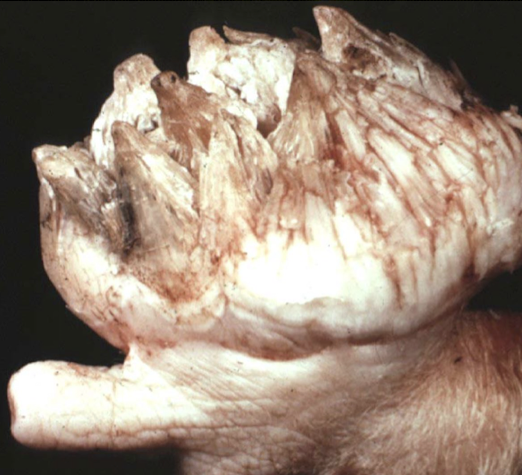
What is this showing?
epithelial tumor (squamous papilloma)
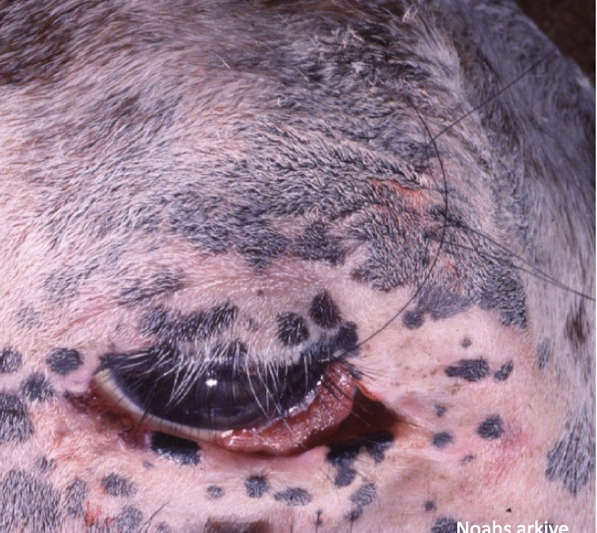
What is this showing?
equine squamous cell carcinoma
benign epithelial tumors projecting from a mucosal surface
polyp
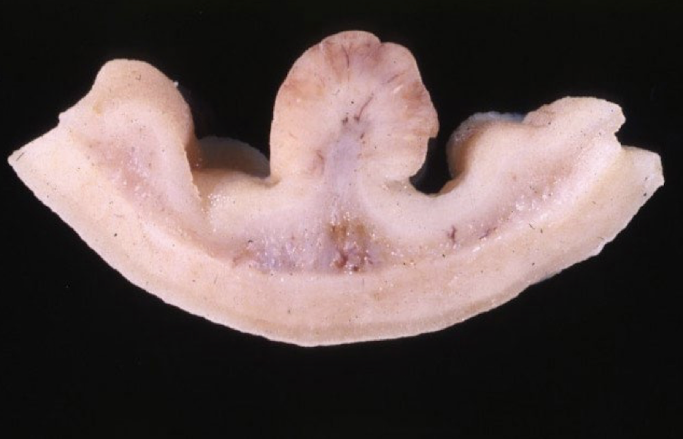
What is this showing?
intestinal polyp
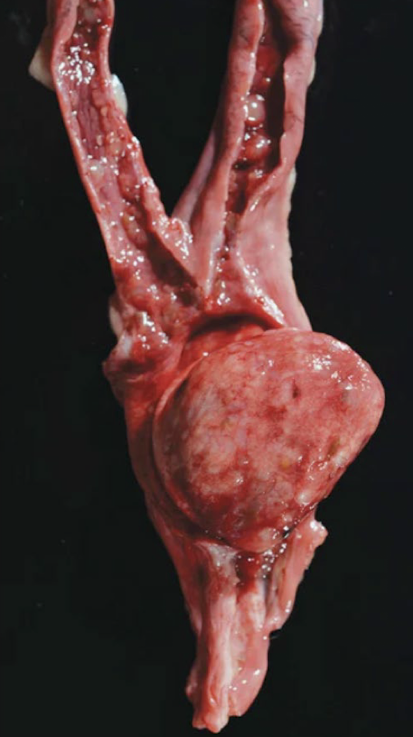
What is this showing?
endometrial polyp
What are malignant tumors of epithelial origin referred to as?
carcinomas
What patterns can carcinomas form? What are these based on?
N
C
T
S
T
nesis
cords
trabeculae
solid
tubular
cell of origin the tumor originates from
When the tumor is glandular in nature, what is it referred to as?
adenocarcinoma
Typically, carcinomas have ________ well-defined borders, are ________-________, can be ________-________ or have a ________ surface, and are ________ in texture.
less; off-white; multi-lobulated; corrugated; firm
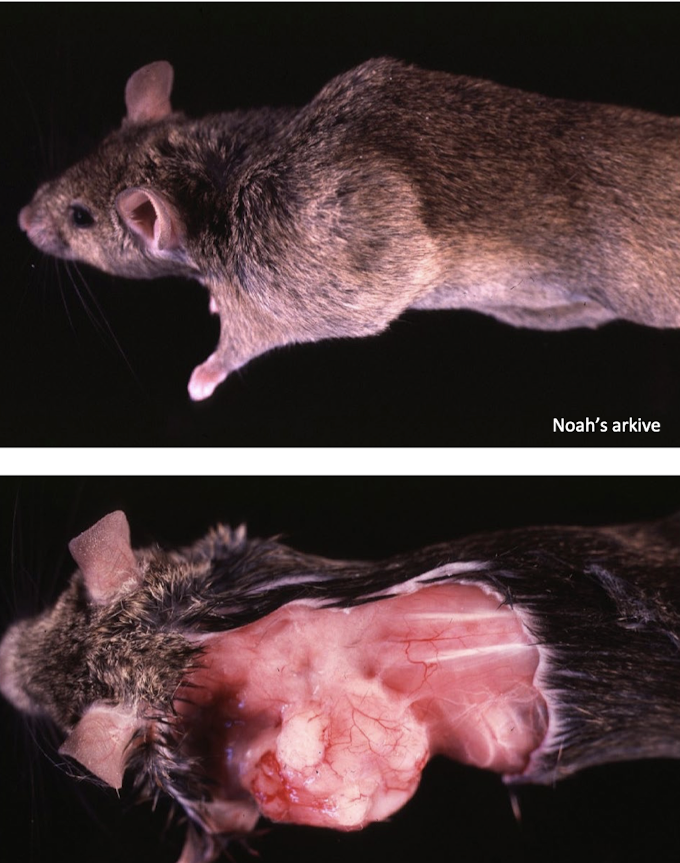
What is this showing?
adenocarcinoma
What tumor type tends to produce a schirrous or desmoplastic response better than most?
carcinomas
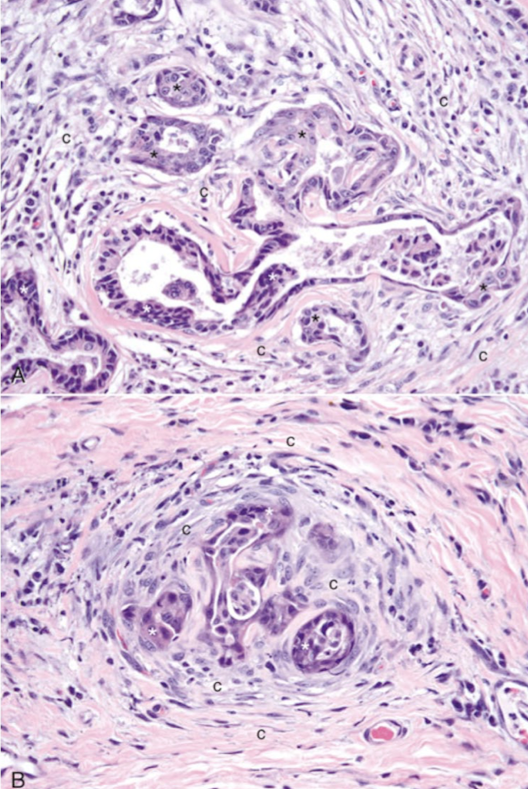
What is this showing?
schirrous or desmoplastic response
derived from the mesoderm embryologically and are an incredibly diverse category of cells that can develop into tumors
mesenchymal tumors
Typically, mesenchymal tumors are tumors of ________ cells from tissues. They can be anything from adipocytes to cells forming bone to muscle cells to astrocytes and oligodendrites or meningeal cells in the brain.
supporting
How do you name a benign mesenchymal neoplasm?
tissue type + “oma” (fibroma)
How do you name a malignant mesenchymal neoplasm?
tissue type + sarcoma (fibrosarcoma)
Sarcomas are typically ________, ________ tumors. There can be exceptions to this rule. Hemangiomas/hemangiosarcomas tend to be ________ and ________ ________.
firm; white; fluctuant; dark red
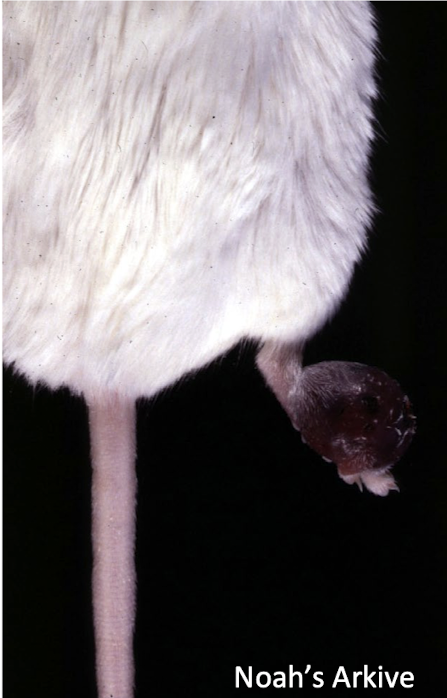

What is this showing?
hemangioma
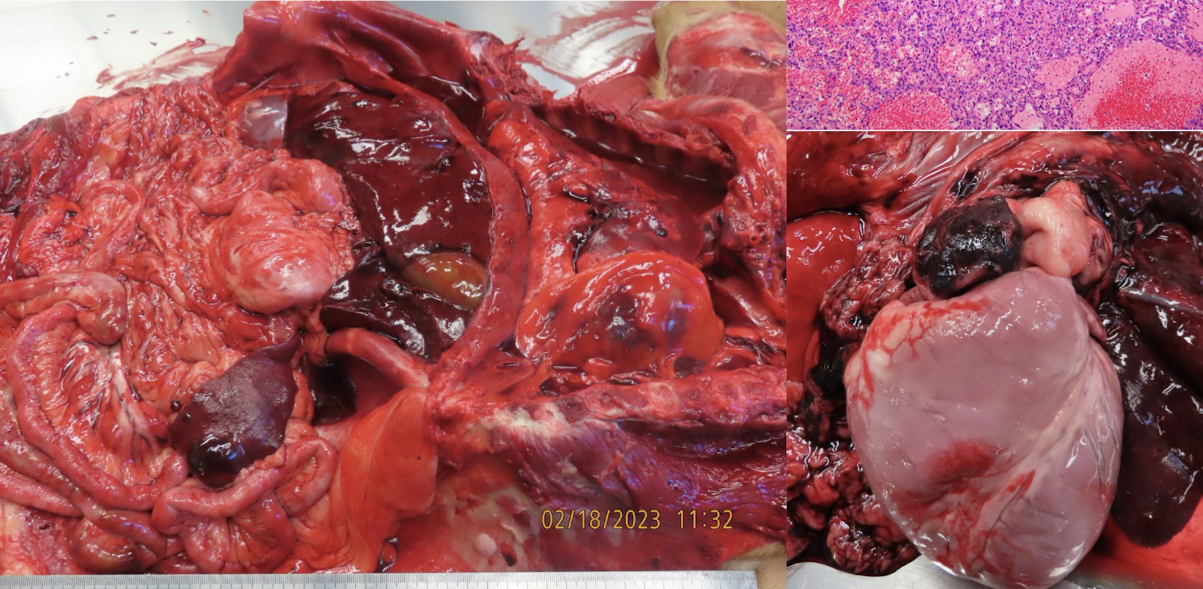
What is this showing?
hemangiosarcoma
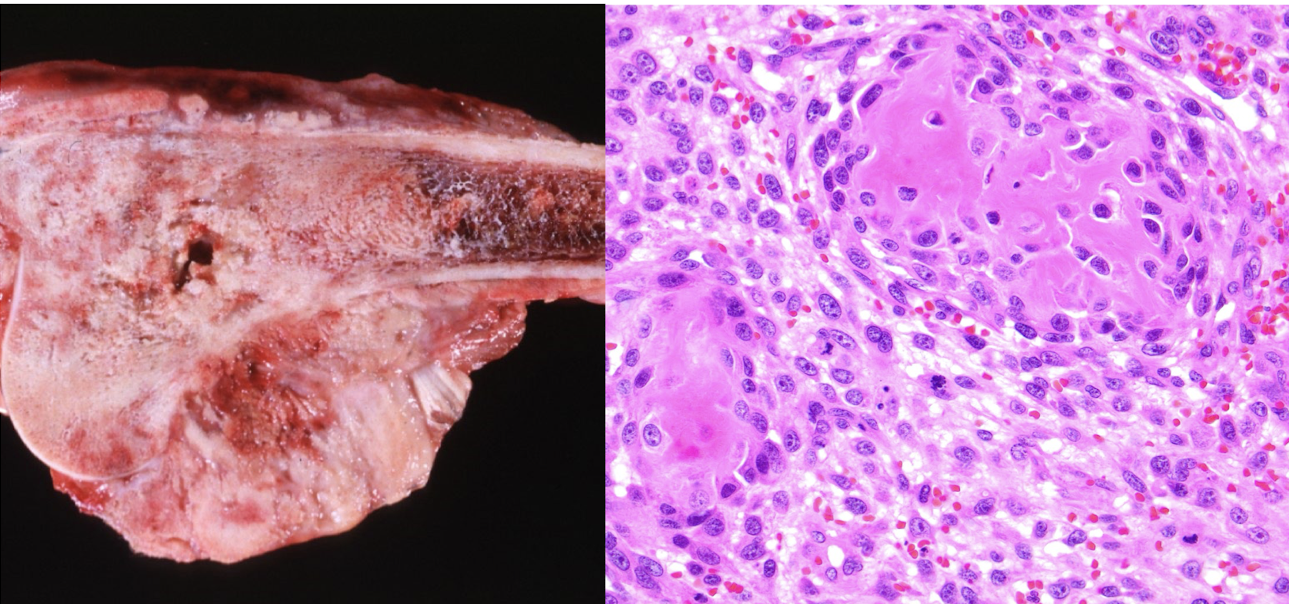
What is this showing?
osteosarcoma
specific category of mesenchymal tumors
round cell tumors
What are the 5 cell types in round cell tumors?
L
M
P
H
T
lymphocytes (B and T cells)
mast cells
plasma cells
histiocytoma
transmissible venereal tumor
leukocytic (including lymphocytic) tumor that is originating in the bone marrow, which ends up in the peripheral blood stream
leukemia
True or false: There is no benign lymphocytic neoplasm, though some forms of lymphoma are referred to as indolent (slow course of progression) whereas others are very aggressive.
true
Lymphomas are typically of what origin? What is an exception?
T or B cell; some can be de-differentiated enough that they do not express those markers
What are the 2 separate patterns of lymphomas?
D
C
diffusely enlarges an organ
creates homogenously soft off white bulging tumors on a cut section
What is this showing?
lymphoma
terminally differentiated B cells producing immunoglobulins
plasma cells
Plasma cell tumors or plasmacytomas are typically ________ and ________ in clinical course. They can be ________.
cutaneous; benign; extracutaneous
How does multiple myeloma appear on serum protein electrophoresis?
hyperglobulinemia + monoclonal gammopathy
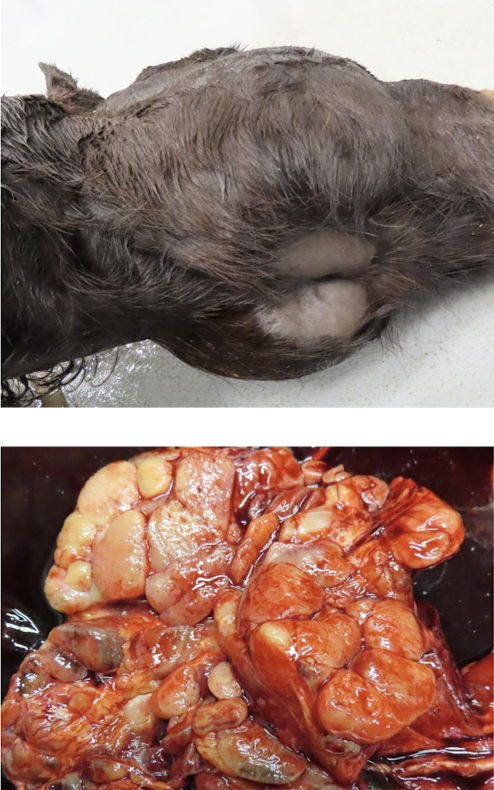
Multiple myeloma has what type of cell infiltrate?
plasma cell
What else is seen in multiple myeloma?
H
O
B
hypercalcemia
osteolytic bone lesions
bence jones proteinuria
What is this showing?
multiple myeloma
tumor that is neither benign nor malignant and have variable biologic behavior
mast cell tumor
What is significant about canine mast cell tumor? What does it mean?
they are graded; the higher the grade, the more aggressive the clinical course
What are the types of grading scales?
2 tier and 3 tier grading scales
2 tier grading scale
Kiupel (low vs. high)
3 tier grading system
Patnaik (I is low, II is intermediate, III is high)
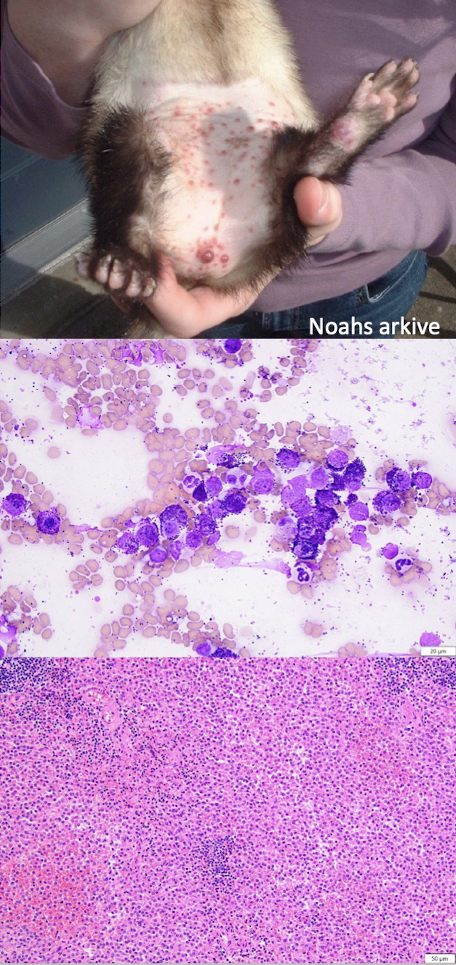

What is this showing?
mast cell tumor
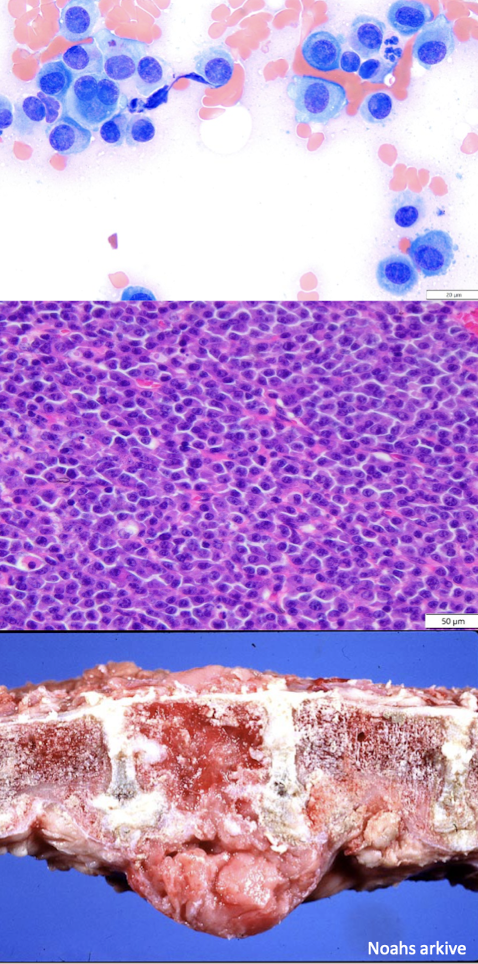
benign cutaneous tumor in dogs that is commonly found on the head and limbs of young dogs, though old dogs can get it too and is described as a button tumor
histiocytoma
What cell is involved in histiocytomas?
langhan’s cells (type of histiocyte)
True or false: Histiocytomas will self regress given time or after traumatized.
true
What is this showing?
histiocytoma
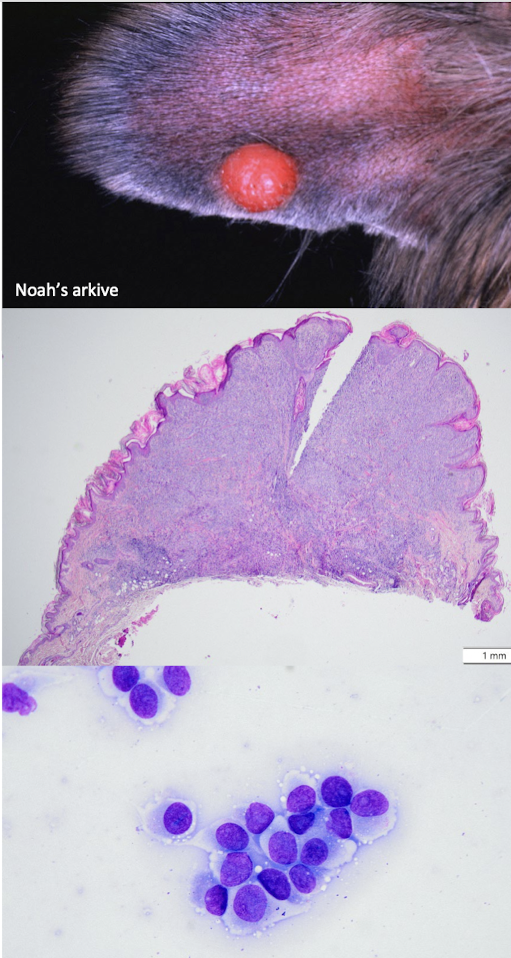
What is transmissible venereal tumor (TVT) thought to arise from? What abnormalities do these cells have?
genetic alteration of canine histiocytes; chromosomal abnormalities
How is TVT transmissible?
through direct contact
Where does TVT occur?
at mucocutaneous junctions
What are the possible outcomes with TVT?
S
I
M
spontaneous regression
indolent growth
metastatic form (frequently fatal)
What is this showing?
transmissible venereal tumor (TVT)
transmissible tumor in tasmanian devils that has a similar concept to TVTs and is decimating the population
tasmanian devil facial tumor
How is tasmanian devil facial tumor spread?
by biting
True or false: Some devils have been found with partial immunity to tasmanian devil facial tumor.
true
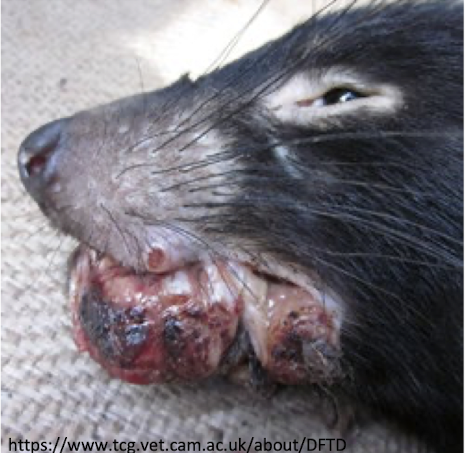

What is this showing?
tasmanian devil facial tumor
From where are neural crest tumors derived?
neural crest cells from the neuroectoderm
What are the cell types involved with neural crest tumors?
M
A
S
G
melanocytes (melanoma)
adrenal medullary cells (pheochromocytoma)
schwann cells (schwannoma)
ganglion cells (ganglioma)
Neural crest tumors are neither ________ nor ________. Therefore, tumors of these types are named differently. Typically, they are still named with oma but malignant is added as a pre-fix for aggressive variants.
mesenchymal; epithelial
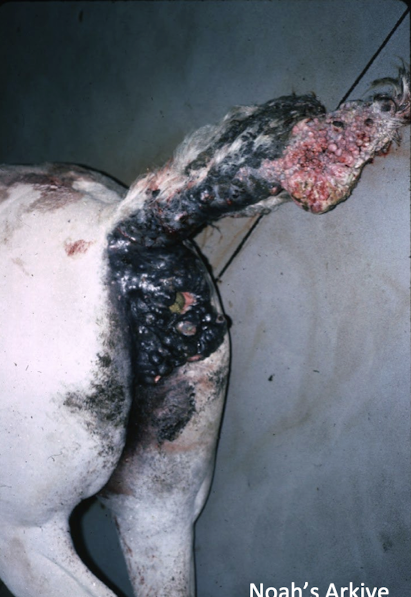
What is this showing?
neural crest tumor
True or false: Some malignant neoplasms are difficult to determine the origin because they are so poorly differentiated (anaplastic).
true
Mixed tumors are believed to arise from what? What are they capable of?
single pluripotent or totipotent stem cell; differentiating into a variety of mature cell types
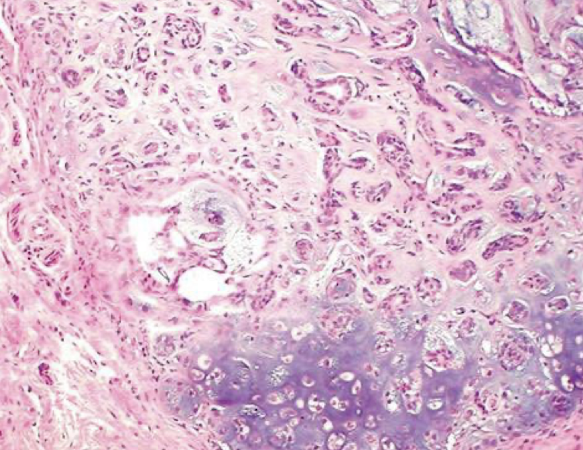
What is this showing?
benign mixed mammary tumor
What do teratoma arise from?
totipotent germ cells
In teratoma, what is usually expressed in the neoplasm?
all three embryonic cell lines
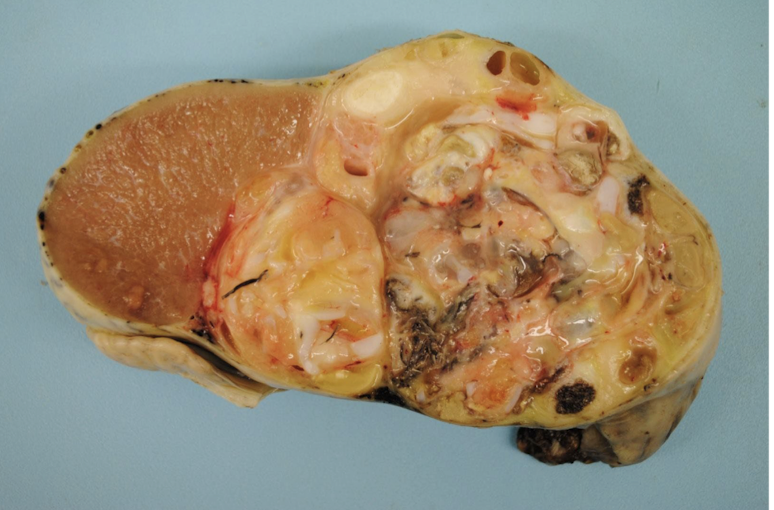
What is this showing?
teratoma
two separate tumor types that are in one location colliding and are originating from two separate cell types
collision tumors
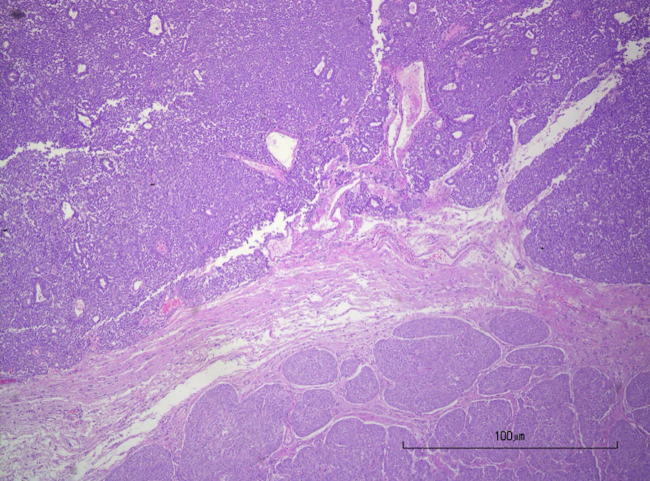
What is this showing?
collision tumor
True or false: Tumor-like masses are not neoplastic but can look like it.
true
mature normal tissues/components in normal locations there is just a lot more present than normal or the structures appear slightly dysplastic
hamartoma
What is an example of hamartoma?
collagenous hamartoma
normal tissue in an abnormal location
choriostoma (aka ectopic)
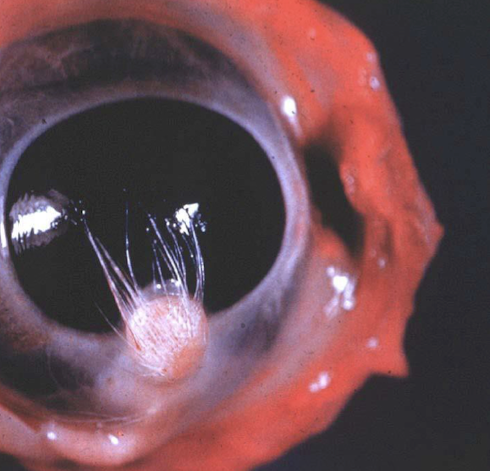
What is this an example of?
choriostoma (corneal dermoid)