Geology-Exoplanets/transits -Doppler Effect - Red Shift
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Geologic Time Scale
A system that divides Earth's history into distinct periods based on major geological and biological events. It is divided into eons, eras, periods, epochs, and ages. It helps scientists understand the timeline of Earth's formation, the evolution of life, and the occurrence of geological events.
Exoplanets
Exoplanets are planets that orbit stars outside of our solar system; studying them helps scientists understand the formation and evolution of planetary systems.
Transit Method
Detection of exoplanets by observing the periodic dimming of a star's light as a planet passes in front of it.
Orbit Speed from Reading a Transit Graph
The amount of time from the start of the dip in the data to the end of the dip.
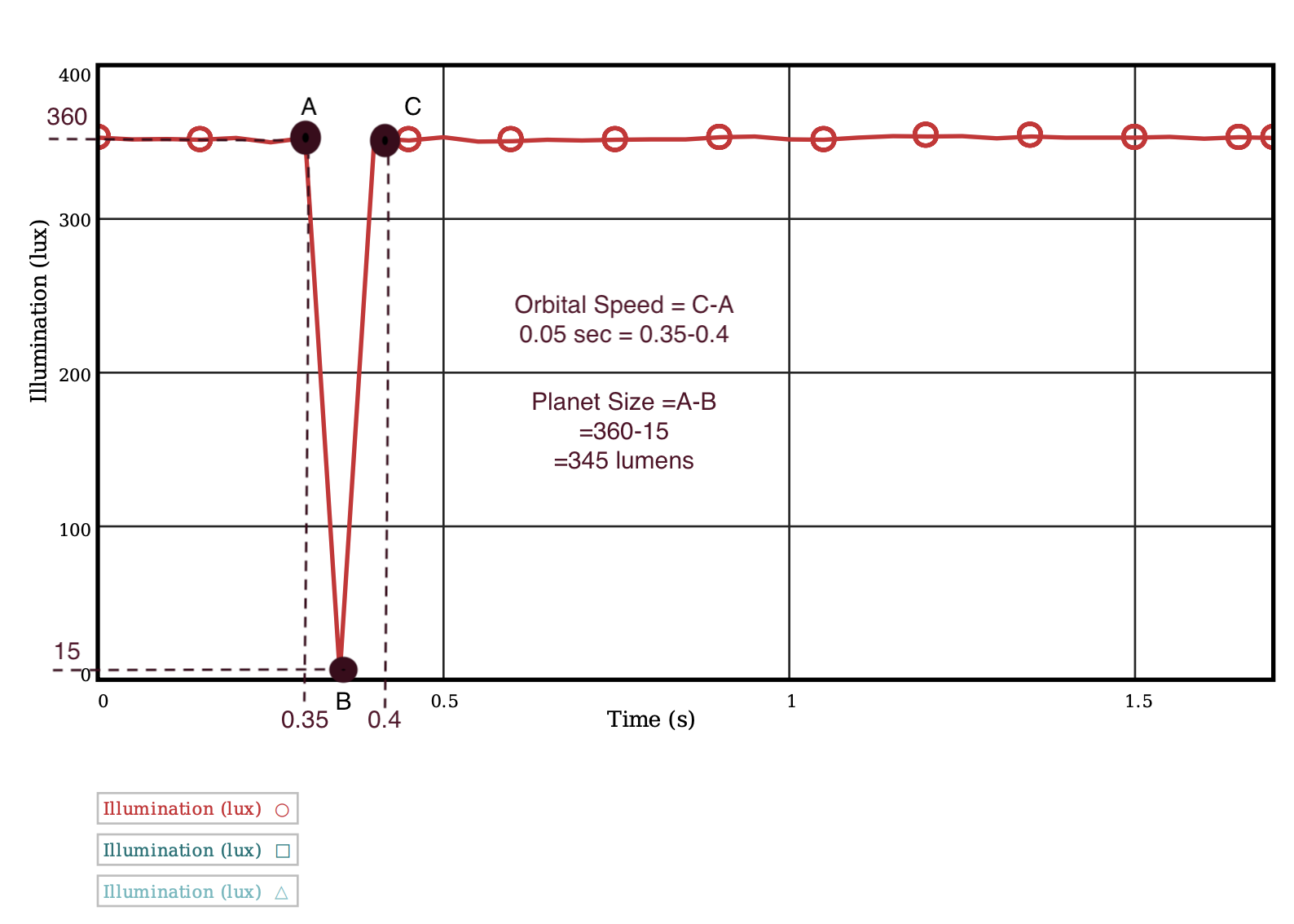
Planet Size from Reading a Transit Graph
Measure the amount of light blocked from before the dip to the lowest point in the dip.
Doppler Effect:
The apparent change in wavelength caused by the relative motion between the source of the wave and the observer
Red Shift
The phenomenon in which light from distant objects appears to be shifted towards longer wavelengths, towards the red end of the spectrum. It is a key observation in astronomy that indicates the expansion of the universe and provides evidence for the Big Bang theory.
Law of Superposition
The principle stating that in undisturbed rock layers, the oldest rocks are found at the bottom, while the youngest rocks are found at the top —> provides relative dates
Radiometric Dating
Process of determining the age of rocks and fossils by measuring the rate of decay of a rock/fossils composition
Absolute Time vs. Relative Time
Absolute Time: A method of dating rocks and fossils using radioactive decay to determine the exact age in years.
Relative Time: A method of dating rocks and fossils based on their position in the geologic column, showing the sequence of events but not the exact age.
Big Idea
The Oceans and Atmosphere fonned and life began during the three eons of the Precambrian, which spans nearly 90 percent of Eaths’s history.