Lecture 2 Synapses, Drugs, Case Study Slides & Study Guide Review
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
What is the mechanism of synaptic transmission affected by?
Cocaine, anti-depressants, anti-anxiety medications, and opioids.
Suppose a cell is no longer just permeable to potassium but isnow more permeable to sodium. What would happen to RMP?
The RMP would depolarize (get more positive).
How is stimulus strength coded in action potentials?
By action potential frequency.
What occurs when potassium concentration outside a neuron is higher than usual?
It would depolarize resting membrane potential
What occurs when sodium concentration outside a neuron is higher than usual?
It would not affect it bc so few leak channels
Resting Membrane Potential
dependent on changes in K+ due to leak channels
Action Potential Duration
Dependent on changes in K+ not Na+ due to Voltage Gated channels in repolarization
What is a synapse?
A cell-to-cell junction between neurons or a neuron and a muscle.
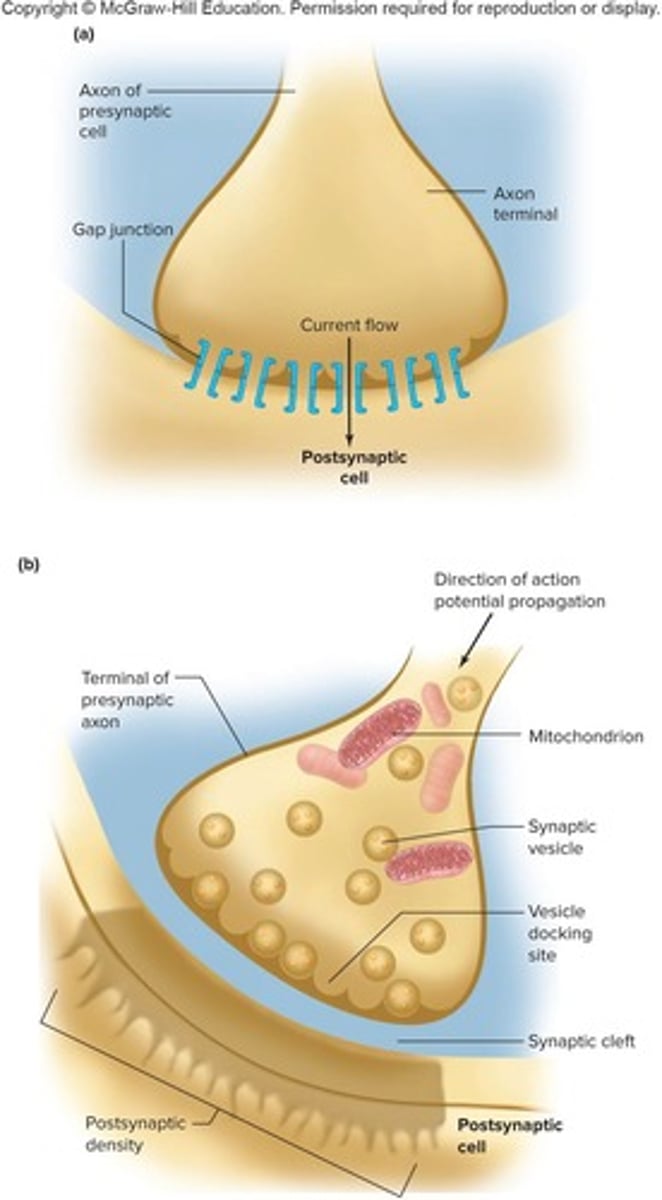
Electrical Synapse
a type of synapse in which the cells are connected by gap junctions, allowing ions (and therefore the action potential) to spread easily from cell to cell
Chemical Synapse
a type of synapse at which a chemical (a neurotransmitter) is released from the axon of a neuron into the synaptic cleft, where it binds to receptors on the next structure (either another neuron or an organ)
Steps 1 in Chemical Transmission
Action Potential propagates down pre-synaptic neuron
Steps 2 in Chemical Transmission
Voltage change from AP opens VG Ca2+ channels, Ca2+ rushes IN to presynaptic terminal
Steps 3 in Chemical Transmission
Ca2+ helps synaptic vesicles fuse w/ pre-synaptic membrane, get release of neurotransmitters into synaptic cleft
Steps 4 in Chemical Transmission
Neurotransmitters bind to receptors on post synaptic cell membrane
Steps 5 in Chemical Transmission
Response in post synaptic cell (general)
Steps 6 in Chemical Transmission
Neurotransmitters removed from synaptic cleft
What determines whether a synapse is excitatory or inhibitory?
The type of neurotransmitter that binds and the ion that flows.
Excitory synapse
synapse at which a neurotransmitter causes the receiving cell to fire, usually becomes more positive
Inhibitory Synapse
a synapse that decreases the likelihood of the downstream neuron sending an action potential. The synapse has become more negative
How do local anesthetics prevent action potentials?
They block voltage-gated channels, preventing them from opening in response to depolarization.
What is the effect of tetrodotoxin on nerve conduction?
It binds to voltage-gated channels and prevents action potentials.
What does the tetanus toxin do to neurotransmitter release?
It destroys SNARE proteins, preventing vesicle fusion and inhibiting neurotransmitter release.
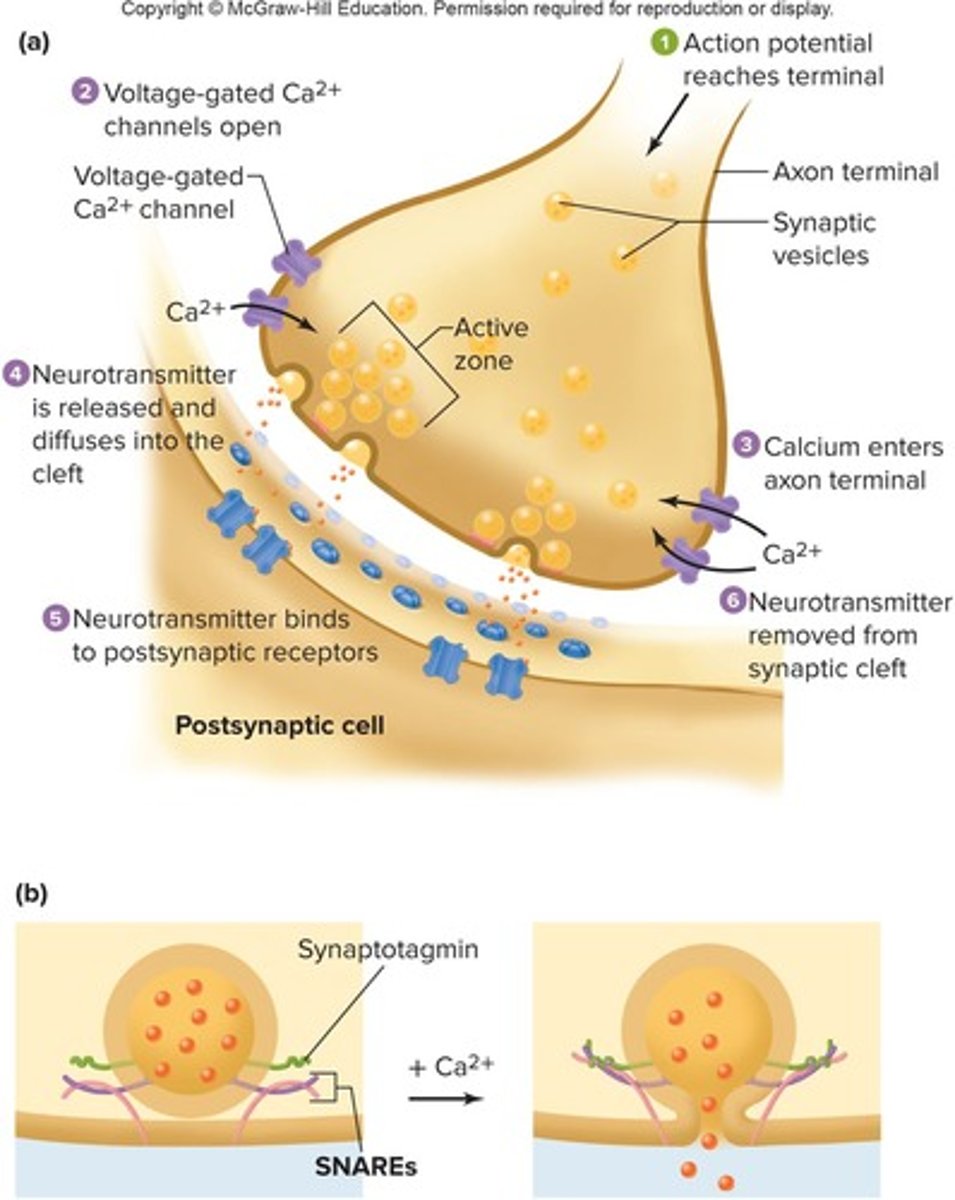
What is the effect of botulinum toxin on neurotransmitter release?
It blocks neurotransmitter release from synaptic vesicles, leading to reduced muscle contraction.
How do benzodiazepines affect GABA receptors?
They increase flux through the GABA receptor, reducing anxiety and inducing sleep.
What happens to a cell's excitability in hyperkalemia?
The cell becomes more excitable.
What is the effect of having more K+ leak channels than normal on cell excitability?
The cell becomes less excitable.
What is the effect of opioids on the presynaptic cell's excitability?
The presynaptic cell becomes more excitable.
What response occurs when a neurotransmitter binds to an ionotropic receptor and permits sodium flux?
Excitatory response.
ionotropic receptors
Is a receptor AND a channel. Ligand binds, channel opens and ions flow out
Metabotropic Receptors
Is a receptor, binding of ligand begins some kind of 2nd msnger cascase (G protein)
A drug might:
A. increase leakage of neurotransmitter from vesicle to cytoplasm, exposing it to enzyme breakdown.
B. increase transmitter release into cleft.
C. block transmitter release.
D. inhibit transmitter synthesis.
E. block transmitter reuptake.
F. block cleft or intracellular enzymes that metabolize transmitter.
G. bind to receptor on postsynaptic membrane to block (antagonist) or mimic (agonist) transmitter action.
H. Inhibit or stimulate second-messenger activity within postsynaptic cell.
SSRIs work by
blocking reuptake protein so that more serotonin stays in the synaptic cleft, which would cause more post-synaptic excitation (because the problem is that there is less serotonin at some synapses)
Cl- is the ion causing the inhibitory response for the neurotransmitter GABA
Benzodiazepine sare GABA agonists and they do so by promoting more GABA transmission and get more postsynaptic inhibition
Opioids inhibit
the modulatory interneuron, thereby causing increase dopamine in the synaptic cleft → pre-synaptic and post-synaptic neuron are excited
What happens when a neurotransmitter binds to a metabotropic receptor that closes a normally open potassium channel?
Excitatory response.
What is the clinical condition diagnosed in the 64-year-old man after gardening in the heat?
Heatstroke.
What is the relationship between the clinical case study and homeostasis?
The man's condition illustrates failure to maintain homeostasis in response to heat.
What is the role of neurotransmitter synthesis, storage, and release in drug action?
Drugs interfere with or stimulate these processes in neurons.
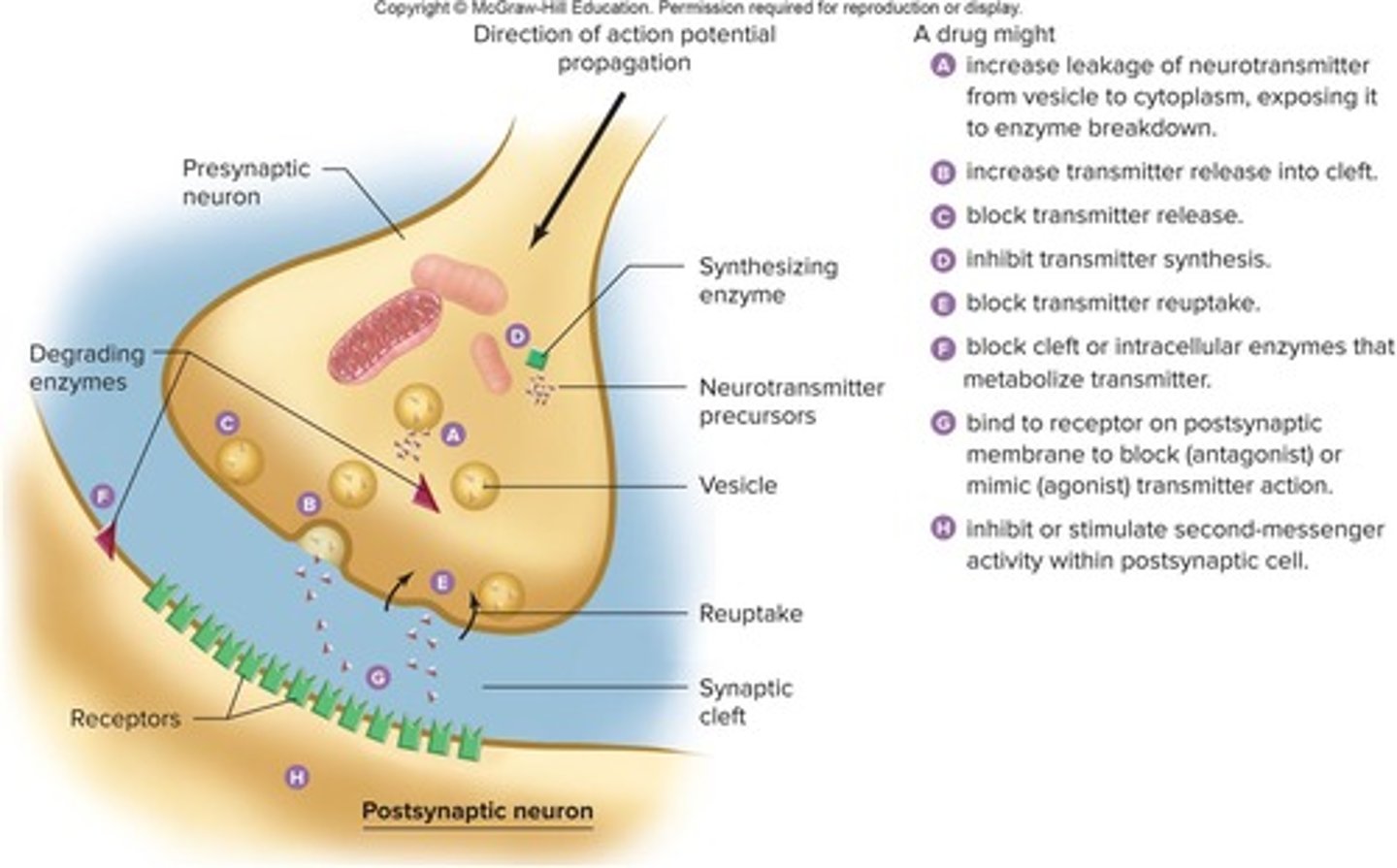
What is the effect of ethanol on GABA synapses?
Ethanol targets synapses that use GABA.