Intro to Human Nutrition Slide Flashcards
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
What functions do nutrients provide?
Energy, heat, structure, and regulatory/signaling molecules.
What are the two main categories of nutrients?
Macronutrients and micronutrients.
What are proteins composed of?
20 common amino acids linked end to end.
What are essential amino acids?
Amino acids the body cannot make (or cannot make in sufficient amounts) but still requires
Why can’t body proteins be synthesized without essential amino acids?
All essential amino acids must be present for protein synthesis.
What are carbohydrates (CHO) composed of?
Simple sugars (1–2 units) and complex carbohydrates (e.g., glycogen).
How much energy do carbohydrates and amino acids provide?
4 kcal/g.
How much energy does fat provide?
9 kcal/g.
What are fats a type of?
Lipids
What are dietary phytochemicals?
Trace chemicals in foods with biological activity.
Why are phytochemicals important?
They affect health and disease risk.
What is fiber made of?
Complex non-digestible carbohydrates.
What are the two types of fiber?
Soluble (binds cholesterol and prevents uptake) and insoluble (adds bulk, promotes movement).
What is the structure of fats in the diet?
Fatty acids (acyl groups + carboxyl function) bound to glycerol = triacylglycerol (TAG) or triglyceride (TG).
Which macronutrient can the human body store the most of?
Fat
Why are vitamins considered micronutrients?
They are required in small amounts.
What functions do vitamins serve?
Co-enzymes, precursors to signaling molecules, regulation of metabolism, normal growth, and cell function.
How are vitamins classified?
Fat-soluble or water-soluble.
How are minerals categorized?
Major (e.g., calcium) and trace (e.g., iron).
Why is water considered a nutrient?
It is the solvent of biological systems, transports substances, regulates temperature, and helps eliminate waste.
What is the predominant component of the human body at normal BMI?
Water
Which type of fiber is most effective at lowering blood cholesterol levels?
Soluble fiber, because it binds cholesterol and prevents absorption in the intestine.
Why does fat provide more energy per gram than carbohydrates or proteins?
Fat has more carbon-hydrogen bonds and less oxygen, making it more reduced and capable of releasing more energy during oxidation.
What role do essential amino acids play in growth and repair?
They provide the necessary building blocks for protein synthesis, which supports tissue growth, repair, and enzyme/hormone production.
How do water-soluble vitamins differ in storage and excretion compared to fat-soluble vitamins?
Water-soluble vitamins are not stored extensively; excess is excreted in urine. Fat-soluble vitamins are stored in fat and the liver, making deficiencies slower to develop but toxicities more likely if overconsumed.
Why can fat be considered the most efficient form of energy storage in the body?
Fat is energy-dense (9 kcal/g) and can be stored compactly without water, unlike glycogen, which is stored with water.
Which nutrient class includes both structural and signaling roles in the body?
Proteins (structural roles in muscle, connective tissue, etc.) and lipids (structural in membranes and signaling as hormones, prostaglandins).
What risks can arise from deficiencies in trace minerals like iron?
Iron deficiency can cause anemia, fatigue, impaired oxygen transport, weakened immunity, and reduced cognitive function
Why is water critical in maintaining homeostasis?
Water regulates temperature, transports nutrients and waste, maintains blood volume/pressure, and provides the medium for biochemical reactions.
How do phytochemicals differ from vitamins and minerals in function and classification?
Phytochemicals are bioactive plant compounds not classified as essential nutrients, but they influence health (e.g., antioxidants, anti-inflammatory, cancer-preventive effects).
What would happen if you ate a cup of ice-cream
(500 Kcal) every midnight for the next 10 years?
- Would you gain almost a pound (~ 3,500
Kcal) of fat every week, indefinitely?
No because of adaptive energy expenditure (AEE)
if you reduced food intake by 500 Kcal/day for
the next 10 years?
- Would you lose almost a pound a week
indefinitely?
No
What is adaptive energy expenditure?
how your body adjusts the number of calories it burns to adapt to things like weight loss, weight gain, or environmental stressors.
Two main factors have been observed for
people with successful long-term weight
loss, defined as >30# for > 5 years
(retrospective analysis of weight loss
registries)
1. Voluntary exercise ~ 3,000 KCal/week
(this is not marathon running! It is do-able)
2. Tendency to be on low energy density/low-fat
diets
What is fitness?
Capacity to do aerobic work (oxygen requiring exercise)
Which is worse, being “skinny” fat or obese for cardiorespiratory fitness (directly correlates to mortality)
“Skinny” fat
what is The major determinant of Resting Energy Expenditure (REE)
Lean muscle mass (burn more calories when resting and working out)
What are the 4 macronutrients?
Lipids/fats, carbohydrates, protein, and water
What are the 2 micronutrients?
Vitamins, minerals,
Humans have a large capacity to store what?
Fat
Cells of lean tissue are made of around…
20% protein
Are a small amount of big fat cells more healthy than a large amount of small fat cells?
No, this is because big fat cells release more fatty acids into the bloodstream, which is where most health problems stem from.
Which is less healthy: Central (Apple shaped) adipose or gluteo-femoral (pear shaped) adipose?
Apple shaped adipose as fat is near vital organs and spillage of fatty acids into these areas is what causes serious health issues.
What are the two main types of carbohydrates?
Simple sugars (ex: sucrose, lactose) and complex carbohydrates (ex: grains, beans)
Vitamins are required because…
Our bodies cannot synthesize (to make ourselves) them
What are the two categories of vitamins?
Fat-soluble (ex: vitamin A,D) and water-soluble (ex: vitamin B and C)
Minerals are under what two categories?
Major (calcium, sodium, potassium) and trace (iron, zinc, copper)
What are the two types of fibers and what do they do for the body?
Insoluble fiber: speeds movement of food through the digestive system
Soluble fiber: absorbs cholesterol and prevents its uptake (prevents build up of plaque from fatty acids in arteries)
What is digestion?
converts chemicals in food into molecules that can be absorbed
What is absorption?
transports digested molecules from the gastrointestinal tract into the interior of the body.
What is transit time?
The time it takes food to go through your gastrointestinal tract (GI) (mouth to anus)
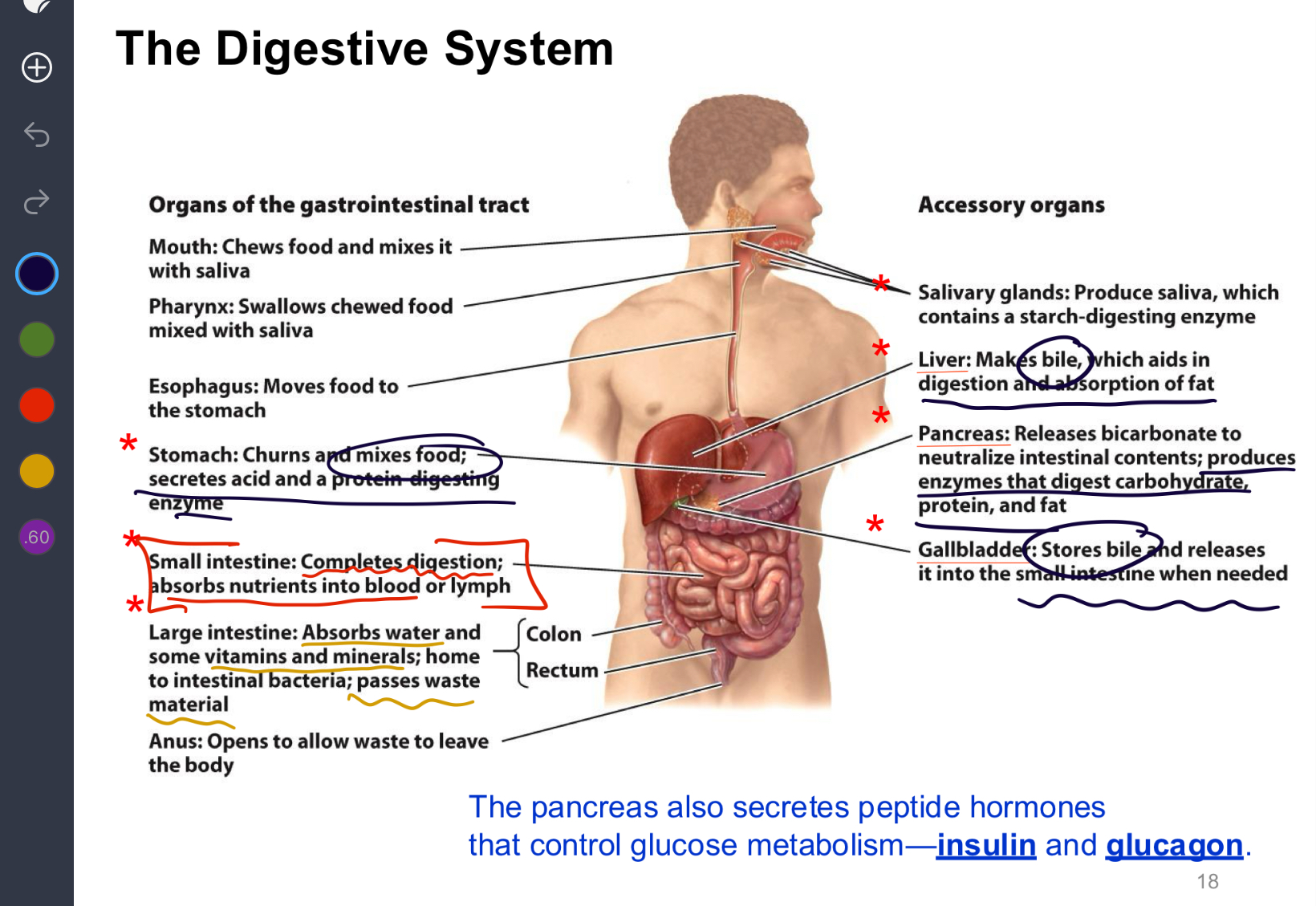
(Study this system)
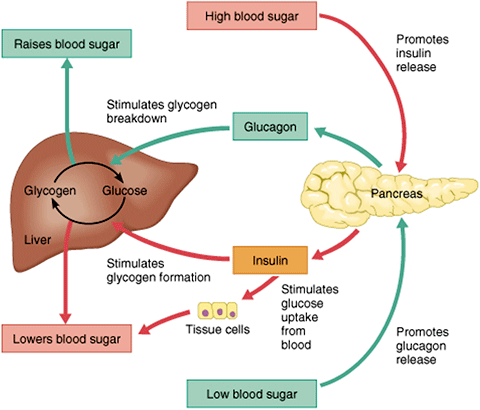
What does insulin do? What does the cycle look like?
What it does:
Secreted by β-cells of the pancreas (islets of Langerhans).
Lowers blood glucose by:
Increasing glucose uptake into muscle and fat cells.
Stimulating glycogen synthesis in liver/muscle (glycogenesis).
Promoting fat storage (lipogenesis).
Enhancing protein synthesis.
Inhibits glycogen breakdown, gluconeogenesis, and lipolysis.
Cycle (when glucose is high, e.g. after a meal):
Blood glucose rises → pancreas releases insulin.
Insulin signals cells to absorb glucose.
Liver converts excess glucose → glycogen.
Blood glucose returns to normal → insulin secretion decreases.
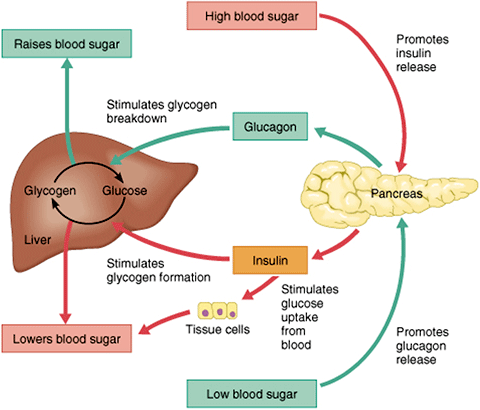
What does glucagon do? What does the cycle look like?
What it does:
Secreted by α-cells of the pancreas.
Raises blood glucose by:
Stimulating glycogen breakdown in the liver (glycogenolysis).
Stimulating glucose production from non-carbs (gluconeogenesis).
Promoting fat breakdown (lipolysis → glycerol for gluconeogenesis, fatty acids for energy).
Cycle (when glucose is low, e.g. fasting/exercise):
Blood glucose drops → pancreas releases glucagon.
Liver breaks down glycogen and makes new glucose.
Glucose enters bloodstream.
Blood glucose returns to normal → glucagon secretion decreases.
Which intestine houses bacteria?
Large Intestine
Which intestine is sterile?
Small intestine
Catabolism
breaking down food chemicals (catabolizes) into smaller molecules so they can be absorbed to be used to generate energy by releasing energy trapped in chemical bonds.
Anabolism
generates complex structures from simple molecules.
ex: amino acids to protein, fatty acids into triglycerides, simple sugars into glycogen, nucleic acid bases into polynucleotides (DNA, RNA)
What do DRIs stand for?
Dietary Reference Intake Values
What do DGAs stand for?
Dietary Reference for Americans