DSA30 - CNS Pathology - Infections including Prion Diseases
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
-Hematogenous
-Direct Implantation
-Transplacental
-Contact from infected birth
-Local extension
-PNS retrograde spread
Name the ways infection can spread into the CNS
From pneumonia, infected heart valve, sepsis
What is/are cause(s) of ARTERIAL hematogenous spread of infection into the CNS?
Retrograde infection from facial veins to meningeal sinuses
What is/are cause(s) VENOUS hematogenous spread of infection into the CNS?
Penetrating traumatic or Iatrogenic spread
What is/are cause(s) of Direct Implantation of infection into the CNS?
Toxoplasmosis or CMV
What is/are cause(s) of Transplacental spread of infection into the CNS?
Herpes Simplex
What is/are cause(s) of Contact infection during birth (thru birth canal) going into the CNS?
-Infection of nasal sinuses/teeth/skull/vertebrae
-Congenital malformation (myelomeningocele - open path to meninges)
What is/are cause(s) of local infection extending into the CNS?
Viruses (rabies, herpes zoster)
What is/are cause(s) of PNS retrograde spread into the CNS?
Inflammatory process involving leptomeninges - usually infectious; only involves subarachnoid space
Define Meningitis
Inflammation from nonbacterial irritant in subarachnoid space
Define Chemical Meningitis
Meningitis caused by infiltration of subarachnoid space by cancerous cells - not predominantly inflammatory
Define Carcinomatous meningitis (meningeal carcinomatosis)
PNS cancer that attacks the meninges - mimics inflammatory process
Define Meningeal lymphomatosis
Inflammatory process involving leptomeninges of the subarachnoid space + brain parenchyma
Define Meningoencephalitis
Bacterial
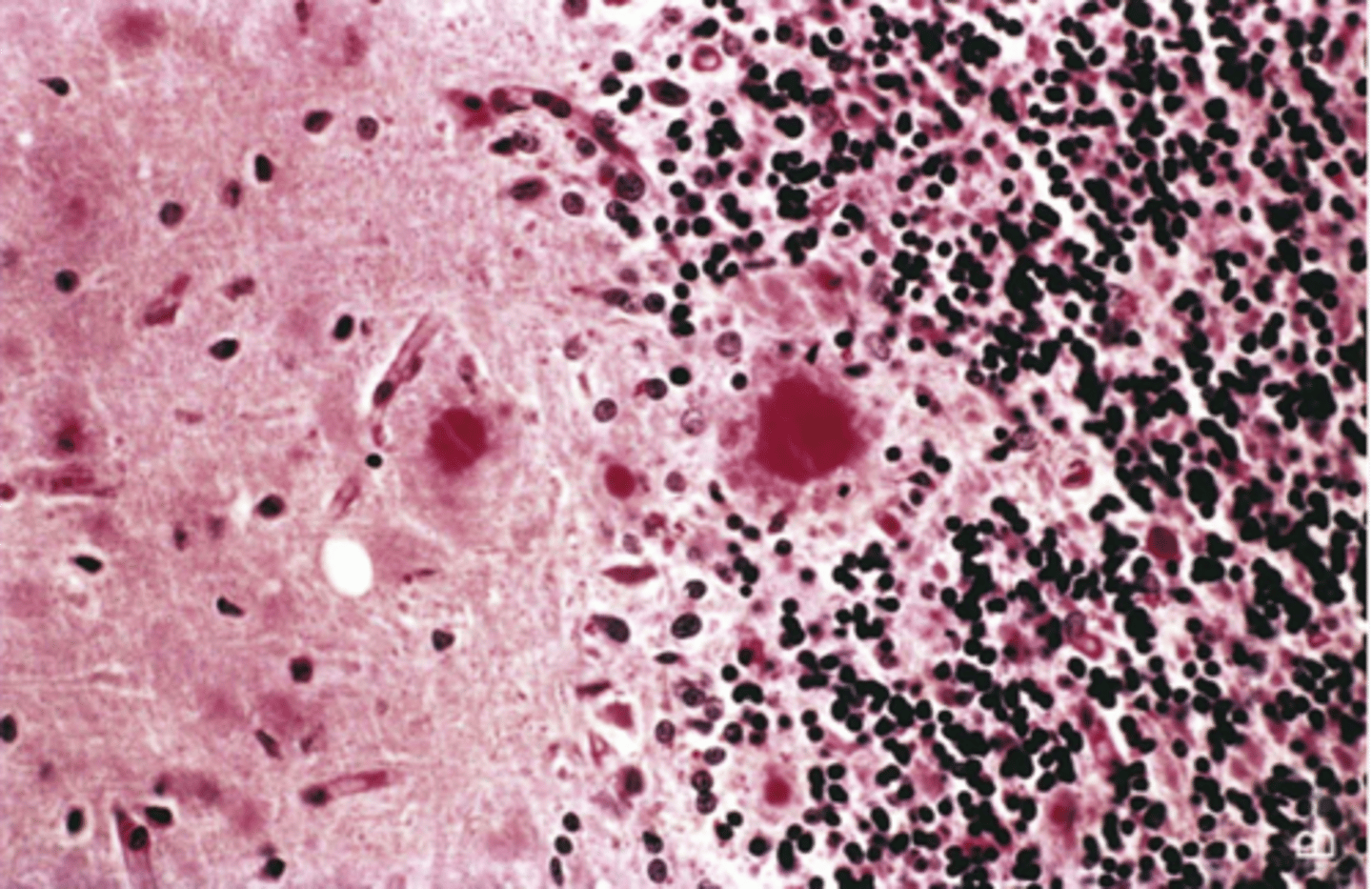
If CSF contents are found to be acutely pyrogenic (aka pus), what can be the cause of infection?
Acute Pyogenic/Bacterial Meningitis
Define Condition:
Neonates = E coli/GBS,
Adolescents = N. menigitidis,
Older = S. pneum or L. monocytogenes
-Sx: fever, headache, stiff neck, photophobia, irritability, clouded consciousness
-Dx: LP = ELEVATED pressure, High Neutrophils, High Protein, LOW GLUCOSE
**Leptomeningeal venous thrombi may occur --> hemorrhagic infarcts**
-Tx: Cured with prompt therapy (otherwise lethal)
Viral
If CSF contents are found to be aseptic (neg culture), what can be the cause of infection?
Aseptic (Viral) Meningitis
Define Condition:
Can be due to rickettsia or Autoimmune condition - MOST due to enteroviruses
-Sx: fever, headache, stiff neck, photophobia, irritability, clouded consciousness
-Dx: NEG Bacterial cultures, LP = Lymphocytosis, Moderate Protein, Normal Glucose; May due serology/nucleic acid testing
-Tx: Self-limited (Tx Sx)
TB, spirochetes or fungi
If CSF contents are found to be of a chronic irritant, what can be the cause of infection?
Tuberculosis and mycobacterioses causing Chronic Bacterial Meningioencephalitis
Define Condition AND Cause:
-Sx: fever, headache, stiff neck, photophobia, irritability, clouded consciousness
-Dx: LP = Mononuclear cells (some neutrophils), VERY HIGH PROTEIN, Low to normal glucose; Histo (long term effects) = Arachnoid fibrosis, hydrocephalus ==> mass (tuberculoma)
Neurosyphilis causing Chronic Bacterial Meningoencephalitis
Define Condition AND Cause:
Occurs in 10% of untreated pts
-Sx: fever, headache, stiff neck, photophobia, irritability, clouded consciousness; certain types:
--Meningovascular
--Paretic (lose mental/physical functions, mood change, dementia)
--Tabes dorsalis (dorsal sensory nerve roots destroyed)
-Dx: LP = Mononuclear cells (some neutrophils), VERY HIGH PROTEIN, Low to normal glucose; For Meningovasc = basal obliterative endarteritis, with plasma cells; Paretic = neuron destruction, microglial proliferations
Neuroborreliosis (from Lyme disease - spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi) causing Chronic Bacterial Meningoencephalitis
Define Condition AND Cause:
Occurs in 10% of untreated pts
-Sx: fever, headache, stiff neck, photophobia, irritability, clouded consciousness - will see sx of meningitis, neuropathies, encephalopathy
-Dx: LP = Mononuclear cells (some neutrophils), VERY HIGH PROTEIN, Low to normal glucose;
-Chronic meningitis (high protein, low glucose, mild lymphocytic pleocytosis)
-Vasculitis, infarcts (Mucor for diabetics & Aspergillus)
-Parenchymal invasion (via Virchow-Robin spaces)
What are the 3 basic patterns of CNS fungal infection?
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)
Mucor infection will often occur in diabetics when they're enduring what?
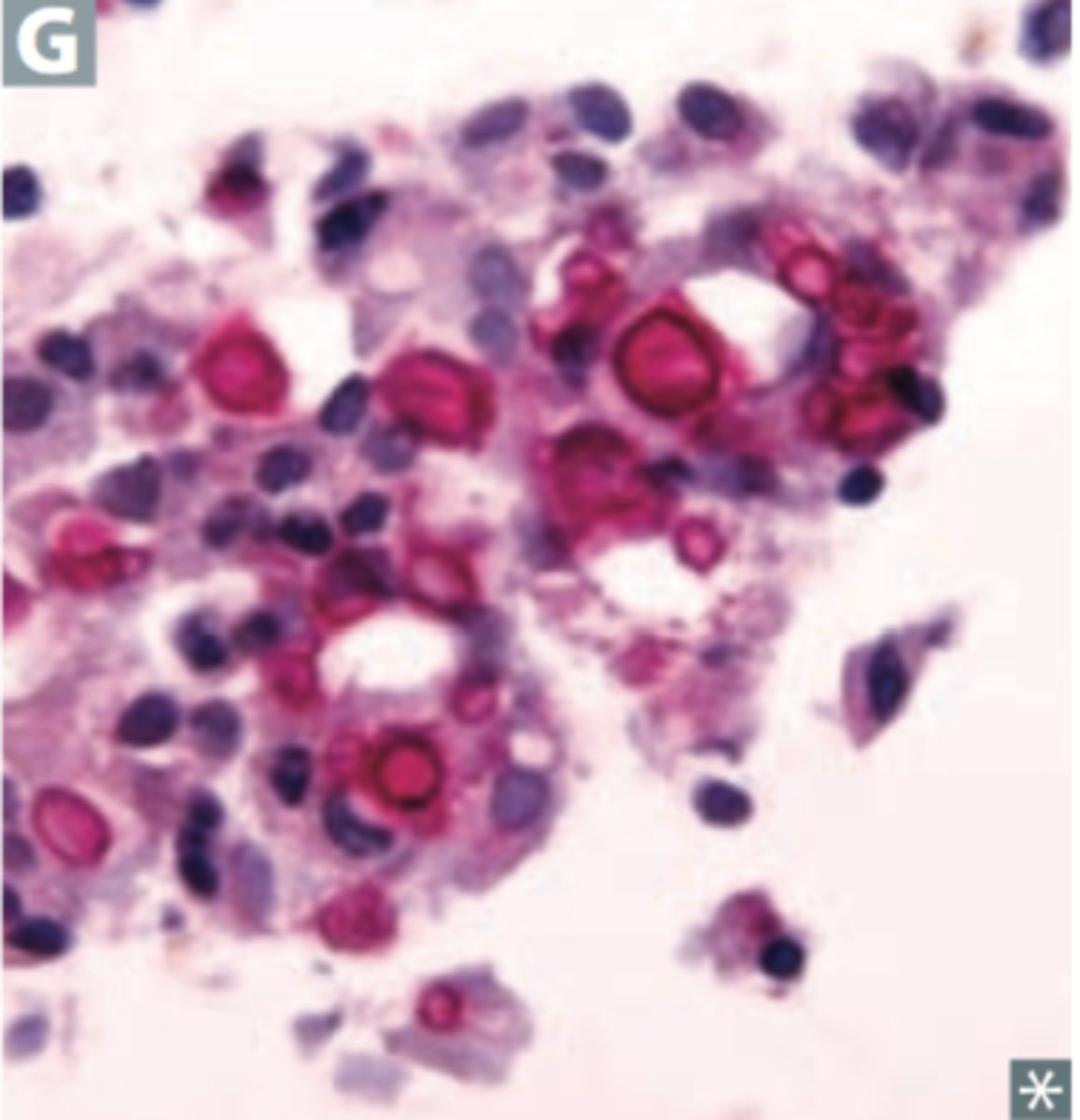
Mucoid capsule with yeast, antigen test, (+) India Ink Stain
What diagnostic characteristics are seen with Cryptococcal meningitis (mainly seen in immunocompromised pts - HIV POSITIVE)?
Tend to see BASILAR MENINGITIS (brainstem)
What diagnostic characteristics are seen with Histoplasmosis meningitis?
Usually produces multiple microabscesses
What diagnostic characteristics are seen with Candida meningitis?
high
Meningitis from Coccidiodes has a (low/high) fatality rate
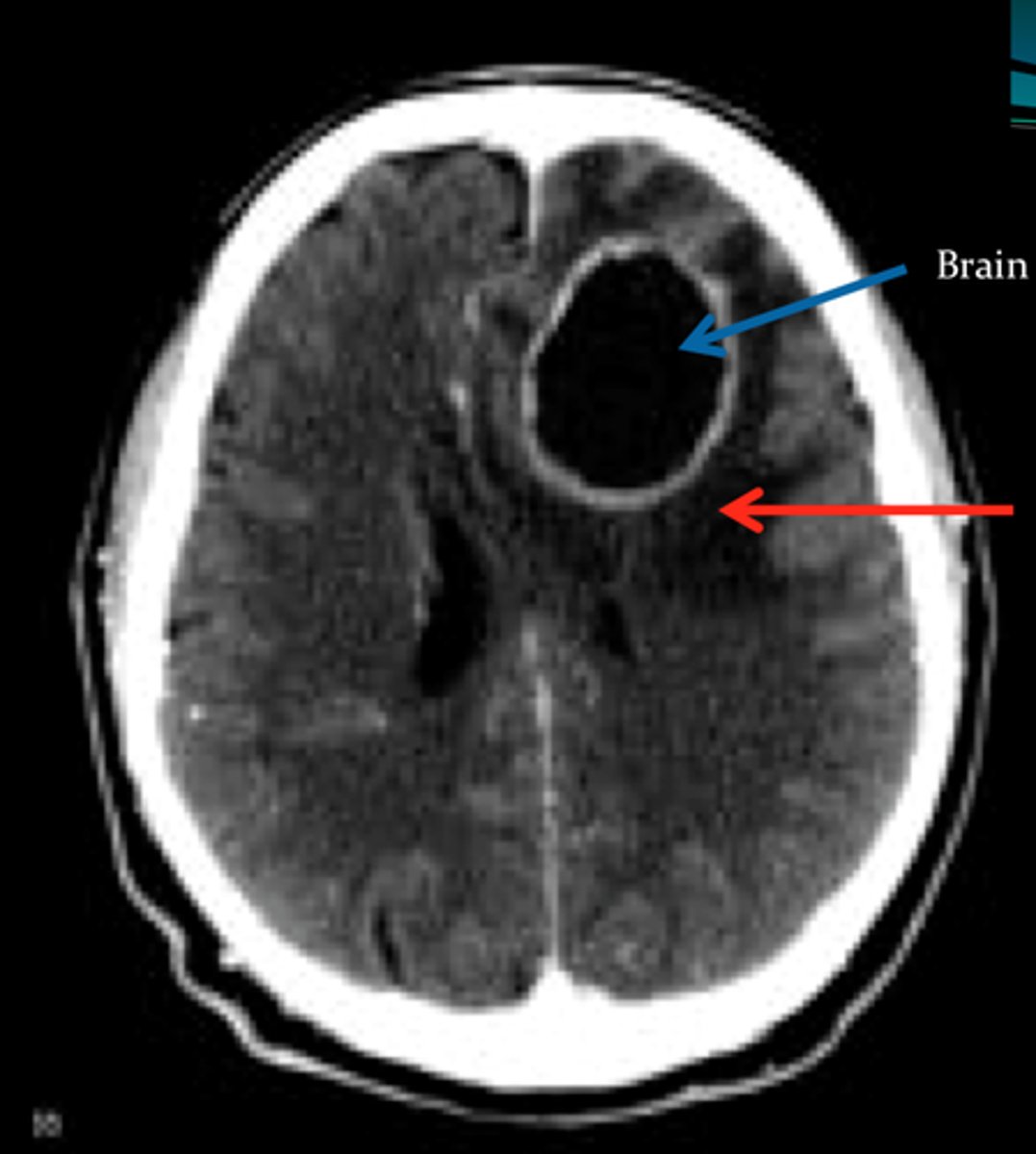
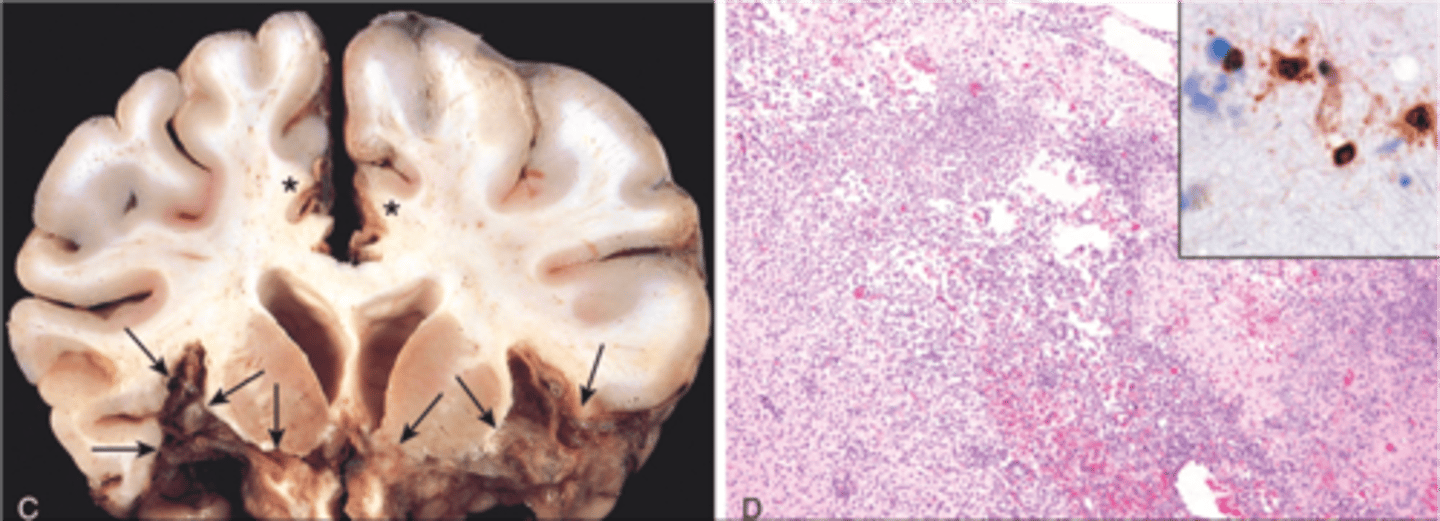
Brain Abscess
Define Condition:
Discrete destructive lesion with liquefactive necrosis, surrounding edema and rim of granulation tissue, with fibrosis and gliosis
-May be implanted, local extension from sinusitis or mastoiditis, hematogenous (STAPH IV spread)
-Dx: IICP, Herniation, LP = HIGH PROTEIN, PMNs, normal glucose (abscess is walled off)
-Tx: surgical drainage plus antibiotics may reduce mortality to 10%.
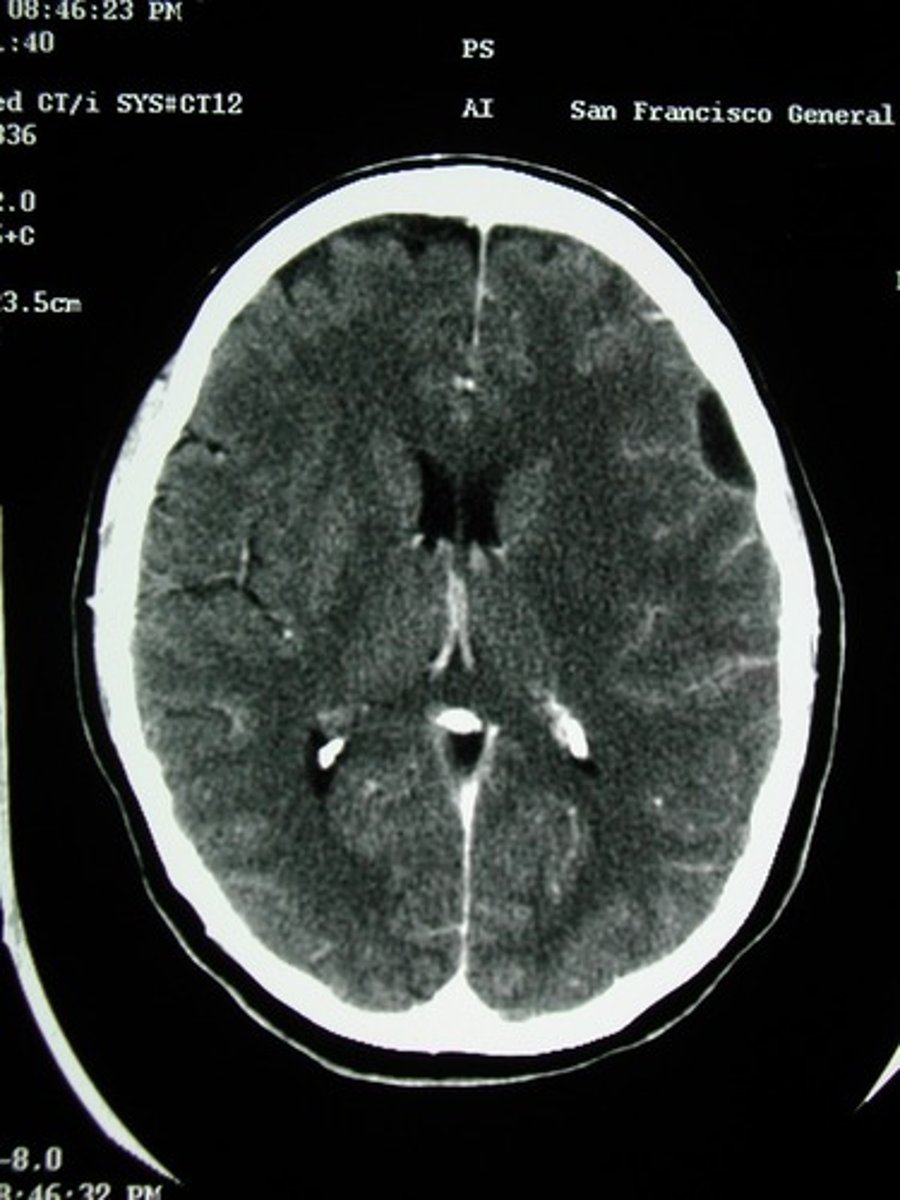
Epidural Abscess
Define Condition:
Collection of pus between the outer covering of the brain and spinal cord and the bones of the skull or spine
-Due to adjacent sinusitis or osteomyelitis
-Dx: IICP, Herniation, LP = HIGH PROTEIN, PMNs
-Tx: surgical emergency if spinal involvement
Subdural empyema
Define Condition:
A collection of pus between the dura and the arachnoid membranes
-Complication of sinus infection, but can also be due to ear infection, cranial trauma or surgery, and bacteremia
-May produce mass effect, arachnoid and subarachnoid areas are spared
-Dx: IICP, Herniation, LP = HIGH PROTEIN, PMNs
All show high CSF cell count and protein, normal glucose
What do Brain Abscess, Epidural Abscess, and Subdural empyema all have in common?
HIGH PROTEIN, High PMNs, VERY LOW GLUCOSE
What are the main signs for BACTERIAL MENINGITIS?
Mod High Protein, High LYMPHOCYTES, normal Glucose
What are the main signs for VIRAL MENINGITIS?
VERY HIGH PROTEIN, High LYMPHOCYTES, LOW to Normal Glucose
What are the main signs for TB/FUNGAL MENINGITIS?
High Protein, High PMNs, Normal Glucose
What are the main signs for ABSCESS?
Perivascular mononuclear infiltrates and Microglial nodules
What are the hallmarks for Viral Meningoencephalitis?
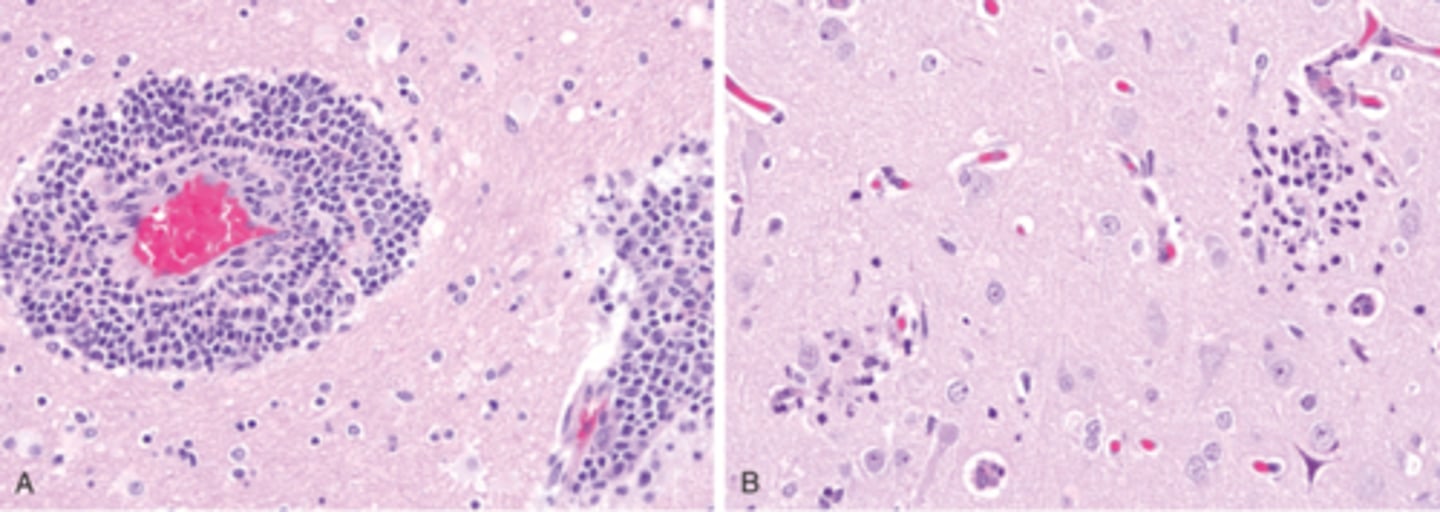
Arbovirus (arthropod-borne, eg West Nile), Viral Meningoencephalitis
Define Virus:
Viral Infection of meninges
Info:
-Lymphocytes
-Necrosis
-Neuronophagia
-Microglial nodules
Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1), Viral Meningoencephalitis
Define Virus:
Viral Infection of meninges
Info:
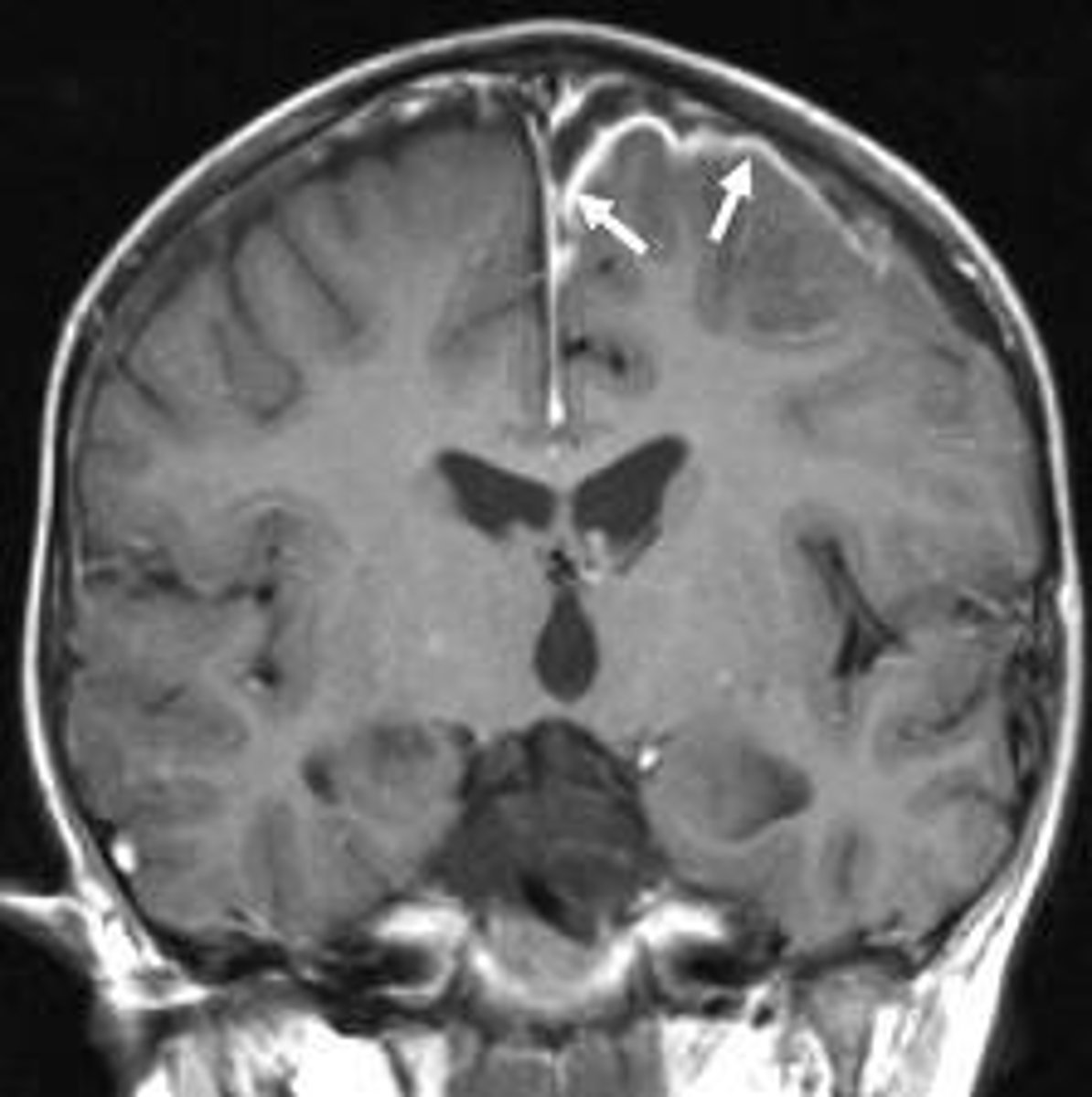
-Seen in inferior bilateral temporal lobes (may see ring enhancing lesion)
-Necrosis
-Cowdry type A VIRAL inclusions (uninucleate cells)
-+PCR Test
Varicella-Zoster, Viral Meningoencephalitis
Define Virus:
Viral Infection of meninges
Info:
-Shingles
-Latency in DRG
Cytomegalovirus (CMV), Viral Meningoencephalitis
Define Virus:
Viral Infection of meninges
Info:
-May be in utero
-Periventricular necrosis
-Has cytoplasmic AND nuclear inclusions
Poliomyelitis, Viral Meningoencephalitis
Define Virus:
Viral Infection of meninges
Info:
-Enterovirus
-Kills motor neurons
-Flaccidity
Rabies, Viral Meningoencephalitis
Define Virus:
Viral Infection of meninges
Info:
-Ascends nerve from bite/contact to CNS
-Negri body (Cytoplasmic inclusions)
-Hyperexcitability (delusional)
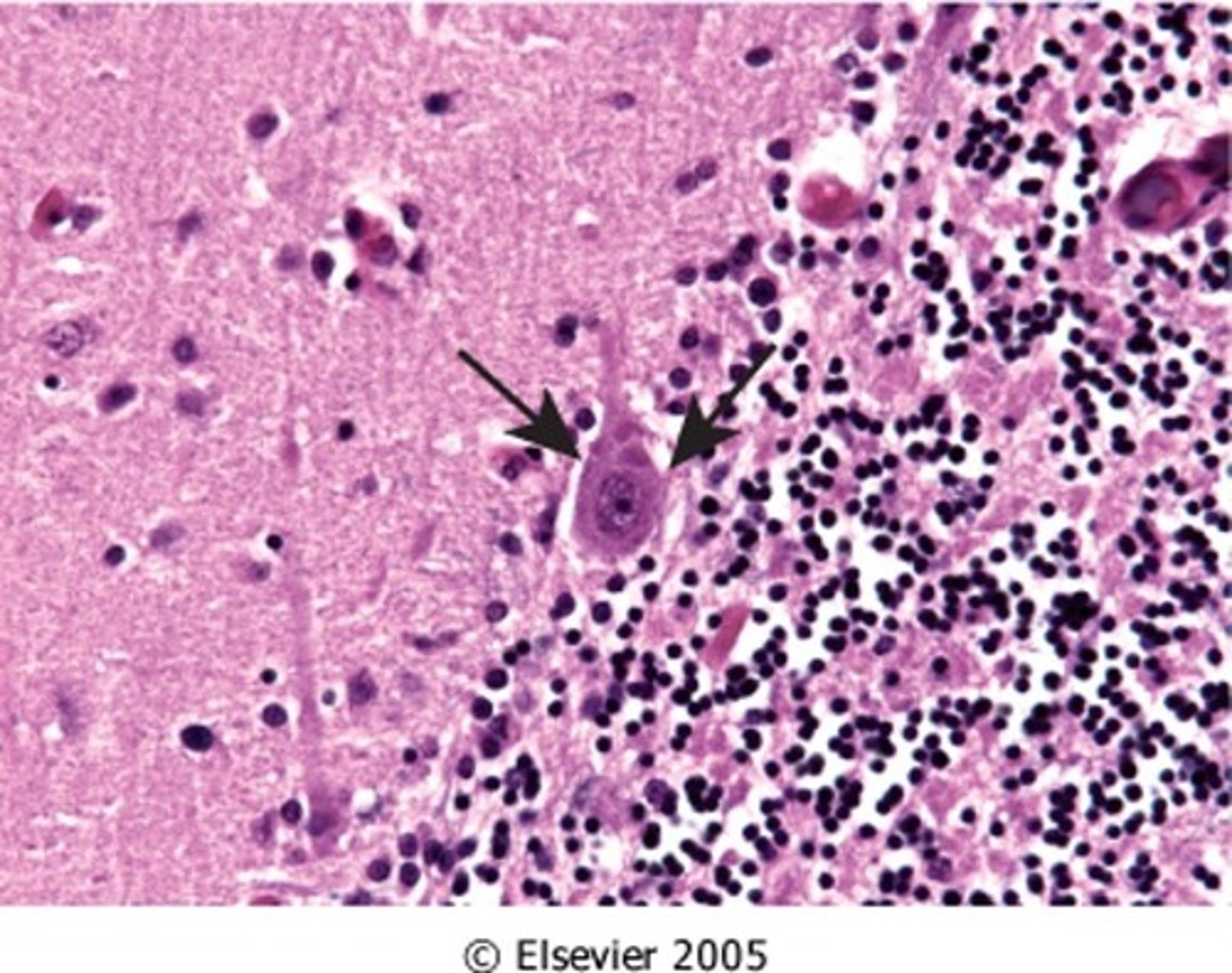
HIV, Viral Meningoencephalitis
Define Virus:
Viral Infection of meninges
Info:
-Microglial Encephalitis (microglial nodules w/ multinucleated macrophages)
-Will live in HISTIOCYTES
-Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome
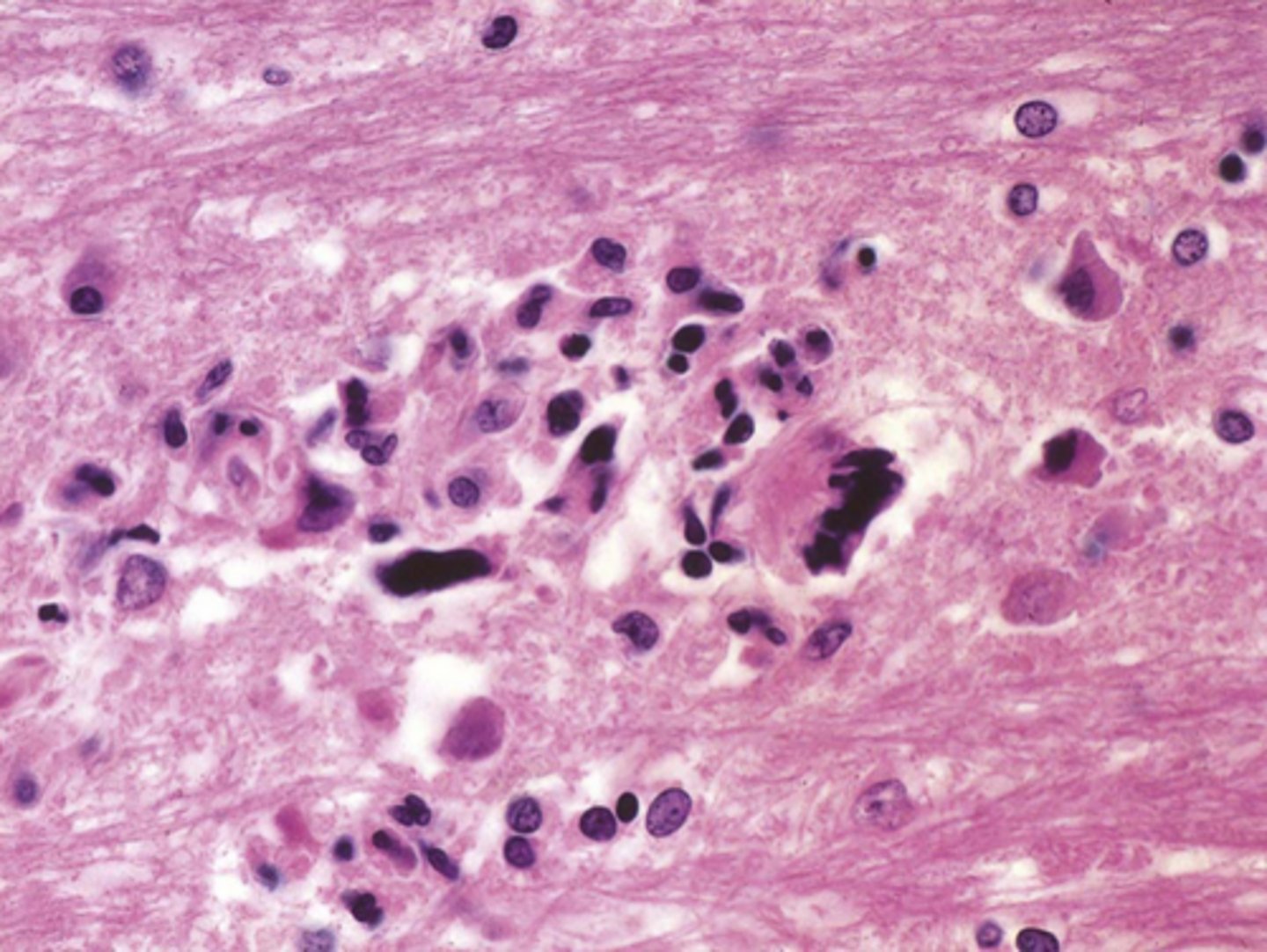
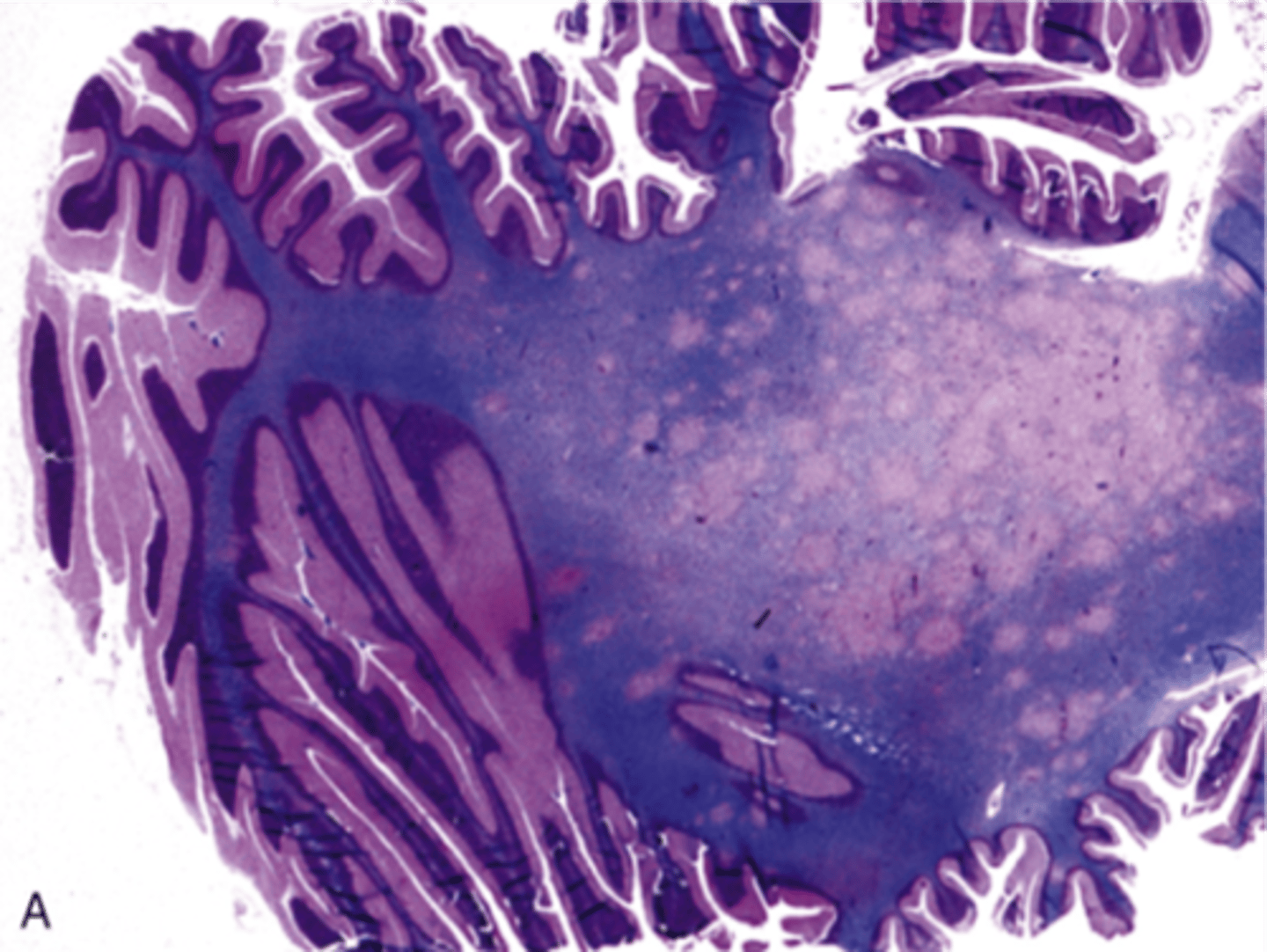
Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML), Viral Meningoencephalitis
Define Virus:
Viral Infection of meninges
Info:
-Due to JC polyomavirus; Possible reactivation of latent virus (esp if immunocompromised)
-Infects oligodendrocytes => demyelination
-Sx: dementia, weakness, visual loss, and ataxia
-FATAL
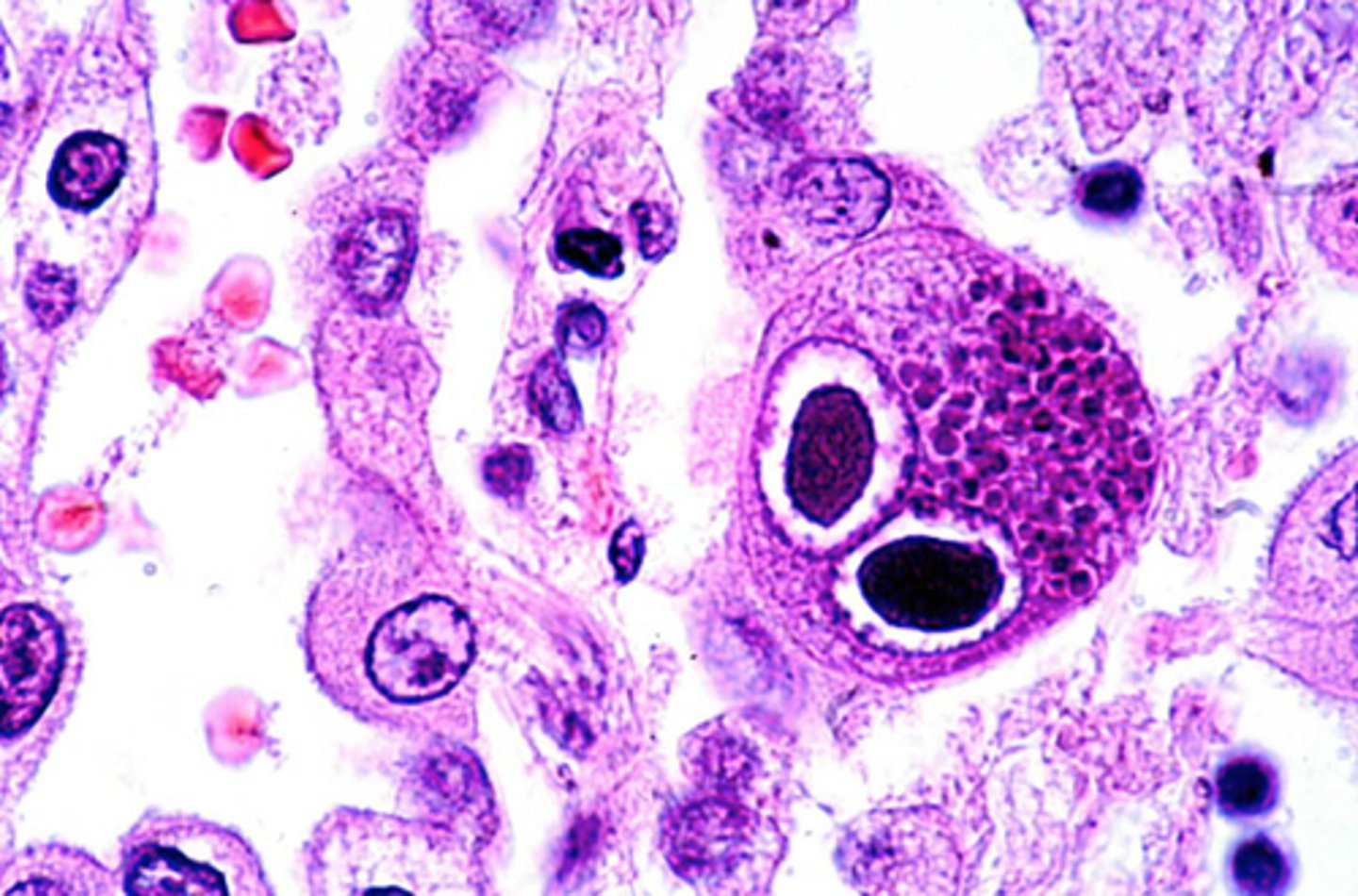
Toxoplasmosis (Toxoplasma gondii)
Define CNS Infection Cause:
-Newborns can be exposed to parasite transplacentally (cat poop) - aka pregnant women susceptible
-Sx: headache, seizures
-Due to Tachyzoites and bradyzoites
-If immunosuppressed --> forms abscess
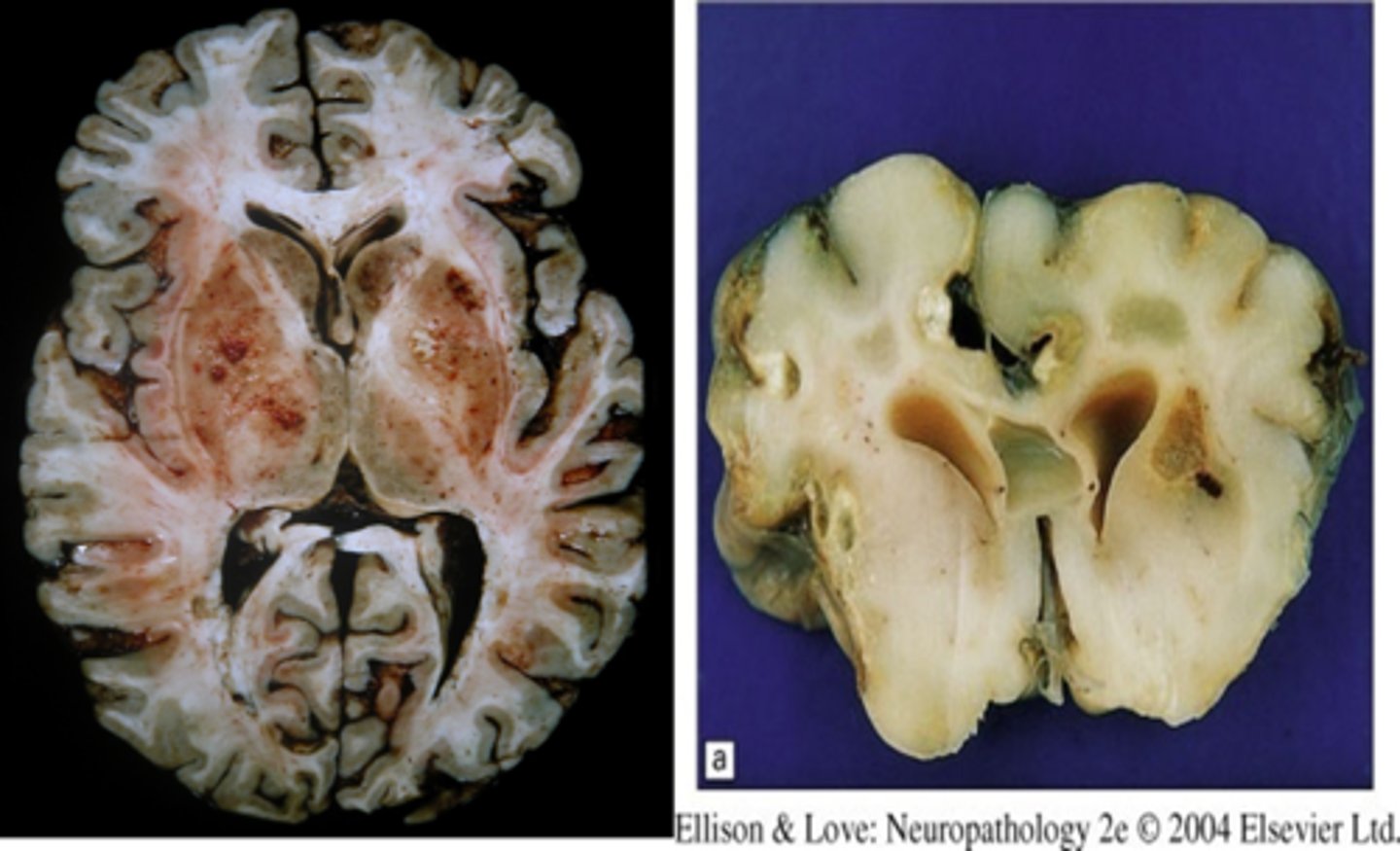
localizes; can spread
In Toxoplasmosis, the abscess (localizes/can spread); In Cryptococcus, the abscess (localizes/can spread)
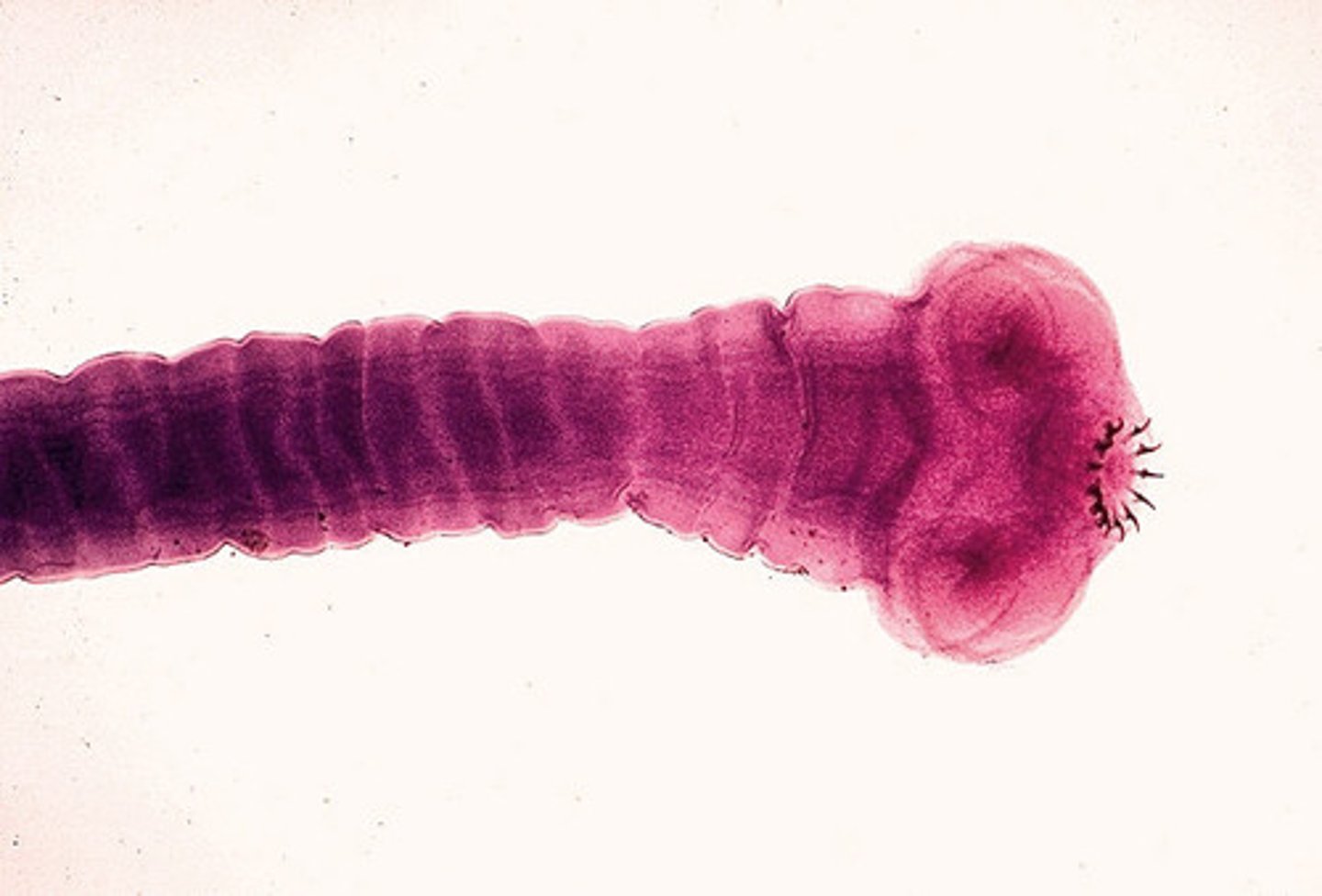
Cysticercosis (Echinococcosis)
Define CNS Infection Cause:
-Via fecal-oral transmission
-Encysted tapeworm in other organs and brain
-Host inflammatory response (influx of eosinophils and gliosis)
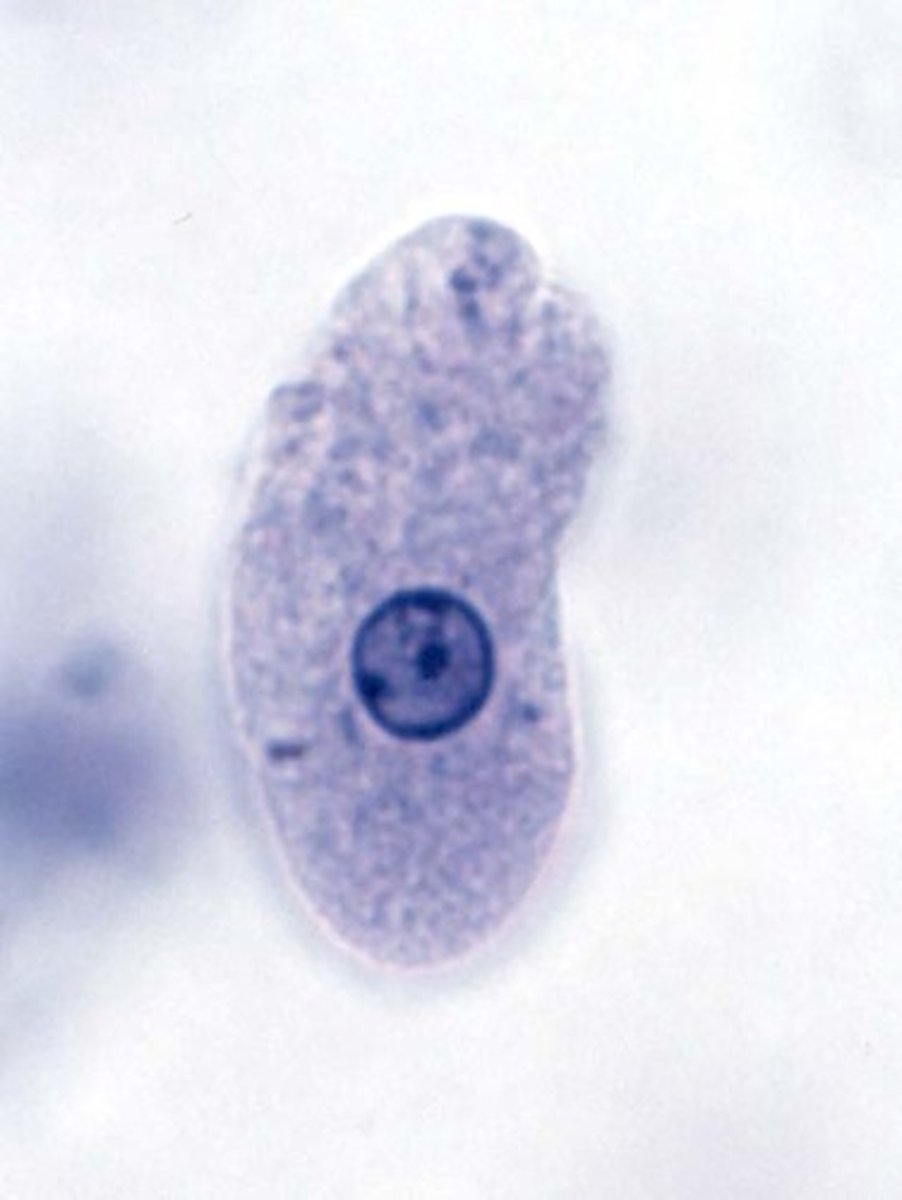
Naegleria
Define CNS Infection Cause:
-Amebic Infection
-Rapidly fatal necrotizing encephalitis
Entameba histolytica
Define CNS Infection Cause:
-Amebic Infection
-Hematogenous spread from colon
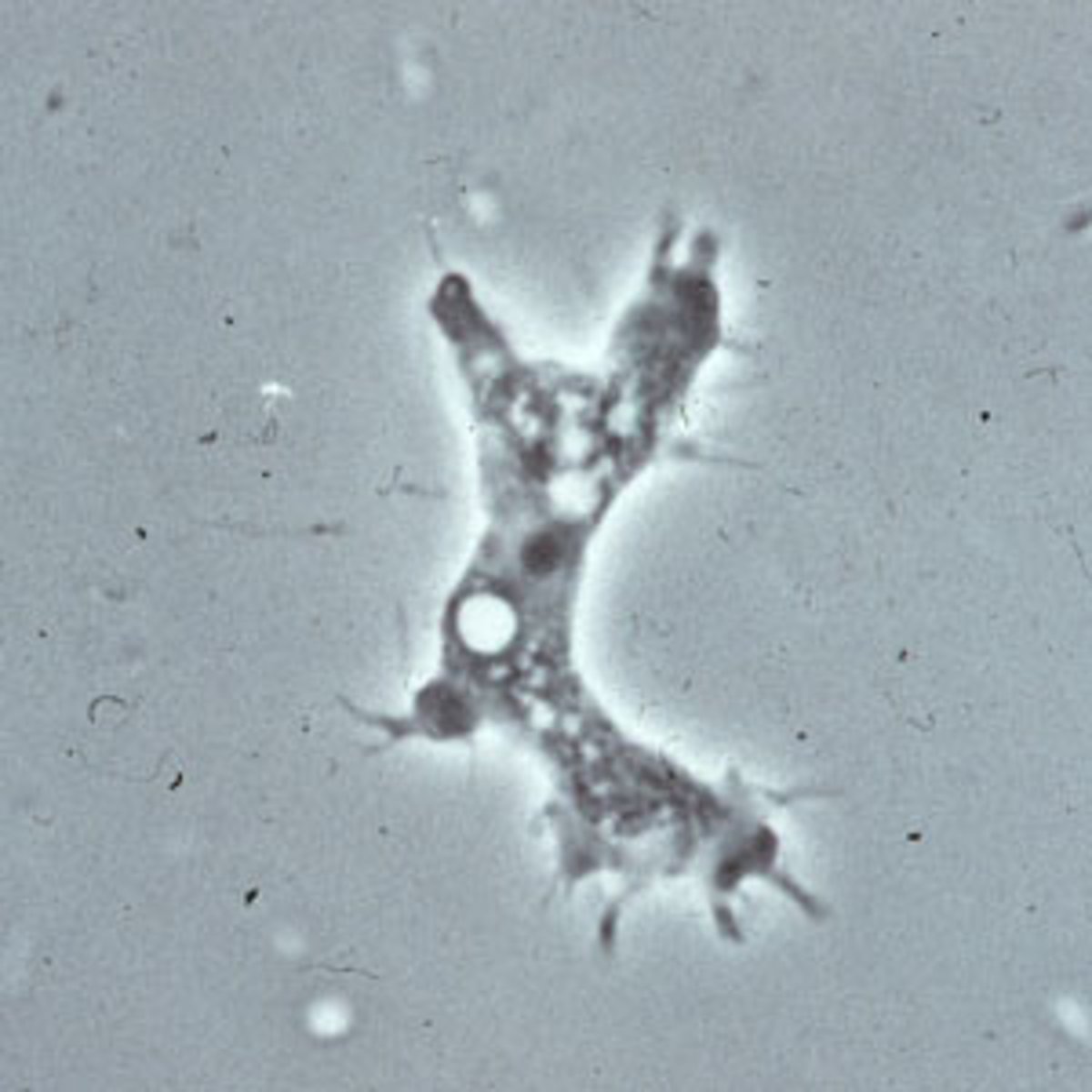
Acanthamoeba
Define CNS Infection Cause:
-Amebic Infection
-Chronic granulomatous disease
Trypanosomiasis (malaria)
Define CNS Infection Cause:
African sleeping sickness
-Spread by the bite of the tsetse fly
-May be seen with Chagas' disease (serious cardiomyopathy)
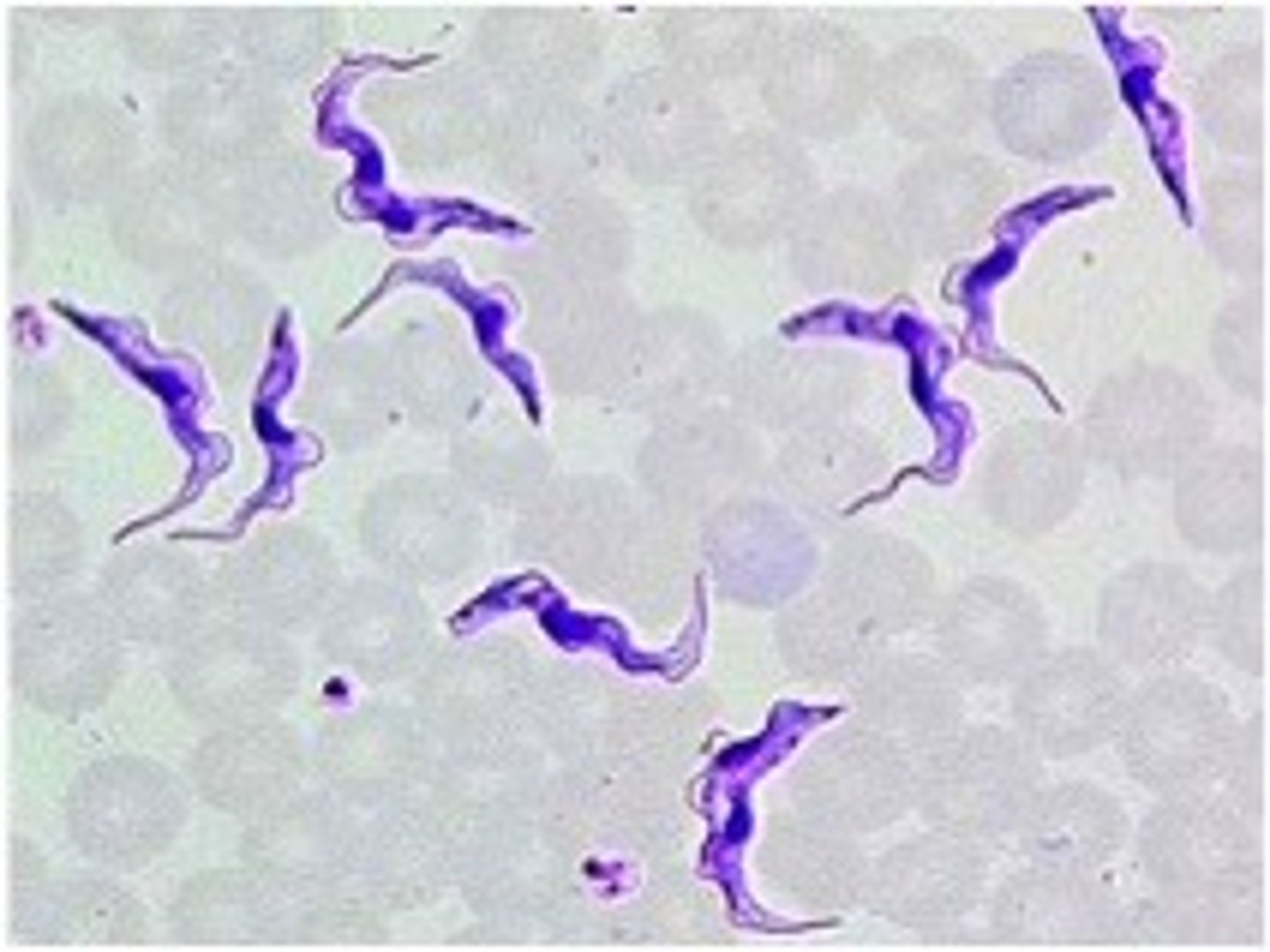
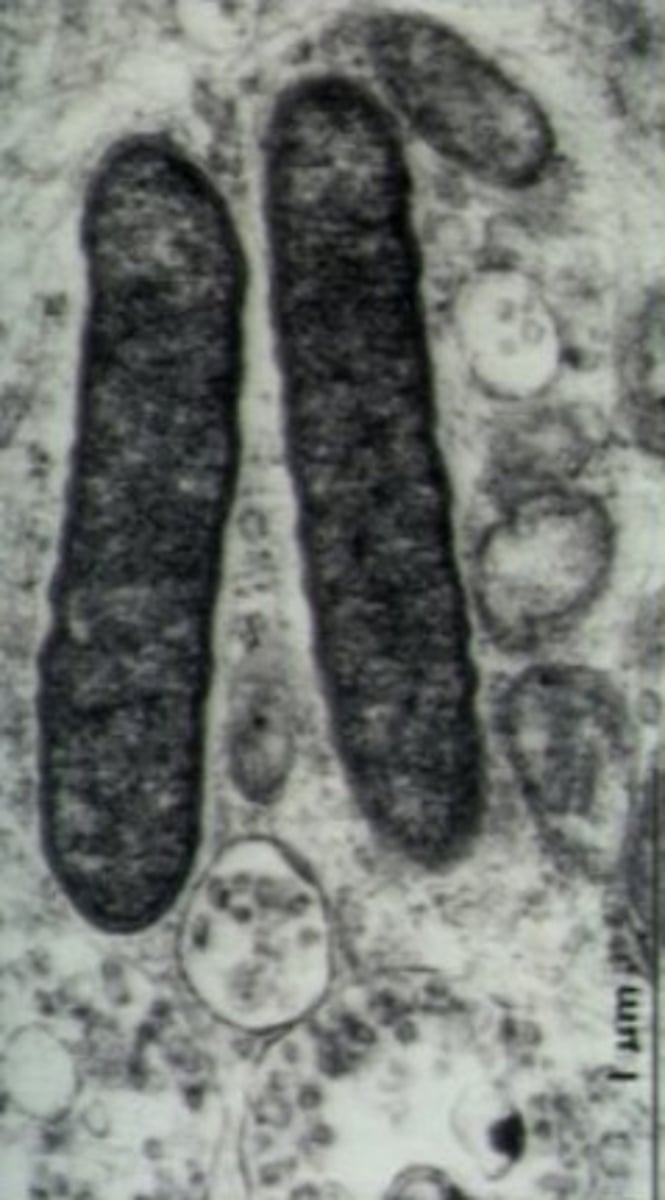
Rickettsia
Define CNS Infection Cause:
-Transmission from bacteria found in lice/fleas
-Can cause Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
Conformational change of normal neuronal prion protein PrP (PRNP) causes it to become resistant to protease digestion --> Induces more protein molecules to change shape, spreads to other cells (transmissible, familial)
What is the etiological basis for Prion Disease?
Normal alpha-helical PrPc proteins change configuration, misfolding to beta-sheet PrPsc abnormal proteins, which recruit more protein molecules to change
How does Prion disease specifically cause protein resistant to digestion (causing accumulation)?
-Spontaneous change
-Change due to PRNP mutation
-Inoculation
-Ingestion
What can initiate Prion disease?
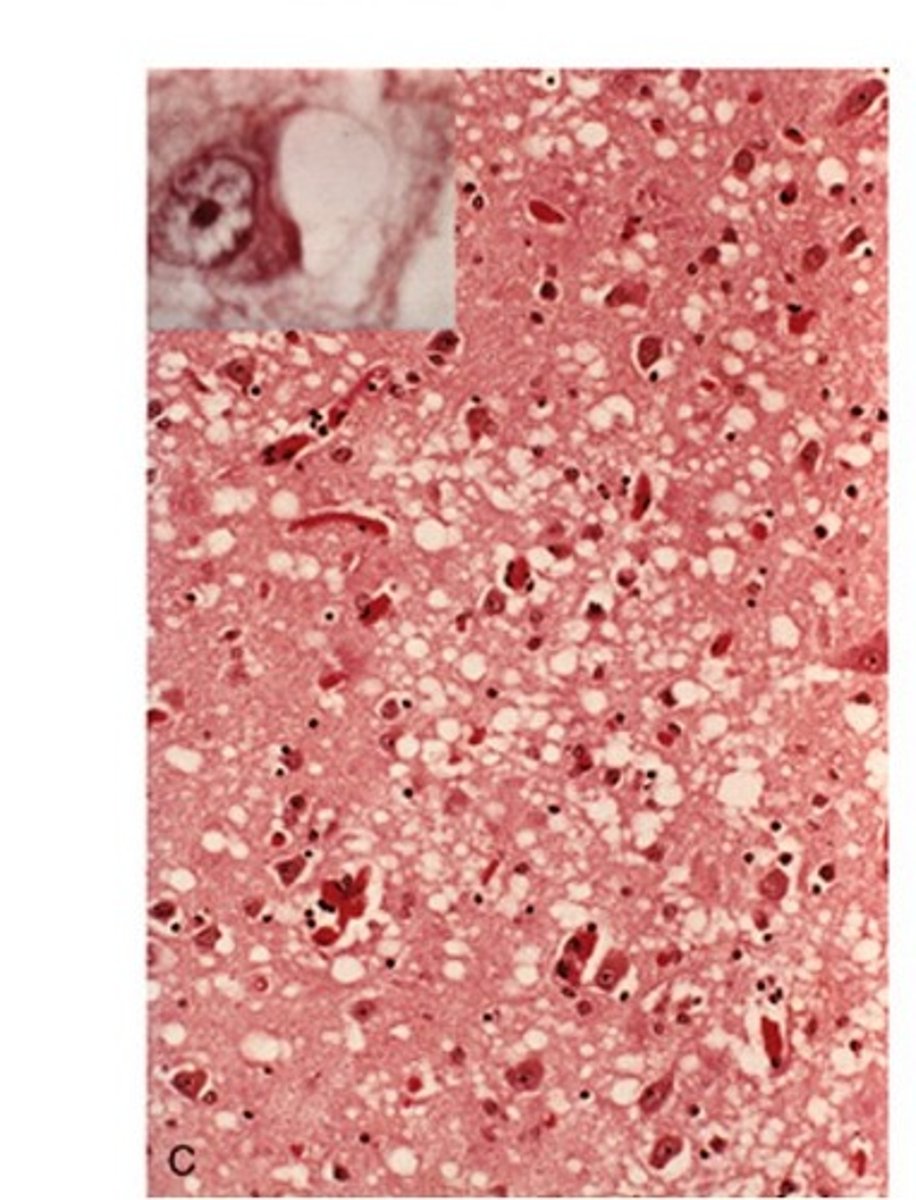
Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD)
Define Condition:
-Prion Disease (Transmissible spongiform encephalopathy)
-Over 70 y/o
-Causes rapidly progressive dementia with initial myoclonus and gait abnormalities
-Duration = 1 yr (onset to death)
Dx:
-Microscopic spongiform change (cortex has holes in it)
-Neuron Loss
-No inflammation
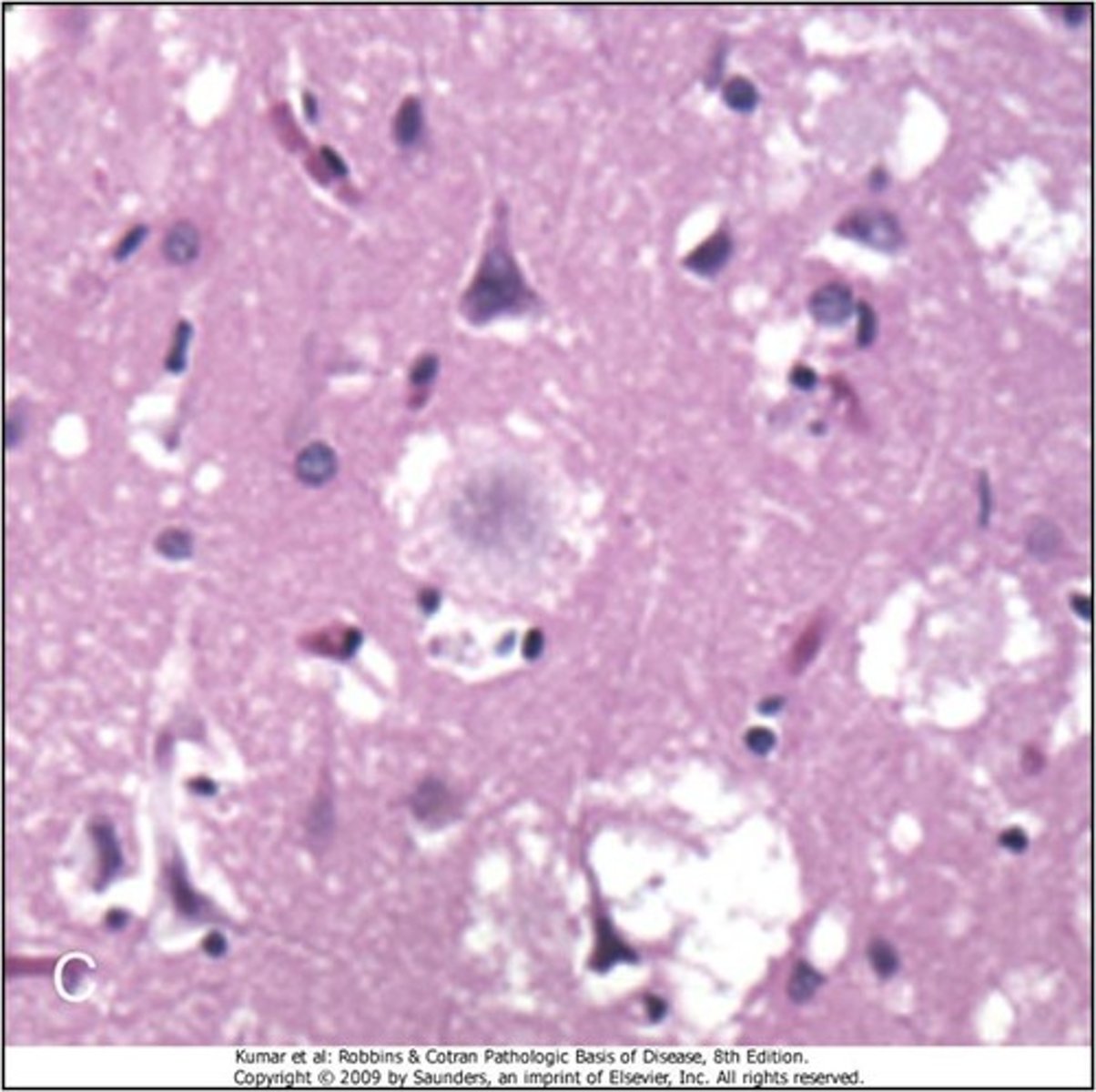
Variant CJD (mad cow disease)
Define Condition:
-Prion Disease linked to BOVINE Spongiform Encephalopathy
-See KURU PLAQUES
-Initially affects young adults
-Behavioral changes predominate initially, slower neurologic progression
Kuru
Define Condition:
-Prion disease
-Suffered by the Fore due to consuming humans through cannibalism (specifically by consuming the brains/nervous system of the dead)
-Sx = insomnia, lack of coordination/balance, eventually death
-See more amyloid plaques