Leaving Cert Home Ec: Lipids
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Elements
Carbon
Hydrogen
Oxygen
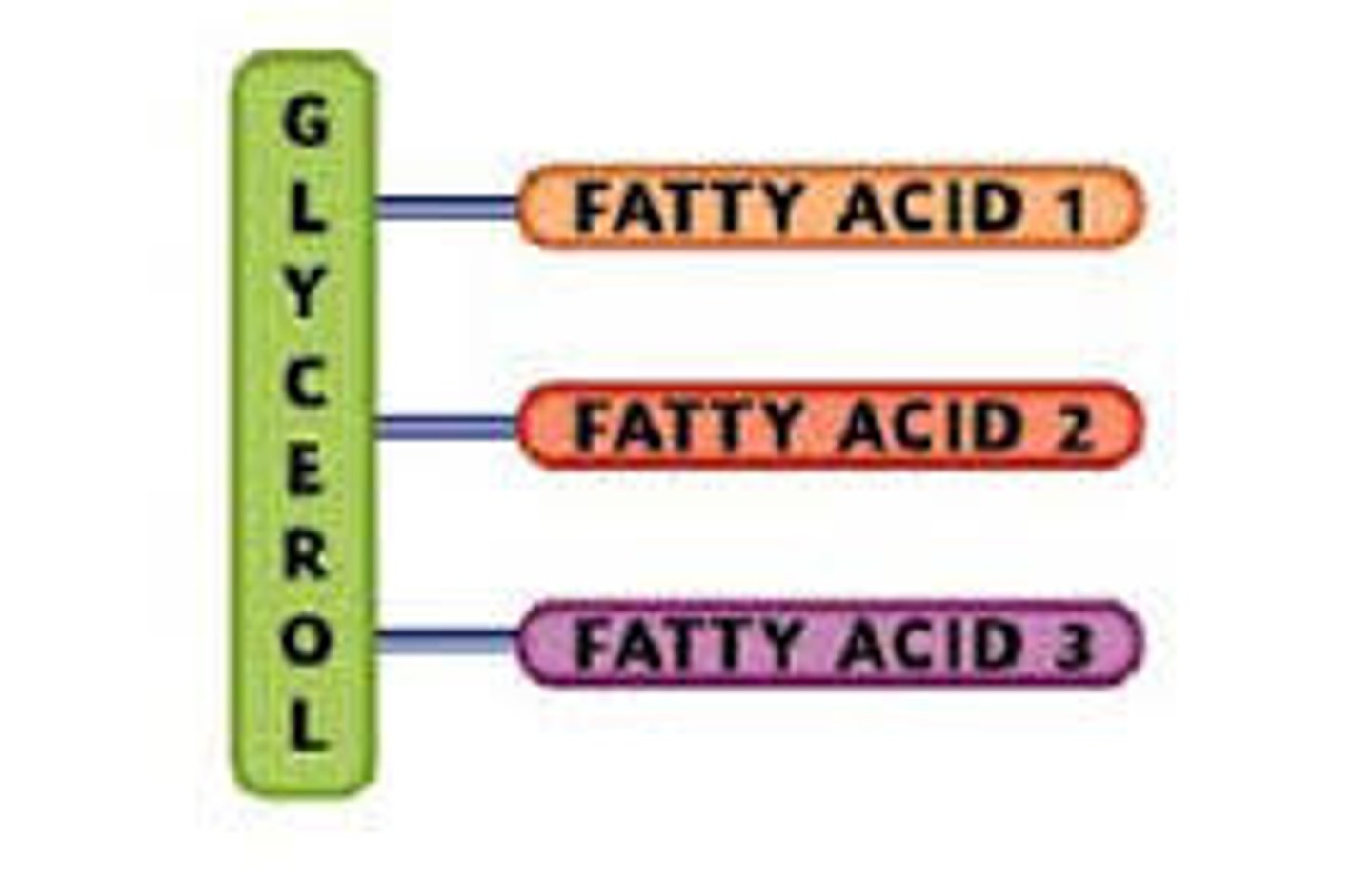
Basic Structure
Triglyceride
(One glycerol and 3 fatty acids)
Classification
1. Saturated
2. Monounsaturated
3. Polyunsaturated
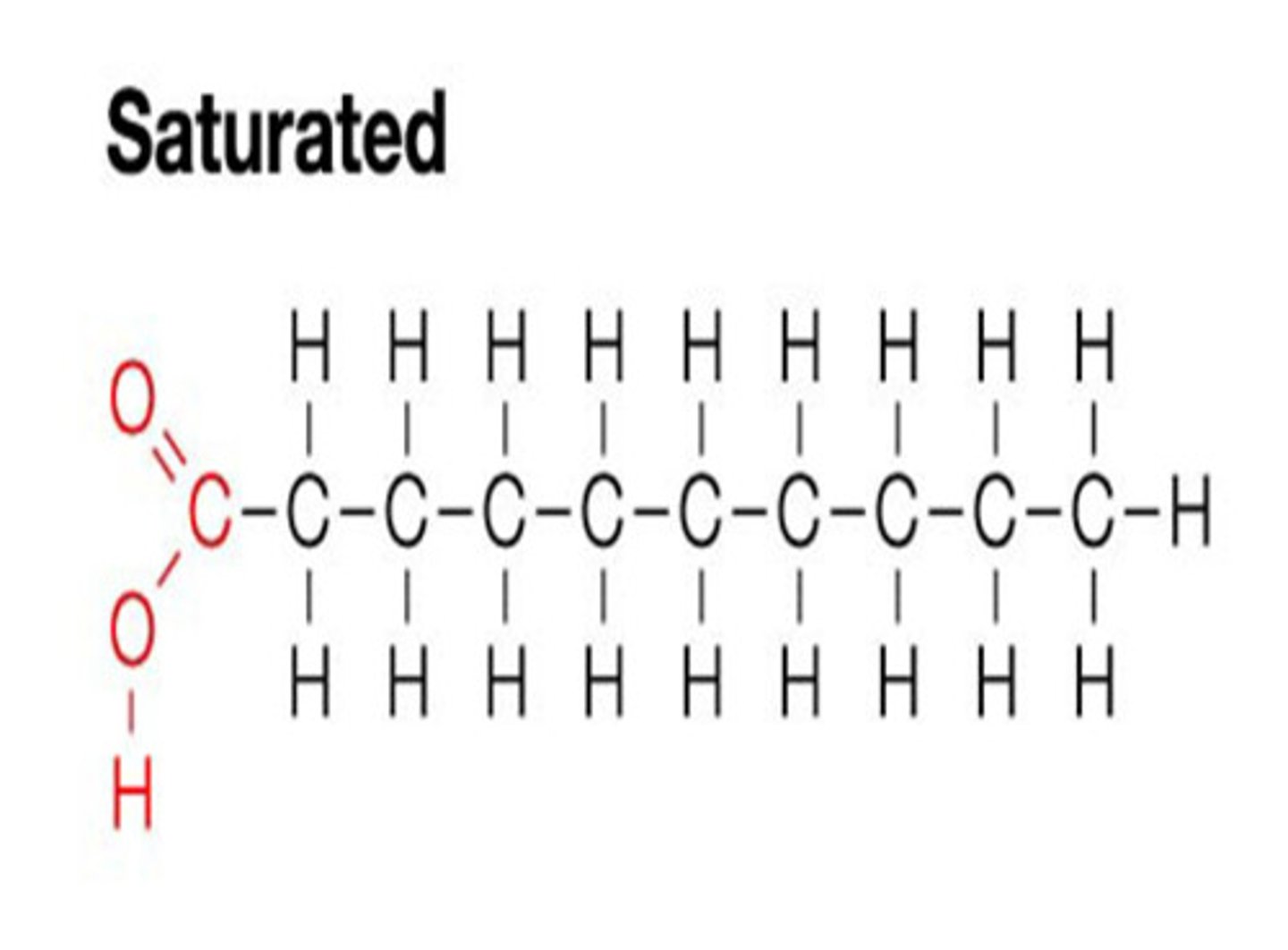
Saturated fatty acids
Have the maximum number of hydrogen atoms possible and no double bonds
Structure of saturated fatty acids
Contain Carboxyl group (COOH) and Methyl group (CH3)
sources of saturated fatty acids
Generally found in animal sources e.g....
-Butyric acid
-Stearic in meat
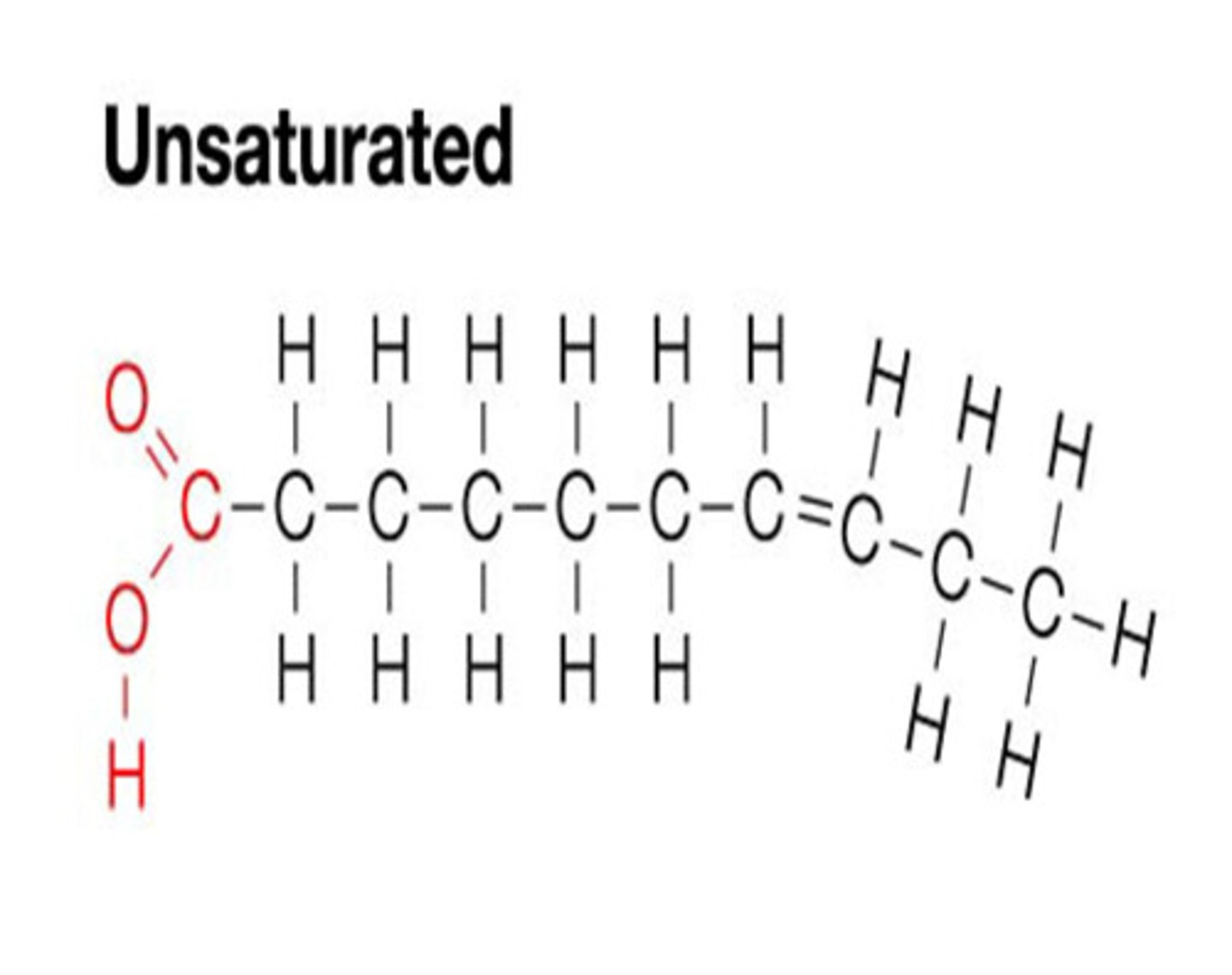
Monounsaturated fatty acids
Each carbon atom is not fully saturated with a full quota of hydrogen atoms, and there is one double bond between the carbon atoms.
structure of monounsaturated fatty acid
Contains carboxyl group (COOH) and methyl group (CH3)
sources of monounsaturated fatty acids
Generally found in plant and marine sources e.g...
-olive oil
-canola oil
-peanut oil
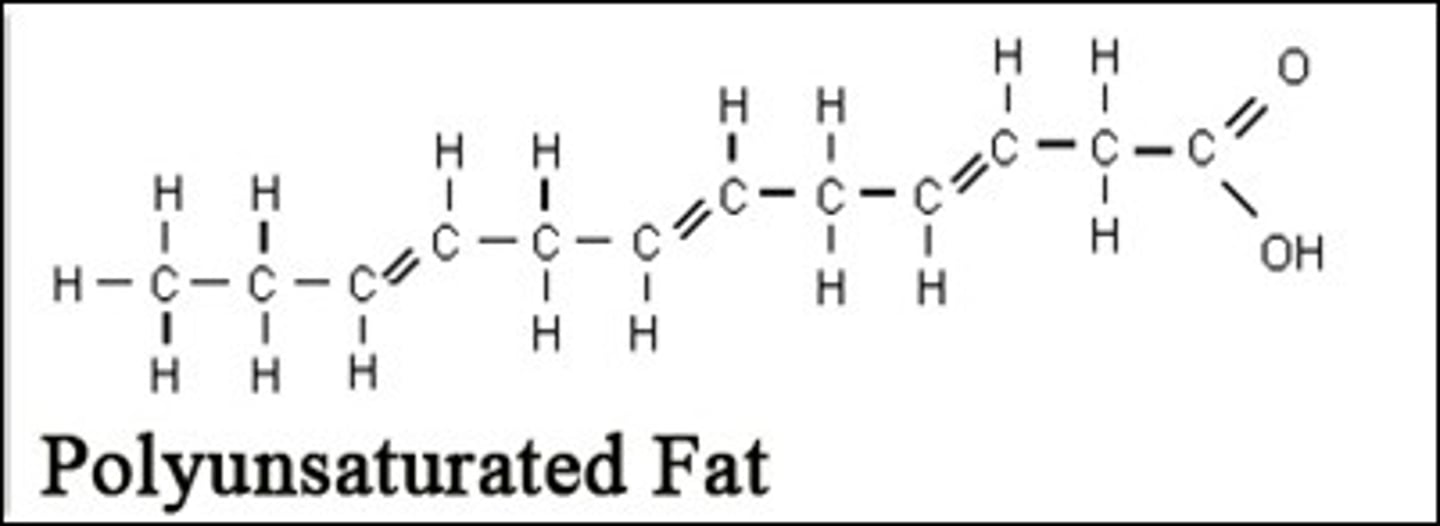
Polyunsaturated fatty acids
Each carbon atom is not fully saturated with its quota of hydrogen atoms and it contains more than one double bond
Structure of polyunsaturated fat
Contains carboxyl group (COOH) anf methyl group (CH3)
Sources of polyunsaturated fats
Generally found in plant or marine sources e.g...
-Linoleic acid in nuts
-Linoleic acid in seeds
-Arachidonic acid in oily fish
Cis and trans fatty acids
Monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats can either be cis or trans fatty acids and the orientation of hydrogen atoms around the Carbon double bond is what distinguishes "cis" fatty acids from "trans" fatty acids.
Cis fatty acids
Hydrogen atoms are on the same side of the double bond (either above or below)
Sources of cis fatty acids
Naturally occurring in foods such as olive oil and oily fish
Health effects of cis fatty acids
Raise HDL (high density lipoprotein) and lower levels of LDL (low density lipoprotein) which is good for health
Trans fatty acids
Hydrogen atoms are on opposite sides of the double bond
Sources of trans fatty acids
-Formed from cis fatty acids during the heating or frying of oils at a high temperature
-Also present in foods that contain hydrogenated fats
Health effects of trans fatty acids
Generally bad for health as they lower HDL and higher LDL which increases risk of coronary heart disease
Essential fatty acids
Fatty acids that cannot be made by the body, so must be gotten from food sources
Sources of EFAs
Nuts
Seeds
Olive oil
Oily fish
Functions of EfAs
Cell membrane formation
Reduce risk of CHD (Coronary heart disease)
Omega-3 fatty acids
Have a double bond between the third and fourth carbon atoms along their hydrocarbon chain
Sources of Omega-3
Flaxseed oil
Walnuts
Fish oils e.g. Cod liver oil
Functions of Omega-3
Reduce the risk of coronary heart disease and strokes
Decrease the viscosity of blood
Aids foetal brain development
Properties of lipids
1.Solubility
2.Absorption of flavours
3.Heating lipids
4.Emulsions
5.Hydrogenation
6.Rancidity
7.Plasticity
1. Solubility
Lipids are insoluble in water, but soluble in other liquids such as ether and benzene
2. Absorption of flavours
Lipids absorb flavours easily
3. Heating lipids
-Melting point: Solid fats melt when heated to 30-40 degrees celsius
-Smoke point: If lipids are heated to 200 degrees they begin to decompose, cause the glycerol to separate from the fatty acids. Glycerol is then broken down to acrolein and produces blue smoke and an acrid smell.
-Flash point: Extreme overheating of lipids to 310 degrees causes a vapour to be emitted that can spontaneously ignite
4. Emulsions
An emulsion is a solution formed when to immiscible liquids are forced to mix together.
Two types: Water in oil emulsions or Oil in water emulsions
5. Hydrogenation
A process whereby hydrogen gas, in the presence of a nickel catalyst , is forced through the double bond of an unsaturated oil, converting the unsaturated oil into a solid, saturated fat.
6. Rancidity
Spoilage or decomposition of lipids which results in an unpleasant odor and taste.
Two types...
Oxidative rancidity: When oxygen in the air combines with the carbons in a double bond of an unsaturated fat.
Hydrolytic rancidity: When enzymes or bacteria break down lipids into glycerol and fatty acids
7. Plasticity
How soft, pliable and malleable a fat is at a given temperature. It is determined by the degree of saturation.
More saturation=More solid
Biological functions of lipids
-Supply body with heat and energy
-Protect delicate organs
-Supply body with fat soluble vitamins
-Excess lipids are stored as adipose tissue under the skin
RDA of lipids
70g per day (Mainly unsaturated)
Digestion of lipids
During digestion, water and enzymes break lipids into glycerol and 3 fatty acids.
This process is called hydrolysis
Mouth
Food is chewed into small pieces
Stomach
Heat within stomach causes the fat to melt
Liver
Secretes bile into duodenum which emulsifies large fat molecules to produce smaller molecules
Pancreas
Secretes pancreatic juice into duodenum which contains enzyme lipase. This begins to break down the lipids into fatty acids and glycerol
Small intestine
The ileum secretes intestinal juice also containing lipase which continues the breaking down of the lipids into their basic form
Absorption and utilisation of lipids
After digestion, the fatty acids and glycerol are ready to be absorbed by small intestine, They pass through wall of villi into lacteals, which forms part of the lymphatic system
Next step
The lymphatic system transports the digested lipids to the thoracic duct, where it is deposited into the bloodstream through the subclavian vein
Excess digested lipids
Stored as adipose tissue under the skin to insulate body and act as an energy reserve