Metabolism: Core Concepts, Pathways, and Regulation in Biochemistry
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
What are the three fundamental questions central to metabolic biochemistry?
1. How does a cell extract energy and reducing power from its environment? 2. How does a cell synthesize the building blocks of its macromolecules? 3. How are the individual pathways and their chemical relationships regulated?
What is ATP's role in biological systems?
ATP is the 'universal currency' of free energy, used as the primary energy donor in most biological processes.

What is the difference between catabolism and anabolism?
Catabolism involves reactions that transform fuels into cellular energy (degradative), while anabolism involves reactions that require energy to synthesize larger molecules (biosynthetic).
What are amphibolic pathways?
Amphibolic pathways have a dual nature, functioning in both catabolic and anabolic processes, such as the TCA cycle.
How do cells maintain a chemical state far from equilibrium?
Cells derive energy from their environment to perform mechanical work, synthesize macromolecules, and actively transport ions against concentration gradients.
What is the significance of reaction coupling in metabolism?
A thermodynamically unfavorable reaction can occur if it is coupled to a favorable reaction, allowing the overall free energy change to be negative.
What is the standard free energy change (ΔGº') equation?
ΔGº' = -RTln(Keq), where Keq is the equilibrium constant.
What happens during the hydrolysis of ATP?
Hydrolysis of ATP releases a large amount of free energy, which can be used to drive other reactions.
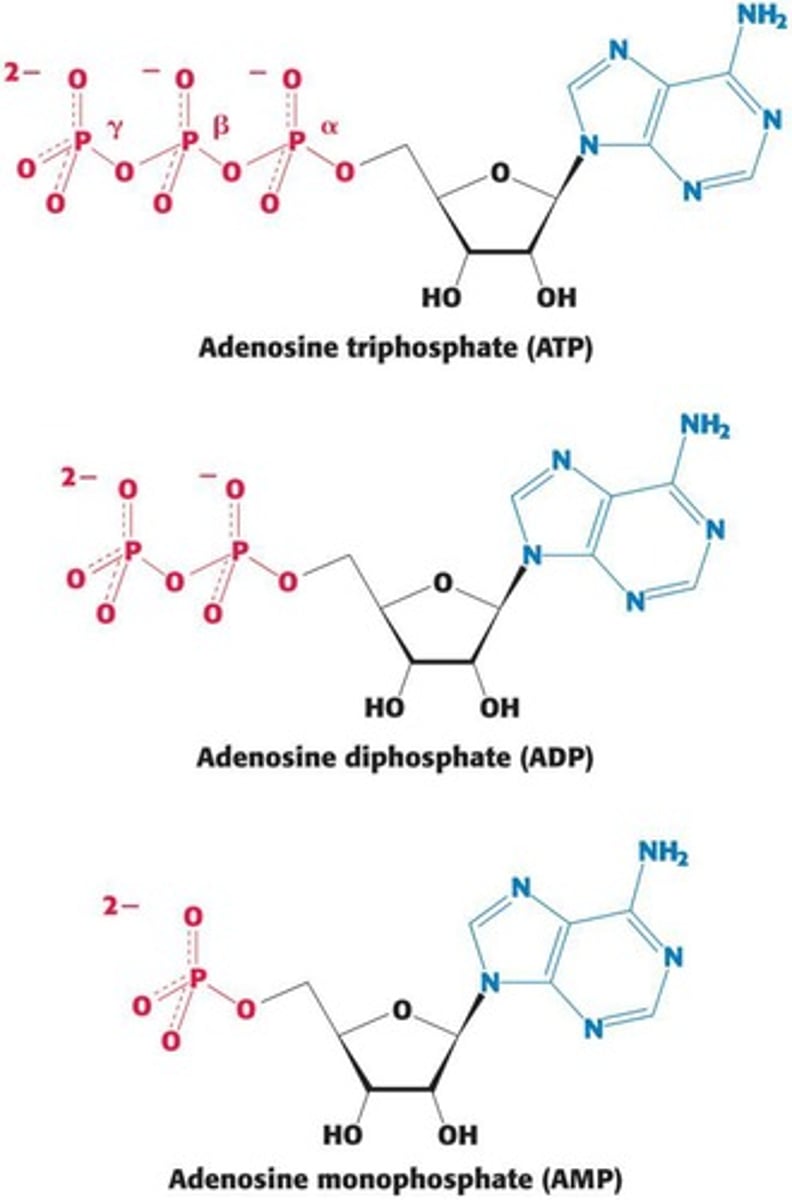
What are the two pathways for ATP hydrolysis?
1. ATP + H2O → ADP + Pi (ΔGº' = -30.5 kJ/mol) 2. ATP + H2O → AMP + PPi (ΔGº' = -45.6 kJ/mol)
How does ATP transfer energy to other nucleoside phosphates?
ATP can transfer a high-energy phosphoryl group to nucleoside monophosphates or diphosphates through enzyme-catalyzed reactions.
What is the relationship between metabolic pathways and thermodynamics?
Metabolic pathways are thermodynamically favorable when the sum of the free energy changes (ΔG) of the individual reactions is negative.
What is phosphoryl group transfer potential?
It refers to the ability of ATP to donate its phosphoryl group to other compounds in a thermodynamically favorable reaction.
Why does the body use more ATP in a single day than is present at any time?
ATP serves as an immediate donor of free energy but is not a long-term storage form, leading to high daily turnover.
What is the caloric expenditure of ATP in a resting human?
A resting human expends the caloric intake stored in about 40 kg of ATP daily, despite containing only about 100 g at any given time.
What is the impact of strenuous exercise on ATP consumption?
During strenuous exercise, such as a 2-hour run, ATP consumption can reach about 60 kg.
What is the role of free energy in cellular functions?
Free energy is used for mechanical work, synthesis of macromolecules, and active transport of ions.
What are the examples of catabolic reactions?
Examples include glycolysis and fatty acid beta-oxidation, which transform fuels into CO2, H2O, and energy.
What are examples of anabolic reactions?
Examples include DNA replication and protein synthesis, which require energy to synthesize larger molecules.
How do metabolic pathways relate to the subway line analogy?
Metabolic pathways can be visualized as interconnected subway lines, where catabolic and anabolic pathways join to form a complex network.
What is the importance of the TCA cycle?
The TCA cycle is an example of an amphibolic pathway, playing a role in both catabolism and anabolism.
How does the concentration of reactants and products affect ΔG?
When concentrations vary, ΔG can change, impacting whether a reaction is favorable or unfavorable.
What is the role of enzymes in nucleoside phosphate reactions?
Enzymes catalyze the transfer of phosphoryl groups between nucleoside phosphates, facilitating energy transfer.
What is the overall free energy change for a coupled reaction?
The overall free energy change is the sum of the free energy changes of the individual steps in the reaction series.
What is the primary source of energy for ATP regeneration in biological systems?
The oxidation of dietary fuel molecules during catabolism.
What is the terminal oxidation product of carbon?
Carbon dioxide (CO2).
How does the energy of oxidation relate to the reduction state of carbon atoms?
The more reduced a carbon atom is, the greater the free energy released upon oxidation.
What is substrate-level phosphorylation?
A series of reactions that yield ATP by transferring a phosphoryl group from a compound with higher transfer potential than ATP.
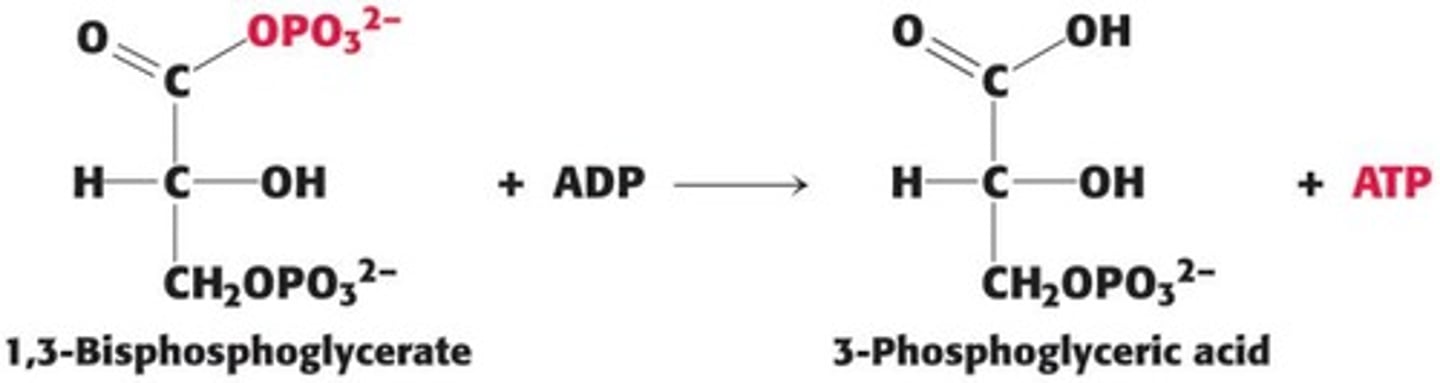
What is the role of 1,3-BPG in ATP synthesis?
1,3-BPG phosphorylates ADP to yield ATP during glycolysis.
What is the significance of electrochemical potential in ATP synthesis?
It is an efficient means of storing free energy and is used to generate ion gradients across membranes.
Where does ATP synthesis primarily occur in mammalian cells?
In the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.
What are the three stages of energy extraction from food?
1. Preparation: breaking down large molecules; 2. Degradation: degrading building blocks; 3. ATP Production: oxidation coupled to ATP synthesis.
What are activated carriers in metabolism?
Molecules that repetitively fulfill specific biological functions, such as ATP for phosphoryl groups.
What are pyridine nucleotides and their role in fuel oxidation?
NADH and NADPH serve as electron carriers during oxidation processes.
How do flavin nucleotides function in oxidation and reduction?
FAD and FMN serve as hydrogen carriers and are involved in dehydrogenation reactions.
What is the primary use of NADPH in metabolic reactions?
As an electron source in reductive biosynthesis, such as fatty acid synthesis.
What is Coenzyme A's role in metabolism?
It acts as a carrier for acyl groups in both catabolism and biosynthesis.
What are the three principal ways metabolic processes are regulated?
1. Amount of enzymes present; 2. Catalytic activity of enzymes; 3. Accessibility of substrates.
How is the catalytic activity of enzymes regulated?
Through gene expression, allosteric regulation, reversible covalent modification, and hormonal control.
What is the importance of compartmentalization in eukaryotic metabolism?
It enhances metabolic regulation and flexibility by segregating opposed reactions.
What is the role of the mitochondrial inner membrane in ATP synthesis?
It houses the electron transport chain, which generates a proton gradient for ATP production.

What is the prototypic reaction for the reduction of NAD+?
NAD+ + H:- → NADH.
What is the significance of the 2'-phosphoester group in NADPH?
It can be considered a 'tag' for its exclusive use in reductive biosynthesis.
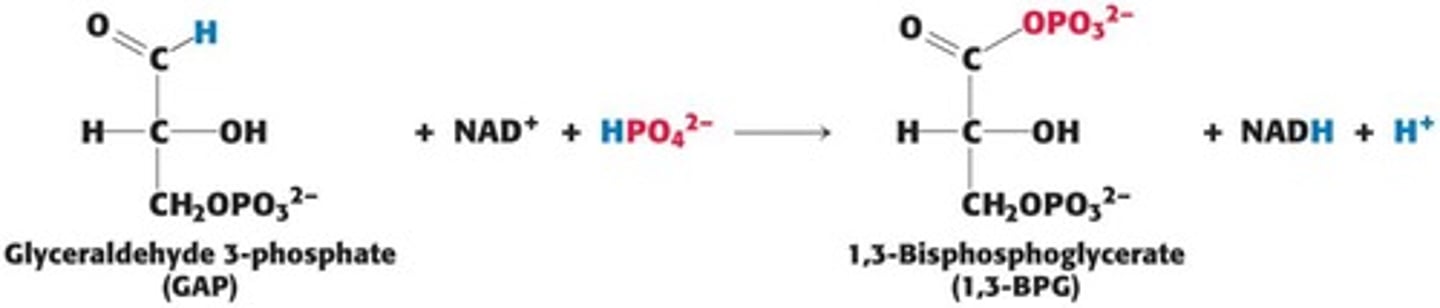
What happens during the oxidation of glyceraldehyde-3-P in glycolysis?
It generates NADH and phosphorylates ADP to yield ATP.
What is the relationship between the oxidation of food molecules and ATP production?
The oxidation of food molecules releases energy that is coupled to ATP synthesis.