Introduction to Mendelian genetics
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What is an allele?
Is a variant of a gene controlling the same trait
Alleles usually occur in pairs
Can be dominant or recessive depending on how they are expressed
What is meant by homozygous?
An individual carrying two copies of the same allele for a given gene, i.e., BB or bb
Dominant = B
Recessive = b
What is meant by heterozygous?
An individual carrying one copy of each of two different alleles for a given gene i.e., B and b
What is a genotype?
Genetic makeup
What is a phenotype?
Physical expression (how the individual looks)
What is a dominant allele?
The allele/trait that is expressed in a heterozygous individual, ‘overriding’ the recessive allele/trait
What is a recessive allele?
The allele/trait that is not expressed in a heterozygous individual, phenotype can appear to disappear in one generation and reappear in a subsequent generation
What did Mendel want to try and figure out?
He wanted to know how traits were transferred from one generation to the next - and why some skip a generation
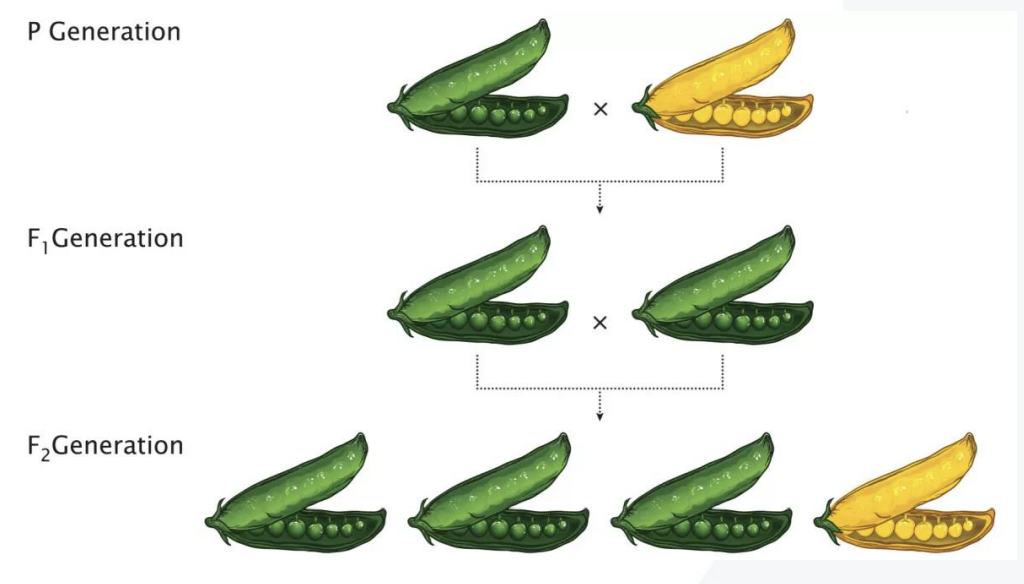
What was involved in Mendel’s experiments?
He studied 7 traits in peas
He noted that some traits appeared to be dominant over others, which were recessive
Only these dominant traits would be visible in the next generation
However, if these plants were crossed with each other, some of the offspring would regain the recessive trait
He also noted that the traits segregated with very specific ratios
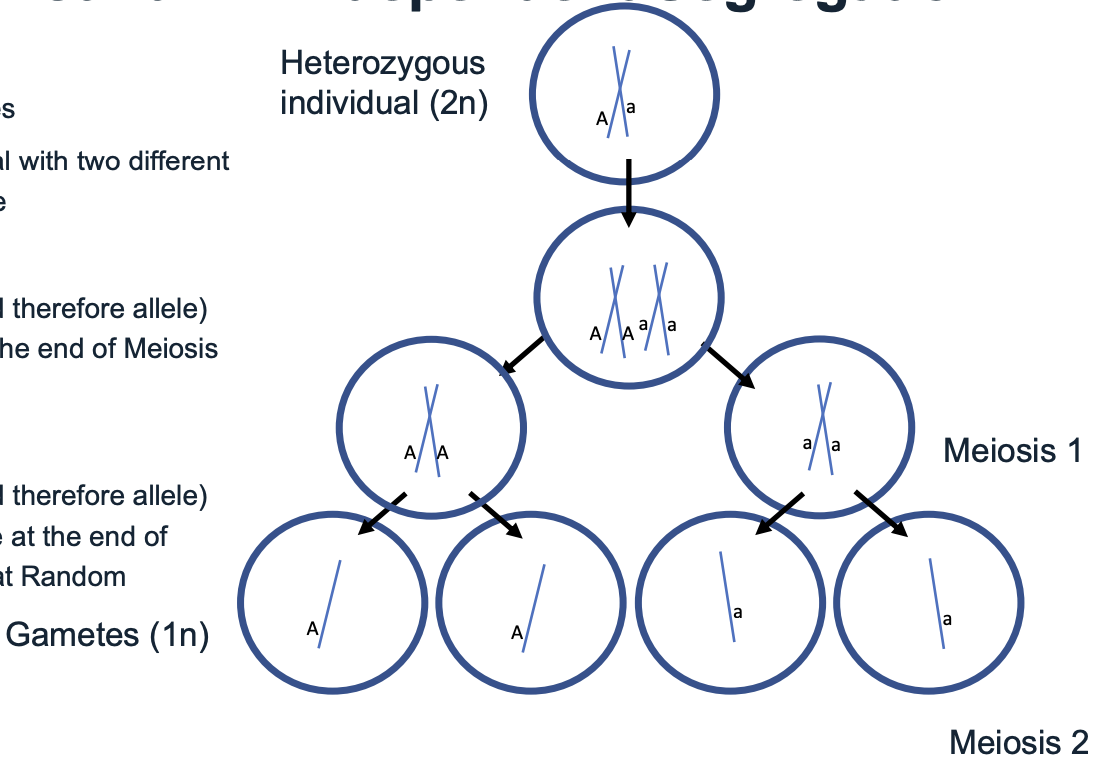
What is involved in Mendel’s first law? Or the law of segregation
One pair of chromosomes
A heterozygous individual with two different alleles for the same gene
Which chromosome (and therefore allele) ends up in which cell at the end of meiosis 1 is completely random
Which chromosome (and therefore allele) ends up in which gamete at the end of meiosis 2 is completely random
For any single gene, the alleles segregate independently into gametes, such that any gamete has an equally likely chance of inheriting either allele
The separation of allele pairs during the formation of gametes (sperm and egg cells) so that each gamete receives only one allele for each trait
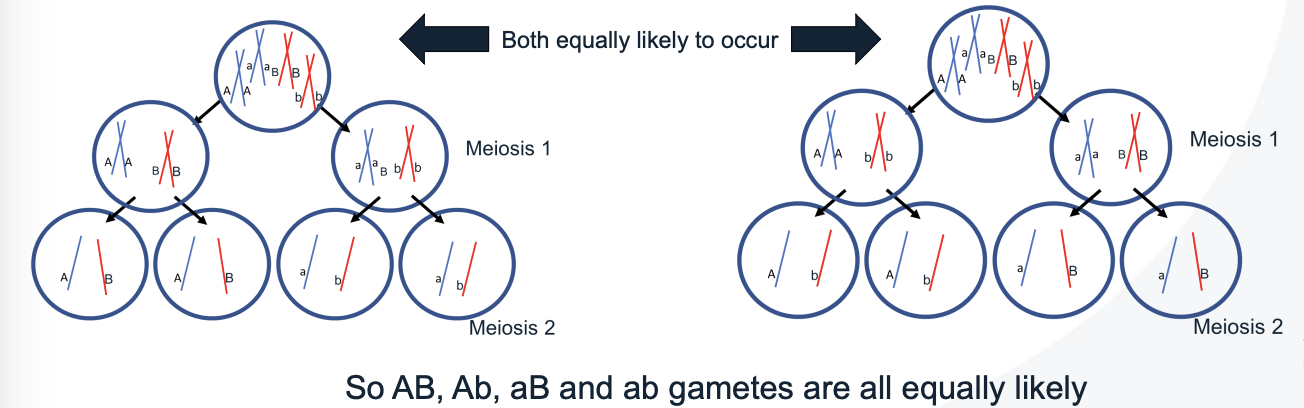
What is involved in Mendel’s second law? Or the law of independent assortment/random assortment
Two pair of chromosomes
A heterozygous individual with two different alleles for the same gene (A) and two different alleles for the same gene (B)
For any pair of genes, the alleles of one gene will sort into gametes independently of the alleles of the second gene
Which allele of gene A a gamete receives does not affect which allele of gene B that same gamete receives
All gametes are equally likely
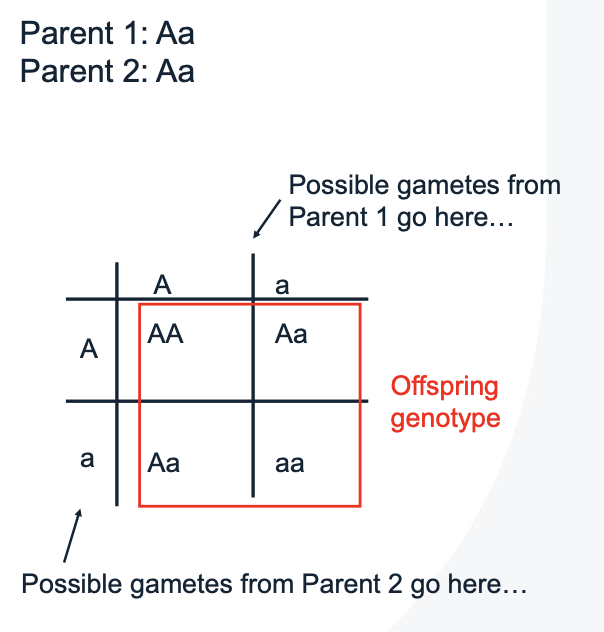
What is a punnet square and what is it used for?
A square diagram used to predict the genotypes of a particular cross
Used to determine the probability of an offspring having a particular genotype
Summary of all possible combinations of maternal alleles with paternal alleles
What is the definition of purebreeding?
Homozygous with homozygous
Purebred crossed with a purebred = predictable results
Every gamete is identical
What is a heterozygote (F1)?
F1= product of crossing two DIFFERENT pure-breeding parents
Monohybrid cross (single gene cross)
e.g., parent 1 AA crossed with parent 2 aa (single gene)
What is a hybrid cross?
Heterozygous with heterozygous
F2 x F1
i.e., one gene Aa x Aa or two gene AaBb x AaBb
One gene hybrid cross = Aa x Aa (MONOhybrid cross)
Two gene hybrid cross = AaBb x AbAb (DIhybrid cross)
What is a test cross?
Heterozygous with homozygous RECESSIVE
i.e., one gene Aa x aa or two gene AaBb x aabb
What is a monohybrid cross and what is the phenotypic ratio of this type of cross?
One gene cross; parents = parent 1 Bb x parent 2 Bb
Progeny = 3 dominant and 1 recessive
Phenotypic ratio = 3:1
What is a dihybrid cross and what is the phenotypic ratio of this type of cross?
Two gene cross; parents = AaBb x AaBb
Phenotypic ratio = 9:3:3:1
9 - dominant A & B
3 - dominant A, recessive b
3 = recessive a, dominant B
1 - recessive a & b
What is a one gene test cross and what is the phenotypic ratio of this type of cross?
One gene cross; parents = Aa x aa
Parent 1 gametes = Aa
Parent 2 gametes = aa
= two dominant and two recessive progeny
Phenotypic ratio= 1:1
What is a two gene test cross and what is the phenotypic ratio of this type of cross?
Two gene cross; parents = AaBb (heterozygous) x aabb (homozygous recessive)
Parent 1 gametes = AB, Ab, aB, ab
Parent 2 gametes = ab
All possible options can be made in progeny
Phenotypic ratio = 1:1:1:1
What is a reciprocal cross?
This type of cross involves reversing the sexes of the parents in a breeding experiment to assess the role of parental sex on inheritance patterns. It essentially involves two crosses: one where a trait is passed from male to female, and another where the same trait is passed from female to male. This technique helps determine if traits are sex-linked, maternally inherited, or influenced by cytoplasmic factors.