AP Government All Units
1/303
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
304 Terms
What is the structure of the AP Government test?
The test consists of 55 multiple choice questions (80 minutes) and 4 free response questions (100 minutes, 25 minutes each).
What are signing statements?
Written statements issued by a president when signing a bill into law, detailing their interpretation of the bill.
What does the 24th Amendment prohibit?
It prohibits both federal and state governments from requiring voters to pay a poll tax or any other tax to vote in federal elections.
How does the federal budget process begin?
The President submits a proposed budget, which Congress reviews, amends, and passes appropriations bills.
What power does Congress have regarding the President's budget?
Congress retains the power to significantly alter the President's budget through its own budget resolutions and committee actions.
What are unfunded mandates?
Regulations or new laws that require state or local governments to perform certain actions without providing federal funds to cover the costs.
What are funded mandates?
Requirements imposed by the federal government on state or local governments to perform specific actions, often tied to funding.
Give an example of a funded mandate.
The National Minimum Drinking Age Act, which tied federal highway funds to states raising the drinking age.
What are conditional categorical grants?
Federal funds given to states with specific conditions attached, requiring adherence to federal guidelines.
Provide an example of a conditional categorical grant.
The Special Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program.
What are block grants?
Federal funding given to state or local governments with broad guidelines, allowing significant flexibility in fund allocation.
What is the political spectrum?
A system that classifies political positions, ranging from radicals who seek extreme changes to reactionaries who want to return to earlier periods.
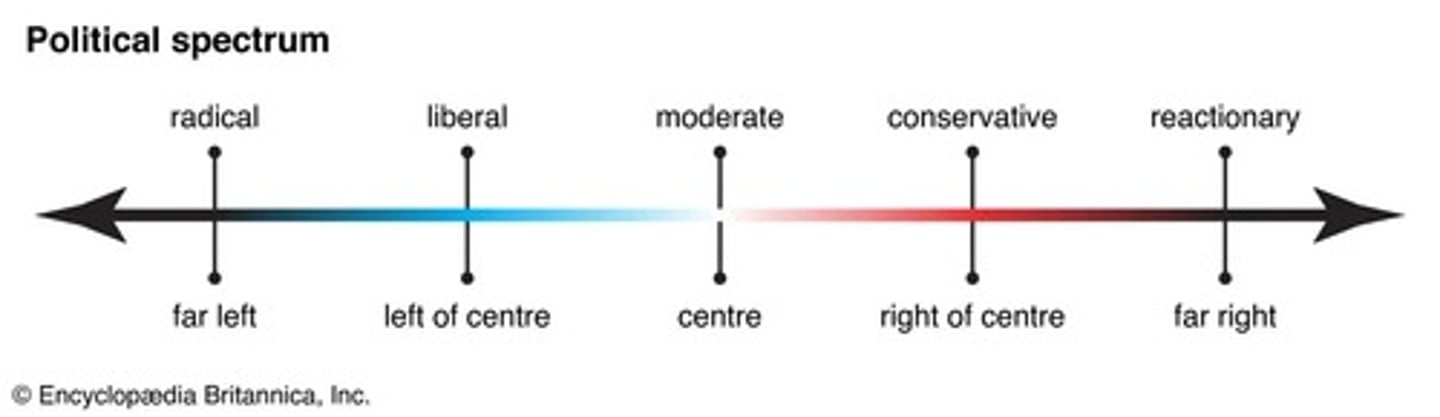
Who are radicals in the political spectrum?
Individuals who want extreme changes in government, such as Malcolm X and certain protest movements.
What do liberals advocate for?
Fundamental changes to be implemented in society through government legislation.
Who is an example of a liberal leader?
Martin Luther King, known for advocating civil rights.
What is the role of moderates in politics?
Moderates believe in a middle ground in political views, often blending ideas from both sides.
What do conservatives aim to do?
They want to maintain the status quo and preserve American political culture.
What is the focus of reactionaries?
They seek to return to an earlier period, often disregarding the negatives of the past.
What is political culture?
The shared set of beliefs, customs, traditions, and values that define the relationship between citizens and government.
What are core American political values?
Individualism, equality of opportunity, the free enterprise system, rule of law, and limited government.
How does Alexis de Tocqueville describe individualism?
He explains it as the belief that individuals should be responsible for themselves, fostered by democracy.
What is the American dream as related to individualism?
The belief that individuals can create a better future for themselves through their own efforts.
What potential downside of individualism does Tocqueville mention?
It could lead to the tyranny of the majority, trampling the rights of the minority.
What is the principle of Rule of Law?
The principle that no one, including public officials, is above the law, supported by Federalist 51 and the Checks and Balances system.
How does the government influence economic decisions in a mixed economy like America?
Economic decisions are primarily left to businesses, but government intervention through taxation, spending, and regulation shapes those decisions.
What is Equality of Opportunity?
A core value that ensures everyone has an equal chance to succeed, based on effort rather than inheritance, as stated in the Declaration of Independence.
What is the significance of Affirmative Action?
Affirmative Action was created to address the uneven playing field and provide support to ensure equal opportunities.
What are John Locke's views on Limited Government?
Locke's theory states that humans have natural rights that the government cannot take away, including life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness.
Political Socialization?
The experiences and factors that shape an individual's political values, attitudes, and behaviors.
What role do families play in Political Socialization?
Families are the primary source of political socialization and contribute to party identification.
How do schools influence Political Socialization?
Schools provide mandatory classes like American Government and introduce students to political participation and volunteering.
What is the Generational Effect in political views?
The impact of historical events experienced by a generation on their political views.
How have religious organizations influenced political ideologies?
Religious organizations have historically influenced political views, with groups like Jews and Catholics shifting from liberal to conservative positions over time.
What is the relationship between civic engagement and political socialization?
Civic engagement, such as volunteering, exposes individuals to different perspectives and enhances political socialization.
What does the concept of Limited Government entail?
It entails that the government's powers are restricted, ensuring citizens' natural rights are protected.
What is the role of the Bill of Rights in American government?
The Bill of Rights limits government power and protects individual liberties.
What is the mixed economy of America characterized by?
A combination of command and free market systems, where government intervention influences economic decisions.
How does individualism manifest in American society?
Individualism is reflected in Americans' preference for a free market and skepticism towards government intervention.
What is the importance of transparency in enhancing the Rule of Law?
Transparency, such as through the Freedom of Information Act, is essential for maintaining public trust in the government.
What is the significance of the Checks and Balances system?
It ensures that no single branch of government becomes too powerful, maintaining a balance of authority.
How do experiences shape political opinions beyond background?
Experiences, especially during significant historical events, can significantly influence an individual's political opinions.
What is the impact of civic organizations like Habitat for Humanity on political socialization?
They provide opportunities for skill development and exposure to diverse perspectives, enhancing civic engagement.
What is the relationship between social services and government spending in America?
American social services are on a smaller scale compared to other developed countries, with less tax allocation but readiness to spend on disaster aid.
What is the role of the judiciary in the Rule of Law?
The independence of the judiciary ensures fairness in trials and upholds the principle that the government must control itself.
How do political ideologies manifest in different demographic groups?
Demographic groups, such as Catholics and Evangelicals, often align with specific political ideologies based on cultural and historical contexts.
What impact did the Vietnam War and the Watergate affair have on public perception of the government?
They made people have less confidence and trust in the government.
What event created more unity and patriotism in the United States?
The 9/11 attacks.
What is the Life-Cycle effect in political views?
It refers to the impact of a person's age and stage in life on their political views, such as high school graduates being more interested in college tuition assistance.
How does globalization affect international and domestic policies?
The rapid growth of globalization has blurred the lines between international and domestic policies.
What are Multinational Corporations (MNCs)?
Companies that make, transport, and market goods and services in two or more countries.
What is a limitation of U.S. regulation on MNCs?
The U.S. may regulate what companies do within its borders, but this is the extent of its authority.
What are NGOs and their purpose?
Nongovernmental organizations that work toward a public cause, providing aid to struggling countries.
What are some criticisms of NGOs?
Some governments oppose NGOs because they highlight the ineffectiveness of local government assistance and can threaten local producers.
What are IGOs and why do countries join them?
Intergovernmental organizations consisting of member states that countries join for benefits that outweigh the loss of sovereignty.
What is an example of an IGO?
The European Union (EU), established after World War II.
What criteria must countries meet to join the EU?
Countries must meet certain criteria for democratic governance.
What is the role of the WTO?
The World Trade Organization emphasizes free markets and sets rules to encourage the free flow of capital, goods, and services between countries.
What is a Bilateral Trade Agreement?
Deals struck between the United States and only one other nation.
What is a Regional Trade Agreement?
An agreement that brings a group of nations into an overall trade agreement.
What was the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA)?
An agreement that increased trade among nations, created some American jobs in design and business services, but also cost jobs in manufacturing.
What is the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP)?
A trade agreement struck between twelve nations along the Pacific Rim, including Mexico, Australia, and various East Asian and South American nations.
What is a pro of globalization related to democratization?
Globalization can encourage democratization by influencing countries to adopt democratic values.
How do NGOs contribute to democratization?
They keep tabs on corrupt and authoritarian countries.
What is a con of globalization regarding MNCs?
MNCs may relocate to countries with less stringent labor or environmental regulations.
What is outsourcing?
When a company moves its business to a location where labor costs are cheaper or production is more efficient.
What cultural concern is associated with globalization?
Globalization may weaken local cultures and lead to a homogenized culture.
Why are elections considered less efficient than polls?
Elections revolve around a small set of issues and are too broad to reveal useful information.
What is Scientific Polling?
A representative poll of randomly selected respondents with a statistically significant sample size using neutral language.
What are Benchmark polls?
Polls conducted by a campaign at the beginning of a race for office.
What is the purpose of polls in a campaign?
To provide a basis for comparison for later polls, allowing candidates to see if their likelihood of winning is increasing or decreasing.
What are opinion polls?
Polls taken by sampling a small section of the public to predict election results or estimate public attitudes on issues.
What are tracking polls?
Surveys determining the level of support for a candidate or issue throughout a campaign, performed repeatedly with the same group.
What is a major con of using polls in media?
They create backlash by focusing on who is winning instead of important issues.
What is a pro of polls?
They can accurately reflect what people feel at the time.
What is a con of polls?
Data can change constantly, and people may lie about their actual intent, skewing the results.
What are entrance polls?
Surveys performed on Election Day as voters enter their voting location.
What are exit polls?
Surveys performed on Election Day as voters exit their voting location, often used by media to determine election results before ballots are counted.
What is a pro of exit polls?
They are timely, as people are more inclined to answer after voting.
What is a con of exit polls?
Respondents can lie or may not accurately portray their true interests.
What is a mass survey?
The most common type of survey that measures public opinion by interviewing a large sample of the population, usually consisting of 1,500 responses.
What is the typical sampling error in larger samples?
Often ± 3 percentage points, meaning 95% of the time, the true percentage lies within those points.
focus group
A small, demographically diverse group assembled for in-depth discussion about specific issues to gauge broader public reactions.
What are internet polls?
Polls that are not scientific and unreliable due to voluntary participation, which may not represent all demographics.
What is a push poll?
A negative campaign tactic disguised as a survey, aiming to present voters with damaging portrayals of opposing candidates.
What is a pro of push polls?
They can yield the desired data.
What is a con of push polls?
They can skew data as people may change their answers based on the information presented.
What are traditional telephone polls?
Surveys conducted via text or call to gather opinions.
What is a pro of traditional telephone polls?
They are easy and accessible to millions of citizens, increasing the likelihood of responses.
What is a con of traditional telephone polls?
They can be unreliable due to impersonation and other factors.
What is a sample in polling?
A group of individuals from a larger population used to measure public opinion.
What is random selection in polling?
A method of choosing poll respondents that does not over- or underrepresent any group of the population.
representative sample?
A sample that reflects the demographics of the population.
stratified sample?
A statistical method ensuring specific subgroups within a population are adequately represented by dividing the population into distinct layers based on shared characteristics.
What is weighting in surveys?
A procedure in which the survey results are adjusted according to the demographics of the larger population.
Sampling Error?
The margin of error in a poll, usually calculated to plus or minus three percentage points.
What is Random Digit Dialing?
The use of telephone numbers randomly generated by a computer to select potential survey respondents, which researchers rely on for public opinion surveys.
What is the impact of Question Order in polls?
The sequencing of questions can influence responses; for example, asking about flag burning after discussing patriotism may lead to more negative opinions.
How does Question Wording affect poll results?
The phrasing of a question can guide respondents to a specific answer, as seen in differing support for military action based on how the question is framed.
What does Veracity refer to in polling?
The accuracy of the data collected in polls.
How did polls predict the 2016 Election outcome?
Many polls predicted Hillary Clinton would win, but Donald Trump won, indicating the results were within the margin of error.