Transition Metal Complexes
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What is a transition metal complex?
A transition metal complex consists of a central metal ion surrounded by ligands bonded by co-ordinate (dative) bonds.
What is a ligand?
A small molecule or ion with a lone pair of electrons that can bond to a transition metal ion.
It forms co-ordinate bonds with the d-orbitals of the transition metal ion.
What is a co-ordinate bond?
A covalent bond where both electrons in the shared pair come from the same species.
How are ligands classified?
By the number of co-ordinate bonds that they can form in complexes.
Ligands that have one atom that can bond to a metal ion are called monodentate. Examples are water, H2Ö:, ammonia, :NH3, chloride ion, Cl-.
Ligands that have two atoms which can bond to the metal ion are called bidentate. An example is 1,2-diaminoethane, H2NCH2CH2NH2 (often shortened to ‘en’).
A complex which has 6 ligands bonded to the central transition metal ion has what shape?
Octahedral.
Give an example of an octahedral complex.
Hexaaquacopper (II) i.e. copper sulfate.
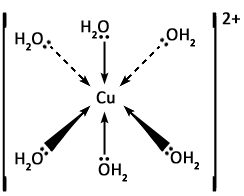
What is the formula for hexaaquacopper (II) complex ion?
[Cu(H2O)6]2+
State the colour of the hexaaquacopper (II) complex ion.
Blue.
Give an example of another octahedral complex.
Tetraaminediaquacopper (II).
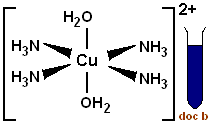
What is the formula for tetraaminediaquacopper(II) complex ion?
[Cu(NH3)4(H2O)2]2+
State the colour of the tetraaminediaquacopper (II) ion.
Royal / deep blue.
A complex which has 4 ligands bonded to the central transition metal ion has what shape?
Tetrahedral.
Give an example of a tetrahedral complex.
Tetrachlorocuprate [CuCl4]2-
![<p><span>Tetrachlorocuprate [CuCl</span><sub>4</sub><span>]</span><sup>2-</sup></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/705d79c6-2ae4-4fc1-8e34-43c57367e096.png)
State the colour of the tetrachlorocuprate ion.
Yellow-green.
What is a ligand exchange reaction?
A reaction in which one ligand in a complex ion is replaced by a different one.
For example, if ammonia solution is added to a solution containing [Cu(H2O)6]2+, ammonia molecules replace four of the water molecules to form a new complex, [Cu(NH3)4(H2O)2]2+.
This is an equilibrium process.
![<p>A reaction <span>in which one ligand in a complex ion is replaced by a different one.</span></p><p></p><p><span>For example, if ammonia solution is added to a solution containing [Cu(H</span><sub>2</sub><span>O)</span><sub>6</sub><span>]</span><sup>2+</sup><span>, ammonia molecules replace four of the water molecules to form a new complex, [Cu(NH</span><sub>3</sub><span>)</span><sub>4</sub><span>(H</span><sub>2</sub><span>O)</span><sub>2</sub><span>]</span><sup>2+</sup><span>.</span></p><p></p><p><span>This is an equilibrium process.</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/574f1e16-6da4-4c79-88a2-98b96d24c31f.png)
What can ligand exchange lead to?
Change in arrangement of complex ion.
Change in geometry of the complex ion.
How can ligand exchange lead to a change in geometry of the complex ion?
If concentrated hydrochloric acid is added to a solution containing [Cu(H2O)6]2+, the six water molecules are replaced by four chloride ions.
This is a reversible reaction.
![<p><span>If concentrated hydrochloric acid is added to a solution containing [Cu(H</span><sub>2</sub><span>O)</span><sub>6</sub><span>]</span><sup>2+</sup><span>, the six water molecules are replaced by four chloride ions. </span></p><p></p><p><span>This is a reversible reaction.</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b96847f0-07fb-4974-9229-9ed1e2c3bff5.png)