chem ch 8
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
1/2massvelocity²
kinetic energy=
temp
ke of a gas is directly proportional to
gas molecules
in continous, rapid, random motion, collide with each other and walls of container but no energy is lost (elastic)
molecular masses
gases with different _ must have same average kinetic energy at same temp, heavier must move slowly, light must move faster
speeds of gases
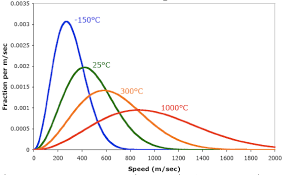
at given temp, molecules have high and low speeds, but have max (peak), as temp increase common speed increases, as temp increases, more molecules will be moving faster
square root u²=square root 3rt/molar mass
mean square speed
diffusion
mixing of gas molecules as a result of random motion, gas of oe mixture interacts with gas of other mixture
effusion
movement of gas molecules through tiny openings
square root molar mass gas 2/molar mass gas 1
rate of effusion of gas 1/rate of effusion of gas2
same
equal volumes of gas at same temp and pressure contain same number of molecules regardless of chemical nature and physical properties
6.022×10²³
one mole