heme lecture exam 3
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
Dendritic cell
lymph node macrophage
monocyte CD markers
CD11b and CD14
lymphoblast
1 or 2 blue nuclei, less basophilic than other blasts (more blue cytoplasm), lacy chromatin
leukocytosis steps
1. demarganilization (increase neutrophils by releasing from marginating pool)
2. BM release (release from storage pool)
3. Increased production (if infection persists, using mitotic pool)
4. recover (decrease neutrophils)
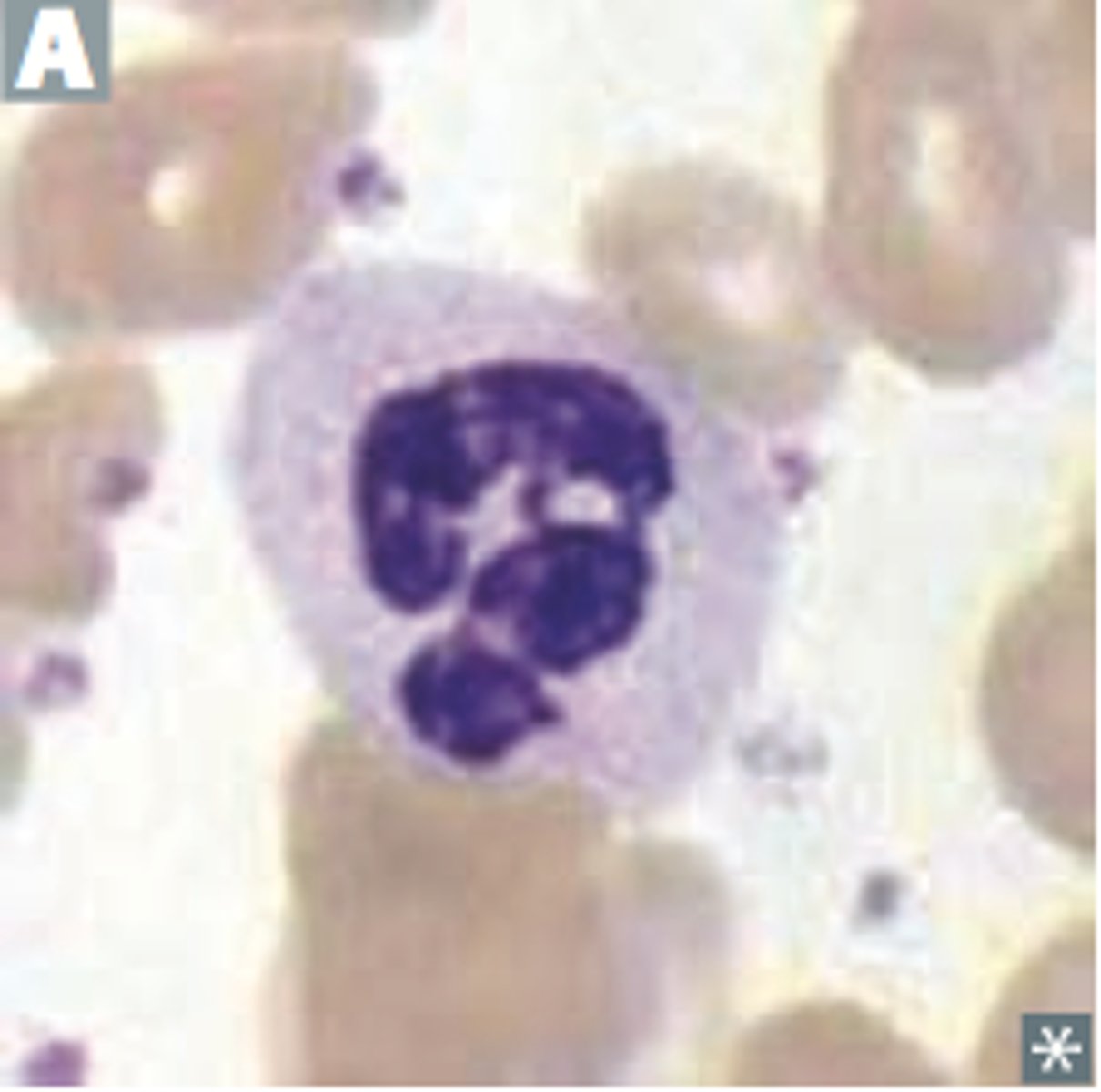
Alder-Reilly Anomoly
Auto-recessive
-Incomplete mucopolysaccharide degradation
-Purple granule with vacuole behind- looks like halo
-NORMAL function
Myeloperoxidase deficiency
Auto-recessive
-absence of MPO, but neuts can use alternative routes to kill so no increase in infection
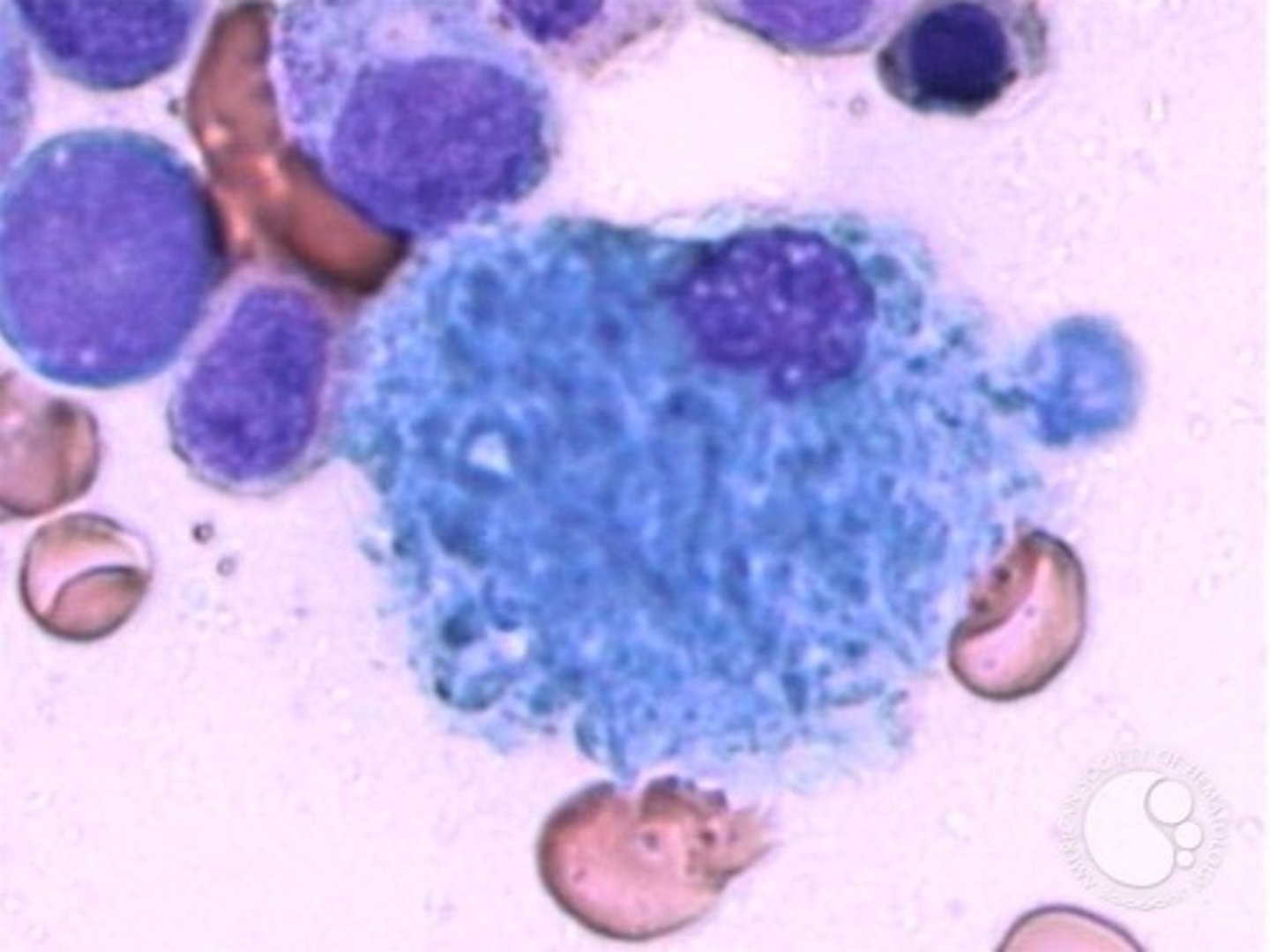
Gaucher disease
Beta glucosidase deficiency, can't break down glucocerebroside, leading to lipid accumulation in macrophages
-Characterized by WRINKLED TISSUE PAPER LOOK in cytoplasm
-leukemia, splenectomy, and anemias
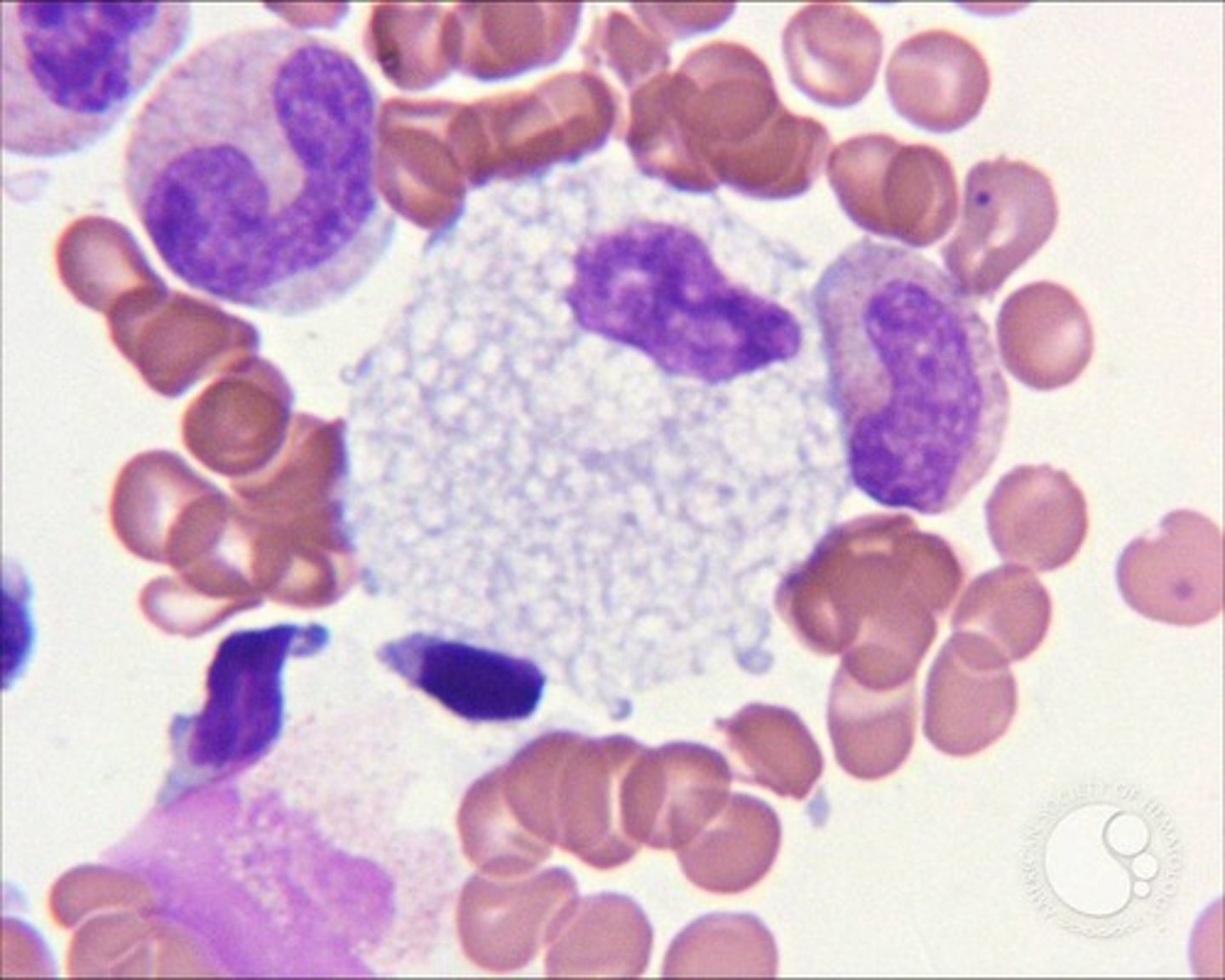
Neimann-Pick disease
Sphingomyelinase deficiency, can't break down lipids
-often fatal by 3 yrs old,
-enlarged livers and spleen, also related to leukemia
-Characterized by FOAMY macrophages
Sea blue histiocytes
Sea blue macrophages in liver, spleen, and bone marrow
-seen in lipid metabolism disorders
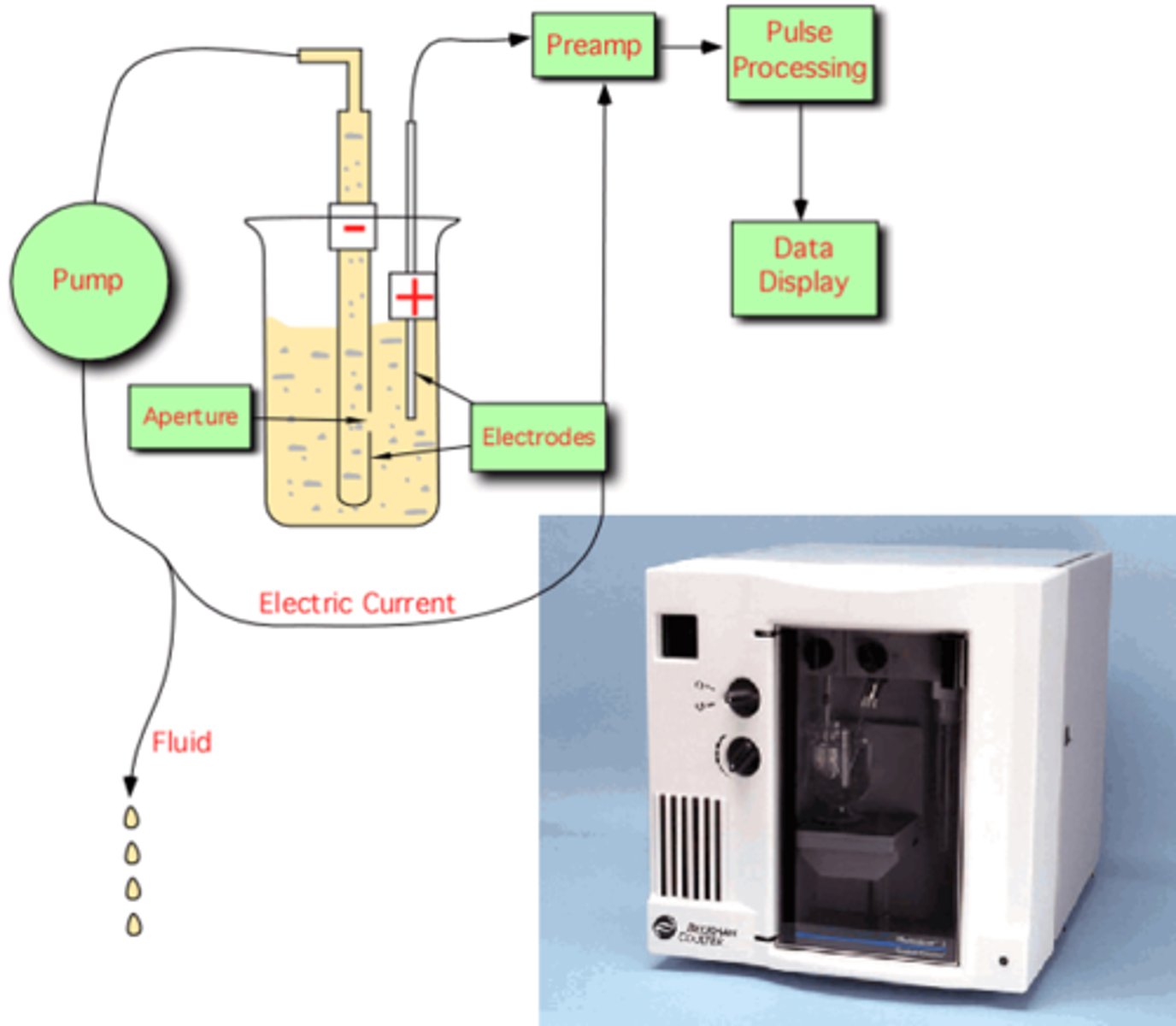
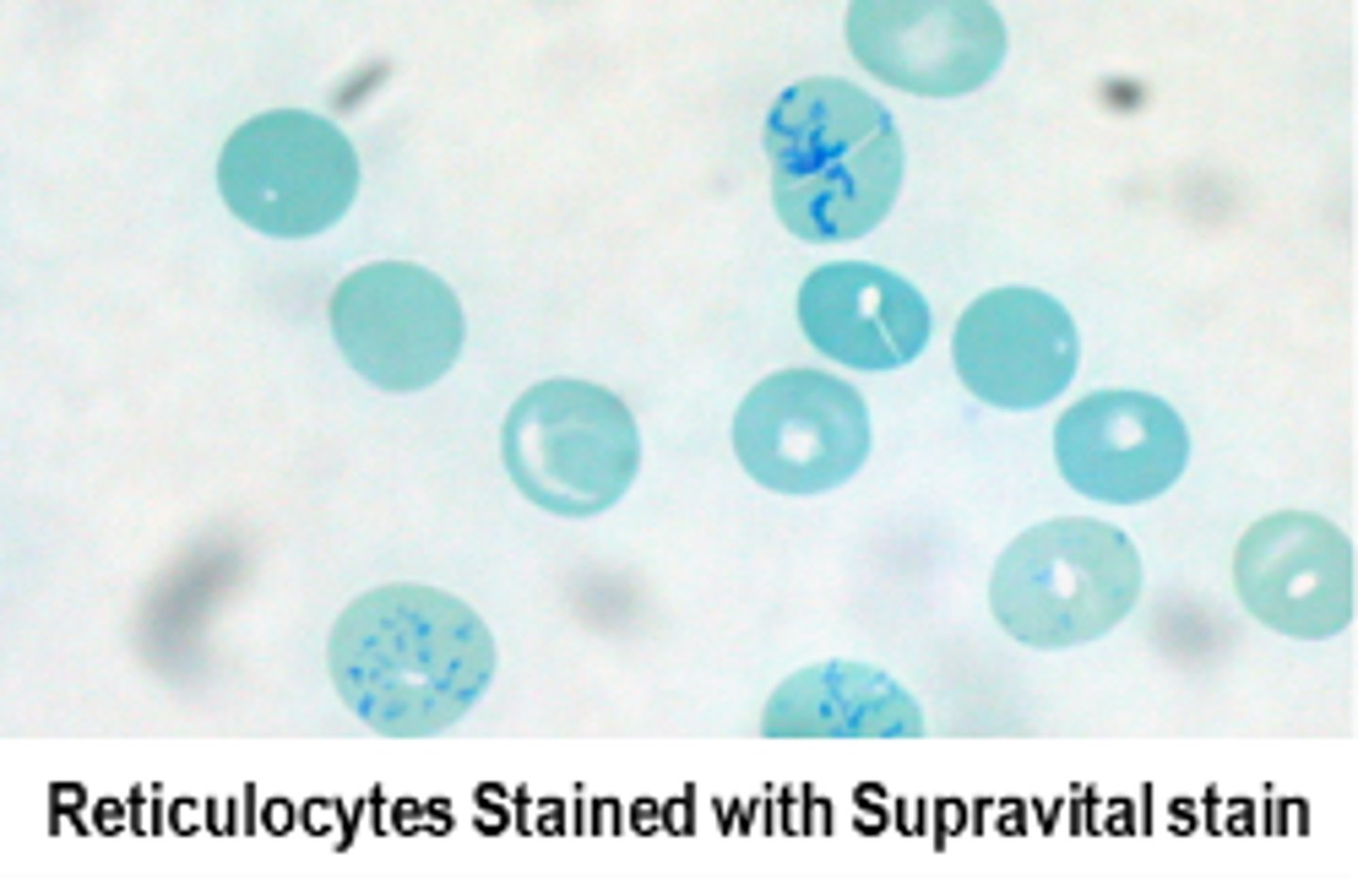
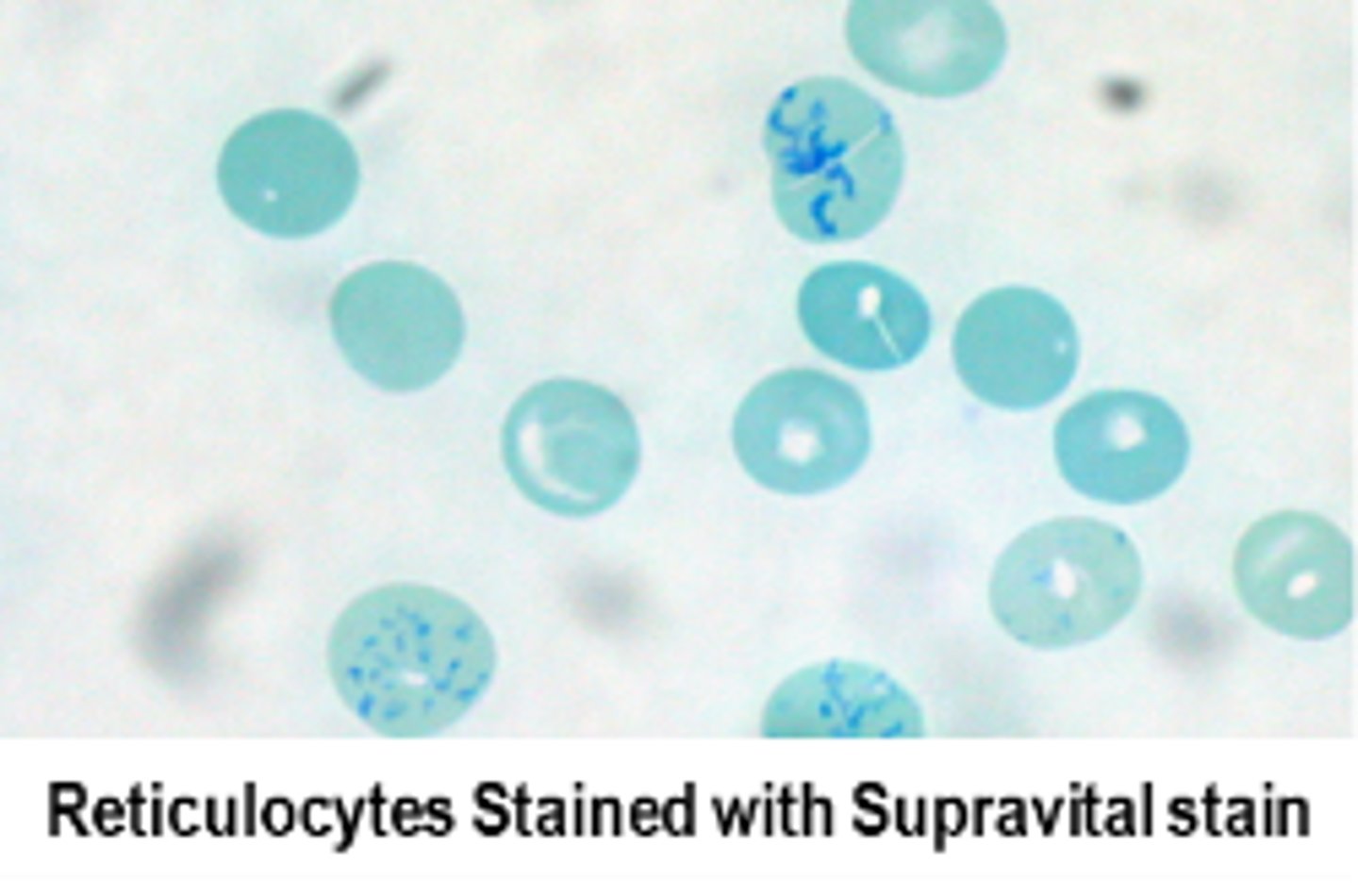
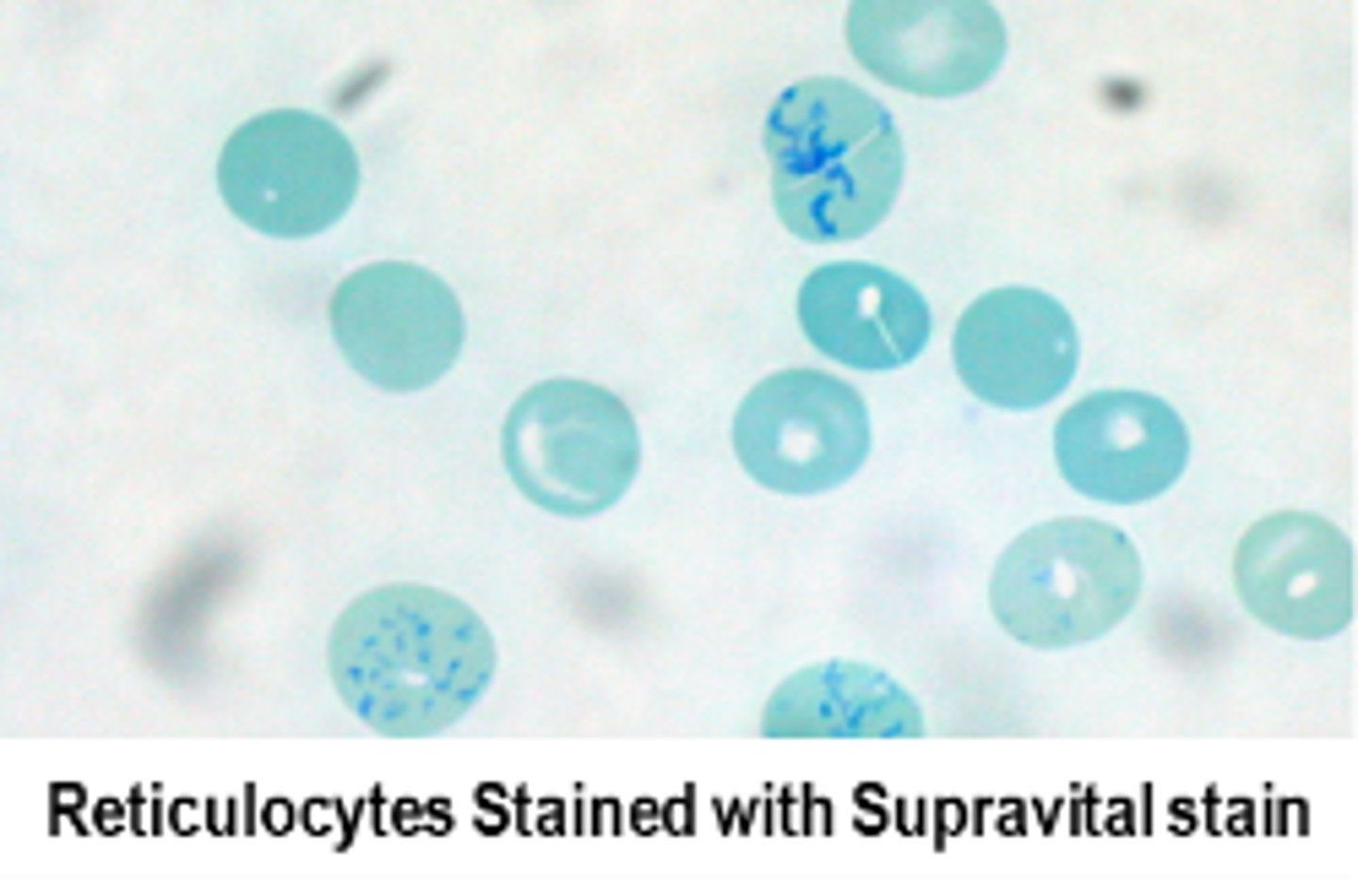
Measuring reticulocytes on Cloulter
Supervital staining and measures volume, conductivity, and scatter (VCS)
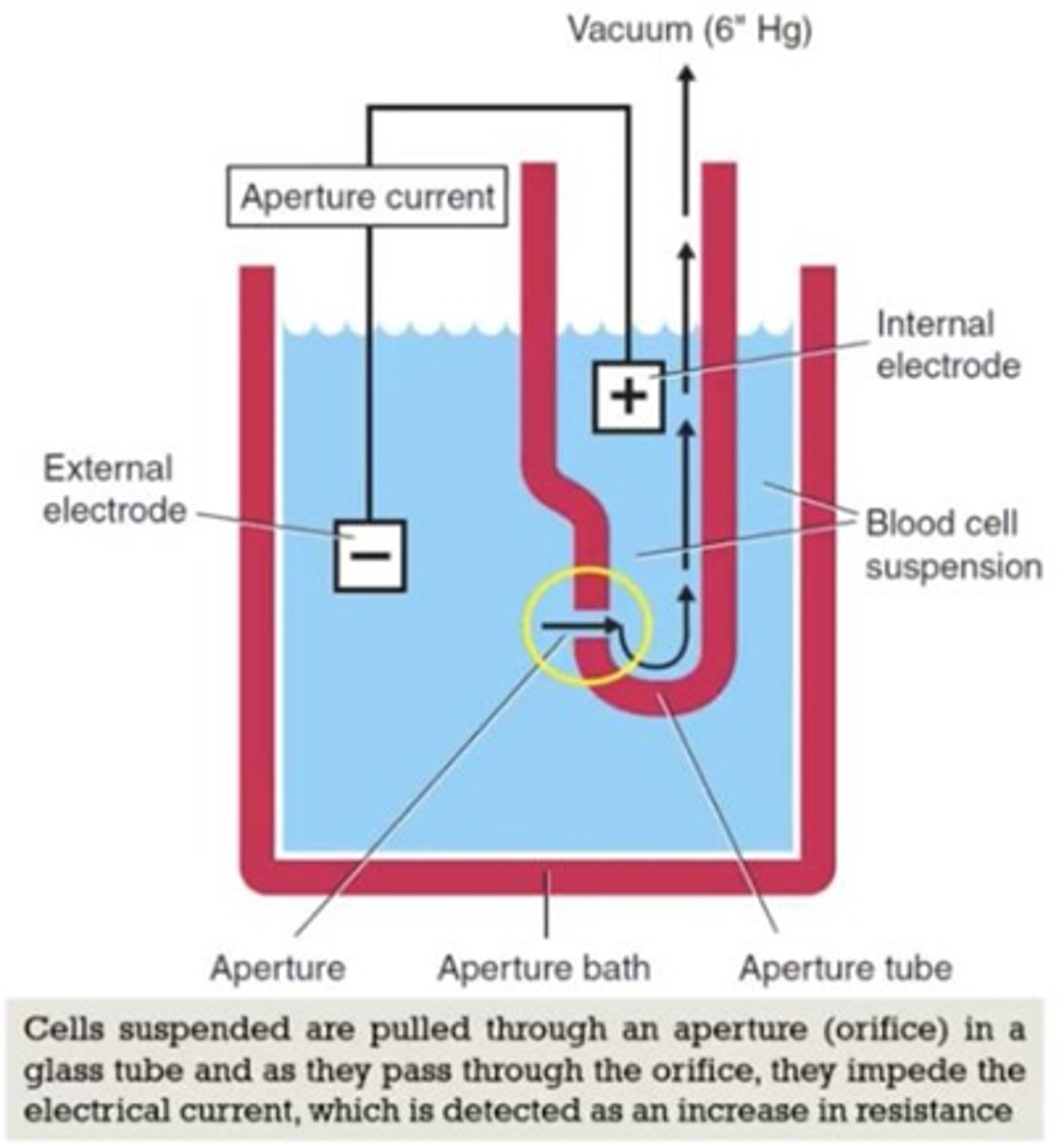
Electronic impedance
low, direct voltage measuring resistance of cell, most common
Coulter and Sysmex measuring WBC, RBC, and PLT
Impedance (electrical opposition)

Abott Cell-dyn measuring WBC, RBC, and PLT
Optical scatter and impedence
Coulter, Abott Cell-Dyn, and Siemens ADVIA measuring HGB
Modified cyanomethemoglobin (all at different nm)

Sysmex measuring HGB
SLB-Hb
Abott Diffs
MAPSS
(Multi-Angle Polymerized Scatter Separation)
RBC baby 1
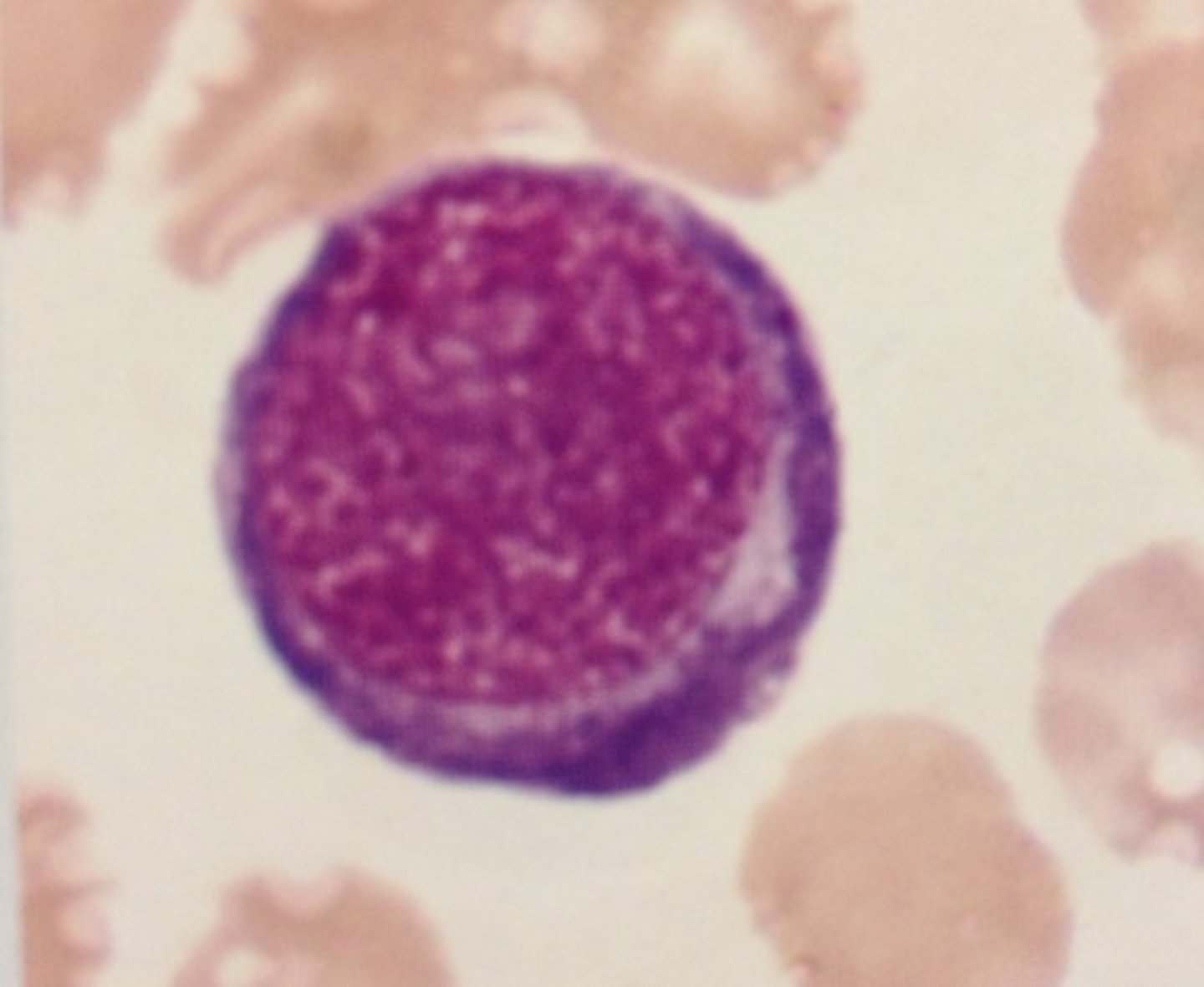
Pronormoblast/ rubriblast/ proerythroblast
-80% nucleus
-Needs EPO
-deep blue cytoplasm and loose nucleus
-1% BM
RBC baby 2
Basophilic normoblast/ prorubicyte/ basophilic erythroblast
- 70% nucleus
-Beginning on HGB synthesis
-nucleus clumps begin
-basophilic cytoplasm
- 1-4% BM
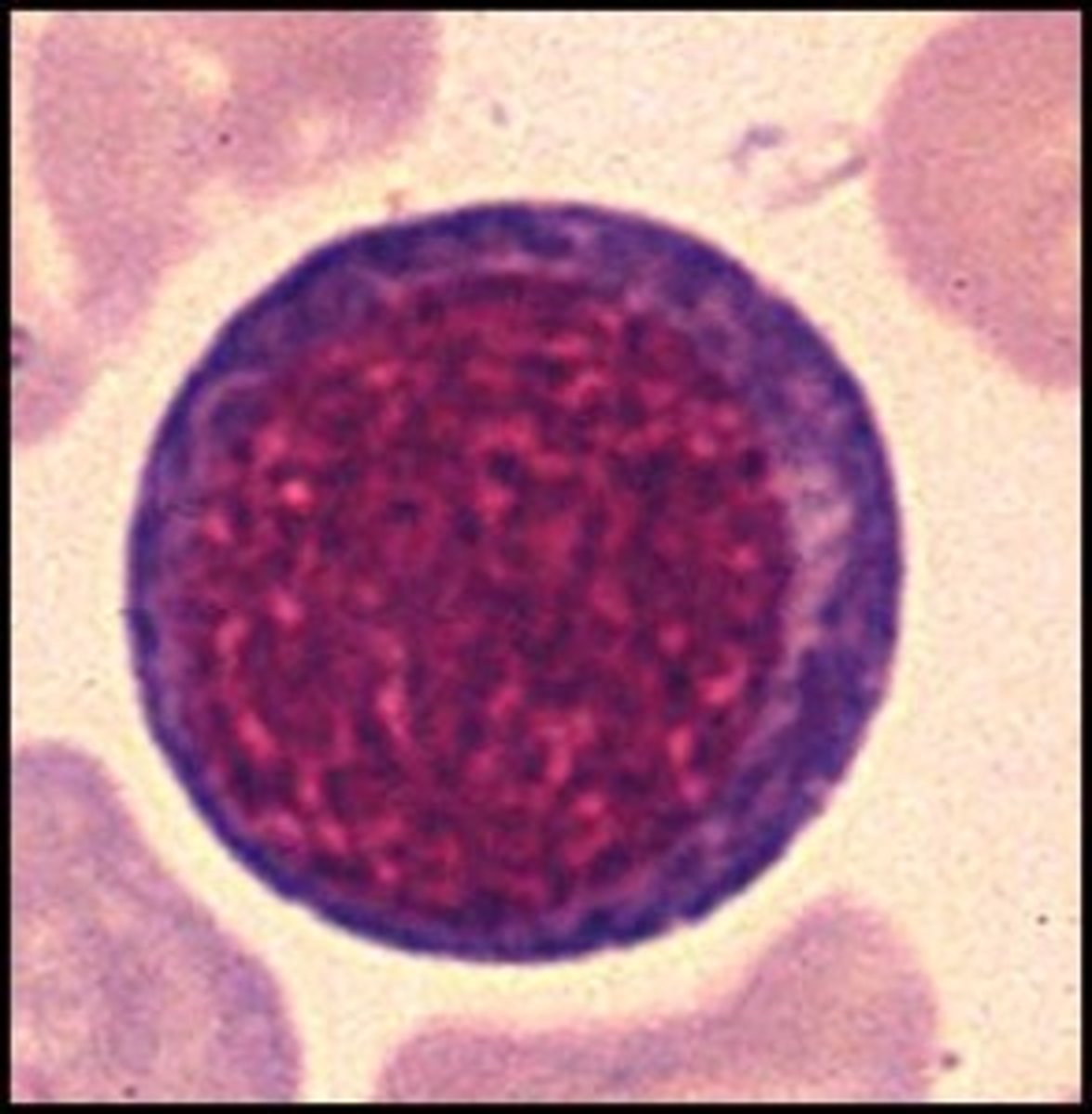
RBC baby 3
Rubricyte/ Polychromatic normoblast/ polychromatic erythroblast
- 60% nucleus
- nucleus is almost completely clumped
-gray cytoplasm
- 3-5% BM
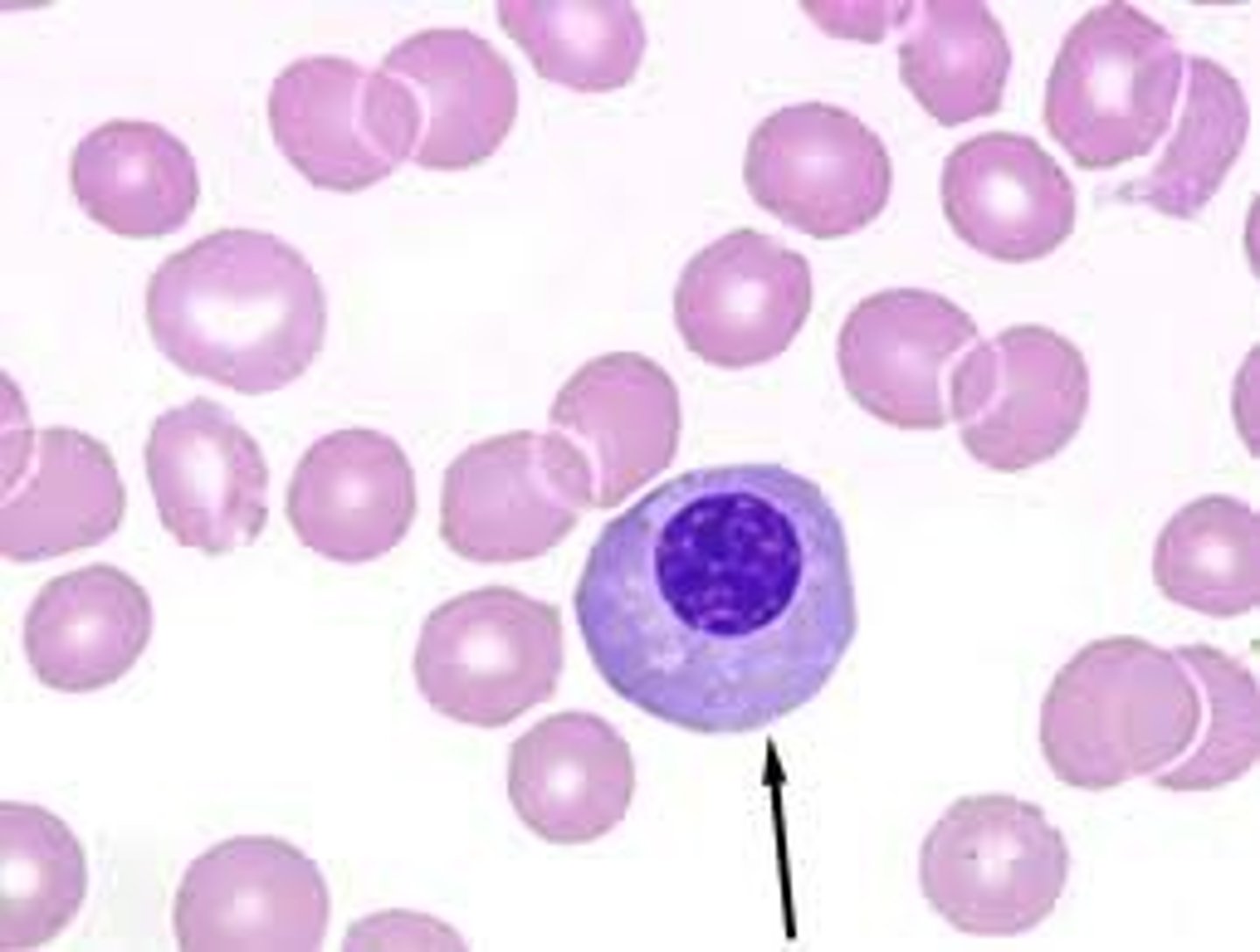
Baby RBC 4
Metarubicyte/ Orthochromic normoblast/ Orthochromic Erythroblast
- 45% nucleus
- very tight nucleus
- orangey cytoplasm
- 1-5% BM
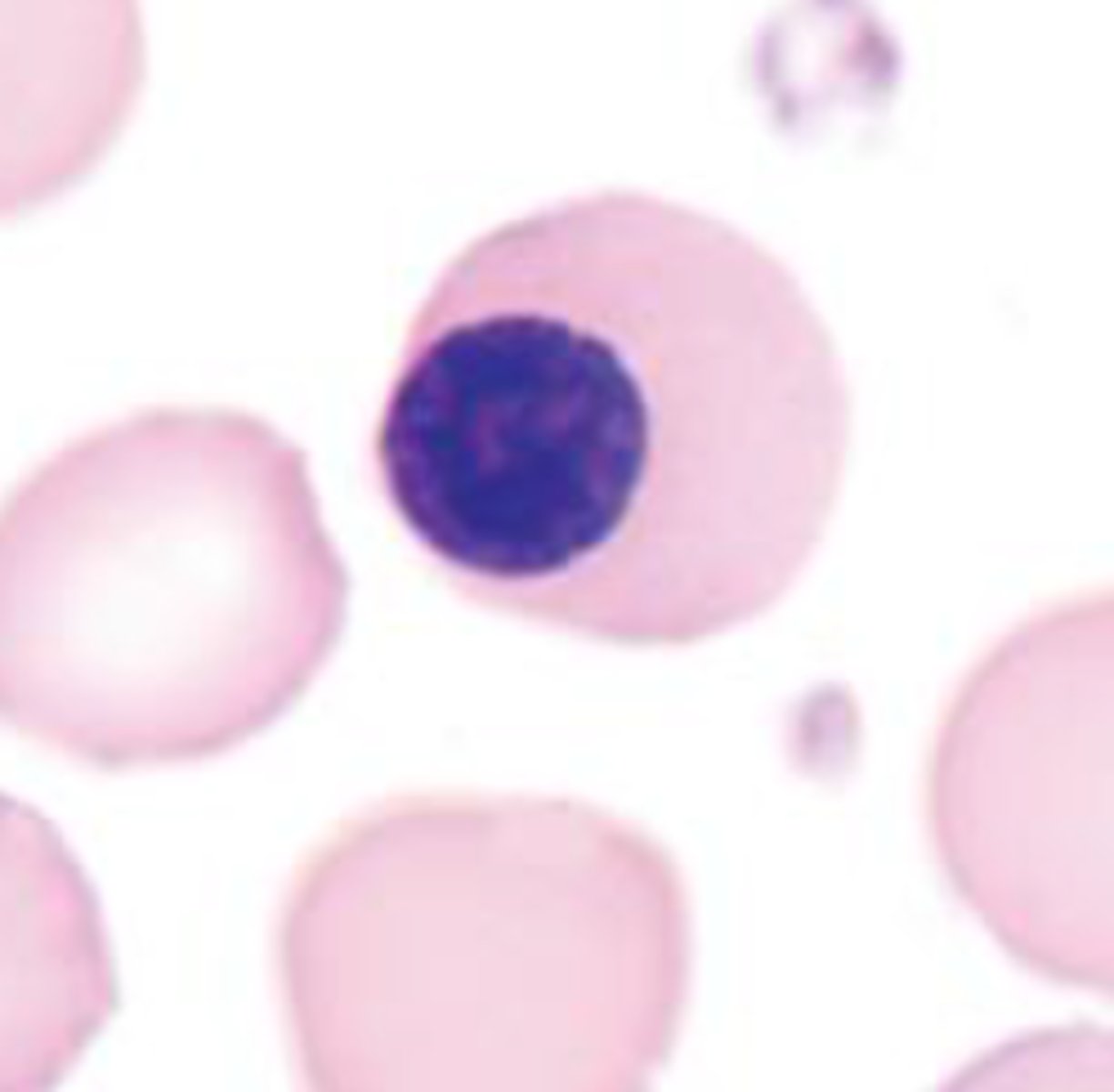
Baby RBC 5
Reticulocyte/ polychromic erythrocyte
- no nucleus
-purple cytoplasm
- 0.5-2.5% BM
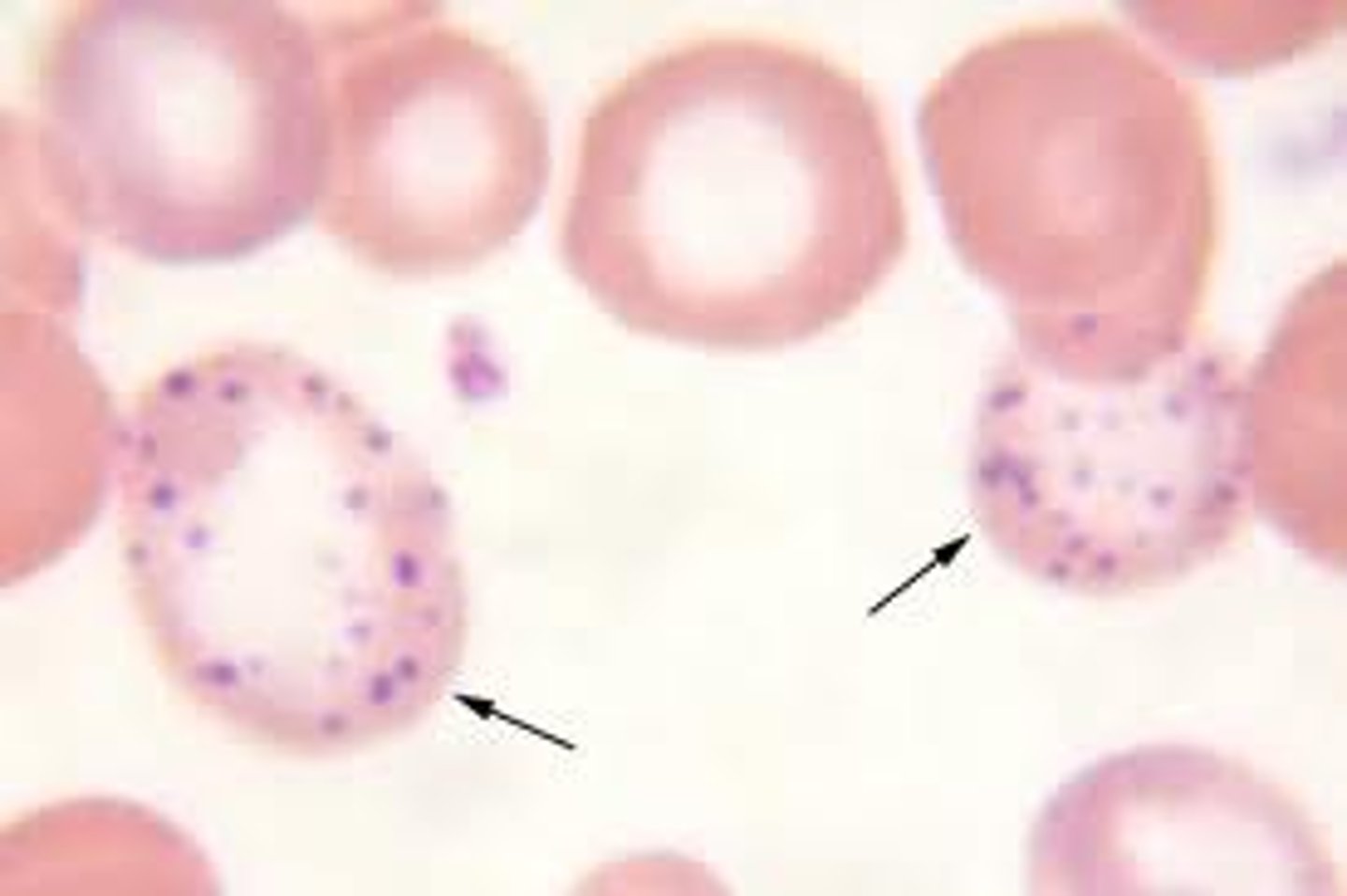
Pappenheimer bodies (RBC inclusion)
-iron inclusion
-splenectomy, hemolytic anemia
Ecchinocyte (Burr)
- Uremia (kidney disease), pyruvate kinase deficiency
Spherocytes
hereditary spherocytosis
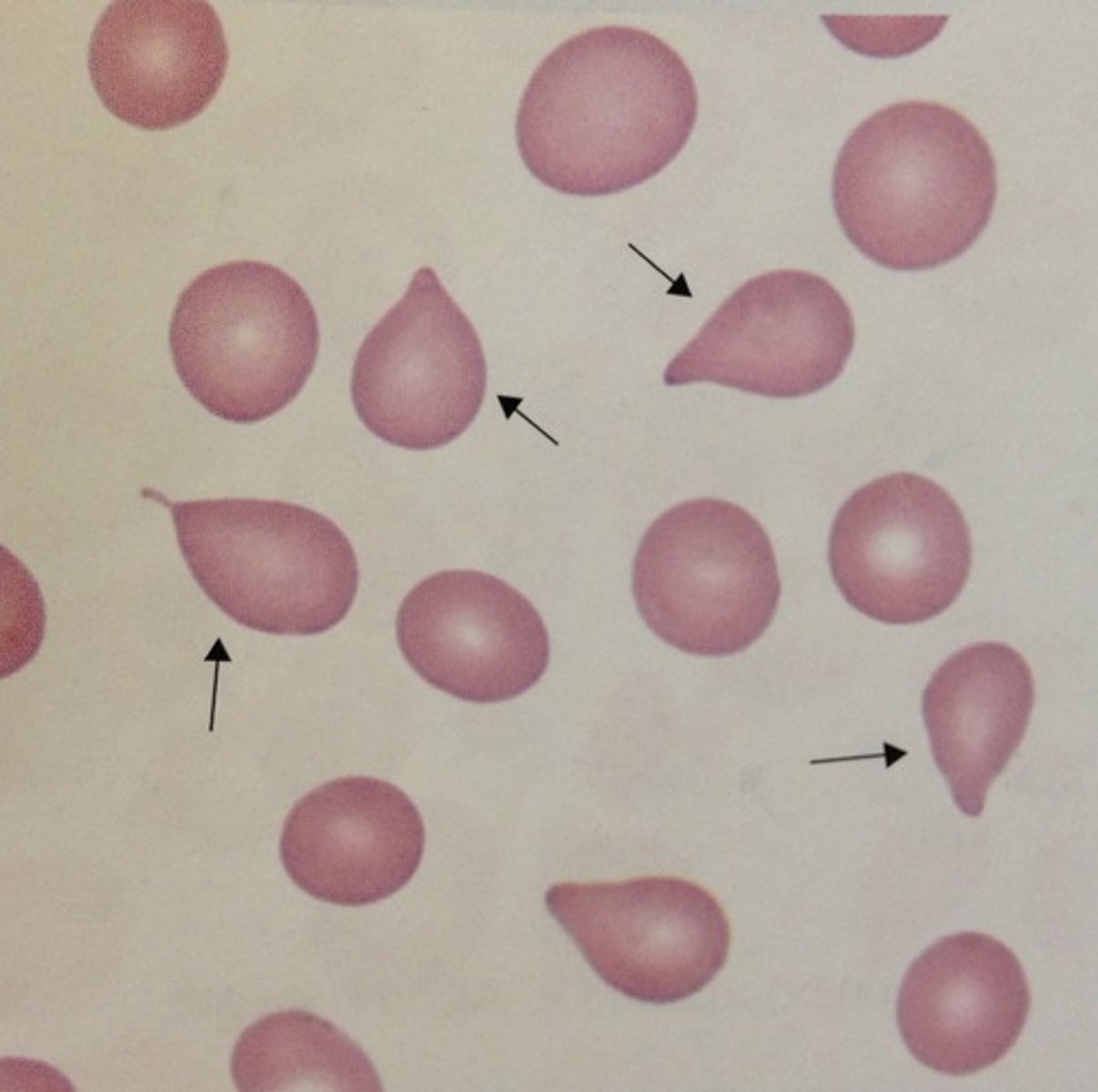
Tear drop cell (dacryocyte)
primary myelofibrosis
Stomatocyte
Hereditary stomatocytosis, alcoholism, liver disease
- among us is an alcoholic
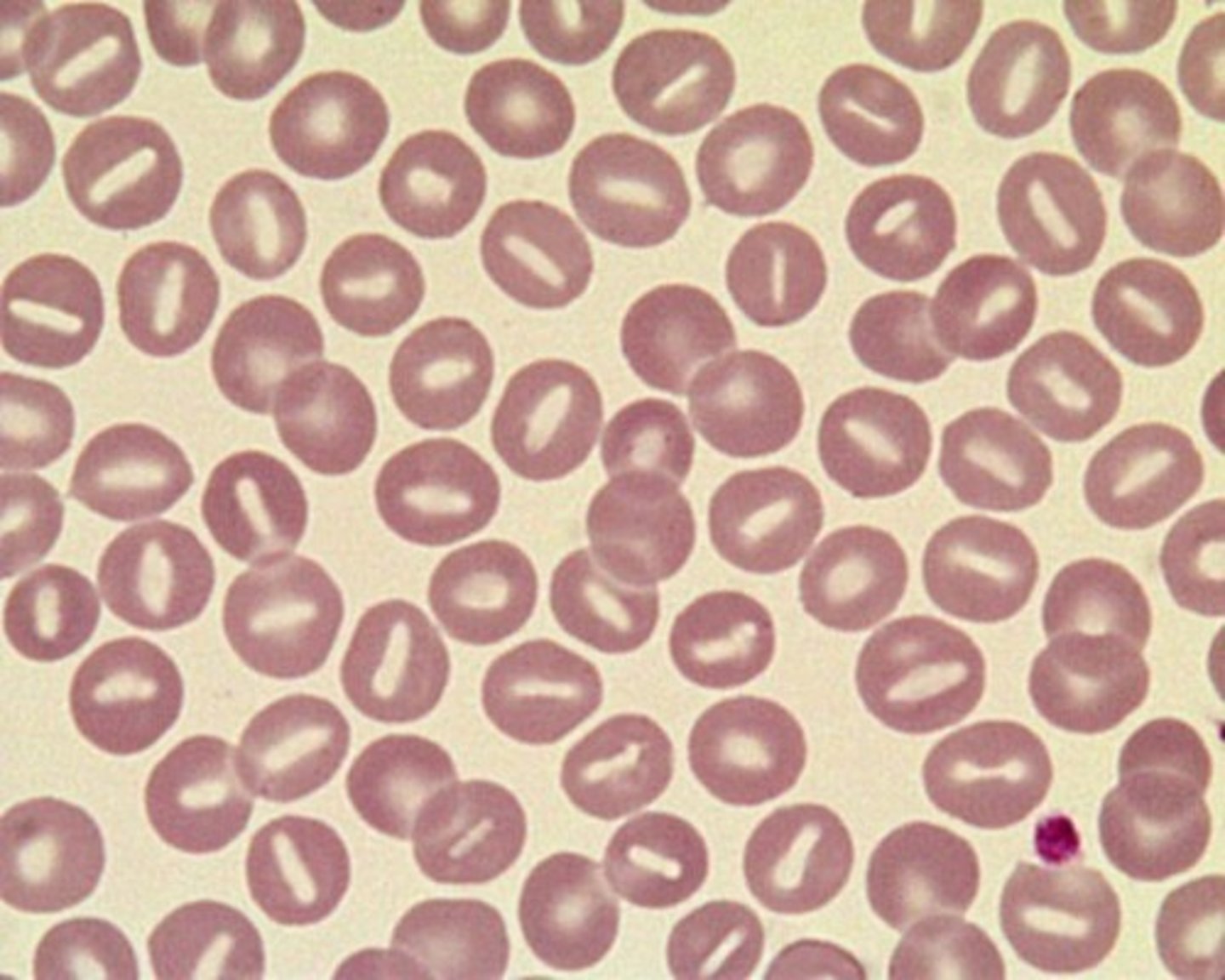
ALDER-REILLY ANOMALY
autosomal recessive, large purple granules in all lymphocytes
-incompletely degraded mucopolysaccharides that accumulate in lysosomes
-cells function normally
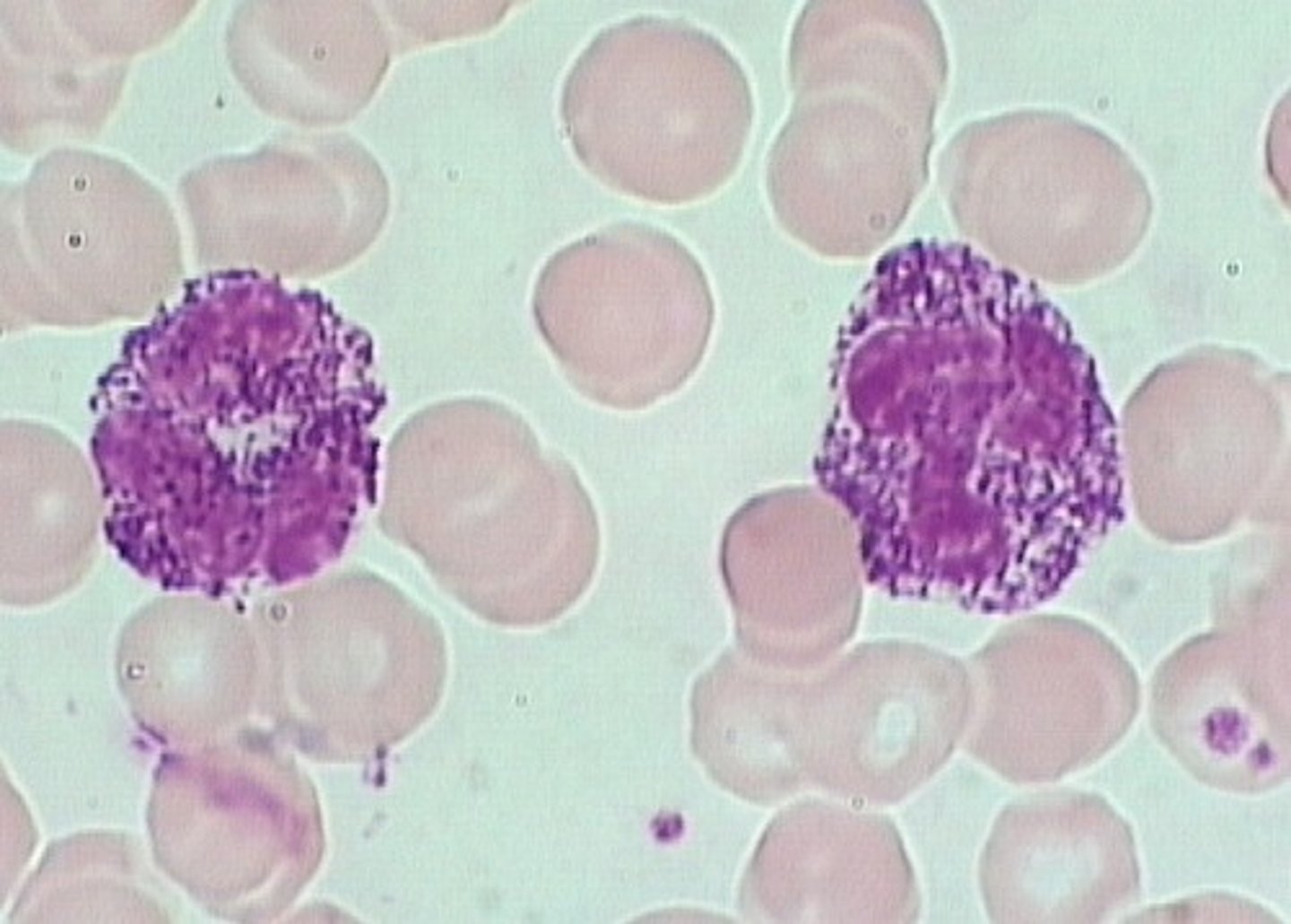
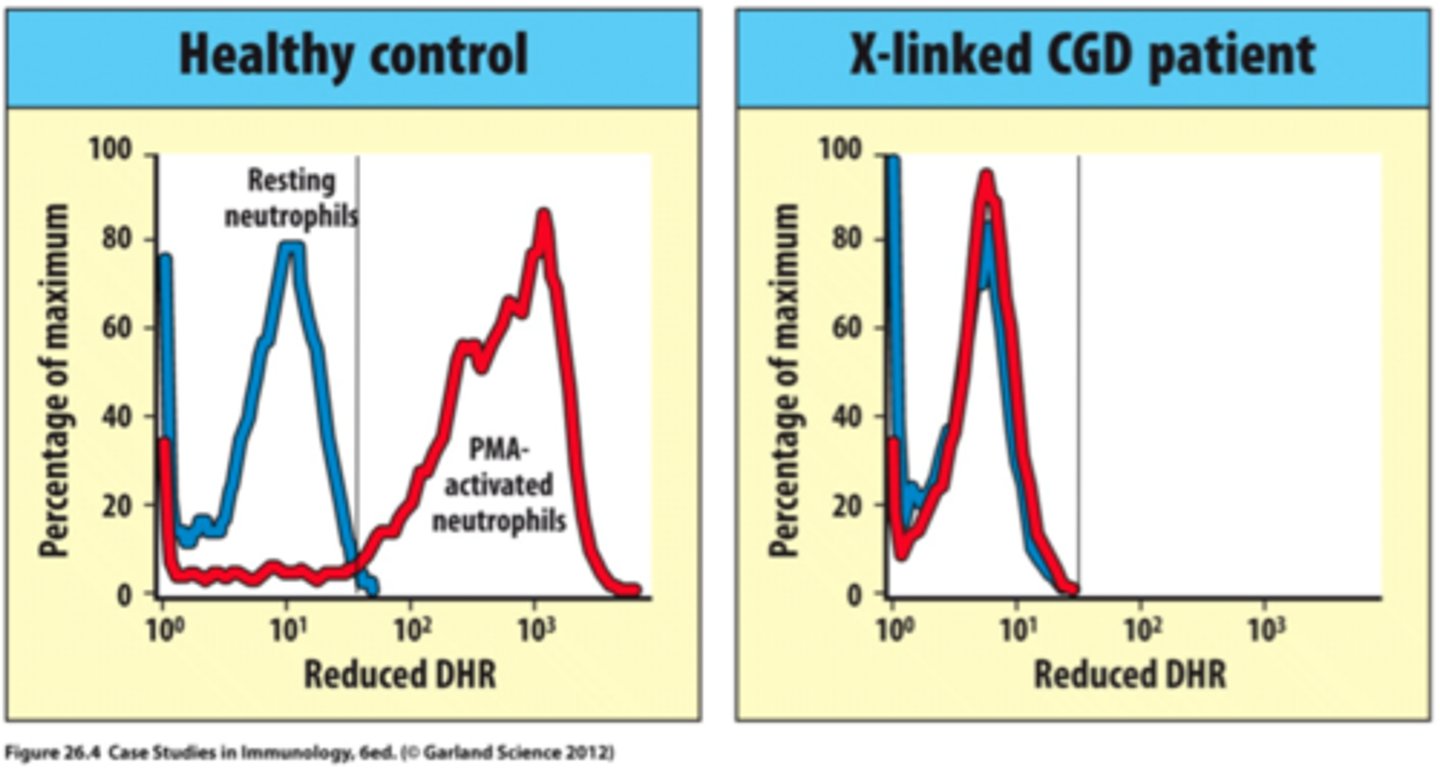
Chronic granulomatous disease
X-linked mutation affecting NADPH oxidase causing dysfunctioning neutrophils and oxidative burst
-IgG increased
-tested through Nitroblue tetrazolium test (NBT) and flow cytometry
-Cannot kill catalase-positive bacteria leading to large masses
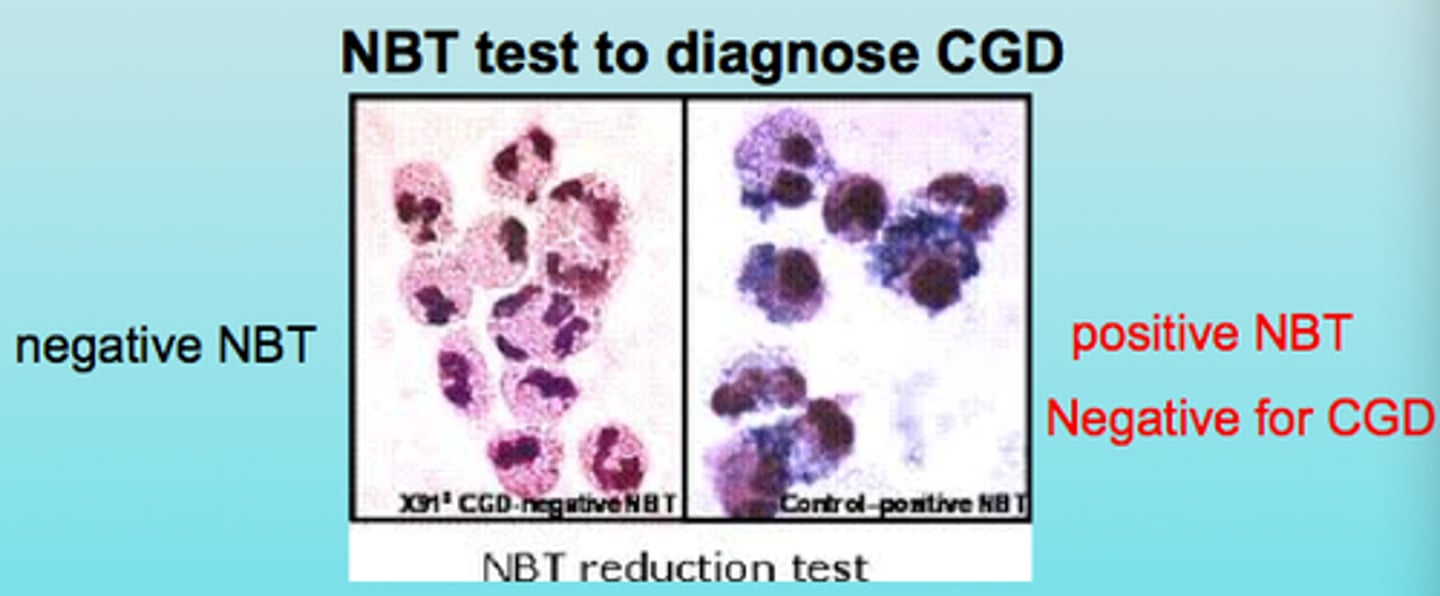
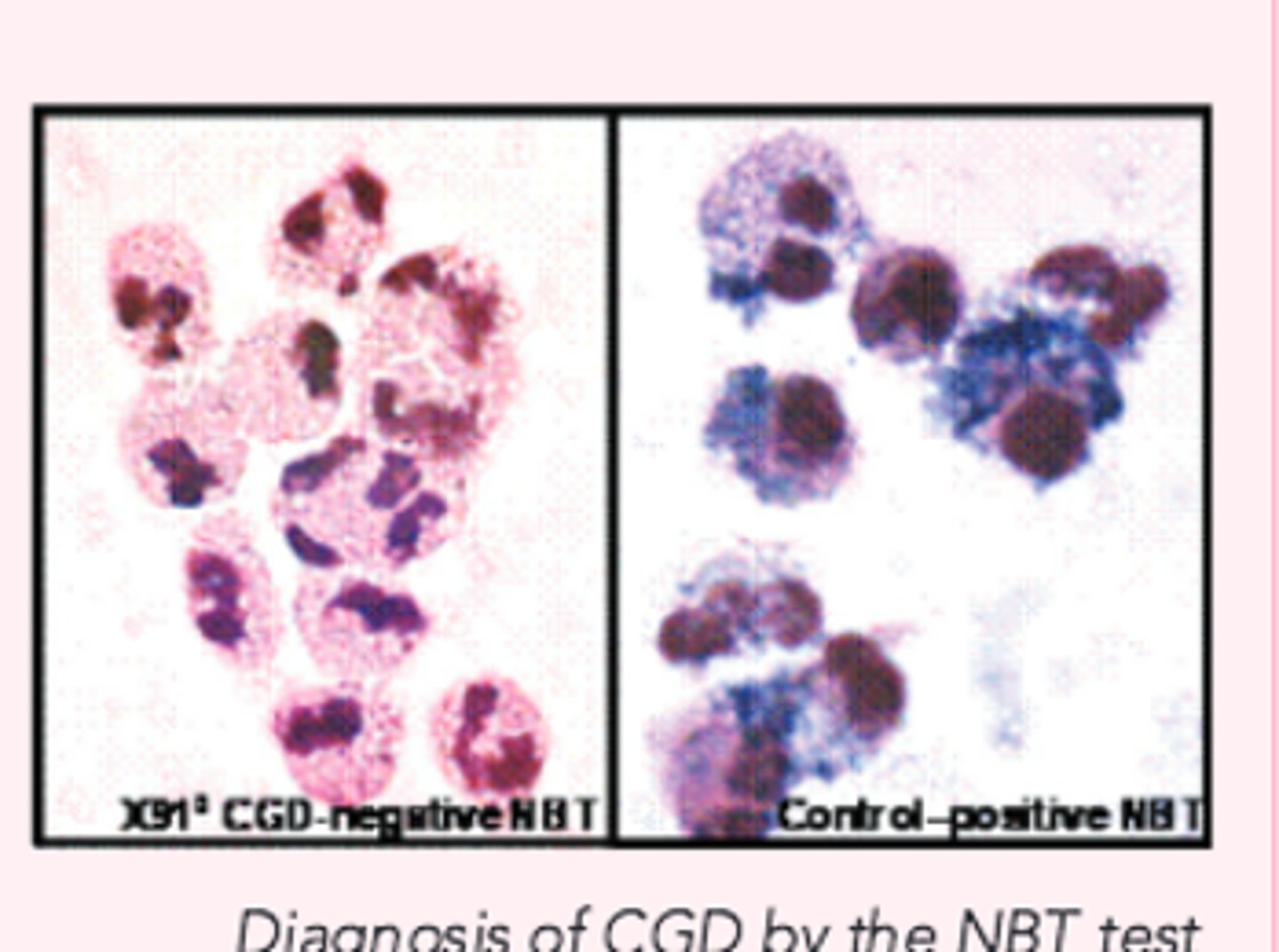
Nitroblue tetrazolium test (NBT)
Reduced to a blue insoluble formazanpigment by O2 generated by activatednormal phagocytes (qualitative)
MYELOPEROXIDASE DEFICIENCY
Defective bactericidal activity• Benign autosomal recessive disorder
- Absence of MPO
- usually no increase in infection (use alt system)
B cell CD markers
CD19, CD20, CD21, CD22
- B cells
T cell CD markers
CD4- helper T cell (mostly in lymph nodes, 60-80% of pb T cells)
CD8- Cytotoxic T cells in BM (~35% of pb)
CD7, CD2, CD5, CD3
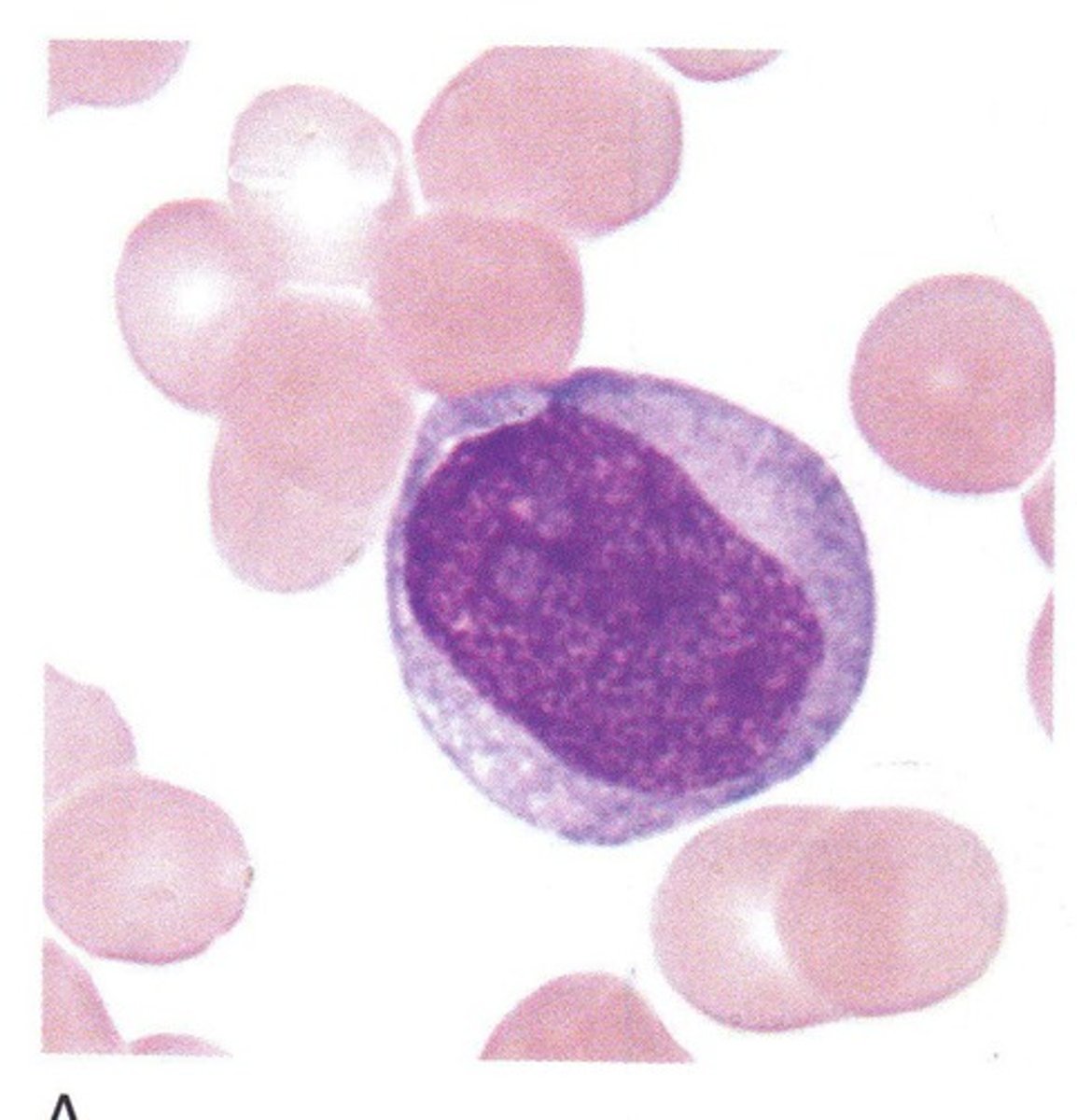
monoblast
blue, grey cytoplasm, round nucleus, agranular
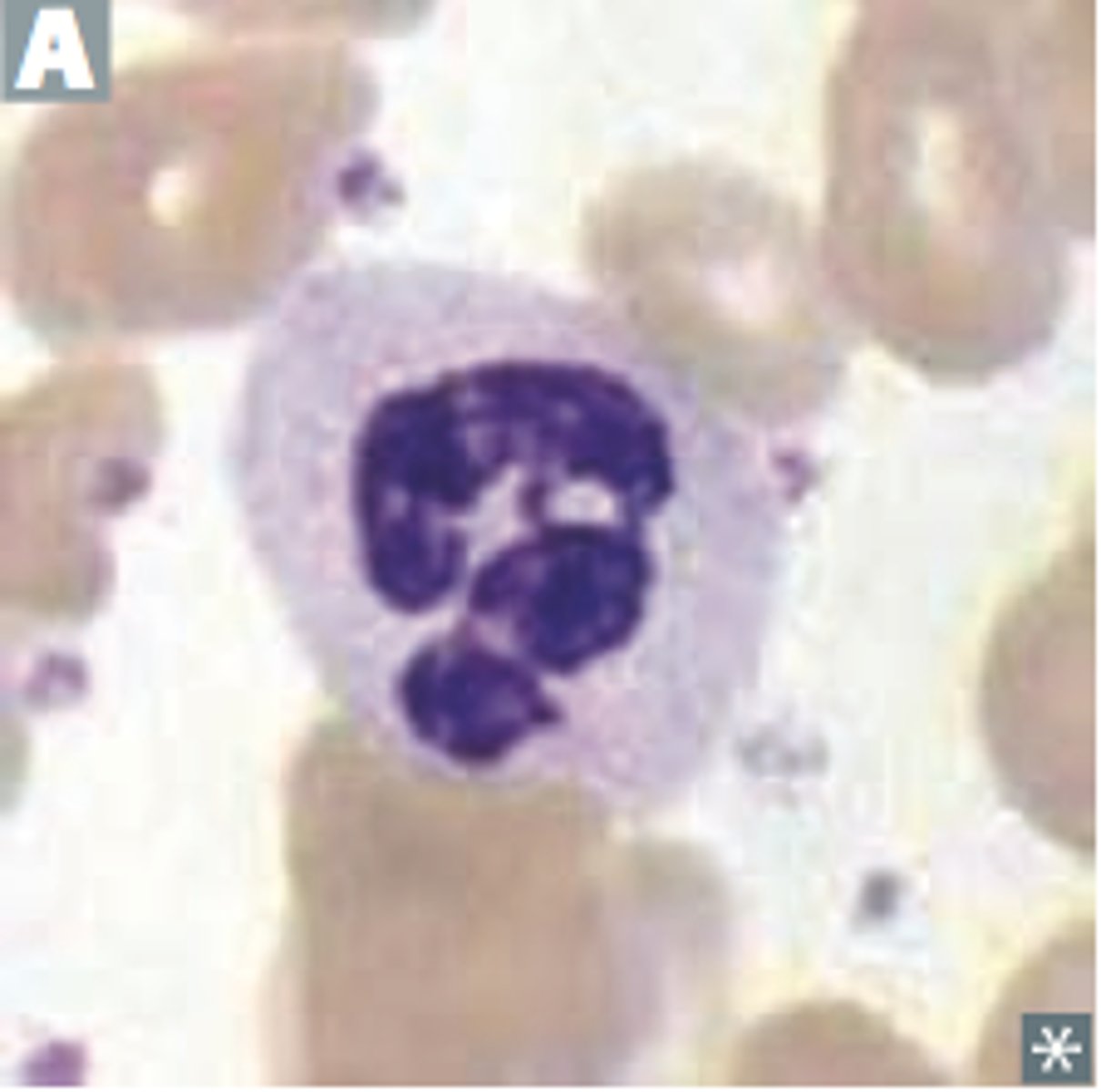
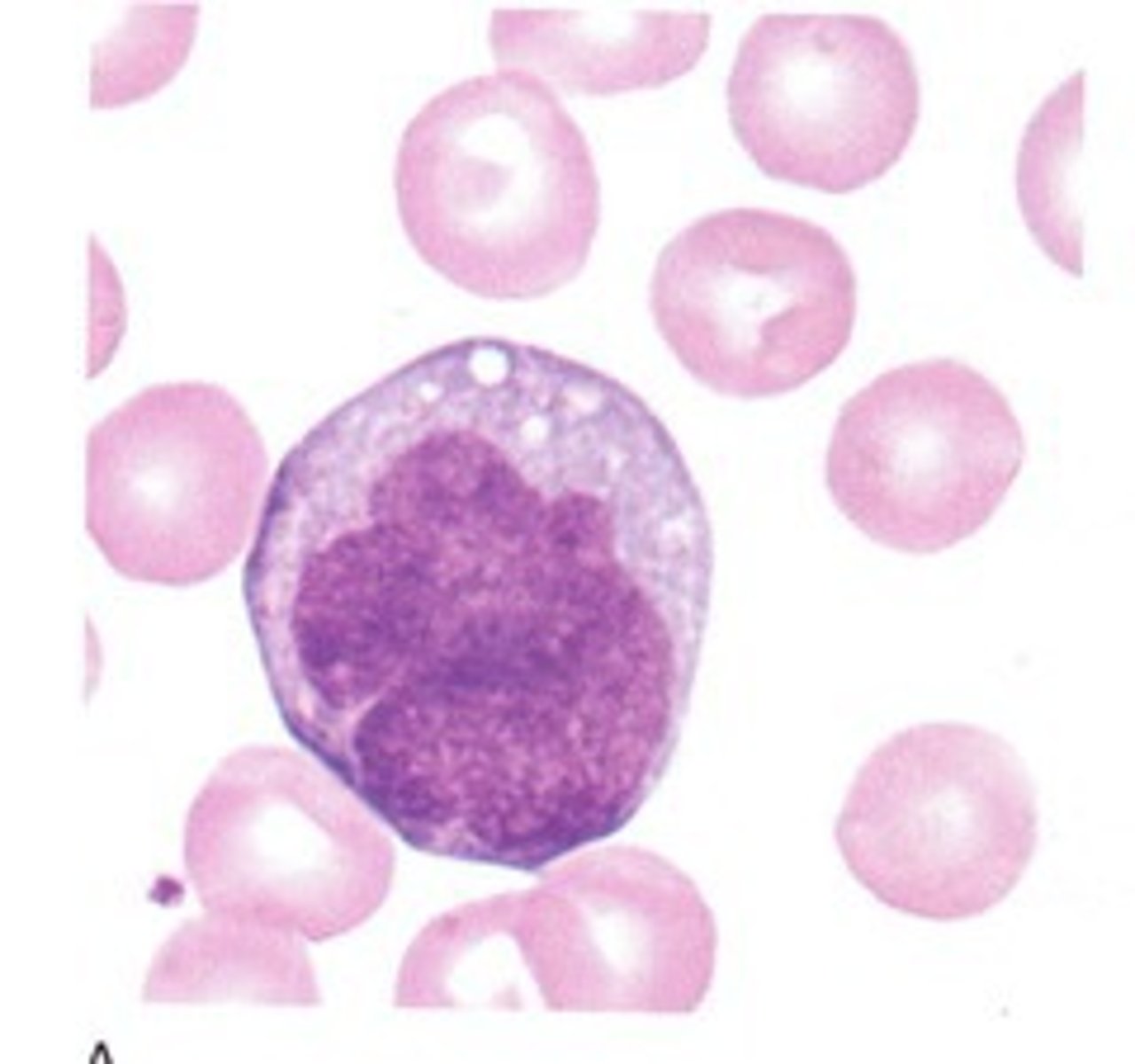
promonocyte
irregular nucleus indented nucleus, coarser look, may have vacuoles or azurophilic granules
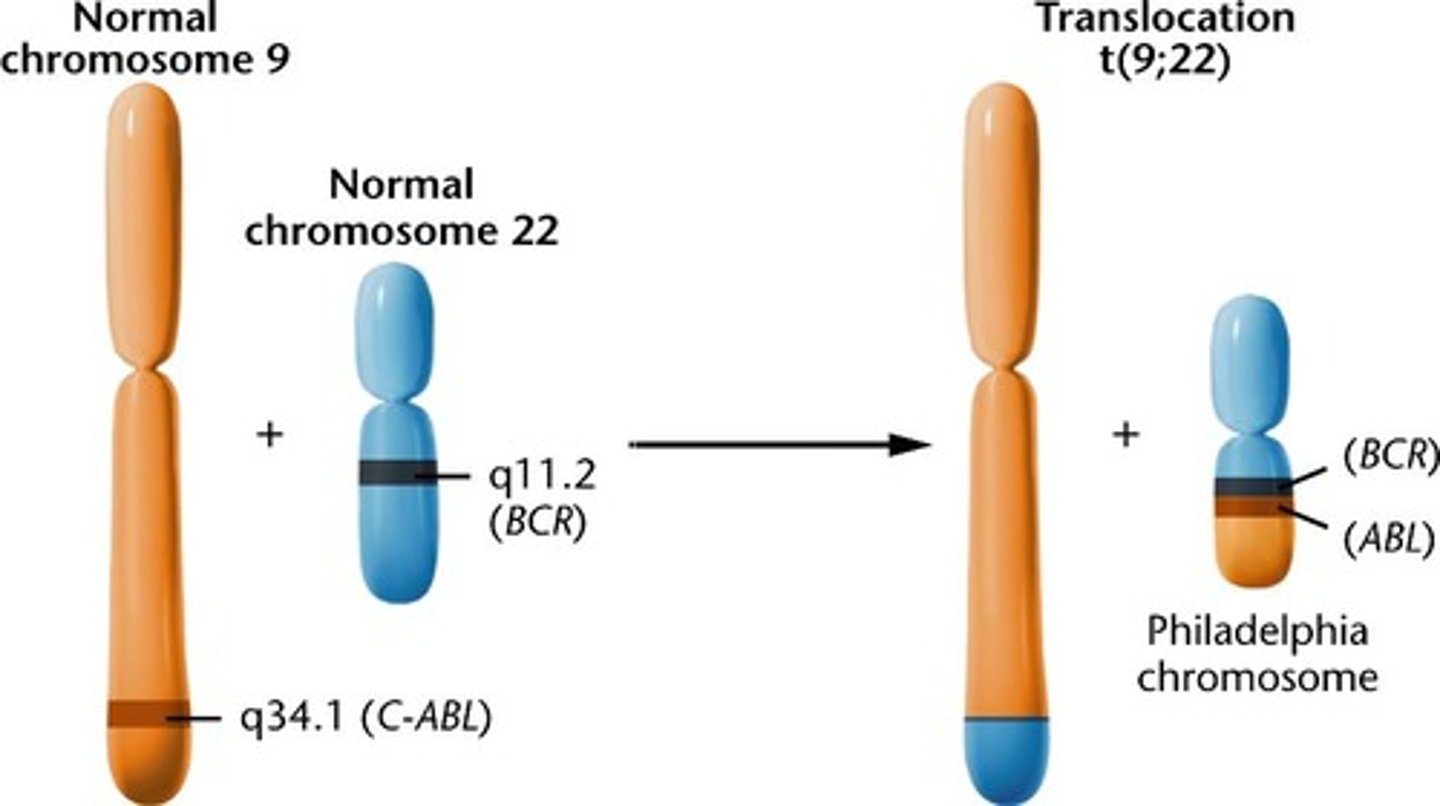
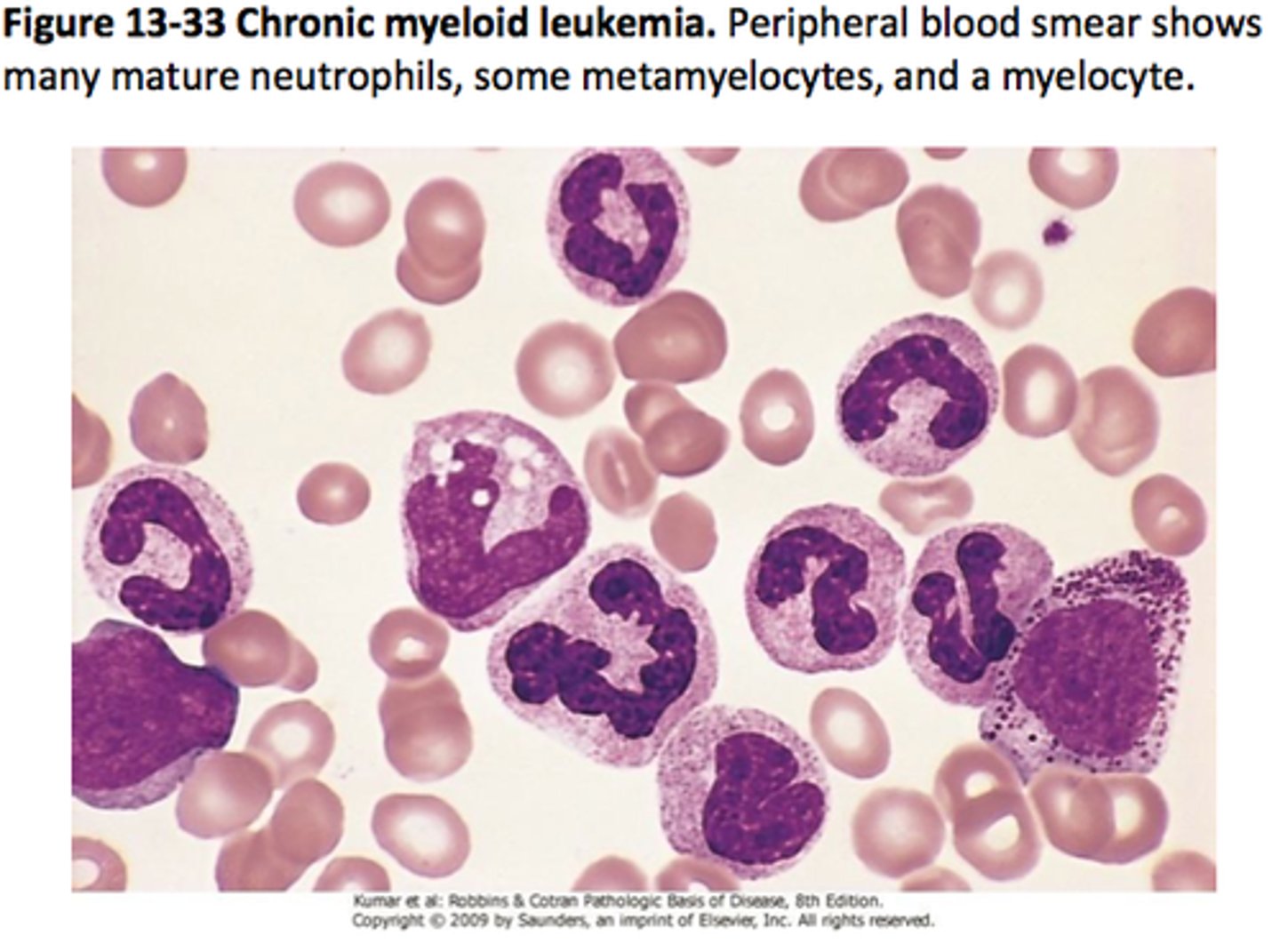
Philadelphia chromosome
mutation where chromosomes 9 and 22 are spliced together leading to uncontrolled tyrosine kinase activity = chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)
Pelger Huet vs. pseudo Pelger Huet
pelger huet= genetic bilobed nuclei with no implications
pseudo= CML
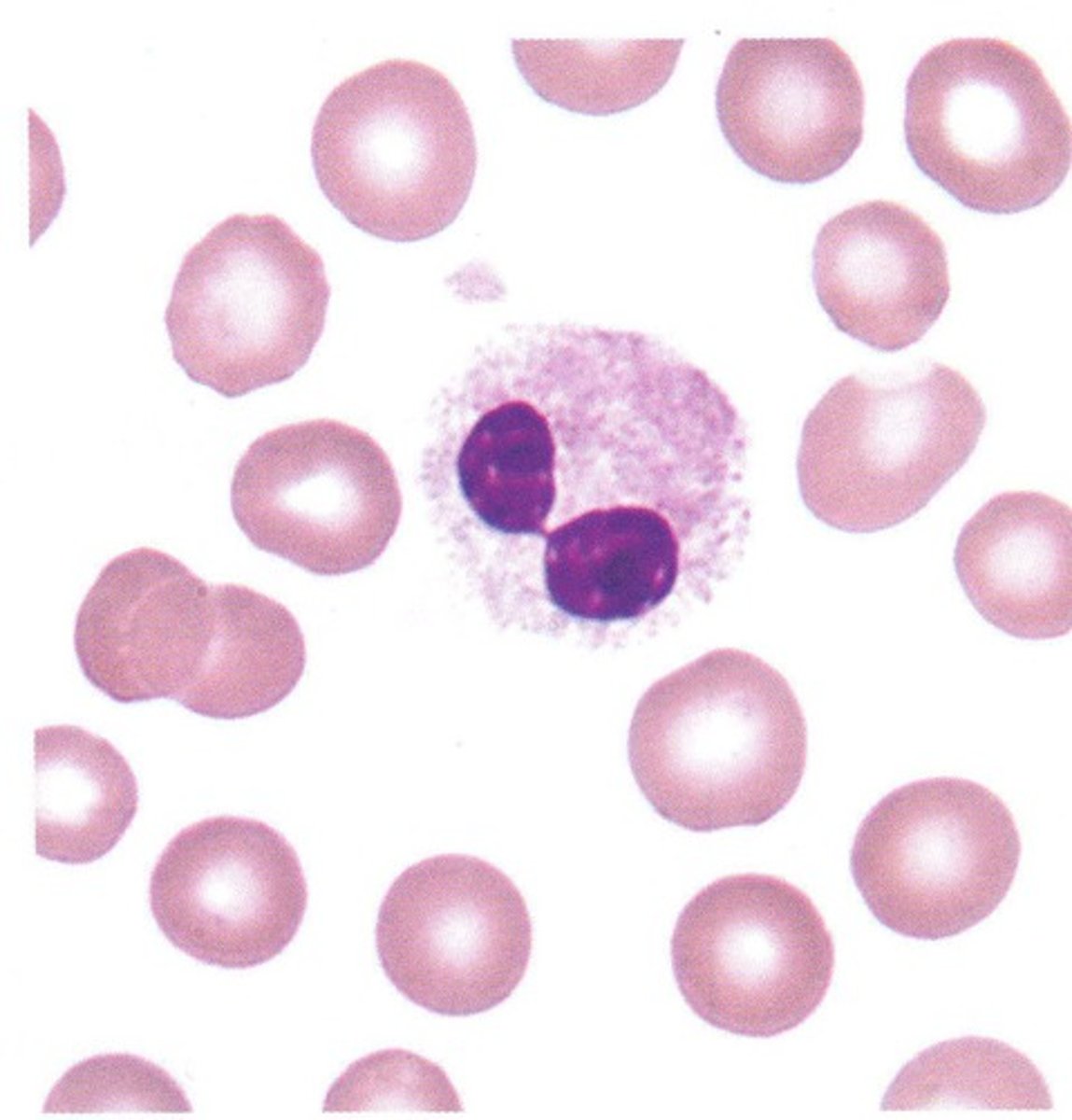
Chediak-Higashi syndrome
Autosomal recessive
- neutropenia and thrombocytopenia with giant lysosomes
-leads to albinism and high mortality for children
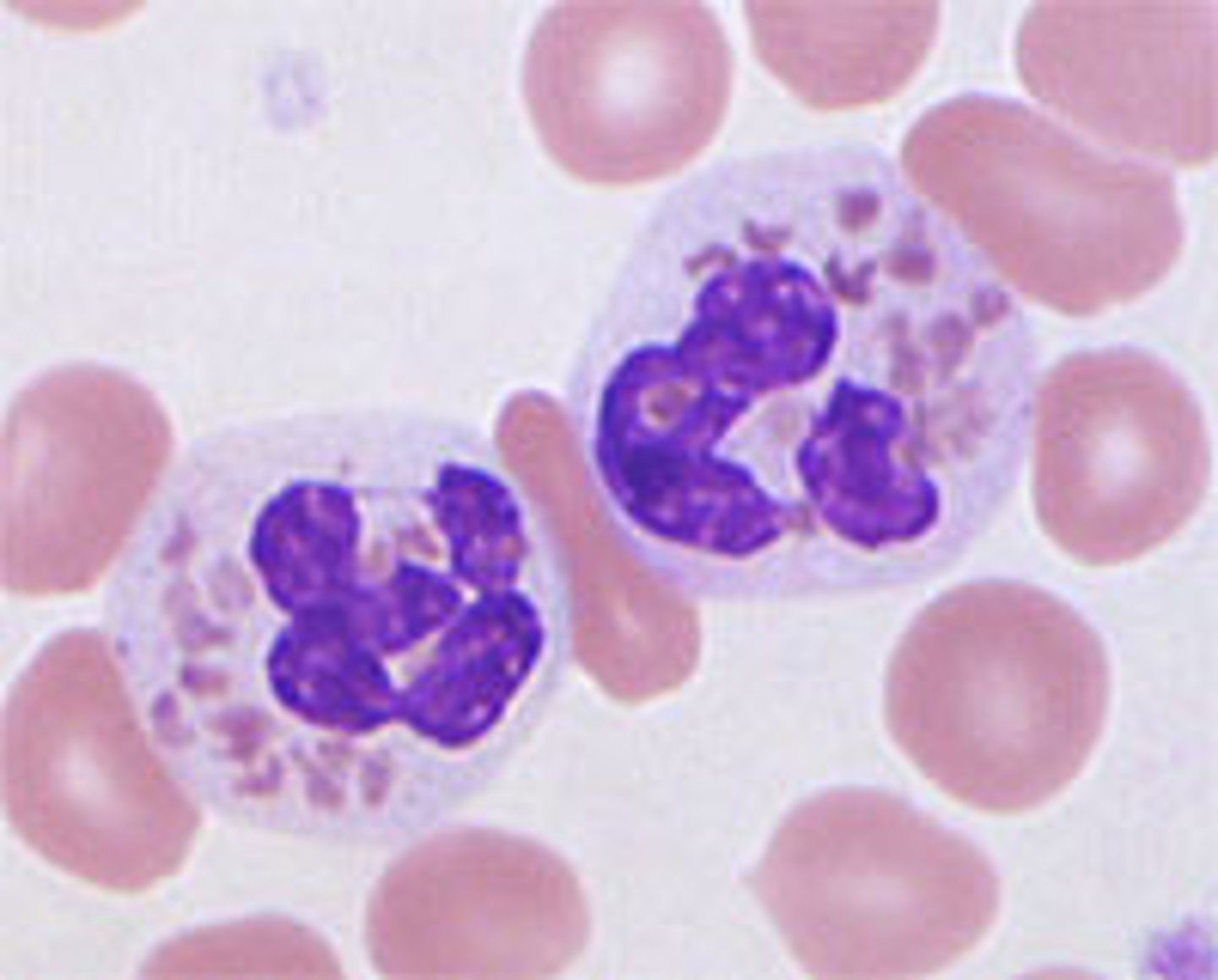
L.E. cells
* L for lupus
-seen in other autoimmune diseases
-Cells with the nuclei of other cells phagocytized inside
-Usually in CSF
- Allowed for 1st "anti-nuclear antibody test" to detect autoimmune disorders
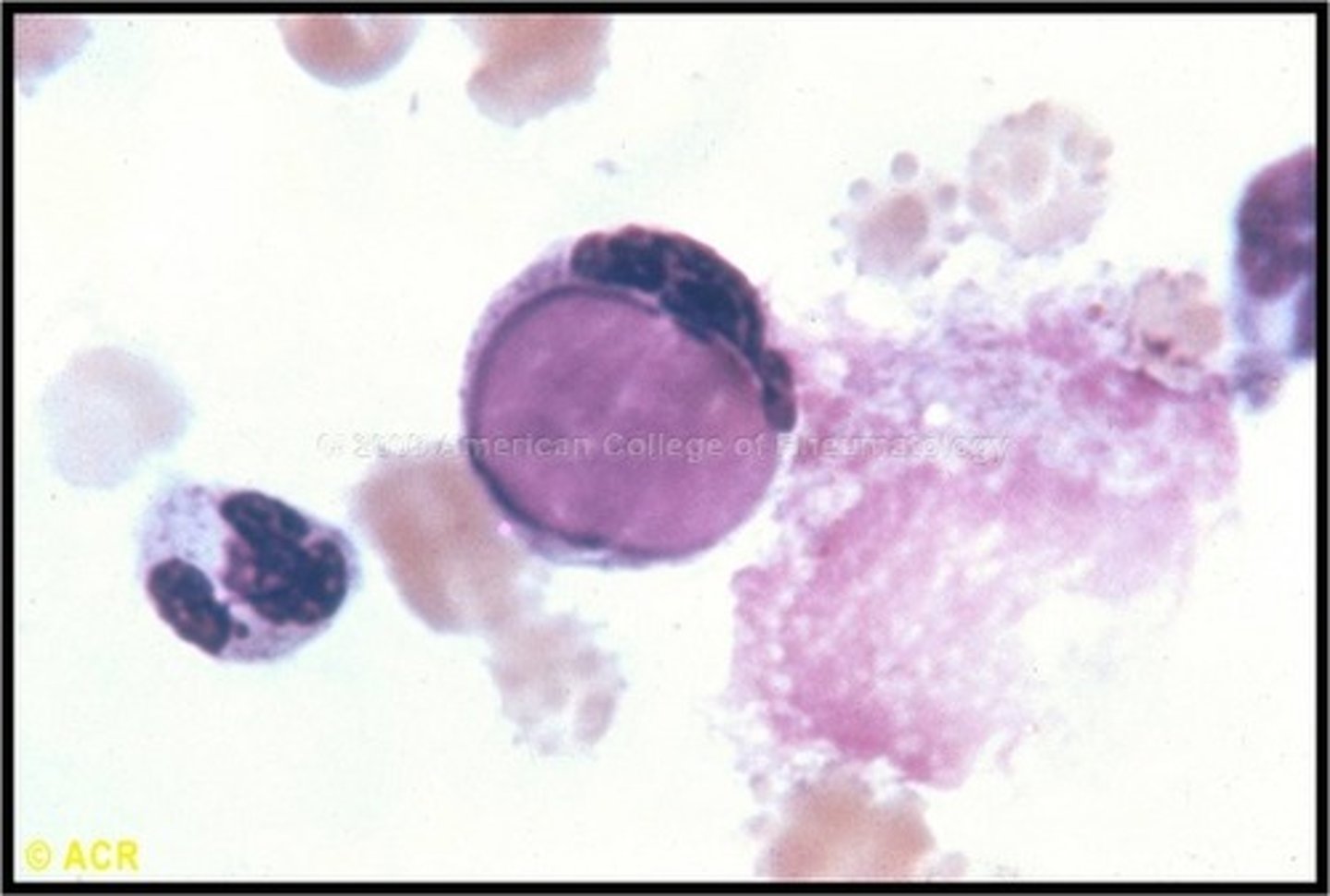
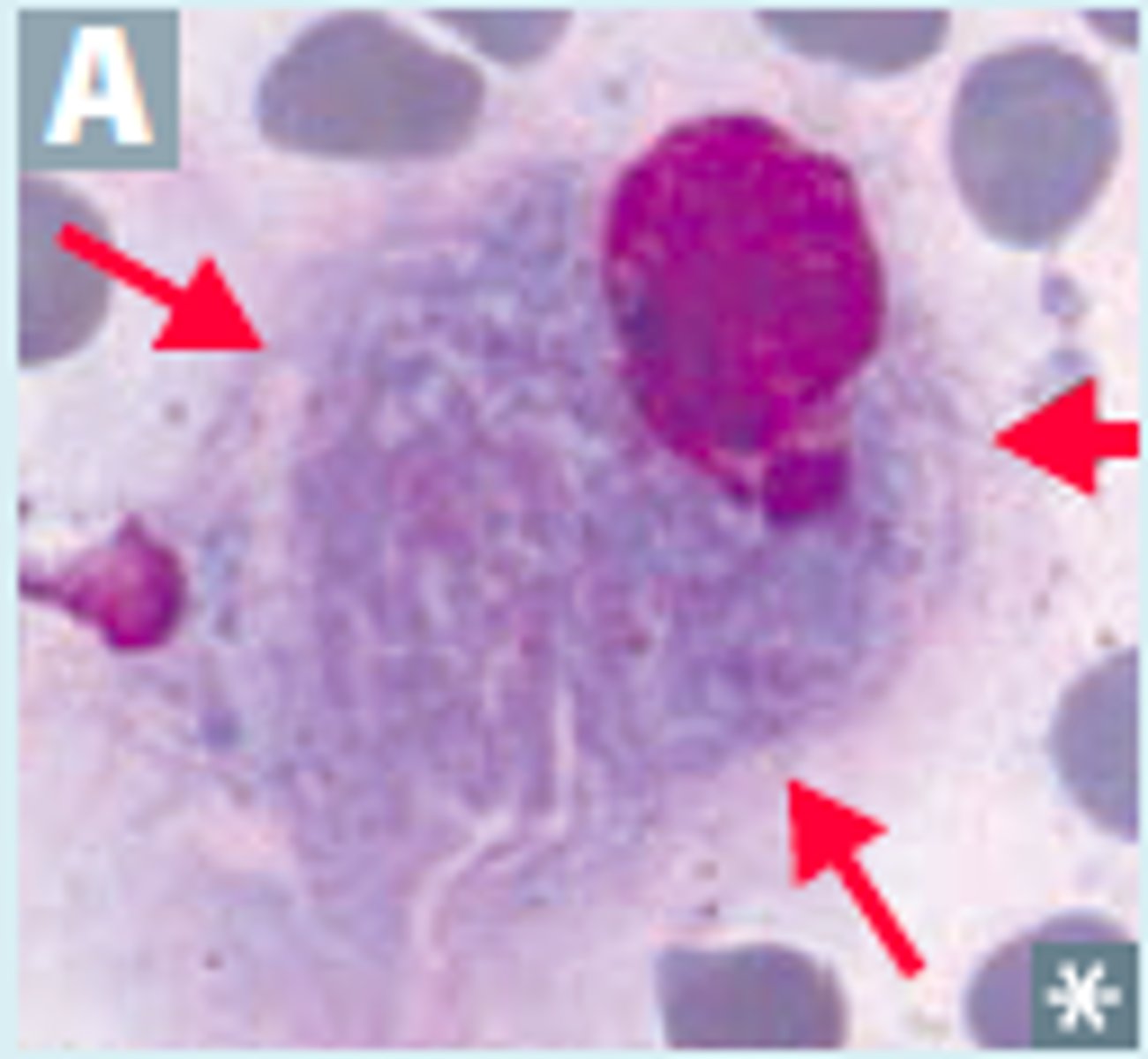
Toxoplasmosis (toxoplasma gondii)
Parasitic infection from cat feces
-leukocytosis, lymphocytosis, negative monostat
- can cause cysts and parasite can be seen in cells

CMV (cytomegalovirus)
Leukocytosis, lymphocytosis, and reactive lymphs
- herpes virus
- usually asymptomatic or mild cold
- in breast milk
-tested with CMV or DNA testing

IgA Multiple Myeloma
-Flame cells
-More Ig than other plasma cells
Measuring Hgb
RBCs + Drabkin's reagent causes Hgb to be released to be measured at 540 nm and compared with Beer's law

Measuring reticulocytes on Sysmex
supervital stain, measures fluorescence
Measuring reticulocytes on Abbot CELL-DYN
Proprietary stain, multi angle scatter and fluorescence measured
Measuring reticulocytes on Siemans ADVIA
Supervital stain, measures high and low angle scatters and absorbance
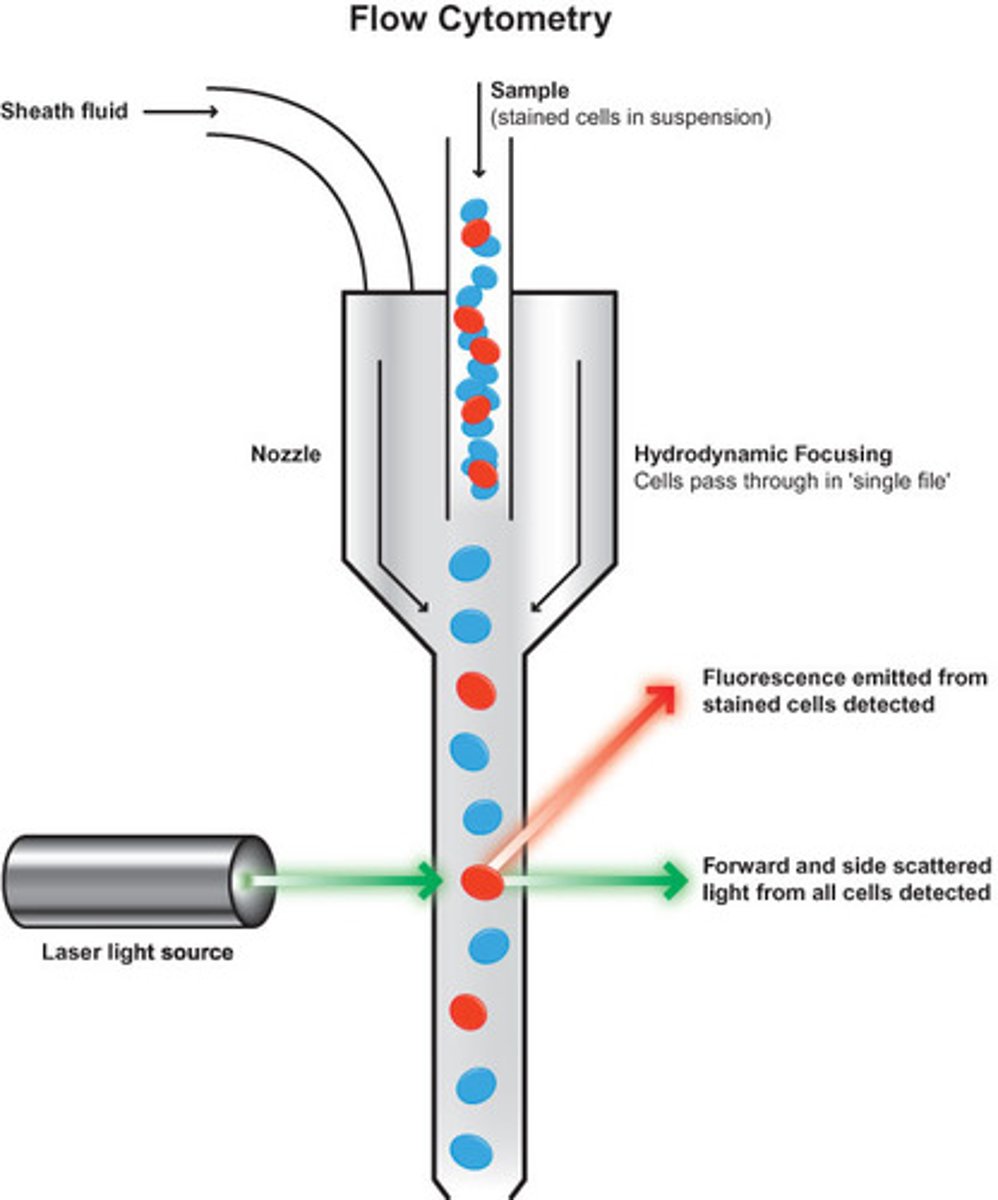
Side scatter
90 degrees, measures internal complexity through refraction of internal structures, granules, and nuclear lobes
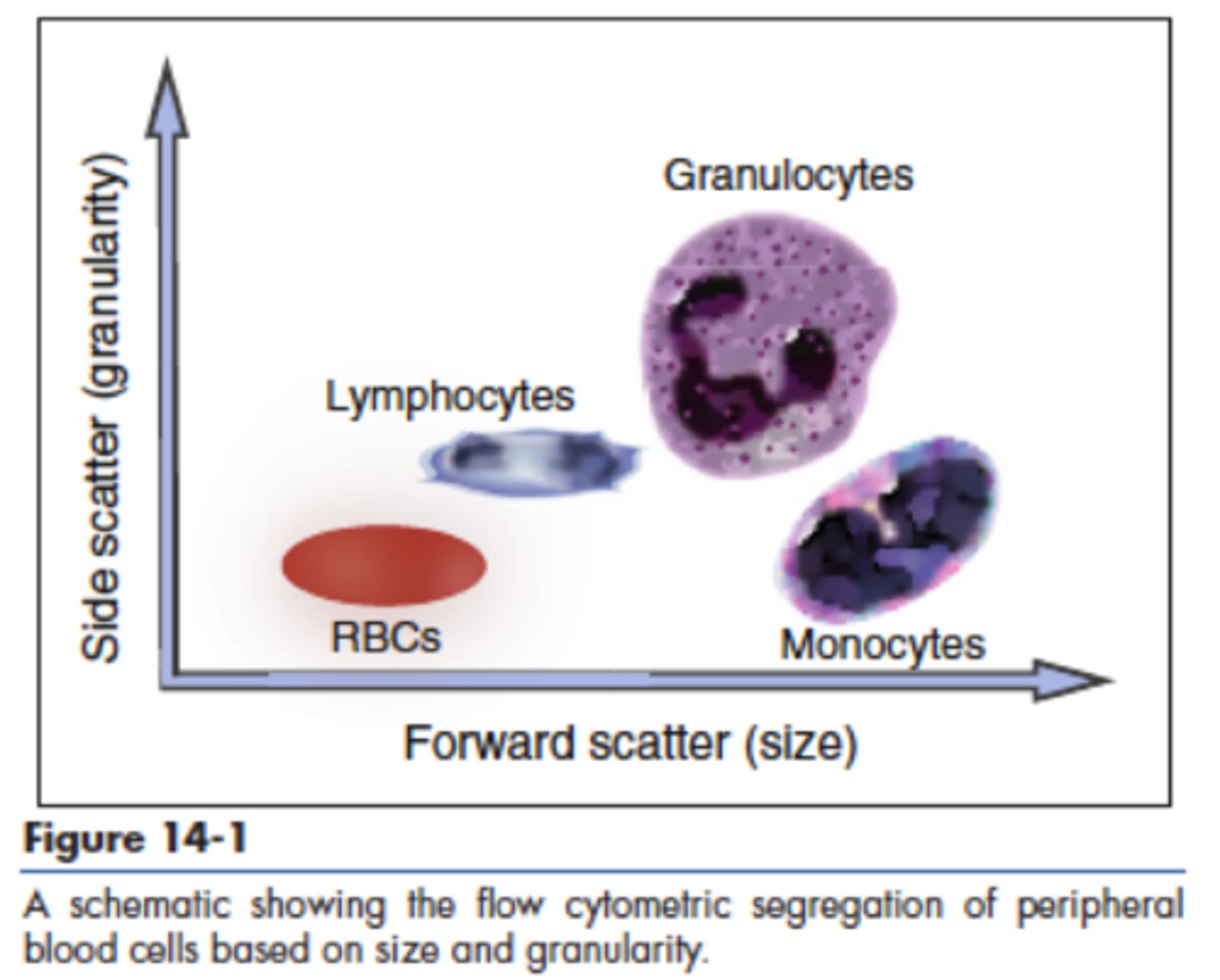
Forward scatter
0 degrees, measures size through diffraction of cell

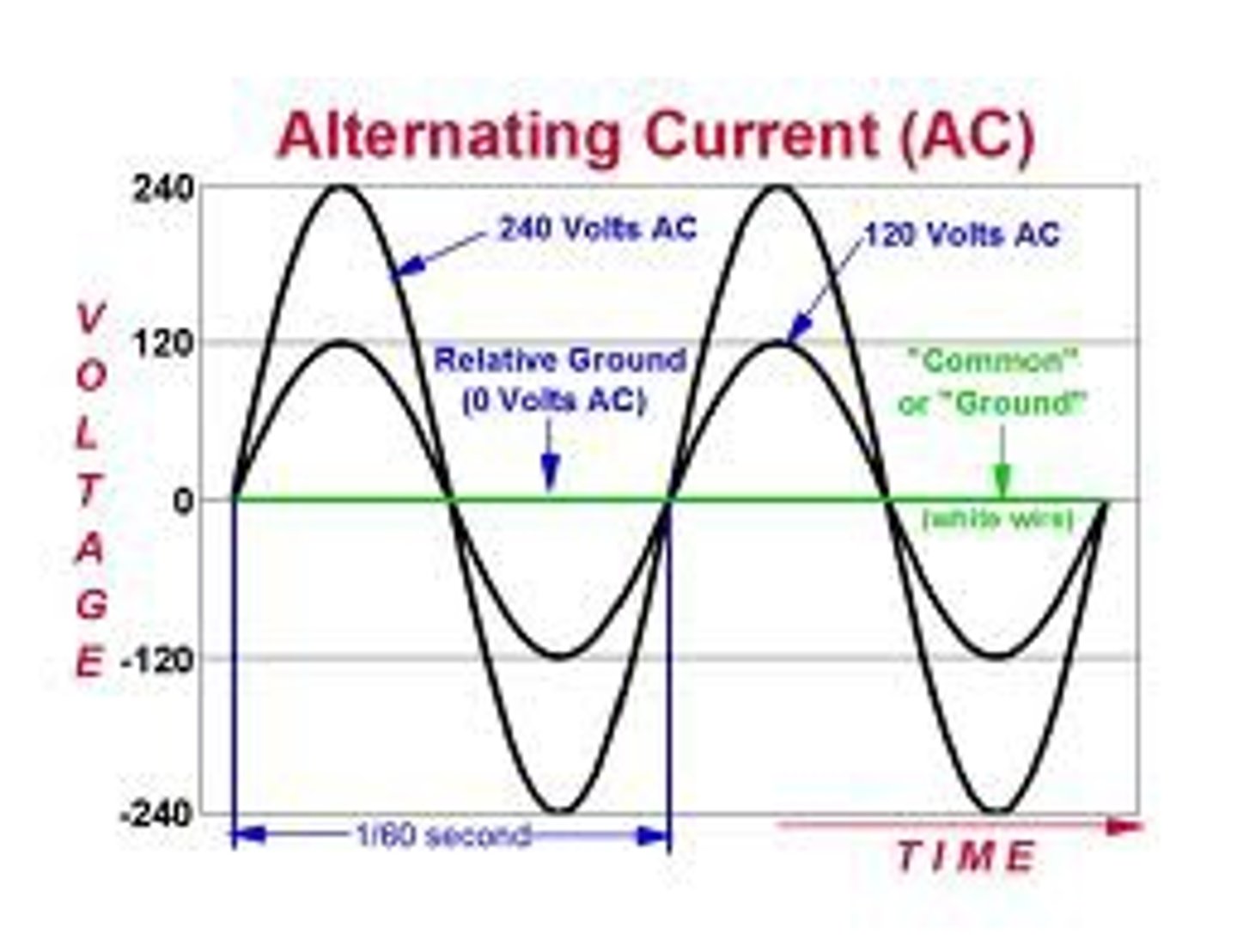
Radio frequency
Alternating current resistence
-sometimes used alongside electronic impedence
7 degree scatter
measures complexity on 5 part differential
Siemens ADVIA measuring WBC, RBC, PLT
Optical scatter
Sysmex diffs
optical scatter and fluerescent staining

Siemens diffs
Peroxidase staining, optical scatter, and absorption for all except
basophils: lyse, laser, high and low scatter used

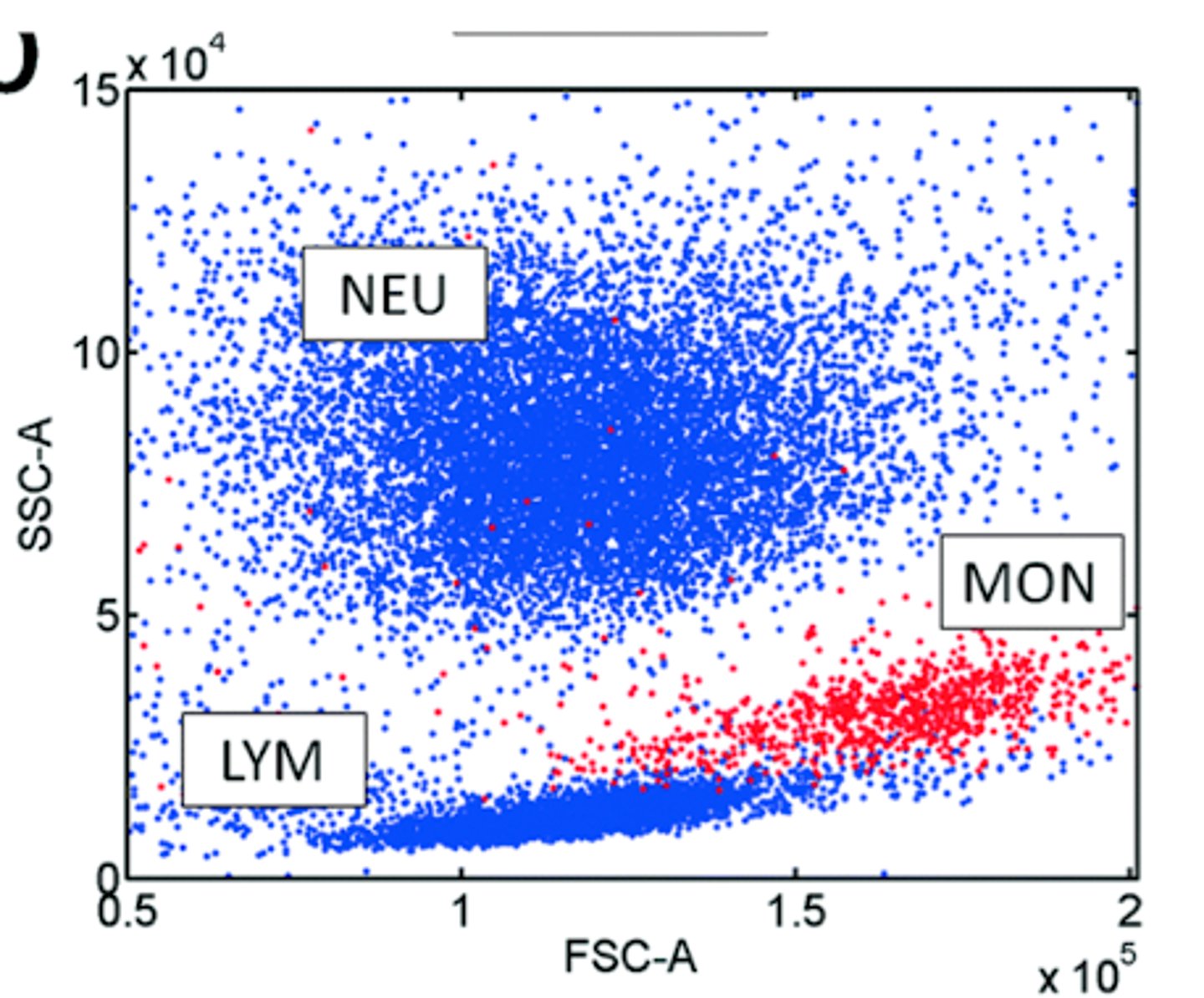
3 part differential
Granulocytes (not neut), Lymphocyte & Monocytes
-Sysmex
(forward scatter on x axis and side scatter on y axis)
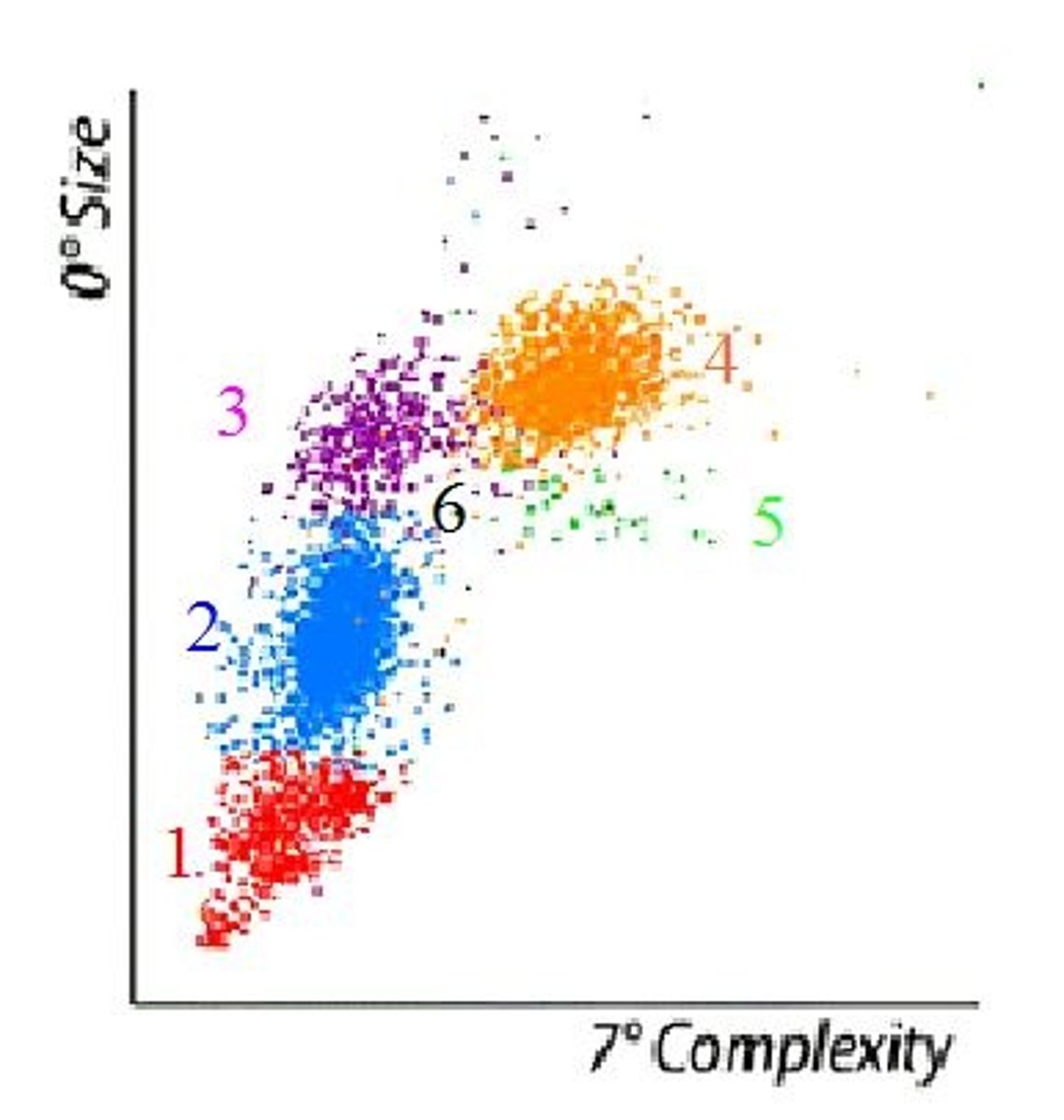
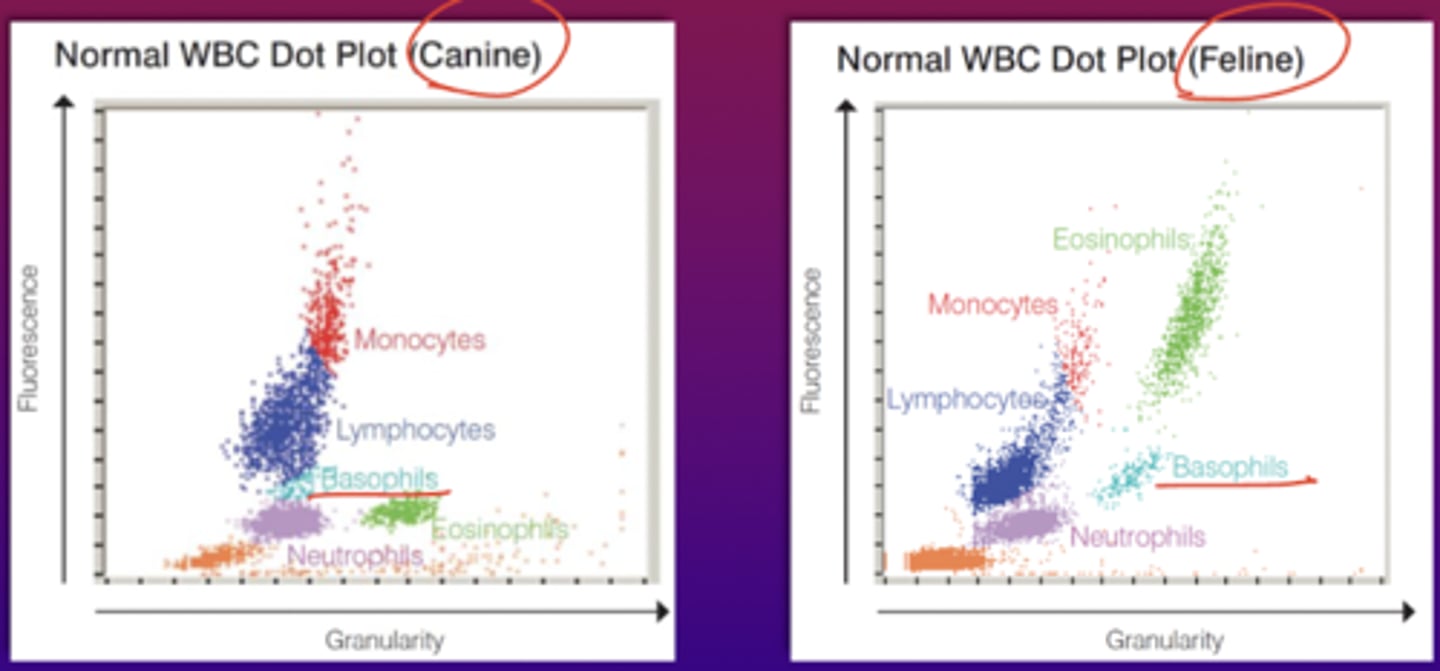
5 part differential
Top to bottom, progressively going left as it goes down
Basophils
Neutrophiles
Monocytes on left and eos on right
Lymphocytes
nRBCs
size on y axis (0 degrees) and complexity on x axis (7 degrees)
-COULTER, Abbot Saphire, Mindray
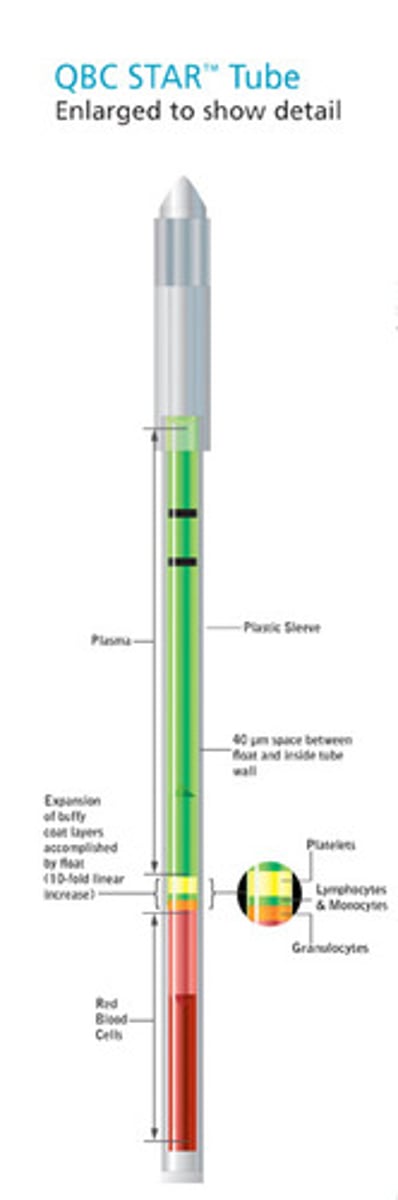
QBC Star
single tube centrifuge and read station
- directyly measures grans, lymphs/monos, Hct
- derives Hgb
-calculates MCHC
-uses dye to differentiate the components
Basophilic stippling (RBC inclusion)
-RNA inclusion
lead intoxication
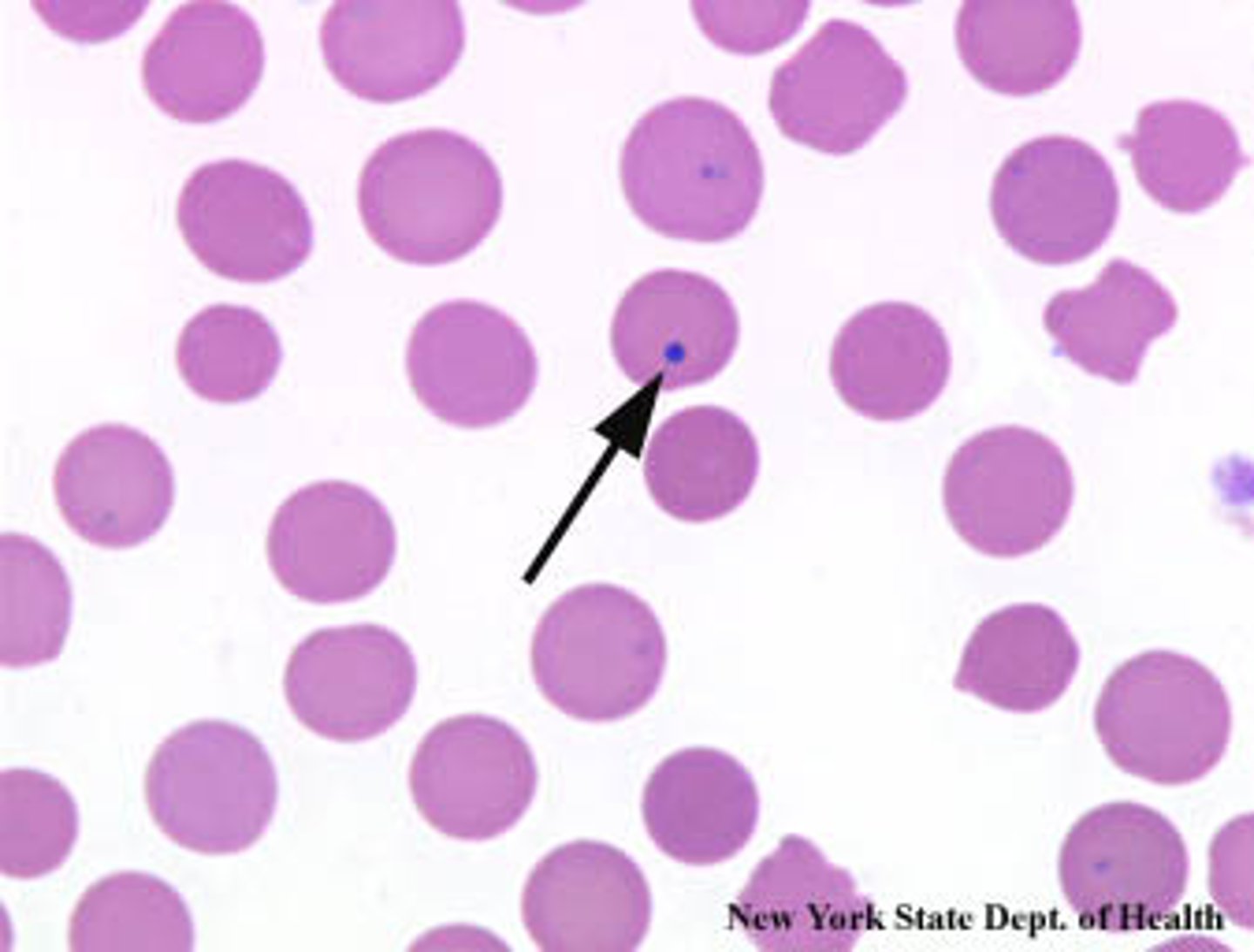
Howell-Jolly bodies (RBC inclusion)
-DNA inclusion
splenectomy, anemias
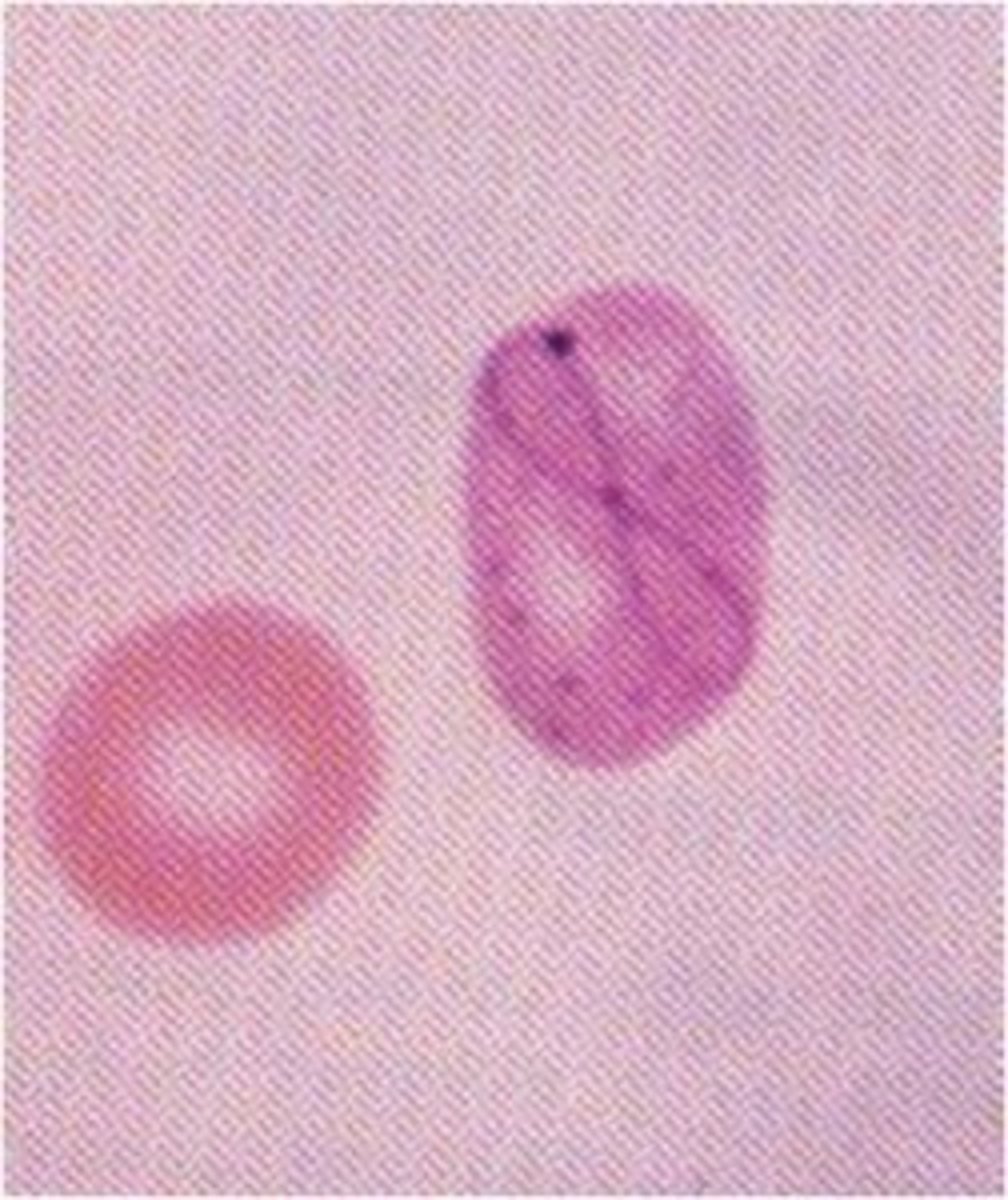
Cabot ring (RBC inclusion)
- chemo and myelodyplastic syndrome
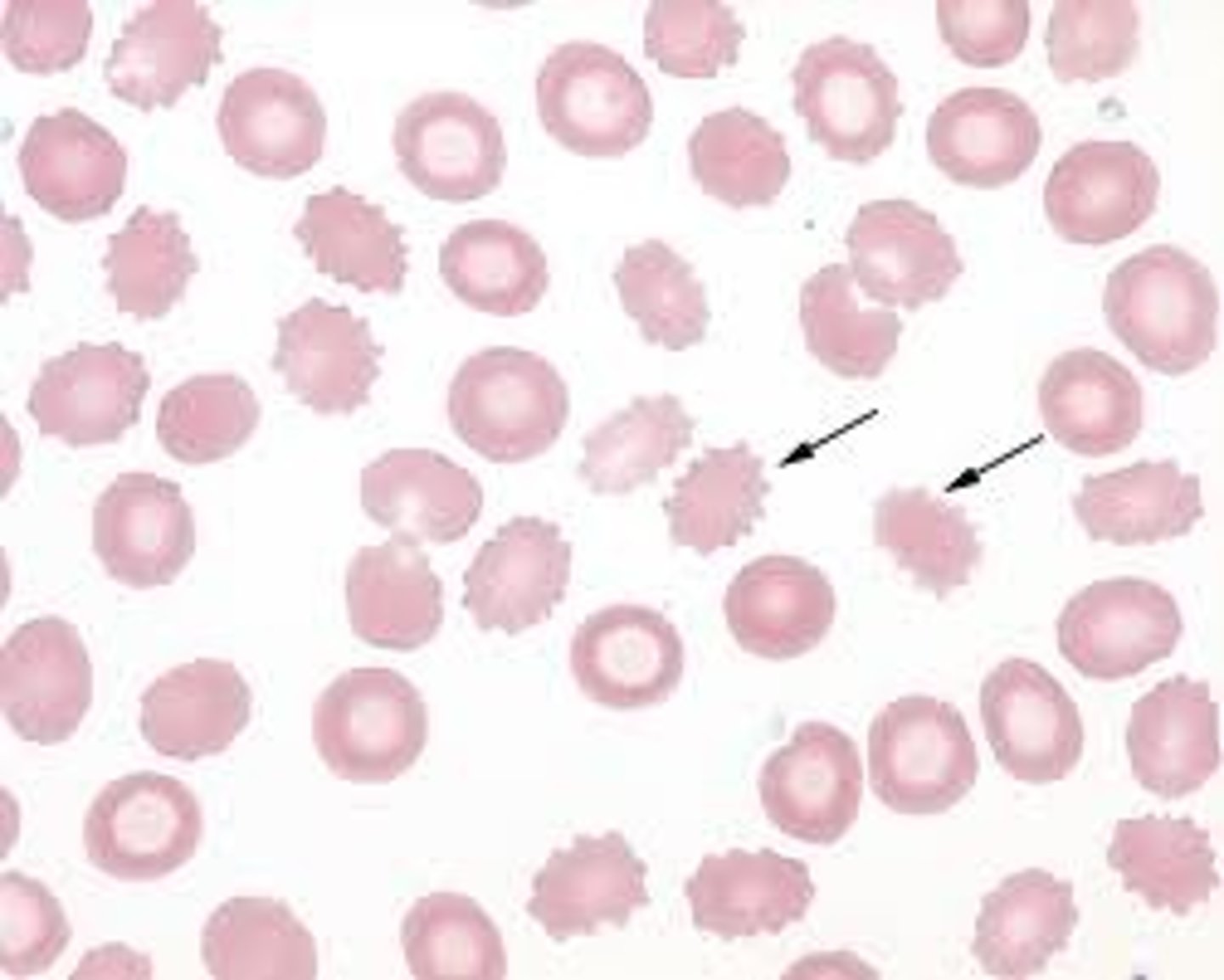
Acanthocyte (Burr cell)
severe liver disease and splenectomy
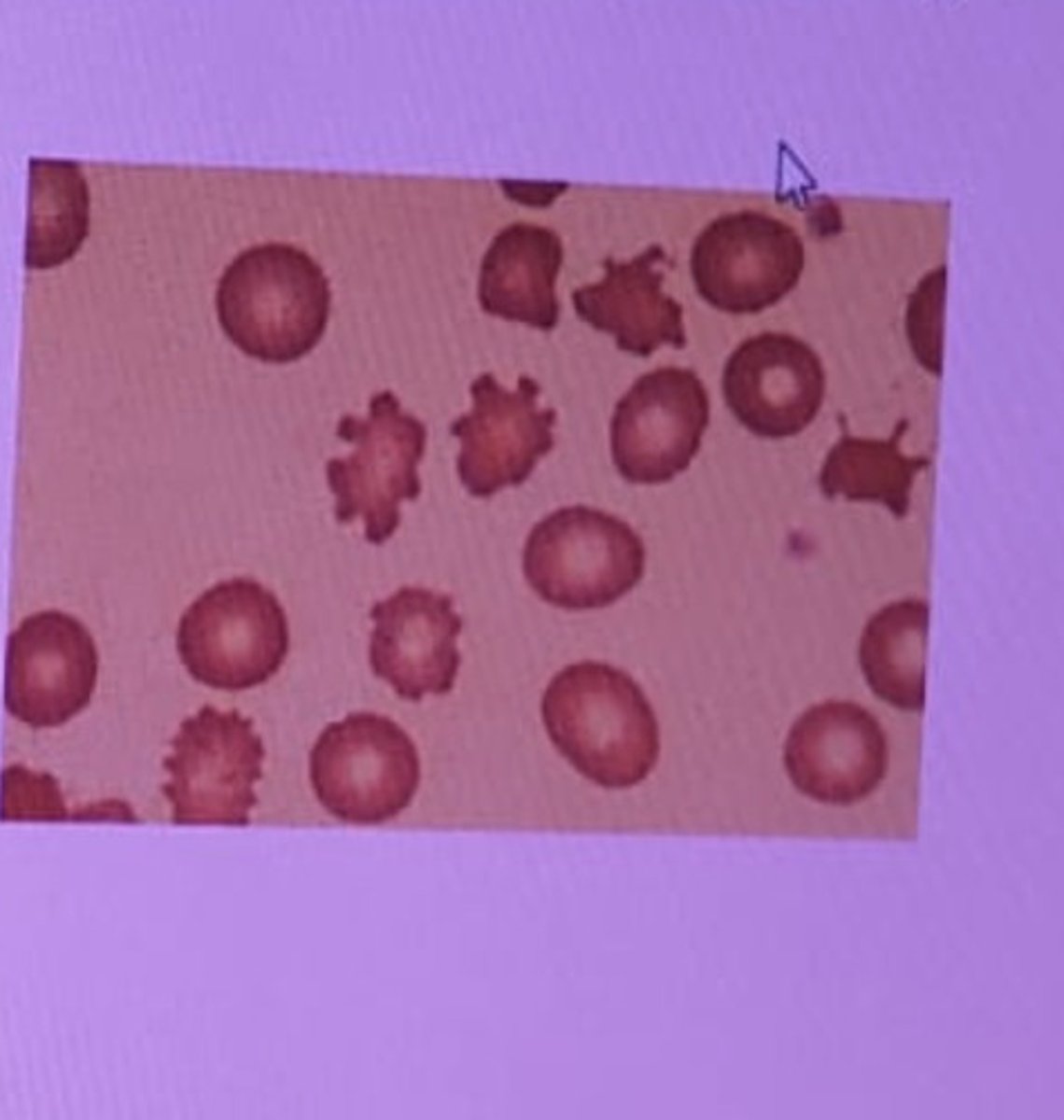
Schistocyte
Clot in vessels, anemias, severe burns
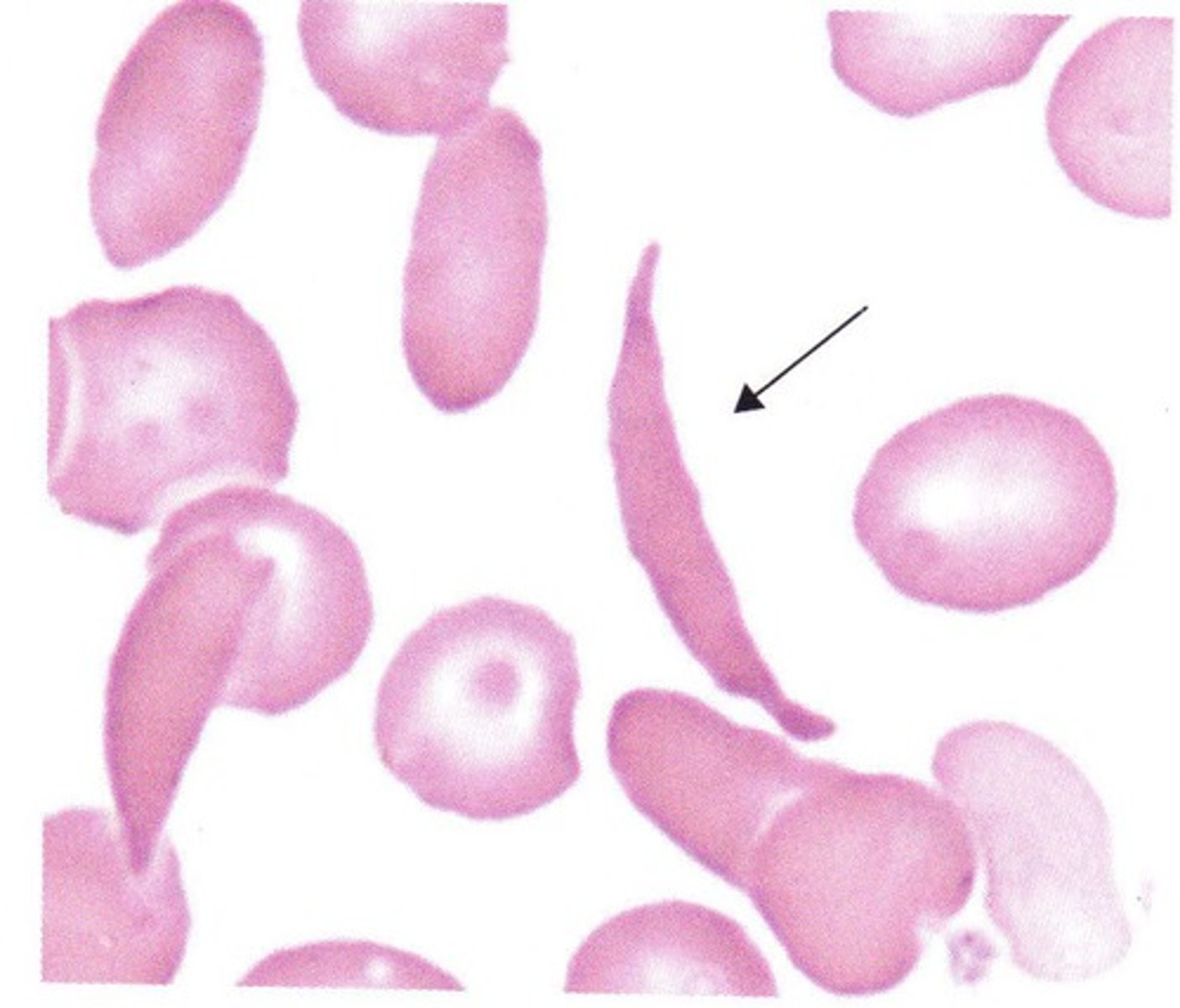
Sickle (drepanocyte)
homozygous hemoglobin S disease (sickle cell anemia)
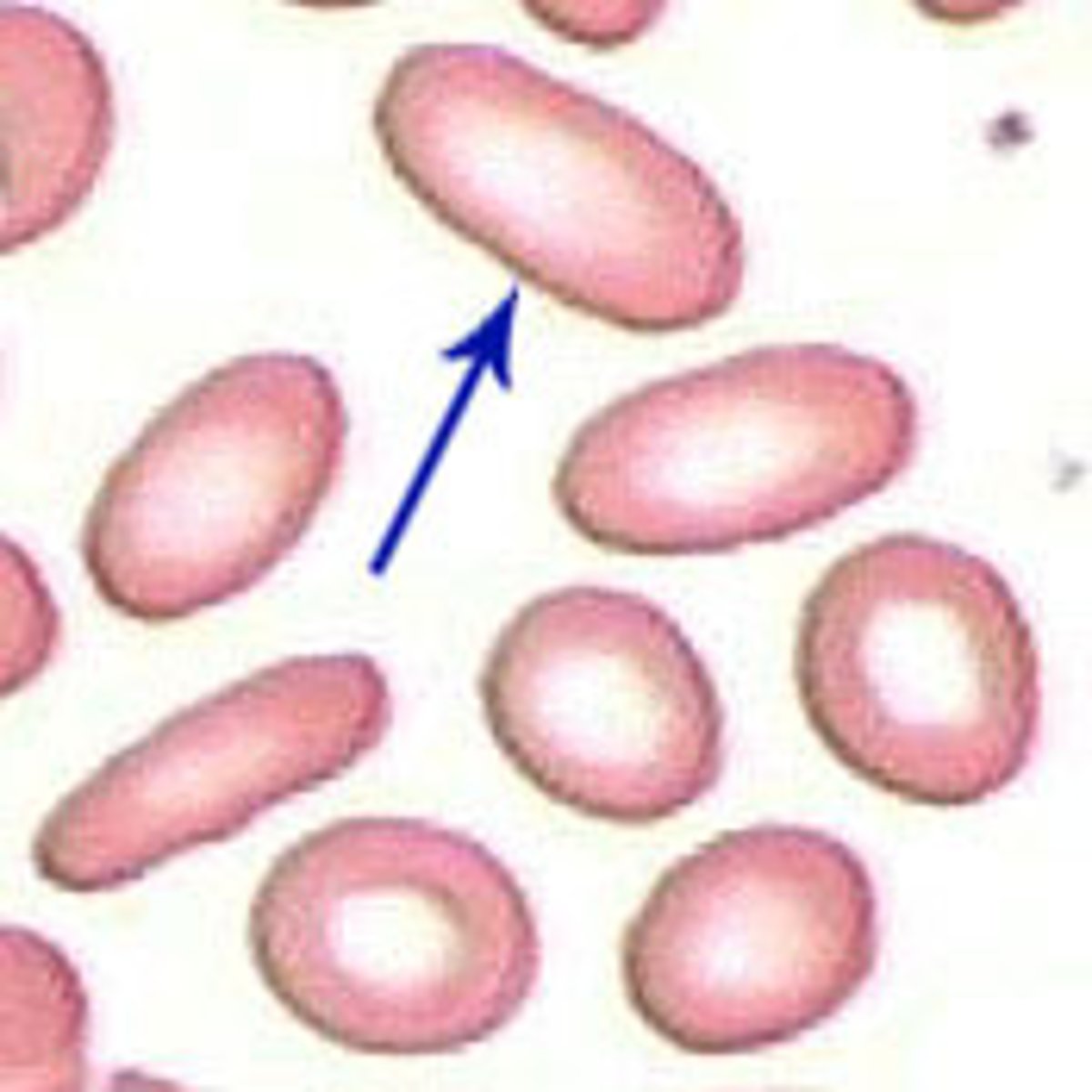
Elliptocyte/ ovalocyte
elliptocyte = cigar shape
ovalocyte= egg
hereditary ellipocytosis or ovalocytosis
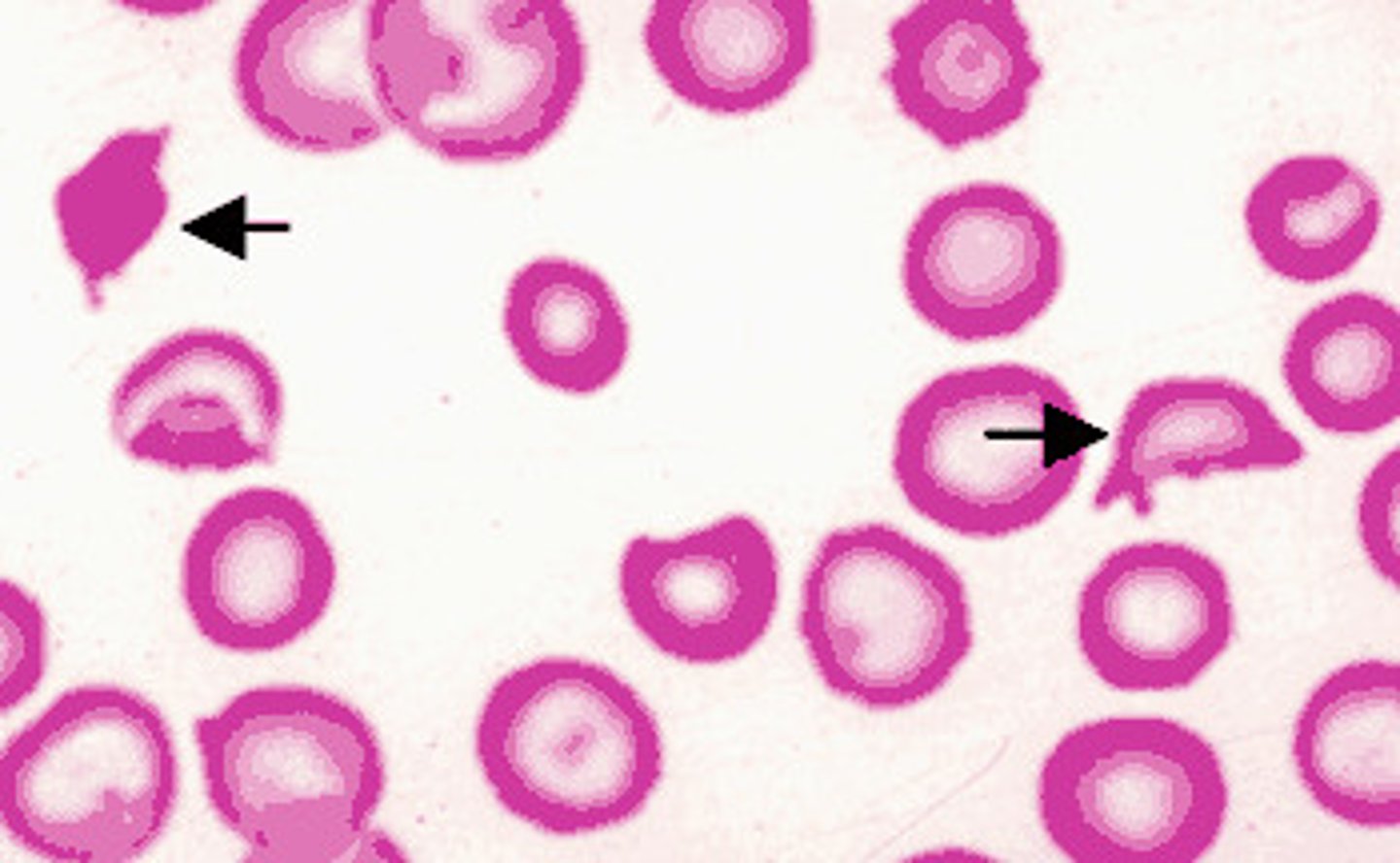
dohle bodies
associated with burns, infections, and cancer
-composed of rough ER RNA
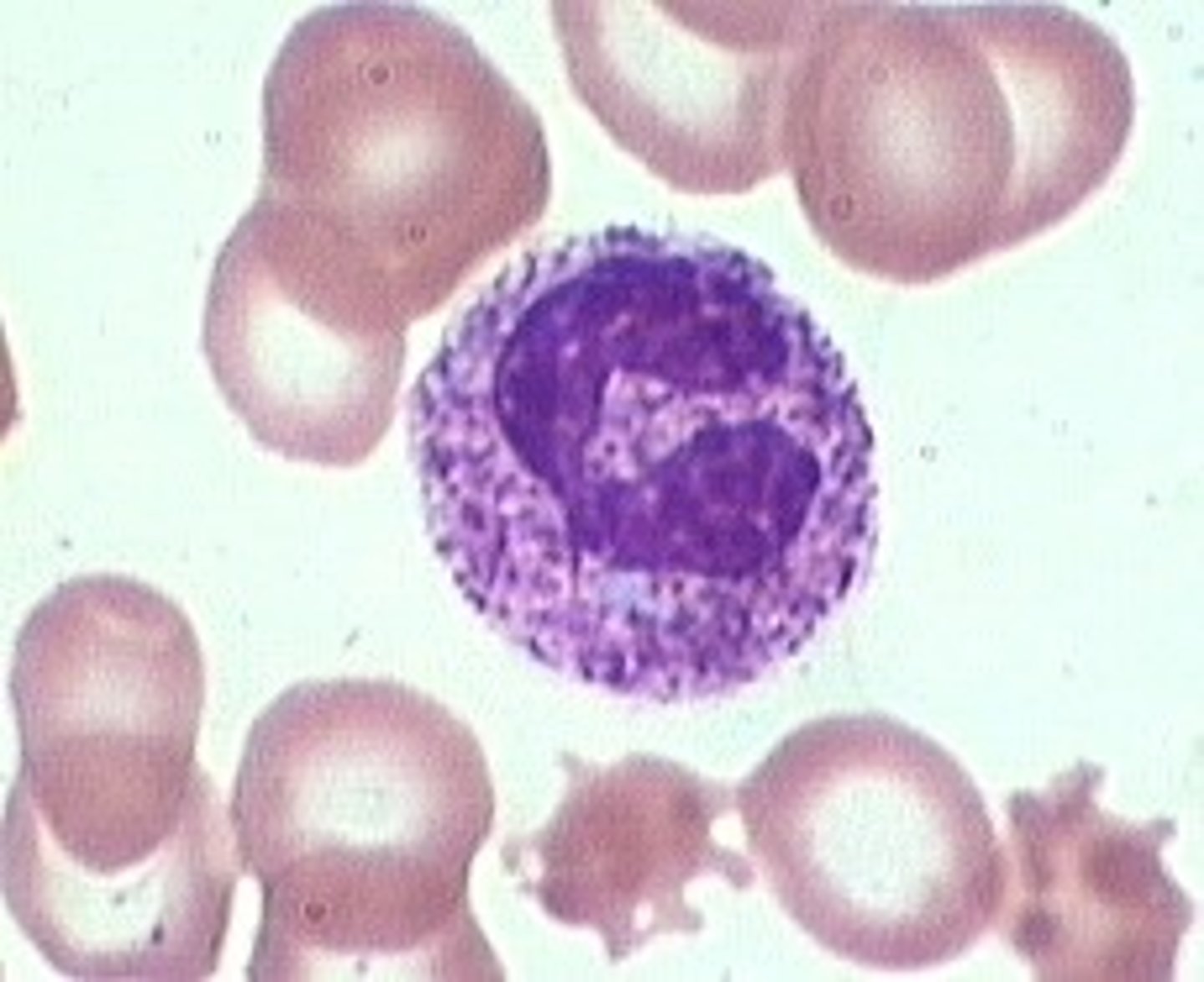
toxic granulation
associated with burns, infections, and cancer
-primary granules
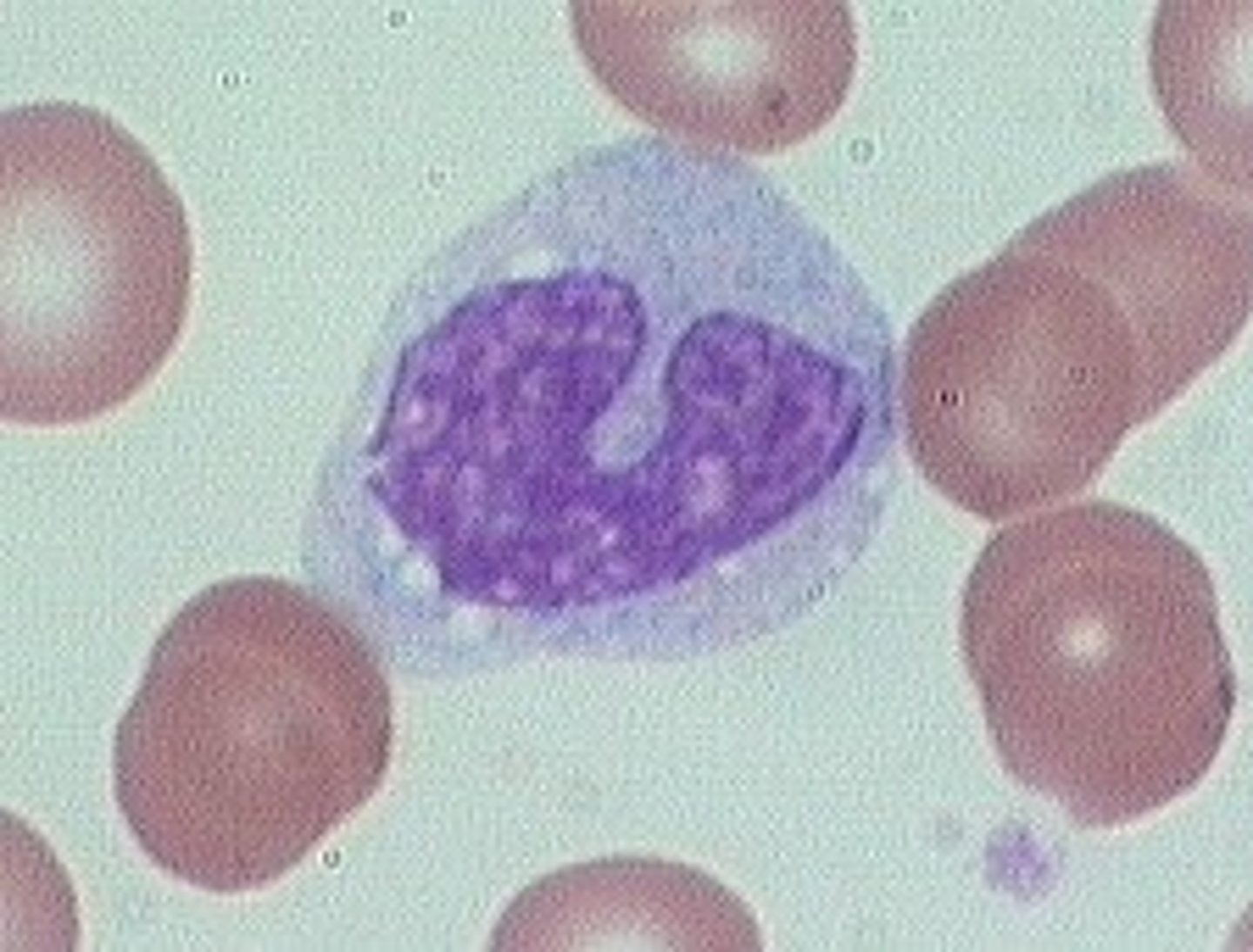
cytoplasmic vacuoles
associated with burns, infections, and cancer
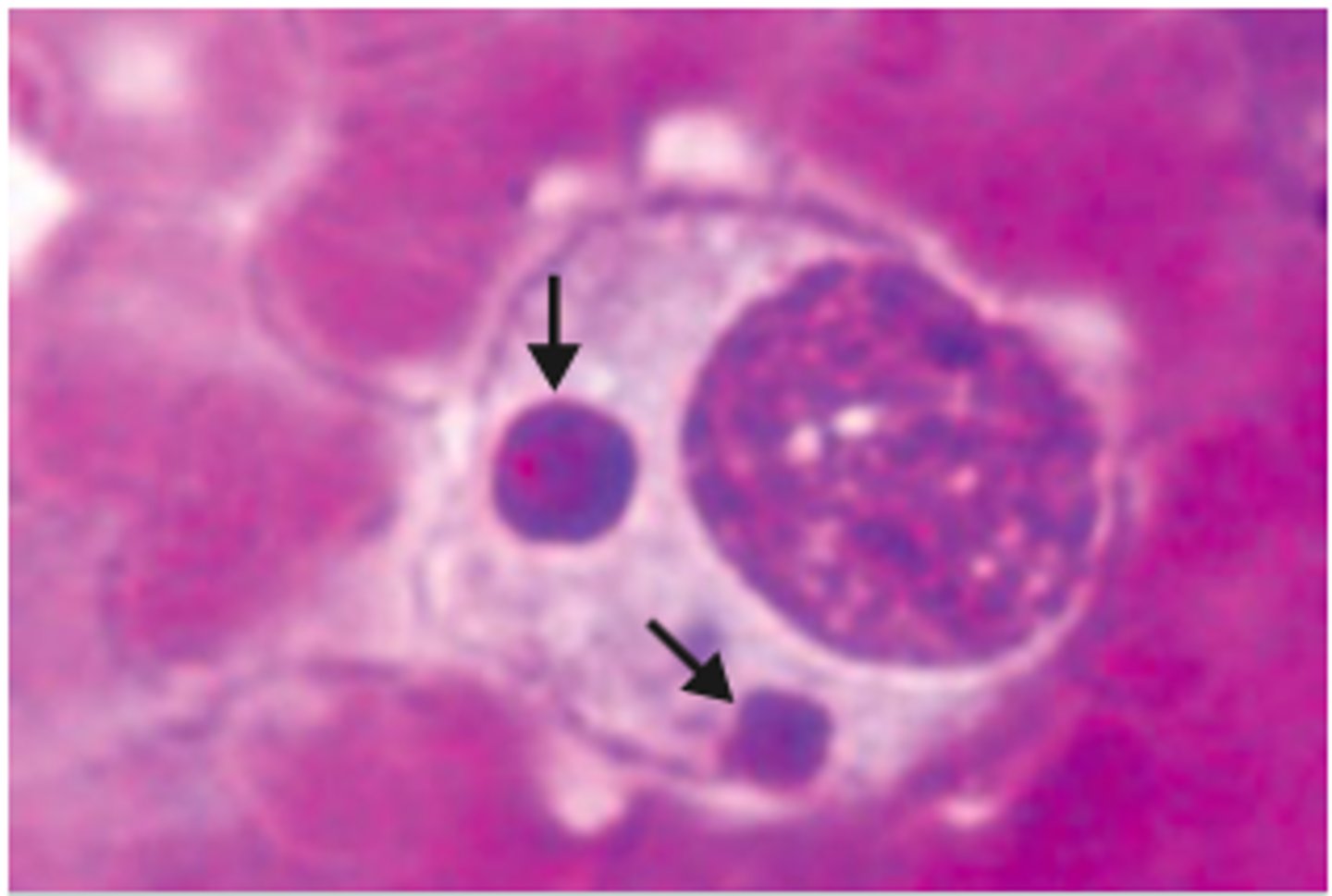
fungi inclusion
slightly larger than bacteria, round or oval
-often in immunosuppressed patient
Morulae
basophilic, irregularly shaped granular, cytoplasmic inclusions found in leukocytes in an infectious disease called ehrlichiosis.
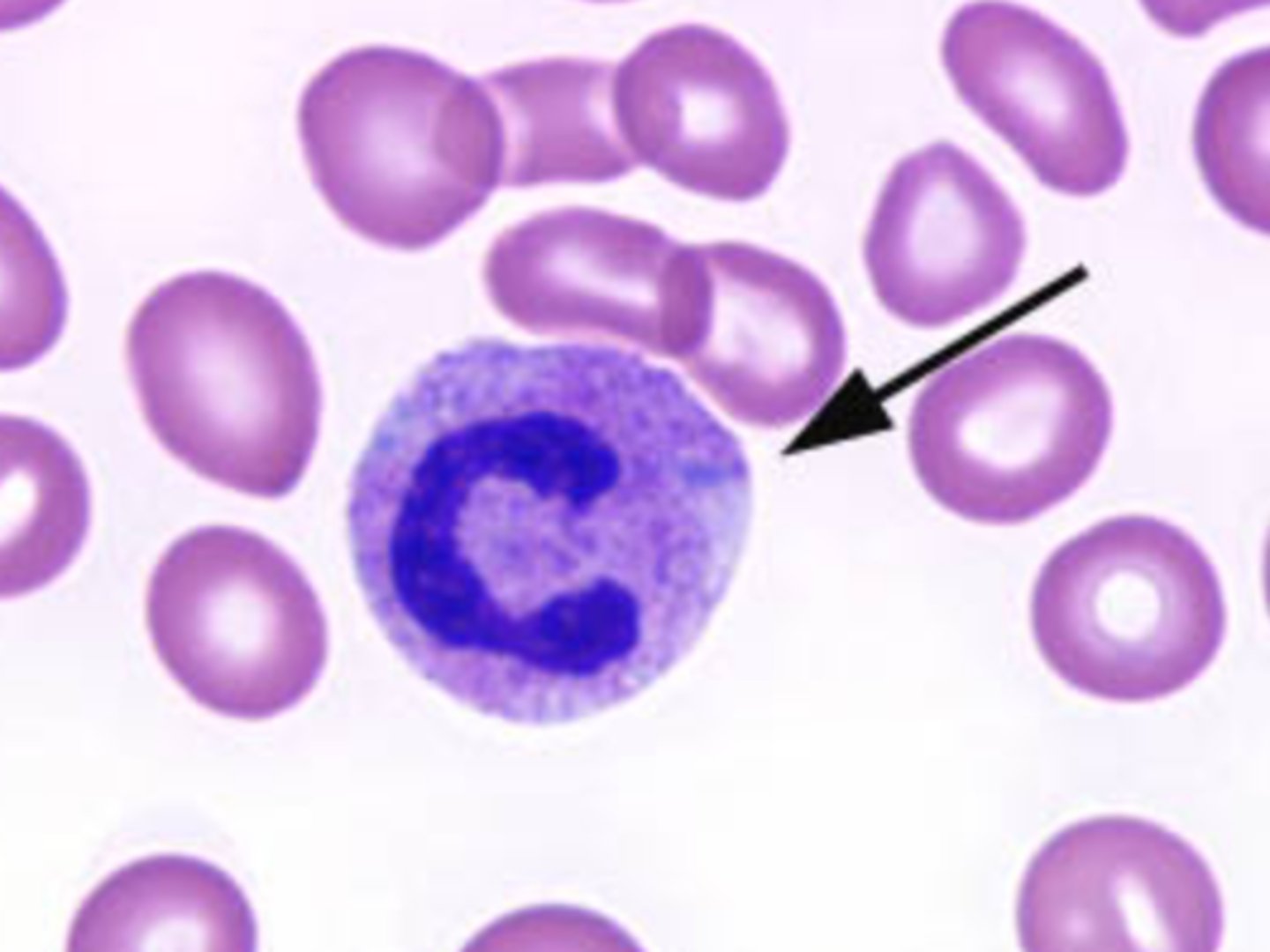
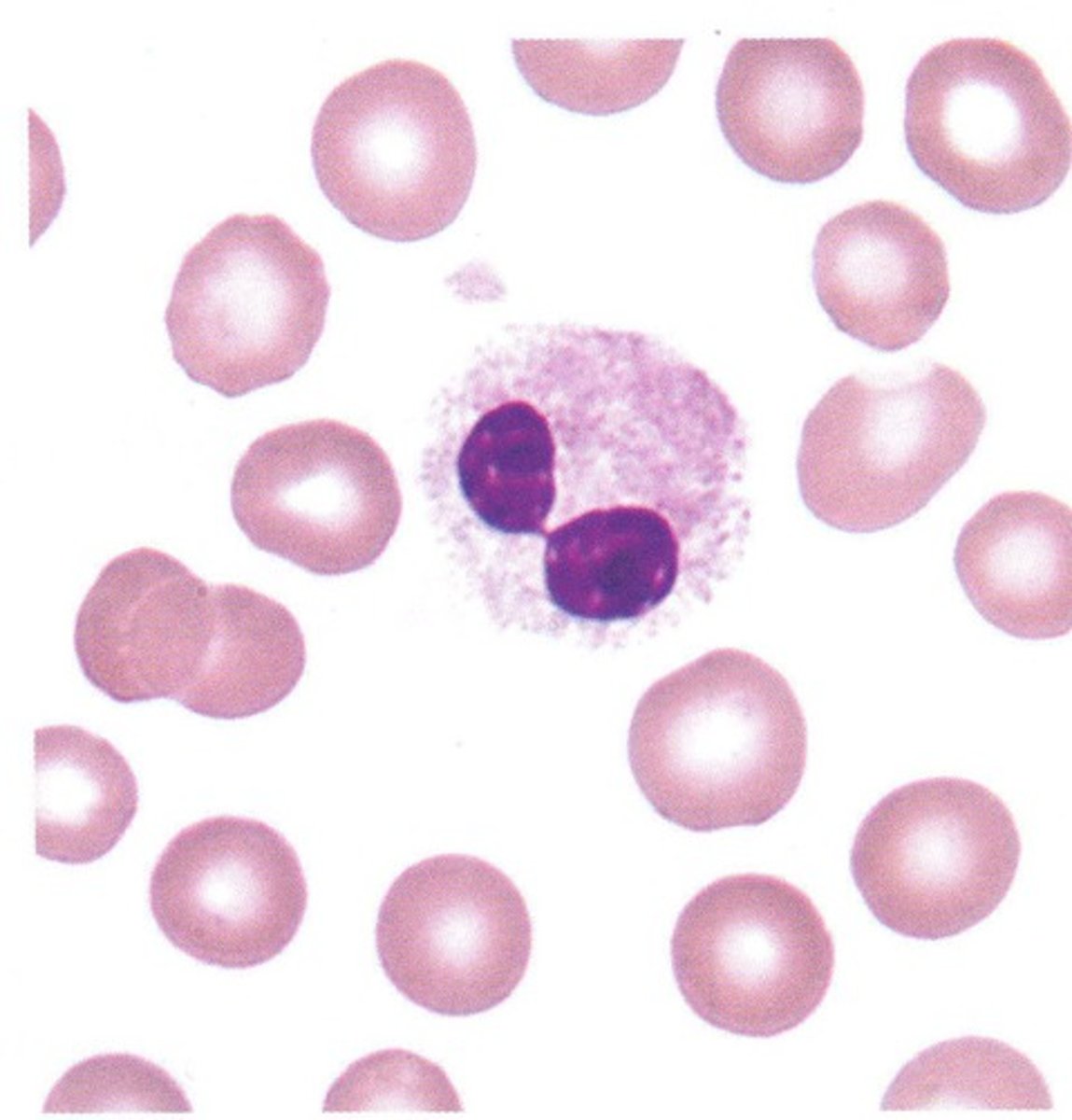
Pelger-Huet
Autosomal dominant condition with bilobed nuclei
-no known adverse effects
-need to know so don't think theres left shift
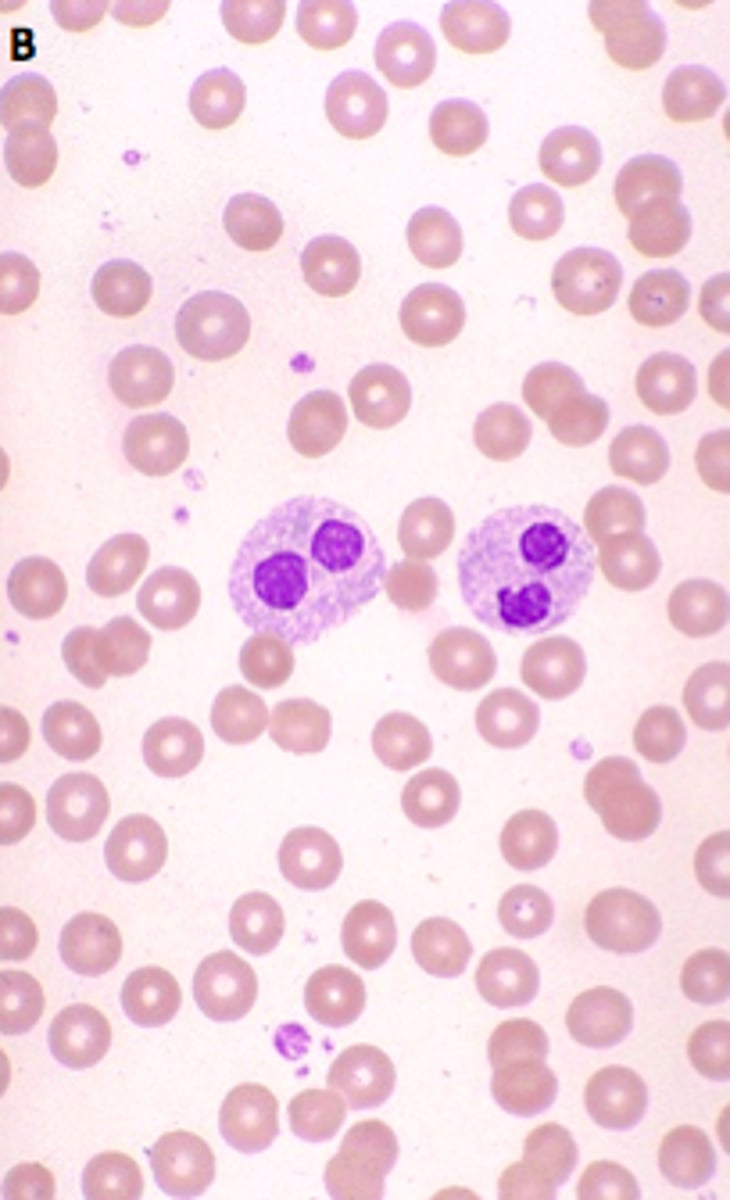
Acquired/ psuedo pelger huet
myeloproliferative state, hypo granular, intense clumping, round nucleus
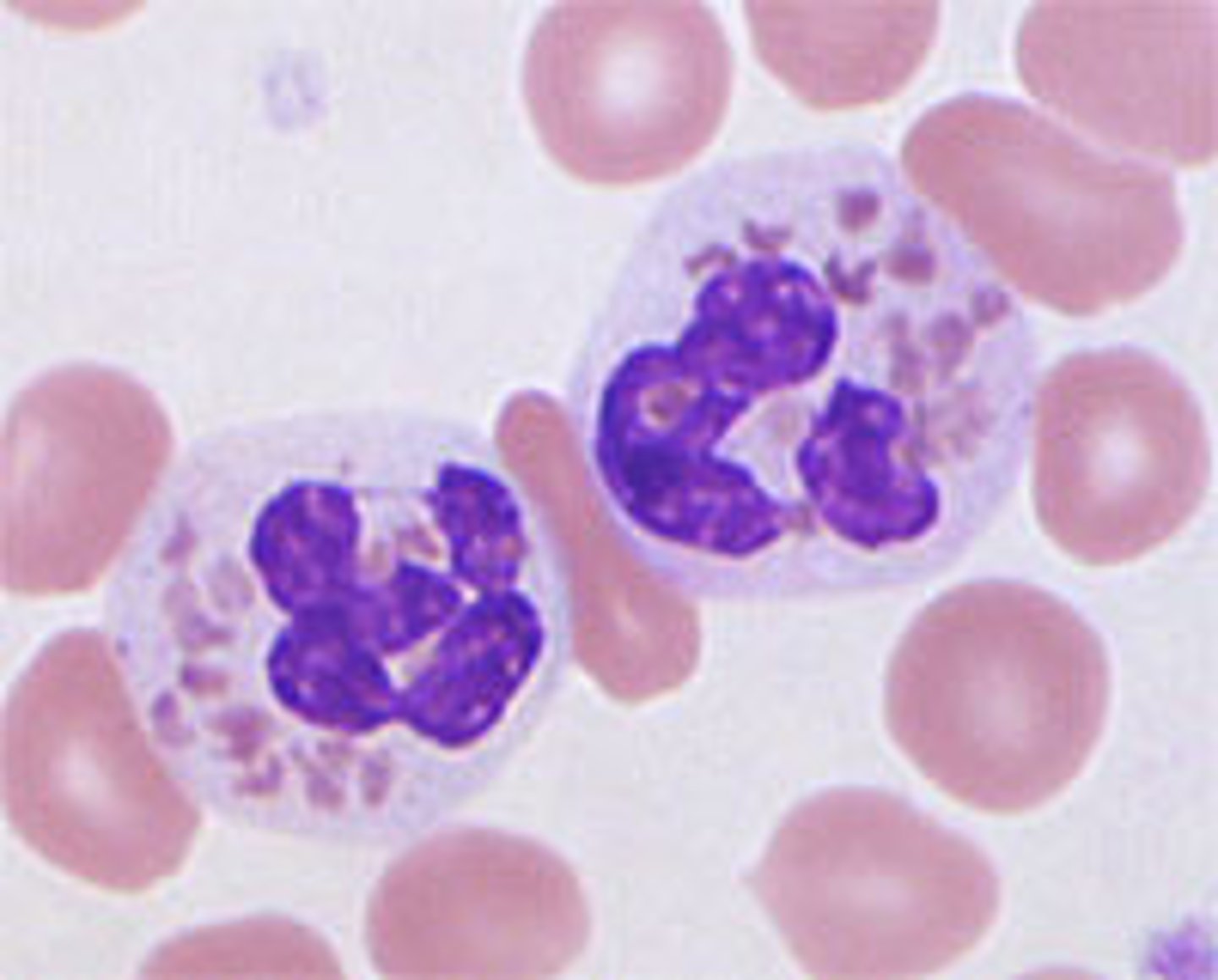
CHÉDIAK-HIGASHI SYNDROM
Rare, recessive disorder
-neutropenia, thrombocytopenia
-albinism
-fusion of neutrophil primary and secondary granules, issues with chemotaxis
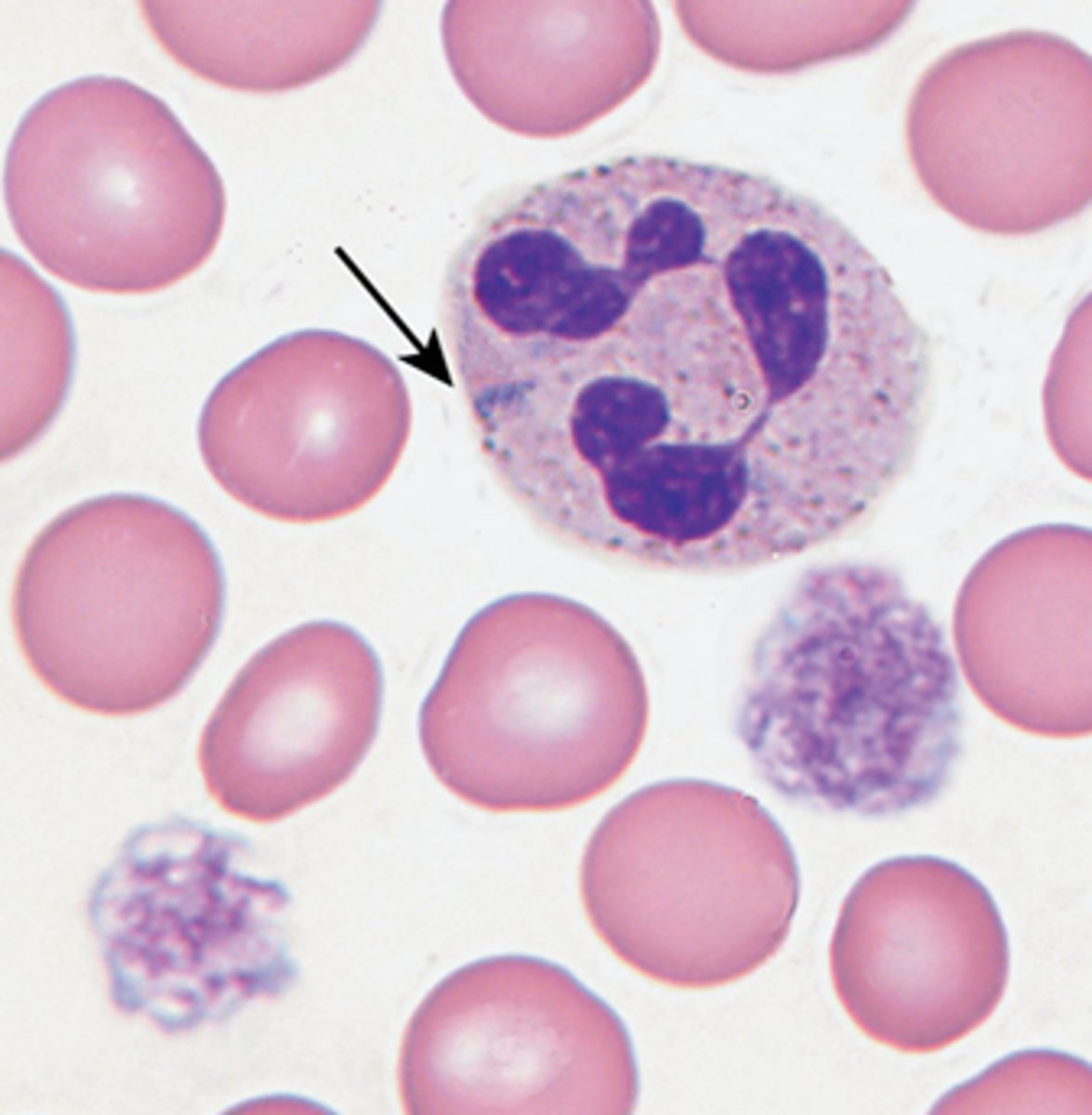
May-Hegglin Anomaly
autosomal dominant trait disorder where neutrophils have blue-staining inclusions that resemble Dohle bodies; thrombocytopenia is also present with giant abnormal platelets
Dihydrorhodamine Test (DHR test)
Normal cells will reduce DHR to fluorescence
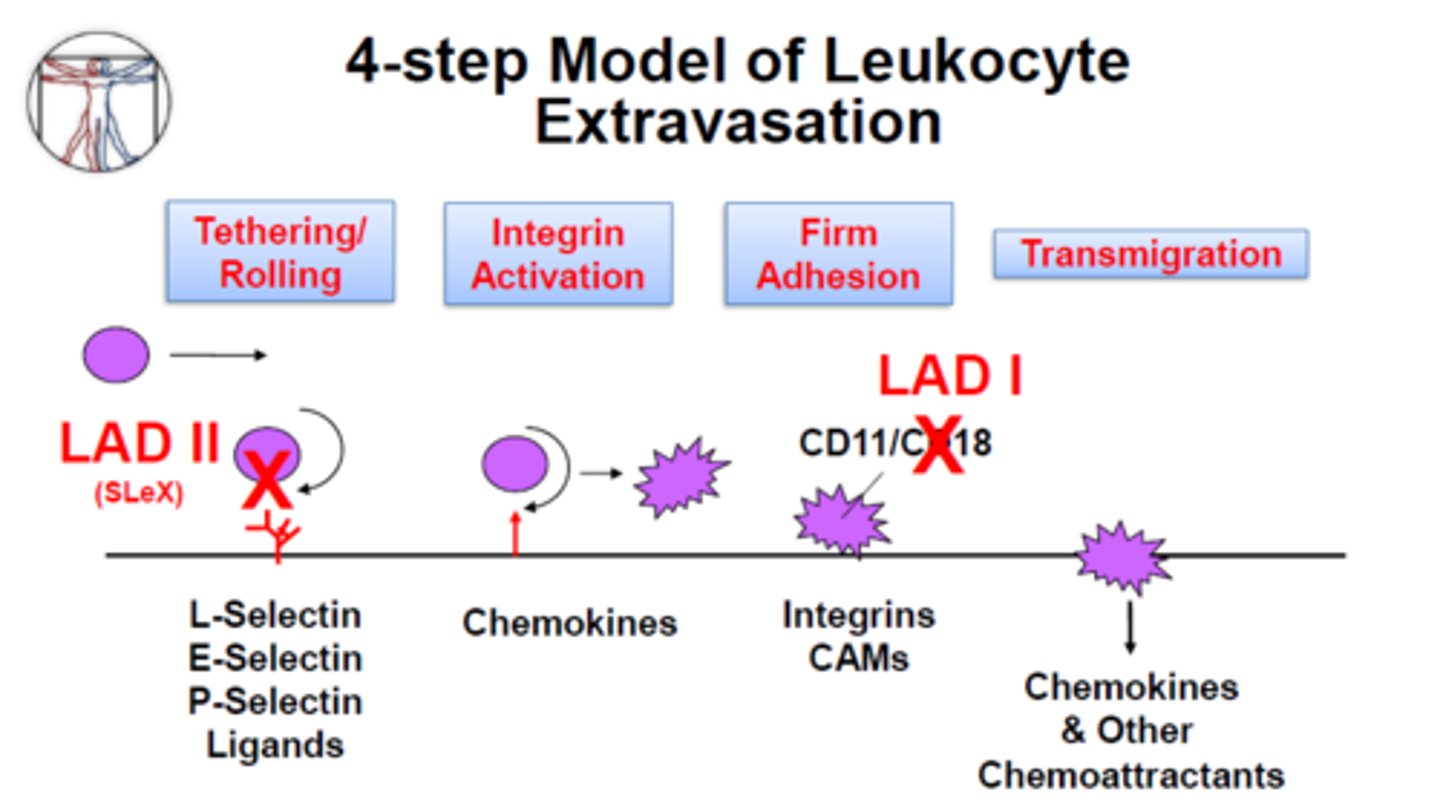
Leukocyte adhesion deficiency: LAD Type 1
Rare autosomal recessive disorder•
↓ or absent leukocyte cell-surface adhesion proteins(CD11/CD18 complex -> β2 integrins)• Unable to recognize C3bi complexes• So No phagocytosis of microbes
• Diagnosis—flow cytometry for CD11b/CD18• Treatment—prophylatic antibiotics105

NK markers
CD56 and CD16
Alveolar mac
lung macrophage
kupffer
liver macrophage
microglia
brain macrophage
osteoclasts
bone macrophage

langerhans
skin macrophage
splenic macrophage
spleen macrophage
macrophage CD markers
CD11b and CD14
GAIN CD68
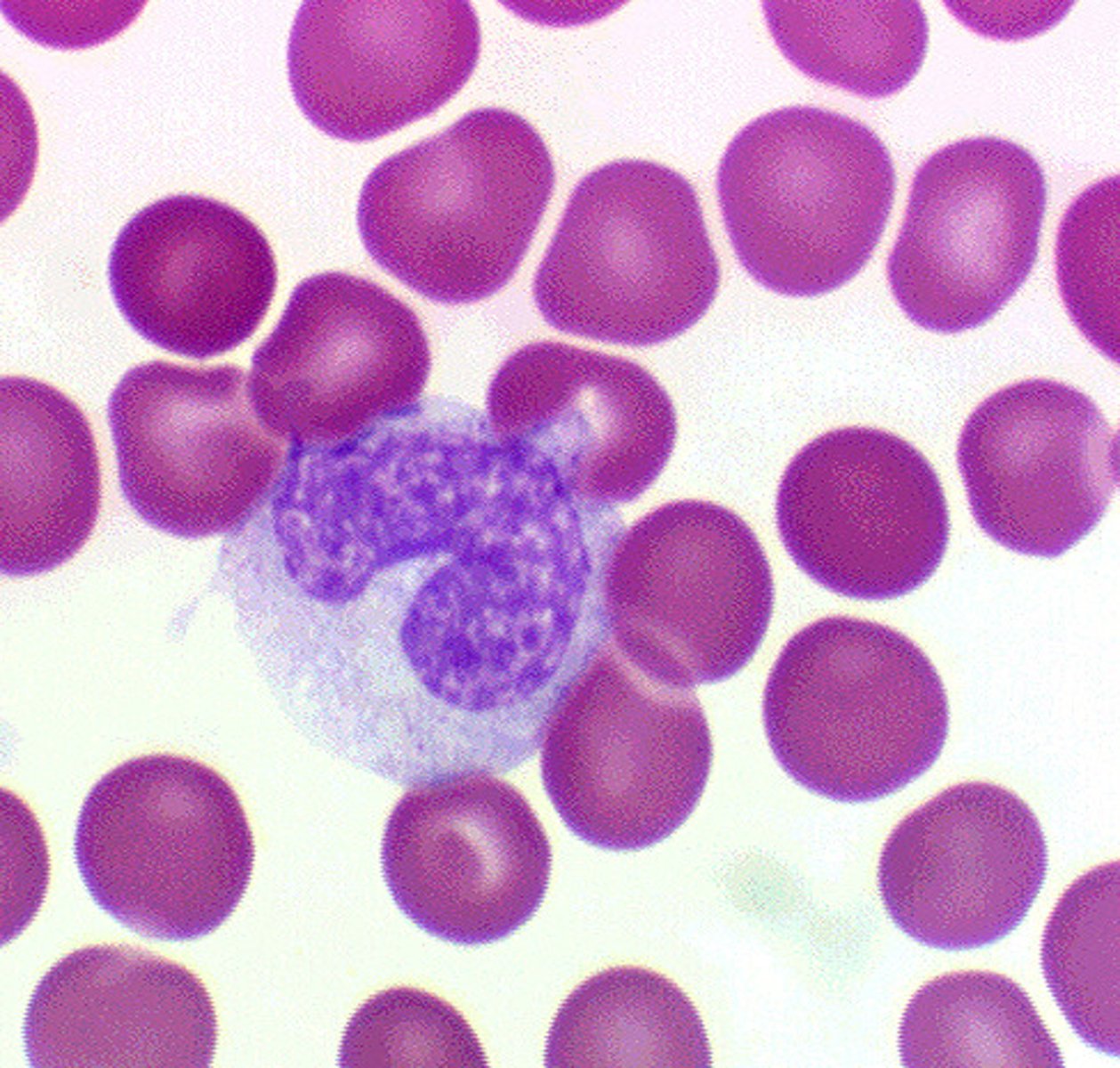
monocyte
big cell, foldy nucleus, ground glass appearance, blue-grey cytoplasm, vacuoles
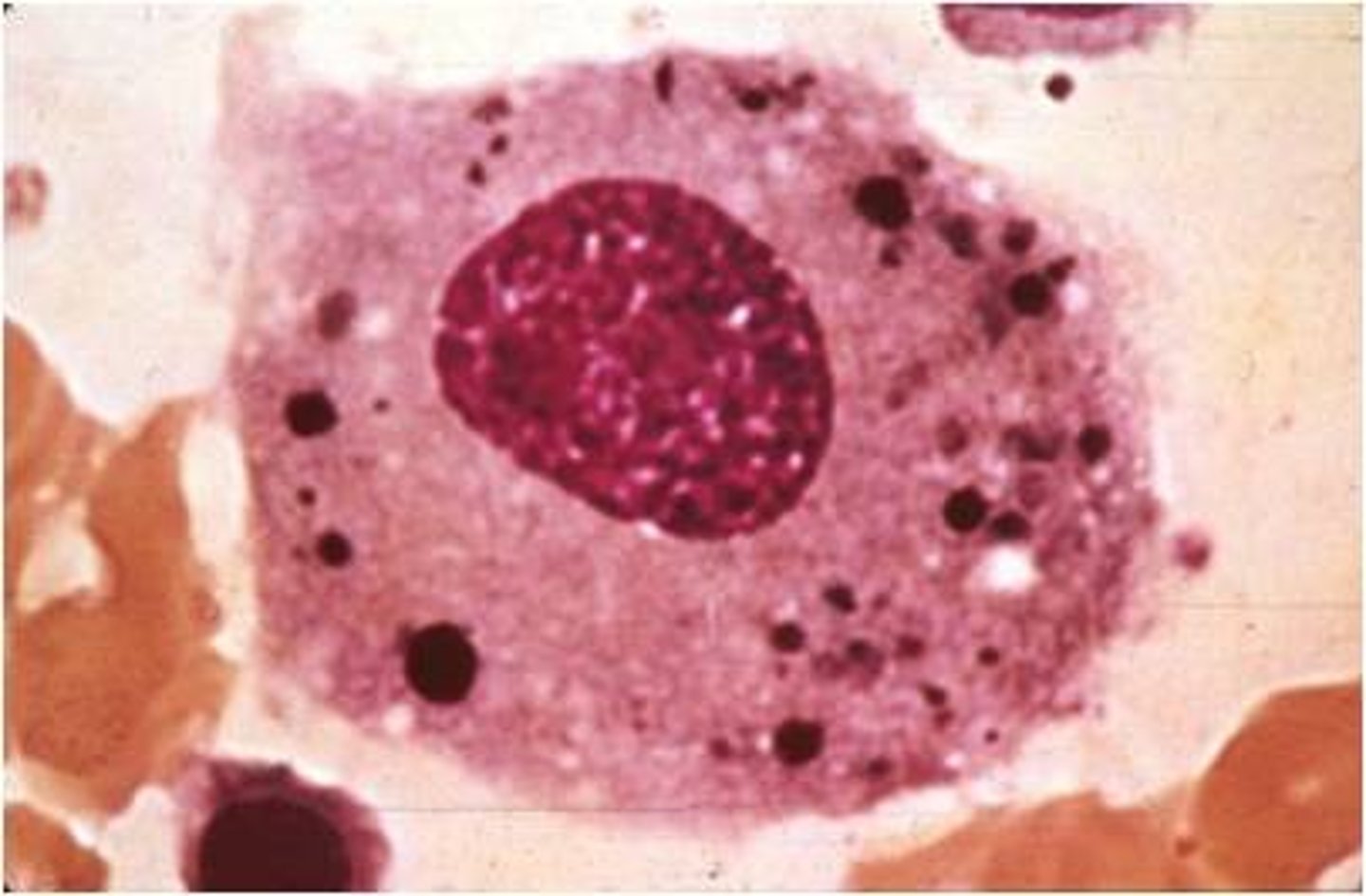
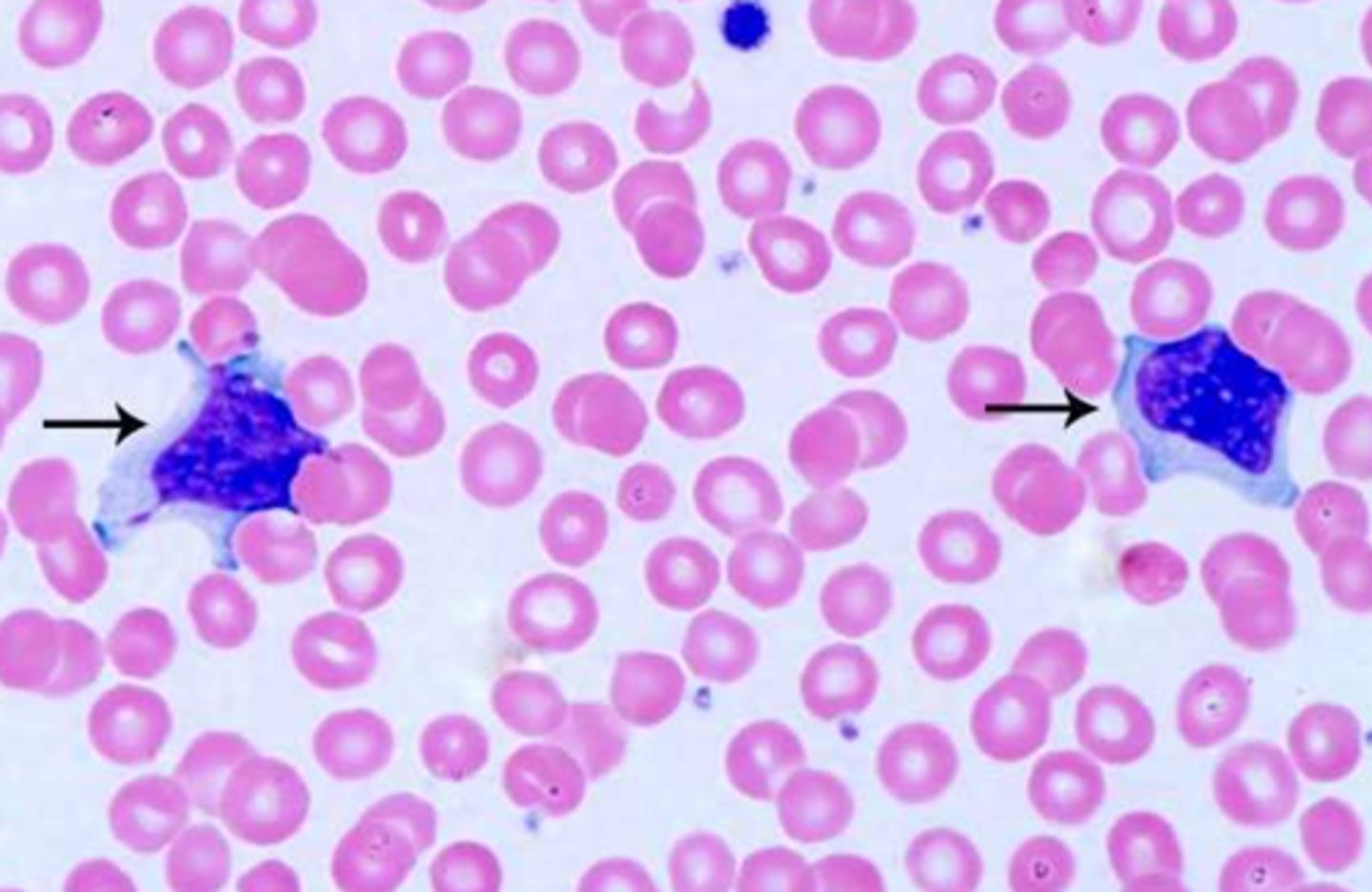
macrophage
huge, weird shape, round nucleus, vacuoles, in tissue but not PB
-nurse rbc in bm
Prolymphoblast
slightly smaller than normal lymphocyte, nuclei still present, clumpy chromatin
marginating pool
neutrophils on blood vessel walls

circulating pool
freely moving neutrophils in blood

mitotic pool
bm cells actively making neutrophils
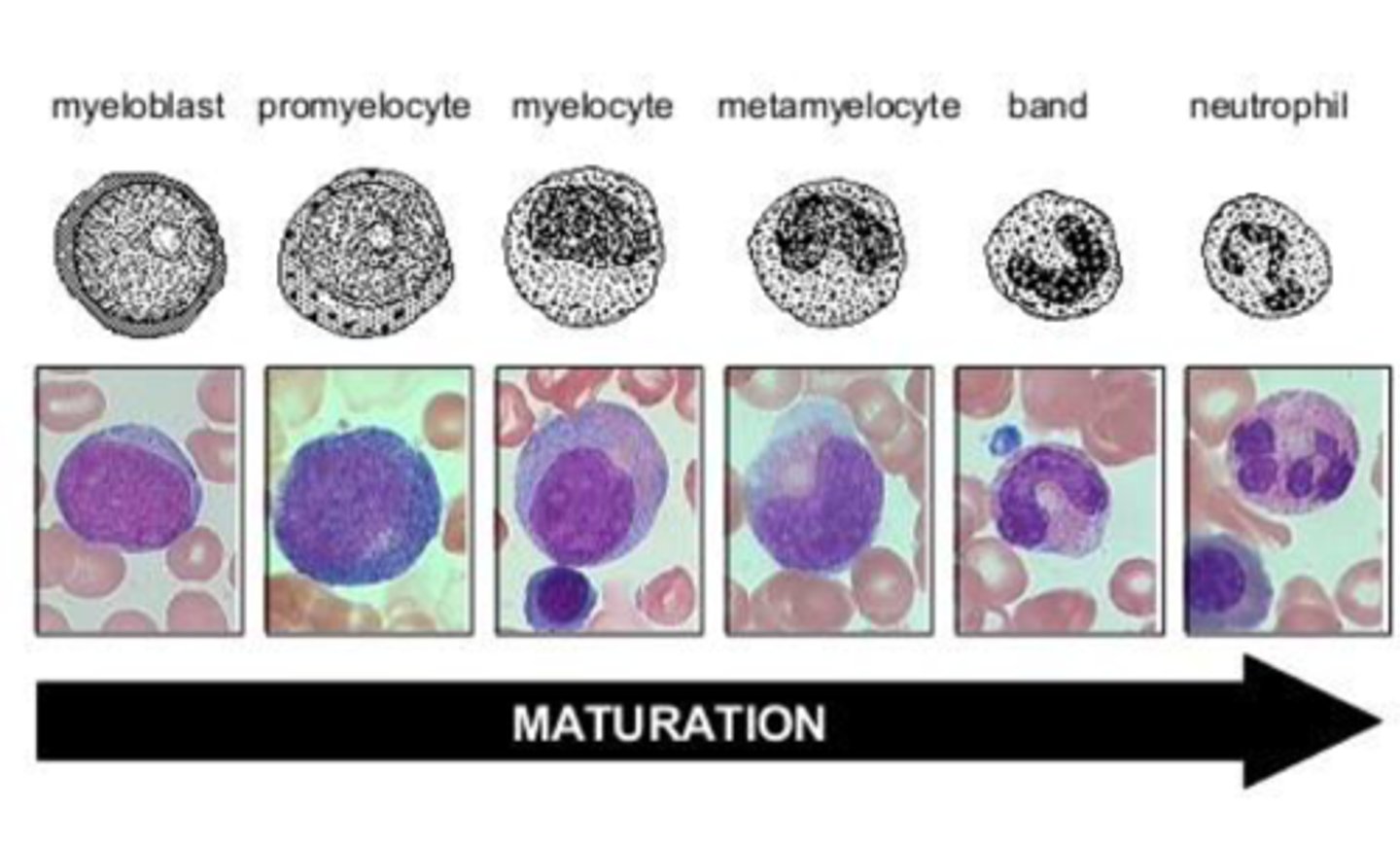
storage pool
mature neutrophils in bm ready to go

LAP score
Low =possibly CML
High = prolly leukemoid reaction
Leukocyte-adhesion deficiency (LAD)
Auto-recessive
-No surface adhesion proteins on leukocytes (CD11/CD18 -> Beta integrin)
-NO PHAGOCYTOSIS
-tested with flow cytometry
EBV (mono)
leukocytosis, lymphocytosis, elevated CRV (c reactive protein)
- heterophiles antibodies and blasts present
- reactive lymphocytes and increased liver enzymes
Coulter DIffs
VCS
(volume, Conductivity, Scatter)