Aviation Physics/Physical Science
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
What all things are made of. It's the foundation for any discussion of physics
Matter
A law which means matter can not be created or destroyed but it is possible to change it's physical state
Law of Conservation
An example of the law of conservation
combustion process of liquid fuel and/or water from solid to liquid to vapor among others
How is mass mathematically stated?
Mass = Weight / Acceleration due to gravity
m=w/g
How is weight mathematically stated?
Weight=mass x gravity
What is the only way to change the mass of an object?
add or take away atoms
What is weight?
pull of gravity acting on the mass of an object
What are the six characteristics of matter?
Mass and weight
Attraction
Porosity
Impenetrability
Density
Specific Gravity
What is mass?
measure of the quantity of matter in an object
What is density?
amount or quantity of mass per unit volume
The density of a gas______ in direct proportion to the _____ exerted on it.
Increases, pressure
What is most commonly used as the standard when comparing the densities gasses?
Air
What is the standard chosen by physicists when comparing the densities of all liquids and solids?
Water
What is energy?
gives the capacity to perform work
What device is used to measure the specific gravity of a liquid?
Hydrometer
What are the two types of energy?
Potential and Kinetic
Energy at rest is said to be what type of energy?
Potential Energy
Formula: U = mgh
What are the 3 classifications of potential energy?
due to position
due to distortion of an elastic body
which produces work through chemical action
What is kinetic energy?
Energy being in motion
What is force?
The intensity of an impetus, or the intensity of an input
What is the unit for force is both English and metric systems?
English-pounds
Metric-newtons
What direction would it take more work to move an object? Horizontally or vertically?
Vertically
What are 3 kinds of friction?
Static Friction
Sliding Friction
Rolling Friction
Is sliding friction always more or less than static friction?
always less
Purpose of stall strips on airplaine wings
ensure the wing root stall first
The concept of power involves work, which was a force being applied over a measured distance, but adds on one more consideration. What is that consideration?
Time
What is the formula for work?
Work=Force x Distance
What is the formula for Power?
Power= Force x Distance divided by time
The units for power depend on how ________ and ______ are measured
Distance and time
How many ft/lbs are in one horse power?
550 ft/lbs
How many watts are in one horse power?
746 watts
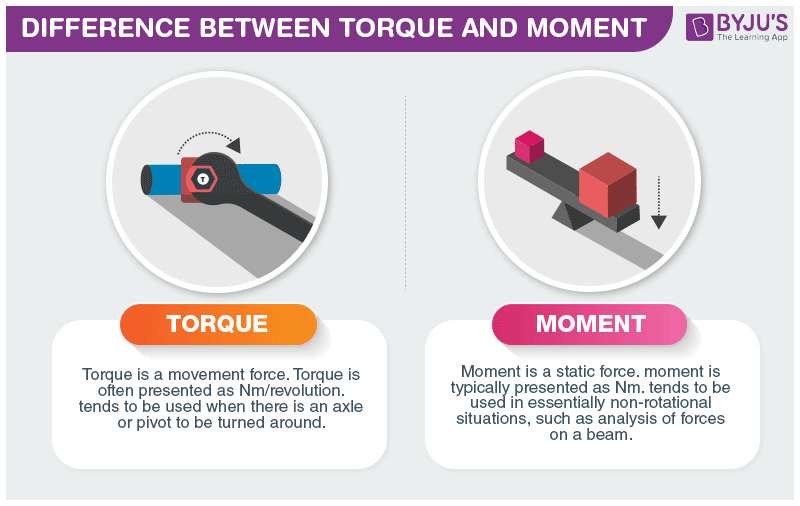
What is torque as applied to physics?
Torque is described as a force acting along a distance; creates twisting and tries to make something rotate.
What is the formula for torque?
Torque= Force x Distance
In the formula for torque, what does distance value represent?
distance along which the force is applied
What is the definition of a machine?
any device with which work may be accomplished
What are the six simple machine?
Lever
Pulley
Wheel and axel
Inclined plane
Screw
Gear
What is mechanical advantage?
a comparison of the output force to the input force / output distance to the input distance
What are the three basic parts of any lever?
Fulcrum
Force or effort
Resistance
The combination of force and distance applied to a lever creates what force that tries to cause rotation?
Torque
Where is the fulcrum located in a first class lever?
between the effort and the resistance
What is the location of the fulcrum and the effort applied in a second class lever?
The fulcrum is at one end and the effort is applied at the other
What is the only advantage of the single fixed pulley?
to change the direction of the force, or pull on the rope
In a single moveable pulley, what will the weight being lifted always be in relation to the effort being applied?
One half
What are bevel gears used for?
to change the plane of rotation
What gear system has an extremely high mechanical advantage?
The worm gear
Name 5 types of stresses found in mechanical bodies?
Tension
Compression
Torsion
Bending
Shear
A type of stress which the forces that tend to pull an object apart
Tension
What is compression?
a force that tries to crush an object
What is torsion?
applied to a material when twisting; combination of both tension and compression
What is shear?
a force that tries to cut or slice through
What's newton's first law state?
A body at rest tends to remain at rest, and a body in motion will remain in uniform motion unless acted on by an outside force
what's newton's second law?
The acceleration produced in a mass by the addition of a given force is directly proportional to the force, and inversely proportional to the mass
Force equals mass times acceleration
What's newton's third law?
For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction
What is speed?
a rate of motion
What is velocity?
the rate of motion in a given direction
What is acceleration?
the increase in the rate of motion over a period of time
A vector quantity must have both _______ and ______
Magnitude and direction
What is centrifugal force?
the force that pulls a spinning object away from its center of rotation
What is centripetal force?
the equal and opposite force required to hold the weight in a circular path
What are the 3 method of heat transfer?
Conduction
Convection
Radiation
What is the boiling point of pure water in degrees centigrade?
100 degrees C
What is Specific heat?
ratio of the amount of heat energy needed to raise the temperature of an specific mass of material; 1 degrees C
What are the four temperature scales?
Centigrade
Fahrenheit
Kelvin
Rankine
What is absolute zero?
lowest temperature that is theoretically possible; heat would be minimal
What temperature does absolute zero occur at?
-459.67 F or -273.15 C( 0 kelvin)
What is pressure?
amount of force acting on a specific amount of surface area
What is absolute pressure equal to?
gauge pressure + atmospheric pressure
What is another name for an aneroid barometer?
Altimeter
GAS LAW
What is Boyle's Law?
States that the pressure and volume of a gas is inversely proportional to temperature when constant; GAS LAW
What's Charles law?
stating how gas tends to expand when heated.
end of gas laws
What is a fluid?
Any substance that is able to flow if its not in some way confined or restricted
What is the difference between fluid and gas?
when a force is applied to a liquid it tends to be incompressible thus gases are highly compressible
A solid body submerged in a liquid or a gas weighs less than when weighed in free space. What is this called?
Buoyancy
What is Pascal's law?
concept of the pressure set up in a fluid and how it relates to the force acting on the fluid and the surface area through which it acts
What is Bernoulli's principle?
flow of a nonconducting fluid, and increase in the speed of the fluid occurs with a decrease in pressure
Low pressure high velocity; High pressure low velocity
What is sound?
series of disturbances in matter that human ears can detect
What are three things necessary for the transmission and reception of sound?
Source
medium for carrying the sound
detector
What are the two basic physical properties which govern the velocity of sound?
Density and elastictiy
What unit is sound intensity measured in?
decibels
What determines the pitch of sound?
By the vibrations or the sounding source
What is the Mach Number?
ratio of the speed of an aircraft to the speed of sound
What happens to the density of the atmosphere with an increase in altitude?
density of air would decrease
Apparent rise in the pitch or frequency of a sound as its source approached the hearer, and the decrease in pitch as the source moves away
DOPPLER EFFECT
transfer of energy when 2 pieces of matter have the same frequency and one starts to vibrate
RESONANCE
The actual amount of the water vapor in a mixture of air and water.
Absolute Humidity
Temperature to which humid air must be cooled at constant pressure to become saturated.
dewpoint
purpose is to create an aerodynamic force that keeps the flight control in a deflected position
Trim Tabs
It installed on the trailing edge of the stabilator
Anti--Servo Tabs
purpose of aircraft wing dihedral
increase lateral stability
Ratio of water vapor actually present in the atmosphere to the amount that would be present in the air were saturated at the prevailing temp. and pressure
Relative Humidity
In mechanical sense, when is work done?
When a resistance is overcome by a force acting through a measurable distance
It is acting like a balance tab, but rather than assisting the normal force that moves the elevator; sole force that makes the elevator move
Servo Tab
What are the types of pressure?
static
Impact
relative
absolute pressure
Newton's 3rd Law
Law of Interaction for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction
What atmospheric range provides best conditions for jet aircraft flight?
stratosphere
intensity of hotness or coldness of a mass measured in degrees
TEMPERATURE
Speed of sound in the atmosphere
changes with a change in TEMPERATURE