Topic 4 - Waves
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
What is a wave?
An oscillation or vibration that transfers energy and information from one place to another.
What do waves transfer?
Energy and Information.
Name the 2 types of waves
Longitudinal and Transverse.
Describe a longitudinal wave
A wave that oscillates/vibrates parallel to the direction of wave travel and energy transfer.
Describe a transverse wave
A wave that oscillates/vibrates perpendicular to the direction of wave travel and energy transfer.
Do longitudinal waves oscillate parallel or perpendicular to the direction of the wave?
Parallel
Do transverse waves oscillate parallel or perpendicular to the direction of the wave?
Perpendicular
What is the difference between a longitudinal and transverse wave?
A longitudinal wave oscillates/vibrates perpendicular to the direction of wave travel and energy transfers whilst a transverse wave oscillates/vibrates parallel to the direction of wave travel and transfer.
Give examples of longitudinal waves
Sound waves, P waves, Ultrasound, Infrasound
Give examples of transverse waves
EM waves, S waves, Water waves
What is the difference between rarefaction and compression?
Rarefaction - High pressure, Fewer particles
Compression - Low pressure, Many particles
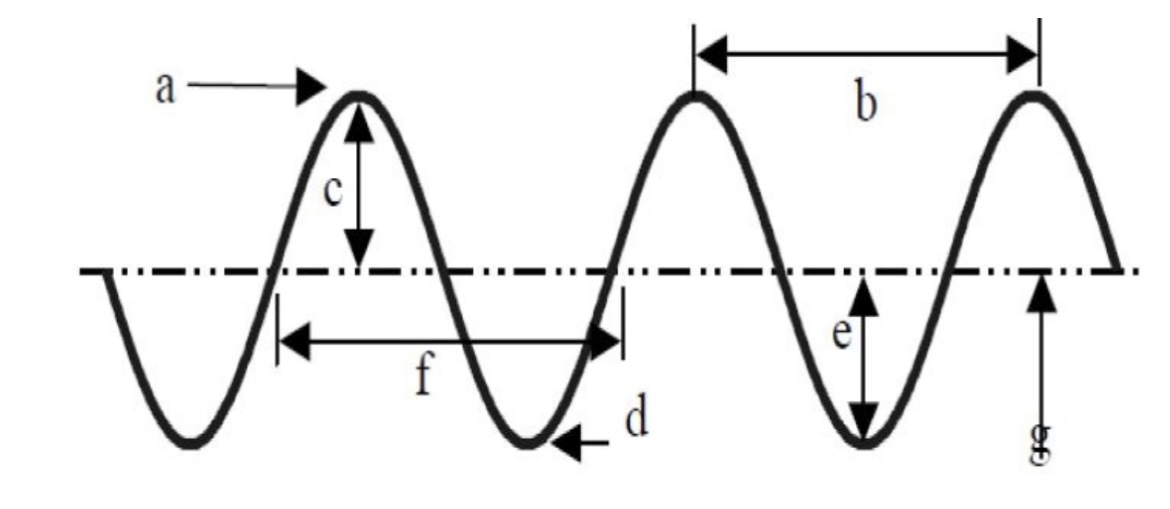
Label the diagram
A - Cres
B - Wavelength
C - Amplitude
D - Trough
E - Amplitude
F - Wavelength
G - Rest position
What is the crest of a wave?
The highest point of a wave above the rest position.
What is the highest point of a wave above the rest position?
Crest
What is the trough of a wave?
The lowest point of a wave above the rest position.
What is the lowest point of a wave above the rest position?
Trough
What is the amplitude of a wave?
Displacement from rest position to crest/trough.
What is displacement from rest position to crest/trough?
Amplitude
What is the wavelength of a wave?
Distance from one point on a wave to the same point/position on the next wave.
What is the distance from one point on a wave to the same point/position on the next wave?
Wavelength
What is the frequency of a wave?
The number of waves passing a point every second.
What is the number of waves passing a point every second?
Frequency
What is the period of a wave?
Time taken for one complete wave to pass.
What is the time taken for one complete wave to pass?
Period
What is the velocity of a wave?
Speed of a wave in the direction that it is moving.
How do you calculate the period of wave?
1 / Frequency
Which 2 calculations can we use for wave speed?
Wave Speed = Frequency x Wavelength
Wave speed = Distance / Time
Which 3 calculations link wave speed, frequency and wavelength?
Wave Speed = Frequency x Wavelength
Frequency = Wave Speed / Wavelength
Wavelength = Wave Speed / Frequency
State the symbols for wave speed, frequency and wavelength.
Wave speed = v
Frequency = f
Wavelength = λ
State the units for wave speed, frequency and wavelength.
Wave speed = m/s
Frequency = Hz
Wavelength = m
What 4 things can a wave do when it hits a boundary/interface?
Reflected, absorbed, transmitted & refracted.
What does it mean if a wave is reflected?
Wave bounces off and is sent back to the material.
What does it mean if a wave is absorbed?
Wave disappears as the energy it had been carrying is transferred to the materials energy store.
What does it mean if a wave is transmitted?
Wave continues to travel through the material.
What does it mean if a wave is refracted?
Wave passes into the new material but changes direction/speed when entering a medium of a different density.
Does the speed of waves change in different materials?
Yes
Does the frequency of waves change in different materials?
No
When moving from a more to less dense medium, does light speed up or slow down?
Speed up.
When moving from a less to more dense medium, does light speed up or slow down?
Slow down.
When moving from a more to less dense medium, does light move away from or towards the normal?
Away
When moving from a less to more dense medium, does light speed up or slow down?
Slow down
When moving from a less to more dense medium, do waves move away from or towards the normal?
Towards
What is specular reflection?
Parallel waves are reflected in a single direction by a smooth surface.
What is diffuse reflection?
Parallel waves that are reflected by a rough surface in all directions.
Does specular or diffuse reflection reflect waves in a single direction?
Specular reflection
Does specular or diffuse reflection reflect waves in all direction?
Diffuse reflection
Does specular or diffuse reflection reflect waves via a smooth surface?
Specular reflection
Does specular or diffuse reflection reflect waves via a rough surface?
Diffuse reflection
What is the normal?
The imaginary line perpendicular to the surface.
What is the the imaginary line perpendicular to the surface called?
Normal
What separates two surfaces?
Boundary
Which angle is equal to the angle of incidence?
Angle of reflection
Which angle is equal to the angle of reflection?
Angle of incidence
What is total internal refraction?
A wave travelling from a more to less dense material is refracted a lot, causing the angle of incidence to be larger than the angle of reflection.
What is it called when light is completely refracted?
Total internal refraction.
During total internal refraction, does light travel from more to less dense or less to more dense?
More to less dense.
During total internal reflection, which angle is bigger?
Angle of incidence to be larger than the angle of reflection.
Are sound waves longitudinal or transverse?
Longitudinal
Describe sound waves when travelling in solids.
When particles travel through solids, they cause changes in pressure on a solid, causing the particles to vibrate in the solid.
Does a sound waves speed change when travelling from one medium to another?
Yes
Does a sound waves frequency change when travelling from one medium to another?
No
Does a sound waves wavelength change when travelling from one medium to another?
No
In which medium do sound waves travel fastest in?
Solid
In which medium do sound waves travel slowest in?
Gases
When the speed of a sound wave increases, does wavelength become longer or shorter?
Longer
When the speed of a sound wave decreases, does wavelength become longer or shorter?
Shorter
Are sound waves longitudinal or transverse?
Longitudinal
What are sound waves caused by?
Vibrating objects.
In which medium do sound waves travel fastest in?
Solids
In which medium do sound waves travel slowest in?
Gases
Why can sound waves not travel in a vacuum?
No particles for it to move/vibrate.
What are reflected sound waves?
Echoes
Describe echoes.
Reflected sound waves.
What is the human audible range?
20 - 20 000 Hz
Suggest why the human audible range is 20 - 20000 Hz
Size of parts of the inner ear.
Eardrum not sensitive enough for high/low frequencies.
Brain cannot interpret low/high frequencies.
Describe the pathway of sound waves in the ear.
Ear canal
Eardrum
Tiny bones - Hammer, Anvil, Stirrup.
Cochlea.
Neurones in auditory nerve.
Brain
Where do sound waves enter in the ear?
Ear canal
What part of the ear do sound waves vibrate?
Ear drum
What is the ear drum?
A thin membrane.
What do tiny bones do to the vibrations?
Amplify
Which part of the ear amplifies vibrations?
Tiny bones
Describe the tiny bones.
Hammer - Attatched to eardrum.
Anvil - In the middle of the chain of bones.
Stirrup - Attatched to membrane.
Describe the cochlea.
Liquid that transmits vibrations from tiny bones to membrane, which detects vibrations in the fluid.
Has tiny hairs found along the membrane that detect vibrations to create electrical impulses.
What is the role of the cochlea?
Has tiny hairs found along the membrane that detect vibrations to create electrical impulses.
Does a thicker membrane fetched a higher or lower frequency?
Higher
Does a thinner membrane fetched a higher or lower frequency?
Lower
What are sounds greater than 20 000 Hz?
Ultrasound
What is ultrasound?
Sounds greater than 20 Hz
What are the uses of ultrasound?
Communication between animals like mice, dogs, dolphins.
Animals detect objects using it like bats, dolphins.
Sonar equipment on ships and submarines.
Images inside the body like pregnancy ultrasound.
Industrial imaging for flaws in objects.
Which animals use ultrasound to communicate?
Dogs, mice and dolphins.
Describe how echo sounding works.
Type of sonar used by boats and submarines to find the distance to the seabed or locate objects in deep water.
Loudspeaker emits pulses of high frequency sound waves.
Ultrasound spreads out in water.
Some is reflected and a special microphone on a ship detects echo returning.
Time taken by each high frequency sound wave being sent out and the echo returning back to detector is measured.
How do you calculate depth under water?
Distance = (Speed x Time) / 2
How does the brain interpret sound?
Based on different volumes and pitches which change based on frequency and intensity.
Does a higher frequency cause our ears to detect a higher or lower pitch?
Higher pitch.
Describe how pregnancy ultrasound works.
Ultrasound pulses sent into woman’s body. Jelly used to ensure is it not reflected by her skin.
When ultrasound waves pass through, some is reflected back at different boundaries (tissue, bones) and detected.
Scanner detects exact timing and distribution of echoes to produce an image of the foetus.
Time taken for pulse of an ultrasound wave to travel is used to calculate distance.
Describe how industrial imaging ultrasound works.
Ultrasound can find flaws or internal cracks in metal objects.
Internal cracks create boundaries in the metals so pulse sor ultrasound are reflected partially and bounce back.
Time taken to reach the base of the metal will be shorter due to cracks.
What is infrasound?
Sounds with frequencies less than 20 Hz.
What are sounds with frequencies less than 20 Hz?
Infrasound
What are seismic waves?
Vibrations caused by earthquakes, travelling inside of the Earth and its crust.
Which piece of equipment detects seismic waves?
Seismometers.