Calc 1 formulas
1/37
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Limit (informal)
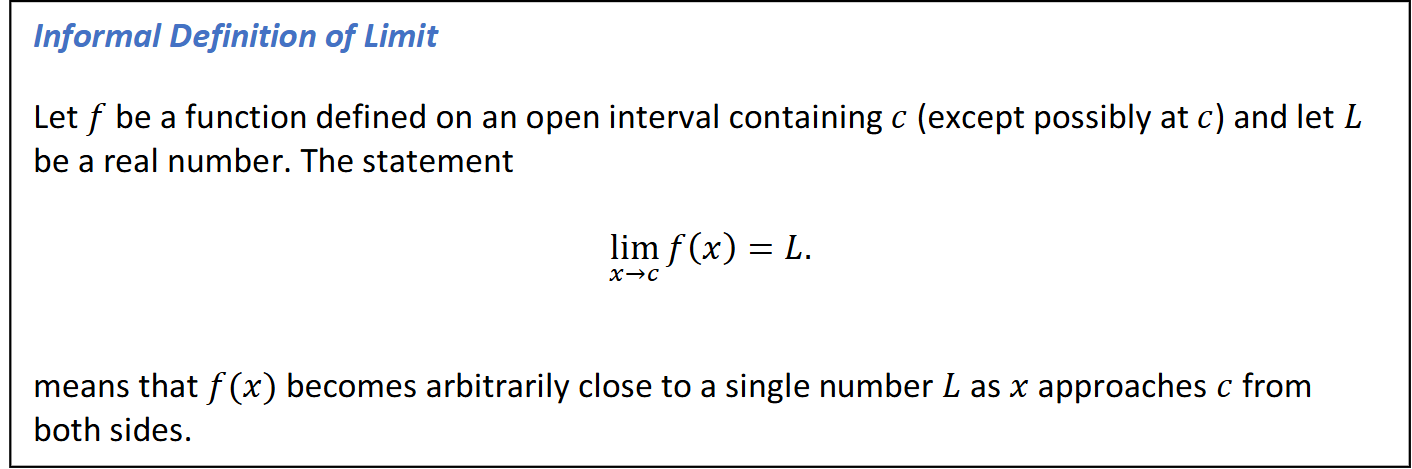
Limit (formal)

Continuity
f(c) is defined
lim x→c f(x) exists
lim x→f(x) =f(c)

Derivative

Concavity

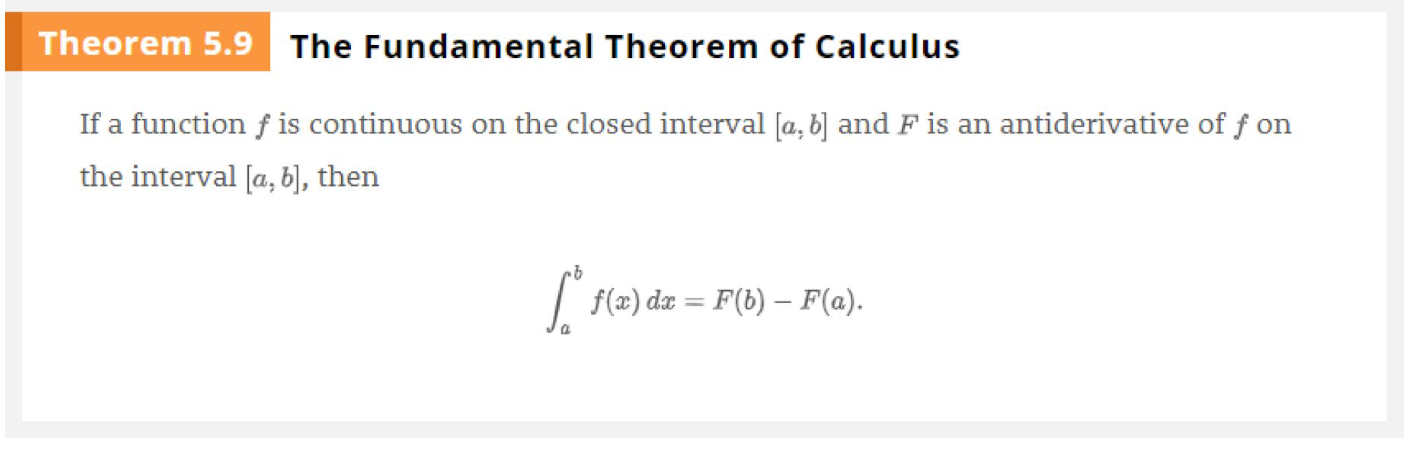
The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
Tangent line
Point Slope Formula
Chain rule
Quotient rule
Product Rule
Power rule
Infinite limits
Trig derivatives

Trig anti-derivatives

Max extrema
Min extrema
extreme value theorem
Mean value theorem
Rolles’s theorem
quadratic formula
Power Rule (Anti Derivatives)
Upper/right sum
Lower/left sum
Trapiziod sum
Midpoint rule formula
Limits of lower and upper sums
Special trig limits
sinax/bx= a/b,
sinax/x=a
tanx/x=sinx/cosx,
only works when x→0
Squeeze theorem
if h(x)≤ f(x) ≤ g(x) for all x in an open interval containing c, except possibly at c itself.
As x equals c, h(x) and g(x) have the same limit, then if f(x) exists, it is equal to L.
must have the same limit
Derivative of sinx
cosx
Derivative of cosx
-sinx
Derivative of tanx
sec²x
Derivative of secx
secxtanx
Derivative of cotx
-csc²x
Derivative of cscx
-cscxcotx
Antiderivative of sinx
-cosx +C
Antiderivative of cosx
sinx +C
Antiderivative of