Muscle System and Joints Review
1/195
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts related to muscles, joints, and their functions in the human body.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
196 Terms
What are the main functions of joints?
Hold bones of the skeleton together and give the skin mobility.
What are the three structural classifications of joints?
Fibrous, Cartilaginous, and Synovial.
What is a sprain?
when the LIGAMENTS of a joint are stretched or torn.
What distinguishes rheumatoid arthritis from osteoarthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease attacking body tissues, while osteoarthritis is caused by wear and tear on joints.
What are the main types of muscle tissue?
Skeletal muscle, Cardiac muscle, and Smooth muscle.
What is the primary function of the sarcoplasmic reticulum in muscle fibers?
To regulate intracellular levels of calcium.
What is the sliding filament theory?
The theory explaining muscle contraction as the sliding of actin over myosin filaments.
What is the role of myoglobin in muscle fibers?
Myoglobin stores oxygen in muscle tissue.
What are prime movers or agonists?
Muscles that provide the major force for producing a specific movement.
How is muscle tension developed during contraction?
By the interaction of actin and myosin filaments within sarcomeres.
What happens during the latent period of muscle contraction?
There is a delay where muscle tension begins but is not yet measurable.
What type of joint movement is abduction?
Abduction is the movement of a limb away from the midline of the body.
What is the significance of having slow and fast muscle fiber types?
Slow oxidative fibers are used for endurance, while fast glycolytic fibers are used for short bursts of power.
What defines isotonic and isometric contractions?
Isotonic contractions involve movement with tension overcoming the load; isometric contractions involve tension without movement.
What muscles are involved in plantar flexion?
Gastrocnemius and soleus.
What is muscle recruitment?
Recruitment occurs when a stimulus exceeds what one motor unit can handle, requiring additional motor units.
What are the three functional Joint classifications?
synarthroses, amphiarthroses, and diarthroses
synarthroses
“Immovable” Joints
amphiarthroses
“Slightly Movable” Joints
diarthroses
“Freely Movable" Joints
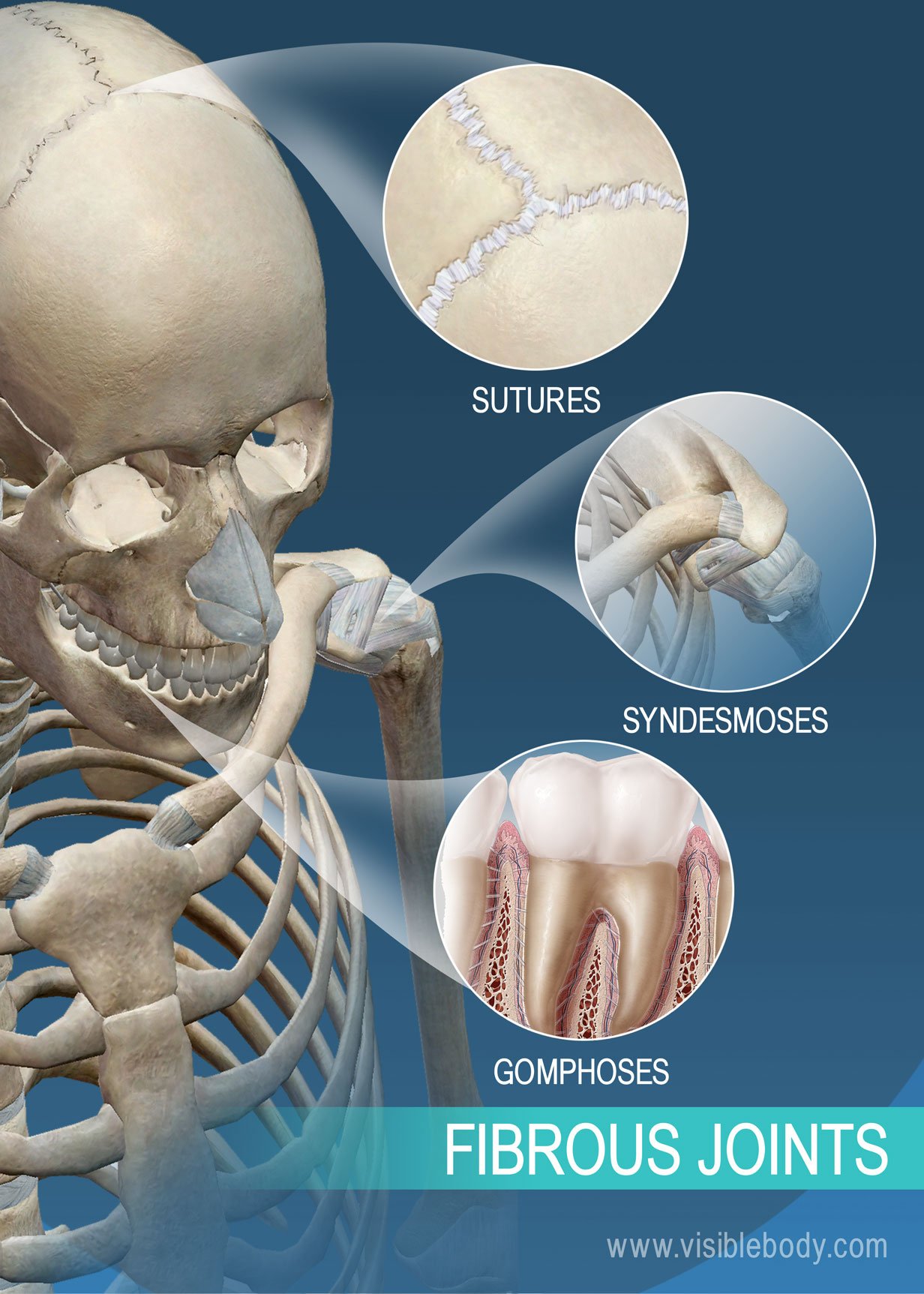
Sutures
Found connecting bones of skull (IMMOVABLE)
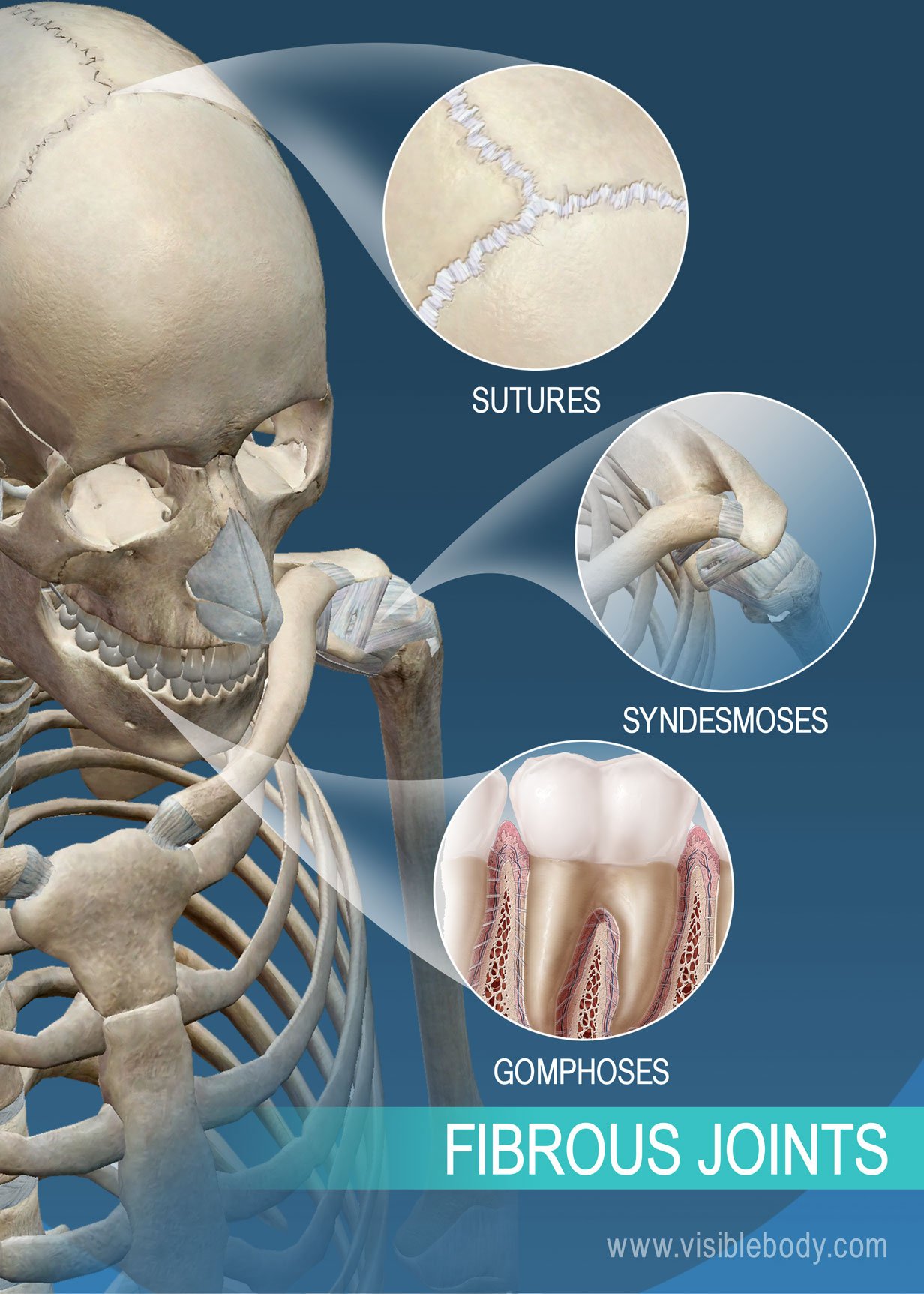
Syndesmoses
Type of joint where bones are connected by ligaments, allowing for slight movement.
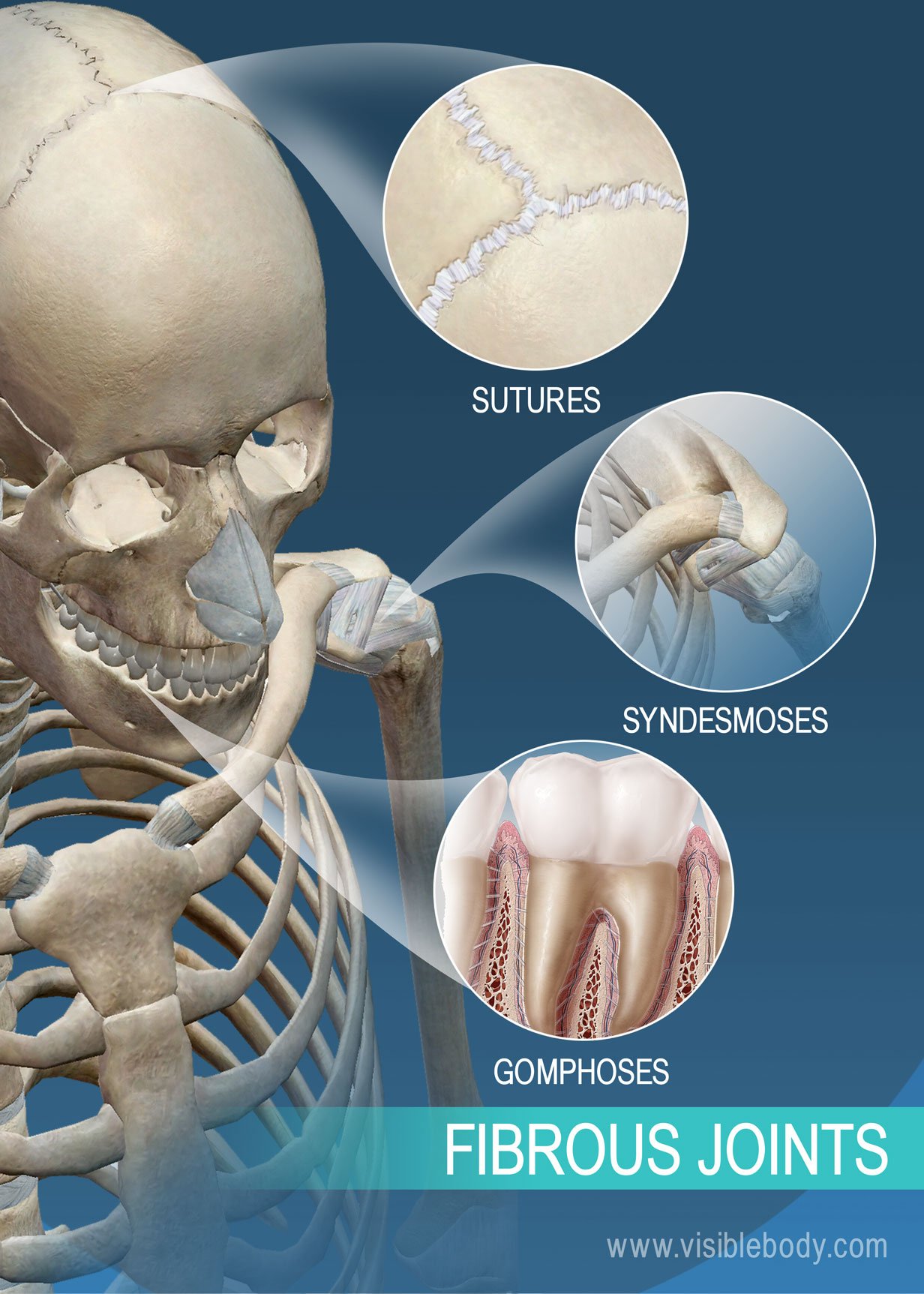
Gomphoses
Type of joint where a peg fits into a socket, such as in the connection of teeth to their sockets in the jaw.
What are the fibrous Joints?
Sutures, Syndesmoses, and Gomphoses
What are the Cartilaginous Joints?
Synchondroses and symphyses
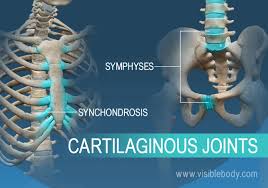
Synchondroses
Immovable Joints that’s a bar or plate of cartilage that join two bones together ( Epiphyseal plate)
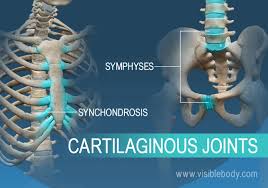
Symphyses
Fibrocartilage sandwiched between articular cartilage and held together by a ligament. (Slightly movable: found in Vertebrae)
Synovial joint Structure:
Bone ends are covered in articular cartilage
Space between the bones is the cavity
Articular capsule: Hold the joint together
-contains: 1. Ligament 2. Synovial membrane (synovial fluid)
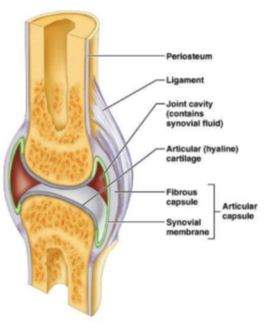
What is Bursa?
Individual sacs of synovial tissue
Muscles attach to bone to provide what?
movement
What is the origin?
The place of attachment which has little to no movement
What is the insertion?
The place of attachment which has the most movement (Moveable bone)
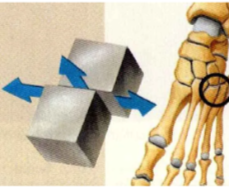
Gliding
a type of joint movement allowing bones to slide past one another.
What bones have gliding movement?
Carpals of the wrist and Tarsals of the foot
What is an angular movement?
Increasing or decreasing the angle between two bones
What are the types of angular movement?
Flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, and circumduction.
What is flexion?
REDUCING the angle between bones
What is extension?
INCREASING the angle between bones.
What is hyperextension?
When the extension goes BEYOND the normal upright position
Flexion of the foot
Can point UP towards the body (Dorsiflexion)
or
can Point DOWN from the body (Plantar Flexion)
Abduction
Movement of the limb away from the midline of the body
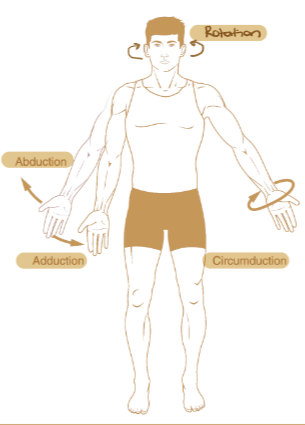
Adduction
Movement of the limb towards the midline of the body.
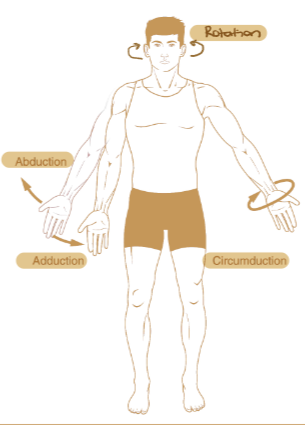
Circumduction
Moving the distal portion of a limb in a circular direction
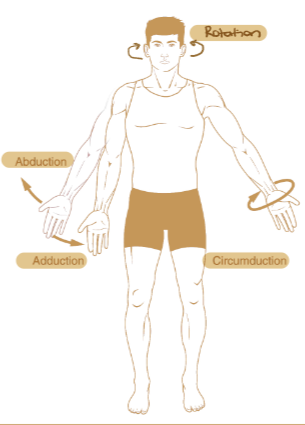
Rotation
The turning of a bone around its long axis
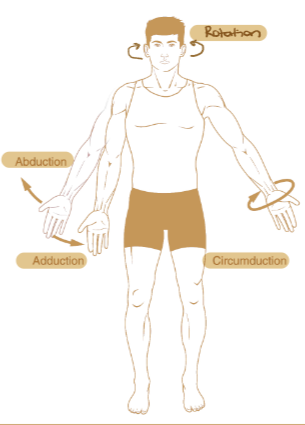
What are the special movements that refer to the movement of the Radius around the Ulna?
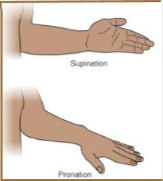
Supination and Pronation
What is Supination?
Turning backward
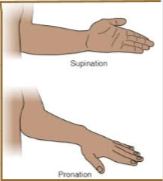
What is Pronation?
Turning forward
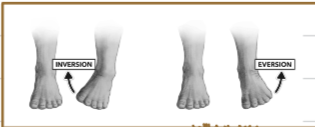
What are the special movements that refer to the movement of the foot?
Inversion and Eversion
What is inversion?
The sole of the foot faces medially
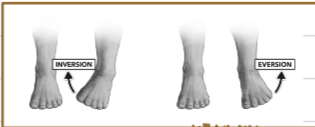
What is Eversion?
The sole of the foot faces laterally
Protraction and Retraction
Movements that involve the anterior and posterior displacement of the scapula or jaw.
Elevation and Depression
Movements that increase or decrease the angle between the body parts, such as lifting the shoulders or lowering the jaw.
What is opposition?
an action that occurs when the thumb moves to touch the tips of other digits
Types of freely moveable joints
Gliding/ Planar, Hinge Joints, Condyloid Joints, Saddle Joints, Pivot Joints, and Ball-and-Socket
Gliding/ Planar joint
Carpal bones of wrist and Tarsal bones of ankle
Hinge Joints
Knee and Elbow
Condyloid Joints
Metatarsals, Metacarpals, and Phalanges
Saddle Joints
Thumb (Metacarpal and Trapezium)
Pivot Joints
Atlas and Axis or Radius and Ulna
Ball & Socket Joints
Shoulder and Hip
What is a strain?
The TENDON of a joint are stretched or torn
Can your directly sprain/strain a ligament or tendon
NO
Dislocations
When bones are forced out of alignment
Subluxation
A partial dislocation of a joint
Bursitis and Tendonitis
inflammation of the bursae or tendons, often caused by repetitive motion or overuse.
What is arthritis?
Inflammatory or degenerative disease which damages the joints
Who had SirenMelia (Mermaid Syndrome)
(Shiloh Pepin) It is a rare congenital condition where a person is born with fused legs resembling a mermaid’s tail. It affects limb development and can also involve other organ systems.
Osteoarthritis
Wear and tear of articular cartilage in the joints which lack the ability to be replaced
common: The elderly
Drug: Capacsin (From peppers)
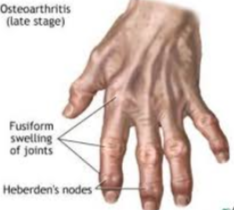
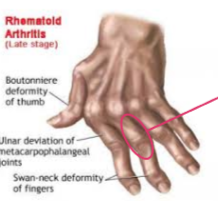
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Caused by an autoimmune disease that attacks the body’s tissue causing joints to shorten and stiffen
common: 40-50
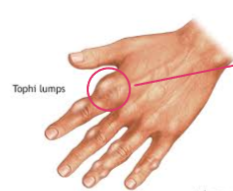
Gouty Arthritis
When excessive Uric acid is deposited in the joints forming crystals (an inflammatory response -usually starts in big toe)
Skeletal Muscle
A type of muscle tissue under voluntary control and attached to bones, enabling locomotion and movement.
Characteristics: displays light and dark bands appearing as stripes and striations
Cardiac Muscle
A type of involuntary muscle tissue found only in the heart, responsible for pumping blood throughout the body.
Characteristics: Contains Striations
Smooth muscle
A type of involuntary muscle tissue found in the walls of hollow organs, responsible for various functions such as digestion and blood vessel regulation.
Characteristics: No striations and operates involuntarily, helping in processes like peristalsis and maintaining blood pressure
Functions of Skeletal muscle
Movement of Skeleton, Maintain posture, stabilize joints, and generate heat
Functions of Smooth muscle
Excitability, contractibility, extensibility, and elastibility
What are the (smaller) functional units of Skeletal muscle?
Muscle(a bundle of muscle fascicles), Fascicle(Bundle of muscle fibers), and Muscle Fiber(the muscle cell)
Types of smooth muscle
Longitudal, and circular muscle
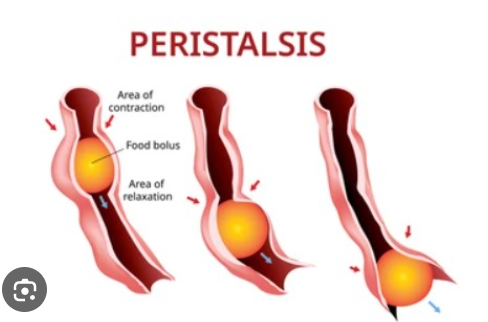
Peristalsis
Alternating contraction and relaxation of opposing muscles
Varicosities
The nerves that innervate smooth muscles
Connective Tissue Sheath
A layer of connective tissue surrounding and supporting muscle fibers, providing structure and facilitating movement.
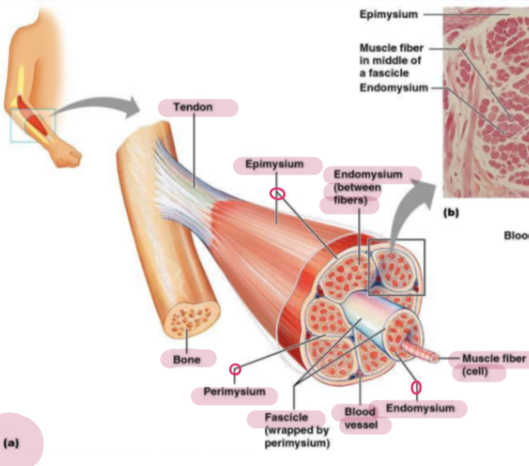
What’s the Endomysium
“Within” the muscle: A sheath of primary reticular fibers that covers the muscle fiber
What’s the perimysium?
“Around” the muscle: A sheath of fibrous connective tissue that covers the muscle fascicle
What’s the Epimysium?
“Outside” of the muscle: A sheath of dense irregular connective tissue that covers the whole muscle
Direct or fleshy attachments
The epimysium fuses to the periosteum of a bone or perichondrium of a cartilage
Indirect attachments
The connective tissue wrappings of the muscle extend beyond the muscle to form either a rope like tendon or sheet like aponeurosis
Muscle Fiber
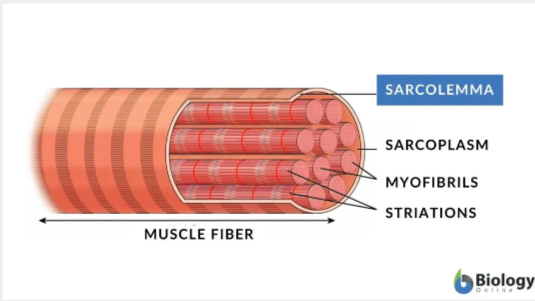
Sarcolemma
Cell membrane of the muscle cell
Sarcoplasm
Cytoplasm of the muscle cell
Myoglobin
Red pigment that stores oxygen in the muscle
Myofibrils
Rod-like fibers that run parallel down the length of the muscle fiber
_______- thousands of these myofibrils can be found in one fiber and can account for 80% of cellular volume
hundredths
Myofibrils
Primarily made of thick and thin filaments
What are Myofibrils composed?
Protein called myosin
Myosin Heads
Globular heads on Myosin that can attach to actin
What are thin filaments primarily composed of?
actin
Tropomyosin
A thin strand that wraps around actin (thin) and blocks the actin sites
Tropopinin
A three polypeptide complex that regulates the position of tropomyosin relative to the actin binding sites
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
An elaborate smooth endoplasmic reticulum that’s primary function is to regulate intercellular levels of calcium
T Tubules
A long tube-like structure that is continuous with the sarcolemma and runs in between 2 sarcoplasmic reticulums
Purpose: initiate the release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum
Muscle Contraction
Shortening of muscle fibers by the activation and movement of actin fibers over myosin fibers causing overlap